Recent from talks
Nothing was collected or created yet.
Murex
View on Wikipedia
| Murex Temporal range:
| |
|---|---|
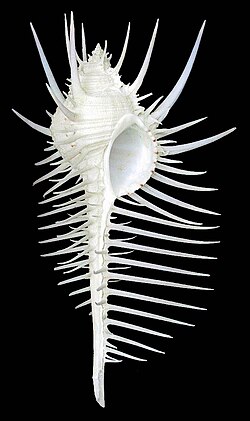
| |
| Apertural view of the shell of Venus comb murex, Murex pecten, anterior end towards the bottom of the page | |
| Scientific classification | |
| Kingdom: | Animalia |
| Phylum: | Mollusca |
| Class: | Gastropoda |
| Subclass: | Caenogastropoda |
| Order: | Neogastropoda |
| Family: | Muricidae |
| Subfamily: | Muricinae |
| Genus: | Murex Linnaeus, 1758 |
| Type species | |
| Murex tribulus Linnaeus, 1758 | |
| Synonyms[1] | |
| |
Murex is a genus of medium to large sized predatory tropical sea snails. These are carnivorous marine gastropod molluscs in the family Muricidae, commonly called "murexes" or "rock snails".[1]
The common name murex is still used for many species in the family Muricidae which were originally given the Latin generic name Murex, but have more recently been regrouped into newer genera. Murex was used in antiquity to describe spiny sea snails, especially those associated with the production of purple dye. Murex is one of the oldest classical seashell names still used by the scientific community.
Aristotle described these mollusks in his History of Animals using the Greek term πορφύρα (porphyra).[2]
Etymology
[edit]The term murex originates from the Latin word mūrex, likely related to the Greek word μύαξ (myax), meaning sea mussel. The connection between these terms suggests a shared linguistic root, possibly linked to the Greek word μῦς (mys), meaning "mouse," due to the perceived resemblance between the shape of certain mollusks and mice.[3]
Fossil records
[edit]This genus is known in the fossil records from the Cretaceous to the Quaternary (age range: from 125.45 to 0.0 million years ago). Fossils of species within this genus have been found all over the world. There are about 25 known extinct species.[4]


Distribution
[edit]Murex is solely an Indo-Pacific genus, as demonstrated by Ponder & Vokes (1988). The species from the western Atlantic that were formerly considered to belong to the genus Murex are now placed in the genus Haustellum.[citation needed]
Habitat
[edit]Most Murex species live in the intertidal or shallow subtidal zone, among rocks and corals.[citation needed]
Shell description
[edit]This genus includes many showy members, their elongate shells highly sculptured with spines or fronds. The inner surfaces of their ornate shells are often brightly colored.[citation needed]
Human use
[edit]Costly and labor-intensive dyes Tyrian purple (or "royal purple") and tekhelet were historically made by the ancient Phoenicians, using mucus from the hypobranchial gland of two species commonly referred to as "murex", Murex brandaris and Murex trunculus, which are the older names for Bolinus brandaris and Hexaplex trunculus.[5] This dye is a rare animal-produced organobromine compound, which the snails make using a specific bromide peroxidase enzyme that operates on dissolved bromide in sea water.[6]
This dye was used in royal robes, other kinds of special ceremonial or ritual garments, or garments indicating high rank. It is hypothesised that the dye was the same dye as that which featured prominently in the ancient Temple in Jerusalem, the clothing of the High Priest of Israel officiating there; it is sometimes still used by Jews today in the ritual fringes (tzitzit) on four-cornered garments.[7] A consensus has yet to be reached regarding the Biblical source of the "blue" dye, though the latest archeological research on dyes in this region indicates that it was indeed the Murex trunculus snail that was used for the ancient tekhelet dye.[8]
Species
[edit]The genus Murex, as originally defined by Linnaeus, encompassed many taxa that are now placed elsewhere in the superfamily Muricoidea. During the 19th century, the definition of Murex was restricted by Lamarck and his contemporaries first to species in the family Muricidae, and then was limited even further to the subfamilies Muricinae and Ocenebrinae. Malacologists of the 19th century including Kiener, Reeve, Küster & Kobelt and Sowerby treated all muricoid forms as belonging to Murex. This is the main reason why Murex has so many synonyms.
The World Register of Marine Species (WoRMS) lists the following species with accepted names within the genus Murex. The subgenera are considered alternate representations.[9]
- Murex acanthostephes Watson, 1883[10]
- Murex aduncospinosus G.B. Sowerby II, 1841:[11]
- Murex africanus Ponder & Vokes, 1988[12]
- Murex altispira Ponder & Vokes, 1988[13] Caltrop murex
- Murex antelmei Viader, 1938
- † Murex bonneti Cossmann, 1903
- Murex brevispina Lamarck, 1822 Short-spined murex
- † Murex camplytropis Tate, 1888
- Murex carbonnieri (Jousseaume, 1881)[14] Carbonnier's murex
- Murex concinnus Reeve, 1845[15]
- Murex coppingeri E. A. Smith, 1884[16]
- † Murex crassiliratus Tate, 1888
- Murex djarianensis Martin, 1895
- Murex djarianensis poppei[17] (synonym : Murex (Murex) poppei Houart, 1979)
- Murex echinodes Houart, 2011
- Murex falsitribulus Ponder & Vokes, 1988[18]
- Murex forskoehlio Röding, 1798[19]
- † Murex grooti H. M. Jenkins, 1864
- † Murex guppyi Ladd, 1977
