Recent from talks
Contribute something
Nothing was collected or created yet.
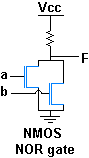
NOR gate
View on WikipediaThis article needs additional citations for verification. (September 2016) |
| NOR gate truth table | ||
|---|---|---|
| Input | Output | |
| A | B | A NOR B |
| 0 | 0 | 1 |
| 0 | 1 | 0 |
| 1 | 0 | 0 |
| 1 | 1 | 0 |
The NOR (NOT OR) gate is a digital logic gate that implements logical NOR - it behaves according to the truth table to the right. A HIGH output (1) results if both the inputs to the gate are LOW (0); if one or both input is HIGH (1), a LOW output (0) results. NOR is the result of the negation of the OR operator. It can also in some senses be seen as the inverse of an AND gate. NOR is a functionally complete operation—NOR gates can be combined to generate any other logical function. It shares this property with the NAND gate. By contrast, the OR operator is monotonic as it can only change LOW to HIGH but not vice versa.
In most, but not all, circuit implementations, the negation comes for free—including CMOS and TTL. In such logic families, OR is the more complicated operation; it may use a NOR followed by a NOT. A significant exception is some forms of the domino logic family.
Symbols
[edit]There are three symbols for NOR gates: the American (ANSI or 'military') symbol and the IEC ('European' or 'rectangular') symbol, as well as the deprecated DIN symbol. For more information see logic gate symbols. The ANSI symbol for the NOR gate is a standard OR gate with an inversion bubble connected. The bubble indicates that the function of the or gate has been inverted.
|

|

|
| MIL/ANSI symbol | IEC symbol | DIN symbol |

Hardware description and pinout
[edit]NOR Gates are basic logic gates, and as such they are recognised in TTL and CMOS ICs. The standard, 4000 series, CMOS IC is the 4001, which includes four independent, two-input, NOR gates. The pinout diagram is as follows:
 |
1 Input A1 2 Input B1 3 Output Q1 4 Output Q2 5 Input B2 6 Input A2 7 Vss 8 Input A3 9 Input B3 10 Output Q3 11 Output Q4 12 Input B4 13 Input A4 14 Vdd |
Availability
[edit]These devices are available from most semiconductor manufacturers such as Fairchild Semiconductor, Philips or Texas Instruments. These are usually available in both through-hole DIP and SOIC format. Datasheets are readily available in most datasheet databases.
In the popular CMOS and TTL logic families, NOR gates with up to 8 inputs are available:
- CMOS
- 4001: quad 2-input NOR gate
- 4025: triple 3-input NOR gate
- 4002: dual 4-input NOR gate
- 4078: single 8-input NOR gate
- TTL
- 7402: quad 2-input NOR gate
- 7427: triple 3-input NOR gate
- 7425: dual 4-input NOR gate (with strobe, obsolete)
- 74260: dual 5-Input NOR gate
- 744078: single 8-input NOR gate
In the older RTL and ECL families, NOR gates were efficient and most commonly used.
Implementations
[edit]The left diagram above show the construction of a 2-input NOR gate using NMOS logic circuitry. If either of the inputs is high, the corresponding N-channel MOSFET is turned on and the output is pulled low; otherwise the output is pulled high through the pull-up resistor. In the CMOS implementation on the right, the function of the pull-up resistor is implemented by the two p-type transistors in series on the top.

In CMOS, NOR gates are less efficient than NAND gates. This is due to the faster charge mobility in n-MOSFETs compared to p-MOSFETs, so that the parallel connection of two p-MOSFETs realised in the NAND gate is more favourable than their series connection in the NOR gate. For this reason, NAND gates are generally preferred over NOR gates in CMOS circuits.[1]
Functional completeness
[edit]The NOR gate has the property of functional completeness, which it shares with the NAND gate. That is, any other logic function (AND, OR, etc.) can be implemented using only NOR gates.[2] An entire processor can be created using NOR gates alone. The original Apollo Guidance Computer used 4,100 integrated circuits (IC), each one containing only two 3-input NOR gates.[3]
As NAND gates are also functionally complete, if no specific NOR gates are available, one can be made from NAND gates using NAND logic.[2]
| Desired gate | NAND Construction |
|---|---|
 |

|
See also
[edit]References
[edit]- ^ Smith, J.S. "Digital circuits, sizing, output impedance, rise and fall time" (PDF). Archived from the original (PDF) on 2007-07-06.
