 | |
| Identifiers | |
|---|---|
3D model (JSmol)
|
|
| ChEBI | |
| ChemSpider | |
PubChem CID
|
|
| UNII | |
CompTox Dashboard (EPA)
|
|
| |
| |
| Properties | |
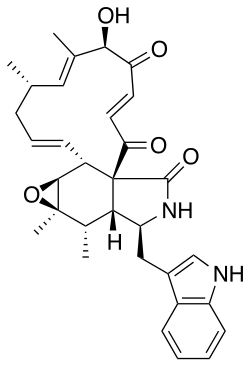
| C32H36N2O5 | |
| Molar mass | 528.649 g·mol−1 |
Except where otherwise noted, data are given for materials in their standard state (at 25 °C [77 °F], 100 kPa).
| |

Chaetoglobosin A is a fungal isolate with anticancer activity in vitro.[1] Derivatives of the compound include MBJ-0038, MBJ-0039, and MBJ-0040.[2]
Chaetoglobosin A biosynthesis begins with a product from hybrid PKS-NRPS encoded by the gene CHGG_01239, followed by multiple oxidations which form different intermediates depending on the order of functional groups oxidized. The PKS-NRPS product undergoes a diels alder, to form prochaetoglobosin I (2) and is subsequently oxidized in different paths as shown in the scheme. Either the epoxide is created first to form prochaetoglobosin IV (5), followed by di-hydroxylation to form 20-dihydrochaetoglobosin A (6), and a final oxidation of one hydroxyl to ketone to form chaetoglobosin A, or di-hydroxylation of (2) occurs first, forming cytoglobosin D (3), followed by one hydroxyl oxidation to form chaetoglobosin J (4), and lastly epoxidation to form chaetoglobosin A. Epoxidation of (3) can also occur prior to hydroxyl oxidation to form (6). [3]
