Recent from talks
Nothing was collected or created yet.
CW Octantis
View on Wikipedia| Observation data Epoch J2000.0 Equinox J2000.0 (ICRS) | |
|---|---|
| Constellation | Octans |
| Right ascension | 17h 00m 58.51777s[2] |
| Declination | −86° 21′ 51.4707″[2] |
| Apparent magnitude (V) | 6.03±0.01[3] |
| Characteristics | |
| Evolutionary stage | subgiant[4] |
| Spectral type | A3 IV[5] |
| U−B color index | +0.02[6] |
| B−V color index | +0.05[6] |
| Variable type | α2 CVn[7] |
| Astrometry | |
| Radial velocity (Rv) | 7.1±0.5[8] km/s |
| Proper motion (μ) | RA: +8.413 mas/yr[2] Dec.: −0.032 mas/yr[2] |
| Parallax (π) | 5.1828±0.0486 mas[2] |
| Distance | 629 ± 6 ly (193 ± 2 pc) |
| Absolute magnitude (MV) | −0.36[9] |
| Details | |
| Mass | 2.98±0.05[4] M☉ |
| Radius | 4.64[10] R☉ |
| Luminosity | 111[11] L☉ |
| Surface gravity (log g) | 3.45±0.07[12] cgs |
| Temperature | 8,791[13] K |
| Metallicity [Fe/H] | +0.6[14] dex |
| Rotation | ≈2.8 days[13] |
| Rotational velocity (v sin i) | 92±6[13] km/s |
| Age | 188±4[4] Myr |
| Other designations | |
| 26 G. Octantis[15], CW Octantis, CD−86°100, CPD−86°333, FK5 921, GC 22519, HD 148542, HIP 83255, HR 6139, SAO 258751[16] | |
| Database references | |
| SIMBAD | data |
CW Octantis, also known as HD 148542, is a solitary, white hued variable star located in the southern circumpolar constellation Octans. It has an apparent magnitude of 6.03, allowing it to be faintly visible to the naked eye. Parallax measurements from Gaia DR3 place the object at a distance of 629 light years. It appears to be receding from the Solar System with a heliocentric radial velocity of 7.1 km/s.
CW Octantis has a stellar classification of A3 IV, indicating that it is an evolved A-type star heading towards the red giant branch. Zorec and Royer (2012) model it as a dwarf star that has just reached the end of its main sequence lifetime.[4] It has 2.98 times the mass of the Sun[4] and 4.6 times its radius.[10] It radiates 111 times the luminosity of the Sun[11] from its photosphere at an effective temperature of 8,791 K.[13] CW Octantis is estimated to be 188 million years old.[4]
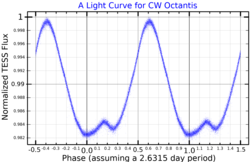
This object is classified as a Alpha2 Canum Venaticorum variable.[7] Most stars of this class have chemical peculiarities in their spectra, but CW Octantis seems to be ordinary. Renson and Manfroid (2009) consider its peculiarity status to be doubtful.[17] Nevertheless, CW Octantis fluctuates between 6.05 and 6.07 in the Hipparcos passband within 2.63 days.[18] It takes 2.8 days to complete a full a rotation, which corresponds to a projected rotational velocity of 92 km/s.[13]
References
[edit]- ^ "MAST: Barbara A. Mikulski Archive for Space Telescopes". Space Telescope Science Institute. Retrieved 1 October 2022.
- ^ a b c d Vallenari, A.; et al. (Gaia collaboration) (2023). "Gaia Data Release 3. Summary of the content and survey properties". Astronomy and Astrophysics. 674: A1. arXiv:2208.00211. Bibcode:2023A&A...674A...1G. doi:10.1051/0004-6361/202243940. S2CID 244398875. Gaia DR3 record for this source at VizieR.
- ^ Høg, E.; Fabricius, C.; Makarov, V. V.; Urban, S.; Corbin, T.; Wycoff, G.; Bastian, U.; Schwekendiek, P.; Wicenec, A. (March 2000). "The Tycho-2 catalogue of the 2.5 million brightest stars". Astronomy and Astrophysics. 355: L27–L30. Bibcode:2000A&A...355L..27H. ISSN 0004-6361.
- ^ a b c d e f Zorec, J.; Royer, F. (January 2012). "Rotational velocities of A-type stars. IV. Evolution of rotational velocities". Astronomy and Astrophysics. 537: A120. arXiv:1201.2052. Bibcode:2012A&A...537A.120Z. doi:10.1051/0004-6361/201117691. ISSN 0004-6361. S2CID 55586789.
- ^ de Vaucouleurs, A. (1 August 1957). "Spectral Types and Luminosities of B, A and F Southern Stars". Monthly Notices of the Royal Astronomical Society. 117 (4): 449–462. Bibcode:1957MNRAS.117..449D. doi:10.1093/mnras/117.4.449. eISSN 1365-2966. ISSN 0035-8711.