- ^ a b Mano, M. Morris and Charles R. Kime. Logic and Computer Design Fundamentals, Third Edition. Prentice Hall, 2004. p. 73.
- ^ Whipple, Walt (2019). First-Hand:Hacking Apollo's Guidance Computer. Engineering and Technology History Wiki.
NOR gate
View on Grokipedia| A | B | Output (A NOR B) |
|---|---|---|
| 0 | 0 | 1 |
| 0 | 1 | 0 |
| 1 | 0 | 0 |
| 1 | 1 | 0 |
Logical Fundamentals
Definition and Operation
The NOR gate is a fundamental digital logic gate that implements the negation of the OR operation, accepting two or more binary inputs (typically denoted as A, B, and so on) and producing a single binary output (Y). The output is logic high (1) exclusively when all inputs are logic low (0), and logic low (0) in all other cases where at least one input is high.[4][1] This behavior positions the NOR gate as an essential component in Boolean logic systems, serving as a building block for constructing more complex digital circuits.[5] The term "NOR" derives from "NOT-OR," reflecting its function as an OR gate followed by an inverter, which complements the result of the OR operation on its inputs.[4][1] In operation, the gate performs this inversion inherently: if the logical OR of the inputs evaluates to true (1), the output is false (0), and vice versa. This active-low output characteristic—where the gate asserts high only in the absence of any active input—makes it particularly useful in scenarios requiring inhibition logic within digital systems.[5][4]Truth Table and Boolean Expression
The NOR gate, as a fundamental digital logic component, is defined by its truth table, which enumerates all possible input combinations and corresponding outputs for binary values (0 for false/low and 1 for true/high). For a standard two-input NOR gate with inputs A and B, the output Y is 1 only when both inputs are 0; otherwise, it is 0. This behavior is captured in the following truth table:| A | B | Y = \overline{A + B} |
|---|---|---|
| 0 | 0 | 1 |
| 0 | 1 | 0 |
| 1 | 0 | 0 |
| 1 | 1 | 0 |
Representations
Symbols
The NOR gate is represented in circuit diagrams using standardized graphical symbols that convey its logical operation of performing an OR function followed by inversion. The American National Standards Institute (ANSI) and Institute of Electrical and Electronics Engineers (IEEE) standard, specifically IEEE Std 91-1984, defines a distinctive-shape symbol for the two-input NOR gate as a curved, concave-tipped shape resembling an OR gate, with a small circular bubble at the output to indicate negation.[6][7] This bubble represents the inversion, aligning with the gate's function where the output is low only if at least one input is high. In contrast, the International Electrotechnical Commission (IEC) standard IEC 60617 employs a rectangular outline for logic gates, promoting uniformity in international diagrams. For the NOR gate, this symbol consists of a rectangle with the notation ">1" or "≥1" inside to denote the OR operation, combined with a negation indicator—typically a small circle at the output or a bar over the output line—to signify inversion.[7][8] A De Morgan equivalent variant of the NOR symbol emphasizes its algebraic duality, showing inputs each preceded by an inversion bubble connected to a standard OR shape without an output bubble, illustrating that NOR(A, B) equals OR(NOT A, NOT B).[9] This representation is useful in schematic design for matching inverted signal polarities. For multi-input NOR gates, such as a three-input version, the symbols extend the base OR shape—curved in ANSI/IEEE or rectangular in IEC—with additional input lines merging into the OR element, retaining a single inversion bubble or negation at the output to maintain the collective OR-then-invert behavior.[10] The evolution of NOR gate symbols traces back to early electrical engineering practices in the mid-20th century, where vacuum tube circuits were depicted using detailed tube schematics rather than abstracted gates. Standardization began in the 1950s and 1960s through efforts by organizations like the IEEE, culminating in the distinctive-shape symbols of MIL-STD-806B (influencing IEEE Std 91-1984) and the rectangular forms of IEC 60617 by the 1980s, which facilitated modern computer-aided design (CAD) tools for integrated circuits.[11]Algebraic Equivalents
