Recent from talks
Nothing was collected or created yet.
Boeing 787 Dreamliner
View on Wikipedia
The Boeing 787 Dreamliner is an American wide-body airliner developed and manufactured by Boeing Commercial Airplanes.
Key Information
After dropping its unconventional Sonic Cruiser project, Boeing announced the conventional 7E7 on January 29, 2003, which focused largely on efficiency. The program was launched on April 26, 2004, with an order for 50 aircraft from All Nippon Airways (ANA), targeting a 2008 introduction. On July 8, 2007, a prototype 787 without major operating systems was rolled out; subsequently the aircraft experienced multiple delays, until its maiden flight on December 15, 2009. Type certification was received in August 2011, and the first 787-8 was delivered in September 2011 and entered commercial service on October 26, 2011, with ANA.
At launch, Boeing targeted the 787 with 20% less fuel burn compared to aircraft like the Boeing 767. It could carry 200 to 300 passengers on point-to-point routes up to 8,500 nautical miles [nmi] (15,700 km; 9,800 mi), a shift from hub-and-spoke travel. The twinjet is powered by General Electric GEnx or Rolls-Royce Trent 1000 high-bypass turbofans. It is the first airliner with an airframe primarily made of composite materials and makes greater use of electrical systems. Externally, it is recognizable by its four-window cockpit, raked wingtips, and noise-reducing chevrons on its engine nacelles. Development and production rely on subcontractors around the world more than for previous Boeing aircraft. Since March 2021 final assembly has been at the Boeing South Carolina factory; it was formerly in the Boeing Everett Factory in Washington State.
The initial 186-foot-long (57 m) 787-8 typically seats 248 passengers over a range of 7,305 nmi (13,529 km; 8,406 mi), with a 502,500 lb (227.9 t) MTOW compared to 560,000 lb (250 t) for later variants. The stretched 787-9, 206 ft (63 m) long, can fly 7,565 nmi (14,010 km; 8,706 mi) with 296 passengers; it entered service on August 7, 2014, with All Nippon Airways. The further stretched 787-10, 224 ft (68 m) long, seating 336 over 6,330 nmi (11,720 km; 7,280 mi), entered service with Singapore Airlines on April 3, 2018.
Early 787 operations encountered several problems caused mainly by its lithium-ion batteries, including fires onboard some aircraft. In January 2013, the US FAA grounded all 787s until it approved the revised battery design in April 2013. Significant quality control issues from 2019 onward caused a production slowdown and, from January 2021 until August 2022, an almost total cessation of deliveries.
The first fatal crash and hull loss of the aircraft occurred on June 12, 2025, with Air India Flight 171. A preliminary report issued on July 12 by the Indian Aircraft Accident Investigation Bureau did not recommend any actions to Boeing, or 787 operators.
Boeing has spent $32 billion on the program; estimates for the number of aircraft sales needed to break even vary between 1,300 and 2,000. As of September 2025[update], the 787 program has received 2,270 orders and made 1,222 deliveries.
Development
[edit]Background
[edit]During the late 1990s, Boeing considered replacement aircraft programs due to slowing sales of the 767 and 747-400. Two new aircraft were proposed. The 747X would have lengthened the 747-400 and improved efficiency, and the Sonic Cruiser would have achieved 15% higher speeds (approximately Mach 0.98) while burning fuel at the same rate as the 767.[2] Market interest for the 747X was tepid; several major American airlines, including Continental Airlines, showed initial enthusiasm for the Sonic Cruiser, although concerns about the operating cost were also expressed.[3] The global airline-market was disrupted by the 9/11 attacks and increased petroleum prices, making airlines more interested in efficiency than speed. The worst-affected airlines, those in the United States, had been considered the most likely customers of the Sonic Cruiser; thus the Sonic Cruiser was officially canceled on December 20, 2002. On January 29, 2003, Boeing announced an alternative product, the 7E7, using Sonic Cruiser technology in a more conventional configuration.[4][5] The emphasis on a smaller midsize twinjet rather than a large 747-size aircraft represented a shift from the hub-and-spoke theory toward the point-to-point theory,[6] in response to analysis of focus groups.[7]
Randy Baseler, Boeing Commercial Airplanes VP Marketing stated that airport congestion comes from large numbers of regional jets and small single-aisles, flying to destinations where a 550-seat Airbus A380 would be too large; to reduce the number of departures, smaller airplanes can increase by 20% in size and airline hubs can be avoided with point-to-point transit.[8]
In 2003, a recent addition to the Boeing board of directors, James McNerney (who would become Boeing's Chairman and CEO in 2005), supported the need for a new aircraft to regain market share from Airbus. The directors on Boeing's board, Harry Stonecipher (Boeing's President and CEO) and John McDonnell issued an ultimatum to "develop the plane for less than 40 percent of what the 777 had cost to develop 13 years earlier, and build each plane out of the gate for less than 60 percent of the 777's unit costs in 2003", and approved a development budget estimated at US$7 billion as Boeing management claimed that they would "require subcontractors to foot the majority of costs." Boeing Commercial Airplanes president Alan Mulally, who had previously served as general manager of the 777 programs contrasted the difference in the approval process by the board between the 777 and 787 saying "In the old days, you would go to the board and ask for X amount of money, and they'd counter with Y amount of money, and then you'd settle on a number, and that's what you'd use to develop the plane. These days, you go to the board, and they say, 'Here's the budget for this airplane, and we'll be taking this piece of it off the top, and you get what's left; don't fuck up.'"[9]
The replacement for the Sonic Cruiser project was named "7E7"[10] (with a development code name of "Y2"). Technology from the Sonic Cruiser and 7E7 was to be used as part of Boeing's project to replace its entire airliner product line, an endeavor called the Yellowstone Project (of which the 7E7 became the first stage).[11] Early concept images of the 7E7 included rakish cockpit windows, a dropped nose, and a distinctive "shark-fin" tail.[12] The "E" was said to stand for various things, such as "efficiency" or "environmentally friendly". In the end, Boeing said it stood for "Eight".[4] In July 2003, a public naming competition was held for the 7E7, for which out of 500,000 votes cast online the winning title was Dreamliner.[13] Other names included eLiner, Global Cruiser, and Stratoclimber.[14][15]

On April 26, 2004, Japanese airline All Nippon Airways (ANA) became the launch customer for the 787, announcing a firm order for 50 aircraft with deliveries to begin in late 2008.[16] The ANA order was initially specified as 30 787-3, 290–330 seat, one-class domestic aircraft, and 20 787-8, long-haul, 210–250 seat, two-class aircraft for regional international routes such as Tokyo-Narita to Beijing-Capital, and could perform routes to cities not previously served, such as Denver, Moscow, and New Delhi.[17] The 787-3 and 787-8 were to be the initial variants, with the 787-9 entering service in 2010.[18]
On October 5, 2012, Indian state carrier Air India became the first carrier to take possession of a Dreamliner that was manufactured in the Charleston, South Carolina, Boeing plant. This was the first 787 that was manufactured outside of Washington.[19] Boeing would go on to use both the Everett and South Carolina plants to deliver the Dreamliner.
The 787 was the first production airliner built with a fuselage comprising one-piece composite barrel sections instead of aluminum-sheet assemblies using many fasteners.[20][21] Boeing selected two new engines to power the 787, the Rolls-Royce Trent 1000 and General Electric GEnx.[4] Boeing stated the 787 would be approximately 20 percent more fuel-efficient than the 767,[22] with approximately 40 percent of the efficiency gain from the engines,[23] plus gains from aerodynamic improvements,[24] increased use of lighter-weight composite materials, and advanced systems.[18] The airframe underwent extensive structural testing during its design.[25][26] The 787-8 and -9 were intended to have a certified 330-minute ETOPS capability,[27] but entered service with 180 minutes.[28] 330-minute certification was delayed until 2014.[29]
During the design phase, the 787 underwent extensive wind tunnel testing at Boeing's Transonic Wind Tunnel, QinetiQ's five-meter wind tunnel at Farnborough, United Kingdom, and NASA Ames Research Center's wind tunnel, as well as at the French aerodynamics research agency, ONERA. The final styling was more conservative than earlier proposals, with the fin, nose, and cockpit windows changed to a more conventional form. By 2005, customer-announced orders and commitments for the 787 reached 237 aircraft.[30] Boeing initially priced the 787-8 variant at US$120 million, a low figure that surprised the industry. By 2007, the list price had increased to US$157–167 million, eventually exceeding US$200 million by the time the aircraft received type certification.[31][32] Airlines and lessors do not pay the full list price, with market prices for the 787-8 being up to 46% lower.[33]
Manufacturing and suppliers
[edit]On December 16, 2003, Boeing announced that the 787 would be assembled in its factory in Everett, Washington.[4] Instead of conventionally building the aircraft from the ground up, the final assembly employed 800 to 1,200 people to join completed subassemblies and integrate systems.[34] Boeing assigned global subcontractors to do more assembly work, delivering completed subassemblies to Boeing for final assembly. This approach was intended to result in a leaner, simpler assembly line and lower inventory,[35] with pre-installed systems reducing final assembly time by three-quarters to three days.[36][37] Subcontractors had early difficulties procuring needed parts and finishing subassemblies on schedule, leaving remaining assembly work for Boeing to complete as "traveled work".[38][39] In 2010, Boeing considered in-house construction of the 787-9 tail; the tail of the 787-8 is made by Alenia.[40] The 787 was unprofitable for some subcontractors; Alenia's parent company, Finmeccanica, had a total loss of €750 million on the project.[41]

Subcontracted assemblies included wing and center wing box (Mitsubishi Heavy Industries, Japan; Subaru Corporation, Japan);[42] horizontal stabilizers (Alenia Aeronautica, Italy; Korea Aerospace Industries, South Korea);[43] fuselage sections (Global Aeronautica, Italy; Boeing, North Charleston, US; Kawasaki Heavy Industries, Japan; Spirit AeroSystems, Wichita, US; Korean Air, South Korea);[44][45][46] passenger doors (Latécoère, France); cargo doors, access doors, and crew escape door (Saab AB, Sweden); software development (HCL Enterprise, India);[47] floor beams (TAL Manufacturing Solutions Limited, India);[48][49] wiring (Labinal, France);[50] wing-tips, flap support fairings, wheel well bulkhead, and longerons (Korean Air, South Korea);[51] landing gear (Messier-Bugatti-Dowty, UK/France);[52][53] and power distribution and management systems, air conditioning packs (Hamilton Sundstrand, Connecticut, US).[50][54]
To speed up deliveries, Boeing modified four used 747-400s into 747 Dreamlifters to transport 787 wings, fuselage sections, and other smaller parts. Japanese industrial participation was key to the project. Japanese companies co-designed and built 35% of the aircraft; the first time that outside firms played a key design role on Boeing airliner wings. The Japanese government supported development with an estimated US$2 billion in loans.[55] On April 26, 2006, Japanese manufacturer Toray Industries and Boeing signed a production agreement involving US$6 billion worth of carbon fiber, extending a 2004 contract.[4] In May 2007, the final assembly on the first 787 began at Everett.[56]
From the outset, 787 chief engineer Walt Gillette and his colleagues realized that the "Working Together" approach to supplier coordination used for the 777 must substantially evolve for the 787. So they created the 787 Dreamliner Partner Council. The council evolved from the Sonic Cruiser effort and a similar approach used in Boeing's defense business unit. The partner council would make 787 decisions together, a departure from Boeing's more hierarchical approach to decision making for the 777. Boeing harnessed not only expertise from the Partner Council, but also benefited from cross-cultural collaboration, according to Walt Gillette, as quoted in The Culture of Collaboration (2024, expanded and updated edition) by Evan Rosen.[57]
Boeing worked to reduce excess weight since assembly of the first airframe began; in late 2006, the first six 787s were overweight, with the first aircraft 5,000 lb (2,300 kg) heavier than required.[58] The seventh and subsequent aircraft would be the first 787-8s expected to meet the weight requirement.[59][60] Accordingly, some parts were redesigned to include more use of titanium.[61][62] In July 2015, Reuters reported that Boeing was considering reducing the use of titanium to reduce the construction cost.[63]
Early built 787s (line numbers under 20) were overweight, increasing their fuel burn and reducing their maximum range, and some carriers decided to take later aircraft. Boeing struggled to sell these aircraft, eventually offering significant discounts and scrapping one.[64][65] Because of their line numbers, these aircraft were nicknamed the "Terrible Teens".[66]

Boeing planned the first flight by the end of August 2007 and premiered the first 787 (registered N787BA) at a rollout ceremony on July 8, 2007.[67] The 787 had 677 orders at this time, which is more orders from launch to roll-out than any previous wide-body airliner.[68] The major systems were not installed at the time; many parts were attached with temporary non-aerospace fasteners requiring replacement with flight fasteners later.[69]
In September 2007, Boeing announced a three-month delay, blaming a shortage of fasteners as well as incomplete software.[70] On October 10, 2007, a second three-month delay to the first flight and a six-month delay to first deliveries were announced due to supply chain problems, a lack of documentation from overseas suppliers, and flight guidance software delays.[71][72] Less than a week later, Mike Bair, the 787 program manager, was replaced.[73] On January 16, 2008, Boeing announced a third three-month delay to the first flight of the 787, citing insufficient progress on "traveled work".[74] On March 28, 2008, to gain more control over the supply chain, Boeing announced plans to buy Vought Aircraft Industries' interest in Global Aeronautica; a later agreement was also made to buy Vought's factory in North Charleston.[75]
On April 9, 2008, a fourth delay was announced, shifting the maiden flight to the fourth quarter of 2008, and delaying initial deliveries by around 15 months to the third quarter of 2009. The 787-9 variant was postponed to 2012 and the 787-3 variant was to follow at a later date.[76] On November 4, 2008, a fifth delay was announced due to incorrect fastener installation and the Boeing machinists strike, stating that the first test flight would not occur in the fourth quarter of 2008.[77][78] After assessing the program schedule with suppliers,[79] in December 2008, Boeing stated that the first flight was delayed until the second quarter of 2009.[80] Airlines, such as United Airlines and Air India, stated their intentions to seek compensation from Boeing for the delays.[81][82]
A secondary factor in the delays faced by the 787 program was the lack of detailed specifications provided to partners and suppliers. In previous programs Boeing had supplied high level design data, but for the 787, decided to provide broad level specifications only, on the assumption that relevant partners had the competencies to perform the design and integration work with the limited data. This decision created several delays as suppliers struggled to work with the limited design data.[83]
Pre-flight ground testing
[edit]As Boeing worked with its suppliers toward production, the design proceeded through a series of test goals. On August 23, 2007, a crash test involving a vertical drop of a partial composite fuselage section from about 15 ft (5 m) onto a 1 in (25 mm)-thick steel plate occurred in Mesa, Arizona;[84][85] the results matched predictions, allowing modeling of various crash scenarios using computational analysis instead of further physical tests.[86][87] While critics had expressed concerns that a composite fuselage could shatter and burn with toxic fumes during crash landings, test data indicated no greater toxicity than conventional metal airframes.[88][89] The crash test was the third in a series of demonstrations conducted to match FAA requirements, including additional certification criteria due to the wide-scale use of composite materials.[85] The 787 meets the FAA's requirement that passengers have at least as good a chance of surviving a crash landing as they would with current metal airliners.[90]

On August 7, 2007, on-time certification of the Rolls-Royce Trent 1000 engine by European and US regulators was received.[91] The alternative GE GEnx-1B engine achieved certification on March 31, 2008.[92] On June 20, 2008, the first aircraft was powered up, for testing the electrical supply and distribution systems.[93] A non-flightworthy static test airframe was built; on September 27, 2008, the fuselage was successfully tested to a differential pressure of 14.9 psi (103 kPa), which is 150 percent of the maximum pressure expected in commercial service.[94] In December 2008, the 787's maintenance program was passed by the FAA.[95]
On May 3, 2009, the first test 787 was moved to the flight line following extensive factory testing, including landing gear swings, systems integration verification, and a total run-through of the first flight.[96] On May 4, 2009, a press report indicated a 10–15% range reduction, about 6,900 nmi (12,800 km; 7,900 mi) instead of the originally promised 7,700 to 8,200 nautical miles (14,300 to 15,200 km; 8,900 to 9,400 mi), for early aircraft that were about 8% overweight. Substantial redesign work was expected to correct this, which would complicate increases in production rates;[97] Boeing stated the early 787-8s would have a range of almost 8,000 nmi (15,000 km; 9,200 mi).[98] As a result, some airlines reportedly delayed deliveries of 787s to take later planes that may be closer to the original estimates.[99] Boeing expected to have the weight issues addressed by the 21st production model.[100]
On June 15, 2009, during the Paris Air Show, Boeing said that the 787 would make its first flight within two weeks. On June 23, the first flight was postponed due to structural reasons.[101][102] Boeing provided an updated 787 schedule on August 27, 2009, with the first flight planned to occur by the end of 2009 and deliveries to begin at the end of 2010.[103] The company expected to write off US$2.5 billion because it considered the first three Dreamliners built unsellable and suitable only for flight tests.[104] On October 28, 2009, Boeing selected Charleston, SC as the site for a second 787 production line, after soliciting bids from multiple states.[105] On December 12, 2009, the first 787 completed high-speed taxi tests, the last major step before flight.[106][107]
Flight testing
[edit]
On December 15, 2009, Boeing conducted the 787-8 maiden flight from Paine Field in Everett, Washington, at 10:27 am PST and landed three hours later at 1:33 p.m. at Seattle's Boeing Field. During the flight the 787 reached a top speed of 180 kn (333 km/h) and maximum altitude of 13,200 ft (4,000 m).[108] Originally scheduled for 5+1/2 hours, the test flight was shortened to three hours due to unfavorable weather conditions.[109] The six-aircraft ground and flight test program was scheduled to be done in eight and a half months and 6800 hours, which was the fastest certification campaign for a new Boeing commercial design.[110]
The flight test program comprised six aircraft, ZA001 through ZA006, four with Rolls-Royce Trent 1000 engines and two with GE GEnx-1B64 engines. The second 787, ZA002 in All Nippon Airways livery, flew to Boeing Field on December 22, 2009, to join the flight test program;[111][112] the third 787, ZA004 made its first flight on February 24, 2010, followed by ZA003 on March 14, 2010.[113] On March 24, 2010, flutter and ground effects testing was completed, clearing the aircraft to fly its entire flight envelope.[114] On March 28, 2010, the 787 completed the ultimate wing load test, which requires that the wings of a fully assembled aircraft be loaded to 150% of the design limit load and held for 3 seconds. The wings were flexed approximately 25 ft (7.6 m) upward during the test.[115] Unlike past aircraft, the wings were not tested to failure.[116][117] On April 7, data showed the test had been a success.[118]
On April 23, 2010, the newest 787, ZA003, arrived at the McKinley Climatic Laboratory hangar at Eglin Air Force Base, Florida, for extreme weather testing in temperatures ranging from 115 to −45 °F (46 to −43 °C), including takeoff preparations at both temperature extremes.[119] ZA005, the fifth 787 and the first with GEnx engines, began ground engine tests in May 2010,[120] and made its first flight on June 16, 2010.[121] In June 2010, gaps were discovered in the horizontal stabilizers of test aircraft due to improperly installed shims; all aircraft were inspected and repaired.[122] That same month, a 787 experienced its first in-flight lightning strike; inspections found no damage.[123] As composites can have as little as 1/1,000th the electrical conductivity of aluminum, conductive material is added to alleviate potential risks and to meet FAA requirements.[88][124][125] The FAA also planned requirement changes to help the 787 show compliance.[126] In December 2019, it was reported that Boeing had removed the copper foil that formed part of the protection against lightning strikes to the wings of the aircraft; it then worked with the FAA to override concerns raised.[127][128]

The 787 made its first appearance at an international air show at the Farnborough Airshow, United Kingdom, on July 18, 2010.[129]
On August 2, 2010, a Trent 1000 engine suffered an uncontained failure at Rolls-Royce's test facility during ground testing.[130] The failure changed the schedule for installing Trent 1000 engines; on August 27, 2010, Boeing stated that the first delivery to launch customer ANA would be delayed until early 2011.[131][132] That same month, Boeing faced compensation claims from airlines owing to ongoing delivery delays.[133] In September 2010, it was reported that two additional 787s might join the test fleet for a total of eight flight test aircraft.[134] On September 10, 2010, a partial engine surge occurred in a Trent engine on ZA001 at Roswell.[135] On October 4, 2010, the sixth 787, ZA006 joined the test program with its first flight.[136]
On November 9, 2010, the second 787, ZA002 made an emergency landing at Laredo International Airport, Texas, after smoke and flames were detected in the main cabin during a test flight.[137][138] The electrical fire caused some systems to fail before landing.[139] Following this incident, Boeing suspended flight testing on November 10, 2010; ground testing continued.[140][141] After investigation, the in-flight fire was primarily attributed to foreign object debris (FOD) that was present in the electrical bay.[142] After electrical system and software changes, the 787 resumed flight testing on December 23, 2010.[143][144]
Test evaluation and certification
[edit]
On November 5, 2010, it was reported that some 787 deliveries would be delayed to address problems found during flight testing.[145][146] In January 2011, the first 787 delivery was rescheduled to the third quarter of 2011 due to software and electrical updates following the in-flight fire.[147][148] By February 24, 2011, the 787 had completed 80% of the test conditions for the Rolls-Royce Trent 1000 engine and 60% of the conditions for the General Electric GEnx-1B engine.[149] In July 2011, ANA performed a week of operations testing using a 787 in Japan.[150] The test aircraft had flown 4,828 hours in 1,707 flights combined by August 15, 2011.[113] During testing, the 787 visited 14 countries in Asia, Europe, North America, and South America to test in extreme climates and conditions and for route testing.[151]
On August 13, 2011, certification testing of the Rolls-Royce powered 787-8 finished.[152] The FAA and European Aviation Safety Agency certified the 787 on August 26, 2011, at a ceremony in Everett, Washington.[153][154]
Entry into service
[edit]
Certification cleared the way for deliveries and in 2011, Boeing prepared to increase 787 production rates from two to ten aircraft per month at assembly lines in Everett and Charleston over two years.[154] Legal difficulties clouded production at Charleston; on April 20, 2011, the National Labor Relations Board alleged that a second production line in South Carolina violated two sections of the National Labor Relations Act.[105] In December 2011, the National Labor Relations Board dropped its lawsuit after the Machinists' union withdrew its complaint as part of a new contract with Boeing.[155] The first 787 assembled in South Carolina was rolled out on April 27, 2012.[156]
The first 787 was officially delivered to All Nippon Airways (ANA) on September 25, 2011, at the Boeing Everett factory. A ceremony to mark the occasion was also held the next day.[157][158] On September 27, it flew to Tokyo Haneda Airport.[159][160] The airline took delivery of the second 787 on October 13, 2011.[161]
On October 26, 2011, an ANA 787 flew the first commercial flight from Tokyo's Narita International Airport to Hong Kong International Airport.[162] The Dreamliner entered service some three years later than originally planned. Tickets for the flight were sold in an online auction; the highest bidder had paid $34,000 for a seat.[163] An ANA 787 flew its first long-haul flight to Europe on January 21, 2012, from Haneda to Frankfurt Airport.[164]
Proposed variants
[edit]Freighter version
[edit]Even after production of the 787 began, Boeing continued to produce the 767 as a freighter. More stringent emissions and noise limits will go into effect in 2028 and prevent 767 sales in its current form.[165] To address this concern, Boeing has widely reported to be working on a freighter version of the 787, showing proposals to customers including FedEx Express.[166][167] As of May 2024[update], production of the 787 Freighter is expected to begin between 2028 and 2033.[168]
787-3
[edit]
The 787-3 would have carried 290–330 passengers in two-class over 2,500–3,050 nmi (4,630–5,650 km; 2,880–3,510 mi) range, limited by a 364,000 lb (165 t) MTOW.[169] In April 2008, to keep the -8 on track for delivery, the -9 stretch was postponed from 2010 to at least 2012 and prioritized before the 787-3 and its 43 orders to follow without a firm delivery date.[76]
It kept the -8 length but its 51.7 m wingspan would have fit in ICAO Aerodrome Reference Code D.[170] It was designed to operate on Boeing 757-300/Boeing 767-200 sized regional routes from airports with restricted gate spacing.[171] The wingspan was decreased by using blended winglets instead of raked wingtips.
