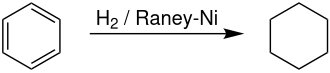Recent from talks
Nothing was collected or created yet.
Cyclohexane
View on Wikipedia
| |||
| |||
| Names | |||
|---|---|---|---|
| Preferred IUPAC name
Cyclohexane[2] | |||
| Other names
Hexanaphthene (archaic)[1]
| |||
| Identifiers | |||
3D model (JSmol)
|
|||
| 1900225 | |||
| ChEBI | |||
| ChEMBL | |||
| ChemSpider | |||
| DrugBank | |||
| ECHA InfoCard | 100.003.461 | ||
| 1662 | |||
| KEGG | |||
PubChem CID
|
|||
| RTECS number |
| ||
| UNII | |||
| UN number | 1145 | ||
CompTox Dashboard (EPA)
|
|||
| |||
| |||
| Properties | |||
| C6H12 | |||
| Molar mass | 84.162 g·mol−1 | ||
| Appearance | Colourless liquid | ||
| Odor | Sweet, gasoline-like | ||
| Density | 0.7739 g/ml (liquid); 0.996 g/ml (solid) | ||
| Melting point | 6.47 °C (43.65 °F; 279.62 K) | ||
| Boiling point | 80.74 °C (177.33 °F; 353.89 K) | ||
| Immiscible | |||
| Solubility | Soluble in ether, alcohol, acetone | ||
| Vapor pressure | 78 mmHg (20 °C)[3] | ||
| −68.13·10−6 cm3/mol | |||
Refractive index (nD)
|
1.42662 | ||
| Viscosity | 1.02 cP at 17 °C | ||
| Hazards | |||
| GHS labelling: | |||
   
| |||
| Danger | |||
| H225, H304, H315, H336 | |||
| P210, P233, P240, P241, P242, P243, P261, P264, P271, P273, P280, P301+P310, P302+P352, P303+P361+P353, P304+P340, P312, P321, P331, P332+P313, P362, P370+P378, P391, P403+P233, P403+P235, P405, P501 | |||
| NFPA 704 (fire diamond) | |||
| Flash point | −20 °C (−4 °F; 253 K) | ||
| 245 °C (473 °F; 518 K) | |||
| Explosive limits | 1.3–8%[3] | ||
| Lethal dose or concentration (LD, LC): | |||
LD50 (median dose)
|
12705 mg/kg (rat, oral) 813 mg/kg (mouse, oral)[4] | ||
LCLo (lowest published)
|
17,142 ppm (mouse, 2 h) 26,600 ppm (rabbit, 1 h)[4] | ||
| NIOSH (US health exposure limits): | |||
PEL (Permissible)
|
TWA 300 ppm (1050 mg/m3)[3] | ||
REL (Recommended)
|
TWA 300 ppm (1050 mg/m3)[3] | ||
IDLH (Immediate danger)
|
1300 ppm[3] | ||
| Thermochemistry | |||
Std enthalpy of
formation (ΔfH⦵298) |
−156 kJ/mol | ||
Std enthalpy of
combustion (ΔcH⦵298) |
−3920 kJ/mol | ||
| Related compounds | |||
Related cycloalkanes
|
Cyclopentane Cycloheptane | ||
Related compounds
|
Cyclohexene Benzene | ||
| Supplementary data page | |||
| Cyclohexane (data page) | |||
Except where otherwise noted, data are given for materials in their standard state (at 25 °C [77 °F], 100 kPa).
| |||
Cyclohexane is a cycloalkane with the molecular formula C6H12. Cyclohexane is non-polar. Cyclohexane is a colourless, flammable liquid with a distinctive detergent-like odor, reminiscent of cleaning products (in which it is sometimes used). Cyclohexane is mainly used for the industrial production of adipic acid and caprolactam, which are precursors to nylon.[5]
Cyclohexyl (C6H11) is the alkyl substituent of cyclohexane and is abbreviated Cy.[6]
Production
[edit]Cyclohexane is one of the components of naphtha, from which it can be extracted by advanced distillation methods. Distillation is usually combined with isomerization of methylcyclopentane, a similar component extracted from naphtha by similar methods. Together these processes cover only a minority (15-20%) of the modern industrial demand and are complemented by synthesis.[7]
Modern industrial synthesis
[edit]On an industrial scale, cyclohexane is produced by hydrogenation of benzene in the presence of a Raney nickel catalyst.[citation needed] Producers of cyclohexane account for approximately 11.4% of global demand for benzene.[8] The reaction is highly exothermic, with ΔH(500 K) = -216.37 kJ/mol. Dehydrogenation commenced noticeably above 300 °C, reflecting the favorable entropy for dehydrogenation.[9]
History of synthesis
[edit]Unlike benzene, cyclohexane is not found in natural resources such as coal. For this reason, early investigators synthesized their cyclohexane samples.[10]
Failure
[edit]- In 1867 Marcellin Berthelot reduced benzene with hydroiodic acid at elevated temperatures.[11][12]
- In 1870, Adolf von Baeyer repeated the reaction[13] and pronounced the same reaction product "hexahydrobenzene".
