Recent from talks
Nothing was collected or created yet.
Pipe Mania
View on Wikipedia| Pipe Mania | |
|---|---|
 Original box art | |
| Developer | The Assembly Line |
| Publishers | Lucasfilm Games (NA) Empire Interactive (EU) Video System (arcade) |
| Designers | Akila Redmer Stephan L. Butler |
| Platforms | Amiga, Amstrad CPC, Apple II, Apple IIGS, Mac, Arcade, Archimedes, Atari ST, BBC Micro, Commodore 64, Game Boy, PC-88, PC-98, NES, MS-DOS, Windows 3.1x, Psion 3a, SAM Coupé, X68000, Super Famicom, ZX Spectrum |
| Release | Amiga, Atari ST, MS-DOS June 1989[1] Electron, Arcade, CPC, Apple II, IIGS, BBC, C64, GB, Mac, NES, ZX 1990 Super Famicom
1992 |
| Genre | Puzzle |
| Mode | Single-player |
Pipe Mania is a puzzle video game developed by The Assembly Line for the Amiga and published in 1989. It was ported to several other platforms by Lucasfilm Games as Pipe Dream; the company distributed the game in the US. The player must connect randomly appearing pieces of pipe on a grid to a given length within a limited time.
The Windows version of the game was included in the MS Windows Entertainment Pack. In 1990, it was released as an arcade video game by Japanese manufacturer Video System Co. Ltd., though with slightly altered gameplay, giving the player the task to connect a source and drain with the random pipe pieces.
Gameplay
[edit]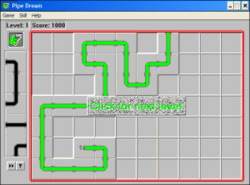
The game is played on a grid of squares, one of which is marked as an entry point for a flow of green slime, referred to in-game as "flooz" or "goo" depending on the version. A column of five pipe sections is displayed to one side as a dispenser. When the player clicks on an empty square, the bottommost piece in the dispenser is placed there and a new piece drops in from the top. Pieces cannot be rotated or flipped and must be used in their original orientation. The objective is to form an unbroken pipeline through which the flooz can flow, starting from the entry point and extending for at least a specified minimum number of squares.
The flooz begins to flow after a set time delay, and continues to do so until it reaches a pipe-end that is either open or blocked by a square/playfield edge. If the pipeline has reached or exceeded the minimum required length, the player advances to the next level; if not, the game ends.
If the flooz has not yet entered a pipe section, the player can click on it to replace it with the next one in the dispenser. However, doing so carries a score penalty and causes a short delay before the next piece can be laid.
Later levels introduce added complications, such as:
- Higher minimum pipeline lengths and shorter delays before the flooz starts to flow.
- Higher flow speeds.
- Obstacles or pipe sections already on the field, which cannot be replaced.
- An end piece into which the flooz must be routed. Failing to do so ends the game, even if the length requirement has been met.
- Openings at opposite edges of the grid, allowing the flooz to wrap around from one to the other.
- Reservoirs that take a few seconds to fill once the flooz enters them, giving the player extra time to place pipes.
- One-way pipe sections that allow flow only in the indicated direction.
The player scores points for every pipe section the flooz crosses, and loses points at the end of each level for any unused sections on the field. Bonus points can be scored for the following:
- Using more than the minimum number of pipe sections.
- Routing the flooz to cross itself in a four-way intersection. Doing so five times in a single level awards a large bonus.
- Filling reservoirs.
- Routing the flooz through pre-placed bonus pipes.
A bonus round is played after every fourth level, in which the player is presented with a grid of pipe sections that has one empty space. Clicking on a piece adjacent to this space will cause it to slide over; the goal is to build as long a pipeline as possible, scoring points for each section used. A password is given after each bonus round, allowing the player to start a game at the level immediately following it.