By January 2010, all orders, from Japan Airlines and All Nippon Airways, had been converted to the 787-8.[172] As it was designed specifically for the Japanese market, Boeing would likely scrap it after they switched orders.[173] The -8's longer wingspan makes it more efficient on stages longer than 200 nmi (370 km; 230 mi).[174] In December 2010, Boeing withdrew the short-haul model as it struggled to produce the 787-8 after program delays of three years.[175]
Market and costs
[edit]
The 787 Dreamliner program has reportedly cost Boeing $32 billion.[176][177] In 2013, the 787 program was expected to be profitable after 1,100 aircraft have been sold.[178] At the end of 2013, the cost of producing a 787 exceeded the purchase price. Boeing's accounting method books sales immediately and distributes estimated production costs over ten years for the 1,300 aircraft it expects to deliver during that time. JPMorgan Chase analyst Joseph Nadol estimated the program's cash loss to be $45 million per airplane, decreasing as the program moves forward. The actual cash flow reflects Boeing collecting most of the purchase price upon delivery; Boeing expects deferred costs to total $25 billion before the company begins to break even on production; the comparable number for the Boeing 777, adjusted for inflation, is $3.7 billion.[179]
Boeing lost $30 million per 787 delivered in the first quarter of 2015, although Boeing planned to break even by the end of the year.[180] The accumulated losses for the 787 totaled almost $27 billion (~$34.8 billion in 2024) by May 2015. The cost of producing the fuselage may increase because of a tentative deal reached with Spirit Aerosystems of Wichita, Kansas, wherein severe price cuts demanded by Boeing would be eased, in return for a comprehensive agreement that lowers the cost of fuselages for other jetliners that Spirit helps Boeing manufacture.[181]
In the second quarter of 2015, Boeing lost $25 million (~$32.2 million in 2024) on each 787 delivered but was planning to break even per plane before the year-end. After that Boeing hoped to build 900 Dreamliners over six years at an average profit of more than $35 million each. But with deferred costs peaking in 2016 at $33 billion, (~$42.2 billion in 2024) Leeham analyst Bjorn Fehrm believes Boeing cannot make an overall profit on the program. Ted Piepenbrock, an academic affiliated with MIT and the University of Oxford, projects losses decreasing through the first 700 airliners and forecasts the cumulative deferred costs to peak beyond $34 billion. The model most favorable to Boeing projects a program loss of $5 billion after delivering 2,000 Dreamliners. Boeing's original development investment, estimated at least at a further $20 billion, is not included in these costs.[182]
To recoup the deferred costs and earn its goal of a "low single-digit" overall profit margin, Boeing has to make an average profit of more than $50 million on the final 205 airplanes of the accounting block to be delivered from 2020: a profit margin of more than 30% while the mature Boeing 737 and 777 programs have 20% to 25% margins. Boeing is reaching it through a larger proportion of the 20% to 40% higher price -9/10s, costing only 5% to 10% more than the -8 with lower production costs from reliability and producibility investments and the expected experience curve. Former Douglas Aircraft chief economist Adam Pilarski notes that two assembly sites slow the experience curve. Boeing assumed a faster improvement than on previous programs which had not happened. Competition with the Airbus A350 and the launch of the A330neo put strong pressure on the 787 pricing.[182]
On July 21, 2016, Boeing reported charges of $847 million against two flight-test 787s built in 2009. Boeing had planned to refurbish and sell them but instead wrote them off as research and development expense.[183] In 2017, Boeing's Jim Albaugh said that the requested return on net assets (RONA) led to outsourcing systems reducing investment, but improving RONA had to be balanced against the risk of loss of control.[184] From 2019, Boeing was to build 14 787s per month (168 per year), helping to offset the $28 billion in deferred production costs accumulated through 2015 and would add 100 aircraft to the current accounting block of 1,300 at the end of 2017 third quarter.[185] In 2019, the list price for a 787-8 was US$248.3M, $292.5M for a 787-9, and $338.4M for a 787-10.[186]
The valuation for a new 787-9 is $145 million in 2018, up from $135 million in 2014, but it may have been sold for $110–115 million to prevent A330neo sales while an A330-900 is worth $115 million.[187] In February 2018, Boeing priced six 787-9s for less than $100–115m each to Hawaiian Airlines, close to their production cost of $80–90m, to overcome its A330-800 order.[188] By late 2018, deferred production costs were reduced from a peak of $27.6 billion in early 2016 to $23.5 billion as assembly efficiency improved and the 800th production started.[189]
Production rate
[edit]By 2014, Boeing planned to improve financial return by reorganizing the production line, renegotiating contracts with suppliers and labor unions, and increasing the 787 production rate, stepwise, to 12 airplanes per month by the end of 2016 and 14 airplanes per month by the end of the decade.[179] By April 2015, the production rate was 10 per month.[190]
From late 2020, the production rate is to be reduced from 14 to 12 airplanes per month due to the China-United States trade war.[191] Production could be trimmed to 10 planes per month as demand for wide-body aircraft falters.[192] On October 1, 2020, Boeing announced the 787 would be produced only in North Charleston from mid-2021 due to the impact of the COVID-19 pandemic on aviation, as the production rate fell to six per month.[193] In December, the monthly rate was further reduced to five.[194]
Quality-control issues (2019–2025)
[edit]2019
[edit]In 2019, reports began to emerge about quality-control issues at the North Charleston plant leading to questions about the jet's safety;[195][196] and later that same year KLM, which had discovered loose seats, missing and incorrectly installed pins, nuts and bolts not fully tightened and a fuel-line clamp left unsecured on its jet, complained that the standard of manufacture was "way below acceptable standards."[197]
2020
[edit]Early in 2020, Boeing engineers complained about depressions in the 787's vertical tail fin, affecting hundreds of planes or the vast majority of the fleet. Workers in Charleston and Everett had improperly discarded shims before the final installation of fasteners, which could lead to structural failure under limited loads. In late August 2020, Boeing grounded eight 787s due to such improper fuselage shimming and inner skin surfacing issues—issues which proved to have been discovered in August 2019 at Boeing South Carolina.[198][199]
The following month, Boeing admitted that "nonconforming" sections of the rear fuselage did not meet engineering standards, and the FAA was investigating quality-control lapses dating back to the introduction of the 787 in 2011 and considering requiring additional inspections for up to 900 of the roughly 1,000 Dreamliners in service.[198] The FAA then began to inquire into the company's Quality Management System (QMS), which Boeing had previously argued justified a reduction of 900 quality inspectors, but which had failed to detect either the shim or skin surface issues.[200] A third quality-control issue then emerged, this time with the 787's horizontal stabilizers, and affecting as many as 893 Dreamliners: workers in Salt Lake City had clamped portions of the tail section too tightly, which could lead to premature material fatigue. At this point Boeing expected a one-time inspection during regularly scheduled maintenance to address the issues[201][202] and expected merely to slow 787 deliveries "in the near term".[203]
2021
[edit]By January 2021, Boeing had halted 787 deliveries to complete the inspection relating to poor quality control,[204] then in March the FAA withdrew Boeing's delegated authority to inspect and sign off on four new 787s, saying that it would extend this withdrawal to further aircraft if needed.[205] Boeing briefly resumed deliveries on March 26, 2021, handing over one 787-9 to United Airlines,[206] but deliveries ceased again in May 2021;[207] meaning that almost all deliveries had been paused for nearly a year.[208] The delay generated $1 billion in abnormal costs and caused the company to cut production to around two planes a month.[209]
On July 13, Boeing discovered gaps at joints in the forward pressure bulkhead and again reduced production; the company also investigated whether the issue affected 787s already in service.[210] Questions were asked about the inspection process used to check the work, and Boeing worked with the FAA to fix the problem, which was said to pose "no immediate threat to flight safety" and did not require 787s already in service to be grounded.[211]
On September 4, the Wall Street Journal reported that the FAA would not accept Boeing's proposed new inspection method, aiming to speed deliveries with targeted checks rather than nose-to-tail teardowns, until at least late October;[212] and in late November it was reported that the FAA had discovered further problems, including additional out of tolerance gaps and contamination and associated weakening of fuselage composites. The rectification process for existing aircraft was made more complex by a lack of detailed configuration data on each aircraft.[213] The new problems and the extension of the 13 month long disruption to 787 deliveries led to anger from buyers; a slide in the company's stock price; and demands by a subcommittee of the US House of Representatives for a review of the FAA's oversight of the plane.[214][215]
2022
[edit]In January 2022, it was reported that deliveries were not anticipated to restart until April 2022.[216] In February, the FAA announced that it would withdraw Boeing's delegated authority to issue airworthiness certificates for individual 787 aircraft until Boeing can demonstrate consistent quality, stable delivery processes, and a robust plan for the rework needed on the undelivered aircraft in storage.[217] In late March Boeing began sounding out suppliers about their ability to support the production of up to seven aircraft a month by late 2023.[218] Vistara, which had been expecting delivery of four Dreamliners in 2022, indicated a lack of confidence in Boeing meeting its delivery aims by arranging to lease aircraft instead.[219] Later in April reports began to emerge of a further delay of at least two months,[220] and it was only in late April that Boeing submitted the necessary certification package laying out the inspections and repairs to be undertaken on already constructed planes. The FAA rejected portions of the package as incomplete and returned it to Boeing, indicating a further delay before the resumption of deliveries.[221] In late July, the FAA approved Boeing's revised certification package, leading the company to anticipate resuming deliveries "within days".[222] Deliveries resumed on August 10, 2022, after the FAA granted clearance.[223]
2023
[edit]In February 2023, a further problem, of an analysis error by a supplier related to the 787 forward pressure bulkhead, was identified, leading to a further temporary halt in deliveries (but not in production) and a 5% drop in the company's share price.[224] On March 10, the FAA approved the resumption of the deliveries.[225]
2024
[edit]In April 2024, Boeing engineer Sam Salehpour reported that the 787's (as well as the 777's) fuselage had been improperly assembled and that it could cause individual aircraft to break apart in mid-air. Salehpour also claimed that he tried to raise these concerns to Boeing but was reprimanded by the company.[226][227] The FAA is investigating Salehpour's allegations.[228] Boeing released a statement rejecting these claims.[229]
2025
[edit]In early 2025, Italian authorities discovered a fraud scheme involving over 4,800 parts.[230] The investigation indicated that Manufacturing Process Specification (MPS), an Italian supplier, and its subcontractors had falsified quality certifications for the components used in the Dreamliner. MPS, however, no longer exists as a company.[231][relevant?]
Design
[edit]

The Boeing 787 Dreamliner is a long-haul, widebody, twin-engine jetliner, designed with lightweight structures that are 80% composite by volume;[232] Boeing lists its materials by weight as 50% composite, 20% aluminum, 15% titanium, 10% steel, and 5% other materials.[233][234] Aluminum has been used throughout the leading edges of wings and tailplanes, titanium is predominantly present within the elements of the engines and fasteners, while various individual components are composed of steel.[234]
External features include a smooth nose contour, raked wingtips, and engine nacelles with noise-reducing serrated edges (chevrons).[235] The longest-range 787 variant can fly up to 7,565 nmi (14,010 km; 8,710 mi),[236] or the even longer Qantas QF 9 flight between Perth and London Heathrow, over 7,828 nmi (14,497 km; 9,008 mi). Its cruising airspeed is Mach 0.85 (488 kn; 903 km/h; 561 mph).[237] The aircraft has a design life of 44,000 flight cycles.[238]
Flight systems
[edit]Among 787 flight systems, a key change from traditional airliners is the electrical architecture. The architecture is bleedless and replaces bleed air with electrically powered compressors and four of six hydraulic power sources with electrically driven pumps while eliminating pneumatics and hydraulics from some subsystems, e.g. engine starters and brakes.[239] Boeing says that this system extracts 35% less power from the engines, allowing increased thrust and improved fuel efficiency.[240] Spoiler electromechanical actuators (SEMAs) control two of the seven spoiler pairs on each wing surface, providing roll control, air and ground speed brake, and droop capabilities similar to those provided by the hydraulic actuators used on the remaining spoiler surfaces. The SEMAs are controlled by electronic motor control units (EMCUs).[241]
The total available onboard electrical power is 1.45 megawatts, which is five times the power available on conventional pneumatic airliners;[242] electrically powered systems include engine start, cabin pressurization, horizontal-stabilizer trim, and wheel brakes.[243] Wing ice protection is another new system; it uses electro-thermal heater mats on the wing slats instead of traditional hot bleed air.[244][245] An active gust alleviation system, similar to the system used on the B-2 bomber, improves ride quality during turbulence.[246][247]

The 787 has a "fly-by-wire" control system similar in architecture to that of the Boeing 777.[248][249] The flight deck features multi-function LCDs, which use an industry-standard graphical user interface widget toolkit (Cockpit Display System Interfaces to User Systems / ARINC 661).[250] The 787 flight deck includes two head-up displays (HUDs) as a standard feature.[251] Like other Boeing airliners, the 787 uses a yoke (as opposed to a side-stick). Under consideration is the future integration of forward-looking infrared into the HUD for thermal sensing, allowing pilots to "see" through clouds.[4] Lockheed Martin's Orion spacecraft will use a glass cockpit derived from Honeywell International's 787 flight deck systems.[252]
Honeywell and Rockwell Collins provide flight control, guidance, and other avionics systems, including standard dual head-up guidance systems,[4] Thales supplies the integrated standby flight display and power management,[4] while Meggitt/Securaplane provides the auxiliary power unit (APU) starting system, electrical power-conversion system, and battery-control system[253][254] with lithium cobalt oxide (LiCoO2) batteries by GS Yuasa.[255][256] One of the two batteries weighs 28.5 kg and is rated 29.6 V, 76 Ah, giving 2.2 kWh.[257] Battery charging is controlled by four independent systems to prevent overcharging, following early lab testing.[258] The battery systems were the focus of a regulatory investigation due to multiple lithium battery fires, which led to the grounding of the 787 fleet starting in January 2013.[259]
A version of Ethernet (Avionics Full-Duplex Switched Ethernet (AFDX) / ARINC 664) transmits data between the flight deck and aircraft systems.[260] The control, navigation, and communication systems are networked with the passenger cabin's in-flight internet systems.[261] In January 2008, FAA concerns were reported regarding possible passenger access to the 787's computer networks; Boeing has stated that various protective hardware and software solutions are employed, including air gaps to physically separate the networks, and firewalls for software separation.[261][262] These measures prevent data transfer from the passenger internet system to the maintenance or navigation systems.[261]
The -9/10 hybrid laminar flow control (HLFC) system delays the critical transition from laminar to turbulent flow as far back as possible on the vertical tail by passive suction from leading-edge holes to mid-fin low-pressure doors but was dropped from the tailplane due to lower benefits than the extra complexity and cost.[263]
Airframe
[edit]
The 787 is the first commercial aircraft to have an airframe majority made of carbon fiber reinforced polymer (CFRP), applied in: the empennage, fuselage, wings, doors, and in most other main components.[264] Each 787 contains approximately 77,000 lb (35 t) of CFRP, made with 51,000 lb (23 t) of pure carbon fiber.[265] CFRP materials have a higher strength-to-weight ratio than conventional aluminum structural materials, which contributes significantly to the 787's weight savings,[234] as well as superior fatigue behavior.[266] Historically, the first CFRP primary structure in Boeing commercial aircraft was put into service in 1984 on the horizontal tail of the Boeing 737 Classic, and in the mid-1990s on both vertical and horizontal tail (empennage) of the Boeing 777.[267] In the early 2000s, while studying the proposed Sonic Cruiser, Boeing built and tested the first CFRP fuselage section for commercial aircraft, to evaluate materials and manufacturing techniques which later applied to the Dreamliner.[268][269] Instead of designing one-piece composite fuselage barrels like the 787, the competing Airbus A350 uses a slightly more conventional approach with CFRP panels on CFRP frames, which is considered less risky in terms of assembly tolerance between fuselage sections.[89]
Safety can be a concern due to lower impact energy absorption and poorer fire, smoke and toxicity capability of CFRP fuselages in the event of a crash landing, leading to whistleblower complaints at Boeing by Vince Weldon, who was fired in 2006.[270][88] The Occupational Safety and Health Administration (OSHA) later denied Weldon whistleblower status "largely on the grounds that Boeing's 787 design does not violate any FAA regulations or standards".[270] Boeing further argued that CFRP structures have been used on empennages and other parts of airliners for many years without incident, and special damage detection procedures will be instituted for the 787 to detect any potential hidden damage.[271]
In the fall of 2004, 787 engineering program leader Walt Gillette made the final decision to use CFRP for the 787’s fuselage, a first for a commercial aircraft. Two distinct Boeing sub-groups with expertise in two different materials—CFRP and aluminum alloy—spent months researching how their material would perform for the 787.[272] Therefore, a "fundamental philosophical dichotomy" existed in the group. This is why a single "collaborative" leader rather than the group needed to make the final call on the material.[273]
In 2006, Boeing launched the 787 GoldCare program.[274] This is an optional, comprehensive life-cycle management service, whereby aircraft in the program are routinely monitored and repaired, as needed. Although the first program of its kind from Boeing, post-sale protection programs are not new; such programs are usually offered by third party service centers. Boeing is also designing and testing composite hardware so inspections are mainly visual. This reduces the need for ultrasonic and other non-visual inspection methods, saving time and money.[275]
The Boeing 787 is equipped with two flight recorders—a Forward Flight Recorder (FWD FR) and an Aft Flight Recorder (AFT FR)—each of which units provides the functions traditionally provided by the Flight Data Recorder and the Cockpit Voice Recorder.[276]
Interior
[edit]

The 787-8 is designed to typically seat 234 passengers in a three-class setup, 240 in two-class domestic configuration, and 296 passengers in a high-density economy arrangement. Seat rows can be arranged in four to seven abreast in first or business—e.g., 1–2–1, 2–2–2, or 2–3–2. Eight or nine abreast are options in economy—e.g., 2–4–2 or 3–3–3. Typical seat room ranges from 46 to 61 in (120 to 150 cm) pitch in first, 36 to 39 in (91 to 99 cm) in business, and 32 to 34 in (81 to 86 cm) in economy.[277][278]
Cabin interior width is approximately 18 feet (550 cm) at armrest level.[277][279] The Dreamliner's cabin width is 15 inches (38 cm) more than that of the Airbus A330 and A340,[280] 5 inches (13 cm) less than the A350,[281] and 16 in (41 cm) less than the 777.[282] The 787's economy seats can be up to 17.5 in (44.4 cm) wide for nine-abreast seating[283] and up to 19 inches (48 cm) wide for eight-abreast seating arrangements. Most airlines are selecting the nine-abreast (3–3–3) configuration.[284][285] The 787's nine-abreast seating for economy provides passengers less space, particularly across the hips and shoulders, than any other jet airliner.[286] Some observers recommended passengers avoid flying 787s with nine-abreast seating,[286][287] although others suggested that the 787 is more comfortable than other airliners.[288]
The 787's cabin windows have dimensions of 10.7 by 18.4 in (27 by 47 cm),[289] and a high eye level so passengers can maintain a view of the horizon.[290] The composite fuselage permits larger windows without the need for structural reinforcement.[291] Instead of plastic window shades, the windows use electrochromism-based smart glass (supplied by PPG Industries)[292] allowing flight attendants[293] and passengers to adjust five levels of sunlight and visibility to their liking,[294] reducing cabin glare while maintaining a view to the outside world,[290][295] but the most opaque setting still has some transparency.[293][296] While the lavatory window also uses smart glass, it was given a traditional sunshade.[294]
The 787's cabin features light-emitting diodes (LEDs)[297] as standard equipment, allowing the aircraft to be entirely "bulbless". LED lights have previously been an option on the Boeing 777 and Airbus aircraft fitted with standard fluorescent lights.[298][299] The system has three-color LEDs plus a white LED.[297] The 787 interior was designed to better accommodate persons with mobility, sensory, and cognitive disabilities. For example, a 56 by 57 in (140 by 140 cm) convertible lavatory includes a movable center wall that allows two separate lavatories to become one large wheelchair-accessible facility.[300]
The 787's internal cabin pressure is the equivalent of a 6,000 feet (1,800 m) cabin altitude, which is a higher pressure than the 8,000 feet (2,400 m) cabin altitude of older conventional aircraft.[301] According to Boeing, in a joint study with Oklahoma State University, this significantly improves passenger comfort.[246][302] Cabin air pressurization is provided by electrically driven compressors, rather than traditional engine-bleed air, thereby eliminating the need to cool heated air before it enters the cabin.[303][304] The cabin's humidity is programmable based on the number of passengers carried and allows 15% humidity settings instead of the 4% found in previous aircraft.[301] The composite fuselage avoids metal fatigue issues associated with higher cabin pressure and eliminates the risk of corrosion from higher humidity levels.[301] The cabin air-conditioning system improves air quality by removing ozone from outside air and, besides standard HEPA filters, which remove airborne particles, uses a gaseous filtration system to remove odors, irritants, and gaseous contaminants, as well as particulates like viruses, bacteria and allergens.[234][295]
Engines
[edit]The Boeing 787 has two engine options: the General Electric GEnx-1B and the Rolls-Royce Trent 1000. As of early 2020, of the 1,484 total 787 orders, 905 (61%) had selected General Electric engines, 476 (32%) had chosen Rolls-Royce engines, and 103 (7%) remained undecided.[305]
Both engines use a standardized electrical interface, enabling airlines to install either model with minimal modifications. This interchangeability reduces the time and cost typically associated with switching engine types and is particularly attractive to lessors, as it allows airlines to maintain a common engine type across their fleet when an aircraft changes ownership.[4] While earlier aircraft could accommodate engines from different manufacturers, swaps were rarely performed due to their complexity and expense.[306][307]
The 787's engines use an all-electric, bleedless system, adapted from the Sonic Cruiser, that eliminates the need for traditional superheated air conduits used for de-icing, cabin pressurization, and other functions.[4][266] As part of its "Quiet Technology Demonstrator 2" program, Boeing integrated several noise-reduction features into the aircraft. These include an air inlet lined with sound-absorbing materials and an exhaust duct with a chevron-toothed pattern to promote quieter mixing of exhaust with ambient air.[235] Boeing says these technologies make the 787 significantly quieter both inside the cabin and in surrounding areas,[308] with sound levels kept below 85 decibels at airport boundaries.[234]
In 2016, Rolls-Royce began flight testing the Trent 1000 TEN engine, an upgraded version of the Trent 1000 featuring a new compressor system derived from the Trent XWB and a new turbine design for extra thrust, up to 78,000 lbf (350 kN).[309]
-
General Electric GEnx with composite fan blades
-
Rolls-Royce Trent 1000 with titanium fan blade
Operational history
[edit]On December 6, 2011, test aircraft ZA006 (sixth 787), powered by General Electric GEnx engines, flew 10,710 nmi (19,830 km; 12,320 mi) non-stop from Boeing Field eastward to Shahjalal International Airport in Dhaka, Bangladesh, setting a new world distance record for aircraft in the 787's weight class, which is between 440,000 and 550,000 lb (200 and 250 t). This flight surpassed the previous record of 9,127 nautical miles (16,903 km; 10,503 mi), set in 2002 by an Airbus A330. The Dreamliner then continued eastbound from Dhaka to return to Boeing Field, setting a world-circling speed record of 42 hours, 27 minutes.[310] In December 2011, Boeing started a six-month promotion 787 world tour, visiting various cities in China, Africa, the Middle East, Europe, United States, and others.[311] In April 2012, an ANA 787 made a delivery flight from Boeing Field to Haneda Airport partially using biofuel from cooking oil.[312]
ANA surveyed 800 passengers who flew the 787 from Tokyo to Frankfurt: expectations were surpassed for 90% of passengers; features that met or exceeded expectations included air quality and cabin pressure (90% of passengers), cabin ambiance (92% of passengers), higher cabin humidity levels (80% of passengers), headroom (40% of passengers) and the larger windows (90% of passengers). 25% said they would go out of their way to again fly on the 787.[313]

After its first six months of service, Rolls-Royce powered ANA aircraft were burning around 21% less fuel than the replaced 767-300ER on international flights, slightly better than the 20% originally expected, and 15–20% on domestic routes, while GE-powered Japan Airlines aircraft were potentially slightly better.[314] Other 787 operators have reported similar fuel savings, ranging from 20 to 22% compared with the 767-300ER.[315] An analysis by consultant AirInsight concluded that United Airlines' 787s achieved an operating cost per seat that was 6% lower than the Airbus A330.[179] In November 2017, International Airlines Group chief Willie Walsh said that for its budget carrier Level the lower cost of ownership of its two A330-200 more than offsets the 13,000 lb (6 t) higher fuel burn ($3,500 on a Barcelona-Los Angeles flight). It would introduce three more A330s as there were not enough 787 pilots.[316]
Early operators discovered that if the APS5000 Auxiliary power unit was shut down with the inlet door closed, heat continued to build up in the tail compartment and cause the rotor shaft to bow. It could take up to two hours for the shaft to straighten again. This was particularly acute on short haul flights as there was insufficient time to allow the unit to cool before a restart was needed. Procedures were modified and the APU was later redesigned to address the issue.[317]
On September 15, 2012, the NTSB requested the grounding of certain 787s due to GE engine failures; GE believed the production problem had been fixed by that time.[318] In December 2012, responding to unhappiness within the airline industry at the continuing issues affecting the aircraft, Boeing CEO James McNerney stated that he regretted the impact on passengers: he went on to say that the 787's issues had been no greater than those experienced with the introduction of other Boeing models such as the 777.[319][320]
In March 2014, Mitsubishi Heavy Industries informed Boeing of a new problem that was caused by a change in manufacturing processes. Employees did not fill gaps with shims to connect wing rib aluminum shear ties to the carbon composite wing panels; the tightened fasteners, without shims, cause excessive stress that creates hairline cracks in the wings, which could enlarge and cause further damage. Forty-two aircraft awaiting delivery were affected, and each required one to two weeks to inspect and repair. Boeing did not expect this problem to affect the overall delivery schedule, even if some airplanes were delivered late.[321]
Dispatch reliability is an industry standard measure of the rate of departure from the gate with no more than 15 minutes delay due to technical issues.[322] The 787-8 started out with a ~96% operational reliability, increasing to ~98.5% in April 2015. Daily utilization increased from five hours in 2013 to twelve hours in 2014.[323] Dispatch reliability grew to 99.3% in 2017.[324]
Airlines have often assigned the 787 to routes previously flown by larger aircraft that could not return a profit. For example, Air Canada offered a Toronto-Pearson to New Delhi route, first utilizing a Lockheed L1011, then a Boeing 747-400, then an Airbus A340-300, but none of these types were efficient enough to generate profit. The airline operated the route profitably with a 787-9, and credits the right number of seats and greater fuel efficiency for this success.[325]
Up to June 30, 2017, after 565 units were delivered since 2011: 60% -8 (340) and 40% -9 (225), the airports with most 787 departures are Haneda Airport with 304 weekly, Narita Airport with 276 and Doha Airport with 265. By the end of 2017, there were 39 airlines operating the 787 on 983 routes with an average length of 5,282 km (2,852 nmi; 3,282 mi), including 163 new routes (17%).[326] As of 24 March 2018[update], the 787's longest route is Qantas' Perth-London Heathrow, a distance of 14,499 km (7,829 nmi; 9,009 mi) and the second-longest regular scheduled flight behind Qatar Airways' 14,529 km (7,845 nmi; 9,028 mi) route from Doha to Auckland, flown with a Boeing 777-200LR.[327] In March 2020, Air Tahiti Nui executed a record commercial flight of 9,765 mi (8,486 nmi; 15,715 km), from Papeete to Paris-Charles de Gaulle, on a route that would typically refuel at Los Angeles but was able to fly the Boeing 787-9 non-stop because it was "nowhere near full" due to the COVID-19 pandemic.[328]
In 2023, the first 787s to be withdrawn from commercial service, two 10-year-old -8s, were torn down by Irish company EirTrade Aviation, as they would otherwise have shortly required 12-year checks and landing-gear overhauls.[329] The used parts were in high demand amid the post-pandemic global shortage.[329] There is no obvious recycling path for the carbon composite airframe.[329]
Variants
[edit]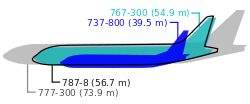
The shortest Dreamliner variant, the 787-8 was the first variant to fly in December 2009, then the longer 787-9 in September 2013, followed by the longest variant, the 787-10, in March 2017. These variants are called B788, B789, and B78X, respectively in the list of ICAO aircraft type designators.[330] The short-range 787-3 was canceled in 2010.