- In 1890 Vladimir Markovnikov believed he was able to distill the same compound from Caucasus petroleum, calling his concoction "hexanaphtene".[citation needed]
Surprisingly, their cyclohexanes boiled higher by 10 °C than either hexahydrobenzene or hexanaphthene, but this riddle was solved in 1895 by Markovnikov, N.M. Kishner, and Nikolay Zelinsky when they reassigned "hexahydrobenzene" and "hexanaphtene" as methylcyclopentane, the result of an unexpected rearrangement reaction.
Success
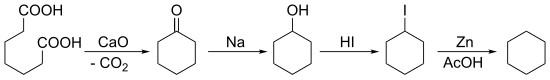
[edit]In 1894, Baeyer synthesized cyclohexane starting with a ketonic decarboxylation of pimelic acid followed by multiple reductions:
In the same year, E. Haworth and W.H. Perkin Jr. (1860–1929) prepared it via a Wurtz reaction of 1,6-dibromohexane.
Reactions and uses
[edit]Although rather unreactive, cyclohexane undergoes autoxidation to give a mixture of cyclohexanone and cyclohexanol. The cyclohexanone–cyclohexanol mixture, called "KA oil", is a raw material for adipic acid and caprolactam, precursors to nylon. Several million kilograms of cyclohexanone and cyclohexanol are produced annually.[9]
It is used as a solvent in some brands of correction fluid. Cyclohexane is sometimes used as a non-polar organic solvent, although n-hexane is more widely used for this purpose. It is frequently used as a recrystallization solvent, as many organic compounds exhibit good solubility in hot cyclohexane and poor solubility at low temperatures.
Cyclohexane is also used for calibration of differential scanning calorimetry (DSC) instruments, because of a convenient crystal-crystal transition at −87.1 °C.[14]
Cyclohexane vapour is used in vacuum carburizing furnaces, in heat treating equipment manufacture.
Conformation
[edit]The 6-vertex edge ring does not conform to the shape of a perfect hexagon. The conformation of a flat 2D planar hexagon has considerable strain because the C-H bonds would be eclipsed. Therefore, to reduce torsional strain, cyclohexane adopts a three-dimensional structure known as the chair conformation, which rapidly interconvert at room temperature via a process known as a chair flip. During the chair flip, there are three other intermediate conformations that are encountered: the half-chair, which is the most unstable conformation, the more stable boat conformation, and the twist-boat, which is more stable than the boat but still much less stable than the chair. The chair and twist-boat are energy minima and are therefore conformers, while the half-chair and the boat are transition states and represent energy maxima. The idea that the chair conformation is the most stable structure for cyclohexane was first proposed as early as 1890 by Hermann Sachse, but only gained widespread acceptance much later. The new conformation puts the carbons at an angle of 109.5°. Half of the hydrogens are in the plane of the ring (equatorial) while the other half are perpendicular to the plane (axial). This conformation allows for the most stable structure of cyclohexane. Another conformation of cyclohexane exists, known as boat conformation, but it interconverts to the slightly more stable chair formation. If cyclohexane is mono-substituted with a large substituent, then the substituent will most likely be found attached in an equatorial position, as this is the slightly more stable conformation.
Cyclohexane has the lowest angle and torsional strain of all the cycloalkanes; as a result cyclohexane has been deemed a 0 in total ring strain.
