Recent from talks
Nothing was collected or created yet.
Rhythmic mode
View on Wikipedia

In medieval music, the rhythmic modes were set patterns of long and short durations (or rhythms). The value of each note is not determined by the form of the written note (as is the case with more recent European musical notation), but rather by its position within a group of notes written as a single figure called a ligature, and by the position of the ligature relative to other ligatures. Modal notation was developed by the composers of the Notre Dame school from 1170 to 1250, replacing the even and unmeasured rhythm of early polyphony and plainchant with patterns based on the metric feet of classical poetry, and was the first step towards the development of modern mensural notation.[1] The rhythmic modes of Notre Dame Polyphony were the first coherent system of rhythmic notation developed in Western music since antiquity.
History
[edit]Though the use of the rhythmic modes is the most characteristic feature of the music of the late Notre Dame school, especially the compositions of Pérotin, they are also predominant in much of the rest of the music of the ars antiqua until about the middle of the 13th century.
Composition types which were permeated by the modal rhythm include Notre-Dame school organum (most famously, the organum triplum and organum quadruplum of Pérotin), conductus, and discant clausulae. Later in the century, the motets by Petrus de Cruce and the many anonymous composers, which were descended from discant clausulae, also used modal rhythm, often with much greater complexity than was found earlier in the century: for example each voice sometimes sang in a different mode, as well as a different language.[citation needed]
In most sources there were six rhythmic modes, as first explained in the anonymous treatise of about 1260, De mensurabili musica (formerly attributed to Johannes de Garlandia, who is now believed merely to have edited it in the late 13th century for Jerome of Moravia, who incorporated it into his own compilation).[2] Each mode consisted of a short pattern of long and short note values ("longa" and "brevis") corresponding to a metrical foot, as follows:[3]
- Long-short (trochee)
- Short-long (iamb)
- Long-short-short (dactyl)
- Short-short-long (anapaest)
- Long-long (spondee)
- Short-short-short (tribrach)
Although this system of six modes was recognized by medieval theorists, in practice only the first three and fifth patterns were commonly used, with the first mode being by far the most frequent.[4] The fourth mode is rarely encountered, an exception being the second clausula of Lux magna in MS Wolfenbüttel 677, fol. 44.[5] The fifth mode normally occurs in groups of three and is used only in the lowest voice (or tenor), whereas the sixth mode is most often found in an upper part.[5]
Modern transcriptions of the six modes usually are as follows:
- Quarter (crotchet), eighth (quaver) (generally barred, therefore, in 3
8 or, because the patterns usually repeat an even number of times, in 6
8)[6]ⓘ
- Eighth, quarter (barred in 3
8 or 6
8)ⓘ
- Dotted quarter, eighth, quarter (barred in 6
8)ⓘ
- Eighth, quarter, dotted quarter (barred in 6
8)ⓘ
- Dotted quarters (barred in either 3
8 or 6
8)ⓘ
- Eighths (barred in 3
8 or 6
8)ⓘ
- Cooper gives the above but doubled in length, thus 1) is

 barred in 3
barred in 3
4, for example.[7] - Riemann is another modern exception, who also gives the values twice as long, in 3
4 time, but in addition holds that the third and fourth modes were really intended to represent the modern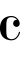 , with duple rhythms (
, with duple rhythms (

 and
and 

 , respectively).[8]
, respectively).[8]
Notation
[edit]
Devised in the last half of the 12th century,[9] the notation of rhythmic modes used stereotyped combinations of ligatures (joined noteheads) to indicate the patterns of long notes (longs) and short notes (breves), enabling a performer to recognize which of the six rhythmic modes was intended for a given passage.
Linked notes in groups of:[10]
- 3, 2, 2, 2, etc. indicate the first mode,
- 2, 2, 2, 2, … 3 the second mode,
- 1, 3, 3, 3, 3, etc. the third mode,
- 3, 3, 3, … 1 the fourth mode,
- 3, 3, 3, 3, etc. the fifth mode,
- and 4, 3, 3, 3, etc. the sixth mode
The reading and performance of the music notated using the rhythmic modes was thus based on context. After recognizing which of the six modes applied to a passage of neumes, a singer would generally continue on in that same mode until the end of a phrase, or a cadence. In modern editions of medieval music, ligatures are represented by horizontal brackets over the notes contained within it.