- † Murex halli d'Archiac & Haime, 1854
- Murex huangi Houart, 2010
- Murex hystricosus Houart & Dharma, 2001[20]
- Murex indicus Houart, 2011
- † Murex irregularis Tate, 1888
- Murex kerslakae Ponder & Vokes, 1988[21]
- † Murex lyelli d'Archiac & Haime, 1854 (accepted > unreplaced junior homonym)
- Murex megapex Neubert, 1998[22]
- † Murex minutus R. M. Johnston, 1880
- † Murex nasongoensis Ladd, 1977
- † Murex noae Holten, 1802
- Murex occa G.B. Sowerby II, 1834[23] Harrowed murex
- † Murex paradoxicus H. M. Jenkins, 1864
- Murex pecten Lightfoot, 1786[24] ': Venus comb murex
- Murex philippinensis Parth, 1994[25]
- Murex protocrassus Houart, 1990
- Murex queenslandicus Ponder & Vokes, 1988[26]
- † Murex roemeri d'Archiac & Haime, 1854
- Murex salomonensis Parth, 1994[27]
- Murex scolopax Dillwyn, 1817[28] False venus comb, woodcock murex
- Murex somalicus Parth, 1990[29]
- Murex spectabilis Ponder & Vokes, 1988[30]
- Murex spicatus Ponder & Vokes, 1988[31]
- Murex spinastreptos Houart, 2010
- † Murex spinicosta Bronn, 1831
- Murex surinamensis Okutani, 1982[32]
- Murex suttipraneeae Gra-tes, 2023
- † Murex tchihatcheffi d'Archiac & Haime, 1854
- Murex tenuirostrum Lamarck, 1822[33]
- Murex ternispina Lamarck, 1822[34]
- Murex trapa Roding, 1798[35] Rare-spined murex
- Murex tribulus Linnaeus, 1758, 1758:[36] Caltrop murex
- Murex troscheli Lischke, 1868[37] Troschel's murex
- Species mentioned as species in current use in the Indo-Pacific Molluscan Database (OBIS)
- Murex singaporensis A.Adams, 1853[38]
- Species brought into synonymy
- Murex aedonius Watson, 1896:[39] synonym of Coralliophila aedonia (Watson, 1885)
- Murex afer Gmelin, 1791: synonym of Afer afer (Gmelin, 1791)
- Murex alocatus: synonym of Pterymarchia barclayana (H. Adams, 1873)
- Murex antillarum : Antilles murex: synonym of Siratus articulatus (Reeve, 1845)
- Murex argo Clench & Farfante, 1945:[40] synonym of Chicoreus (Triplex) spectrum (Reeve, 1846)
- Murex belcheri Hinds, 1843 : synonym of Forreria belcheri (Hinds, 1843)
- Murex bellus Reeve, 1845: synonym of Vokesimurex bellus (Reeve, 1845)
- Murex blakeanus Vokes, 1967:[41] synonym of Vokesimurex blakeanus (Vokes, 1967)
- Murex brandaris Linnaeus, 1758: synonym of Bolinus brandaris (Linnaeus, 1758)
- Murex canaliculatus Linnaeus, 1758: synonym of Busycotypus canaliculatus (Linnaeus, 1758)
- Murex capitellum Linnaeus, 1758: synonym of Vasum capitellum (Linnaeus, 1758)
- Murex corallinus Scacchi, 1836: synonym of Ocinebrina aciculata (Lamarck, 1822)
- Murex corneus Linnaeus, 1758: synonym of Euthria cornea (Linnaeus, 1758)
- Murex coronatus Born, 1778: synonym of Pseudovertagus aluco (Linnaeus, 1758)
- Murex edwardsii:[42] synonym of Ocinebrina edwardsii (Payraudeau, 1826)
- Murex garciai Petuch, 1987: synonym of Vokesimurex garciai (Petuch, 1987)
- Murex gubbi Reeve, 1849:[43] synonym of Chicocenebra gubbi (Reeve, 1849)
- Murex inconspicuus G.B. Sowerby II, 1841: synonym of Ocinebrina aciculata (Lamarck, 1822)
- Murex intertextus Helbling, 1779:[44] synonym of Cumia reticulata
- Murex jickelii Tapparone Canefri, 1875: synonym of Naquetia jickelii (Tapparone Canefri, 1875)
- Murex lindajoycae Petuch, 1987: synonym of Vokesimurex lindajoycae (Petuch, 1987)
- Murex longicornis Dunker, 1864: synonym of Chicoreus longicornis (Dunker, 1864)
- Murex maroccensis Gmelin, 1791:[45] synonym of Fusinus maroccensis
- Murex monodon Sowerby, 1825:[46] synonym of Chicoreus (Chicoreus) cornucervi (Röding, 1798)
- Murex nassa Gmelin, 1791:[47] synonym of Leucozonia nassa (Gmelin, 1791)
- Murex nebula Montagu, 1803: synonym of Bela nebula (Montagu, 1803)
- Murex peritus Hinds, 1844a:[48] synonym of Favartia (Favartia) perita (Hinds, 1844)
- Murex pistacia Reeve, 1845: synonym of Ocinebrina aciculata (Lamarck, 1822)
- Murex purpuroides Dunker:[49] synonym of Vaughtia purpuroides (Reeve, 1845)
- Murex recurvirostris:[50] synonym of Vokesimurex recurvirostrum (Broderip, 1833)
- Murex rota Sowerby:[51] synonym of Homalocantha anatomica (Perry, 1811)
- Murex rubidus:[52] synonym of Vokesimurex rubidus (F.C. Baker, 1897)
- Murex serratospinosus Dunker, 1883: synonym of Vokesimurex mindanaoensis (G.B. Sowerby II, 1841)
- Murex subaciculatus Locard, 1886: synonym of Ocinebrina aciculata (Lamarck, 1822)
- Murex taxus Dillwyn, 1817: synonym of Clavatula taxea (Röding, 1798)
- † Murex textilis Brocchi, 1814:[53] synonym of † Rimosodaphnella textilis (Brocchi, 1814)
- Murex triqueter:[54] synonym of Naquetia triqueter (Born, 1778)
- Murex tulipa Linnaeus, 1758:[55] synonym of Fasciolaria tulipa (Linnaeus, 1758)
- Murex turbinellus Linnaeus, 1758: synonym of Vasum turbinellus (Linnaeus, 1758)
- Murex vittatus Broderip, 1833:[56] synonym of Favartia (Favartia) vittata (Broderip, 1833)
References
[edit]- ^ a b Houart, R.; Gofas, S. (2010). Murex Linnaeus, 1758. In: Bouchet, P.; Gofas, S.; Rosenberg, G. (2010) World Marine Mollusca database. Accessed through: World Register of Marine Species at http://www.marinespecies.org/aphia.php?p=taxdetails&id=138196 on 2011-04-09
- ^ Aristotle. (1902). History of animals in ten books. London: G. Bell.
- ^ "murex | Etymology of murex by etymonline". www.etymonline.com. Retrieved 28 November 2024.
