Recent from talks
Contribute something
Nothing was collected or created yet.
Epsilon Cephei
View on Wikipedia| Observation data Epoch J2000 Equinox J2000 | |
|---|---|
| Constellation | Cepheus[1] |
| Right ascension | 22h 15m 02.197s[2] |
| Declination | +57° 02′ 36.85″[2] |
| Apparent magnitude (V) | 4.15 to 4.21[3] |
| Characteristics | |
| Evolutionary stage | main sequence[2][4] |
| Spectral type | F0 V (Sr II)[5] or F0 IV[6] |
| U−B color index | +0.073[7] |
| B−V color index | +0.277[7] |
| Variable type | δ Sct[3] |
| Astrometry | |
| Radial velocity (Rv) | −4.7±0.8[8] km/s |
| Proper motion (μ) | RA: +423.159 mas/yr[2] Dec.: +52.691 mas/yr[2] |
| Parallax (π) | 38.1598±0.2432 mas[2] |
| Distance | 85.5 ± 0.5 ly (26.2 ± 0.2 pc) |
| Absolute magnitude (MV) | +2.13[1] |
| Details | |
| ε Cep Aa | |
| Mass | 1.64[9] M☉ |
| Radius | 1.86[10] R☉ |
| Luminosity | 11.65[1] L☉ |
| Surface gravity (log g) | 4.11±0.14[9] cgs |
| Temperature | 7,514±255[9] K |
| Metallicity [Fe/H] | +0.08[1] dex |
| Rotational velocity (v sin i) | 91[11] km/s |
| Age | 1.097[9] Gyr |
| ε Cep Ab | |
| Mass | 0.57[12] M☉ |
| Other designations | |
| ε Cephei, 23 Cephei, BD+56 2741, HD 211336, HIP 109857, HR 8494, SAO 34227[13] | |
| Database references | |
| SIMBAD | data |
Epsilon Cephei is a star in the northern constellation of Cepheus. Its name is a Bayer designation that is Latinized from ε Cephei, and abbreviated Epsilon Cep or ε Cep. Based upon an annual parallax shift of 38.16 mas as seen from the Earth,[14] it is located about 85.5 light-years (26.2 pc) from the Sun. The star is visible to the naked eye with an apparent visual magnitude that varies around 4.18.[7]
Properties
[edit]Physical characteristics
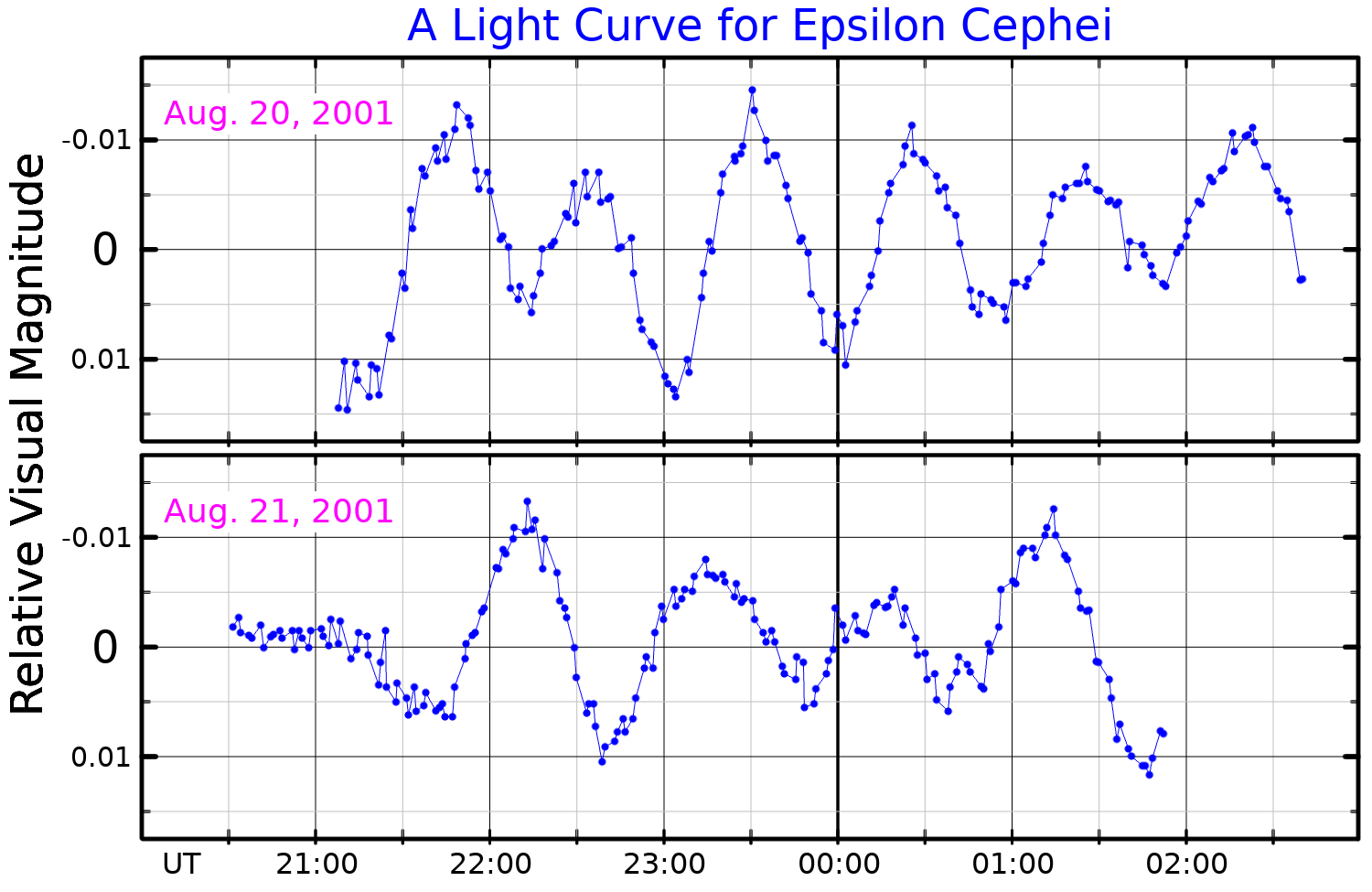
[edit]