Solid phases
[edit]Cyclohexane has two crystalline phases. The high-temperature phase I, stable between 186 K and the melting point 280 K, is a plastic crystal, which means the molecules retain some rotational degree of freedom. The low-temperature (below 186 K) phase II is ordered. Two other low-temperature (metastable) phases III and IV have been obtained by application of moderate pressures above 30 MPa, where phase IV appears exclusively in deuterated cyclohexane (application of pressure increases the values of all transition temperatures).[15]
| No | Symmetry | Space group | a (Å) | b (Å) | c (Å) | Z | T (K) | P (MPa) |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| I | Cubic | Fm3m | 8.61 | 4 | 195 | 0.1 | ||
| II | Monoclinic | C2/c | 11.23 | 6.44 | 8.20 | 4 | 115 | 0.1 |
| III | Orthorhombic | Pmnn | 6.54 | 7.95 | 5.29 | 2 | 235 | 30 |
| IV | Monoclinic | P12(1)/n1 | 6.50 | 7.64 | 5.51 | 4 | 160 | 37 |
Here Z is the number structure units per unit cell; the unit cell constants a, b and c were measured at the given temperature T and pressure P.
See also
[edit]- The Flixborough disaster, a major industrial accident caused by an explosion of cyclohexane
- Hexane
- Ring flip
- Cyclohexane (data page)
References
[edit]- ^ "Hexanaphthene". dictionary.com. Archived from the original on 2018-02-12.
- ^ "Front Matter". Nomenclature of Organic Chemistry : IUPAC Recommendations and Preferred Names 2013 (Blue Book). Cambridge: The Royal Society of Chemistry. 2014. pp. P001 – P004. doi:10.1039/9781849733069-FP001. ISBN 978-0-85404-182-4.
- ^ a b c d e NIOSH Pocket Guide to Chemical Hazards. "#0163". National Institute for Occupational Safety and Health (NIOSH).
- ^ a b "Cyclohexane". Immediately Dangerous to Life or Health Concentrations (IDLH). National Institute for Occupational Safety and Health (NIOSH).
- ^ Campbell, M. Larry (2011). "Cyclohexane". Ullmann's Encyclopedia of Industrial Chemistry. doi:10.1002/14356007.a08_209.pub2. ISBN 978-3527306732.
- ^ "Standard Abbreviations and Acronyms" (PDF). The Journal of Organic Chemistry. Archived from the original (PDF) on 1 Aug 2018.
- ^ Weissermel, Klaus; Arpe, Hans-Jürgen (2008-07-11). Industrial Organic Chemistry. John Wiley & Sons. p. 345. ISBN 978-3-527-61459-2.
- ^ Ceresana. "Benzene - Study: Market, Analysis, Trends 2021 - Ceresana". www.ceresana.com. Archived from the original on 21 December 2017. Retrieved 4 May 2018.
- ^ a b Michael Tuttle Musser (2005). "Cyclohexanol and Cyclohexanone". Ullmann's Encyclopedia of Industrial Chemistry. Weinheim: Wiley-VCH. doi:10.1002/14356007.a08_217. ISBN 978-3527306732.
- ^ Warnhoff, E. W. (1996). "The Curiously Intertwined Histories of Benzene and Cyclohexane". J. Chem. Educ. 73 (6): 494. Bibcode:1996JChEd..73..494W. doi:10.1021/ed073p494.
- ^ Bertholet (1867). "Nouvelles applications des méthodes de réduction en chimie organique" [New applications of reduction methods in organic chemistry]. Bulletin de la Société Chimique de Paris (in French). series 2 (7): 53–65.
- ^ Bertholet (1868). "Méthode universelle pour réduire et saturer d'hydrogène les composés organiques" [Universal method for reducing and saturating organic compounds with hydrogen]. Bulletin de la Société Chimique de Paris (in French). series 2 (9): 8–31.
En effet, la benzine, chauffée à 280° pendant 24 heures avec 80 fois son poids d'une solution aqueuse saturée à froid d'acide iodhydrique, se change à peu près entièrement en hydrure d'hexylène, C12H14, en fixant 4 fois son volume d'hydrogène: C12H6 + 4H2 = C12H14 … Le nouveau carbure formé par la benzine est un corps unique et défini: il bout à 69°, et offre toutes les propriétés et la composition de l'hydrure d'hexylène extrait des pétroles.
[In effect, benzene, heated to 280° for 24 hours with 80 times its weight of an aqueous solution of cold saturated hydroiodic acid, is changed almost entirely into hydride of hexylene, C12H14, [Note: this formula for hexane (C6H14) is wrong because chemists at that time used the incorrect atomic mass for carbon.] by fixing [i.e., combining with] 4 times its volume of hydrogen: C12H6 + 4H2 = C12H14 The new carbon compound formed by benzene is a unique and well-defined substance: it boils at 69° and presents all the properties and the composition of hydride of hexylene extracted from oil.)] - ^ Adolf Baeyer (1870). "Ueber die Reduction aromatischer Kohlenwasserstoffe durch Jodphosphonium" [On the reduction of aromatic compound by phosphonium iodide [H4IP]]. Annalen der Chemie und Pharmacie. 55: 266–281.