- ^ Fossilworks
- ^ Sukenik, Naama; Iluz, David; Amar, Zohar; Varvak, Alexander; Shamir, Orit; Ben-Yosef, Erez (2021). "Early evidence of royal purple dyed textile from Timna Valley (Israel)". PLOS ONE. 16 (1) e0245897. Bibcode:2021PLoSO..1645897S. doi:10.1371/journal.pone.0245897. PMC 7842898. PMID 33507987.
- ^ Jannun R., Nuwayhid N. and Coe E. (1981) Biological bromination – bromoperoxidase activity in the Murex sea-snail. FASEB. J. 40, 1774.
- ^ Tekhelet - Biblical Blue Dye for Tzitzit
- ^ Newman, Marissa. "Linking ancient snails to an Israeli flag in space, a common thread". The Times of Israel. ISSN 0040-7909. Retrieved 2 February 2025.
- ^ WoRMS : Murex 23 December 2010
- ^ Murex acanthostephes Watson, 1883. Retrieved through: World Register of Marine Species on 25 April 2010.
- ^ ^Houart, R. (2009). Murex aduncospinosus Sowerby, 1841. Accessed through: World Register of Marine Species at http://www.marinespecies.org/aphia.php?p=taxdetails&id=215644 on 2010-08-06
- ^ Murex africanus Ponder & Vokes, 1988. Retrieved through: World Register of Marine Species on 25 April 2010.
- ^ Murex altispira Ponder & Vokes, 1988. Retrieved through: World Register of Marine Species on 25 April 2010.
- ^ Murex carbonnieri (Jousseaume, 1881). Retrieved through: World Register of Marine Species on 25 April 2010.
- ^ Murex concinnus Reeve, 1845. Retrieved through: World Register of Marine Species on 25 April 2010.
- ^ Murex coppingeri E. A. Smith, 1884. Retrieved through: World Register of Marine Species on 25 April 2010.
- ^ Houart, R. (2009). Murex djarianensis poppei Houart, 1979. Accessed through the World Register of Marine Species at http://www.marinespecies.org/aphia.php?p=taxdetails&id=404977 on 2010-08-06
- ^ Murex falsitribulus Ponder & Vokes, 1988. Retrieved through: World Register of Marine Species on 25 April 2010.
- ^ Murex forskoehli Röding, 1798. Retrieved through: World Register of Marine Species on 25 April 2010.
- ^ Murex hystricosus Houart & Dharma, 2001. Retrieved through: World Register of Marine Species on 25 April 2010.
- ^ Murex kerslakae Ponder & Vokes, 1988. Retrieved through: World Register of Marine Species on 25 April 2010.
- ^ Murex megapex Neubert, 1998. Retrieved through: World Register of Marine Species on 25 April 2010.
- ^ Murex occa Sowerby, 1834. Retrieved through: World Register of Marine Species on 25 April 2010.
- ^ Murex pecten Lightfoot, 1786. Retrieved through: World Register of Marine Species on 25 April 2010.
- ^ Murex philippinensis Parth, 1994. Retrieved through: World Register of Marine Species on 25 April 2010.
- ^ Murex queenslandicus Ponder & Vokes, 1988. Retrieved through: World Register of Marine Species on 25 April 2010.
- ^ Murex salomonensis Parth, 1994. Retrieved through: World Register of Marine Species on 25 April 2010.
- ^ Murex scolopax Dillwyn, 1817. Retrieved through: World Register of Marine Species on 25 April 2010.
- ^ Murex somalicus Parth, 1990. Retrieved through: World Register of Marine Species on 25 April 2010.
- ^ Murex spectabilis Ponder & Vokes, 1988. Retrieved through: World Register of Marine Species on 25 April 2010.
- ^ Murex spicatus Ponder & Vokes, 1988. Retrieved through: World Register of Marine Species on 25 April 2010.
- ^ Murex surinamensis Okutani, 1982. Retrieved through: World Register of Marine Species on 25 April 2010.
- ^ Murex tenuirostrum Lamarck, 1822. Retrieved through: World Register of Marine Species on 25 April 2010.
- ^ Murex ternispina Lamarck, 1822. Retrieved through: World Register of Marine Species on 25 April 2010.
- ^ Murex trapa Roding, 1798. Retrieved through: World Register of Marine Species on 25 April 2010.
- ^ Murex tribulus Linnaeus, 1758. Retrieved through: World Register of Marine Species on 25 April 2010.
- ^ Murex troscheli Lischke, 1868. Retrieved through: World Register of Marine Species on 25 April 2010.
- ^ Indo-Pacific Molluscan Database : Murex (Murex) singaporensis
- ^ Murex aedonius Watson, 1896. Retrieved through: World Register of Marine Species on 25 April 2010.
- ^ Murex argo Clench & Farfante, 1945. Retrieved through: World Register of Marine Species on 25 April 2010.
- ^ Murex blakeanus Vokes, 1967. Retrieved through: World Register of Marine Species on 25 April 2010.
- ^ Murex edwardsi. Retrieved through: World Register of Marine Species on 25 April 2010.
- ^ Murex gubbi Reeve, 1849. Retrieved through: World Register of Marine Species on 25 April 2010.
- ^ Murex intertextus Helbling, 1779. Retrieved through: World Register of Marine Species on 25 April 2010.
- ^ Murex maroccensis Gmelin, 1791. Retrieved through: World Register of Marine Species on 25 April 2010.
- ^ Murex monodon Sowerby, 1841. Retrieved through: World Register of Marine Species on 25 April 2010.
- ^ Murex nassa Gmelin, 1791. Retrieved through: World Register of Marine Species on 25 April 2010.
- ^ Murex peritus Hinds, 1844a. Retrieved through: World Register of Marine Species on 25 April 2010.
- ^ Murex purpuroides Dunker. Retrieved through: World Register of Marine Species on 25 April 2010.
- ^ Murex recurvirostris. Retrieved through: World Register of Marine Species on 25 April 2010.
- ^ Murex rota Sowerby. Retrieved through: World Register of Marine Species on 25 April 2010.
- ^ Murex rubidus. Retrieved through: World Register of Marine Species on 25 April 2010.
- ^ Murex textilis Gabb, 1873. Retrieved through: World Register of Marine Species on 25 April 2010.
- ^ Murex triqueter. Retrieved through: World Register of Marine Species on 25 April 2010.