Reception
[edit]In Japan, Game Machine listed the arcade version of Pipe Mania as the most successful table arcade unit of October 1990.[2]
The game was reviewed in 1994 in Dragon #211 by Jay & Dee in the "Eye of the Monitor" column. Jay did not rate the game, but Dee gave the Macintosh version of the game 21⁄2 out of 5 stars, and the Windows version 41⁄2 stars.[3] Macworld named the Macintosh version of Pipe Dream the Best Arcade Game of 1990, putting it into the Macintosh Game Hall of Fame, and called it an "addictive strategy game".[4]
The editors of Game Player's PC Strategy Guide gave Pipe Dream their 1989 "Best PC Strategy Game" award. They wrote: "Pipe Dream is destined to become a classic on the order of Tetris or Breakout".[5]
Reviews
[edit]| Publication | Score |
|---|---|
| Electronic Gaming Monthly | 5/10, 7/10, 6/10, 7/10 (Game Boy)[6] |
| Publication | Award |
|---|---|
| Crash | Crash Smash |
| Sinclair User | SU Classic |
- Commodore Format (February 1993)[7]
- Computer and Video Games (February 1990)[8]
- Zero (March 1990)[9]
- ACE (Advanced Computer Entertainment) (January 1991)[10]
- ACE (Advanced Computer Entertainment) (April 1990)[11]
- Sinclair User (February 1993)[12]
- ACE (Advanced Computer Entertainment) (October 1990)[13]
- Your Sinclair (June 1990)[14]
- Crash! (June 1990)[15]
- Your Sinclair (January 1991)[16]
- The One (March 1990)[17]
- Zero (March 1991)[18]
- Crash! (January 1991)[19]
- Mean Machines (January 1991)[20]
- The Games Machine (UK) (June 1990)[21]
- Game Power (Brazil) (October 1992)[22]
- TOS-Magazin (May 1990)[23]
- VideoGame (July 1991)[24]
- Power Play (February 1990)[25]
- Video Games (October 1992)[26]
- ST Format (April 1990)[27]
- ASM (Aktueller Software Markt) (March 1990)[28]
- VideoGame (December 1991)[29]
Legacy
[edit]Many clones of Pipe Mania have been produced, under titles such as Wallpipe, Oilcap, Oilcap Pro, MacPipes, Pipe Master, Pipeworks, DragonSnot, PipeNightDreams, and Fun2Link. Many Nokia cell phones come with a free version of the game called Canal Control.[citation needed]
A version with 3D graphics was released for the PlayStation in 2000, titled Pipe Dreams 3D in the US and Pipe Mania 3D in the UK.
In September 2008, Empire Interactive released a remake of Pipe Mania for Windows, PlayStation 2, Nintendo DS, and PlayStation Portable.[30] It was developed by Razorworks.[31]
Within BioShock, a variation of the game exists as a means of hacking vending machines, robots, and cameras.[32]
References
[edit]- ^ "Games". Archived from the original on 2006-04-28.
- ^ "Game Machine's Best Hit Games 25 - テーブル型TVゲーム機 (Table Videos)". Game Machine (in Japanese). No. 391. Amusement Press, Inc. 1 November 1990. p. 25.
- ^ Jay; Dee (November 1994). "Eye of the Monitor" (PDF). Dragon. No. 211. p. 40. Retrieved September 3, 2021.
- ^ Levy, Steven (December 1990). "Game Hall of Fame". Macworld. International Data Group. p. 213. Retrieved September 3, 2021.
- ^ "Game Player's First Annual PC Game Awards 1989". Game Player's PC Strategy Guide. Vol. 3, no. 2. Signal Research. March–April 1990. p. 12. Retrieved September 3, 2021.
- ^ Harris, Steve; Semrad, Ed; Alessi, Martin; Sushi-X (November 1990). "Review Crew". Electronic Gaming Monthly. No. 16. p. 23. Retrieved February 10, 2026 – via Video Game History Foundation.
- ^ "Roger Frames". p. 49.
- ^ "CVG Magazine Issue 099". February 1990.
- ^ "Zero Magazine Issue 05". March 1990.
- ^ "ACE Magazine Issue 40". January 1991.
- ^ "ACE Magazine Issue 31". April 1990.
- ^ "Sinclair User Magazine Issue 132". February 1993.
- ^ "ACE Magazine Issue 37". October 1990.
- ^ "Your Sinclair Magazine Issue 54". June 1990.
- ^ "CRASH 77 - Pipe Mania".
- ^ "Your Sinclair Magazine Issue 61". January 1991.
- ^ "TheOne Magazine Issue 18". March 1990.
- ^ "Zero Magazine Issue 17". March 1991.
- ^ "Crash Magazine Issue 84". January 1991.
- ^ "Pipe Dream - Nintendo Gameboy - Mean Machines review". Archived from the original on 2020-01-08. Retrieved 2022-03-20.
- ^ "The Games Machine Issue 31".
- ^ "GamePower - Ano 1 No. 04 (1992-10) (Nova Cultural) (BR) (pt)". October 1992.
- ^ "TOS :05/1990 Pipe Mania: Denkspiel für Leitungsbauer". www.stcarchiv.de.
- ^ "VideoGame - Ano 1 Numero 05 (1991-07) (Sigla Editora) (BR) (pt)". July 1991.
- ^ "Kultpower.de - die Powerplay und ASM Fan Site".
- ^ "Pipe Dream (Super NES) - N.i.n.Retro (New is not Retro) v3+".
- ^ "Empire Pipe Mania" (PDF). p. 37.
- ^ "Kultboy.com - DIE Kult-Seite über die alten Spiele-Magazine und Retro-Games!". www.kultboy.com.
- ^ "VideoGame - Ano 1 Numero 09 (1991-12) (Sigla Editora) (BR) (pt)". December 1991.