787-8
[edit]
With a typical capacity of 248 passengers and a range of 7,305 nautical miles (13,529 km; 8,406 mi), the -8 is the base model of the 787 family and was the first to enter service in 2011.[236] The 787-8 is targeted to replace the Boeing 767-200ER as well as expand into new non-stop markets where larger planes would not be economically viable.[331] As of January 2023[update], approximately 26% of 787 orders are for the 787-8 with 386 delivered.
In 2018, Boeing said it would change the -8 manufacturing to raise its commonality with the -9 above the current 30% to be more like the 95% commonality between the -9 and -10, as it will benefit from learning from those.[332] When it was launched, a new 787-8 was to cost only slightly more than the 767-300ER, valued new for $85 million at its 1990s peak, but it ended being 20% more costly.[333] It competes with the Airbus A330-200 and Airbus A330-800.[citation needed]
787-9
[edit]Keeping the same wingspan as the 787-8, the 787-9 is a lengthened and strengthened variant with a 20-foot (6.1 m) longer fuselage and a 54,500-pound (24.7 t) higher maximum take-off weight (MTOW), seating 296 passengers in a typical two-class cabin configuration over a 7,565-nautical-mile (8,706 mi; 14,010 km) range.[236] It features active boundary-layer control on the tail surfaces, reducing drag.[334] The 787-9 is targeted to replace the Boeing 767-300ER. It competes with the Airbus A330-300 and Airbus A330-900.
In 2005, the entry into service (EIS) was planned for 2010. The firm configuration was finalized on July 1, 2010.[335] By October 2011, deliveries were scheduled to begin in 2014.[336]
The prototype 787-9 made its maiden flight from Paine Field on September 17, 2013.[337] By November 8, 2013, it had flown 141 hours.[338] A 787-9 was on static display at the 2014 Farnborough Air Show prior to first delivery.[339] On July 8, 2014, launch customer Air New Zealand took its first 787-9, in a distinctive black livery in a ceremony at Paine Field.[340] The first revenue service was operated by All Nippon Airways on August 7, 2014.[citation needed] Air New Zealand operated its first commercial flight from Auckland to Sydney on August 9, 2014.[341]

The 787-9 was to begin commercial service with All Nippon Airways on August 7, 2014.[342] United Airlines was to start the longest nonstop scheduled 787 service between Los Angeles and Melbourne in October 2014.[343] Air China started a 787-9 route between Beijing and Chengdu in May 2016.[344] As of January 2023[update], 63% of all 787 orders are for the 787-9, with 580 deliveries. A 2014 787-9 leased for $1.05 million per month, and fell to $925,000 per month in 2018.[345]
The 20-foot (6.1 m) stretch was achieved by adding 10-foot (3.0 m) (five-frame) extensions forward and aft of the wing. The 787-8 and 787-9 have 50% commonality: the wing, fuselage and systems of the 787-8 had required radical revision to achieve the payload-range goals of the 787-9. Following a major revamp of the original 787-8 wing, the latest configuration for the 787-9 and -10 is the fourth design evolution.[346]
On March 25, 2018, a Qantas 787-9 completed the first scheduled non-stop flight between Australia and the UK flying seventeen hours from Perth to London Heathrow.[347] On October 20, 2019, a Qantas 787-9 was flight tested from New York to Sydney with a restricted payload. A team of researchers monitored passengers and crew to investigate wellness and performance on long flights.[348] On March 16, 2020, an Air Tahiti Nui 787-9 achieved the longest commercial flight of 8,485 nmi (15,714 km; 9,764 mi).[349]
787-10
[edit]
In December 2005, pushed by the interest of Emirates and Qantas, Boeing was studying the possibility of stretching the 787-9 further to seat 290 to 310 passengers. This variant would be similar to the capacity of the Boeing 777-200 and the Airbus A350-900, although with a shorter range.[350] Customer discussions were continuing in early 2006.[351] Mike Bair, Boeing's vice president and general manager for the 787 development program at the time, said it was easier to proceed with the 787-10 development after other customers followed Emirates' request. This variant is targeted to replace the Boeing 767-400ER and Airbus A330-300.[352]
On May 30, 2013, Singapore Airlines became the launch customer by stating it would order 30 787-10s (provided Boeing launched the program), to be delivered in 2018–2019.[353][354] On June 18, 2013, Boeing officially launched the 787-10 at the Paris Air Show, with orders or commitments for 102 aircraft from Air Lease Corporation (30), Singapore Airlines (30), United Airlines (20), British Airways (12), and GE Capital Aviation Services (10).[355] As of January 2023, the aircraft has 189 orders out of which 115 have been delivered, 7 of which are stored.[356]
This variant was envisioned as replacing Boeing 777-200 and Airbus A340-500 aircraft.[357] It competes with the Airbus A350-900, and according to Boeing, it offers better economics than its Airbus competitor on shorter routes.[358] Steven Udvar-Hazy said, "If it's identically configured, the -10 has a little bit of an edge on the -900", but smaller than Boeing's estimate of 10 percent.[359] The 787-10 is 224 ft (68 m) long, seats 336 passengers in a two-class cabin configuration, and has a range of 6,330 nmi (11,720 km; 7,280 mi).[360]
Boeing completed detailed design for the -10 on December 2, 2015.[361] Major assembly began in March 2016.[362] Designers targeted 90% commonality between the 787-9 and -10 and achieved 95%; the 18-foot (5.5 m) stretch was reached by adding 10 ft (3 m) forward of the wing and 8 ft (2.4 m) aft, and by strengthening the fuselage for bending loads in the center wingbox. Because of the length and additional tail strike protection needed, a semilevered landing gear enables rotation over the aft wheels rather than at the bogie center, like the 777-300ER, and the cabin air conditioning system has 15% more capacity. The first and third -10 test-platforms incorporate Rolls-Royce's new Trent 1000 TEN engines, while the second is powered by the competing General Electric GEnx-1B engine.[346]
Major fuselage parts were received for final assembly on November 30, 2016. The 787-10's mid-fuselage sections are too large for transport to Everett, Washington and it is built only in Charleston, South Carolina;[363] it is the first Boeing airliner assembled exclusively there.[364] The first -10 was rolled out on February 17, 2017.[365] The variant's first flight took place on March 31, 2017, and lasted 4 hours and 48 minutes.[366]
The first test 787-10 aircraft is engaged in flight envelope expansion work and the second joined the program in early May 2017, while the third with a passenger cabin interior to test the uprated environmental control system and Trent fuel-burn performance was scheduled to join in June. The -10 was scheduled to appear at the 2017 Paris Air Show.[364] The second -10 is being used to prove the GE Aviation engines and the third made its first flight on June 8, 2017, when the flight-test programme was 30% complete.[367] Boeing finished final assembly and painting of the first production 787-10 in October 2017, before its certification.[368] The last stages of flight tests focused on fuel burn validation and revised flight control software.[369][needs update]

At the start of the November 2017 Dubai Air Show, the 787-10 had 171 orders; Emirates committed to 40 787-10s, in two- and three-class cabins for 240 to 330 passengers, to be delivered from 2022 and with conversion rights to the smaller 787-9.[370][371] These aircraft are adapted for 7–8.5 hour missions, in a 280-seat three–class layout.[372] Emirates' Tim Clark was doubtful it would meet its MTOW for the payload-range required with initial 70,000–72,000 lbf (310–320 kN) thrust engines, but with the current 76,000 lbf (340 kN) turbofans and the -9 early margins gave the -10 "stellar economics".[373] By early 2019, Emirates was considering canceling its 787-10 order, due to engine margins being insufficient for the hot Dubai weather, in favor of the Airbus A350 (which would also replace its last Airbus A380 order).[374] At the 2019 Dubai Air Show, Emirates placed an order for 30 787-9 aircraft rather than the 787-10.[375]
In January 2018, the -10 was certified by the FAA after testing for 900 flight hours.[376] Boeing received its production certificate on February 15.[377] It was first delivered to launch customer Singapore Airlines on March 25, 2018.[378] Fitted with 337 seats, 36 in business and 301 in economy,[379] the -10 began commercial service on April 3, 2018.[380]
The 8.7% fuselage stretch from the -9 to the -10 likely increased empty weight at a lower rate than the 7.4% growth from the -8 to the -9 due to the 10.7% stretch.[263] Software changes increased the tailplane effectiveness to avoid modifying it. With the same wing but a longer fuselage than the -9, the flutter margin was reduced for the -10 but to avoid stiffening the wing or adding wingtip counterweights for commonality, software oscillates the elevators in the flaps up vertical mode suppression system (F0VMS), similar to the vertical gust load alleviation system.[263]
To replace Air New Zealand's 777-200 fleet, Boeing wants to increase the 787-10 MTOW by over 13,000 pounds (5.9 t) to 572,000 pounds (259 t) with some reinforcements and updated fuel systems. This would allow more range, such as the 5,600 nmi (10,400 km; 6,400 mi) trip from Auckland to Los Angeles with no passenger restrictions and some cargo. The increased performance could trickle down to the 787-9, allowing Auckland to New York flights.[381]
BBJ 787
[edit]
The 787-8 and -9 are offered as Boeing Business Jets, the first offering 2,415 sq ft (224.4 m2) of floor space and a range of 9,945 nmi (18,418 km; 11,445 mi)), the other 2,775 sq ft (257.8 m2) and 9,485 nmi (17,566 km; 10,915 mi), both with 25 passengers. Through June 2018, fifteen have been ordered, twelve delivered and four were in service.[382]
Experimental
[edit]Two 787 aircraft have been used in Boeing's ecoDemonstrator program which aims to develop technology and techniques to reduce the environmental effects of aviation. The testing involves many partner organizations including engine and systems manufacturers, NASA, academic, research, and regulatory institutions. The program started in 2011 with a different airframe being used each year.[383]
In 2014, the fourth prototype 787-8 was used for tests including use of sustainable aviation fuel, ceramic matrix composite engine exhaust nozzles, and systems for improved air traffic control (ATC) communications and closer landing approach spacing.[384] In 2020, a new 787-10 took part in the program, including intensive noise reduction trials, and including text-based ATC communications and cabin hygiene and cleansing tests related to the COVID-19 pandemic. After removal of the test equipment, the aircraft was delivered to Etihad Airways.[385]
In April 2023, Boeing announced the ecoDemonstrator Explorer program, which would run alongside the ecoDemonstrator program. The first Explorer program in 2023 tested international route planning (trajectory-based operations – a major aim of the FAA's NextGen project) and maximization of sustainable aviation fuel use for a planned 10% fuel efficiency gain, using a 787-10.[386][387]
Operators
[edit]
There are 1,006 Boeing 787 aircraft in airline service as of February 2022[update], comprising 377 Boeing 787-8s, 568 787-9s and 61 787-10s,[citation needed] with outstanding orders for further 481 aircraft.[1][needs update] As of August 2019[update], the largest operators are All Nippon Airways (77), United Airlines (63), Japan Airlines (47), and American Airlines (46).[388][needs update]
Orders and deliveries
[edit]In September 2011, the 787 was first officially delivered to launch customer All Nippon Airways.[389] As of December 2018[update], the top five identified 787 customers are American Airlines with 89 orders (37 -8s and 52 -9s), All Nippon Airways with 83 orders (36 -8s, 44 -9s and three -10s), ILFC (an aircraft leasing company) with 74 orders (23 -8s and 51 -9s), and United Airlines (12 -8s, 38 -9s and 21 -10s) and Etihad Airways (41 -9s and 30 -10s), both with 71 orders.
On December 13, 2018, the 787th Boeing 787 was delivered to AerCap and leased to China Southern Airlines. By then the 787 had flown 300 million passengers on 1.5 million flights and opened 210 new nonstop routes.[390] The 1000th Dreamliner, a 787-10 for Singapore Airlines, made its maiden flight on April 3, 2020.[391]
| Total orders | Total deliveries | Unfilled | |
| 787‑8 | 427 | 399 | 28 |
| 787‑9 | 1,425 | 695 | 730 |
| 787‑10 | 418 | 128 | 290 |
| Total | 2,270 | 1,222 | 1,048 |
| 2021 | 2022 | 2023 | 2024 | 2025 | Total | ||
| Net orders | −11 | 114 | 301 | 48 | 322 | 2,270 | |
| Deliveries | 787‑8 | 2 | 9 | 10 | 1 | 2 | 399 |
| 787‑9 | 12 | 10 | 40 | 29 | 48 | 695 | |
| 787‑10 | – | 12 | 23 | 21 | 11 | 128 | |
| Total | 14 | 31 | 73 | 51 | 61 | 1,222 | |
| 2004 | 2005 | 2006 | 2007 | 2008 | 2009 | 2010 | 2011 | 2012 | 2013 | 2014 | 2015 | 2016 | 2017 | 2018 | 2019 | 2020 | ||
| Net orders | 56 | 235 | 157 | 369 | 93 | −59 | −4 | 13 | −12 | 182 | 41 | 71 | 58 | 94 | 109 | 82 | 20 | |
| Deliveries | 787‑8 | – | – | – | – | – | – | – | 3 | 46 | 65 | 104 | 71 | 35 | 26 | 10 | 10 | 5 |
| 787‑9 | – | – | – | – | – | – | – | – | – | – | 10 | 64 | 102 | 110 | 120 | 114 | 36 | |
| 787‑10 | – | – | – | – | – | – | – | – | – | – | – | – | – | – | 15 | 34 | 12 | |
| Total | – | – | – | – | – | – | – | 3 | 46 | 65 | 114 | 135 | 137 | 136 | 145 | 158 | 53 | |
Boeing 787 orders and deliveries (cumulative, by year):

Accidents and incidents
[edit]The Boeing 787 has been involved in eight accidents and incidents as of June 2025[update], including one fatal hull loss.[393][394]
Accidents with fatalities
[edit]
On June 12, 2025, Air India Flight 171, an 11-year-old Boeing 787-8 registered as VT-ANB[395] operating from Ahmedabad Airport to London Gatwick Airport, crashed into the hostel building of B. J. Medical College shortly after takeoff. According to the preliminary Aircraft Accident Investigation Bureau report released on July 8, 2025, the crash was caused by both engines shutting down after their fuel control switches moved from the "RUN" to "CUTOFF" position.[396]: 13–14 The cause of the switch movement remains under investigation. The report did not recommend any actions to Boeing, or 787 operators.[397][396]: 15 All but one of the 242 people on board were killed, as well as 19 people on the ground.[398] The sole survivor was a British national seated in 11A, next to an emergency exit. This marked the first fatal crash and hull loss of a 787.[399][400]
Accidents and incidents without fatalities
[edit]
A Japan Airlines (JAL) 787 experienced a fuel leak on January 8, 2013, and its flight from Boston was canceled.[401] The next day, United Airlines reported a problem in one of its six 787s with the wiring near the main batteries. Soon, the US National Transportation Safety Board opened a safety probe.[402] Fuel leaks also occurred on January 11, 2013[403] and on January 13, 2013, at Narita International Airport outside Tokyo. The aircraft reportedly was the same one that had a fuel leak on January 8.[404][405] Japan's transport ministry also launched an investigation.[406]
On January 11, 2013, the FAA completed a comprehensive review of the 787's critical systems including the design, manufacture, and assembly. The Department of Transportation secretary Ray LaHood stated the administration was "looking for the root causes" behind the recent issues. The head of the FAA, Michael Huerta, said that so far nothing found "suggests [the 787] is not safe."[407]
On July 12, 2013, a fire started on an empty Ethiopian Airlines 787 parked at Heathrow Airport before it was extinguished by the airport fire and rescue service. No injuries were reported.[408][409] The fire caused extensive heat damage to the aircraft.[410] The FAA and NTSB sent representatives to assist in the investigation.[411] The initial investigation found no direct link with the aircraft's main batteries.[412] Further investigations indicated that the fire was due to lithium-manganese dioxide batteries powering an emergency locator transmitter (ELT).[413] The UK Air Accidents Investigation Branch (AAIB) issued a special bulletin on July 18, 2013, requesting the US FAA ensure that the locator is removed or disconnected in Boeing 787s and to review the safety of lithium battery-powered ELT systems in other aircraft types.[414] On August 19, 2015, the Associated Press reported that the fire was started by a short circuit caused by crossed wires located under the battery. The Air Accidents Investigation Branch's investigators recommended that "the US Federal Aviation Administration, together with similar bodies in Europe and Canada, should conduct a review of equipment powered by lithium metal batteries to ensure they have 'an acceptable level of circuit protection.'"[415]
On July 26, 2013, ANA said it had found wiring damage on two 787 locator beacons. United Airlines also reported that it had found a pinched wire in one 787 locator beacon.[416] On August 14, 2013, the media reported a fire extinguisher fault affecting three ANA airplanes, which caused the fire extinguishers to discharge into the opposite engine from the one requested.[417] The fault was caused by a supplier assembly error.[418]
On November 22, 2013, Boeing issued an advisory to airlines using General Electric GEnx engines on 787 and 747-8 aircraft to avoid flying near high-level thunderstorms due to an increased risk of icing on the engines. The problem was caused by a buildup of ice crystals just behind the main fan causing a brief loss of thrust on six occasions.[419]
On January 21, 2014, a Norwegian Air Shuttle 787 experienced a fuel leak which caused a 19-hour delay to a flight from Bangkok to Oslo.[420] The leak became known to pilots only after it was pointed out by concerned passengers.[421] It was found later that a faulty valve was responsible.[422] This fuel leak is one of numerous problems experienced by Norwegian Air Shuttle's 787 fleet.[420] Mike Fleming, Boeing's vice president for 787 support and services, subsequently met with executives of Norwegian Air Shuttle and expressed Boeing's commitment to improving the 787's dispatch reliability, "we're not satisfied with where the airplane is today, flying at a fleet average of 98 percent...The 777 today flies at 99.4 percent...and that's the benchmark that the 787 needs to attain."[423][424]
In March 2016, the FAA accelerated the release of an airworthiness directive in response to reports indicating that in certain weather conditions "erroneous low airspeed may be displayed..." There was concern "abrupt pilot control inputs in this condition could exceed the structural capability of the airplane." Pilots were told not to apply "large, abrupt control column inputs" in the event of an "unrealistic" drop in displayed airspeed.[425][426]
On April 22, 2016, the FAA issued an airworthiness directive following a January 29, 2016 incident in which a General Electric GEnx-1B PIP2 engine suffered damage and non-restartable power loss while flying at an altitude of 20,000 feet. The damage is thought to have been caused by a fan imbalance resulting from fan ice shedding.[427][428]
On March 11, 2024, LATAM Airlines Flight 800 experienced a sudden drop in altitude, resulting in 50 injuries to those aboard and 12 with serious injuries being hospitalized. As of March 13, 2024, the cause is still under investigation.[429]
On January 24, 2025, United Airlines Flight 613, a Boeing 787‑8 registered N27903, operating from Lagos, Nigeria to Washington Dulles, US, experienced a sudden and unexpected altitude drop over Ivory Coast airspace. The autopilot disengaged following the failure of both inertial reference units (IRUs), prompting a rapid descent that injured 38 individuals (including four passengers and two crew members seriously). The aircraft returned safely to Lagos.[430] The US National Transportation Safety Board (NTSB) launched a joint investigation with Nigerian authorities. A preliminary report released in March 2025 confirmed the IRU malfunction as the likely cause.[431]
Lithium-ion battery problems
[edit]

On January 16, 2013, All Nippon Airways Flight 692, en route from Yamaguchi Ube Airport to Tokyo Haneda, had a battery problem warning followed by a burning smell while climbing from Ube about 35 nautical miles (65 km; 40 mi) west of Takamatsu, Japan. The aircraft diverted to Takamatsu and was evacuated via the slides; three passengers received minor injuries during the evacuation. Inspection revealed a battery fire. A similar incident in a parked Japan Airlines 787 at Boston's Logan International Airport within the same week led the Federal Aviation Administration to ground all 787s.[432] On January 16, 2013, both major Japanese airlines ANA and JAL voluntarily grounded their fleets of 787s after multiple incidents involving different 787s, including emergency landings. At the time, these two carriers operated 24 of the 50 787s delivered.[433][434] The grounding reportedly cost ANA some 9 billion yen (US$93 million) in lost sales.[435]
On January 16, 2013, the FAA issued an emergency airworthiness directive ordering all American-based airlines to ground their Boeing 787s until yet-to-be-determined modifications were made to the electrical system to reduce the risk of the battery overheating or catching fire.[436] This was the first time that the FAA had grounded an airliner type since 1979.[437] Industry experts disagreed on consequences of the grounding: Airbus was confident that Boeing would resolve the issue[438] and that no airlines will switch plane type,[439][440] while other experts saw the problem as "costly"[441] and "could take upwards of a year".[442]
The FAA also conducted an extensive review of the 787's critical systems. The focus of the review was on the safety of the lithium-ion batteries[437] made of lithium cobalt oxide (LiCoO2). The 787 battery contract was signed in 2005,[256] when this was the only type of lithium aerospace battery available, but since then newer and safer[443] types (such as LiFePO4), which provide less reaction energy with virtually no cobalt content to avoid cobalt's thermal runaway characteristic, have become available.[444][445] FAA approved a 787 battery in 2007 with nine "special conditions".[446][447] A battery approved by FAA (through Mobile Power Solutions) was made by Rose Electronics using Kokam cells;[448] the batteries installed in the 787 are made by Yuasa.[253]
The first big hurdle for Boeing was that the ranks of commercial aircraft engineers lacked lithium-ion battery expertise in that lithium-ion batteries had never before been used on a Boeing commercial jet.[57] Boeing chief technology officer John Tracy began canvassing the entire organization for lithium-ion battery experts.[57] He also began calling his contacts outside the aerospace industry. Within a day, about a dozen Boeing engineers from across the United States assembled at Boeing's Everett, Washington engineering center.
The collaborators began ongoing collaborative group sessions—not just a series of meetings—that lasted weeks with breaks only for meals and sleep. Evan Rosen writes in The Culture of Collaboration (2024, expanded and updated edition) that for the Boeing 787 battery effort, hierarchy was out the window, because the collaborators were working outside of their usual reporting structure. There was no chain of command. Hidden agendas and internal competition were gone, because everybody had the same goal, Rosen writes.[57]
On January 20, the NTSB declared that overvoltage was not the cause of the Boston incident, as voltage did not exceed the battery limit of 32 V,[449] and the charging unit passed tests. The battery had signs of short circuiting and thermal runaway.[450] Despite this, by January 24, the NTSB had not yet pinpointed the cause of the Boston fire; the FAA would not allow US-based 787s to fly again until the problem was found and corrected. In a press briefing that day, NTSB Chairwoman Deborah Hersman said that the NTSB had found evidence of failure of multiple safety systems designed to prevent these battery problems, and stated that fire must never happen on an airplane.[451]
The Japan Transport Safety Board (JTSB) said on January 23 that the battery in ANA jets in Japan reached a maximum voltage of 31 V (below the 32 V limit like the Boston JAL 787), but had a sudden unexplained voltage drop[452] to near zero.[453] All cells had signs of thermal damage prior to runaway.[454] ANA and JAL had replaced several 787 batteries before the mishaps.[453] As of January 29, 2013[update], JTSB approved the Yuasa factory quality control[455][456] while the NTSB examined the Boston battery for defects.[457] The failure rate, with two major battery thermal runaway events in 100,000 flight hours, was much higher than the rate of one in 10 million flight hours predicted by Boeing.[432]
The only American airline that operated the Dreamliner at the time was United Airlines, which had six.[458] Chile's Directorate General of Civil Aviation (DGAC) grounded LAN Airlines' three 787s.[459] The Indian Directorate General of Civil Aviation (DGCA) directed Air India to ground its six Dreamliners. The Japanese Transport Ministry made the ANA and JAL groundings official and indefinite following the FAA announcement.[460] The European Aviation Safety Agency also followed the FAA's advice and grounded the only two European 787s operated by LOT Polish Airlines.[461] Qatar Airways grounded their five Dreamliners.[462] Ethiopian Airlines was the final operator to temporarily ground its four Dreamliners.[463] By January 17, 2013, all 50 of the aircraft delivered to date had been grounded.[463][464] On January 18, Boeing halted 787 deliveries until the battery problem was resolved.[465]
On February 7, 2013, the FAA gave approval for Boeing to conduct 787 test flights to gather additional data.[466][467] In February 2013, FAA oversight of the 787's 2007 safety approval and certification was under scrutiny.[468] On March 7, 2013, the NTSB released an interim factual report about the Boston battery fire on January 7, 2013. The investigation[469] stated that "heavy smoke and fire coming from the front of the APU battery case." Firefighters "tried fire extinguishing, but smoke and flame (flame size about 3 inches, or 8 cm) did not stop".[470][471]
Boeing completed its final tests on a revised battery design on April 5, 2013.[472] The FAA approved Boeing's revised battery design with three additional, overlapping protection methods on April 19, 2013.[473] The FAA published a directive on April 25 to provide instructions for retrofitting battery hardware before the 787s could return to flight.[474][475] The repairs were expected to be completed in weeks.[473] Following the FAA approval in the U.S. effective April 26,[476] Japan approved resumption of Boeing 787 flights in the country on April 26, 2013.[477] On April 27, 2013, Ethiopian Airlines took a 787 on the model's first commercial flight after battery system modifications.[475][476]
On January 14, 2014, a battery in a JAL 787 emitted smoke from the battery's protection exhaust while the aircraft was undergoing pre-flight maintenance at Tokyo Narita Airport.[478][479] The battery partially melted in the incident;[480] one of its eight lithium-ion cells had its relief port vent and fluid sprayed inside the battery's container.[481] It was later reported that the battery may have reached a temperature as high as 1,220 °F (660 °C), and that Boeing did not understand the root cause of the failure.[482]
The NTSB criticized the FAA, Boeing, and battery manufacturers for the faults in a 2014 report.[483][484][485][486] It also criticized the GE-made flight data and cockpit voice recorder in the same report.[487] The enclosure Boeing added is 185 lb (84 kg) heavier, negating the lighter battery potential.[488]
Aircraft on display
[edit]
All three prototype 787-8s are preserved in museums.