- ^ Murex tulipa Linnaeus, 1758. Retrieved through: World Register of Marine Species on 25 April 2010.
- ^ Murex vittatus Broderip, 1833. Retrieved through: World Register of Marine Species on 25 April 2010.
- Merle, D., Garrigues, B. & Pointier, J.-P. 2011. Fossil and Recent Muricidae of the World, Part Muricinae. 648 pp., 182 colour plates, Hackenheim. ISBN 978-3-939767-32-9.
- Ponder, W.F. & E.H. Vokes. 1988. A revision of the Indo-West Pacific fossil and Recent species of Murex s.s. and Haustellum (Mollusca: Gastropoda: Muricidae). Records of the Australian Museum, Supplement 8. 160 pp.
External links
[edit]Murex
View on GrokipediaEtymology and Taxonomy
Etymology
The genus name Murex derives from the Latin mūrex, referring to a shellfish or sea mussel valued for producing purple dye, with possible roots in the Greek myax (μύαξ), denoting a type of mussel or similar marine mollusk.[4][5] This etymological link highlights the ancient association of these spiny gastropods with their glandular secretions used in dyeing, rather than a direct reference to their physical spines.[6] In ancient Roman literature, the term mūrex appears prominently in Pliny the Elder's Natural History (circa 77 CE), where he describes the murex as a predatory sea snail with a "famous flower of purple" located in its throat, used to extract the coveted Tyrian purple dye for textiles.[7] Pliny distinguishes the murex from related snails like the buccinum and purpura, noting their spiny shells and the labor-intensive process of harvesting their hypobranchial glands to obtain the dye, which underscores the term's early connotation of economic and cultural significance.[8] In modern taxonomy, the term Murex, established by Carl Linnaeus in 1758 as the type genus of the family Muricidae, has evolved to denote a more restricted group of Indo-Pacific predatory gastropods characterized by elaborate, spinose shells, distinguishing it from related genera such as Chicoreus or Hexaplex through phylogenetic revisions based on molecular and morphological data.[9][10] This refinement, beginning in the 19th century and accelerating with 20th-century cladistic analyses, has led to the reclassification of many species originally placed in Murex into numerous other genera within Muricidae (over 200 genera total in the family), preserving the name for 38 valid extant species while emphasizing its role in superfamily Muricoidea.[11][12]Taxonomy and Classification
The genus Murex belongs to the phylum Mollusca, class Gastropoda, subclass Caenogastropoda, order Neogastropoda, superfamily Muricoidea, family Muricidae, and subfamily Muricinae.[13] This placement reflects its status as a carnivorous marine gastropod characterized by spiny, club-shaped shells adapted for predatory lifestyles in tropical and subtropical waters. According to the World Register of Marine Species (WoRMS), Murex Linnaeus, 1758, remains an accepted genus as of November 2025, encompassing 38 valid extant species primarily distributed in the Indo-West Pacific region.[11] The type species is Murex tribulus Linnaeus, 1758, designated by subsequent monotypy following the original description by Linnaeus.[13] WoRMS maintains this classification based on integrated morphological and molecular evidence, ensuring consistency with the International Code of Zoological Nomenclature, including recent additions such as Murex maresinensis described in 2025.[14] Key taxonomic revisions have refined the boundaries of Murex sensu stricto (Murex s.s.), particularly in the Western Atlantic, where several species formerly assigned to Murex were transferred to the genus Haustellum Schumacher, 1817, due to differences in shell morphology such as axial spine arrangement and varical processes.[15] This separation was further supported by molecular phylogenetic analyses, which demonstrated that Atlantic Haustellum species form a distinct clade separate from the Indo-Pacific core Murex group, resolving polyphyly in earlier classifications. These revisions emphasize the role of combined morphological and genetic data in stabilizing muricid taxonomy.Evolutionary History
Fossil Record
The fossil record of the genus Murex begins in the Early Cretaceous period, approximately 125 million years ago, and extends through the Paleogene, Neogene, and into the Quaternary period up to the present day.[16] This temporal span reflects the genus's persistence as a component of marine gastropod faunas in tropical and subtropical environments, with fossils primarily consisting of well-preserved shells that retain diagnostic features such as elongated siphonal canals and prominent varices.[17] The preserved morphologies often exhibit the characteristic spiny or frilled outer lips and axial ribs typical of modern Murex species, providing evidence of morphological stasis over millions of years despite environmental changes.[18] Numerous extinct species have been documented within the genus, with key taxonomic revisions recognizing at least several dozen fossil taxa worldwide, though exact counts vary due to ongoing reclassifications within the Muricidae family.[19] Major discoveries occur in Indo-Pacific sediments, where diverse assemblages highlight the region's role as a center of muricid diversification during the Cenozoic.[20] For instance, Murex trapa represents an extinct species from Pliocene deposits in Java, featuring robust shells with pronounced spines adapted for rocky substrates.[20] Key fossil sites are associated with ancient Tethyan marine deposits, including Eocene formations in the Paris Basin of France, where early Murex-like forms show buccinoid shells with developing spiral sculpture, and Miocene strata in Florida's Alum Bluff Group, yielding species like M. chipolanus with elongated, thorned whorls.[18] Additional significant localities include Early Pleistocene sediments in Timor and various Western Pacific islands, where fossils preserve intricate shell ornamentation indicative of predatory adaptations in shallow-water habitats.[21] These sites underscore the genus's broad paleogeographic distribution across ancient seaways connecting Europe, Africa, and Asia.Phylogenetic Relationships
