Recent from talks
Nothing was collected or created yet.
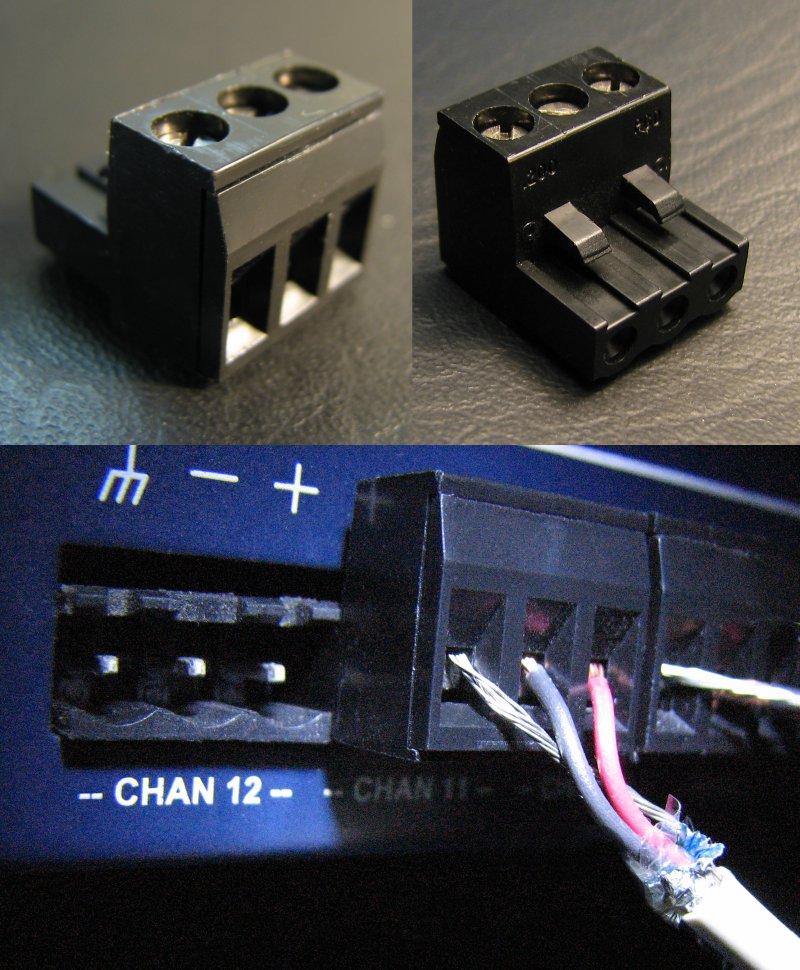
Euroblock
View on WikipediaThis article has multiple issues. Please help improve it or discuss these issues on the talk page. (Learn how and when to remove these messages)
|

Euroblock, short for "European-style terminal block",[1] is an extra-low voltage disconnectable (or pluggable) connector and terminal block combination commonly used for microphone- and line level-audio signals, and for control signals such as RS-232 or RS-485.
It is also known as the Phoenix connector from one of the manufacturers, Phoenix Contact, a German company whose US operations were established in 1981 in Harrisburg, Pennsylvania; though there are many manufacturers who make compatible products.[1] It is also known as "Combicon", which might be a Phoenix brand name; or more generically as a "pluggable terminal block" or a "two piece terminal block".[2][3]
The Euroblock is a solderless connector that uses screw terminals to clamp connecting wires. Once the wires are installed, the entire assembly is plugged into a matching socket in the electronic device. Euroblocks are more convenient than the terminal strips they replace as the signal cables can be quickly disconnected from or connected to the electronic device, rather than unscrewing and re-screwing each wire individually.[1]
References
[edit]- ^ a b c Bohn, Dennis. "Phoenix-blocks (or -connectors or -strips)". Pro Audio Reference. Tukwila, Washington: AES. Retrieved 2017-12-17.
Bohn, Dennis. "Connectors: Euroblocks". Pro Audio Reference. Tukwila, Washington: AES. Retrieved 2017-12-17. - ^ "PCB connectors | Phoenix Contact" from Phoenix Contact
- ^ "PCB Connections" from Altech Corporation