- N787BA (ZA001) – Chubu Centrair Airport in Nagoya, Japan—first prototype aircraft[489]
- N787EX (ZA002) – Pima Air & Space Museum in Tucson, Arizona, United States—second prototype aircraft[490]
- N787BX (ZA003) – Museum of Flight in Seattle, Washington, United States—third prototype aircraft[491][492]
Specifications
[edit]
| External image | |
|---|---|
| Boeing 787 cutaway | |
| Model | 787-8 | 787-9 | 787-10 |
|---|---|---|---|
| Cockpit crew | Two | ||
| Seating, 2-class | 242: 24J @85" + 218Y @32" | 290: 28J @85" + 262Y @32" | 330: 32J @85" + 298Y @32" |
| Seating, 1-class | Max. 359, exit limit 381 | Max. 406, exit limit 420 | Max. 440, exit limit 440 |
| Length | 186 ft 1 in (56.72 m) | 206 ft 1 in (62.81 m) | 224 ft (68.28 m) |
| Wing[494] | 9.59 aspect ratio, 4,058 sq ft (377 m2) area, 32.2° wing sweep[495] | ||
| Wingspan[494] | 197 ft 3 in (60.12 m) span, 20.58 feet (6.27 m) mean chord | ||
| Height[493] | 55 ft 6 in (16.92 m) | 55 ft 10 in (17.02 m) | |
| Fuselage | Cabin width: 18 ft 0 in (5.49 m);[496] External width: 18 ft 11 in (5.77 m) Height: 19 ft 6 in (5.94 m) | ||
| Cargo capacity | 4,826 cu ft / 136.7 m3 28 LD3 or 9 (88×125) pallets |
6,090 cu ft / 172 m3 36 LD3 or 11 (96×125) pallets |
6,722 cu ft / 190.3 m3 40 LD3 or 13 (96×125) pallets |
| Maximum takeoff weight[497] | 502,500 lb / 227,900 kg | 571,500 lb / 259,200 kg | 574,000 lb / 260,400 kg |
| Maximum payload | 90,500 lb / 41,100 kg | 116,000 lb / 53,000 kg | 126,300 lb / 57,277 kg |
| Operating empty weight | 264,500 lb / 120,000 kg | 284,000 lb / 129,000 kg | 298,700 lb / 135,500 kg |
| Fuel capacity | 33,340 US gal / 126,206 L 223,378 lb / 101,343 kg |
33,399 US gal / 126,429 L 223,773 lb / 101,522 kg | |
| Speed | Max: Mach 0.90 (594 mph; 516 kn; 956 km/h);[494] Cruise: Mach 0.85 (561 mph; 488 kn; 903 km/h) | ||
| Range[a][236] | 7,305 nmi (13,530 km; 8,410 mi) | 7,565 nmi (14,010 km; 8,710 mi) | 6,330 nmi (11,720 km; 7,280 mi) |
| Takeoff[b] | 8,500 ft (2,600 m) | 9,300 ft (2,800 m) | 9,100 ft (2,800 m) |
| Ceiling[498] | 43,100 ft (13,100 m) | 41,100 ft (12,500 m) | |
| Engines (×2) | General Electric GEnx-1B or Rolls-Royce Trent 1000 | ||
| Thrust (×2) | 64,000 lbf (280 kN) | 71,000 lbf (320 kN) | 76,000 lbf (340 kN) |
| ICAO designation | B788 | B789 | B78X |
See also
[edit]Related development
Aircraft of comparable role, configuration, and era
Related lists
References
[edit]Citations
[edit]- ^ a b Boeing: Orders and Deliveries (updated monthly) (Report). Chicago: Boeing. September 30, 2025. Retrieved October 14, 2025.
- ^ Gunter, Lori (July 2002). "The Need for Speed, Boeing's Sonic Cruiser team focuses on the future". Boeing Frontier magazine. Retrieved January 21, 2011.
- ^ Banks, Howard (May 28, 2001). "Paper plane: That Mach 0.95 Sonic Cruiser from Boeing will never fly. Here's why". Forbes. Archived from the original on October 16, 2007. Retrieved June 7, 2007.
- ^ a b c d e f g h i j Norris, G; Thomas, G; Wagner, M; Forbes Smith, C (2005). Boeing 787 Dreamliner – Flying Redefined. Aerospace Technical Publications International. ISBN 978-0-9752341-2-9.
- ^ "History of the Boeing 787". The Seattle Times. Associated Press. June 23, 2000. Archived from the original on June 6, 2013. Retrieved October 28, 2012.
- ^ Cannegieter, Roger. "Long Range vs. Ultra High Capacity". Aerlines.nl. Retrieved October 12, 2015.
- ^ Babej, Marc E.; Pollak, Tim (May 24, 2006). "Boeing Versus Airbus". Forbes. Retrieved April 8, 2010.
- ^ Randy Baseler (May 20, 2005). "Kangaroo hop". Randy's Journal. The Boeing Company.
- ^ Tkacik, Maureen (September 18, 2019). "Crash Course". The New Republic.
- ^ "Maximizing the Middle, Finding the sweet spot in the market" (Press release). Boeing Frontier magazine. March 2003.
- ^ "Boeing Achieves 787 Power On" (Press release). Boeing. June 20, 2008. Archived from the original on January 2, 2013.
- ^ "Daydream believer: How different is the Boeing 787?". Flight International. Retrieved December 14, 2010.
- ^ "Name Your Plane sweepstakes". Boeing Frontiers Online. July 2003. Retrieved September 28, 2007.
- ^ Norris & Wagner 2009, p. 40.
- ^ "New Boeing 7E7 Airplane Gets a Name". Boeing, June 15, 2003.
- ^ "Boeing Launches 7E7 Dreamliner" (Press release). Boeing. April 26, 2004.
- ^ "ANA says Denver still in hunt for non-stop to Tokyo". Metro Denver. April 8, 2009. Archived from the original on January 3, 2011. Retrieved December 14, 2010.
- ^ a b Shifrin, Carole (March 27, 2006). "Dream start". Flight International. Retrieved September 27, 2015.
- ^ "Air India takes delivery of first South Carolina-made Boeing 787". Reuters. October 5, 2012. Retrieved July 23, 2020.
- ^ "The Dream of Composites". R&D Magazine. November 20, 2006. Archived from the original on April 5, 2012. Retrieved November 23, 2012.
- ^ Walz, Martha (November 20, 2006). "The Dream of Composites". RD mag. Retrieved September 2, 2011.
- ^ Norris, Guy (January 9, 2009). "Boeing Rules Out 787 Window Change". Aviation Week.
- ^ Ogando, Joseph (June 7, 2007). "Design News – Features – Boeing's 'More Electric' 787 Dreamliner Spurs Engine Evolution". designnews.com. Archived from the original on April 6, 2012. Retrieved September 7, 2011.
- ^ Norris & Wagner 2009, p. 48.
- ^ Gates, Dominic (September 18, 2007). "Boeing news – Fired engineer calls 787's plastic fuselage unsafe". The Seattle Times. Archived from the original on October 16, 2012.
- ^ "Review – History of 787 Composites Project at Boeing" (PDF). csmres.co.uk.
- ^ Pandey, Mohan (2010). How Boeing Defied the Airbus Challenge. USA: Createspace. ISBN 978-1-4505-0113-2.
- ^ http://787updates.newairplane.com/Boeing787Updates/media/Boeing787Updates/ETOPS-Presentation.pdf
- ^ "Boeing Receives 330-Minute ETOPS Certification for 787s".
- ^ Marsh, George (2009). "Boeing's 787: trials, tribulations, and restoring the dream". Reinforced Plastics. 53 (8): 16–21. doi:10.1016/S0034-3617(09)70311-X. ISSN 0034-3617.
- ^ "Boeing boosts aircraft prices 5.5% on rising cost of labor, materials". Air Transport World. June 26, 2007. Retrieved September 2, 2011.
- ^ "Jet Prices". March 22, 2013. Archived from the original on March 22, 2013. Retrieved March 8, 2025.
- ^ "How Much Does a Boeing 787 Really Cost?" (PDF). AirInsight. May 18, 2016. Archived from the original (PDF) on April 13, 2019.
- ^ "Boeing Unveils 787 Final Assembly Factory Flow." Boeing, December 6, 2006. Retrieved September 3, 2011.
- ^ "Boeing's Big Dream". Fortune. May 5, 2008. p. 182.. (online version) Archived July 30, 2013, at the Wayback Machine
- ^ "Boeing unveils 787 Dreamliner; Airbus sends congrats". USA Today. July 9, 2007. Retrieved September 2, 2011.
- ^ "Boeing's Big Dream". Fortune. May 5, 2008. p. 187.
- ^ "Boeing Revises 787 First Flight and Delivery Plans; Adds Schedule Margin to Reduce Risk of Further Delays" (Press release). Boeing. April 9, 2008. Archived from the original on September 15, 2011. Retrieved September 2, 2011.
- ^ "Boeing's Big Dream", Fortune, May 5, 2008, p. 182.
- ^ "Boeing considers moving 787-9 tail build in-house". ATW Online. October 30, 2010. Retrieved October 30, 2010.
- ^ Thisdell, Dan (February 4, 2013). "In focus: Debt dogs Finmeccanica". Flightglobal. Retrieved April 18, 2015.
- ^ "Boeing's Big Dream", Fortune, May 5, 2008, p. 184.
- ^ Seo, Sookyung (September 29, 2010). "Boeing 787 Supplier Korea Aerospace Hires Share-Sale Arrangers". Bloomberg. Retrieved September 2, 2011.
- ^ "Boeing Completes Acquisition of Vought Operations in South Carolina" (Press release). Boeing. July 30, 2009. Retrieved September 2, 2011.
- ^ Gates, D. (September 11, 2005). "Boeing 787: Parts from around world will be swiftly integrated". The Seattle Times. Retrieved September 2, 2011.
- ^ "Korean Air to Buy 10 '787 Dreamliners'". The Korea Times. July 12, 2007.
- ^ "Boeing" (PDF). HCL Technologies. Retrieved January 20, 2013.
- ^ "India's Tata Group to Supply Parts for Boeing Dreamliner". IndustryWeek. Agence France-Presse. February 6, 2008. Retrieved October 6, 2025.
- ^ "Boeing and TAL Manufacturing Solutions celebrate delivery of the 25,000th floor beam for the Boeing 787 Dreamliner" (Press release). Boeing. August 27, 2019. Retrieved October 6, 2025.
- ^ a b "787 Dreamliner International team facts" (Press release). Boeing. Retrieved June 10, 2010.
- ^ "Korean Air ready for 787 ramp up". The Brisbane Times. September 30, 2010. Retrieved September 3, 2011.
- ^ "Boeing's Big Dream". Fortune. May 5, 2008. p. 189.
- ^ Kennedy, Bill. "Wheels up", Cutting Tool Engineering, March 2009. Retrieved January 14, 2014.
- ^ Coulom, Dan (August 20, 2007). "Hamilton Sundstrand delivers first cabin air conditioning packs for Boeing 787 Dreamliner" (press release). Hamilton Sundstrand. Archived from the original on August 28, 2007. Retrieved August 21, 2007.
- ^ Moores, Victoria. "Pictures: Boeing begins 787 final assembly". Flight International, May 22, 2007.
- ^ a b c d Rosen, Evan (2024). The Culture of Collaboration (expanded and updated edition). Red Ape Publishing. ISBN 978-0-9774617-9-0 OCLC 1405190585
- ^ "Weight remains challenge for Boeing as 787 progresses". Flightglobal. November 6, 2006. Retrieved May 23, 2015.
- ^ "Boeing Still Working On 787 Weight Issue, Carson Says". Associated Press. December 7, 2006. Archived from the original on October 12, 2016. Retrieved July 22, 2016.
- ^ "Boeing to deliver test 787s to its customers". Financial Times. July 6, 2007. Archived from the original on December 10, 2022.
- ^ Wallace, James (December 7, 2006). "Virtual rollout of the 78". Seattle Post-Intelligencer. Hearst Communications Inc. Retrieved September 2, 2011.
- ^ Dominic Gates (December 23, 2009). "Boeing's 787 Dreamliner is no lightweight". Los Angeles Times. Retrieved January 21, 2013.
- ^ Scott, Alwyn (July 24, 2015). "Boeing looks at pricey titanium in bid to stem 787 losses". Reuters. Seattle. Archived from the original on July 27, 2015. Retrieved August 2, 2015.
- ^ Johnsson, Julie (February 24, 2015). "Boeing Lining Up Buyers for Early Overweight Dreamliners". Bloomberg.
- ^ Gates, Dominic (April 20, 2018). "Early 787 test plane is dismantled for reuse, recycling, or scrap". The Seattle Times. Retrieved February 18, 2024.
- ^ "A Boeing 787-9 joins the Terrible Teens". HeraldNet.com. August 28, 2014. Retrieved February 18, 2024.
- ^ "Boeing Celebrates the Premiere of the 787 Dreamliner" (Press release). Boeing. July 8, 2007. Retrieved June 14, 2011.
- ^ "Boeing Celebrates the Premiere of the 787 Dreamliner" (Press release). Boeing. July 8, 2007. Archived from the original on June 29, 2011. Retrieved January 21, 2011.
- ^ Trimble, Stephen (September 10, 2007). "Boeing 787 first flight suffers two-month delay". Flight International. Retrieved September 2, 2011.
- ^ "Boeing Delays 787's First Flight to November–December (Update4)". Bloomberg. September 5, 2007. Retrieved September 3, 2011.
- ^ Clark, Nicola (October 10, 2007). "Boeing Delays Deliveries of 787". The New York Times. Retrieved December 22, 2007.
- ^ "Boeing Reschedules Initial 787 Deliveries and First Flight". Boeing. October 10, 2007. Archived from the original on November 3, 2011. Retrieved September 3, 2011.
- ^ "787 Program Chief Replaced at Boeing". The New York Times. Associated Press. October 17, 2007. Retrieved November 24, 2007.
- ^ "Boeing Shifts Schedule for 787 First Flight" (Press release). Boeing. January 16, 2008. Archived from the original on January 19, 2008.
- ^ Sanders, Peter (July 8, 2009). "Boeing Sets Deal to Buy a Dreamliner Plant". The Wall Street Journal.
- ^ a b Trimble, Stephen (April 11, 2008). "787 variants delayed to at least 2012". Flight International. Archived from the original on October 15, 2008.
- ^ Gates, Dominic (November 5, 2008). "Fasteners incorrectly installed". The Seattle Times. Retrieved November 11, 2008.
- ^ "Boeing says 787 test flight delayed again". CNN. November 4, 2008. Archived from the original on November 8, 2008.
- ^ "Boeing Reviews Dreamliner Schedule for More Delays (Update2)". Bloomberg. December 4, 2008. Retrieved September 2, 2011.
- ^ "Boeing confirms 787 first flight pushed back to 2Q 2009". Flight International. December 11, 2008. Retrieved December 14, 2010.
- ^ "United may seek damages for 787 delays". PSBJ. February 27, 2012. Retrieved March 14, 2012.
- ^ "Govt approves Air India compensation package for Dreamliner delay". July 25, 2012. Retrieved July 25, 2012.
- ^ Kotha, Suresh (2013). Managing A Global Partnership Model: Lessons from the Boeing 787 'Dreamliner' Program. Hoboken, NJ: Blackwell Publishing. pp. 41–66.
- ^ "Boeing performs crash test on 787 fuselage section". Komo News. August 23, 2007. Retrieved July 22, 2016.
- ^ a b Snyder, Sean, ed. (August 29, 2007). "Boeing Performs Crash Test on 787 Dreamliner: Tests currently under analysis". Design News. Reed Elsevier. Archived from the original on December 17, 2011. Retrieved September 9, 2011.
- ^ Gillespie, Elizabeth M (September 6, 2007). "Boeing Says 787 Fuselage Test a Success". Forbes. Retrieved September 7, 2007. [dead link] Alt URL
- ^ Snyder, Sean, ed. (September 6, 2007). "Announcement of Boeing Fuselage Crash Test Results". Design News. Archived from the original on December 17, 2011. Retrieved September 9, 2011.
- ^ a b c Gates, Dominic (September 18, 2007). "Fired engineer calls 787's plastic fuselage unsafe". The Seattle Times. Retrieved November 24, 2007.
- ^ a b Matlack, Carol (June 26, 2009). "More Boeing 787 Woes as Qantas Drops Order". Bloomberg BusinessWeek. Bloomberg. Archived from the original on June 29, 2009. Retrieved December 14, 2010.
- ^ Gates, Dominic. (September 18, 2007) "Boeing news |Fired engineer calls 787's plastic fuselage unsafe". The Seattle Times. Retrieved March 13, 2014.
- ^ "European and US regulators certify Trent 1000 for Boeing 787". Flight International. Retrieved December 14, 2010.
- ^ "GEnx-1B Engine Receives FAA Certification" (press release). GE Aviation. March 31, 2008. Archived from the original on April 5, 2008. Retrieved April 4, 2008.
- ^ "PowerOn Interactive Site". TPN interactive. Archived from the original on July 27, 2011. Retrieved December 14, 2010.
- ^ "Boeing Completes 787 Dreamliner 'High Blow' Test" (Press release). Boeing. September 27, 2008. Retrieved September 2, 2011.
- ^ "FAA Approves Boeing 787 Dreamliner Maintenance Program" (Press release). Boeing. December 22, 2008. Retrieved September 2, 2011.
- ^ "Boeing 787 Dreamliner Moves to Flight Line for Testing" (Press release). Boeing. May 3, 2009. Archived from the original on May 5, 2009. Retrieved May 3, 2009.
- ^ "Bernstein Research sees further 787 delays, bigger range shortfall". ATW Daily News. May 4, 2009. Retrieved September 9, 2011.
- ^ Ostrower, Jon. "Boeing confirms 787 weight issues". Flight International, May 7, 2009. Retrieved September 2, 2011.
- ^ Ostrower, Jon. "Concerns raised over expected 787 range shortfall". Flight International, March 9, 2009. Retrieved September 2, 2011.
- ^ Ostrower, Jon. "Shanghai casts doubt over early 787 delivery slots". Flight International, March 14, 2009. Retrieved September 2, 2011.
- ^ "Boeing Postpones 787 First Flight" (Press release). Boeing. June 23, 2009.
- ^ "Dreamliner 787 Composites Approach Takes Another Big Hit". Design News. September 10, 2009. Archived from the original on September 24, 2009. Retrieved September 11, 2009.
- ^ "Boeing Announces New 787 Schedule and Third-Quarter Charge" (Press release). Boeing. August 27, 2009.
- ^ Gates, Dominic (August 28, 2009). "Boeing still sure delayed 787 will be profitable". The Seattle Times. Retrieved September 23, 2009.
- ^ a b Cohen, Aubrey (April 20, 2011). "Boeing illegally put second 787 line in S.C., complaint says". Seattle Post-Intelligencer.
- ^ "Boeing Completes 787 Dreamliner High-Speed Taxi Test" (Press release). Boeing. December 12, 2009. Retrieved September 3, 2011.
- ^ "787 approaches final gauntlet testing". Flight International. December 8, 2009. Retrieved December 15, 2009.
- ^ "Boeing 787 Dreamliner Completes First Flight" (Press release). Boeing. December 15, 2009.
- ^ Dominic Gates (December 16, 2009). "Rain shortens 787 first flight, fails to dampen optimism". The Seattle Times. Archived from the original on November 19, 2018. Retrieved June 8, 2017.
- ^ Jon Ostrower (December 22, 2009). "787 first flight is just the start for gruelling programme". Flight International.
- ^ "Boeing Commercial Airplane Group No.2". FlightAware. December 22, 2009.
- ^ "Second Boeing 787 Dreamliner Completes First Flight". Boeing, December 22, 2009. Retrieved September 2011.
- ^ a b "787 Dreamliner Flight Test site". Boeing. Retrieved August 15, 2011.
- ^ Ostrower, Jon. "Boeing completes 787 flutter and ground effects testing". Flight International, March 24, 2010. Retrieved September 3, 2011.
- ^ "Boeing Completes Ultimate-Load Wing Test on 787" (Press release). Boeing. March 28, 2010. Archived from the original on April 7, 2012. Retrieved March 30, 2010.
- ^ Sanders, Peter (March 30, 2010). "Boeing's Dreamliner Lags Testing Schedule". The Wall Street Journal. Retrieved September 2, 2011.
- ^ Paur, Jason (March 29, 2010). "Boeing 787 Passes Incredible Wing Flex Test". Wired.
- ^ "Boeing Confirms Success on 787 Wing, Fuselage Ultimate Load Test" (Press release). Boeing. April 7, 2010.
- ^ "Boeing 787 in hot/cold testing in Florida". UPI, April 23, 2010. Retrieved September 3, 2011.
- ^ "First 787 GEnx Engine Runs Complete". Boeing, May 12, 2010.
- ^ "VIDEO: GEnx powered 787 completes maiden flight". Flight International. Retrieved July 21, 2010.
- ^ "Horizontal stabiliser gaps force 787 inspections and reduced flight envelope". Flight International. June 25, 2010. Retrieved June 26, 2010.
- ^ Jason Paur (June 17, 2010). "Boeing 787 Withstands Lightning Strike". Wired.
- ^ "FAA Probes American's Inspections". The Wall Street Journal, May 16, 2008, p. B1.
- ^ Gates, Dominic. "Building the 787, When lightning strikes". The Seattle Times, March 5, 2006. Retrieved September 3, 2011.
- ^ Gates, Dominic (February 8, 2009). "FAA to loosen fuel-tank safety rules, benefiting Boeing's 787". The Seattle Times. Retrieved September 2, 2011.
- ^ "FAA engineers objected to Boeing's removal of some 787 lightning protection measures". The Seattle Times. December 2019. Retrieved January 5, 2020.
- ^ "Boeing discarded 787 lightning protection, despite FAA objections". Aerotime Hub. December 11, 2019. Archived from the original on September 15, 2020. Retrieved February 9, 2020.
- ^ "Dreamliner lands at Farnborough". BBC News, July 18, 2010. Retrieved July 18, 2010.
- ^ Mustoe, Howard (August 24, 2010). "Rolls-Royce Blowout Shutters Boeing, Airbus Test Bed". Bloomberg. Archived from the original on January 18, 2013. Retrieved August 29, 2010.
- ^ "Boeing delays delivery of 787 aircraft until next year". BBC. August 27, 2010. Retrieved August 27, 2010.
- ^ Ostrower, Jon (August 28, 2010). "Lack of production engine for Airplane Nine drives 787 delay". Flight International. Retrieved August 29, 2010.
- ^ "Boeing faces claim on 787 delays; sixth flight test aircraft won't fly until September". ATW Online. August 16, 2010. Retrieved August 16, 2010.
- ^ "787 flight test fleet to expand". ATW Online. September 10, 2010. Retrieved September 9, 2010.
- ^ Norris, Guy (September 16, 2010). "Boeing 787 Suffers Engine Surge During Tests; Deliveries May Slip Again". Aviation Week.
- ^ "Sixth Boeing 787 Makes First Flight, Testing Program Making Good Progress". Boeing, October 4, 2010.
- ^ Gates, Dominic (November 9, 2010). "Electrical fire forces emergency landing of 787 test plane". The Seattle Times. Retrieved November 9, 2010.
- ^ "Boeing 787 Makes Emergency Landing On Test Flight". NPR. Associated Press. November 9, 2010. Archived from the original on November 14, 2010. Retrieved November 9, 2010.
- ^ "787 electrical fire raises prospect of further delay". Flightglobal. November 15, 2010. Retrieved November 15, 2010.
