Recent from talks
Nothing was collected or created yet.
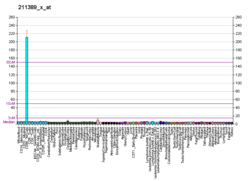
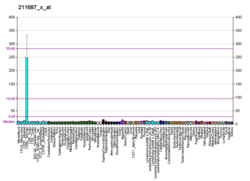
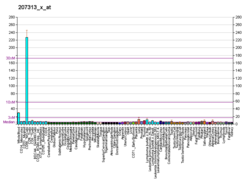
KIR3DL1
View on Wikipedia
Killer cell immunoglobulin-like receptor 3DL1 is a protein that in humans is encoded by the KIR3DL1 gene.[5][6][7]
Killer cell immunoglobulin-like receptors (KIRs) are transmembrane glycoproteins expressed by natural killer cells and subsets of T cells. The KIR genes are polymorphic and highly homologous and they are found in a cluster on chromosome 19q13.4 within the 1 Mb leukocyte immunoglobulin-like receptor complex (LRC). The gene content of the KIR gene cluster varies among haplotypes, although several "framework" genes are found in all haplotypes (KIR3DL3, KIR3DP1, KIR3DL4, KIR3DL2). The KIR proteins are classified by the number of extracellular immunoglobulin domains (2D or 3D) and by whether they have a long (L) or short (S) cytoplasmic domain. KIR proteins with the long cytoplasmic domain transduce inhibitory signals upon ligand binding via an immune tyrosine-based inhibitory motif (ITIM), while KIR proteins with the short cytoplasmic domain lack the ITIM motif and instead associate with the TYRO protein tyrosine kinase binding protein to transduce activating signals. The ligands for several KIR proteins are subsets of HLA class I molecules; thus, KIR proteins are thought to play an important role in regulation of the immune response.[7]
See also
[edit]References
[edit]- ^ a b c ENSG00000274146, ENSG00000278368, ENSG00000273775, ENSG00000276501, ENSG00000278427, ENSG00000274948, ENSG00000274036, ENSG00000274920, ENSG00000275786, ENSG00000276329, ENSG00000277272, ENSG00000283954, ENSG00000275486, ENSG00000275545, ENSG00000278079, ENSG00000273518, ENSG00000275717, ENSG00000277175, ENSG00000167633, ENSG00000283729, ENSG00000283731, ENSG00000276423, ENSG00000275659, ENSG00000278856, ENSG00000284426, ENSG00000275288, ENSG00000284093, ENSG00000283827, ENSG00000284177, ENSG00000276379, ENSG00000284342 GRCh38: Ensembl release 89: ENSG00000284589, ENSG00000274146, ENSG00000278368, ENSG00000273775, ENSG00000276501, ENSG00000278427, ENSG00000274948, ENSG00000274036, ENSG00000274920, ENSG00000275786, ENSG00000276329, ENSG00000277272, ENSG00000283954, ENSG00000275486, ENSG00000275545, ENSG00000278079, ENSG00000273518, ENSG00000275717, ENSG00000277175, ENSG00000167633, ENSG00000283729, ENSG00000283731, ENSG00000276423, ENSG00000275659, ENSG00000278856, ENSG00000284426, ENSG00000275288, ENSG00000284093, ENSG00000283827, ENSG00000284177, ENSG00000276379, ENSG00000284342 – Ensembl, May 2017
- ^ a b c GRCm38: Ensembl release 89: ENSMUSG00000057439 – Ensembl, May 2017
- ^ "Human PubMed Reference:". National Center for Biotechnology Information, U.S. National Library of Medicine.
- ^ "Mouse PubMed Reference:". National Center for Biotechnology Information, U.S. National Library of Medicine.
- ^ Colonna M, Samaridis J (May 1995). "Cloning of immunoglobulin-superfamily members associated with HLA-C and HLA-B recognition by human natural killer cells". Science. 268 (5209): 405–8. Bibcode:1995Sci...268..405C. doi:10.1126/science.7716543. PMID 7716543.
- ^ Wagtmann N, Biassoni R, Cantoni C, Verdiani S, Malnati MS, Vitale M, Bottino C, Moretta L, Moretta A, Long EO (Jun 1995). "Molecular clones of the p58 NK cell receptor reveal immunoglobulin-related molecules with diversity in both the extra- and intracellular domains". Immunity. 2 (5): 439–49. doi:10.1016/1074-7613(95)90025-X. PMID 7749980.
- ^ a b "Entrez Gene: KIR3DL1 killer cell immunoglobulin-like receptor, three domains, long cytoplasmic tail, 1".
Further reading
[edit]- Selvakumar A, Steffens U, Dupont B (1997). "Polymorphism and domain variability of human killer cell inhibitory receptors". Immunol. Rev. 155 (1): 183–96. doi:10.1111/j.1600-065X.1997.tb00951.x. PMID 9059894. S2CID 7040904.
