Bob
Have a question related to this hub?
Alice
Got something to say related to this hub?
Share it here.
This article needs additional citations for verification. (April 2019) |


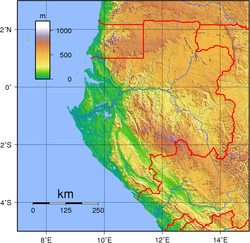
Gabon is a country in Central Africa, lying along the Atlantic Ocean, just south of the Bight of Biafra.
Gabon has a total of 3,261 km of international boundaries. It borders Equatorial Guinea (335 km) and Cameroon (349 km) to the north and the Republic of the Congo (2,567 km) to the east and south. Gabon lies on the equator.
| Land Use | (2012) |
|---|---|
| • Arable land | 1.26% |
| • Permanent crops | 0.66% |
| • Other | 98.08% |

Narrow coastal plain with patches of Central African mangroves; hilly interior; savanna in east and south. A recent global remote sensing analysis suggested that there were 420 km2 of tidal flats in Gabon, making it the 50th ranked country in terms of tidal flat area.[1]
International agreements:
Party to: Biodiversity, Climate Change, Desertification, Endangered Species, Hazardous Wastes, Law of the Sea, Marine Dumping, Ozone Layer Protection, Ship Pollution, Tropical Timber 83, Tropical Timber 94, Wetlands, Whaling
The equatorial location of Gabon means that it has a tropical monsoon climate (Köppen Am) and a tropical savanna climate (Köppen Aw), with the temperature being hot year-round and humid, although the Benguela Current can moderate temperatures.
| Climate data for Libreville (1961–1990) | |||||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Month | Jan | Feb | Mar | Apr | May | Jun | Jul | Aug | Sep | Oct | Nov | Dec | Year |
| Mean daily maximum °C (°F) | 29.5 (85.1) |
30.0 (86.0) |
30.2 (86.4) |
30.1 (86.2) |
29.4 (84.9) |
27.6 (81.7) |
26.4 (79.5) |
26.8 (80.2) |
27.5 (81.5) |
28.0 (82.4) |
28.4 (83.1) |
29.0 (84.2) |
28.6 (83.5) |
| Daily mean °C (°F) | 26.8 (80.2) |
27.0 (80.6) |
27.1 (80.8) |
26.6 (79.9) |
26.7 (80.1) |
25.4 (77.7) |
24.3 (75.7) |
24.3 (75.7) |
25.4 (77.7) |
25.7 (78.3) |
25.9 (78.6) |
26.2 (79.2) |
25.9 (78.6) |
| Mean daily minimum °C (°F) | 24.1 (75.4) |
24.0 (75.2) |
23.9 (75.0) |
23.1 (73.6) |
24.0 (75.2) |
23.2 (73.8) |
22.1 (71.8) |
21.8 (71.2) |
23.2 (73.8) |
23.4 (74.1) |
23.4 (74.1) |
23.4 (74.1) |
23.3 (73.9) |
| Average rainfall mm (inches) | 250.3 (9.85) |
243.1 (9.57) |
363.2 (14.30) |
339.0 (13.35) |
247.3 (9.74) |
54.1 (2.13) |
6.6 (0.26) |
13.7 (0.54) |
104.0 (4.09) |
427.2 (16.82) |
490.0 (19.29) |
303.2 (11.94) |
2,841.7 (111.88) |
| Average rainy days | 17.9 | 14.8 | 19.5 | 19.2 | 16.0 | 3.7 | 1.7 | 4.9 | 14.5 | 25.0 | 22.6 | 17.6 | 177.4 |
| Average relative humidity (%) | 86 | 84 | 84 | 84 | 84 | 81 | 81 | 81 | 84 | 87 | 87 | 86 | 84 |
| Mean monthly sunshine hours | 175.2 | 176.8 | 176.9 | 176.8 | 159.5 | 130.6 | 119.2 | 90.4 | 95.9 | 112.9 | 134.6 | 167.8 | 1,716.6 |
| Source: NOAA[2] | |||||||||||||
| Climate data for Port-Gentil (1961–1990, extremes 1950–present) | |||||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Month | Jan | Feb | Mar | Apr | May | Jun | Jul | Aug | Sep | Oct | Nov | Dec | Year |
| Record high °C (°F) | 32.6 (90.7) |
38.0 (100.4) |
34.6 (94.3) |
33.7 (92.7) |
33.2 (91.8) |
33.2 (91.8) |
30.8 (87.4) |
33.1 (91.6) |
33.3 (91.9) |