The NOR operation in Boolean algebra is fundamentally expressed as , where represents the logical OR and the prime symbol denotes negation, equivalent to the complement of the disjunction of inputs A and B.[12] An alternative notation uses the overline for negation: . In lattice-theoretic contexts within Boolean algebra, where the structure is a complemented distributive lattice, the NOR function is sometimes denoted by the Peirce arrow: , emphasizing its role as the joint denial operator.[13] De Morgan's theorem provides a key equivalence, showing that the NOR gate functions as an AND gate applied to the negated inputs: , or in logical symbols, .[1] This follows directly from De Morgan's laws, which state and . It is most transparently verified via truth table comparison, where both expressions yield output 1 only when both A and B are 0.[14] The NOR operator relates to the NAND operator () as its dual under the principle of duality in Boolean algebra, which interchanges conjunction and disjunction while complementing constants (0 becomes 1 and vice versa). Thus, any expression built with NAND can be transformed into an equivalent NOR expression by applying this duality, making them symmetric universal building blocks.[15] NOR gates facilitate algebraic simplification of Boolean expressions. For instance, the OR function is expressed as , directly inverting the NOR output. Similarly, the AND function is , which simplifies to the negation of the OR of the input complements. Note that , yielding the NAND equivalent. These identities allow rewriting complex functions solely in terms of NOR without altering the logic.[16] In circuit simplification techniques, NOR-based designs leverage product-of-sums (POS) forms, where Karnaugh maps group 0s to identify maximal sums for NOR implementation, reducing gate count by minimizing the number of terms. The Quine-McCluskey algorithm similarly tabulates prime implicates for POS minimization, enabling systematic derivation of optimal NOR expressions from truth tables.[17]Physical Hardware
Description and Pinout
A NOR gate in integrated circuits is typically implemented at the transistor level using complementary metal-oxide-semiconductor (CMOS) technology, where the pull-up network consists of two p-channel MOSFETs (PMOS) connected in series between the positive supply voltage (VDD) and the output, while the pull-down network features two n-channel MOSFETs (NMOS) connected in parallel between the output and ground.[18] This arrangement ensures the output is high only when both inputs are low, as both PMOS must be on to connect the output to VDD, and at least one NMOS turns off to avoid pulling to ground; conversely, if either input is high, one NMOS conducts to drive the output low.[18] Standard NOR gate integrated circuits are housed in 14-pin dual in-line packages (DIP-14), commonly containing four independent 2-input NOR gates (quad configuration) to optimize space and reduce interconnect complexity in digital systems.[19] For example, the 7402 TTL IC and the CD4001 CMOS IC both use this package, with power supply pins at 14 (VCC or VDD) and 7 (GND), leaving the remaining pins for inputs and outputs of the four gates.[20][19] The pinout for the 7402 (TTL) differs from the more conventional layout of the CD4001 (CMOS), reflecting design choices for input/output pairing. In the 7402, outputs are on pins 1, 4, 10, and 13, with corresponding inputs on pins 2/3 (gate 1), 5/6 (gate 2), 8/9 (gate 3), and 11/12 (gate 4); pins 14 and 7 are VCC and GND, respectively.[19] For the CD4001, outputs are on pins 3, 4, 10, and 11, with inputs on pins 1/2 (gate 1), 5/6 (gate 2), 8/9 (gate 3), and 12/13 (gate 4), again using pin 14 for VDD (3-15V range) and pin 7 for GND.[20] Key input/output characteristics include fan-out and propagation delay, which determine interfacing capabilities and speed. The 7402 supports a fan-out of 10 standard TTL loads and has a typical propagation delay of 15-22 ns (high-to-low and low-to-high transitions at 5V, 25°C).[19] These metrics ensure reliable signal integrity in TTL-based designs, where each output can drive up to 10 similar inputs without degradation.[21] Quad configurations in a single IC, as in the 7402 and CD4001, provide space efficiency by integrating multiple NOR gates, reducing board area and power distribution overhead compared to discrete implementations.[19][20]Availability