All the modes adhere to a ternary principle of metre, meaning that each mode would have a number of beat subdivisions divisible by the number 3. Some medieval writers explained this as veneration for the perfection of the Holy Trinity, but it appears that this was an explanation made after the event, rather than a cause.[11] Less speculatively, the flexibility of rhythm possible within the system allows for variety and avoids monotony. Notes could be broken down into shorter units (called fractio modi by Anonymous IV) or two rhythmic units of the same mode could be combined into one (extensio modi).[12] An alternative term used by Garlandia for both types of alteration was "reduction".[13] These alterations may be accomplished in several ways: extensio modi by the insertion of single (unligated) long notes or a smaller-than-usual ligature; fractio modi by the insertion of a larger-than-usual ligature, or by special signs. These were of two types, the plica and the climacus.[14]
The plica was adopted from the liquescent neumes (cephalicus) of chant notation, and receives its name (Latin for "fold") from its form which, when written as a separate note, had the shape of a U or an inverted U. In modal notation, however, the plica usually occurs as a vertical stroke added to the end of a ligature, making it a ligatura plicata. The plica usually indicates an added breve on a weak beat.[14] The pitch indicated by the plica depends on the pitches of the note it is attached to and the note following it. If both notes are the same, then the plica tone is the upper or lower neighbor, depending on the direction of the stem. If the interval between the main notes is a third, then the plica tone fills it in as a passing tone. If the two main notes are a second apart, or at an interval of a fourth or larger, musical context must decide the pitch of the plica tone.[15]
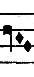

The climacus is a rapid descending scale figure, written as a single note or a ligature followed by a series of two or more descending lozenges. Anonymous IV called these currentes (Latin "running"), probably in reference to the similar figures found in pre-modal Aquitanian and Parisian polyphony. Franco of Cologne called them coniunctura (Latin for "joined [note]"). When consisting of just three notes (coniunctura ternaria) it is rhythmically identical with the ordinary three-note ligature, but when containing more notes this figure may be rhythmically ambiguous and therefore difficult to interpret.[14] The difficulty was compounded in the later half of the 13th century, when the lozenge shape came also to be used for the semibreve. A general rule is that the last note is a longa, the second-last note is a breve, and all the preceding notes taken together occupy the space of a longa. However, the exact internal rhythm of these first notes of the group requires some interpretation according to context.[16]
It was also possible to change from one mode to another without a break, which was called "admixture" by Anonymous IV, writing around 1280.[13]

Because a ligature cannot be used for more than one syllable of text, the notational patterns can only occur in melismatic passages. Where syllables change frequently or where pitches are to be repeated, ligatures must be broken up into smaller ligatures or even single notes in so-called "syllabic notation", often creating difficulty for the singers, as was reported by Anonymous IV.[17][13]
An ordo (plural ordines) is a phrase constructed from one or more statements of one modal pattern and ending in a rest. Ordines were described according to the number of repetitions and the position of the concluding rest. "Perfect" ordines ended with the first note of the pattern followed by a rest substituting for the second half of the pattern, and "imperfect" ordines ended in the last note of the pattern followed by a rest equal to the first part. Imperfect ordines are mostly theoretical and rare in practice, where perfect ordines predominate.[18]
Other writers who covered the topic of rhythmic modes include Anonymous IV, who mentions the names of the composers Léonin and Pérotin as well as some of their major works, and Franco of Cologne, writing around 1260, who recognized the limitations of the system and whose name became attached to the idea of representing the duration of a note by particular notational shapes, though in fact the idea had been known and used for some time before Franco.[19] Lambertus described nine modes, and Anonymus IV said that, in England, a whole series of irregular modes was in use.[20]
References
[edit]- Apel, Willi. 1961. The Notation of Polyphonic Music, 900–1600, fifth edition, revised and with commentary. Publications of the Mediaeval Academy of America, no. 38. Cambridge, Mass.: Mediaeval Academy of America.