The genus Murex occupies a distinct position within the family Muricidae, specifically in the subfamily Muricinae, which molecular phylogenies have consistently recovered as monophyletic. Within Muricinae, Murex forms part of the core clade alongside genera such as Chicoreus, from which it diverged during the Eocene-Oligocene boundary, approximately 34 million years ago, based on time-calibrated analyses integrating molecular data and fossil constraints.[22] This divergence is supported by Bayesian inference of multi-locus datasets, highlighting Murex as sister to other muricine lineages rather than basal within the subfamily.[23] Phylogenetic reconstructions combining DNA sequences with the fossil record indicate that the Muricidae family originated in the late Cretaceous, around 80 million years ago, with early diversification centered in the Indo-Pacific region, where the highest species diversity persists today.[22] For Murex specifically, fossil calibrations from species like Murex trapa (Pliocene, approximately 5.3–0.01 million years ago) align with molecular estimates placing genus-level radiation in the Paleogene, integrating paleontological evidence of Indo-Pacific dominance to refine divergence timelines across the family tree.[22] Recent mitogenomic studies from the 2020s, including analyses of complete mitochondrial genomes from 24 muricid species, have further confirmed the monophyly of Murex and Muricinae using maximum likelihood and Bayesian methods, with strong posterior probabilities (PP > 0.95). These post-2021 investigations reveal deep splits between Indo-Pacific Murex lineages and Atlantic representatives in related clades, such as Ergalataxinae, where Atlantic taxa like Morula nodulosa form basal sisters to predominantly Indo-Pacific groups, underscoring vicariant events shaping trans-oceanic distributions.Description and Biology
Shell Description
The shells of the genus Murex exhibit an elongate fusiform shape, characterized by a high spire and an overall spindle-like form that tapers toward the base. This morphology typically results in shells measuring 50 to 200 mm in length, though most species fall within the 5 to 20 cm range, with the body whorl dominating the overall profile. The aperture is ovate and often lacks a pronounced outer lip, contributing to the shell's streamlined yet robust appearance.[24] Ornamentation is a hallmark of Murex shells, featuring highly variable and elaborate sculpture that distinguishes the genus within the Muricidae family. Early teleoconch whorls bear 9 to 14 angulate or rounded axial ribs, with every third rib developing into a thickened varix that supports 3 primary spines—simple and non-ramose, often directed apically or recurved. These varices form prominent, long spines along the shoulder, periphery, and base, while spiral cords interlace the surface in primary, secondary, and tertiary threads, creating a textured, frilled effect. The siphonal canal extends dramatically, frequently equaling or exceeding the combined length of the spire and aperture, and is adorned with 5 to 12 recurved spines that enhance the shell's defensive profile.[24][25] Coloration in Murex shells varies across species but generally includes external patterns of creamy white to tan bases overlaid with golden brown, reddish-brown, or purple markings along the cords, spines, and interspaces. For instance, species like Bolinus brandaris (formerly Murex brandaris) display intense pinks and purples externally, while others show subtler brown hues. Internally, the aperture reveals a bright white or lilac ground, often with brown spots or lines, and exhibits purple iridescence attributable to the nacreous layer lining the shell. This mother-of-pearl structure provides a lustrous, reflective quality that contrasts sharply with the ornate exterior.[24][26][27]Anatomy and Physiology
Murex snails, as members of the Muricidae family, possess a specialized feeding apparatus adapted for predation on bivalves and other mollusks. The radula, a chitinous ribbon-like structure with rows of teeth, is used in conjunction with an accessory boring organ to drill holes into prey shells, often aided by enzymatic dissolution from the ventral pedal gland. Once the shell is breached, the extensible proboscis, a muscular extension of the mouth, is inserted to inject salivary secretions containing proteolytic enzymes and toxins that liquefy and paralyze the prey's tissues, facilitating external digestion and nutrient absorption.[28] The glandular systems of Murex are notable for their production of bioactive compounds, particularly in the hypobranchial gland, a ductless structure located along the inner mantle wall. This gland secretes precursors such as tyrindoxyl sulfate and 6-bromoisatin, which are stored separately from the enzyme purpurase to prevent premature reaction; upon exposure to air and light, purpurase hydrolyzes the precursors into indoxyl derivatives that oxidize to form indigotin (indigo) and brominated compounds like 6,6'-dibromoindigo, the primary component of Tyrian purple. In dye-producing species such as Bolinus brandaris, these pigments constitute 77-91% 6,6'-dibromoindigo, with minor amounts of 6-bromoindigo (1-16%) and 6,6'-dibromoindirubin (1-14%); Hexaplex trunculus (formerly M. trunculus) produces a more variable composition including non-brominated pigments (e.g., 3-76% dibromoindigo). These compounds serve potential roles in chemical defense or signaling.[29] Respiratory and circulatory systems in Murex are typical of prosobranch gastropods, optimized for the fluctuating oxygen levels of intertidal habitats. The mantle cavity, positioned anteriorly and housing paired ctenidia (comb-like gills), facilitates gas exchange through a unidirectional water current drawn in via the inhalant siphon and expelled through the exhalant siphon, allowing efficient oxygen uptake even during partial emersion. An open circulatory system circulates hemocyanin-rich hemolymph from a central heart (with auricle and ventricle) through sinuses and the gills for oxygenation, supporting tolerance to low-oxygen conditions by enabling aerial respiration when submerged gills trap air bubbles.[30]Life Cycle and Reproduction
Murex species are dioecious, with distinct male and female individuals exhibiting separate reproductive systems.[31] Internal fertilization takes place through the transfer of spermatophores from males to females during copulation, allowing sperm storage in the female's seminal receptacle for extended periods.[32] Following fertilization, females deposit eggs within protective gelatinous capsules, often in clusters attached to firm substrates like rocks or conspecific shells to ensure stability during development.[33] These capsules vary in shape and size across species and can collectively hold hundreds to thousands of eggs per cluster, with individual capsules containing dozens to hundreds of eggs. Intracapsular development occurs over approximately 3–4 weeks, during which embryos progress through stages including trochophore and veliger, nourished by yolk and nurse eggs within the capsule. Most species hatch as benthic juveniles without a free-swimming planktonic stage, though veligers may develop intracapsularly (e.g., in B. brandaris, hatching as crawlers after ~22 days at 25°C). Juveniles then undergo benthic growth, reaching sexual maturity in 1–2 years at shell lengths of 55–65 mm, as observed in B. brandaris.[31][33][34] This rapid post-metamorphic growth phase supports annual reproductive cycles in many species, synchronized with seasonal temperature rises.[33]Distribution and Habitat