- ^ a b Johnson, H. L.; Mitchell, R. I.; Iriarte, B.; Wisniewski, W. Z. (1966). "UBVRIJKL Photometry of the Bright Stars". Communications of the Lunar and Planetary Laboratory. 4: 99–110. Bibcode:1966CoLPL...4...99J.
- ^ a b Samus’, N. N.; Goranskii, V. P.; Durlevich, O. V.; Zharova, A. V.; Kazarovets, E. V.; Kireeva, N. N.; Pastukhova, E. N.; Williams, D. B.; Hazen, M. L. (July 2003). "An electronic version of the second volume of the General Catalogue of Variable Stars with improved coordinates". Astronomy Letters. 29 (7): 468–479. Bibcode:2003AstL...29..468S. doi:10.1134/1.1589864. eISSN 1562-6873. ISSN 1063-7737. S2CID 16299532.
- ^ Gontcharov, G. A. (November 2006). "Pulkovo Compilation of Radial Velocities for 35,495 Hipparcos stars in a common system". Astronomy Letters. 32 (11): 759–771. arXiv:1606.08053. Bibcode:2006AstL...32..759G. doi:10.1134/S1063773706110065. eISSN 1562-6873. ISSN 1063-7737. S2CID 119231169.
- ^ Anderson, E.; Francis, Ch. (May 2012). "XHIP: An extended hipparcos compilation". Astronomy Letters. 38 (5): 331–346. arXiv:1108.4971. Bibcode:2012AstL...38..331A. doi:10.1134/S1063773712050015. eISSN 1562-6873. ISSN 1063-7737. S2CID 119257644.
- ^ a b Kervella, Pierre; Arenou, Frédéric; Thévenin, Frédéric (2022). "Stellar and substellar companions from Gaia EDR3". Astronomy & Astrophysics. 657: A7. arXiv:2109.10912. Bibcode:2022A&A...657A...7K. doi:10.1051/0004-6361/202142146. eISSN 1432-0746. ISSN 0004-6361.
- ^ a b McDonald, I.; Zijlstra, A. A.; Boyer, M. L. (21 November 2012). "Fundamental parameters and infrared excesses of Hipparcos stars: Parameters and IR excesses from Hipparcos". Monthly Notices of the Royal Astronomical Society. 427 (1): 343–357. arXiv:1208.2037. Bibcode:2012MNRAS.427..343M. doi:10.1111/j.1365-2966.2012.21873.x. ISSN 0035-8711.
- ^ Stassun, Keivan G.; et al. (9 September 2019). "The Revised TESS Input Catalog and Candidate Target List". The Astronomical Journal. 158 (4): 138. arXiv:1905.10694. Bibcode:2019AJ....158..138S. doi:10.3847/1538-3881/ab3467. eISSN 1538-3881.
- ^ a b c d e Reiners, A.; Royer, F. (February 2004). "First signatures of strong differential rotation in A-type stars". Astronomy & Astrophysics. 415 (1): 325–329. arXiv:astro-ph/0311341. Bibcode:2004A&A...415..325R. doi:10.1051/0004-6361:20034175. eISSN 1432-0746. ISSN 0004-6361.
- ^ Rainer, M.; Poretti, E.; Mistò, A.; Panzera, M. R.; Molinaro, M.; Cepparo, F.; Roth, M.; Michel, E.; Monteiro, M. J. P. F. G. (5 December 2016). "The SpaceInn-SISMA Database: Characterization of a Large Sample of Variable and Active Stars by Means of Harps Spectra". The Astronomical Journal. 152 (6): 207. arXiv:1611.02715. Bibcode:2016AJ....152..207R. doi:10.3847/0004-6256/152/6/207. eISSN 1538-3881.
- ^ Gould, Benjamin Apthorp (1878). "Uranometria Argentina : brillantez y posicion de las estrellas fijas, hasta la septima magnitud, comprendidas dentro de cien grados del polo austral : con atlas". Resultados del Observatorio Nacional Argentino. 1. Bibcode:1879RNAO....1.....G.
- ^ "CW Oct". SIMBAD. Centre de données astronomiques de Strasbourg. Retrieved October 1, 2022.
- ^ Renson, P.; Manfroid, J. (19 March 2009). "Catalogue of Ap, HgMn and Am stars". Astronomy & Astrophysics. 498 (3): 961–966. Bibcode:2009A&A...498..961R. doi:10.1051/0004-6361/200810788. eISSN 1432-0746. ISSN 0004-6361.
- ^ Watson, C. L.; Henden, A. A.; Price, A. (May 2006). "The International Variable Star Index (VSX)". Society for Astronomical Sciences Annual Symposium. 25: 47. Bibcode:2006SASS...25...47W.