- ^ Norris, Guy. "787s Grounded After Emergency Landing". Aviation Week, November 10, 2010. Retrieved June 14, 2011.
- ^ Norris, Guy (November 11, 2010). "787s Remain Grounded As Investigation Continues". Aviation Week.
- ^ Rothman, Andrea. "Boeing 787 Fire Sparked by Stray Tool". Bloomberg, November 25, 2010.
- ^ Ostrower, Jon. "787 flight tests resume, final schedule unclear". Air Transport Intelligence, December 23, 2010. Retrieved September 2, 2011.
- ^ "Boeing Resumes 787 Flight Testing". Boeing, December 23, 2010.
- ^ "Boeing faces prospect of further 787 delay". Flight International. November 5, 2010. Retrieved November 6, 2010.
- ^ "JAL hit by further 787 delivery delay". Air Transport Intelligence. November 4, 2010. Retrieved November 6, 2010.
- ^ "Boeing Sets 787 First Delivery for Third Quarter" (Press release). Boeing. January 18, 2011. Retrieved September 2, 2011.
- ^ "Boeing expects first 787 delivery in the third quarter". Flight International. January 18, 2011.
- ^ Ostrower, Jon (February 24, 2011). "Boeing passes 1,000 787 flights". Air Transport Intelligence. Retrieved September 2, 2011.
- ^ Koh, Quintella (July 4, 2011). "All Nippon Airways starts week-long 787 validation". Air Transport Intelligence. Retrieved July 6, 2011.
- ^ Ostrower, Jon (August 15, 2011). "Certification flight testing complete, the 787 fleet is still busy". Flightblogger on Flightglobal.com. Archived from the original on December 21, 2011.
- ^ Ostrower, Jon. "Boeing confirms 787 certification flight test completion". Air Transport Intelligence, August 17, 2011. Retrieved September 2, 2011.
- ^ "787 wins certification from FAA and EASA". Air Transport Intelligence. August 26, 2011. Retrieved August 26, 2011.
- ^ a b "FAA Approves Production of Boeing 787 Dreamliner" (press release). FAA. August 26, 2011. Archived from the original on September 8, 2011. Retrieved August 29, 2011.
- ^ Hananel, Sam (December 9, 2011). "Labor board drops high-profile Boeing complaint". Boston Globe. Associated Press.
- ^ Peterson, Kyle (April 27, 2012). "Boeing Debuts First 787 Dreamliner in South Carolina". Reuters. Archived from the original on May 2, 2012. Retrieved June 30, 2017.
- ^ Ostrower, Jon (September 25, 2011). "Boeing formally delivers first 787 to ANA". Flight International.
- ^ "Boeing, ANA Complete Contractual Delivery of First 787 Dreamliner" (Press release). Boeing. September 25, 2011.
- ^ Tim Hepher (September 27, 2011). "First delivered Boeing 787 takes off for Japan". Reuters. Archived from the original on September 27, 2011. Retrieved June 30, 2017.
- ^ "Boeing delivers first 787". Associated Press. September 26, 2011.
- ^ "Boeing delivers its second 787 and jumbo freighter". The Seattle Times. October 13, 2011.
- ^ Tim Kelly (October 26, 2011). "Dreamliner carries its first passengers and Boeing's hopes". Reuters. Archived from the original on October 27, 2011. Retrieved June 30, 2017.
- ^ "Boeing's Dreamliner completes first commercial flight". BBC News. October 26, 2011.
- ^ "ANA launches first long-haul service to Europe on 787 Dreamliner" (PDF) (Press release). ANA. October 5, 2011.
- ^ Hamilton, Scott (June 16, 2022). "FAA adopts ICAO 2027 emissions, noise rules; death knell for new production 767F, 777F". Leeham News and Analysis. Retrieved February 26, 2024.
- ^ Hamilton, Scott (September 20, 2022). "Boeing shows FedEx concepts for 787F and NMA-F". Leeham News and Analysis. Retrieved May 8, 2024.
- ^ Kulisch, Eric (September 16, 2022). "Boeing CEO says 787 freighter is frontrunner to succeed 767F". Freight Waves. Retrieved May 8, 2024.
- ^ Ostrower, Jon; Guisbond, Will (May 7, 2024). "Congress poised to give Boeing five more years to build 767 freighters". The Air Current. Retrieved May 8, 2024.
- ^ "Boeing 787-3 Dreamliner Fact Sheet". Boeing. Archived from the original on November 19, 2007. Retrieved November 23, 2007.
- ^ Rich Breuhaus (May 20, 2008). "787 Dreamliner: A New Airplane for a New World" (PDF). ACI-NA Commissioners Conference. Boeing. Archived from the original (PDF) on March 7, 2017. Retrieved March 6, 2017.
- ^ Norris & Wagner 2009, p. 38.
- ^ Jon Ostrower (January 8, 2010). "ANA abandons 787-3". Flight International.
- ^ "Boeing will likely scrap 787-3". The Seattle Times. February 2, 2010.
- ^ "SINGAPORE 2010: 757 replacement gets new focus as 787-3 dwindles". Flightglobal. February 3, 2010.
- ^ Susanna Ray (December 13, 2010). "Boeing raises aircraft prices 5.2%, cancels short-haul 787". The Seattle Times.
- ^ Gates, Dominic (September 24, 2011). "Boeing celebrates 787 delivery as program's costs top $32 billion". The Seattle Times. Retrieved September 26, 2011.
- ^ "The eye of the storm". The Economist. May 14, 2016. ISSN 0013-0613.
- ^ Jonathan R. Laing (April 27, 2013). "Will Boeing's Battery Fix Fly?". Barron's.
- ^ a b c Ostrower, Jon (June 10, 2014). "Boeing's Key Mission: Cut Dreamliner Cost". The Wall Street Journal. p. B1. Retrieved June 10, 2014.
- ^ Trimble, Stephen (April 22, 2015). "Boeing 787 unit loss declines, but deferred costs rise". Flightglobal.
- ^ Jon Ostrower (May 4, 2015). "Boeing Pursues Fresh Deal With Spirit AeroSystems". The Wall Street Journal.
- ^ a b Dominic Gates (October 17, 2015). "Will 787 program ever show an overall profit? Analysts grow more skeptical". Seattle Times.
- ^ Walker, Karen (July 21, 2016). "Boeing 787 financial hit underscores cost of launching a new airliner". Air Transport World.
- ^ James Albaugh (December 4, 2017). "Opinion: Jim Albaugh's Lessons Of Aerospace Success". Aviation Week & Space Technology.
- ^ Trimble, Stephen (September 13, 2017). "Boeing commits to next production-rate increase for 787". Flightglobal.
- ^ "About Boeing Commercial Airplanes: Prices". Boeing.
- ^ Aircraft Value News (June 11, 2018). "Intense A330/B787 Competition Could Impact Values".
- ^ "Boeing displaces Airbus at Hawaiian, wins 787-9 deal; airline cancels A330-800 order". Leeham. February 20, 2018.
- ^ Guy Norris; Jens Flottau; Bradley Perrett (December 17, 2018). "Boeing And Airbus Hope To Leave Production Glitches Behind In 2019". Aviation Week & Space Technology.
- ^ Bjorn Fehrm (April 23, 2015). "Bjorn's Corner: Boeing's 787 and Airbus' 350 programs, a snapshot". Leeham News and Comment.
- ^ "Boeing to cut 787 production rate, cites global trade environment". Leeham News. October 23, 2019.
- ^ Julie Johnsson and Siddharth Vikram Philip (January 24, 2020). "Boeing Mulls Another Cut to 787 Output in New Threat to Cash". Bloomberg.
- ^ "Boeing to Consolidate 787 Production in South Carolina in 2021" (Press release). Boeing. October 1, 2020.
- ^ Scott Hamilton (December 4, 2020). "Boeing further trims 787 production; now sees 5/mo in 2021". Leeham News.
- ^ Kiersz, Andy (April 21, 2019). "'I never plan to fly on it': Workers reportedly recount poor practices at a Boeing factory in South Carolina that could spell trouble for Dreamliner plane". New York: Axel Springer SE. Retrieved July 16, 2021.
- ^ Kitroeff, Natalie; Gelles, David (April 20, 2019). "Claims of Shoddy Production Draw Scrutiny to a Second Boeing Jet". The New York Times. Charleston.
- ^ Slotnick, David (August 5, 2019). "Airlines flying Boeing's 787-10 Dreamliner are complaining about quality they say is 'way below acceptable standards'". Business Insider. New York: Axel Springer SE. Retrieved July 16, 2021.
- ^ a b Tangel, Andrew; Pasztor, Andy (September 7, 2020). "Production Problems Spur Broad FAA Review of Boeing Dreamliner Lapses". The Wall Street Journal. Charleston: Dow Jones & Company. ISSN 0099-9660. Retrieved September 7, 2020.
- ^ Ostrower, Jon (August 27, 2020). "Boeing pulls eight 787s from service over structural issue". Air Current. Retrieved September 7, 2020.
- ^ Ostrower, Jon (September 8, 2020). "Scarce quality data on 787 skins as FAA peels back onion on Boeing". Air Current. Retrieved September 8, 2020.
- ^ Shepardson, David (September 10, 2020). "Boeing in talks with FAA about new reported 787 production issue". Reuters. Seattle. Retrieved September 10, 2020.
- ^ Harger, Charlie (September 10, 2020). "Report raises new questions about structural integrity of Boeing 787 Dreamliner". KOMO News. Retrieved September 10, 2020.
- ^ Cameron, Doug; Pasztor, Andy (September 8, 2020). "Boeing Flags Additional 787 Production Problem". The Wall Street Journal. Salt Lake City: Dow Jones & Company. Retrieved September 8, 2020.
- ^ Jon Hemmerdinger (January 28, 2021). "Boeing to resume 787 deliveries no sooner than February". FlightGlobal. DVV Media Group. Retrieved February 22, 2021.
- ^ Tangel, Andrew (March 18, 2021). "Boeing Faces New Hurdle in Delivering Dreamliners". The Wall Street Journal. Washington, D.C.: Dow Jones & Company. ISSN 0099-9660. Retrieved March 18, 2021.
- ^ Johnsson, Julie; Bachman, Justin (March 26, 2021). "Boeing Delivers First 787 in Months as Inspections Continue". New York: Bloomberg L.P. Bloomberg News. Retrieved April 2, 2021.
- ^ Gates, Dominic (October 12, 2021). "As orders trickle in, Boeing ramps up 737 MAX but 787 deliveries are still blocked". The Seattle Times. Seattle.
- ^ Tangel, Andrew (September 6, 2021). "Boeing's Delivery of New 787 Dreamliners Likely Delayed Until at Least Late October". Wall Street Journal. Chicago: Dow Jones & Company.
- ^ Josephs, Leslie (October 27, 2021). "Boeing posts loss as Dreamliner flaws drive up costs, but airplane sales rise". CNBC. Chicago: NBCUniversal News Group.
- ^ Jones, Callum (July 14, 2021). "Boeing cuts 787 production after structural fault found". The Times of London. Chicago.
- ^ Isidore, Chris (July 13, 2021). "Boeing discloses a new problem with the 787 Dreamliner". CNN Business. CNN. New York: Warner Bros. Discovery.
- ^ "Boeing's Delivery of New 787 Dreamliners Likely Delayed Until at Least Late October". The Wall Street Journal. September 4, 2021.
- ^ Gates, Dominic (November 19, 2021). "FAA memo reveals more Boeing 787 manufacturing defects, including contamination of carbon fiber composites". The Seattle Times. Seattle.
- ^ Johnsson, Julie; Levin, Alan (November 20, 2021). "Boeing Buyers' Ire Builds as 787 Disruptions Pass 13-Month Mark". New York: Bloomberg L.P. Bloomberg News. Retrieved February 26, 2022.
- ^ "U.S. House panel wants answers on Boeing 787". Yahoo News. Reuters. November 19, 2021 – via Yahoo! News UK.
- ^ Nall, Marissa (December 13, 2021). "Region's Boeing 787 suppliers could see production delays into spring". Puget Sound Business Journal. Seattle: American City Business Journals.
- ^ Hemmerdinger, Jon (February 15, 2022). "FAA to issue 787 airworthiness certificates, taking authority from Boeing". FlightGlobal. DVV Media GROUP.
- ^ "Exclusive-Boeing tests suppliers on 787 output hikes -sources". MarketScreener.com. March 11, 2022. Retrieved April 20, 2022.
- ^ "Vistara takes Dreamliner aircraft on lease to boost international ops". Business Standard. August 6, 2022. Retrieved January 6, 2024 – via Press Trust of India.
- ^ Tangel, Andrew (April 27, 2022). "Boeing Looked for Flaws in Its Dreamliner and Couldn't Stop Finding Them". The Wall Street Journal. Chicago: Dow Jones & Company. Retrieved April 28, 2022.
- ^ Johnson, Eric M.; Shepardson, David (May 13, 2022). "Exclusive: U.S. FAA finds Boeing 787 certification documents incomplete -sources". Reuters.
- ^ "U.S. Approves Boeing inspection, rework plan to resume 787 deliveries". CNBC. July 30, 2022.
- ^ Josephs, Leslie (August 10, 2022). "Boeing delivers first 787 Dreamliner since 2021 ending pause over manufacturing flaws". CNBC. Retrieved August 10, 2022.
- ^ Ganapavaram, Abhijith; Insinna, Valerie (February 24, 2023). "Boeing shares fall after new Dreamliner delivery halt". Reuters – via reuters.com.
- ^ "FAA Approves Resumption of B787 Dreamliner Deliveries". March 13, 2023. Retrieved March 17, 2023.
- ^ "F.A.A. Investigates Claims by Boeing Whistle-Blower About Flaws in 787 Dreamliner". The New York Times. April 9, 2024. Retrieved April 12, 2024.
- ^ Senanayake, Natalia (April 12, 2024). "Boeing Whistleblower Reportedly Claims 787 Planes Could Break Apart Mid-Air Due to Construction Flaws". Peoplemag. Retrieved April 12, 2024.
- ^ Gates, Dominic (April 9, 2024). "New Boeing whistleblower alleges serious structural flaws on 787 and 777 jets". The Seattle Times. Retrieved April 12, 2024.
- ^ Rose, Joel (April 12, 2024). "Another Boeing whistleblower says he faced retaliation for reporting 'shortcuts'". National Public Radio. Retrieved April 12, 2024.
- ^ "Boeing's Dreamliner Turning into Nightmares Due to Repeated Quality and Production Issues". March 17, 2025.
- ^ "More than 500 Boeing 787s with faulty parts cleared audits during Italian fraud". March 14, 2025.
- ^ "Boeing 787: A Matter of Materials – Special Report: Anatomy of a Supply Chain". IndustryWeek.com, December 1, 2007.
- ^ "787 Dreamliner Program Fact Sheet". Boeing web page. The Boeing Company. Retrieved July 10, 2007.
- ^ a b c d e Hawk, Jeff (May 25, 2005). The Boeing 787 Dreamliner: More Than an Airplane (PDF). AIAA/AAAF Aircraft Noise and Emissions Reduction Symposium. American Institute of Aeronautics and Astronautics. Archived from the original (PDF) on August 8, 2007. Retrieved July 15, 2007.
- ^ a b Zaman, K. B. M. Q.; Bridges, J. E.; Huff, D. L. "Evolution from 'Tabs' to 'Chevron Technology' – a Review" (PDF). Proceedings of the 13th Asian Congress of Fluid Mechanics December 17–21, 2010, Dhaka, Bangladesh. NASA Glenn Research Center. Cleveland, Ohio, US: 47–63. Archived from the original (PDF) on November 20, 2012. 1.34 MB.
- ^ a b c d "787 performance summary". Boeing.
- ^ "Boeing 787 program background". Retrieved May 4, 2007.
- ^ Ostrower, Jon. "FARNBOROUGH: Boeing presses on with 787 flight-testing (Jul 11, 2010)". FlightGlobal. Retrieved April 2, 2017.
- ^ "Boeing 787 from the Ground Up". Boeing, Aero magazine, QTR_04/06.
- ^ Sinnet, Mike (2007). "Saving Fuel and enhancing operational efficiencies" (PDF). Boeing. Retrieved January 17, 2013.
- ^ Boeing 787-8 Critical System Review Team (March 19, 2014). "Boeing 787-8 Design, Certification, and Manufacturing Systems Review" (PDF). Federal Aviation Administration.
- ^ Susanna Ray, Thomas Black & Mary Jane Credeur. "Boeing 787 Groundings Traced to One-of-a-Kind Technology" Bloomberg, January 17, 2013. Retrieved January 17, 2013.
- ^ "Taking to the skies", p. 47. Aviation Week & Space Technology, December 10, 2012.
- ^ "787 No Bleed Systems". Boeing Aero magazine, Quarter 4, 2007.
- ^ 787 integrates new composite wing deicing system. Composites World, December 30, 2008.
- ^ a b Croft, John (July 2006). "Airbus and Boeing spar for middleweight" (PDF). American Institute of Aeronautics and Astronautics. Archived from the original (PDF) on July 10, 2007. Retrieved July 8, 2007.
- ^ Universal-type gust alleviation system for aircraft, United States Patent 4905934. Free patents online, original publication March 6, 1990. Retrieved December 9, 2009.
- ^ "Taking to the skies". Aviation Week & Space Technology. December 10, 2012. p. 48.
- ^ Ramsey, James W. (June 1, 2005). "Boeing 787: Integration's Next Step". Aviation Today.
- ^ "What is ARINC 661?" Web archive of Engenuity Technologies page.
- ^ "Boeing Unveils 787 Dreamliner Flight Deck Archived April 9, 2007, at the Wayback Machine Boeing, August 31, 2005. Retrieved September 2, 2011.
- ^ Coppinger, Rob (October 6, 2006). "NASA Orion crew vehicle will use voice controls in Boeing 787-style Honeywell smart cockpit". Flight International. Retrieved October 6, 2006.
- ^ a b Brewin, Bob (January 22, 2013). "A 2006 battery fire destroyed Boeing 787 supplier's facility". nextgov.com. Retrieved January 23, 2013.
- ^ "Power conversion". Meggitt/Securaplane. Retrieved January 30, 2013.
- ^ "Lithium Power". GS Yuasa. Archived from the original on January 16, 2013. Retrieved January 20, 2013.
- ^ a b "Thales selects GS Yuasa for Lithium ion battery system in Boeing's 787 Dreamliner" (PDF). GS Yuasa. Retrieved January 18, 2013.
- ^ "Development of Large-sized Lithium-ion Battery for Aviation Applications" (PDF). GS Yuasa. Archived from the original (PDF) on February 3, 2013. Retrieved January 20, 2012.
- ^ "Boeing: 787 battery blew up in '06 lab test, burned down building". Seattle Times. January 24, 2013. Retrieved January 24, 2013.
- ^ "FAA Statement". Federal Aviation Administration. January 16, 2013. Retrieved January 17, 2013.
- ^ McHale, John (April 2005). "AFDX technology to improve communications on Boeing 787". mae.pennet.com. mae.pennnet.com. Archived from the original on August 3, 2004. Retrieved July 8, 2007.
- ^ a b c Zetter, Kim (January 4, 2008). "FAA: Boeing's New 787 May Be Vulnerable to Hacker Attack". Wired. Retrieved January 6, 2008.
- ^ "Special Conditions: Boeing Model 787-8 Airplane; Systems and Data Networks Security—Isolation or Protection From unauthorized Passenger Domain Systems Access". Federal Aviation Administration. U.S. Government Printing Office (GPO). January 3, 2008. Retrieved November 1, 2012.
For these design features, the applicable airworthiness regulations do not contain adequate or appropriate safety standards for protection and security of airplane systems and data networks against unauthorized access.
- ^ a b c Trimble, Stephen (March 28, 2018). "Boeing 787-10 technical description and cutaway". Flightglobal.
- ^ Marsh, George (April 8, 2014). "Composites flying high (Part 1)". Materials Today. Archived from the original on September 16, 2015. Retrieved May 23, 2015.
- ^ "Market Research Report: Strategic Business Expansion of Carbon Fiber, Torayca" (PDF) (press release). Toray Industries. April 12, 2005. Archived from the original (PDF) on February 4, 2007. Retrieved July 9, 2007.
- ^ a b Wallace, James (June 29, 2007). "How the 787 'Dream' was born". Seattle Post-Intelligencer.
- ^ William G. Roeseler; Branko Sarh; Max U. Kismarton (July 9, 2007). "COMPOSITE STRUCTURES: THE FIRST 100 YEARS" (PDF). 16TH INTERNATIONAL CONFERENCE ON COMPOSITE MATERIALS.[dead link]
- ^ "Boeing Testing Sample Sonic Cruiser Fuselage". Boeing. July 24, 2002. Archived from the original on December 5, 2008.
- ^ "Development Work on Boeing 787 Noses Ahead". Boeing. July 13, 2005. Archived from the original on May 5, 2010. Retrieved June 14, 2011.
- ^ a b Haines, Lester (September 19, 2007). "787 unsafe, claims former Boeing engineer". The Register.
- ^ Wallace, James (January 9, 2006). "Airbus to use composites". Seattle Post-Intelligencer. Hearst Communications Inc.
- ^ “Excerpts”-The Culture of Collaboration-Expanded and Updated Edition,” web site of The Culture of Collaboration.
- ^ “Excerpts”-The Culture of Collaboration-Expanded and Updated Edition,” web site of The Culture of Collaboration.
- ^ Bickers, Chaz (July 2006). "Good as GoldCare: Revolutionary 787 fleet support program complements airplane's technical achievements" (PDF). Boeing Frontiers. Boeing. Retrieved September 2, 2011.
- ^ Johnsson, Julie (September 2, 2007). "Boeing coining plan for composite parts". Chicago Tribune. Tribune Interactive.
- ^ "Inside the Black Box: How the Boeing 787 records flight data and what happens when power fails". @mathrubhumi. June 21, 2025.
- ^ a b "Section 2.4 Interior Arrangements; Section 2.5 Cabin Cross–Sections" (PDF). D6-58331, Boeing 787 Airplane Characteristics for Airport Planning. Boeing Commercial Aircraft. December 2015. pp. 10, 13.
- ^ Flynn, David (December 12, 2012). "BA reveals Airbus A380, Boeing 787 Dreamliner seatmaps". Australian Business Traveller. Retrieved December 21, 2012.
- ^ Wallace, James (November 18, 2005). "Boeing details 787 improvements". Seattle Post-Intelligencer. Hearst Communications. Retrieved September 2, 2011.
- ^ "A330 and A340 family specifications". Airbus. Archived from the original on March 4, 2008.
- ^ "A350 XWB Xtra comfort". Airbus. Archived from the original on February 5, 2008.
- ^ "Airbus unveils widebody, says A350 XWB will top 787 and 777". Seattle Post-Intelligencer. July 18, 2006. Archived from the original on June 11, 2007.
- ^ "British Airways 787-8 Seat Map". SeatGuru. Retrieved August 28, 2014.
- ^ Wallace, James (February 22, 2006). "Aerospace Notebook: More seats sought on 787". Seattle-PI. Retrieved February 12, 2012.
- ^ Verghese, Vijay. "A survey of the best airline economy seats". Smart travel Asia. Retrieved February 12, 2012.
- ^ a b "Why I tell people to avoid flying on a 787". January 22, 2015. Retrieved September 5, 2016.
- ^ "Negative feedback prompts British Airways to widen seats for 787-9". August 23, 2015. Retrieved September 5, 2016.
- ^ Morrison, Geoffrey. "15 hours on a Boeing 787 Dreamliner, in coach". Retrieved September 5, 2016.
- ^ Wallace, James (June 5, 2007). "Aerospace Notebook: In Airbus, Boeing duel, jet windows a shut case". Seattle Post-Intelligencer. Retrieved September 2, 2011.
- ^ a b Wallace, James (November 26, 2008). "Continental plans Dreamliner seats to be roomy, with a view". Seattle Post-Intelligencer. Retrieved November 28, 2008. [dead link] Alt URL Archived September 28, 2015, at the Wayback Machine
- ^ Norris & Wagner 2009, p. 49.
- ^ Norris, Guy (December 20, 2005). "Qantas deal sees launch of 787-9". Flight International. Reed Elsevier.
- ^ a b Schofield, Adrian (June 24, 2012). "The 787 windows issue (with pics)". Aviation Week. Archived from the original on January 20, 2013. Retrieved January 29, 2013.
- ^ a b Parker Brown, David (June 21, 2012). "ANA is NOT Looking to Install Sunshades on their Boeing 787s — No Complaints Were Received". Airline Reporter. Retrieved January 27, 2013.
- ^ a b Turner, Edgar (2010). The Birth of the 787 Dreamliner. Kansas City, MO: Andrews McMeel. p. 220. ISBN 978-0-7407-9667-8.
- ^ Flynn, David (October 26, 2011). "Light fantastic: Boeing 787 Dreamliner's digital window tinting". Australian Business Traveller. Retrieved January 27, 2013.
- ^ a b "Interior Lighting Systems, Mood Lighting". Germany: Diehl Aerospace. Archived from the original on March 17, 2012. Retrieved May 1, 2007.
- ^ "Mood Lighting System". Diehl Aerospace. 2012. Archived from the original on January 20, 2012. Retrieved January 1, 2012.
- ^ Gubisch, Michael (December 20, 2005). "In Focus: Cabin interior advances beyond seats and IFE". Flight International. Reed Elsevier.
- ^ Cram, Jennifer (March 26, 2007). "Boeing Unveils Improved Access Features on the 787". Boeing press release. Boeing. Archived from the original on October 11, 2007. Retrieved July 10, 2007.
