Recent from talks
All channels
Be the first to start a discussion here.
Be the first to start a discussion here.
Be the first to start a discussion here.
Be the first to start a discussion here.
Welcome to the community hub built to collect knowledge and have discussions related to Calcium lactate gluconate.
Nothing was collected or created yet.
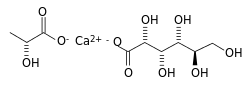
Calcium lactate gluconate
View on Wikipediafrom Wikipedia
 | |
 | |
| Names | |
|---|---|
| IUPAC name
calcium; (R/S)-2-hydroxypropanoate; (2R,3S,4R,5R)-2,3,4,5,6-pentahydroxyhexanoate
| |
| Identifiers | |
3D model (JSmol)
|
|
| ChemSpider | |
| ECHA InfoCard | 100.031.223 |
PubChem CID
|
|
| UNII | |
CompTox Dashboard (EPA)
|
|
| |
| |
| Properties | |
| C9H16CaO10 | |
| Molar mass | 324.295 g·mol−1 |
| Appearance | white, taste- and odourless, crystalline solid |
| 400 g/L | |
| Pharmacology | |
| A12AA06 (WHO) | |
Except where otherwise noted, data are given for materials in their standard state (at 25 °C [77 °F], 100 kPa).
| |
Calcium lactate gluconate, also known as GLOCAL, is a soluble salt of calcium, lactic acid and gluconic acid used in effervescent calcium tablets.[1] Its chemical formula is Ca5(C3H5O3)6·(C6H11O7)4·2H2O. It was first developed by Sandoz, Switzerland. Calcium lactate gluconate is used in the functional and fortified food industry due to its good solubility and neutral taste.[2] In addition, it is used in various spherification techniques in molecular gastronomy. It can also be used to help neutralize HF (hydrofluoric acid) poisoning.[citation needed]
References
[edit]- ^ Haberfeld, H, ed. (2009). Austria-Codex (in German) (2009/2010 ed.). Vienna: Österreichischer Apothekerverlag. ISBN 978-3-85200-196-8.
- ^ Gerhard Gerstner (2002). "Calcium Lactate Gluconate – the innovative solution for extra calcium" (PDF). Innovations in Food Technology. 3: 2–3. Archived from the original (PDF) on 2012-01-11. Retrieved 2012-01-08.