- Hoppin, Richard H. (1978). Medieval Music. New York City: W. W. Norton & Co. ISBN 0-393-09090-6.
- Hughes, Dom Anselm. 1954a. "Music in Fixed Rhythm". In New Oxford History of Music, vol. 2: "Early Medieval Music up to 1300", edited by Dom Anselm Hughes, 311–52. London, New York City, & Toronto: Oxford University Press.
- Hughes, Dom Anselm. 1954b. "The Motet and Allied Forms". In New Oxford History of Music, vol. 2: "Early Medieval Music up to 1300", edited by Dom Anselm Hughes, 353–404. London New York City, & Toronto: Oxford University Press.
- Reese, Gustave. 1940. Music in the Middle Ages. New York City: W. W. Norton & Company. ISBN 0-393-09750-1.
- Sadie, Stanley; Tyrrell, John, eds. (2001). The New Grove Dictionary of Music and Musicians (2nd ed.). London: Macmillan. ISBN 9780195170672.
- Seay, Albert. 1975. Music in the Medieval World, second edition. Englewood Cliffs, NJ: Prentice-Hall, Inc. ISBN 0-13-608133-9 (cloth); ISBN 0-13-608125-8 (pbk).
Footnotes
- ^ Hoppin 1978, p. 221.
- ^ New Grove Dict. 2001, "Johannes de Garlandia [Johannes Gallicus]" by Rebecca A. Baltzer.
- ^ Reese 1940, pp. 207–9.
- ^ Apel 1961, p. 223.
- ^ a b Hughes 1954a, p. 320.
- ^ Apel 1961, p. 221.
- ^ Cooper, Paul. 1973. Perspectives in Music Theory: An Historical-Analytical Approach. New York: Dodd, Mead. p. 30. ISBN 0-396-06752-2.
- ^ Riemann, Hugo. 1962. History of Music Theory, Books I and II: Polyphonic Theory to the Sixteenth Century, translated, with a preface, commentary, and notes by Raymond H. Haggh. Lincoln: University of Nebraska Press. p. 135. Corrected second printing, 1966. Reprinted New York City: Da Capo Press, 1974. ISBN 0-306-70637-7.
- ^ Seay 1975, p. 97.
- ^ Hughes 1954a, pp. 323–4.
- ^ Reese 1940, p. 274; Hughes 1954a, pp. 319–20.
- ^ Seay 1975, pp. 98–9.
- ^ a b c New Grove Dict. 2001, "Rhythmic Modes [Modal Rhythm]" by Edward. H. Roesner.
- ^ a b c New Grove Dict. 2001, "Notation, §III, 2: Polyphony and Secular Monophony to c1260" by David Hiley and Thomas B. Payne.
- ^ Apel 1961, p. 227.
- ^ Apel 1961, p. 240.
- ^ Apel 1961, p. 225.
- ^ Hoppin 1978, p. 223.
- ^ Hughes 1954b, pp. 379–80.
- ^ Reese 1940, p. 288.
Further reading
[edit]- Articles. 1980. "Rhythmic Mode", "Johannes de Garlandia", "Franco of Cologne". The New Grove Dictionary of Music and Musicians, edited by Stanley Sadie. 20 vols. London, Macmillan Publishers Ltd. ISBN 1-56159-174-2.
- Grout, Donald Jay, J. Peter Burkholder, and Claude V. Palisca. 2006. A History of Western Music, seventh edition. New York: W. W. Norton. ISBN 0-393-97991-1.
- Hiley, David. 1984. "The Plica and Liquescence". In Gordon Athol Anderson (1929–1981) in memoriam: Von seinen Studenten, Freunden und Kollegen, 2 vols., 2:379–91. Wissenschaftliche Abhandlungen, no. 39. Henryville, PA: Institute of Mediæval Music.
- Parrish, Carl. 1957. The Notation of Medieval Music. London: Faber & Faber.
- Randel, Don Michael, and Willi Apel (eds.). 1986. The New Harvard Dictionary of Music. Cambridge, Massachusetts: Belknap Press of Harvard University Press. ISBN 0-674-61525-5.