This is a yellow-white hued, F-type star with a stellar classification of F0 V (Sr II)[5] or F0 IV.[6] Thus it may either be an F-type main sequence star showing an abundance excess of strontium, or it could be a more evolved subgiant star. It is a Delta Scuti variable star that cycles between magnitudes 4.15 and 4.21 every 59.388 minutes.[3] The star displays an infrared excess, indicating the presence of a debris disk with a temperature of 65 K orbiting at a radius of 62 AU. This dust has a combined mass equal to 6.6% of the Earth's mass.[10]
Binary
[edit]There is a faint companion star at an angular separation of 330±50 mas along a position angle of 90°±10°. This corresponds to a projected physical separation of 8.6±1.4 AU. The probability of a random star being situated this close to Epsilon Cephei is about one in a million, so it is most likely physically associated. If so, then the debris disk is probably circumbinary. The fact that this companion was not detected during the Hipparcos mission may indicate its orbit has a high eccentricity. The companion star has a K-band magnitude of 7.8 and is probably of class K8–M2.[6]
Naming
[edit]In Chinese, 螣蛇 (Téng Shé), meaning Flying Serpent, refers to an asterism consisting of ε Cephei, α Lacertae, 4 Lacertae, π2 Cygni, π1 Cygni, HD 206267, β Lacertae, σ Cassiopeiae, ρ Cassiopeiae, τ Cassiopeiae, AR Cassiopeiae, 9 Lacertae, 3 Andromedae, 7 Andromedae, 8 Andromedae, λ Andromedae, κ Andromedae, ι Andromedae, and ψ Andromedae. Consequently, the Chinese name for ε Cephei itself is 螣蛇九 (Téng Shé jiǔ, English: the Ninth Star of Flying Serpent).[16]
References
[edit]- ^ a b c d Anderson, E.; Francis, Ch. (2012), "XHIP: An extended hipparcos compilation", Astronomy Letters, 38 (5): 331, arXiv:1108.4971, Bibcode:2012AstL...38..331A, doi:10.1134/S1063773712050015. XHIP record for this object at VizieR.
- ^ a b c d e Vallenari, A.; et al. (Gaia collaboration) (2023), "Gaia Data Release 3. Summary of the content and survey properties", Astronomy and Astrophysics, 674: A1, arXiv:2208.00211, Bibcode:2023A&A...674A...1G, doi:10.1051/0004-6361/202243940, S2CID 244398875. Gaia DR3 record for this source at VizieR.