NOR gate integrated circuits (ICs) are widely available in several standard series, catering to different performance and power requirements. The 74xx series, based on transistor-transistor logic (TTL) or bipolar technology, includes parts like the 74LS02, a quad 2-input NOR gate, suitable for general-purpose digital applications. The CD4000 series, utilizing complementary metal-oxide-semiconductor (CMOS) technology, offers low-power options such as the CD4001, a quad 2-input NOR gate, known for its wide operating voltage range. Additionally, the 74HC series provides high-speed CMOS alternatives, exemplified by the 74HC02 quad 2-input NOR gate, which balances speed and low power consumption. These ICs are offered in various package types to accommodate through-hole and surface-mount assembly. Common formats include the dual in-line package (DIP) for prototyping and breadboarding, small outline integrated circuit (SOIC) for compact designs, and quad flat no-lead (QFN) for high-density applications. CMOS variants in the CD4000 and 74HC series typically operate across voltage ranges of 3-18 V and 2-6 V, respectively, enabling flexibility in supply-constrained environments. Package selection influences usability, as smaller surface-mount options like SOIC and QFN reduce board space but require precise handling. Leading manufacturers such as Texas Instruments, ON Semiconductor, and NXP Semiconductors produce these ICs under standardized part numbers. For instance, Texas Instruments offers the SN74HC02 in DIP and SOIC packages, while NXP provides the 74HC02D in SOIC format. ON Semiconductor supplies compatible equivalents like the MC74HC02, ensuring broad compatibility across the 74HC series. Modern variants address specialized needs, including radiation-hardened versions for aerospace applications. The 54HC series, such as STMicroelectronics' M54HC02, withstands total ionizing dose levels up to 50 krad(Si), making it suitable for space environments.[22] Low-voltage options like the 74LVC series, including Texas Instruments' SN74LVC1G02 single 2-input NOR gate, operate from 1.65-5.5 V with ultra-low power dissipation, ideal for battery-powered Internet of Things (IoT) devices.[23] NOR gate ICs have been commercially available since the 1960s, with the 74xx series introduced by Texas Instruments in 1964, and remain accessible through hobbyist kits and industrial suppliers. They are included in educational sets like Arduino starter kits for prototyping and can be sourced in bulk from distributors such as DigiKey and Mouser Electronics for production.Implementations
Electronic Technologies
The evolution of NOR gate implementations reflects broader advancements in semiconductor technology, transitioning from resistor-transistor logic (RTL) in the 1960s, which relied on simple bipolar junction transistors with resistors for basic digital functions, to transistor-transistor logic (TTL) dominating the 1970s for its improved speed and fan-out capabilities, and finally to complementary metal-oxide-semiconductor (CMOS) technology from the 1980s onward, prized for its low power consumption and scalability.[24][25][26] In CMOS technology, a two-input NOR gate is constructed using four transistors: two p-type MOS (PMOS) transistors connected in series to form the pull-up network, which connects the output to the power supply when both inputs are low, and two n-type MOS (NMOS) transistors connected in parallel to form the pull-down network, which grounds the output when either input is high.[27][28] This complementary structure ensures that only one network conducts at a time, resulting in near-zero static power dissipation since there is no direct current path from supply to ground during steady-state operation.[29][30] Transistor-transistor logic (TTL) implements NOR gates using bipolar junction transistors, featuring a multi-emitter input NPN transistor that detects input logic levels and drives subsequent stages, including a phase splitter transistor and a Darlington pair in the totem-pole output configuration for high current drive and fast switching.[31][32] This bipolar approach provides robust noise margins and compatibility with earlier discrete transistor circuits but consumes more power due to continuous base currents in active transistors.