- ^ a b c Adams, Marilyn (November 1, 2006). "Breathe easy, Boeing says". USA Today.
- ^ "Boeing 7E7 Offers Preferred Cabin Environment, Study Finds" (Press release). Boeing. July 19, 2004. Archived from the original on November 6, 2011. Retrieved June 14, 2011.
- ^ Ogando, Joseph, ed. (June 4, 2007). "Boeing's 'More Electric' 787 Dreamliner Spurs Engine Evolution: On the 787, Boeing eliminated bleed air and relied heavily on electric starter generators". Design News. Archived from the original on April 6, 2012. Retrieved September 9, 2011.
- ^ Dornheim, Michael (March 27, 2005). "Massive 787 Electrical System Pressurizes Cabin". Aviation Week & Space Technology.
- ^ Kingsley-Jones, Max (February 26, 2020). "Can Rolls-Royce win back confidence in 787 engine market?". Flight Global. Retrieved November 1, 2020.
- ^ Corliss, Bryan (June 21, 2009). "What's new, different about the 787". The Daily Herald. Retrieved January 22, 2011.
- ^ ""787 Isn't Meeting 24-hour Engine Change Promo, lessor says" (PDF). Leeham News and Analysis. July 18, 2005. Archived from the original (PDF) on September 23, 2006.
- ^ "GR & Boeing Demo. Quiet Technology" (press release). Goodrich. August 16, 2005. Archived from the original on October 19, 2007. Retrieved July 10, 2007.
- ^ "Trent 1000". Rolls-Royce. Retrieved May 2, 2025.
- ^ "Boeing 787 Dreamliner Sets Speed, Distance Records" (Press release). Boeing. December 8, 2011.
- ^ "Boeing Announces 787 Dream Tour". Boeing. November 23, 2011.
- ^ "Boeing, ANA Celebrate First 787 Biofuel Flight" (Press release). Boeing. April 17, 2012.
- ^ Steve Creedy (June 12, 2012). "Rave reviews for Boeing's 787". The Australian.
- ^ Guy Norris (June 26, 2012). "Operators Reporting Positive 787 Fuel-Burn Results". Aviation Week.
- ^ Guy Norris; Cathy Buyck; Adrian Schofield; Madhu Unnikrishnan; Jeremy Torr (July 14, 2014). "Airlines Singing Praises of 787". Aviation Week and Space Technology. Archived from the original on April 17, 2015.
- ^ David Kaminski Morrow (November 6, 2017). "IAG lauds ownership-cost benefit of Level A330s". Flightglobal.
- ^ "Boeing tackles 787 APU overheating issue". Aviation Week. May 27, 2013. Retrieved December 8, 2014.
- ^ "NTSB urges grounding for certain GEnx-powered 787 and 747-8s". Flight International. September 15, 2012.
- ^ "Boeing: Problems with 787 Dreamliner "Normal"". frequentbusinesstraveler.com. December 16, 2012. Archived from the original on December 30, 2012. Retrieved December 16, 2012.
- ^ "Boeing 787 Dreamliner: a timeline of problems". The Telegraph. London. July 28, 2013. Archived from the original on January 11, 2022. Retrieved August 14, 2013.
- ^ Ostrower, Jon (March 8–9, 2014). "New Boeing woe: 787 wing defect". The Wall Street Journal. pp. B1, B4.
- ^ Wyndham, David (October 1, 2012). "Aircraft Reliability". AvBuyer. World Aviation Communication Ltd.
- ^ Guy Norris (November 24, 2015). "With Better Dispatch Reliability, Boeing 787 Deliveries Reach 350". Aviation Week & Space Technology.
- ^ Bjorn Fehrm (May 11, 2017). "ISTAT Asia 2017: The fight for the lead". Leeham.
- ^ Brian Sumers (January 22, 2016). "Air Canada's 787 Expansion Plans Still In Play". Aviation Week & Space Technology.
- ^ "787: Living the dream with amazing new routes? (Or just another great replacement aircraft?)". Airline Network News & Analysis. August 9, 2017.
- ^ "Jet makes history on flight from Australia". BBC News. March 25, 2018. Retrieved March 26, 2018.
- ^ Street, Francesca (March 17, 2020). "Virus creates world's longest passenger flight". CNN. Retrieved March 17, 2020.
- ^ a b c Howard Hardee (June 1, 2023). "Advanced materials emerge as challenging new frontier for aircraft recycling". Flightglobal.
- ^ "aircraft type designators" (PDF). International Civil Aviation Organization. Archived from the original (PDF) on March 24, 2022. Retrieved March 26, 2017.
- ^ "The ultimate guide to aircraft variants". Key Publishing. October 6, 2020. Retrieved January 6, 2024.
- ^ "Boeing to implement structural design change in 787-8 for production commonality". Leeham News. April 17, 2018.
- ^ "B767-300ER Historical Value Behavior Defy Expectations". Aircraft Value News. October 29, 2018.
- ^ Kingsley-Jones, Max (July 18, 2014). "Aero secrets of Boeing's new Dreamliner". Flightglobal. Archived from the original on July 24, 2014. Retrieved July 24, 2014.
- ^ "Boeing clears firm configuration hurdle for 787-9". Flight International. July 1, 2010. Retrieved July 2, 2010.
- ^ "Boeing delays first 747-8I and 787-9 deliveries". Flightglobal. October 27, 2011. Retrieved January 20, 2013.
- ^ "Boeing 787-9 takes off for maiden flight". Flightglobal. September 17, 2013.
- ^ "Boeing completes first flight of 2nd 787-9". Flight Global. November 8, 2013.
- ^ Stake, Tim (July 7, 2014). "Air NZ 787-9 To Be Showcased at Famous Airshow". Fairfax New Zealand. Retrieved July 12, 2014.
- ^ Durston, James (July 9, 2014). "Air New Zealand shows off stunning, all-black Dreamliner". CNN. Retrieved July 9, 2014.
- ^ "Air New Zealand operates first 787 service". Australian Aviation. August 9, 2014. Retrieved August 10, 2014.
- ^ "ANA sets date for first scheduled flights with Boeing 787-9". All Nippon Airways. Retrieved November 6, 2014.
- ^ "United Airlines to Launch Nonstop Service Between Los Angeles and Melbourne, Australia". United Airlines. February 20, 2014. Archived from the original on October 15, 2014. Retrieved March 1, 2014.
- ^ "Air China Brings China's First Boeing 787-9 Home". China Aviation Daily. Retrieved July 8, 2016.
- ^ Aircraft Value News (May 14, 2018). "A350-900 Lease Rentals Hold Steady".
- ^ a b Guy Norris (December 19, 2016). "Simplicity Is Vital To Boeing 787-10 Execution". Aviation Week & Space Technology.
- ^ "Australia-UK: First non-stop flight arrives in London from Perth". BBC News. March 25, 2018. Retrieved March 25, 2018.
- ^ "Le plus long vol direct de l'histoire a duré plus de 19 heures". La Presse. Agence France-Presse. October 20, 2019. Retrieved October 20, 2019.
- ^ "New Record For World's Longest Flight". Air Tahiti Nui (Press release). March 20, 2020.
- ^ James Wallace (December 21, 2005). "Everett work force for 787 pegged at 1,000". Seattle Post-Intelligencer.
- ^ Baseler, Randy (February 8, 2006). "Dash 10". Boeing Blog.
- ^ Lunsford, J. Lynn (March 28, 2006). "Boeing to Offer Larger Version of 787 Dreamliner". The Wall Street Journal.
- ^ Kaminski-Morrow, David (May 30, 2013). "Singapore to launch 787-10X with order for 30". Flight International.
- ^ Flynn, David (May 30, 2013). "Singapore Airlines signs up for Boeing's 787-10X Dreamliner". Australian Business Traveller.
- ^ "Boeing Launches 787-10 Dreamliner". Boeing. June 18, 2013.
- ^ "787 Model Summary Through June 2018". Boeing. Archived from the original on July 19, 2018.
- ^ Trimble, Stephen (June 18, 2013). "PARIS: Boeing launches 787-10 with five customers". Flight International. Retrieved June 29, 2013.
- ^ Metcalf, Eddy (June 19, 2013). "Boeing To Launch 787-10 Dreamliner The Most Efficient Jetliner In History". Aviation Online Magazine. Archived from the original on August 9, 2013. Retrieved July 6, 2013.
- ^ "Air Lease's Hazy Says Boeing 787-10 Beats Airbus on Fuel". Bloomberg. June 18, 2013.
- ^ "Boeing 787 Dreamliner (Technical Specs)". Boeing. February 2022.
- ^ "Boeing Completes Detailed Design for the 787-10 Dreamliner" (Press release). Boeing. December 2, 2015.
- ^ "Boeing 787-10 Dreamliner Begins Major Assembly" (Press release). Boeing. March 15, 2016.
- ^ David Wren (November 30, 2016). "Boeing's first 787-10 Dreamliner moves into final assembly". Charleston Post and Courier.
- ^ a b "Civil Aviation Programs To Watch". Aviation Week & Space Technology. June 9, 2017.
- ^ "Boeing Debuts 787-10 Dreamliner" (Press release). Boeing. February 17, 2017.
- ^ Trimble, Stephen (March 31, 2017). "Boeing achieves first flight of Charleston-built 787-10". FlightGlobal.
- ^ Max Kingsley-Jones (June 18, 2017). "Boeing completes a third of 787-10 testing". Flightglobal.
- ^ Trimble, Stephen (October 3, 2017). "Boeing rolls out first 787-10 built for customer". Flightglobal.
- ^ Guy Norris (November 22, 2017). "Boeing Targets 787-10 Test Completion In December". Aviation Week & Space Technology.
- ^ David Kaminski Morrow (November 12, 2017). "Emirates set to push 787-10 backlog over 200". Flightglobal.
- ^ Wall, Robert; Parasie, Nicolas (November 12, 2017). "Emirates Airline Orders 40 Boeing 787 Dreamliners". The Wall Street Journal. New York City, New York, United States. Retrieved November 13, 2017.
- ^ Jens Flottau (November 14, 2017). "Emirates Dismisses A380plus Concept As Negotiations Continue". Aviation Week.
- ^ David Kaminski Morrow (November 14, 2017). "Emirates' faith in 787-10 closes window to A350". Flightglobal.
- ^ Scott Hamilton (February 4, 2019). "787-10 engines too small for Emirates". Leeham News.
- ^ Kaminski-Morrow, David (November 20, 2019). "DUBAI: Emirates to take 30 787-9s and trims 777X deal". Flightglobal.com. Retrieved November 27, 2019.
- ^ Trimble, Stephen (January 22, 2018). "FAA approves 787-10 for airworthiness". Flightglobal.
- ^ "Boeing receives 787-10 production certificate". Flightglobal. February 16, 2018.
- ^ "Boeing Delivers World's First 787-10 Dreamliner to Singapore Airlines" (Press release). Boeing. March 25, 2018.
- ^ Firdaus Hashim (February 8, 2018). "SIA 787-10 will make May debut to Osaka". Flightglobal.
- ^ "Singapore Airlines takes delivery of its first Boeing 787-10". Australian Aviation. June 3, 2018. Retrieved June 17, 2018.
- ^ Jon Ostrower (May 30, 2019). "Boeing chases range frontier on 787 and 777X to win Air New Zealand, Qantas deals". The air current.
- ^ "Boeing Business Jets". Boeing. June 2018.
- ^ "Backgrounder: The Boeing ecoDemonstrator Program (June 2022)" (PDF). Boeing. Retrieved November 21, 2022.
- ^ "Boeing ecoDemonstrator 787 Tests Innovations for More Efficient Air Travel" (Press release). Boeing. November 17, 2014. Retrieved January 6, 2024.
- ^ "Etihad ecoDemonstrator Programme". Etihad Aviation Group. Retrieved November 21, 2022.
- ^ Hemmerdinger, Jon (April 28, 2023). "Boeing adds 787-10 to 2023 ecoDemonstrator technology programme". FlightGlobal. DVV Media. Retrieved April 29, 2023.
- ^ Waldron, Greg (June 15, 2023). "ANSPs demonstrate trajectory-based operations in Asia-Pacific". FlightGlobal. DVV Media. Retrieved November 17, 2023.
- ^ Thisdell and Seymour. Flight International, July 30 – August 5, 2019, p. 42.
- ^ Michael (August 26, 2011). "Boeing 787 Dreamliner – Date for First Delivery". Flight Story. Archived from the original on July 9, 2015. Retrieved August 26, 2011.
- ^ "Boeing Delivers the 787th 787 Dreamliner" (Press release). Boeing. December 13, 2018.
- ^ Gary Eaton (April 3, 2020). "Maiden flight of the 1000th production Boeing 787 Dreamliner".
- ^ "Orders & Deliveries". The Boeing Company. September 30, 2025. Retrieved October 14, 2025.
- ^ "Boeing 787 Accident Statistics". Aviation Safety Network. Retrieved March 8, 2025.
- ^ "Boeing 787 occurrences". Aviation Safety Network. Retrieved March 8, 2025.
- ^ "Flight history for aircraft - VT-ANB". Flightradar 24.
- ^ a b Preliminary Report Accident involving Air India's B787-8 aircraft bearing registration VT-ANB at Ahmedabad on 12 June 2025 (PDF) (Report). Aircraft Accident Investigation Bureau. July 11, 2025. Archived (PDF) from the original on July 11, 2025. Retrieved July 11, 2025.
- ^ "Unexpected fuel cutoff preceded Air India plane crash, preliminary report says". The Washington Post. July 11, 2025. ISSN 0190-8286. Retrieved August 7, 2025.
- ^ Khanna, Sumit (June 24, 2025). "Authorities identify all but one of 260 victims of Air India plane crash". Reuters. Retrieved June 26, 2025.
- ^ "Fiery Air India crash kills 241 people aboard, leaving 1 survivor, airline says". AP News. June 12, 2025. Retrieved June 14, 2025.
- ^ "Air India Ahmedabad-London flight crashes near airport in Meghani nagar area". The Times of India. June 12, 2025. Retrieved June 12, 2025.
- ^ "Two Boeing 787 incidents raise concerns about jet". Reuters. January 9, 2013. Archived from the original on March 7, 2016. Retrieved January 9, 2013.
- ^ "U.S. Opens Dreamliner Safety Probe". The Wall Street Journal. January 9, 2013. Retrieved January 9, 2013.
- ^ "U.S. to review Dreamliner amid two more mishaps in Japan". Chicago Tribune. January 11, 2013. Archived from the original on February 15, 2013. Retrieved January 11, 2013.
- ^ "Japan Airlines Reports New Fuel Leak in Boeing 787". Yahoo! News. Associated Press. January 14, 2013. Retrieved September 27, 2015.
- ^ "JAL's grounded Dreamliner jet leaks fuel in tests". Reuters. January 13, 2013. Archived from the original on February 16, 2013. Retrieved January 13, 2013.
- ^ Mukai, Anna (January 15, 2013). "Japan to Investigate Boeing 787 Fuel Leak as FAA Reviews". Bloomberg. Retrieved January 20, 2013.
- ^ Topham, Gwyn (January 11, 2013). "Boeing 787 Dreamliner to be investigated by US authorities". The Guardian. London. Retrieved January 11, 2013.
- ^ "Heathrow shut after Boeing Dreamliner 787 fire". BBC News. July 12, 2013. Retrieved July 12, 2013.
- ^ "Ethiopian 787 In Heathrow Fire Incident". Aviation Week. July 12, 2013. Archived from the original on November 3, 2013. Retrieved July 12, 2013.
- ^ Goad, Ben (July 13, 2013). "British investigators: No evidence Dreamliner fire related to batteries". The Hill. Retrieved July 13, 2013.
- ^ Martinez, Michael (July 12, 2013). "Fire, 'technical issue' on two Dreamliners raise new worries". CNN. Retrieved July 12, 2013.
- ^ "Batteries 'not linked' to 787 fire". BBC. July 13, 2013. Retrieved July 13, 2013.
- ^ "Heathrow fire on Boeing Dreamliner 'started in battery component'". Guardian newspaper, July 18, 2013.
- ^ "Special Bulletin S5/2013 – Boeing 787, ET-AOP" (PDF). Air Accidents Investigation Branch. July 18, 2013. Archived from the original (PDF) on August 4, 2013. Retrieved May 7, 2017.
- ^ "UK: 2013 Dreamliner fire caused by crossed wires". Associated Press. Archived from the original on March 5, 2016.
- ^ "Qatar grounds a 787 as glitches pile up on Boeing jet". Reuters, July 27, 2013.
- ^ Kiyotaka Matsuda & Robert Wall (August 14, 2013). "Boeing 787 Hit by Setback With Fire-Extinguisher Wiring Flaw". Bloomberg. Retrieved August 16, 2013.
- ^ Ostrower, Jon (August 16, 2013). "Boeing Traces Improperly Assembled Engine-Fire Extinguishers to Supplier's Bottles". The Wall Street Journal. Retrieved August 16, 2013.
- ^ "Boeing warns of engine icing risk on 747-8s, Dreamliners". Yahoo! Finance (October 15, 2013). Retrieved March 13, 2014.
- ^ a b Boeing 787 Dreamliners Disrupt Norwegian Air Shuttle's Operations Archived January 24, 2014, at the Wayback Machine. Businessweek (January 22, 2014). Retrieved March 13, 2014.
- ^ Bangkok to Oslo flight halted after fuel seen leaking from wing. UPI.com. Retrieved March 13, 2014.
- ^ UPDATE 1-Fuel leak on Boeing 787 delays Norwegian Air flight Archived September 28, 2015, at the Wayback Machine. Reuters (January 21, 2014). Retrieved March 13, 2014.
- ^ Koranyi, Balazs. (January 24, 2014) Boeing says Dreamliner reliability 'better, but not satisfactory' Archived September 28, 2015, at the Wayback Machine. Reuters. Retrieved March 13, 2014.
- ^ Treloar, Stephen. (January 24, 2014) 787 Dreamliner's reliability needs to improve further, Boeing exec says |Business & Technology. The Seattle Times. Retrieved March 13, 2014.
- ^ Trimble, Stephen (March 31, 2016). "Boeing, FAA warn 787 pilots of bad airspeed data". Flightglobal.com.
- ^ Michael Kaszycki. "Federal Aviation Administration,Airworthiness Directives; The Boeing Company Airplanes" (PDF). rgl.faa.gov. Archived from the original (PDF) on January 31, 2017. Retrieved April 12, 2016.
- ^ Lorenzetti, Laura. "FAA Says Boeing 787 Dreamliners Have 'Urgent Safety Issue'". Fortune.
- ^ "Federal Aviation Administration-14 CFR Part 39" (PDF). i2.cdn.turner.com.
- ^ "Aircraft systems issue possible cause of LATAM incident – commentator". 1News. Retrieved March 12, 2024.
- ^ "38 hurt as United flight from Nigeria to DC experiences unexpected aircraft movement". NBC News. NBCUniversal. January 25, 2025. Retrieved June 26, 2025.
- ^ "Navigation parts failure led to 'altitude excursions' on United flight: NTSB". AeroTime. AeroTime Hub. March 19, 2025. Retrieved June 26, 2025.
- ^ a b "Accident: ANA B788 near Takamatsu on January 16, 2013, battery problem and burning smell on board". Aviation Herald. Retrieved February 8, 2013.
- ^ "Japanese airlines ground Boeing 787s after emergency landing". Reuters. January 16, 2013. Archived from the original on November 15, 2015. Retrieved January 16, 2013.
- ^ McCurry, Justin (January 16, 2013). "787 emergency landing: Japan grounds entire Boeing Dreamliner fleet". The Guardian. London. Retrieved January 16, 2013.
- ^ Cooper, Chris; Matsuda, Kiyotaka (May 1, 2013). "Boeing Dreamliner Grounding Hurts ANA, Japan Airlines Sales". Bloomberg. Tokyo. Retrieved May 27, 2013.
- ^ "Press Release". Federal Aviation Administration. January 16, 2013. Retrieved January 17, 2013.
- ^ a b "Dreamliner: Boeing 787 planes grounded on safety fears". News. BBC. January 17, 2013. Retrieved January 17, 2013.
- ^ "Airbus CEO 'Confident' Boeing Will Find Fix for 787" (video). Bloomberg. January 17, 2013.
- ^ Wall, Robert; Rothman, Andrea (January 17, 2013). "Airbus Says A350 Design Is 'Lower Risk' Than Troubled 787". Bloomberg. Retrieved January 17, 2013.
'I don't believe that anyone's going to switch from one airplane type to another because there's a maintenance issue,' Leahy said. 'Boeing will get this sorted out.'
- ^ "Boeing 787 Dreamliner design riskier than our plane: Airbus | The Star". The Toronto Star. January 17, 2013.
- ^ "'Big Cost' Seen for Boeing Dreamliner Grounding". Bloomberg. January 17, 2013.
- ^ White, Martha C (January 17, 2013). "Is the Dreamliner Becoming a Financial Nightmare for Boeing?". Time.
- ^ Dudley, Brier (January 17, 2013). "Lithium-ion batteries pack a lot of energy — and challenges". The Seattle Times. Retrieved January 24, 2013.
iron phosphate "has been known to sort of be safer."
- ^ Dalløkken, Per Erlien (January 17, 2013). "Her er Dreamliner-problemet". Teknisk Ukeblad (in Norwegian). Archived from the original on January 16, 2016. Retrieved January 17, 2013. English translation
- ^ "Energy storage technologies – Lithium". Securaplane. Retrieved January 24, 2013.
- ^ "Special Conditions: Boeing Model 787-8 Airplane; Lithium Ion Battery Installation" (PDF) (PDF). FAA / Federal Register. October 11, 2007. Retrieved January 30, 2013.
NM375 Special Conditions No. 25–359–SC
- ^ Scott, Alwyn; Saito, Mari. "FAA approval of Boeing 787 battery under scrutiny". NBC News. Reuters. Retrieved January 24, 2013.
- ^ Supko; Iverson (2011). "Li battery UN test report applicability" (PDF). nextgov.com. Retrieved January 23, 2013.
- ^ Nantel, Kelly (January 20, 2013). "NTSB Provides Third Investigative Update on Boeing 787 Battery Fire in Boston". NTSB. Retrieved January 21, 2013.
- ^ "Press Release". NTSB. January 26, 2013. Retrieved January 24, 2013.
- ^ Weld, Matthew; Mouwad, Jad (January 25, 2013). "Protracted Fire Inquiry Keeping 787 on Ground". The New York Times. Retrieved January 26, 2013.
- ^ Mitra-Thakur, Sofia (January 23, 2013). "Japan says 787 battery was not overcharged". Engineering & Technology. Archived from the original on January 25, 2013. Retrieved January 23, 2013.
- ^ a b Drew, Christopher; Tabuchi, Hiroko; Mouawad, Jad (January 29, 2013). "Boeing 787 Battery Was a Concern Before Failure". The New York Times. Retrieved January 30, 2013.
- ^ Hradecky, Simon (February 5, 2013). "ANA B788 near Takamatsu on January 16, 2013, battery problem and burning smell on board". Aviation Herald. Retrieved February 6, 2013.
- ^ Tabuchi, Hiroko (January 28, 2013). "No Quality Problems Found at Battery Maker for 787". The New York Times. Retrieved January 30, 2013.
- ^ Cooper, Chris; Matsuda, Kiyotaka (January 28, 2013). "GS Yuasa Shares Surge as Japan Ends Company Inspections". Bloomberg BusinessWeek. Archived from the original on August 23, 2014. Retrieved January 29, 2013.
- ^ Knudson, Peter (January 29, 2013). "NTSB issues sixth update on JAL Boeing 787 battery fire investigation". NTSB. Retrieved January 29, 2013.
- ^ "FAA grounding all Boeing 787s". KIRO TV. Archived from the original on January 19, 2013. Retrieved January 16, 2013.
- ^ "LAN suspende de forma temporal la operación de flota Boeing 787 Dreamliner". La Tercera. January 16, 2013. Archived from the original on January 17, 2013. Retrieved January 16, 2013.
- ^ "DGCA directs Air India to ground all six Boeing Dreamliners on safety concerns". The Economic Times. January 17, 2013. Retrieved January 17, 2013.
- ^ "European safety agency to ground 787 in line with FAA". Reuters. January 16, 2013. Archived from the original on March 20, 2013. Retrieved January 17, 2013.
- ^ "Qatar Airways grounds Boeing Dreamliner fleet". Reuters. January 17, 2013. Archived from the original on March 20, 2013. Retrieved January 17, 2013.
- ^ a b "U.S., others ground Boeing Dreamliner indefinitely". Reuters. January 16, 2013. Archived from the original on January 20, 2013. Retrieved January 17, 2013.
- ^ Boeing 787 Dreamliner: The impact of safety concerns. BBC News. January 17, 2013. Retrieved January 17, 2013.
- ^ "Dreamliner crisis: Boeing halts 787 jet deliveries". BBC News. UK. January 1, 1970. Retrieved January 20, 2013.
- ^ "FAA approves test flights for Boeing 787". The Seattle Times. February 7, 2013. Retrieved September 27, 2015.
- ^ Norris, Guy (February 7, 2013). "FAA Gives All Clear For 787 Test Flights". Aviation Week. Archived from the original on May 20, 2013. Retrieved February 9, 2013.
- ^ "Boeing 787's battery woes put US approval under scrutiny". Business Standard. February 22, 2013. Retrieved February 22, 2013.
- ^ "Auxiliary Power Unit Battery Fire Japan Airlines Boeing 787-8, JA829J". National Transportation Safety Board. Archived from the original on December 26, 2014.
- ^ "Interim factual report" (PDF). National Transportation Safety Board. March 7, 2013.