Geographic Distribution
The genus Murex exhibits a primary distribution across the Indo-Pacific oceans, extending eastward from the Red Sea and the East African coast across the Indian Ocean to the remote islands of the Pacific Ocean, such as those in the Coral Sea and beyond.[19][1] This range encompasses tropical and subtropical waters, where species are typically found in shallow to moderate depths up to several hundred meters.[35] Notable endemic hotspots for Murex occur within the Coral Triangle, a marine biodiversity center spanning Indonesia, the Philippines, Papua New Guinea, and adjacent regions, where elevated species richness reflects historical accumulation of diversity. The genus is absent from the Atlantic Ocean, owing to taxonomic reclassifications that have reassigned former Atlantic Murex species—such as those previously identified as M. brandaris—to distinct genera like Bolinus or Hexaplex.[23] Speciation patterns in Murex are closely tied to Indo-Pacific oceanographic dynamics, including prevailing currents like the Indonesian Throughflow and monsoon-driven circulations, which facilitate larval dispersal while promoting isolation in fragmented island archipelagos and semi-enclosed seas. These processes have contributed to the diversification of approximately 38 living species currently accepted in the genus.[23][1]Preferred Habitats
Murex species, belonging to the family Muricidae, primarily occupy intertidal to shallow subtidal zones, favoring rocky or coral reef substrates that provide structural complexity.[36] These environments support their predatory lifestyle by offering ample surfaces for attachment and hunting.[37] Within these zones, Murex individuals show a strong preference for crevices in rocks or rubble, as well as algae-covered surfaces, which aid in camouflage to evade predators and allow close proximity to prey such as bivalves lodged in the substrate.[38] Algal encrustations on their shells further enhance this blending with the surroundings, particularly in coral reef settings.[38] Murex gastropods demonstrate tolerance to salinity fluctuations typical of intertidal areas, as well as temperature ranges of approximately 18–29°C in their predominantly tropical and subtropical distributions.[35]Ecology
Diet and Predation
Murex species, belonging to the family Muricidae, are carnivorous predators with a diet primarily consisting of bivalve mollusks and barnacles.[39] They preferentially target live prey, though some species also consume carrion or encrusting organisms like bryozoans when available.[39] For example, the giant eastern murex (Muricanthus fulvescens, sometimes classified under Murex) preys on bivalves at a laboratory rate of approximately 3.5 per week.[40] This diet supports their role as active hunters in marine environments, where they employ specialized feeding mechanisms to subdue and digest shelled prey. The hunting strategy of Murex involves a combination of mechanical and chemical methods to access prey. Predators use their radula to drill beveled holes into the shells of bivalves and barnacles, often at the margin or randomly, while the accessory boring organ secretes a mixture of acids, enzymes, and chelating agents to dissolve shell material.[39] Once the shell is penetrated, the extensible proboscis is inserted to inject paralytic agents, such as urocanoylcholine from the hypobranchial gland, which immobilize the prey, followed by enzymatic digestion of soft tissues via salivary glands containing proteolytic enzymes like trypsin-like proteases.[39] This process can take several hours, with borehole excavation in muricids averaging around 73 hours, as observed in related species like Nucella lapillus.[39] The radula and proboscis, as key anatomical features, enable precise rasping and fluid delivery during feeding.[39] Foraging behavior in Murex involves emerging from rocky crevices or substrates to locate prey using chemoreceptive cues. They actively search for suitable targets, often selecting smaller or more vulnerable individuals, and exhibit size-dependent prey choice.[39] Daily consumption rates vary by species and environmental conditions but generally range from 1 to 2 prey items, as observed in muricids like Rapana venosa, which averages 1.45 mussels per day under laboratory conditions equivalent to natural temperatures.[41] This rate corresponds to approximately 5-12% of the predator's tissue wet weight, ensuring efficient energy intake without excessive risk exposure.[41]Ecological Role
Murex snails, belonging to the family Muricidae, serve as significant predators in marine benthic ecosystems, primarily targeting bivalves, barnacles, and other invertebrates, which helps regulate prey populations and maintain community structure.[42] By exerting top-down control on these sessile organisms, muricids prevent excessive dominance of filter-feeding bivalves that could otherwise alter habitat availability for other species on rocky substrates and reefs.[43] Their predatory activities contribute to overall biodiversity by promoting a balanced trophic structure, as evidenced in intertidal and subtidal zones where muricid predation influences the dynamics of associated invertebrate assemblages.[44] In addition to predation, Murex species engage in interactions that enhance ecosystem complexity. For instance, certain muricids exhibit commensal relationships through inquilinism, where they inhabit the shells of larger gastropods without harming the host, thereby utilizing available shelter while contributing to microhabitat diversity.[45] These associations underscore the role of Muricidae in facilitating indirect ecological linkages among benthic species. Muricids also play a part in nutrient cycling within marine environments, particularly through scavenging behaviors observed in species like Phyllonotus oculatus. By consuming carrion and organic debris on reefs, these gastropods facilitate the decomposition and redistribution of nutrients, supporting primary production and energy flow in coastal ecosystems.[44] However, anthropogenic pressures pose substantial threats to Murex populations, with overfishing and habitat degradation leading to declines that disrupt reef biodiversity. Studies from the 2020s indicate range contractions and population reductions in Mediterranean muricids such as Hexaplex trunculus and Bolinus brandaris (formerly Murex brandaris), attributed to intensive harvesting and environmental changes, resulting in diminished predatory control and cascading effects on bivalve-dominated communities.[46][47] In the Levant region, overfishing has exacerbated these declines, altering benthic community composition and reducing overall ecosystem resilience.[48]Human Use and Conservation
Historical and Cultural Significance