- D'Andrea A, Chang C, Franz-Bacon K, et al. (1995). "Molecular cloning of NKB1. A natural killer cell receptor for HLA-B allotypes". J. Immunol. 155 (5): 2306–10. doi:10.4049/jimmunol.155.5.2306. PMID 7650366.
- Litwin V, Gumperz J, Parham P, et al. (1994). "NKB1: a natural killer cell receptor involved in the recognition of polymorphic HLA-B molecules". J. Exp. Med. 180 (2): 537–43. doi:10.1084/jem.180.2.537. PMC 2191610. PMID 8046332.
- Döhring C, Samaridis J, Colonna M (1996). "Alternatively spliced forms of human killer inhibitory receptors". Immunogenetics. 44 (3): 227–30. doi:10.1007/BF02602590. PMID 8662091. S2CID 38478576.
- Pende D, Biassoni R, Cantoni C, et al. (1996). "The natural killer cell receptor specific for HLA-A allotypes: a novel member of the p58/p70 family of inhibitory receptors that is characterized by three immunoglobulin-like domains and is expressed as a 140-kD disulphide-linked dimer". J. Exp. Med. 184 (2): 505–18. doi:10.1084/jem.184.2.505. PMC 2192700. PMID 8760804.
- Wagtmann N, Rajagopalan S, Winter CC, et al. (1996). "Killer cell inhibitory receptors specific for HLA-C and HLA-B identified by direct binding and by functional transfer". Immunity. 3 (6): 801–9. doi:10.1016/1074-7613(95)90069-1. PMID 8777725.
- Valiante NM, Uhrberg M, Shilling HG, et al. (1998). "Functionally and structurally distinct NK cell receptor repertoires in the peripheral blood of two human donors". Immunity. 7 (6): 739–51. doi:10.1016/S1074-7613(00)80393-3. PMID 9430220.
- Uhrberg M, Valiante NM, Shum BP, et al. (1998). "Human diversity in killer cell inhibitory receptor genes". Immunity. 7 (6): 753–63. doi:10.1016/S1074-7613(00)80394-5. PMID 9430221.
- Vyas Y, Selvakumar A, Steffens U, Dupont B (1999). "Multiple transcripts of the killer cell immunoglobulin-like receptor family, KIR3DL1 (NKB1), are expressed by natural killer cells of a single individual". Tissue Antigens. 52 (6): 510–9. doi:10.1111/j.1399-0039.1998.tb03081.x. PMID 9894849.
- Kwon D, Chwae YJ, Choi IH, et al. (2000). "Diversity of the p70 killer cell inhibitory receptor (KIR3DL) family members in a single individual". Mol. Cells. 10 (1): 54–60. doi:10.1007/s10059-000-0054-0. PMID 10774747. S2CID 21075797.
- Crum KA, Logue SE, Curran MD, Middleton D (2001). "Development of a PCR-SSOP approach capable of defining the natural killer cell inhibitory receptor (KIR) gene sequence repertoires". Tissue Antigens. 56 (4): 313–26. doi:10.1034/j.1399-0039.2000.560403.x. PMID 11098931.
- Gardiner CM, Guethlein LA, Shilling HG, et al. (2001). "Different NK cell surface phenotypes defined by the DX9 antibody are due to KIR3DL1 gene polymorphism". J. Immunol. 166 (5): 2992–3001. doi:10.4049/jimmunol.166.5.2992. PMID 11207248.
- Yamochi T, Semba K, Tsuji K, et al. (2002). "ik3-1/Cables is a substrate for cyclin-dependent kinase 3 (cdk 3)". Eur. J. Biochem. 268 (23): 6076–82. doi:10.1046/j.0014-2956.2001.02555.x. PMID 11733001.
- Shilling HG, Guethlein LA, Cheng NW, et al. (2002). "Allelic polymorphism synergizes with variable gene content to individualize human KIR genotype". J. Immunol. 168 (5): 2307–15. doi:10.4049/jimmunol.168.5.2307. PMID 11859120.
- Martin MP, Gao X, Lee JH, et al. (2002). "Epistatic interaction between KIR3DS1 and HLA-B delays the progression to AIDS". Nat. Genet. 31 (4): 429–34. doi:10.1038/ng934. PMID 12134147. S2CID 6805903.
- Chwae YJ, Chang MJ, Park SM, et al. (2002). "Molecular mechanism of the activation-induced cell death inhibition mediated by a p70 inhibitory killer cell Ig-like receptor in Jurkat T cells". J. Immunol. 169 (7): 3726–35. doi:10.4049/jimmunol.169.7.3726. PMID 12244166.
- Strausberg RL, Feingold EA, Grouse LH, et al. (2003). "Generation and initial analysis of more than 15,000 full-length human and mouse cDNA sequences". Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. U.S.A. 99 (26): 16899–903. Bibcode:2002PNAS...9916899M. doi:10.1073/pnas.242603899. PMC 139241. PMID 12477932.
This article incorporates text from the United States National Library of Medicine, which is in the public domain.