Recent from talks
Be the first to start a discussion here.
Be the first to start a discussion here.
Be the first to start a discussion here.
Be the first to start a discussion here.
Contribute something
Welcome to the community hub built to collect knowledge and have discussions related to Tenma.
Nothing was collected or created yet.
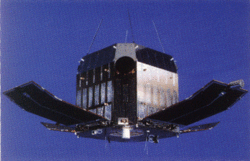
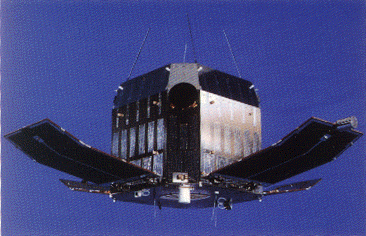
Tenma
View on Wikipediafrom Wikipedia
 Tenma (Japanese for "Pegasus") | |||||||||
| Names | ASTRO-B | ||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Mission type | X-ray astronomy | ||||||||
| Operator | ISAS | ||||||||
| COSPAR ID | 1983-011A | ||||||||
| SATCAT no. | 13829 | ||||||||
| Mission duration | 5 years, 9 months, 27 days | ||||||||
| Spacecraft properties | |||||||||
| Launch mass | 216 kg (476 lb)[1] | ||||||||
| Dimensions | 0.94 m × 0.895 m (3.08 ft × 2.94 ft) | ||||||||
| Start of mission | |||||||||
| Launch date | 20 February 1983, 05:10 UTC | ||||||||
| Rocket | M-3S | ||||||||
| Launch site | Kagoshima Space Center | ||||||||
| End of mission | |||||||||
| Disposal | Decommissioned | ||||||||
| Last contact | 17 December 1988[2] | ||||||||
| Decay date | 19 January 1989 | ||||||||
| Orbital parameters | |||||||||
| Reference system | Geocentric[1] | ||||||||
| Regime | Low Earth | ||||||||
| Perigee altitude | 489 km (304 mi) | ||||||||
| Apogee altitude | 503 km (313 mi) | ||||||||
| Inclination | 31.5° | ||||||||
| Period | 94 minutes | ||||||||
| |||||||||
Tenma, known as ASTRO-B before launch, was a Japanese X-ray astronomy satellite developed by the Institute of Space and Astronautical Science. It was launched on 20 February 1983, using a M-3S rocket on the M-3S-3 mission. It was the second X-ray observatory successfully operated by Japan after Hakucho (CORSA-B),[3][a] and it had a superior temporal and spectral sensitivity compared to its predecessor.[5]
Battery failure in July 1984 caused the operation to become limited, and continuing problems lead to the termination of X-ray observation on 11 November 1985,[6] however it remained in sporadic contact until 17 December 1988.[2] It reentered the atmosphere on 19 January 1989.[b]
Highlights
[edit]References
[edit]Notes
[edit]Citations
[edit]- ^ a b G. D. Krebs. "Astro B (Tenma)". Gunter's Space Page. Retrieved 18 August 2025.
- ^ a b c "Tenma | Spacecraft". isas.jaxa.jp. JAXA / ISAS. Retrieved 19 August 2025.
- ^ Y. Tanaka; M. Fujii; H. Inoue; et al. (1984). "X-ray astronomy satellite Tenma" (PDF). Publications of the Astronomical Society of Japan. 36 (4): 641–658. Bibcode:1984PASJ...36..641T. doi:10.1093/pasj/36.4.641. ISSN 0004-6264.
- ^ G. D. Krebs. "Corsa A, B (Hakucho)". Gunter's Space Page. Retrieved 20 August 2025.
- ^ C. Simpson (1984). "Tenma - Japan's X-ray satellite". Spaceflight. Vol. 26. p. 284. Bibcode:1984SpFl...26..284S. ISSN 0038-6340.
- ^ a b L. Angelini; J. Allen (7 October 2003). "The Tenma [Astro-B] satellite". heasarc.gsfc.nasa.gov. NASA / GSFC. Retrieved 20 August 2025.
- ^ T. S. Kelso. "CelesTrak: Search Satellite Catalog". Retrieved 3 June 2020.
External links
[edit]- Tenma at ISAS
- Tenma at NASA Archived 2017-04-01 at the Wayback Machine