The production of Tyrian purple, a renowned dye derived from the hypobranchial glands of the sea snails Bolinus brandaris (formerly Murex brandaris) and the related muricid Hexaplex trunculus, originated with the Phoenicians around 1200 BCE in the city of Tyre and spread throughout the Mediterranean during the Roman era.[49] The labor-intensive process involved extracting the snails' mucous secretions, fermenting them for several days, and then boiling the mixture to yield the vibrant purple pigment, which was highly prized for its fastness and imperial hue.[50] To produce just one gram of the dye, approximately 10,000 snails were required, underscoring the scale of exploitation and the economic value of coastal murex populations.[50] In ancient societies, Tyrian purple held profound cultural symbolism as a marker of royalty, divinity, and authority, reserved for elite garments and sacred textiles. Phoenician and Roman elites dyed luxurious robes and sails—such as those of Cleopatra's barge—in this color, while Roman law in 301 CE valued it at over three times the price of gold by weight.[50] In biblical contexts, a variant known as tekhelet, a blue-purple shade from H. trunculus, was mandated for the priestly robes and fringes of the Tabernacle, symbolizing holiness and divine covenant as described in Exodus.[51] The dye's trade fueled Phoenician maritime networks, extending from the Levant ports of Tyre and Sidon across the Mediterranean to North Africa, Spain, and beyond, establishing economic dominance through controlled production and export.[52] Production of Tyrian purple declined sharply after the fall of Constantinople in 1453 CE, exacerbated by overharvesting of murex snails and the eventual rise of synthetic aniline dyes in the mid-19th century, which rendered the natural process obsolete.[50] Archaeological evidence from sites like Tel Dor in Israel reveals remnants of this industry, including heaps of crushed murex shells, dye-stained pottery, and processing pits dating to the Persian and Hellenistic periods, confirming localized workshops that supported regional trade.[53] These findings highlight the environmental toll and the dye's integral role in ancient Levantine economies.[53]Modern Uses and Conservation Status
In modern times, harvesting of Murex species occurs on a limited scale for artisanal production of Tyrian purple dye, primarily through extraction from snail glands in small-scale operations inspired by ancient techniques, as demonstrated by enthusiasts in Tunisia who produce the dye for textiles and artistic applications. [54] The resulting pigment, valued for its historical significance, finds niche use in cosmetics and high-end fabric dyeing, though commercial production remains rare due to the labor-intensive process requiring thousands of snails per gram. [55] Murex shells are also collected for crafts and jewelry, particularly in coastal regions like Indonesia, where species such as Murex pecten are fashioned into decorative items and sold through local markets and online platforms. In some areas, shell harvesting supports tourist-oriented crafts using marine shells. Conservation efforts for Murex face challenges from incidental capture as bycatch in bottom-trawl and trap fisheries targeting other marine species, which can lead to population declines in heavily fished areas, though direct impacts vary by region and gear type. [56] Most Murex species are classified as Data Deficient or Not Evaluated on the IUCN Red List, indicating a need for further assessment of threats like overexploitation, habitat degradation, and international shell trade. [1] For example, Bolinus brandaris (formerly M. brandaris) is Not Evaluated. [57] In the Indo-Pacific, 2025 expansions of marine protected areas (MPAs), including 200,000 hectares of new conservation zones in Indonesia, incorporate regulations to limit fishing activities and protect benthic habitats where Murex reside, aiming to reduce bycatch and support biodiversity. [58] Recent research emphasizes sustainable aquaculture and ecological restoration to mitigate harvesting pressures. Studies on Bolinus brandaris growth in semi-intensive earthen ponds have demonstrated feasible rearing rates, offering a potential alternative to wild capture for food and shell production. [59] Post-2021 investigations into population genetics provide molecular markers for assessing genetic diversity and informing conservation strategies against fragmentation in exploited populations. These efforts highlight the role of genetic data in restoration projects, such as restocking initiatives in degraded coastal ecosystems.Diversity
Accepted Species
The genus Murex comprises 38 accepted species as of 2025, according to the World Register of Marine Species (WoRMS), all of which are predatory marine gastropods in the family Muricidae, predominantly found in tropical and subtropical waters.[1] These species are distinguished by their robust, fusiform shells featuring prominent varices armed with spines, long siphonal canals, and apertures often bordered by tooth-like processes, with adult sizes typically ranging from 5 to 15 cm in length. Shell coloration varies from white or cream to brown or purple tones, adapted for camouflage on coral reefs and rocky substrates. Molecular studies have validated several taxa within this strict sense of the genus, refining boundaries from broader historical classifications.[1] While comprehensive morphological details are available for core species, the following table enumerates all accepted species with their authorship, key shell traits (focusing on distinctive features where documented), and distribution summaries, drawing from taxonomic authorities. Representative examples highlight variations in spine development and regional endemism.| Species Name | Author and Year | Key Shell Traits | Distribution |
|---|---|---|---|
| Murex acanthostephes | R. B. Watson, 1883 | Heavy shell with prominent, curved spines on varices; size up to 10 cm. | Indo-Pacific (e.g., Philippines to Australia).[1] |
| Murex aduncospinosus | G. B. Sowerby II, 1841 | Short, bent spines on three strong varices per whorl; ovate body whorl; size 5–12 cm, cream to brown. | Indo-Pacific (Andaman Sea to Japan and Queensland, Australia).[60][61] |
| Murex africanus | Ponder & E. H. Vokes, 1988 | Slender spines and elongated siphonal canal; size ~8 cm. | West Africa (Gulf of Guinea).[1] |
| Murex altispira | Ponder & E. H. Vokes, 1988 | High-spired with fine, radiating spines; size 6–9 cm. | Indo-Pacific (Australia).[1] |
| Murex antelmei | Viader, 1938 | Moderate spines on varices; fusiform outline; size up to 10 cm. | Indo-Pacific (Madagascar to Indonesia).[1] |
| Murex brevispina | Lamarck, 1822 | Short, blunt spines; broad body whorl; size 7–11 cm. | Indo-Pacific (Indian Ocean to western Pacific).[1] |