Bei der Reduction mit Natriumamalgam oder Jodphosphonium addiren sich im höchsten Falle sechs Atome Wasserstoff, und es entstehen Abkömmlinge, die sich von einem Kohlenwasserstoff C6H12 ableiten. Dieser Kohlenwasserstoff ist aller Wahrscheinlichkeit nach ein geschlossener Ring, da seine Derivate, das Hexahydromesitylen und Hexahydromellithsäure, mit Leichtigkeit wieder in Benzolabkömmlinge übergeführt werden können.
[During the reduction [of benzene] with sodium amalgam or phosphonium iodide, six atoms of hydrogen are added in the extreme case, and there arise derivatives, which derive from a hydrocarbon C6H12. This hydrocarbon is in all probability a closed ring, since its derivatives — hexahydromesitylene [1,3,5 - trimethyl cyclohexane] and hexahydromellithic acid [cyclohexane-1,2,3,4,5,6-hexacarboxylic acid] — can be converted with ease again into benzene derivatives.] - ^ Price, D. M. (1995). "Temperature Calibration of Differential Scanning Calorimeters". Journal of Thermal Analysis. 45 (6): 1285–1296. doi:10.1007/BF02547423. S2CID 97402835.
- ^ a b Mayer, J.; Urban, S.; Habrylo, S.; Holderna, K.; Natkaniec, I.; Würflinger, A.; Zajac, W. (1991). "Neutron Scattering Studies of C6H12 and C6D12 Cyclohexane under High Pressure". Physica Status Solidi B. 166 (2): 381. Bibcode:1991PSSBR.166..381M. doi:10.1002/pssb.2221660207.
External links
[edit]- International Chemical Safety Card 0242
- National Pollutant Inventory – Cyclohexane fact sheet
- NIOSH Pocket Guide to Chemical Hazards
- Cyclohexane@3Dchem
- Hermann Sachse and the first suggestion of a chair conformation.
- NLM Hazardous Substances Databank – Cyclohexane
- Methanol Discovered in Space
- Calculation of vapor pressure, liquid density, dynamic liquid viscosity, surface tension of cyclohexane
- Cyclohexane production process flowsheet, benzene hydrogenation technique
Cyclohexane
View on GrokipediaStructure and conformation
Molecular structure
Cyclohexane has the molecular formula C₆H₁₂ and a molecular weight of 84.16 g/mol.[1] It is a saturated cycloalkane composed of a six-membered carbon ring in which adjacent carbon atoms are connected by single bonds, with each carbon atom exhibiting sp³ hybridization and bonded to two hydrogen atoms.[1][7] The C–C–C bond angles in the ring are approximately 109.5°, aligning closely with the ideal tetrahedral geometry and resulting in minimal angle strain relative to smaller cycloalkanes such as cyclopropane (60°) or cyclobutane (90°).[1][8][7] Due to its highly symmetric structure and absence of polar functional groups, cyclohexane is a non-polar molecule with no net dipole moment.[1] The molecule is commonly represented in Kekulé form, which explicitly shows all six carbon atoms, twelve hydrogen atoms, and the single bonds forming the ring, or in skeletal formula, where carbon atoms are implied at the vertices of a hexagon and hydrogen atoms are omitted for simplicity (equivalent to the SMILES notation C1CCCCC1).[1]Conformational analysis
Cyclohexane adopts a variety of conformations due to the flexibility of its six-membered ring, with the chair conformation representing the global energy minimum. In this form, all carbon-carbon bonds are staggered, and the hydrogen atoms are positioned either axially (perpendicular to the ring plane) or equatorially (roughly in the ring plane), minimizing torsional strain and avoiding eclipsed interactions./12%3A_Cycloalkanes_Cycloalkenes_and_Cycloalkynes/12.03%3A_Conformations_of_Cycloalkanes) Alternative conformations include the boat and twist-boat forms, which are higher in energy relative to the chair. The boat conformation features eclipsed bonds along four carbons and flagpole hydrogens that introduce steric repulsion, resulting in an energy approximately 6.9 kcal/mol above the chair. The twist-boat, a distorted version that relieves some of these interactions, lies about 5.5 kcal/mol higher than the chair but serves as a local minimum.[9][10] Ring inversion in cyclohexane interconverts equivalent chair forms through a half-chair transition state, where one bond becomes nearly planar, leading to significant torsional strain. This process has an activation barrier of approximately 10-12 kcal/mol, allowing rapid equilibration at room temperature on the order of 10^5 times per second.