33.0 (91.4) |
34.0 (93.2) |
35.0 (95.0) |
38.0 (100.4) |
| Mean daily maximum °C (°F) | 29.5 (85.1) |
30.2 (86.4) |
30.3 (86.5) |
30.0 (86.0) |
29.0 (84.2) |
26.7 (80.1) |
25.9 (78.6) |
27.4 (81.3) |
27.7 (81.9) |
28.3 (82.9) |
28.6 (83.5) |
29.0 (84.2) |
28.5 (83.3) |
| Daily mean °C (°F) | 26.9 (80.4) |
27.3 (81.1) |
27.3 (81.1) |
27.1 (80.8) |
26.6 (79.9) |
24.4 (75.9) |
23.5 (74.3) |
24.7 (76.5) |
25.4 (77.7) |
25.9 (78.6) |
26.1 (79.0) |
26.5 (79.7) |
26.0 (78.8) |
| Mean daily minimum °C (°F) | 24.2 (75.6) |
24.4 (75.9) |
24.3 (75.7) |
24.2 (75.6) |
24.1 (75.4) |
22.0 (71.6) |
21.1 (70.0) |
21.9 (71.4) |
23.0 (73.4) |
23.5 (74.3) |
23.5 (74.3) |
24.0 (75.2) |
23.3 (73.9) |
| Record low °C (°F) | 17.6 (63.7) |
19.4 (66.9) |
19.5 (67.1) |
18.0 (64.4) |
19.0 (66.2) |
16.4 (61.5) |
16.0 (60.8) |
13.2 (55.8) |
18.2 (64.8) |
19.5 (67.1) |
15.8 (60.4) |
18.2 (64.8) |
13.2 (55.8) |
| Average precipitation mm (inches) | 247.8 (9.76) |
177.8 (7.00) |
266.8 (10.50) |
299.3 (11.78) |
150.6 (5.93) |
11.5 (0.45) |
3.4 (0.13) |
5.0 (0.20) |
31.8 (1.25) |
179.9 (7.08) |
352.2 (13.87) |
227.1 (8.94) |
1,953.2 (76.90) |
| Average precipitation days | 14.8 | 12.7 | 16.4 | 15.5 | 10.2 | 0.9 | 0.5 | 3.4 | 9.0 | 17.4 | 19.6 | 13.9 | 134.3 |
| Average relative humidity (%) | 84 | 84 | 83 | 84 | 85 | 84 | 83 | 82 | 82 | 84 | 86 | 84 | 84 |
| Mean monthly sunshine hours | 150.4 | 160.8 | 154.5 | 151.5 | 147.8 | 156.3 | 163.1 | 135.3 | 125.7 | 116.1 | 115.1 | 147.2 | 1,723.8 |
| Source 1: NOAA[3] | |||||||||||||
| Source 2: Meteo Climat (record highs and lows)[4] | |||||||||||||
| Climate data for Lambaréné (1961–1990) | |||||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Month | Jan | Feb | Mar | Apr | May | Jun | Jul | Aug | Sep | Oct | Nov | Dec | Year |
| Mean daily maximum °C (°F) | 31.5 (88.7) |
32.2 (90.0) |
32.3 (90.1) |
32.5 (90.5) |
31.3 (88.3) |
28.9 (84.0) |
27.9 (82.2) |
28.4 (83.1) |
30.0 (86.0) |
31.0 (87.8) |
30.8 (87.4) |
30.9 (87.6) |
30.6 (87.1) |
| Daily mean °C (°F) | 27.2 (81.0) |
27.6 (81.7) |
27.6 (81.7) |
27.8 (82.0) |
27.2 (81.0) |
25.3 (77.5) |
23.9 (75.0) |
24.7 (76.5) |
26.1 (79.0) |
26.9 (80.4) |
26.9 (80.4) |
27.1 (80.8) |
26.5 (79.7) |
| Mean daily minimum °C (°F) | 22.9 (73.2) |
22.9 (73.2) |
22.8 (73.0) |
23.1 (73.6) |
23.1 (73.6) |
21.7 (71.1) |
19.9 (67.8) |
20.9 (69.6) |
22.2 (72.0) |
22.8 (73.0) |
23.0 (73.4) |
23.2 (73.8) |
22.4 (72.3) |
| Average precipitation mm (inches) | 175.3 (6.90) |
145.2 (5.72) |
253.8 (9.99) |
212.8 (8.38) |
162.2 (6.39) |
20.9 (0.82) |
3.2 (0.13) |
6.9 (0.27) |
71.0 (2.80) |
347.7 (13.69) |
393.9 (15.51) |
172.0 (6.77) |
1,968.9 (77.52) |
| Average precipitation days | 12.1 | 10.7 | 15.0 | 14.1 | 13.8 | 2.9 | 2.1 | 5.1 | 9.6 | 21.9 | 20.8 | 12.5 | 140.6 |
| Average relative humidity (%) | 83 | 81 | 81 | 81 | 83 | 84 | 82 | 81 | 80 | 81 | 83 | 84 | 82 |
| Mean monthly sunshine hours | 142.9 | 145.2 | 145.1 | 143.1 | 123.9 | 74.2 | 70.6 | 53.4 | 55.9 | 70.9 | 117.1 | 129.4 | 1,271.7 |
| Source: NOAA[5] | |||||||||||||
| Climate data for Makokou (1961–1990, extremes 1949–present) | |||||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Month | Jan | Feb | Mar | Apr | May | Jun | Jul | Aug | Sep | Oct | Nov | Dec | Year |