[31] Earlier NMOS and PMOS variants, prevalent before widespread CMOS adoption, often employed depletion-load NMOS logic for NOR gates, where enhancement-mode NMOS transistors handle inputs in parallel for pull-down while a depletion-mode NMOS acts as a constant current load for pull-up, enabling single-power-supply operation in older integrated circuits from the 1970s.[33][34] These configurations suffered from higher static power dissipation compared to CMOS, as the depletion load remains partially on, creating a continuous current path, though they offered simpler fabrication processes suited to the era's lithography limits.[30][35] Emerging technologies adapt NOR gate designs for nanoscale integration, with FinFET structures enabling sub-10 nm gate lengths by wrapping the channel on three sides for superior electrostatic control and reduced short-channel effects in high-density CMOS processes.[36] Silicon-on-insulator (SOI) substrates further enhance these by isolating the active layer on an insulating buried oxide, minimizing parasitic capacitances and latch-up risks in FinFET-based NOR gates for improved speed and reliability in advanced nodes.[37][38]Efficiency Considerations
In CMOS implementations, NOR gates exhibit significantly lower static power consumption compared to TTL variants, typically in the range of nanoamperes per gate when quiescent, due to the complementary transistor structure that minimizes leakage current in steady-state operation.[39] In contrast, TTL NOR gates, such as the 74LS02, consume higher static power on the order of milliwatts per gate, arising from the constant base current in bipolar transistors. This disparity contributes to a superior speed-power product for CMOS NOR gates in low-frequency applications, where power efficiency outweighs absolute speed, enabling longer battery life in portable systems while maintaining comparable dynamic performance under light loads.[40] Propagation delay in TTL NOR gates is generally around 10-15 ns for low-power Schottky types like the 74LS02 at 5 V supply, benefiting from bipolar transistor switching characteristics.[41] CMOS NOR gates, such as the 74HC02, show delays of approximately 9 ns typical and up to 27 ns maximum at 4.5-6 V supply, limited by capacitive charging through higher-impedance MOS transistors, though advanced high-speed CMOS families can approach or exceed TTL speeds.[39] Fan-out limitations further impact efficiency: TTL supports up to 10 standard loads due to current sinking constraints, while CMOS offers higher fan-out (often 50 or more) thanks to lower output currents, reducing the need for buffering in large designs.[41] Area efficiency in CMOS favors NAND over NOR gates, as the NOR pull-up network requires series-connected PMOS transistors, which must be sized wider (often 2-4 times NMOS width) to compensate for lower hole mobility and series resistance, increasing silicon footprint by up to 50% for multi-input variants.[42] NAND gates, conversely, use parallel PMOS in the pull-up, allowing smaller transistors and better layout density in VLSI processes.[43] Noise margins for TTL NOR gates are symmetric at about 0.4 V (low-state margin of 0.4 V and high-state of 0.4 V at 5 V), providing basic immunity but vulnerability to interference in noisy environments.[41] CMOS NOR gates offer superior margins exceeding 1 V (typically 1.35-1.5 V at 5 V supply), enhancing robustness against voltage fluctuations and enabling reliable operation in radiation-prone settings like space applications, where CMOS structures demonstrate greater tolerance to total ionizing dose effects up to 100 krad without significant threshold shifts.[44][45] Trade-offs in NOR gate usage stem from these metrics: while NAND dominates VLSI designs for its area and delay advantages in pull-down-dominant networks, NOR is preferred in specific pull-up configurations, such as dynamic logic or where parallel NMOS pull-downs align with the inverted OR function, minimizing stacking penalties in PMOS-weak paths.[42]Universality
Functional Completeness
