Recent from talks
Nothing was collected or created yet.
Trimethylborane
View on Wikipedia | |||
| |||
| Names | |||
|---|---|---|---|
| Preferred IUPAC name
Trimethylborane[1] | |||
| Other names
Trimethylborine
Trimethylboron | |||
| Identifiers | |||
3D model (JSmol)
|
|||
| ChemSpider | |||
| ECHA InfoCard | 100.008.926 | ||
| EC Number |
| ||
PubChem CID
|
|||
CompTox Dashboard (EPA)
|
|||
| |||
| |||
| Properties | |||
| C3H9B | |||
| Molar mass | 55.92 g/mol | ||
| Appearance | Colorless gas or liquid | ||
| Density | 0.625 g/cm3 at −100 °C[3] | ||
| Melting point | −161.5 °C (−258.7 °F; 111.6 K) | ||
| Boiling point | −20.2 °C (−4.4 °F; 253.0 K) | ||
| Slight, highly reactive | |||
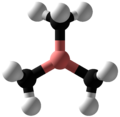
| Structure | |||
| Δ | |||
| Hazards | |||
| Occupational safety and health (OHS/OSH): | |||
Main hazards
|
Spontaneously flammable in air; causes burns | ||
| GHS labelling: | |||
 
| |||
| Danger | |||
| H220, H250, H280, H314 | |||
| P210, P222, P260, P264, P301+P330+P331, P302+P334, P303+P361+P353, P304+P340, P305+P351+P338, P310, P321, P363, P370+P378, P377, P381, P403, P405, P410+P403, P422, P501 | |||
| NFPA 704 (fire diamond) | |||
| Flash point | Not applicable, pyrophoric gas | ||
| −40 °C (−40 °F; 233 K)[4] | |||
| Safety data sheet (SDS) | MSDS from Voltaix | ||
| Related compounds | |||
Related compounds
|
|||
Except where otherwise noted, data are given for materials in their standard state (at 25 °C [77 °F], 100 kPa).
| |||
Trimethylborane (TMB) is a toxic, pyrophoric gas with the formula B(CH3)3 (which can also be written as Me3B, with Me representing methyl).
Properties
[edit]As a liquid it is colourless. The strongest line in the infrared spectrum is at 1330 cm−1 followed by lines at 3010 cm−1 and 1185 cm−1.
Its melting point is −161.5 °C, and its boiling point is −20.2 °C.
Vapour pressure is given by log P = 6.1385 + 1.75 log T − 1393.3/T − 0.007735 T, where T is temperature in kelvins.[5] Molecular weight is 55.914. The heat of vapourisation is 25.6 kJ/mol.[4]
Preparation
[edit]Trimethylborane was first described in 1862 by Edward Frankland,[6] who also mentioned its adduct with ammonia.[7] Due to its dangerous nature the compound was no longer studied until 1921, when Alfred Stock and Friedrich Zeidler took advantage of the reaction between boron trichloride gas and dimethylzinc.[8] Although the substance can be prepared using Grignard reagents the output is contaminated by unwanted products from the solvent. Trimethylborane can be made on a small scale with a 98% yield by reacting trimethylaluminium in hexane with boron tribromide in dibutyl ether as a solvent.[5] Yet other methods are reacting tributyl borate with trimethylaluminium chloride, or potassium tetrafluoroborate with trimethylaluminium,[9] or adding boron trifluoride in ether to methyl magnesium iodide.[10]
Reactions
[edit]Trimethylborane spontaneously ignites in air if the concentration is high enough. It burns with a green flame producing soot.[11] Slower oxidation with oxygen in a solvent or in the gas phase can produce dimethyltrioxadiboralane, which contains a ring of two boron and three oxygen atoms. However the major product is dimethylborylmethylperoxide, which rapidly decomposes to dimethoxymethylborane.[12]
Trimethylborane is a strong Lewis acid. B(CH3)3 can form an adduct with ammonia: (NH3):B(CH3)3.[13] as well as other Lewis bases. The Lewis acid properties of B(CH3)3 have been analyzed by the ECW model yielding EA= 2.90 and CA= 3.60. When trimethylborane forms an adduct with trimethylamine, steric repulsion between the methyl groups on the B and N results. The ECW model can provide a measure of this steric effect.