- ^ "NTSB Report Details: Boeing 787 Battery Fire Was Difficult to Control". Time. March 7, 2013. Archived from the original on March 9, 2013.
- ^ "Airlines Prepare to Relaunch Their Dreamliners: ANA, Qatar, United Schedule First Flights". Frequent Business Traveler.
- ^ a b Drew, Christopher; Mouawad, Jad (April 20, 2013). "Boeing Fix for Battery Is Approved by FAA". The New York Times.
- ^ Yeo, Ghim-Lay (April 19, 2013). "FAA approves 787 battery changes". Flight International. Retrieved April 19, 2013.
- ^ a b "Boeing 787 Dreamliner returns to service in Ethiopia flight". BBC News. April 27, 2013.
- ^ a b Gates, Dominic. "Grounding order formally lifted for Boeing 787". The Seattle Times/The Columbian. Retrieved May 1, 2013.
- ^ "Japan OKs 787s to fly again". CNN. April 26, 2013. Retrieved April 26, 2013.
- ^ "Boeing 787 aircraft grounded after battery problem in Japan". BBC News. January 14, 2014. Retrieved January 16, 2014.
- ^ "No damage to JAL 787 in battery incident". Flight International. January 15, 2013. Retrieved January 16, 2014.
- ^ Thomson, Iain (January 16, 2014). "Boeing bent over for new probe as 787 batteries vent fluid, start to MELT". www.theregister.co.uk.
- ^ Ostrower, John, "JAL reports malfunction in battery on Boeing 787", The Wall Street Journal, January 15, 2014, p. B1.
- ^ Temperature in failed Dreamliner battery hit 660 Celsius. The Daily Telegraph. Retrieved March 13, 2014.
- ^ Knudson, Peter. "NTSB Recommends Process Improvements for Certifying Lithium-ion Batteries as it Concludes its Investigation of the 787 Boston Battery Fire Incident" NTSB, December 1, 2014. Retrieved December 2, 2014.
- ^ Hemmerdinger, Jon (December 1, 2014). "NTSB faults Boeing, FAA and contractors for 787 battery fire". Flightglobal. Archived from the original on December 2, 2014. Retrieved December 2, 2014.
- ^ Hemmerdinger, Jon (December 1, 2014). "Temperature in 787 battery cells spikes in cold conditions: NTSB". Flightglobal. Archived from the original on December 2, 2014. Retrieved December 2, 2014.
- ^ Hemmerdinger, Jon (December 1, 2014). "NTSB 787 battery report details quality concerns at GS Yuasa". Flightglobal. Archived from the original on December 2, 2014. Retrieved December 2, 2014.
- ^ Hemmerdinger, Jon (December 2, 2014). "NTSB details issues with 787 flight and data recorder". Flightglobal. Archived from the original on December 2, 2014. Retrieved December 2, 2014.
- ^ Thierry Dubois (June 27, 2017). "Lithium-ion Batteries Prove Value On A350". Aviation Week & Space Technology.
- ^ "Boeing donates the first 787-8 prototype (N787BA, ZA001) to Nagoya, Japan". World Airline News. June 22, 2015. Archived from the original on June 22, 2015. Retrieved January 7, 2016.
- ^ "DREAMLINER". Pima Air & Space Museum. Archived from the original on January 19, 2016. Retrieved January 7, 2016.
- ^ "Boeing 787 Dreamliner". The Museum of Flight. Retrieved April 5, 2015.
- ^ "Museum Opens World's First Boeing 787 Dreamliner Exhibit Nov 8". The Museum of Flight. November 3, 2014. Retrieved November 8, 2014.
- ^ a b "787 Airplane Characteristics for Airport Planning" (PDF). Boeing Commercial Aircraft. February 2023.
- ^ a b c "Type certificate data sheet for Boeing 787" (PDF). EASA. November 16, 2017. Archived from the original (PDF) on January 11, 2018. Retrieved January 10, 2018.
- ^ "Boeing 787 -8 (Dreamliner) sample analysis". Lissys Ltd. 2006.
- ^ "Everything about the Boeing 787 Dreamliner". Flightglobal. July 7, 2007.
- ^ https://www.boeing.com/content/dam/boeing/boeingdotcom/commercial/airports/acaps/787_ACAP_Rev_Q.pdf
- ^ "Updated EASA Type certificate data sheet for Boeing 787" (PDF). EASA. October 28, 2019. Archived from the original (PDF) on December 31, 2019. Retrieved November 30, 2019.
Bibliography
[edit]- Norris, Guy; Wagner, Mark (2009). Boeing 787 Dreamliner. Minneapolis, Minn.: Zenith Press. ISBN 978-0-7603-2815-6.
- Thisdell, Dan; Seymour, Chris (August 5, 2019). "World Airliner Census". Flight International. Vol. 196, no. 5697. pp. 24–47. ISSN 0015-3710.
- Rosen, Evan (2024). The Culture of Collaboration: Deserializing Time, Talent and Tools to Create Value in the Local and Global Economy. San Francisco, CA.: Red Ape Publishing. ISBN 978-0-9774617-9-0.
External links
[edit]- Official website

- Fred George (December 10, 2012). "Aviation Week Evaluates Boeing 787". Aviation Week & Space Technology. and Aviation Week (December 7, 2012). Aviation Week Pilot Report: Flying the Boeing 787. Youtube. Archived from the original on October 28, 2021.
- Boeing 787-8 Critical System Review Team (March 19, 2014). "Boeing 787-8 Design, Certification, and Manufacturing Systems Review" (PDF). Federal Aviation Administration.
- Al Jazeera Investigates – Broken Dreams: The Boeing 787. Al Jazeera. September 10, 2014. Archived from the original on October 28, 2021 – via YouTube.
- Richard Aboulafia (February 2015). "Boeing 787 Dreamliner Program Briefing" (PDF). Teal Group. Archived from the original (PDF) on June 16, 2016.
- Boeing (June 11, 2015). Boeing Prepares the 787-9 Dreamliner for the 2015 Paris Air Show. Youtube. Archived from the original on October 28, 2021. Steep climb after takeoff.
- British Airways (September 30, 2015). Building the 787-9 Dreamliner. Youtube. Archived from the original on October 28, 2021. Construction time-lapse.
- "Type Certificate data sheet T00021SE" (PDF). FAA. January 19, 2018. Archived from the original (PDF) on September 11, 2020. Retrieved February 16, 2018.
- "Review: Celebrating Eleven Years of Boeing 787 Dreamliner". Airways International. July 8, 2018. Archived from the original on July 9, 2018. Retrieved July 9, 2018.
- "Boeing 787-8 Seating & Review". April 23, 2024.
Boeing 787 Dreamliner
View on GrokipediaDevelopment
Background and Announcement
In the early 2000s, Boeing sought to address the evolving demands of the commercial aviation market, which increasingly favored efficient, point-to-point long-haul flights with mid-sized twin-engine aircraft capable of serving routes previously dominated by larger, less flexible widebodies like the Boeing 767. This shift was driven by the rise of low-cost carriers and a preference for direct connections over hub-and-spoke models, positioning the 787 as a successor to the 767 in the 200- to 300-passenger segment and a direct competitor to Airbus's A330 family. Following the cancellation of the futuristic Sonic Cruiser concept in late 2002, Boeing pivoted to a more conventional design emphasizing fuel efficiency, reduced operating costs, and enhanced passenger experience to capture this growing segment.[8] Boeing publicly unveiled the 7E7 program—later renamed the 787 Dreamliner—on January 29, 2003, releasing the first conceptual rendering of the aircraft and outlining its core objectives. The program aimed for a 20% improvement in fuel efficiency compared to the Boeing 767 through advanced aerodynamics, lighter materials, and efficient engines, while incorporating composites for approximately 50% of the airframe's weight to reduce maintenance needs and enable longer ranges of up to 8,000 nautical miles. Additionally, Boeing emphasized passenger comfort features, such as larger windows, improved cabin pressurization, and higher humidity levels to mitigate jet lag on long flights. This announcement marked a strategic departure from Boeing's traditional in-house development, introducing a groundbreaking global outsourcing model where key partners would handle major component design and production.[9][10] The 787 program was officially launched on April 26, 2004, when All Nippon Airways (ANA) placed a firm order for 50 aircraft valued at approximately $6 billion, becoming the launch customer and securing the largest initial commitment for a new Boeing commercial jet at the time. Early supplier partnerships were central to the initiative, with Boeing selecting risk-sharing collaborators from around the world to accelerate development and distribute costs; notable among them were Spirit AeroSystems in the United States for the forward fuselage sections and Mitsubishi Heavy Industries in Japan for the wings and center fuselage, reflecting a supply chain spanning over 50 partners across 135 sites globally. This collaborative approach aimed to leverage international expertise while aligning with customer preferences, particularly from Asian airlines like ANA, which influenced the program's focus on efficient regional and trans-Pacific operations.[11][12]Design and Manufacturing Innovations
The Boeing 787 Dreamliner marked a significant shift in aircraft design through its extensive use of carbon-fiber-reinforced polymer (CFRP) for the fuselage and wings, comprising approximately 50% of the airframe by weight. This material choice enabled a lighter structure compared to traditional aluminum designs, with the one-piece composite fuselage barrels alone achieving about 20% weight savings over equivalent aluminum sections.[13][14] To accelerate development and distribute risk, Boeing adopted a global supplier model, outsourcing roughly 50% of the airframe to international partners while retaining final assembly at its Everett facility in Washington and, later, North Charleston in South Carolina. This approach involved tiered suppliers producing major sections, such as fuselage barrels and wings, which were then shipped for integration, fostering innovation through specialized expertise worldwide.[15] Key innovations included the fabrication of one-piece CFRP barrel sections for the fuselage, eliminating the need for thousands of fasteners and rivets used in metal construction, which enhanced structural integrity and reduced maintenance. The aircraft also incorporated a more-electric architecture, replacing hydraulic systems in areas like environmental controls and wing ice protection with electrical alternatives powered by advanced generators, thereby simplifying systems and improving efficiency. Modular assembly processes further streamlined production, allowing pre-assembled sections to be joined with precision using automated tooling.[16][17] Notable milestones in this innovative process included the delivery of the first composite fuselage sections to Everett in May 2007, arriving via Boeing's specially designed Dreamlifter cargo aircraft and representing the initial integration of global supplier contributions. In 2011, Boeing opened its North Charleston final assembly line to boost production capacity and efficiency, with the facility commencing operations in July of that year.[18][19]Testing and Certification
The testing and certification phase of the Boeing 787 Dreamliner involved extensive ground and flight evaluations to verify the aircraft's structural integrity, systems performance, and compliance with regulatory standards. Ground testing began with static load assessments on major components, including the wings, which were subjected to ultimate loads equivalent to 150% of the design limit to simulate extreme flight conditions. These tests, conducted between September 2008 and March 2010, flexed the wings upward by approximately 25 feet (7.6 meters) while the fuselage was pressurized to 150% of its maximum operating differential, confirming no structural failures occurred.[7][20] Fatigue testing followed, using a full-scale airframe in a dedicated rig from August 2010 to September 2015 to replicate operational stresses over the aircraft's expected lifespan. This multiyear program simulated 165,000 flight cycles—more than three times the 787's design service objective of approximately 44,000 cycles—through repeated pressurization, bending, and vibration loads, with no evidence of composite airframe fatigue detected.[7][21] The tests incorporated hydraulic actuators and sensors to monitor thousands of data points per second, validating the durability of the composite materials and overall structure under prolonged use.[7] Flight testing commenced with the maiden flight of the first 787-8 prototype, ZA001, on December 15, 2009, from Paine Field in Everett, Washington, lasting about three hours and confirming basic aerodynamics and handling qualities.[3] The program utilized six dedicated test aircraft, accumulating over 3,100 flight hours and approximately 3,700 ground test hours across diverse conditions, including high-altitude climbs, hot-weather trials in Australia, and cold-weather evaluations in Alaska.[22] By completion in mid-2011, the fleet had logged around 1,600 flights, encompassing systems integration checks for avionics, propulsion, and environmental controls, which identified and resolved minor anomalies to ensure operational reliability.[22] The certification process culminated in joint approvals from the Federal Aviation Administration (FAA) and European Union Aviation Safety Agency (EASA) on August 26, 2011, after addressing several integration challenges through iterative testing and design refinements.[23][24] Key issues included software validation for flight controls and avionics, where requirements flowdown discrepancies were rectified via enhanced review processes to prevent potential glitches during critical phases.[23] Lightning protection concerns, particularly for the composite fuselage and wings, were resolved by implementing bonding checks and dielectric fasteners in fuel tank areas, ensuring electromagnetic compatibility without systemic vulnerabilities.[23] Additionally, wing ice formation tests validated the anti-icing systems' effectiveness in preventing accretion during flight, incorporating ground simulations and in-flight data to confirm safe performance in icing conditions.[23] These resolutions, supported by over 150 issue papers and thousands of engineering hours, enabled the FAA to issue the type certificate, affirming the 787's airworthiness for commercial operations.[25]Production Challenges and Quality Issues
The production of the Boeing 787 Dreamliner encountered significant delays during its early years, culminating in a three-year setback from the original timeline. A machinists' strike in 2008, lasting nearly two months, halted assembly work and exacerbated existing issues with incorrectly installed fasteners, pushing back the first test flight from late 2008 to the first quarter of 2009.[26] Supply chain disruptions, stemming from the program's innovative global outsourcing model involving over 50 tier-one suppliers, further compounded these problems by causing shortages of critical components like fuselage sections and wings.[27] Additionally, extensive battery testing in 2010, part of the certification process for the aircraft's lithium-ion auxiliary power unit, revealed integration challenges that required design adjustments and contributed to the overall postponement.[28] These factors delayed the first delivery to All Nippon Airways until September 2011, three years later than the initial 2008 target.[29] Quality control problems persisted into the late 2010s and 2020s, particularly involving shims and fasteners. In 2019, inspections uncovered improperly sized shims in the fuselage assembly, which failed to meet skin flatness specifications, prompting Boeing to halt deliveries temporarily in 2020 while reworking affected aircraft.[30] The fuselage gap defects, related to this improper shimming, led to a delivery halt from 2020 to 2022. In 2024, Boeing engineer Sam Salehpour raised whistleblower concerns about potential excessive gaps in fuselage joints due to assembly practices, prompting FAA investigations and the issuance of airworthiness directives in 2025 requiring inspections on in-service 787s built from 2019 onward. Specifically, AD 2025-23-05 (published December 2025, effective January 13, 2026) requires inspections and repairs for nonconformances, such as excessive gaps in the forward pressure bulkhead, to prevent fatigue cracks.[31] Boeing completed rework on over 120 stored aircraft affected by these gaps by early 2025, delaying handovers but without posing immediate safety risks and highlighting ongoing challenges in assembly precision.[32][33] Additional examples include AD 2026-02-10 (published February 2, 2026, effective March 9, 2026), which addresses undetected water leaks from faucet control modules that could damage flight-critical equipment, requiring repetitive inspections, replacements of the modules with improved designs, and installations of moisture management devices.[34] These ADs are examples of multiple airworthiness directives issued by the FAA in 2025 and early 2026 addressing various safety issues on the 787-8, 787-9, and 787-10 models, as documented in the FAA's Dynamic Regulatory System.[35] By 2024, a separate issue emerged with hundreds of fasteners on undelivered 787s installed at incorrect angles, leading to FAA-mandated investigations and additional inspections across the production line to ensure structural integrity. These shim, gap, and fastener defects, spanning 2019 to 2025, necessitated enhanced quality assurance protocols and slowed output as Boeing addressed non-conformances in joint assemblies. Supply chain disruptions intensified these issues during the COVID-19 pandemic from 2020 to 2022, as global lockdowns and logistics breakdowns reduced supplier output for engines, avionics, and interiors, forcing Boeing to scale back 787 production to minimal levels.[36] Labor shortages from 2023 to 2025, driven by industry-wide hiring difficulties and competition for skilled workers, further hindered ramp-up efforts, stabilizing output at 5 to 7 aircraft per month by mid-2025 despite FAA approvals for higher rates.[37][38] In response to these challenges and rising demand, Boeing broke ground in November 2025 on a $1 billion expansion of its South Carolina facility, adding a second final assembly line to increase 787 production to 10 aircraft per month by 2026 and create over 1,000 jobs.[39] This investment aims to mitigate supply constraints and accelerate delivery backlogs.Entry into Service and Market Impact
The Boeing 787 Dreamliner entered commercial service with launch customer All Nippon Airways (ANA) after receiving its first delivery on September 25, 2011, at Boeing's Everett facility in Washington state.[40] The aircraft arrived in Tokyo on September 28, 2011, following a delivery flight from the United States.[40] ANA operated the inaugural revenue flight on October 26, 2011, a four-hour route from Tokyo Narita International Airport to Hong Kong International Airport, carrying 245 passengers and marking the type's commercial debut after years of development delays.[41] By November 2025, the 787 program had secured more than 2,250 firm orders from 90 customers worldwide, reflecting robust market demand for its efficiency and range capabilities.[42] This adoption has facilitated over 425 new nonstop routes globally, many previously uneconomical, including ultra-long-haul services like Qantas's Perth to London flight spanning approximately 7,800 nautical miles.[1] The Dreamliner's ability to connect distant city pairs has expanded airline networks, particularly in the Asia-Pacific and transoceanic markets, carrying more than one billion passengers on nearly five million flights since entry into service.[1] Economically, the 787 delivers fuel savings of up to 25% per seat compared to earlier widebody aircraft like the Boeing 767, driven by its composite airframe, advanced engines, and aerodynamic design, which reduce operating costs and emissions.[1] These efficiencies prompted Airbus to accelerate development of the A350 family in direct response to the 787's innovations, intensifying competition in the long-haul segment and pushing industry-wide advancements in fuel economy.[43] The program has generated substantial revenue for Boeing through deliveries and services, bolstering the company's position in the widebody market despite initial challenges. To address early production setbacks and broaden appeal, Boeing developed stretched variants such as the 787-9 and 787-10, enhancing capacity and range for high-density routes, while proposing freighter adaptations to capture cargo demand amid rivalry from Airbus's A350F.[44]Design Features
Airframe and Composite Materials
The Boeing 787 Dreamliner features an airframe composed of approximately 50% composite materials by weight, primarily carbon fiber reinforced polymer (CFRP) used in the wings, fuselage, tail, and other primary structures.[45] This extensive application of composites, totaling around 32,000 kg per aircraft, replaces traditional aluminum alloys and reduces overall weight while enhancing corrosion resistance and fatigue life.[46] The CFRP construction enables design innovations such as larger windows—the largest of any widebody jet—and a quieter cabin environment, achieved through fewer fasteners (saving about 50,000 rivets per plane) that minimize vibration transmission and noise propagation compared to metal airframes.[1][47] Aerodynamically, the 787 incorporates raked wingtips, which sweep upward at the ends to mitigate wingtip vortices and induced drag. Research by Boeing and NASA indicates these wingtips provide a drag reduction of about 5.5%, surpassing the 3.5-4.5% achieved by conventional winglets, contributing to improved fuel efficiency without adding structural weight.[48] The airframe also integrates with engine chevron nozzles in a manner that supports overall noise reduction, though the primary aerodynamic benefits stem from the composite wings' flexibility and smooth contours. The baseline 787-8 variant measures 57 meters in length and has a wingspan of 60 meters, providing a scalable platform for the family. This common wing and cross-section design allows variants like the 787-9 and 787-10 to extend the fuselage length (to 63 meters and 68 meters, respectively) without requiring a full airframe redesign, optimizing production and commonality across models.[1] To verify structural integrity, Boeing subjected a full-scale 787 fuselage to durability testing simulating 165,000 flight cycles—equivalent to over three times the design service objective of 44,000 cycles or about 75 years of operation—revealing no fatigue cracks or significant degradation in the composite structure.[7][49]Flight Control and Avionics Systems
The Boeing 787 Dreamliner incorporates a fly-by-wire (FBW) flight control system that replaces traditional mechanical linkages with electronic signaling, enabling precise control and enhanced stability. This system features a triple-redundant architecture, utilizing three independent flight control computers to monitor and cross-check inputs, ensuring continued operation even if one or two fail. Additionally, the FBW includes envelope protection functions that automatically limit control inputs to prevent stalls, excessive bank angles, or other unsafe maneuvers, thereby improving safety during critical phases of flight.[50][51] The aircraft's avionics suite is centered on the Honeywell Primus Epic integrated modular avionics system, which provides a unified platform for flight management, displays, and surveillance functions with scalable processing capabilities. This modular design includes up to 25 Flight Deck Control Panel (FDCP) units, consisting of switch and control panels that support the advanced flight deck architecture.[52] Key enhancements include dual head-up displays (HUDs) as standard equipment, projecting primary flight information such as attitude, airspeed, and navigation data directly into the pilots' forward field of view to reduce head-down time and improve situational awareness. The system also integrates Honeywell's SmartView synthetic vision technology, rendering a three-dimensional terrain and obstacle view on the primary flight displays, particularly beneficial in low-visibility conditions. Furthermore, predictive windshear detection, powered by the aircraft's weather radar, scans ahead for hazardous shear conditions and issues early aural and visual alerts to enable timely go-around decisions.[53][51][54][55][56] A hallmark of the 787's design is its more-electric architecture, which eliminates the use of engine bleed air for most secondary systems, including cabin pressurization, environmental control, and wing anti-icing, thereby reducing fuel consumption and maintenance needs. Power is supplied by four 250 kVA variable-frequency starter/generators—two per engine—along with two APU generators, collectively delivering up to 1.45 megawatts during flight, equivalent to the output of a small power plant. This shift to electrical actuation results in approximately 10% weight savings compared to conventional pneumatic systems, achieved through lighter wiring and the removal of heavy bleed air ducts.[17][51][57] Navigation on the 787 relies on seamless integration of the Global Positioning System (GPS) with dual Inertial Reference Systems (IRS), providing hybrid positioning that combines satellite accuracy with inertial drift compensation for reliable performance in GPS-denied environments. The flight management system (FMS) processes this data to support required navigation performance (RNP) standards, enabling efficient routing on long-haul flights. For communication, particularly over oceanic routes where VHF coverage is limited, the aircraft employs Controller-Pilot Data Link Communications (CPDLC) via satellite or VHF datalink, allowing text-based clearance exchanges with air traffic control to streamline operations in remote airspace.[51][58][59]Propulsion and Engines
The Boeing 787 Dreamliner is powered by two high-bypass turbofan engine options selected by operators: the General Electric GEnx-1B or the Rolls-Royce Trent 1000.[16] The GEnx-1B offers thrust ratings ranging from 64,000 to 76,000 lbf (284 to 338 kN), depending on the variant and aircraft model.[60] The Trent 1000 provides thrust ratings up to 78,000 lbf (347 kN), depending on the variant.[61] Both engines incorporate advanced technologies that achieve approximately 15% greater fuel efficiency compared to the engines on the Boeing 767, contributing significantly to the 787's overall performance and range capabilities.[62] A key innovation in the 787's propulsion system is its bleedless architecture, which eliminates the traditional pneumatic bleed air extraction from the engines for cabin pressurization and other systems. Instead, variable-frequency electric generators drive dedicated compressors to supply conditioned air, optimizing engine operation by avoiding efficiency losses from bleed air. This design reduces fuel burn by about 3% relative to conventional bleed systems.[63] To address environmental concerns, both engine types feature noise-reduction technologies, including chevron-shaped nozzles on the nacelles, introduced with the 787's entry into service in 2011 on the GEnx-1B and Trent 1000 engines, that enhance mixing of exhaust and bypass air to lower jet noise despite incurring a minor 0.5% fuel burn penalty from aerodynamic drag; these are retained as the noise benefits meet requirements without necessitating costly redesigns, and composite fan blades that reduce blade passing frequency noise. These elements enable the 787 to meet ICAO Chapter 4 (QC2) noise certification standards, resulting in a noise footprint up to 60% smaller than comparable previous-generation aircraft.[64][2][65] In terms of operational reliability, the GEnx-1B and Trent 1000 engines have demonstrated dispatch rates exceeding 99.9% since entering service, minimizing delays and enhancing airline utilization. Maintenance intervals for these engines extend up to 20,000 flight hours between major overhauls, supported by advanced health monitoring systems that predict component needs and reduce unscheduled maintenance.[66][67]Cabin and Interior Design
The Boeing 787 Dreamliner's cabin design prioritizes passenger comfort through innovative features that enhance space, light, and air quality. The interior incorporates a vaulted ceiling and broad entryway to create a sense of openness, while larger overhead bins—the largest in the industry—accommodate more carry-on luggage, designed specifically for standard roll-aboard bags.[2] These bins allow for efficient storage without encroaching on under-seat space, improving overall cabin usability. Additionally, the more-electric architecture enables advanced environmental controls that support these passenger-centric elements.[68] Key visual and ambiance features include the largest windows on any widebody commercial jet, which are 70 percent larger than those on previous-generation aircraft, positioned higher for better outward views.[69] These windows employ electrochromic technology for dimming, allowing individual or crew-controlled adjustments without mechanical shades, reducing glare while maintaining natural light. Complementing this, modern adjustable LED lighting offers customizable hues and intensities to mimic natural daylight cycles, helping to mitigate jet lag by supporting passengers' circadian rhythms.[2] The 787's environmental control system employs a bleedless design in which electric compressors draw and condition ambient outside air directly, without relying on engine bleed air, thereby eliminating risks of contamination from engine oil or hydraulic fluid. This system maintains a cabin altitude equivalent to 6,000 feet—lower than the 8,000 feet standard on most aircraft—resulting in reduced fatigue and improved oxygenation during flights.[68] It is paired with higher humidity levels of up to 15 percent, compared to the 3-5 percent typical in older jets, which helps alleviate dry skin, eyes, and respiratory discomfort.[70] Air quality is further enhanced by HEPA filters that capture 99.97 percent of airborne particles down to 0.3 microns, including bacteria and viruses, with the entire cabin air volume refreshed every three minutes through a mix of fresh bleedless air and filtered recirculation.[71] These systems contribute to sustainability by optimizing energy use in cabin operations, supporting the aircraft's overall 20-25 percent reduction in fuel consumption and emissions relative to prior models.[16] Seating configurations on the 787 are flexible and modular, allowing airlines to tailor interiors to their needs while adhering to the aircraft's baseline design. Typical two-class layouts seat 248 passengers on the 787-8, 296 on the 787-9, and 336 on the 787-10, with options for premium economy and business class arrangements that leverage the wider 17.5-foot cabin for enhanced legroom and recline.[16] This modularity facilitates quick reconfiguration for different routes, emphasizing efficiency and passenger satisfaction without compromising the core comfort features.[2]Variants