- ^ "Pipe Mania 2008 remake website". Empire Interactive. 2008-09-03. Archived from the original on 2008-09-30. Retrieved 2008-09-03.
- ^ "Games". Razorworks. Empire Interactive. Archived from the original on 31 May 2010. Retrieved 23 January 2023.
- ^ Qualls, Eric. "BioShock Review (X360) at Xbox.about.com". About.com Tech. About.com. Archived from the original on 2007-08-29. Retrieved 2007-11-04.
External links
[edit]- KLOV entry for Pipe Dream
- Pipe Mania at SpectrumComputing.co.uk
Pipe Mania
View on GrokipediaDevelopment and release
Development
Pipe Mania was developed by The Assembly Line, a UK-based studio, initially for the Amiga platform. The game originated as an original design for the Amiga, with development leading to its 1989 release.[1] The core concept was created by designers Akila Redmer and Stephan L. Butler, who devised the real-time pipe-laying puzzle mechanic centered on connecting pipe segments to guide a flowing substance known as "flooz" through a grid.[2] This mechanic drew from real-world plumbing principles, requiring players to build pathways under time pressure to prevent overflow.[3] Initial prototyping occurred on Amiga hardware, emphasizing the simulation of fluid dynamics as the "flooz" animated through completed pipes after a delay.[1] The studio collaborated with Empire Interactive for the European release under the title Pipe Mania.[1] Lucasfilm Games acquired rights for North American distribution, adapting and porting the game while renaming it Pipe Dream.[4] Amiga and Atari ST versions were programmed by John Dale and Martin Day.[2] Technical development focused on optimizing the grid-based rendering system and timer mechanics to accommodate 1989 hardware constraints, ensuring smooth real-time piece placement and flow animation across targeted platforms.[2]Release and ports
Pipe Mania was initially released in June 1989 for the Amiga, Atari ST, and MS-DOS platforms. In Europe, it was published by Empire Interactive, while in North America, Lucasfilm Games handled distribution under the title Pipe Dream.[5] The game saw numerous ports between 1990 and 1992, expanding to a wide array of systems. These included the Amstrad CPC, Apple II, Apple IIgs, BBC Micro, Commodore 64, ZX Spectrum, Macintosh, Nintendo Entertainment System (NES, released September 1990 in North America), Game Boy (July 1990 in Japan, September 1990 in North America), PC-88, PC-98 (September 1991 in Japan), Sharp X68000 (November 1992 in Japan), and Super Famicom (August 7, 1992 in Japan), all primarily handled by Empire Interactive in Europe and Bullet-Proof Software or Lucasfilm Games in other regions.[5][6] Regional variations affected the game's title and presentation: it was titled Pipe Mania in Europe and Pipe Dream in North America and Japan. The 1990 arcade adaptation, developed and published by Video System Co., Ltd. in Japan, featured minor gameplay tweaks, such as requiring connections for a minimum number of pipe sections, and achieved notable popularity, appearing on Japanese arcade charts.[5][7][8] Marketing for the original release highlighted the game's addictive puzzle mechanics, often drawing comparisons to Tetris for its compulsive tile-placement challenges. Packaging included detailed instruction manuals with scoring strategies, such as maximizing points by creating loops and reservoirs before advancing levels, earning 50 points per pipe section up to the minimum required length and 100 points per extra section thereafter, with bonuses up to 1000 points for configurations like end pieces and reservoirs after the minimum, while advising players to plan ahead and minimize replacements to avoid penalties of 50 points each and 100 points per unused piece.[9][10] During its original run through the early 1990s, Pipe Mania received no major updates or expansions, though some ports like the DOS and Amiga versions incorporated minor bug fixes for stability.[1][11]| Platform | Release Year | Publisher (Region) |
|---|---|---|
| Amiga | 1989 | Empire Interactive (EU), Lucasfilm Games (NA) |
| Atari ST | 1989 | Empire Interactive (EU), Lucasfilm Games (NA) |
| MS-DOS | 1989 | Empire Interactive (EU), Lucasfilm Games (NA) |
| Macintosh | 1989 | Lucasfilm Games (NA) |
| Amstrad CPC | 1990 | Empire Interactive (EU) |
| Apple II | 1990 | Lucasfilm Games (NA) |
| Apple IIgs | 1990 | Lucasfilm Games (NA) |
| BBC Micro | 1990 | Empire Interactive (EU) |
| Commodore 64 | 1990 | Empire Interactive (EU), Lucasfilm Games (NA) |
| ZX Spectrum | 1990 | Empire Interactive (EU) |
| NES | 1990 | Bullet-Proof Software/Lucasfilm Games (NA) |
| Game Boy | 1990 | Bullet-Proof Software (JP/NA) |
| Arcade | 1990 | Video System (JP) |
| PC-98 | 1991 | Bullet-Proof Software (JP) |
| Super Famicom | 1992 | Bullet-Proof Software (JP) |