| Record high °C (°F) | 34.0 (93.2) |
41.5 (106.7) |
37.0 (98.6) |
39.5 (103.1) |
41.1 (106.0) |
37.3 (99.1) |
32.5 (90.5) |
33.0 (91.4) |
35.4 (95.7) |
37.2 (99.0) |
36.0 (96.8) |
33.5 (92.3) |
41.5 (106.7) |
| Mean daily maximum °C (°F) | 29.2 (84.6) |
30.1 (86.2) |
30.5 (86.9) |
30.5 (86.9) |
29.8 (85.6) |
27.7 (81.9) |
25.8 (78.4) |
26.6 (79.9) |
28.7 (83.7) |
29.2 (84.6) |
28.7 (83.7) |
27.6 (81.7) |
28.7 (83.7) |
| Daily mean °C (°F) | 24.4 (75.9) |
24.9 (76.8) |
25.2 (77.4) |
25.3 (77.5) |
24.8 (76.6) |
23.4 (74.1) |
22.2 (72.0) |
22.5 (72.5) |
24.0 (75.2) |
24.4 (75.9) |
24.1 (75.4) |
23.5 (74.3) |
24.1 (75.4) |
| Mean daily minimum °C (°F) | 19.5 (67.1) |
19.7 (67.5) |
19.8 (67.6) |
20.0 (68.0) |
19.8 (67.6) |
19.0 (66.2) |
18.6 (65.5) |
18.4 (65.1) |
19.2 (66.6) |
19.5 (67.1) |
19.5 (67.1) |
19.3 (66.7) |
19.4 (66.9) |
| Record low °C (°F) | 15.9 (60.6) |
15.0 (59.0) |
16.3 (61.3) |
16.6 (61.9) |
16.8 (62.2) |
14.2 (57.6) |
11.5 (52.7) |
13.0 (55.4) |
13.5 (56.3) |
15.0 (59.0) |
17.0 (62.6) |
15.2 (59.4) |
11.5 (52.7) |
| Average precipitation mm (inches) | 88.1 (3.47) |
106.9 (4.21) |
190.0 (7.48) |
206.7 (8.14) |
187.7 (7.39) |
54.1 (2.13) |
9.0 (0.35) |
29.3 (1.15) |
142.9 (5.63) |
297.3 (11.70) |
225.7 (8.89) |
103.3 (4.07) |
1,641 (64.61) |
| Average precipitation days | 7.3 | 8.9 | 13.7 | 14.7 | 15.4 | 6.5 | 2.6 | 3.6 | 11.2 | 20.9 | 17.9 | 8.8 | 131.5 |
| Average relative humidity (%) | 82 | 79 | 79 | 79 | 80 | 83 | 85 | 83 | 80 | 80 | 81 | 83 | 81 |
| Mean monthly sunshine hours | 131.6 | 137.4 | 158.2 | 160.5 | 150.4 | 101.5 | 60.9 | 58.1 | 95.5 | 134.1 | 132.3 | 122.8 | 1,443.3 |
| Source 1: NOAA[6] | |||||||||||||
| Source 2: Meteo Climat (record highs and lows)[7] | |||||||||||||
Gabon is highly vulnerable to climate change due to its dense coastal population, economic hubs along the shore, and dependence on rain-fed agriculture.[8] Rising sea levels threaten to erode the coastline and contaminate freshwater sources with saltwater. The country is already experiencing more frequent and severe extreme weather events, such as floods, droughts, and storms, which damage infrastructure, displace communities, and disrupt food security and livelihoods.[9]
To adapt, Gabon prioritises protecting its coastal areas, as well as its fishing, agriculture, and forestry industries.[8] Gabon's vast forests act as a net carbon sink.[10][11] It is recognized as a global leader in climate action and is widely considered the most carbon-positive country in the world, due to its strong conservation efforts.[9] However, Gabon’s economy remains heavily dependent on oil and other natural resources, leaving it exposed to global market shifts and climate-related risks. In 2023, the country accounted for just over 0.04% of global greenhouse gas emissions (24.7 million tonnes). Gabon has pledged to stay carbon neutral beyond 2050 and, with adequate support, aims to maintain net carbon removals of 100 million tons CO2 equivalent per year beyond that date.[12] It also seeks to expand its renewable energy sector.[13]

![]() This article incorporates public domain material from The World Factbook. CIA.
This article incorporates public domain material from The World Factbook. CIA.