Recent from talks
Nothing was collected or created yet.
W Virginis
View on Wikipedia| Observation data Epoch J2000 Equinox J2000 | |
|---|---|
| Constellation | Virgo[2] |
| Right ascension | 13h 26m 01.99288s[3] |
| Declination | −03° 22′ 43.4311″[3] |
| Apparent magnitude (V) | 9.46 - 10.75[4] |
| Characteristics | |
| Spectral type | F0Ib-G0Ib[4] |
| B−V color index | +0.40[5] (+0.43 - +0.99[6]) |
| Variable type | W Virginis[4] |
| Astrometry | |
| Radial velocity (Rv) | −65.5[7] km/s |
| Proper motion (μ) | RA: −4.007±0.022[3] mas/yr Dec.: +1.105±0.012[3] mas/yr |
| Parallax (π) | 0.4728±0.0222 mas[3] |
| Distance | 6,900 ± 300 ly (2,120 ± 100 pc) |
| Details | |
| Mass | 0.4[8] M☉ |
| Radius | 35[9] (22 - 52[6]) R☉ |
| Luminosity | 851[8] (474 - 1,247[6]) L☉ |
| Surface gravity (log g) | 0.0[10] cgs |
| Temperature | 4,280 - 6,550[6] K |
| Metallicity | −1.0[10] |
| Other designations | |
| HIP 65531, SAO 139335, BD−02°3683, HD 116802[11] | |
| Database references | |
| SIMBAD | data |
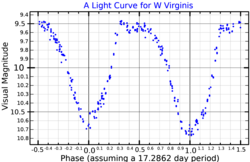
W Virginis is the prototype W Virginis variable, a subclass of the Cepheid variable stars. It is located in the constellation Virgo, and varies between magnitudes 9.46 and 10.75 over a period of approximately 17 days.[4] The star was discovered by Eduard Schönfeld in 1866.[12]
There are variations in the light curve apparently due to multiple pulsation periods rather than inherent instabilities in the pulsation. The dominant pulsation mode has a period of 17.27134 days with a period decrease detected over a 75-year period.[13]
The pulsations cause changes in both temperature and size, leading to large changes in the luminosity and brightness. The maximum temperature occurs when the star is at its brightest visually, when the star is also at its smallest. The minimum temperature and maximum radius occur at around phase 0.5 when the brightness is decreasing and nearly at minimum. Because relatively more infrared radiation is produced when the star is cooler, the maximum brightness in the infrared occurs when the visual brightness is already decreasing, and the maximum bolometric luminosity occurs at around phase 0.25 around halfway from maximum to minimum visual brightness.[6]
W Virginis stars are old helium shell burning stars with masses less than the sun. They have supergiant spectral luminosity classes despite their modest masses and actual luminosities, because they are highly inflated evolved stars with very low surface gravities. W Virginis itself is typical, with a mass less than half the sun, pulsating between 20 and 50 times the sun's radius, and a luminosity that varies from less than 500 L☉ to over a thousand L☉.
References
[edit]- ^ Plachy, E.; Molnár, L.; Jurkovic, M. I.; Smolec, R.; Moskalik, P. A.; Pál, A.; Szabados, L.; Szabó, R. (February 2017). "First observations of W Virginis stars with K2: detection of period doubling". Monthly Notices of the Royal Astronomical Society. 465 (1): 173–179. arXiv:1610.05488. doi:10.1093/mnras/stw2703.
- ^ Roman, Nancy G. (1987). "Identification of a constellation from a position". Publications of the Astronomical Society of the Pacific. 99 (617): 695. Bibcode:1987PASP...99..695R. doi:10.1086/132034. Constellation record for this object at VizieR.
- ^ a b c d e Vallenari, A.; et al. (Gaia collaboration) (2023). "Gaia Data Release 3. Summary of the content and survey properties". Astronomy and Astrophysics. 674: A1. arXiv:2208.00211. Bibcode:2023A&A...674A...1G. doi:10.1051/0004-6361/202243940. S2CID 244398875. Gaia DR3 record for this source at VizieR.
- ^ a b c d Samus, N. N.; Durlevich, O. V.; et al. (2009). "VizieR Online Data Catalog: General Catalogue of Variable Stars (Samus+ 2007–2013)". VizieR On-line Data Catalog: B/GCVS. Originally Published in: 2009yCat....102025S. 1: 02025. Bibcode:2009yCat....102025S.
- ^ Van Leeuwen, F. (2007). "Validation of the new Hipparcos reduction". Astronomy and Astrophysics. 474 (2): 653–664. arXiv:0708.1752. Bibcode:2007A&A...474..653V. doi:10.1051/0004-6361:20078357. S2CID 18759600.
- ^ a b c d e Barker, Timothy; Baumgart, Leona D.; Butler, Dennis; Cudworth, Kyle M.; Kemper, Edward; Kraft, Robert P.; Lorre, Jean; Kameswara Rao, N.; Reagan, Glenn H.; Soderblom, David R. (1971). "Abundance Analysis of Population II Variable Stars. I. W Virginis". Astrophysical Journal. 165: 67. Bibcode:1971ApJ...165...67B. doi:10.1086/150877.
- ^ Wilson, Ralph Elmer (1953). "General catalogue of stellar radial velocities". Washington: 0. Bibcode:1953GCRV..C......0W.
- ^ a b Böhm-Vitense, E.; Szkody, P.; Wallerstein, G.; Iben, I. (1974). "Masses and luminosities of population II cepheids". Astrophysical Journal. 194: 125. Bibcode:1974ApJ...194..125B. doi:10.1086/153229.
- ^ Balog, Z.; Vinko, J.; Kaszas, G. (1997). "Baade-Wesselink Radius Determination of Type II Cepheids". Astronomical Journal. 113: 1833. Bibcode:1997AJ....113.1833B. doi:10.1086/118394.
- ^ a b Maas, Thomas; Giridhar, Sunetra; Lambert, David L. (2007). "The Chemical Compositions of the Type II Cepheids-The BL Herculis and W Virginis Variables". The Astrophysical Journal. 666 (1): 378–392. arXiv:0706.2029. Bibcode:2007ApJ...666..378M. doi:10.1086/520081. S2CID 18862838.
- ^ "V* W Vir". SIMBAD. Centre de données astronomiques de Strasbourg. Retrieved 28 September 2014.
- ^ Cannon, Annie J. (1907). "Second catalogue of variable stars". Annals of Harvard College Observatory. 55: 1–94. Bibcode:1907AnHar..55....1C. Retrieved 16 August 2025.
- ^ Templeton, M. R.; Henden, A. A. (2007). "Multicolor Photometry of the Type II Cepheid Prototype W Virginis". The Astronomical Journal. 174 (5): 1999–2005. arXiv:0709.0401. Bibcode:2007AJ....134.1999T. doi:10.1086/522945. S2CID 14717181.