Trimethylborane reacts with water and chlorine at room temperature. It also reacts with grease but not with teflon or glass.[5]
Trimethylborane reacts with diborane to disproportionate to form methyldiborane and dimethyldiborane: (CH3)BH2.BH3 and (CH3)2BH.BH3.
It reacts as a gas with trimethylphosphine to form a solid Lewis salt with a heat of formation of −41 kcal per mol. This adduct has a heat of sublimation of −24.6 kcal/mol. No reaction occurs with trimethylarsine or trimethylstibine.[10]
Methyl lithium reacting with the Trimethylborane produces a tetramethylborate salt: LiB(CH3)4.[14] The tetramethylborate ion has a negative charge and is isoelectronic with neopentane, tetramethylsilane, and the tetramethylammonium cation.
Use
[edit]Trimethylborane has been used as a neutron counter.[15] For this use it has to be very pure.[13] It is also used in chemical vapour deposition where boron and carbon need to be deposited together.
References
[edit]- ^ IUPAC Chemical Nomenclature and Structure Representation Division (2013). "P-6". In Favre, Henri A.; Powell, Warren H. (eds.). Nomenclature of Organic Chemistry: IUPAC Recommendations and Preferred Names 2013. IUPAC–RSC. ISBN 978-0-85404-182-4.. p. 974.
- ^ Graner, G.; Hirota E.; Iijima T.; Kuchitsu K.; Ramsay, D. A.; Vogt, J.; Vogt, N. (2001). "C3H9B Trimethylborane". C3H9B Trimethylborane. Molecules and Radicals. Landolt-Börnstein - Group II. Vol. 25C: Molecules containing three or four carbon atoms. p. 1370. doi:10.1007/10688787_381. ISBN 978-3-540-66774-2.
- ^ See MSDS
- ^ a b "Trimethylborane" (2009) at the Online Chemical Dictionary. Archived 2012-03-16 at the Wayback Machine.
- ^ a b c Rees, William S. Jr.; et al. (1990). Ginsberg, Alvin P. (ed.). Trimethylborane. Inorganic Syntheses. Vol. 27. p. 339.
- ^ Frankland, Edward (1862). "Ueber eine neue Reihe organischer Verbindungen, welche Bor enthalten". Justus Liebigs Ann. Chem. 124: 129–157. doi:10.1002/jlac.18621240102.
- ^ Nishiyabu R.; Kubo Y.; James, T. D.; Fossey, J. S. (2011). "Boronic acid building blocks: tools for self assembly". Chem. Commun. 47 (4): 1124–1150. doi:10.1039/C0CC02921A. PMID 21113558.
- ^ Stock, A.; Zeidler, F. (1921). "Zur Kenntnis des Bormethyls und Boräthyls". Ber. Dtsch. Chem. Ges. A/B. 54 (3): 531–541. doi:10.1002/cber.19210540321.
- ^ Köster, Roland; Binger, Paul; Dahlhoff, Wilhelm V. (1973). "A convenient preparation of trimethylborane and triethylborane". Synthesis and Reactivity in Inorganic and Metal-Organic Chemistry. 3 (4): 359–367. doi:10.1080/00945717308057281.
- ^ a b Mente, Donald Charles (May 1975). The Reactions of Trimethyl Group Va Lewis Bases with Simple Boron Lewis Acids (PDF) (PhD thesis). Texas Tech. Archived from the original (PDF) on 2011-08-15. Retrieved 2010-09-23.
- ^ Ellern, Herbert (1968). Military and Civilian Pyrotechnics. Chemical Publishing Company. p. 24. CiteSeerX 10.1.1.137.1104. ISBN 978-0-8206-0364-3.
- ^ Barton, Lawrence; Crump, John M.; Wheatley, Jeffrey B. (June 1974). "Trioxadiborolanes from the oxidation of methyldiborane". Journal of Organometallic Chemistry. 72 (1): C1 – C3. doi:10.1016/s0022-328x(00)82027-6.
- ^ a b Ross, Gaylon S.; et al. (2 October 1961). "Preparation of High Purity Trimethylborane" (PDF). Journal of Research of the National Bureau of Standards Section A. 66 (1). Archived from the original (PDF) on 19 October 2011. Retrieved 22 September 2010.
- ^ Georg Wittig in 1958
- ^ Ferguson, G. A. Jr; Jablonski, F. E. (2004-12-29). "Electron Mobility in Boron Trimethyl". Review of Scientific Instruments. 28 (11): 893. doi:10.1063/1.1715757. ISSN 0034-6748.