- Smith, Norman E. 1988. "The Notation of Fractio Modi". Current Musicology, nos. 45–47 (Fall: Studies in Medieval Music: Festschrift for Ernest H. Sanders, edited by Peter M. Lefferts and Leeman L. Perkins): 283–304.
- Wellesz, Egon (ed.). 1957. New Oxford History of Music, vol. 1: "Ancient and Oriental Music". London & New York: Oxford University Press.
Rhythmic mode
View on Grokipedia- Long-breve (mode 1)
- Breve-long (mode 2)
- Long-breve-breve (mode 3)
- Breve-breve-long (mode 4)
- Long-long (mode 5, with the second long imperfect)
- Breve-breve (mode 6)[3]
Fundamentals
Definition and Characteristics
Rhythmic modes constitute a system of fixed rhythmic patterns composed of long (L) and short (S) note values, utilized in 13th-century European polyphony, particularly for the upper voices in forms such as organum and motets. These modes emerged around 1200–1250 in France, forming a cornerstone of the Ars Antiqua period, during which polyphonic music evolved from earlier monophonic traditions.[3] The system addressed the need for rhythmic organization in multi-voiced compositions without precise durational measurement, relying instead on repetitive sequences to coordinate voices against a sustained tenor.[4] Central characteristics of rhythmic modes include their non-isochronous nature, where rhythms do not follow equal temporal divisions but instead draw from the metrical structures of Latin poetry, such as trochaic (long-short) or iambic (short-long) feet.[4] This contrasts sharply with later mensural notation, in which note values bear proportional durations relative to one another; rhythmic modes, by comparison, impose standardized patterns without time signatures, fostering intricate polyphonic interplay through mode adherence.[3] The modes enabled composers to create rhythmic vitality and complexity, as upper voices moved in measured discant style over a slower-moving chant-based line, enhancing the expressive depth of sacred and emerging secular genres. Key to the system's operation is the ligature, a grouped notation of two to four notes serving as the fundamental unit or "trope" that embodies a mode's pattern.[4] Within these patterns, the long note typically divides either binarily (into two equal shorts, ratio 2:1) or ternarily (into three equal shorts, ratio 3:1), reflecting the prevalent triple-meter emphasis derived from poetic prosody.[3] For instance, in two-voice conductus, both voices often adhere to the same mode for rhythmic unison, while in clausulae—brief polyphonic segments substituting for melismas in organum—the modes organize contrasting voice movements to heighten musical tension and resolution. Ligatures indicate these divisions through their shape and strokes: for example, a descending stroke often marks a long, while ascending or no stroke indicates a breve, with the overall pattern fitting units of three tempora (a perfectio).The Six Modes
The six rhythmic modes, as codified in the 13th century, consist of repeating patterns of long (L) and short (S) notes derived from classical poetic feet, providing the rhythmic foundation for polyphonic music in the Notre Dame school.[5] These modes were systematically described in the anonymous treatise De mensurabili musica (c. 1260), formerly attributed to Johannes de Garlandia, though earlier anonymous treatises also reference them.[6] Each mode is typically notated through ligatures—groups of two or three notes connected by strokes—where the shape and orientation of the ligature indicate the rhythmic values, with the long note generally worth twice the short note in binary modes and divisions aligning with ternary perfection (three tempora per long).[7] The modes are enumerated as follows, with their core patterns and ligature representations:| Mode | Poetic Foot | Pattern | Ligature Grouping | Subdivision Type |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| 1 | Trochaic | L S | Two-note ligature, descending stroke on first note | Binary (long divided into two shorts) |
| 2 | Iambic | S L | Two-note ligature, ascending stroke on first note | Binary (short as half long) |
| 3 | Dactylic | L S S | Three-note ligature, descending stroke on first note | Ternary (long divided into three equal shorts) |
| 4 | Anapestic | S S L | Three-note ligature, no stroke on first two notes | Ternary (long divided into three equal shorts) |
| 5 | Spondaic | L L | Two-note ligature, no strokes (second long imperfect) | Ternary (longs divided into three) |
| 6 | Pyrrhic | S S | Two-note ligature, both ascending strokes or separate notes | Binary (two equal shorts) |