- ^ a b c "eps Cep", AAVSO Website, American Association of Variable Star Observers, retrieved 2017-05-07.
- ^ Zorec, J.; Royer, F. (2012). "Rotational velocities of A-type stars. IV. Evolution of rotational velocities". Astronomy and Astrophysics. 537: A120. arXiv:1201.2052. Bibcode:2012A&A...537A.120Z. doi:10.1051/0004-6361/201117691.
- ^ a b Gray, R. O.; et al. (2001), "The Physical Basis of Luminosity Classification in the Late A-, F-, and Early G-Type Stars. I. Precise Spectral Types for 372 Stars", The Astronomical Journal, 121 (4): 2148–2158, Bibcode:2001AJ....121.2148G, doi:10.1086/319956.
- ^ a b c Mawet, D.; et al. (September 2011), "A Dim Candidate Companion to epsilon Cephei", The Astrophysical Journal Letters, 738 (1): 5, arXiv:1107.3872, Bibcode:2011ApJ...738L..12M, doi:10.1088/2041-8205/738/1/L12, S2CID 37505271, L12.
- ^ a b c Breger, M. (March 1968), "UBV and narrow-band UVBY photometry of bright stars", Astronomical Journal, 73: 84–85, Bibcode:1968AJ.....73...84B, doi:10.1086/110602.
- ^ Gontcharov, G. A. (2006), "Pulkovo Compilation of Radial Velocities for 35 495 Hipparcos stars in a common system", Astronomy Letters, 32 (11): 759–771, arXiv:1606.08053, Bibcode:2006AstL...32..759G, doi:10.1134/S1063773706110065, S2CID 119231169
- ^ a b c d David, Trevor J.; Hillenbrand, Lynne A. (2015), "The Ages of Early-Type Stars: Strömgren Photometric Methods Calibrated, Validated, Tested, and Applied to Hosts and Prospective Hosts of Directly Imaged Exoplanets", The Astrophysical Journal, 804 (2): 146, arXiv:1501.03154, Bibcode:2015ApJ...804..146D, doi:10.1088/0004-637X/804/2/146, S2CID 33401607.
- ^ a b Rhee, Joseph H.; et al. (May 2007), "Characterization of Dusty Debris Disks: The IRAS and Hipparcos Catalogs", The Astrophysical Journal, 660 (2): 1556–1571, arXiv:astro-ph/0609555, Bibcode:2007ApJ...660.1556R, doi:10.1086/509912, S2CID 11879505.
- ^ Royer, F.; et al. (February 2007), "Rotational velocities of A-type stars. III. Velocity distributions", Astronomy and Astrophysics, 463 (2): 671–682, arXiv:astro-ph/0610785, Bibcode:2007A&A...463..671R, doi:10.1051/0004-6361:20065224, S2CID 18475298.
- ^ De Rosa, R. J.; et al. (2013), "The VAST Survey - III. The multiplicity of A-type stars within 75 pc", Monthly Notices of the Royal Astronomical Society, 437 (2): 1216, arXiv:1311.7141, Bibcode:2014MNRAS.437.1216D, doi:10.1093/mnras/stt1932.
- ^ "eps Cep", SIMBAD, Centre de données astronomiques de Strasbourg, retrieved 2024-01-28.
- ^ van Leeuwen, F. (2007), "Validation of the new Hipparcos reduction", Astronomy and Astrophysics, 474 (2): 653–664, arXiv:0708.1752, Bibcode:2007A&A...474..653V, doi:10.1051/0004-6361:20078357, S2CID 18759600.
- ^ Bruntt, H.; et al. (January 2007), "Asteroseismology with the WIRE satellite I. Combining ground- and space-based photometry of the δ Scuti star ɛ Cephei", Astronomy and Astrophysics, 461 (2): 619–630, arXiv:astro-ph/0610539, Bibcode:2007A&A...461..619B, doi:10.1051/0004-6361:20065766.
- ^ (in Chinese) AEEA (Activities of Exhibition and Education in Astronomy) 天文教育資訊網 2006 年 7 月 7 日 Archived 2011-05-21 at the Wayback Machine