[10] In the chair conformation, axial and equatorial positions differ in their steric environment; axial substituents experience 1,3-diaxial interactions with syn-axial hydrogens, which contribute to higher energy for axial orientations compared to equatorial. These gauche-like interactions, each worth about 0.9 kcal/mol for hydrogen pairs, are absent in the unsubstituted ring but explain substituent preferences./12%3A_Cycloalkanes_Cycloalkenes_and_Cycloalkynes/12.03%3A_Conformations_of_Cycloalkanes) The low ring strain in cyclohexane, totaling 0.0-1.0 kcal/mol, arises from near-zero angle strain (bond angles close to the ideal 109.5°) and minimized torsional strain in the chair due to staggered arrangements, making it a strain-free model for cycloalkanes./Alkanes/Properties_of_Alkanes/Cycloalkanes/Ring_Strain_and_the_Structure_of_Cycloalkanes) The conformational equilibrium between chair and twist-boat is governed by with a free energy difference of about 5.5 kcal/mol favoring the chair, resulting in population ratios at room temperature of approximately 99.9% chair and 0.1% twist-boat.[10]Solid phases
Cyclohexane displays two primary solid phases, distinguished by their molecular ordering and thermodynamic properties. The high-temperature phase I, known as the plastic crystal phase, exists between approximately 186 K and the melting point of 6.5 °C (279.7 K). In this phase, the molecules exhibit significant orientational freedom, rotating nearly isotropically about their centers of mass while maintaining positional order in a face-centered cubic lattice with space group . This disorder contributes to the plastic-like mechanical behavior observed in such crystals.[1][11] The low-temperature phase II forms below 186 K and represents a fully ordered crystalline state with a monoclinic structure in the space group . Here, the cyclohexane molecules adopt fixed chair conformations, aligned in the lattice without the rotational mobility seen in phase I; as noted in conformational analyses, the chair form is the predominant low-energy structure for cyclohexane. The intermolecular interactions in this phase are primarily van der Waals forces, stabilizing the ordered arrangement.[12][13] The transition between phase II and phase I at 186.09 K is a first-order phase change, marked by a significant entropy increase of 35.93 J/mol·K due to the onset of orientational disordering in the higher-temperature phase. This entropy change reflects the gain in rotational degrees of freedom as the system moves from the rigid ordered lattice of phase II to the more dynamic plastic phase I. The melting point of 6.5 °C further delineates the upper limit of the solid state, with the liquid density at 25 °C measured at 0.7785 g/cm³, providing context for the material's behavior near the solid-liquid boundary.[2][1]Properties
Physical properties
Cyclohexane is a colorless liquid at room temperature, exhibiting a mild, characteristic odor reminiscent of petroleum or chloroform.[1] Its phase transition temperatures include a boiling point of 80.7 °C at standard atmospheric pressure and a melting point of 6.5 °C.[14] The density of liquid cyclohexane is 0.7785 g/cm³ at 20 °C.[15] Cyclohexane is practically insoluble in water, with a solubility of 0.0058 g/100 mL at 25 °C, due to its non-polar nature. It is miscible with common organic solvents such as ethanol, ether, acetone, and benzene.[16][1] The refractive index is 1.426 at 20 °C, and the dynamic viscosity is 0.98 cP at the same temperature.[1] Thermodynamic properties include a heat of vaporization of 30.0 kJ/mol at the boiling point and a molar heat capacity of 155.5 J/mol·K for the liquid phase at 25 °C.[14][17] Regarding flammability, cyclohexane has a flash point of -20 °C and an autoignition temperature of 245 °C.[1]| Property | Value | Conditions | Source |
|---|---|---|---|
| Boiling point | 80.7 °C | 760 mm Hg | NIST WebBook |
| Melting point | 6.5 °C | - | PubChem |
| Density | 0.7785 g/cm³ | 20 °C | LSU Solvents |
| Solubility in water | 0.0058 g/100 mL | 25 °C | ICSC |
| Refractive index | 1.426 | 20 °C | PubChem |
| Viscosity | 0.98 cP | 20 °C | PubChem |
| Heat of vaporization | 30.0 kJ/mol | Boiling point | NIST WebBook |
| Molar heat capacity (liquid) | 155.5 J/mol·K | 25 °C | NIST WebBook |
| Flash point | -20 °C | Closed cup | PubChem |
| Autoignition temperature | 245 °C | - | PubChem |