| Endocrine glands | |
|---|---|
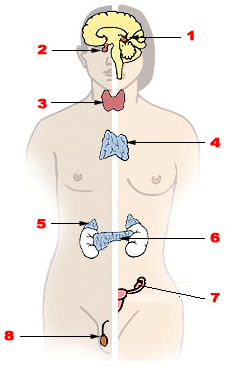 | |
| Major endocrine glands. (Male left, female right.) 1. Pineal gland 2. Pituitary gland 3. Thyroid gland 4. Thymus 5. Adrenal gland 6. Pancreas 7. Ovary 8. Testes | |
| Specialty | Endocrinology |
Endocrine diseases are disorders of the endocrine system. The branch of medicine associated with endocrine disorders is known as endocrinology.
Broadly speaking, endocrine disorders may be subdivided into three groups:[1]
Endocrine disorders are often quite complex, involving a mixed picture of hyposecretion and hypersecretion because of the feedback mechanisms involved in the endocrine system. For example, most forms of hyperthyroidism are associated with an excess of thyroid hormone and a low level of thyroid stimulating hormone.[2]

In endocrinology, medical emergencies include diabetic ketoacidosis, hyperosmolar hyperglycemic state, hypoglycemic coma, acute adrenocortical insufficiency, phaeochromocytoma crisis, hypercalcemic crisis, thyroid storm, myxoedema coma and pituitary apoplexy.[7]
Emergencies arising from decompensated pheochromocytomas or parathyroid adenomas are sometimes referred for emergency resection when aggressive medical therapies fail to control the patient's state, however the surgical risks are significant, especially blood pressure lability and the possibility of cardiovascular collapse after resection (due to a brutal drop in respectively catecholamines and calcium, which must be compensated with gradual normalization).[8][9] It remains debated when emergency surgery is appropriate as opposed to urgent or elective surgery after continued attempts to stabilize the patient, notably in view of newer and more efficient medications and protocols.[10][11][12]