| Murex carbonnieri | Jousseaume, 1881 | Robust with three-winged varices bearing short spines; size ~10 cm. | Indo-Pacific (Red Sea to Philippines).[1] |
| Murex concinnus | Reeve, 1845 | Delicate, curved spines; slender form; size 6–10 cm. | Indo-Pacific (East Africa to Japan).[1] |
| Murex coppingeri | E. A. Smith, 1884 | Prominent axial spines; size up to 12 cm. | Indo-Pacific (Australia and Pacific islands).[1] |
| Murex djarianensis | K. Martin, 1895 | Short spines and nodulose shoulder; size ~8 cm. | Indonesia (Java Sea).[1] |
| Murex echinodes | Houart, 2011 | Echinulate (spiny) varices with hedgehog-like projections; size 7–10 cm; recent addition validated by morphological analysis. | Indo-Pacific (Philippines).[1] |
| Murex falsitribulus | Ponder & E. H. Vokes, 1988 | Mimics M. tribulus with false-spine varices; size 8–12 cm. | Indo-Pacific (Australia).[1] |
| Murex forskoehlii | Röding, 1798 | Strong, triangular spines on four varices; size up to 10 cm. | Red Sea and Indo-Pacific (Persian Gulf to India).[1] |
| Murex heros | Fulton, 1936 | Elongated spines and high spire; size 9–13 cm. | Indo-Pacific (South China Sea).[1] |
| Murex huangi | Houart, 2010 | Dense, short spines; size ~9 cm; validated via comparative anatomy. | Indo-Pacific (Taiwan).[1] |
| Murex hystricosus | Houart & Dharma, 2001 | Porcupine-like long spines; size 10–14 cm. | Indonesia (Bali Sea).[1] |
| Murex indicus | Houart, 2011 | Fine, hooked spines; size 7–11 cm. | Indian Ocean (Andaman Islands).[62] |
| Murex kerslakae | Ponder & E. H. Vokes, 1988 | Slender with reduced spines; size 6–10 cm. | Indo-Pacific (Australia).[1] |
| Murex maresinensis | Garrigues & Houart, 2025 | Newly described with elongated varical spines; size ~10 cm. | Indo-Pacific (recent validation).[1] |
| Murex megapex | Neubert, 1998 | Long, flared siphonal canal with large spines; size up to 12 cm. | Indo-Pacific (Oman to Maldives).[1] |
| Murex occa | G. B. Sowerby II, 1834 | Smooth varices with minor spines; size 8–12 cm. | Indo-Pacific (Philippines to Japan).[1] |
| Murex pecten | Lightfoot, 1786 | Long, comb-like curved spines along siphonal canal and whorls; yellowish shell; size 10–15 cm. | Indo-Pacific, Red Sea, Indian Ocean (Philippines to East Africa).[63][64] |
| Murex philippinensis | Parth, 1994 | Robust spines on three varices; size 9–13 cm. | Philippines.[1] |
| Murex protocrassus | Houart, 1990 | Thick varices with broad spines; size ~11 cm. | Indo-Pacific (South China Sea).[1] |
| Murex queenslandicus | Ponder & E. H. Vokes, 1988 | Regional variant with short spines; size 7–10 cm. | Queensland, Australia.[1] |
| Murex salomonensis | Parth, 1994 | Elongate with fine spines; size 8–12 cm. | Solomon Islands.[1] |
| Murex scolopax | Dillwyn, 1817 | Snipe-like long canal with spines; size 6–9 cm. | Indo-Pacific (Indian Ocean).[1] |
| Murex somalicus | Parth, 1990 | Strong axial spines; size up to 11 cm. | Somalia (Gulf of Aden).[1] |
| Murex spectabilis | Ponder & E. H. Vokes, 1988 | Showy, long spines; size 9–12 cm. | Indo-Pacific (Australia).[1] |
| Murex spicatus | Ponder & E. H. Vokes, 1988 | Spike-like projections on varices; size 7–10 cm. | Indo-Pacific (Australia).[1] |
| Murex spinastreptos | Houart, 2010 | Twisted, streptos-like spines; size ~10 cm. | Indo-Pacific (Philippines).[1] |
| Murex surinamensis | Okutani, 1982 | Moderate spines; size 8–11 cm. | Indo-Pacific (Japan).[1] |
| Murex suttipraneeae | Gra-tes, 2023 | Fine spines and nodulose sculpture; size ~9 cm. | Indo-Pacific (Thailand).[1] |
| Murex tenuirostrum | Lamarck, 1822 | Slender rostrum with short spines; size 10–14 cm. | Indo-Pacific (Fiji to Tonga).[1] |
| Murex ternispina | Lamarck, 1822 | Three-spined varices per whorl; size 8–12 cm. | Indo-Pacific (Indian Ocean to Pacific).[1] |
| Murex trapa | Röding, 1798 | Rare, slender curving spines on varices; long siphonal canal; size 5–12 cm. | Indo-West Pacific (Madagascar to Japan).[65] |
| Murex tribulus | Linnaeus, 1758 (type species) | Caltrop-like strong spines on varices; high-spired; size 10–16 cm, white to brown. | Indo-West Pacific (Red Sea to Australia).[66] |
| Murex troscheli | Lischke, 1868 | Dense, short spines; size 7–11 cm. | Indo-Pacific (Japan to Indonesia).[1] |
Synonyms and Reclassifications
The genus Murex has undergone extensive taxonomic revisions since its establishment by Linnaeus in 1758, with numerous species originally placed within it later reclassified based on morphological differences in shell structure, such as the number of varices and spine development.[9] For instance, Murex trunculus Linnaeus, 1758, a well-known species historically significant for purple dye production, was reclassified to Hexaplex trunculus in the mid-20th century as part of broader efforts to delineate subgenera within Muricidae, with the change reflecting distinctions in siphonal canal shape and overall shell robustness.[68] These reclassifications were initially driven by detailed morphological analyses, but subsequent DNA-based studies in the 2010s confirmed the separation by highlighting genetic divergences in mitochondrial genes.[23] In the 2000s, revisions by Roland Houart addressed misclassifications involving smaller murex-like forms previously lumped under Murex, leading to the recognition of genera like Muricopsis Bucquoy & Dautzenberg, 1882, for species with finer spiral cords and reduced spines, though many Muricopsis taxa were later synonymized or transferred to Murexsul Iredale, 1917, based on ontogenetic shell development patterns. Houart's comprehensive review of Mediterranean and Atlantic Muricidae species resolved over 20 junior synonyms within the complex, emphasizing radular and opercular traits to distinguish valid taxa from earlier misidentifications.[69] This period saw a consolidation of Murex sensu stricto to 38 accepted species, excluding those with atypical variceal formations now assigned to genera like Siratus Jousseaume, 1879, and Vokesimurex Petuch, 1988.[70] Genomic advancements in the 2020s, particularly mitogenomic phylogenies, have further refined synonymy within Muricidae by integrating whole-mitochondrial genome sequences, resulting in the synonymization of several Murex-related names and an overall reduction of about 10-15% in accepted species counts across the family through mergers like those in Muricanthus Schüter, 1838.[22] For example, molecular and morphological data confirmed Muricanthus radix Gmelin, 1791, and Muricanthus ambiguus Reeve, 1845, as conspecific, resolving long-standing ambiguities with RADseq analyses that revealed minimal genetic differentiation despite shell variations.[71] These studies have also prompted subfamily restructurings, such as the integration of Muricopsinae into Aspellinae, underscoring the role of high-throughput sequencing in stabilizing Murex taxonomy.[72]References
- https://en.wiktionary.org/wiki/murex