787-8
The Boeing 787-8 is the baseline variant and launch model of the 787 Dreamliner family, with the program officially announced on April 26, 2004, following an initial order for 50 aircraft from All Nippon Airways.[13] Development emphasized advanced composite materials and efficient systems to enable point-to-point long-haul flights, marking a shift from traditional hub-and-spoke operations. The first 787-8 was delivered to All Nippon Airways on September 25, 2011, entering commercial service shortly thereafter on routes within Asia.[72] Key specifications for the 787-8 include a maximum range of 7,305 nautical miles (13,530 km) and a typical two-class passenger capacity of 242, making it suitable for nonstop transcontinental and transoceanic missions.[1] At 57 meters (186 feet) long, it features the shortest fuselage among the 787 variants, providing a compact design that balances payload and fuel efficiency for routes such as transatlantic crossings between North America and Europe.[1] This configuration allows operators to serve medium- to long-haul sectors with reduced operating costs, leveraging the aircraft's 20% improvement in fuel efficiency over predecessors like the Boeing 767.[2] Production of the 787-8 began ramping up in the early 2010s at Boeing's facilities in Everett, Washington, and North Charleston, South Carolina, with the variant serving as the foundation for route proving and certification flights that validated the Dreamliner's performance.[2] By November 2025, 399 units had been delivered worldwide, enabling airlines to pioneer new direct routes and demonstrate the model's reliability in early operations. The 787-8's design prioritizes efficiency on medium- to long-haul networks, with its lightweight airframe and advanced aerodynamics contributing to lower emissions and enhanced economic viability for carriers.[73] As the original Dreamliner, the 787-8 laid the groundwork for subsequent stretched variants like the 787-9 and 787-10, which offer increased capacity for higher-density routes.[1]787-9
The Boeing 787-9 is the mid-size stretched variant of the 787 Dreamliner family, designed to provide greater passenger capacity and revenue potential while maintaining the efficiency of the baseline model. Boeing announced the 787-9's firm configuration in July 2010 during the Farnborough Airshow, building on the core 787-8 design with an extended fuselage to accommodate higher-density operations. The variant achieved its maiden flight on September 17, 2013, from Boeing's facility in Paine Field, Washington, marking a key milestone in its development program. It received FAA certification in August 2014 and entered commercial service with launch customer Air New Zealand on August 11, 2014, on a route from Auckland to Sydney.[74] Measuring 63 meters (206 feet) in overall length—6 meters (20 feet) longer than the 787-8—the 787-9 supports a typical two-class seating arrangement for up to 296 passengers, with a maximum range of 7,565 nautical miles (14,010 kilometers). This extension, achieved through additional fuselage sections forward and aft of the wings, enhances its suitability for medium- to long-haul routes without requiring larger engines. The aircraft retains the same propulsion options as the 787-8, including the General Electric GEnx-1B or Rolls-Royce Trent 1000 high-bypass turbofans, ensuring comparable fuel efficiency of about 20% better than previous-generation widebodies.[1][2] Compared to the 787-8, the 787-9 delivers approximately 20% greater passenger capacity, enabling airlines to achieve up to 25% higher revenue on similar routes due to increased seat availability and operational flexibility. Its design prioritizes high-density configurations for busy international corridors, such as transatlantic or transpacific flights, where demand supports fuller loads. By late 2025, the 787-9 had become the most produced member of the family, accounting for the majority of the fleet with 699 units delivered, reflecting its appeal to operators seeking a balance of range, efficiency, and profitability.[75] Demand for the 787-9 continues to grow, exemplified by Uzbekistan Airways' finalization of an order for eight additional aircraft on November 6, 2025, converting options into firm commitments and raising their total 787-9 order book to 22 units. This move underscores the variant's role in expanding long-haul networks for emerging carriers in regions like Central Asia.[76]787-10
The Boeing 787-10, the longest variant in the 787 Dreamliner family, was announced in 2013 as a stretched derivative of the 787-9 to offer higher capacity for long-haul routes.[77] It completed its first flight on March 31, 2017, from Boeing's South Carolina facility, marking a key milestone in the development of the largest member of the Dreamliner lineup. The aircraft entered commercial service in April 2018 with Singapore Airlines, the launch customer, initially operating on routes such as Singapore to Perth and Osaka.[78] At 68 meters (223 feet) in length, the 787-10 provides seating for up to 336 passengers in a typical two-class configuration, enabling airlines to maximize revenue on dense, high-demand corridors.[79] Its design incorporates reinforced fuselage structures, including enhanced skins and frames in high-stress areas, to manage the increased loads from the 5.5-meter stretch over the 787-9 while minimizing added weight.[80] The aircraft is powered by either General Electric GEnx-1B or Rolls-Royce Trent 1000 high-bypass turbofan engines, with the Rolls-Royce variant achieving FAA certification first in January 2018, followed by the GE option later that year.[81] These enhancements contribute to a maximum range of 6,430 nautical miles (11,910 km), suitable for transcontinental operations while prioritizing passenger throughput over ultra-long distances.[79] By late 2025, Boeing had produced approximately 200 units of the 787-10, reflecting steady demand from carriers seeking efficient high-capacity widebodies amid recovering global travel.[82] The variant excels in hub-to-hub applications, such as Los Angeles to Singapore, where its ability to carry more passengers than shorter 787 models supports high-frequency services on premium trans-Pacific lanes.[83] Despite its advantages in capacity, the 787-10 faces challenges in operating economics compared to competitors like the Airbus A350-1000, with per-seat-hour costs estimated at around $25.86 versus the A350-1000's $22.81, driven by differences in fuel efficiency and overall design optimization for longer ranges.[84] This positions the 787-10 as a niche option for airlines prioritizing density over the broadest possible operational flexibility.Business and Special Variants
The Boeing Business Jet (BBJ) 787 is a VIP-configured variant of the 787 Dreamliner, designed for private and corporate use with extensive customization options for interiors, including multiple staterooms, conference rooms, and lounges to accommodate up to 25 passengers in luxury.[85] The BBJ 787-8 offers a maximum range of 9,960 nautical miles, enabling nonstop flights between nearly any two cities worldwide, while maintaining the core airframe's efficiency through its composite construction and advanced engines.[85] Deliveries of the BBJ 787 began in December 2013, with the first aircraft handed over to an undisclosed customer; by July 2025, a total of 13 BBJ 787 aircraft had been delivered across the -8, -9, and -10 variants.[86][87] Experimental applications of 787-derived technology have drawn from NASA collaborations, such as the X-48B blended wing body demonstrator, which advanced composite materials research and aerodynamic testing that informed the 787's airframe design and efficiency features.[88] Military proposals have explored 787 adaptations, incorporating learnings from programs like the P-8 Poseidon in systems integration and production processes, though no dedicated 787-based military variant has entered production. Boeing proposed a 787F freighter concept in the early 2020s, targeting a payload capacity of approximately 47 metric tons and a range of 4,180 nautical miles with full load, positioned as a replacement for aging 767 freighters.[89] However, amid production challenges and shifting market priorities, the 787F development was shelved by 2025, with Boeing focusing instead on conversions of existing 787s to freighter configurations by third-party providers.[44] Some undelivered 787 orders have been converted for special missions, including passenger-to-freighter (P2F) modifications to meet growing air cargo demand, with interest from operators seeking efficient mid-size freighters without new production lines.[90]Operations and Operators
Orders, Deliveries, and Production Rates
As of November 2025, the Boeing 787 Dreamliner has accumulated more than 2,250 firm orders from 90 customers worldwide, establishing it as the best-selling widebody aircraft in history.[91] Among these, United Airlines holds the largest order with 221 aircraft, followed by All Nippon Airways with 127.[92] This strong demand reflects the aircraft's efficiency and range advantages for long-haul operations. Recent developments include Uzbekistan Airways firming an order for eight additional 787-9s on November 6, 2025.[93] Deliveries have exceeded 1,200 units by late 2025, with Boeing handing over aircraft at a monthly rate of 5 to 7 throughout the year, stabilizing at seven per month by mid-year.[37] Specific monthly figures include seven deliveries in September and seven in October, comprising a mix of 787-9 and 787-10 variants.[94][95] The unfilled backlog stands at nearly 1,000 aircraft as of October 2025, equivalent to about six years of production at current rates.[96] Production trends have been influenced by enhanced quality inspections implemented after 2024, which temporarily slowed output but have since allowed stabilization.[37] Boeing aims to increase the rate to 10 aircraft per month in 2026, supported by a $1 billion expansion of its South Carolina facility, with groundbreaking on November 7, 2025.[96][91]Major Operators and Routes
All Nippon Airways (ANA), the largest operator of the Boeing 787 with a fleet of 86 aircraft as of August 2025, has adopted an all-787 strategy for its international operations, deploying the type exclusively on long-haul routes to North America, Europe, and across Asia to support growing demand in these markets.[97] This approach aligns with ANA's fleet expansion plans, including an order for 18 additional 787-9s announced in February 2025, aimed at increasing available seat kilometers on international routes by 1.5 times compared to fiscal year 2023 levels by 2030.[98] United Airlines follows as the second-largest operator with 79 Dreamliners as of September 2025, utilizing them extensively for trans-Pacific services such as the San Francisco to Singapore route, which spans 8,440 miles and operates 732 times in 2025, highlighting the aircraft's efficiency on ultra-long-haul Pacific crossings.[97][99][100] Qatar Airways, with 60 aircraft, integrates the 787 into its Doha-based hub network for routes connecting the Middle East to Europe, including services to destinations like London and Paris, where the type's range enables direct flights averaging over 3,700 miles.[97][101] Among the longest 787 routes in 2025, United's San Francisco-Singapore flight covers approximately 7,333 nautical miles (8,440 statute miles), exemplifying trans-Pacific endurance.[102] LATAM Airlines has upgraded its 787-8 fleet with refreshed premium cabins, deploying them on South America-to-Europe routes such as Santiago to Madrid, which measures 6,715 miles and supports the carrier's connectivity between Latin American hubs and European markets.[103][102] In October 2025, Virgin Atlantic announced connectivity modifications across its 787 fleet in partnership with Boeing, enabling high-speed, streaming-quality Wi-Fi to enhance passenger experience on transatlantic and other long-haul operations.[104] The 787's adoption in the Asia-Pacific region has driven a shift toward point-to-point network models over traditional hub-and-spoke systems, allowing airlines like ANA and Singapore Airlines to serve direct routes between secondary cities and major markets without reliance on central hubs, thereby reducing layover times and improving efficiency on medium- to long-haul flights.[105] This regional growth underscores the Dreamliner's role in enabling flexible, non-stop connectivity, with over 43% of global 787 orders originating from Asia-Pacific carriers as of recent analyses.[106]Operational Milestones
The Boeing 787 Dreamliner achieved a significant regulatory milestone in May 2014 when the U.S. Federal Aviation Administration granted it 330-minute Extended-range Twin-engine Operational Performance Standards (ETOPS) certification, allowing operations up to 5.5 hours from the nearest suitable airport and enabling expanded long-haul routing flexibility for operators.[107] This built on the initial 180-minute ETOPS approval upon entry into service in 2011, facilitating routes over remote areas like the Pacific Ocean.[108] The 787-10 variant marked its commercial debut with Singapore Airlines in April 2018, with initial revenue flights on short-haul routes for crew familiarization; the first long-haul service to Perth, Australia, began on May 7, 2018, showcasing the stretched model's capacity for up to 336 passengers over 6,430 nautical miles.[78][109] This entry expanded the Dreamliner's family capabilities, with the -10 variant emphasizing higher-density configurations for medium- to long-haul efficiency. In terms of records, the 787 operates some of the world's longest commercial routes, such as United Airlines' San Francisco to Singapore at approximately 7,333 nautical miles. By April 2025, the global 787 fleet had carried over 1 billion passengers across nearly 5 million flights and more than 30 million flight hours, reaching this benchmark faster than any other widebody aircraft in history.[6] Recent service expansions include LATAM Airlines' 2025 rollout of upgraded 787 cabins featuring Recaro R7 premium business suites with sliding doors for enhanced privacy, deployed on international routes starting in April to improve passenger experience on long-haul flights.[110] Similarly, Turkish Airlines integrated additional 787s into its fleet following a September 2025 order for up to 75 aircraft, supporting network growth with deliveries slated to begin in 2029 and enhancing connectivity across Europe, Asia, and the Americas.[111] On the sustainability front, All Nippon Airways conducted the first 787 biofuel demonstration flight in April 2012, using a blend primarily from used cooking oil that reduced CO2 emissions by an estimated 30% compared to conventional jet fuel.[112] The Dreamliner's composite airframe and advanced engines contribute to about 20% better fuel efficiency than previous-generation aircraft, playing a key role in airlines' net-zero emissions goals by 2050 through reduced consumption and compatibility with sustainable aviation fuels.[1]Incidents and Accidents
Early Battery Fires and Groundings
The Boeing 787 Dreamliner experienced two significant lithium-ion battery incidents in early January 2013, prompting intense scrutiny of its electrical systems. On January 7, 2013, a Japan Airlines (JAL) Boeing 787-8, registration JA829J, suffered a fire in its auxiliary power unit (APU) battery while parked at Boston's Logan International Airport. Cleaning personnel discovered smoke emanating from the aft electronics bay around 10:21 a.m. EST, and firefighters extinguished the blaze, which caused extensive thermal damage to the battery but no injuries to personnel or passengers, as the aircraft was unoccupied.[113] The incident resulted in significant structural damage to the aircraft, rendering it inoperable until repairs were completed.[113] Nine days later, on January 16, 2013, an All Nippon Airways (ANA) Boeing 787-8, registration JA804A, encountered battery overheating during a domestic flight from Yamaguchi Ube Airport to Tokyo Haneda Airport. The crew declared an emergency and diverted to Takamatsu Airport, where the aircraft landed safely, and all 137 passengers and 11 crew members evacuated without injury. Smoke was observed from the APU battery compartment upon landing, but no fire occurred, though the battery exhibited signs of thermal distress. These back-to-back events, involving the same battery type, raised immediate concerns about the reliability of the 787's lithium-ion batteries, which were selected for their high energy density to support the aircraft's advanced electrical architecture.[23] In response to the ANA incident, the U.S. Federal Aviation Administration (FAA) issued an emergency airworthiness directive on January 16, 2013, grounding all 35 Boeing 787s then operating in the United States until the battery issue could be resolved. This action triggered a global grounding, as aviation authorities in Japan, Europe, India, and elsewhere followed suit, halting operations of the entire fleet of over 50 delivered aircraft. The worldwide grounding lasted 116 days, from January 16 until the first modified 787 returned to service on May 13, 2013, severely disrupting airline schedules and costing Boeing an estimated $1 billion in lost revenue and modification expenses.[114][115] The National Transportation Safety Board (NTSB) led the investigation into both incidents, determining that the root cause was thermal runaway initiated by an internal short circuit within individual lithium-ion battery cells. In the JAL case, a short circuit in one cell generated excessive heat, leading to thermal runaway that propagated to adjacent cells, producing intense heat up to 500°F (260°C) and releasing electrolyte vapors that fueled the fire. The ANA event involved a similar short-circuit mechanism, though propagation was contained before full ignition. Contributing factors included inadequate cell separation, insufficient venting, and the battery's enclosure design, which allowed heat and flames to escape uncontained.[116][113] To address these deficiencies, Boeing redesigned the APU battery system in collaboration with the FAA and international regulators. Key modifications included encasing the battery in a corrosion-resistant stainless steel containment box capable of fully containing a thermal runaway event, increasing physical separation between cells to prevent propagation, and installing an enhanced venting system with a titanium discharge tube to safely expel heat, gases, and potential flames overboard away from the aircraft structure. Additional improvements encompassed upgraded battery management monitoring, better insulation, and corner relief vents to mitigate pressure buildup. The FAA approved Boeing's certification plan on March 12, 2013, and validated the fixes through extensive testing, including over 1,000 thermal runaway simulations, leading to full recertification on April 19, 2013. Global authorities endorsed the solution by late April, allowing operators to resume flights after completing the modifications, which took four to five days per aircraft.Non-Fatal Incidents
The Boeing 787 Dreamliner has experienced several non-fatal operational incidents since entering service in 2011, primarily involving turbulence encounters, engine malfunctions, and hydraulic system faults, though none resulted in aircraft hull losses or fatalities. These events, occurring between 2014 and 2025, have prompted regulatory scrutiny and airworthiness directives from authorities like the FAA and EASA to enhance safety monitoring without grounding the fleet. Unlike the early battery issues that led to a 2013 grounding, these later incidents reflect diverse in-service challenges addressed through targeted inspections and maintenance protocols.[117] Turbulence events have been among the most notable non-fatal incidents, often causing passenger and crew injuries due to sudden altitude changes. On September 6, 2024, Scoot Airlines Flight TR100, a Boeing 787-9 operating from Singapore to Guangzhou, encountered severe turbulence during descent near waypoint TAMOT at around 18,700 feet, injuring 7 people, one of whom was hospitalized; the aircraft landed safely, and the incident was attributed to an undetected storm cell not visible on weather radar.[118] Similarly, on March 27, 2025, United Airlines Flight UA1, a Boeing 787-9 from San Francisco to Singapore, hit unexpected severe turbulence over the Philippines near Claveria at flight level 400, resulting in five injuries—one serious to a flight attendant and minor injuries to three crew members and one passenger; the flight continued to destination after the event.[119] These turbulence cases underscore the role of convective weather in long-haul operations but involved no structural damage to the aircraft. Technical faults, particularly with engines and hydraulics, have also led to diversions and groundings for inspection without escalating to safety risks. From 2019 to 2023, Rolls-Royce Trent 1000 engines on several 787s suffered from corrosion-related fatigue cracking in intermediate-pressure turbine blades, as seen in a January 2019 Norwegian Air Shuttle incident in Rome where dozens of cracked blades were found post-failure, prompting ongoing blade inspections and replacements; EASA issued warnings in 2023 for potential low-pressure turbine blade cracks, affecting operators worldwide but resulting in no in-flight failures beyond controlled shutdowns.[120][121] In 2024, multiple hydraulic leaks were reported, including an All Nippon Airways 787-8 at Sapporo in April that lost hydraulic pressure after landing, requiring towing and inspection, and an Ethiopian Airlines 787-8 at Goma in the same month with a similar system fault leading to a precautionary diversion; these incidents involved no loss of control and were resolved through routine maintenance.[122][123] Ground-based incidents and quality-related inspections in 2025 further highlighted proactive regulatory responses to manufacturing concerns. Following quality alerts on fuselage assembly, the FAA mandated inspections in March 2025 for certain 787-9 and -10 models to check for gaps in the fuselage skin, with Boeing completing reviews on 122 aircraft by early that year to ensure structural integrity.[124] An additional FAA airworthiness directive in July 2025 required enhanced checks on ram air turbine fittings and other components across the 787 fleet, stemming from production quality lapses but uncovering no immediate safety defects.[125] Overall, these non-fatal incidents have not resulted in any hull losses for the 787, with the FAA issuing directives for bolstered monitoring, including mandatory reporting and periodic inspections, to mitigate risks without broad operational disruptions.[117][126]Fatal Accidents
The sole fatal accident involving a Boeing 787 Dreamliner occurred on June 12, 2025, when Air India Flight 171, operating a 787-8 (registration VT-ANB), crashed approximately 30 seconds after takeoff from Sardar Vallabhbhai Patel International Airport in Ahmedabad, India.[127] The flight was en route to London Gatwick Airport with 230 passengers and 12 crew members aboard, of whom 241 perished; one passenger survived with injuries. The crash also killed 19 people on the ground, for a total of 260 fatalities, marking the first fatalities associated with the aircraft type since its commercial introduction in 2011.[128] The aircraft stalled during the initial climb phase, impacting multiple buildings near the airport perimeter and resulting in a post-crash fire.[129] Both the flight data recorder and cockpit voice recorder were recovered intact from the wreckage, enabling investigators to reconstruct the sequence of events.[130] A preliminary report issued by India's Aircraft Accident Investigation Bureau on July 12, 2025, indicated that the stall was preceded by a sudden loss of thrust in both engines, potentially due to a system failure affecting the fuel control mechanisms.[131] The report highlighted that the engine fuel cutoff switches appeared to move to the "cutoff" position shortly after rotation, starving the engines of fuel, though the exact cause—whether inadvertent crew action, mechanical malfunction, or an electrical anomaly—remains under detailed examination. As of November 2025, the investigation is ongoing, with controversies including legal challenges alleging bias in the probe and debates over responsibility between pilot actions and potential Boeing or engine system faults; international participation from the U.S. National Transportation Safety Board and Boeing continues, including simulations and component testing.[132][133][134] In the immediate aftermath, Air India grounded three of its 787-8 aircraft for comprehensive inspections focused on engine control systems and electrical wiring, a precautionary measure coordinated with India's Directorate General of Civil Aviation.[135] This event represented the first hull loss of a 787 Dreamliner in passenger service, prompting enhanced safety protocols across the global fleet.[136] The crash has intensified regulatory oversight, leading to renewed FAA and Boeing quality assurance reviews amid persistent production and supply chain challenges identified in 2024-2025 audits.[137]Specifications
General Characteristics
The Boeing 787 Dreamliner requires a flight crew of two pilots.[73] It is designed to carry between 242 and 330 passengers in a typical dual-class seating arrangement, depending on the variant, with the 787-8 accommodating 242, the 787-9 up to 290, and the 787-10 up to 330.[51] The aircraft's dimensions vary by variant: the 787-8 measures 57 meters (186 feet) in length, the 787-9 63 meters (206 feet), and the 787-10 68 meters (224 feet), while all share a wingspan of 60 meters (197 feet) and a height of 17 meters (56 feet).[1] The operating empty weight ranges from 118 metric tons for the 787-8 to 134 metric tons for the 787-10, with maximum takeoff weights between 228 metric tons for the 787-8 and 254 metric tons for the 787-9 and 787-10.[138][73] By weight, the 787's airframe consists of 50% composites (primarily carbon fiber reinforced plastic), 20% aluminum, and 15% titanium, enabling significant reductions in structural weight compared to traditional aluminum designs.[13] The aircraft has a service ceiling of 43,100 feet (13,100 meters).[138] It is certified for extended-range twin-engine operational performance standards (ETOPS) up to 330 minutes, allowing operations far from suitable diversion airports.[139]| Variant | Length (m/ft) | Operating Empty Weight (metric tons) | Max Takeoff Weight (metric tons) | Typical Dual-Class Passengers |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| 787-8 | 57 / 186 | 118 | 228 | 242 |
| 787-9 | 63 / 206 | 128 | 254 | 290 |
| 787-10 | 68 / 224 | 134 | 254 | 330 |
Performance Metrics
The Boeing 787 Dreamliner family achieves a long-range cruise speed of Mach 0.85, equivalent to 488 knots (903 km/h) at typical operating altitudes. Its maximum operating speed is Mach 0.90, corresponding to approximately 560 knots true airspeed. These speeds enable efficient transoceanic and long-haul flights while maintaining passenger comfort through advanced aerodynamics and engine technology.[140][141][142] Range performance varies by variant and payload, with the 787-8 offering up to 7,305 nautical miles (13,530 km), the 787-9 up to 7,565 nautical miles (14,010 km) under typical two-class loading conditions with maximum payload, while the 787-10 provides 6,430 nautical miles (11,910 km). This capability supports nonstop routes such as New York to Sydney for the smaller variants and London to Perth for the 787-9. The aircraft's fuel capacity of 126,206 liters (33,340 US gallons) across all variants underpins these distances, with a cruise fuel burn rate of approximately 5.0 metric tons per hour for the 787-8 under standard conditions.[1][73][143][144] Takeoff performance is optimized for modern runways, requiring about 2,500 meters (8,200 feet) of field length at maximum takeoff weight under sea-level standard conditions, which supports operations from a wide range of airports. Overall, the 787 delivers approximately 20% better fuel efficiency per seat compared to the Boeing 777, achieved through composite materials, efficient engines, and aerodynamic design that reduce drag and weight.[73][1]| Variant | Range (nm) | Fuel Burn at Cruise (tons/hour, approx.) | Takeoff Field Length at MTOW (m, approx.) |
|---|---|---|---|
| 787-8 | 7,305 | 5.0 | 2,500 |
| 787-9 | 7,565 | 5.3 | 2,600 |
| 787-10 | 6,430 | 5.6 | 2,700 |
_(cropped).jpg/250px-Boeing_787_N1015B_ANA_Airlines_(27611880663)_(cropped).jpg)
_(cropped).jpg/2000px-Boeing_787_N1015B_ANA_Airlines_(27611880663)_(cropped).jpg)



