Recent from talks
Nothing was collected or created yet.
Frail gourami
View on WikipediaThis article needs additional citations for verification. (December 2023) |
| Frail gourami | |
|---|---|

| |
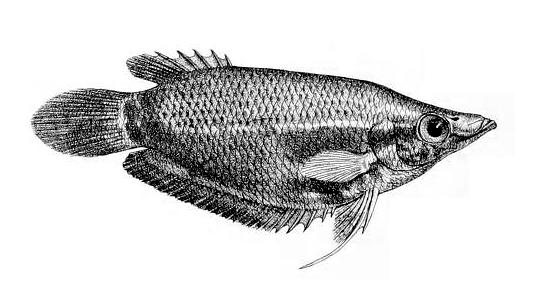
| Male gourami showing breeding and/or defensive colors and posture | |
| Scientific classification | |
| Kingdom: | Animalia |
| Phylum: | Chordata |
| Class: | Actinopterygii |
| Order: | Anabantiformes |
| Family: | Osphronemidae |
| Subfamily: | Luciocephalinae |
| Genus: | Ctenops McClelland, 1845 |
| Species: | C. nobilis
|
| Binomial name | |
| Ctenops nobilis McClelland, 1845
| |

| |
| Synonyms | |
| |
The frail gourami (Ctenops nobilis) or noble gourami is a mouth brooding species of gourami native to northeastern India and Bangladesh.[1][2] It grows to a length of 10 cm (3.9 in). It is only seldom found in the aquarium trade, due to its extreme sensitivity to shipping stress and high levels of aggression.[3] The frail gourami is the only known member of its genus.[2]
Growth habits
[edit]As these fish grow as juveniles, socialization is shown, but as maturity is reached, then their entire personalities flip upside down with high levels of aggression to others of their kind and potentially other fish as well.[citation needed]
Life cycle
[edit]Females have a slimmer head and jaw shape compared to males. Males have a rounder jaw for mouth brooding (carrying eggs in the mouth). The ritual can last for many hours. The female, after laying the eggs, diligently collects every one of them and expels them from her mouth for the male to hold with his anal fin and place in his mouth. They continue this process until every egg is laid and guard the area at the same time. The males are then the parental egg-bearer and gain a cryptic and strange marble patterning.[citation needed] Feeding then is greatly reduced in the male, or ceases altogether. The eggs stay in his mouth for about 7–20 days, and then release free-swimming fry. This intelligent species shows a learning process in younger or inexperienced individuals as they gain knowledge of how to hold the eggs properly without swallowing them.
Natural habitat
[edit]These micro-predators live in the clear, overgrown, slow-flowing waters of eastern India, northern Bangladesh, the Sikkim state, west Bengal, Bihar, the Assam states, and just discovered, Nepal. This adaptive species have also been recorded where foliage and vegetation is scarce. In their native habitat, during the months of June and July, monsoons are common. Temperatures range from 59–90 degrees Fahrenheit, or 15–32 degrees Celsius, with the cold extremes at the most northerly reaches of its range. Its habitats are subject to severe seasonal changes in water change, volume, and flow. In Bangladesh, in a slow-moving, shallow stream containing clear water with a substrate of sand and organic detritus, the frail gourami was observed alongside sympatric species including Pseudolaguvia muricata, Barilius barna, B. bendelisis, B. tileo, Devario devario, Oreichthys cosuatis, Psilorhynchus sucatio, Lepidocephalichthys guntea, Acanthocobitis botia, Schistura corica, S. savona, Amblyceps mangois, Mystus bleekeri, Olyra longicaudata, Conta conta, Hara jerdoni, Pseudolaguvia ribeiroi, P. shawi, Aplocheilus panchax, Xenentodon cancila, Microphis deocata, Chanda nama, Pseudambassis baculis, Pseudambassis ranga, Channa gachua, Badis badis, Nandus nandus, Glossogobius giuris, Mastacemelus pancalus and Tetraodon cutcutia.[citation needed]

In the Suthimari River basin, West Bengal frail gouramis were collected in early September in the early afternoon alongside Danio rerio from a habitat containing relatively clear, moderately-flowing water with some suspended sediment and there was no aquatic vegetation present.[citation needed]
References
[edit]- ^ a b Vishwanath, W. (2010). "Ctenops nobilis". IUCN Red List of Threatened Species. 2010 e.T166599A6244543. doi:10.2305/IUCN.UK.2010-4.RLTS.T166599A6244543.en. Retrieved 20 November 2021.
- ^ a b Froese, Rainer; Pauly, Daniel (eds.). "Ctenops nobilis". FishBase. February 2014 version.
- ^ "Ctenops nobilis (Frail Gourami) — Seriously Fish".