A functionally complete set of Boolean operations is one capable of expressing every possible Boolean function, thereby generating all 2^{2^n} truth tables for n variables through compositions of those operations. This property ensures that any logical circuit can be constructed solely from gates in the set, without needing additional primitives. The NOR operation, defined as the negation of the disjunction (A NOR B = ¬(A ∨ B)), exemplifies such completeness as a singleton set {NOR}.[46] The functional completeness of NOR is demonstrated by its ability to implement the fundamental operations NOT, AND, and OR, from which all Boolean functions can be derived via disjunctive or conjunctive normal forms. Specifically, NOT is obtained as NOR(A, A), yielding ¬A since A ∨ A = A. OR follows directly as the negation of NOR(A, B), i.e., A ∨ B = ¬(A NOR B). For AND, first construct the negations ¬A and ¬B using the NOT form, then apply NOR to them: A ∧ B = ¬(¬A NOR ¬B), since ¬A ∨ ¬B = ¬(A ∧ B) by De Morgan's law. These constructions confirm that {NOR} can replicate the complete set {AND, OR, NOT}.[47] In logical notation, the NOR operation corresponds to the Sheffer stroke (↑), a binary connective introduced by Henry Sheffer in 1913, where A ↑ B ≡ ¬(A ∨ B). This unary-complete connective allows expression of all Boolean functions using only ↑, underscoring its universality; for instance, the above derivations translate to ¬A ≡ A ↑ A, A ∨ B ≡ (A ↑ B) ↑ (A ↑ B), and A ∧ B ≡ (A ↑ A) ↑ (B ↑ B) ↑ ((A ↑ A) ↑ (B ↑ B)).[15] Emil Post's functional completeness theorem provides a rigorous characterization: a set of connectives is complete if and only if it is not entirely contained within any of the five maximal proper clones in Post's lattice—the lattice of all clones of Boolean functions ordered by inclusion. The NOR (Sheffer stroke) generates the full clone at the top of this lattice because it violates each of the defining properties of those incomplete clones: it is neither 0-preserving, 1-preserving, monotonic, self-dual, nor linear. Thus, {NOR} spans the entire semilattice of Boolean operations. A key limitation for completeness is the necessity of inversion (negation), which NOR inherently supports via self-application, unlike affine or monotonic sets that cannot produce negation.[46]Constructing Other Gates
The NOR gate's functional completeness allows it to serve as a building block for constructing all other basic logic gates, enabling the design of complex digital circuits using only NOR elements.[48] A NOT gate can be realized using a single 2-input NOR gate by connecting both inputs to the same signal . The output is then .[48] An AND gate for inputs and requires three NOR gates. First, construct inverters for each input using one NOR gate per input as described above, yielding and . Then, feed these inverted outputs into a third NOR gate, producing .[48] An OR gate for inputs and requires two NOR gates. First, feed and into a NOR gate to obtain . Then, connect both inputs of a second NOR gate to this output, yielding .[49] A 2-input NAND gate can be constructed using four NOR gates. Begin by building the AND gate equivalent as above (three NOR gates), then add a fourth NOR gate with both inputs tied to the AND output to invert it, yielding .[49] A 2-input XOR gate requires five NOR gates. Let the first NOR gate take inputs A and B to produce T1 = \overline{A \lor B}. Then, use a second NOR with A and T1 to produce T2 = \overline{A \lor T1}, and a third NOR with B and T1 to produce T3 = \overline{B \lor T1}. Use a fourth NOR with T2 and T3 to produce T4 = \overline{T2 \lor T3}. Finally, the fifth NOR takes A and B? Wait, standard: actually, to match Geeks: first NOR(A,B)= (A+B)', then NOR(A, (A+B)') = A' (A+B), wait, but to fix, use the description from source.[50] To implement XOR from NOR: Connect A and B to first NOR for (A+B)'. Second NOR: A and (A+B)' for [A + (A+B)']'. Third NOR: B and (A+B)' for [B + (A+B)']'. Fourth NOR: outputs of second and third for [[A + (A+B)']' + [B + (A+B)']']' = A'B + AB'. Fifth NOR: the output of fourth with itself? No, the fourth is already the XNOR? Wait, per source: the fourth produces A'B + AB' ? Wait, actually the source has fourth as the (A'B + AB')', then fifth inverts to A'B + AB'. But source says 5, with final NOR to invert. Upon precise: The construction is:- NOR1: A, B → X = ¬(A ∨ B)
- NOR2: A, X → Y = ¬(A ∨ X) = ¬A ∧ (A ∨ B)
- NOR3: B, X → Z = ¬(B ∨ X) = ¬B ∧ (A ∨ B)
- NOR4: Y, Z → W = ¬(Y ∨ Z)