Recent from talks
Nothing was collected or created yet.
UTC−05:00
View on Wikipedia
Key Information

| Standard | DST | ||
|---|---|---|---|
| GMT−05:00 | GMT−04:00 | Eastern Time | |
| GMT−05:00 (year round) | Eastern Time | ||
| GMT−06:00 | GMT−05:00 | Central Time | |
| GMT−07:00 | GMT−06:00 | Mountain Time | |

| Standard | DST | US time zone | |
|---|---|---|---|
| Red | UTC−06:00 | UTC−05:00 | Central Time |
| Yellow | UTC−05:00 | UTC−04:00 | Eastern Time |

| Mexican time zone | Standard | DST | U.S. equivalent | |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Zona Sureste | UTC−05:00 | Eastern Standard Time | ||
| Zona Centro | UTC−06:00 | UTC−05:00 | Central Time | |
| UTC−06:00 | Central Standard Time | |||
| Zona Pacífico | UTC−07:00 | UTC−06:00 | Mountain Time | |
| UTC−07:00 | Mountain Standard Time | |||
| Zona Noroeste | UTC−08:00 | UTC−07:00 | Pacific Time | |

| ACT | Acre Time | UTC−5 | (BRT–2) | |
| AMT | Amazon Time | UTC−4 | (BRT−1) | |
| BRT | Brasília Time | UTC−3 | (BRT) | |
| FNT | Fernando de Noronha Time | UTC−2 | (BRT+1) |
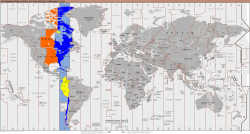
UTC−05:00 is an identifier for a time offset from UTC of −05:00. In North America, it is observed in the Eastern Time Zone during standard time, and in the Central Time Zone during the other eight months (see Daylight saving time). The western Caribbean uses it year round.
As standard time (Northern Hemisphere winter)
[edit]Principal cities: New York, Washington, Philadelphia, Boston, Atlanta, Miami, Detroit, Columbus, Baltimore, Cleveland, Pittsburgh, Indianapolis, Orlando, Charlotte, Charleston, Wilmington, Key West, Toronto, Montreal, Ottawa, Quebec City, Iqaluit, Nassau, Havana, Kingston, Port-au-Prince, Cockburn Town, Providenciales
North America
[edit]- Canada (Eastern Time Zone)
- United States (Eastern Time Zone)[2]
- Delaware
- District of Columbia
- Florida
- Entire state except the counties of Bay, Calhoun, Escambia, Holmes, Jackson, Okaloosa, Santa Rosa, Walton, and Washington, and northern Gulf county (panhandle)
- Georgia
- Indiana[3]
- Kentucky
- Maine
- Maryland
- Michigan[4]
- New England (states of Connecticut, Massachusetts, Maine, New Hampshire, Rhode Island and Vermont)[2]
- New Jersey
- New York
- North Carolina
- Ohio
- Pennsylvania
- South Carolina
- Tennessee
- Virginia
- West Virginia
Caribbean
[edit]- Bahamas
- Cuba
- Haiti
- Navassa Island
- United Kingdom
As daylight saving time (Northern Hemisphere summer)
[edit]Principal cities: Winnipeg, Chicago, Dallas, Houston, St. Louis, Minneapolis, Austin, Memphis, Kansas City, San Antonio, Nashville, New Orleans, Milwaukee, Oklahoma City, Reynosa
North America
[edit]- Canada (Central Time Zone)
- Manitoba
- Nunavut
- All of Kivalliq Region (Coral Harbour)
- Ontario
- West of 90° west longitude[1]
- Mexico (near US border with Texas)
- Chihuahua
- The municipalities of Coyame del Sotol, Ojinaga and Manuel Benavides[5]
- Coahuila de Zaragoza
- Nuevo León
- The municipality of Anahuac
- Tamaulipas
- The municipalities of Nuevo Laredo, Guerrero, Mier, Miguel Alemán, Camargo, Gustavo Díaz Ordaz, Reynosa, Río Bravo, Valle Hermoso and Matamoros
- Chihuahua
- United States (Central Time Zone)
- Alabama
- Arkansas
- Florida[2]
- The counties of Bay, Calhoun, Escambia, Holmes, Jackson, Okaloosa, Santa Rosa, Walton, and Washington, and northern Gulf county (panhandle)
- Illinois
- Indiana[3]
- Iowa
- Kansas
- Entire state except westernmost counties
- Kentucky
- Louisiana
- Michigan[4]
- The western counties of Dickinson, Gogebic, Iron and Menominee
- Minnesota
- Mississippi
- Missouri
- Nebraska
- Central and eastern Nebraska
- North Dakota
- Entire state except southwest
- Oklahoma
- Entire state except Kenton
- South Dakota
- Eastern half
- Tennessee
- Texas
- All except westernmost counties
- Wisconsin
As standard time (year-round)
[edit]Principal cities: Cancún, Bogotá, Lima, Kingston, Quito, Panama City, George Town
South America
[edit]- Brazil[8]
- Acre
- Amazonas (13 western municipalities, approximately marked by a line between Tabatinga and Porto Acre)
- Colombia – Time in Colombia
- Ecuador – Time in Ecuador (except Galápagos Islands)
- Peru – Time in Peru
Caribbean
[edit]- Jamaica – Time in Jamaica
- United Kingdom
- United States
North America
[edit]- Canada – Eastern Time Zone
- Mexico (Zona Sureste)
- Panama
As daylight saving time (Southern Hemisphere summer)
[edit]See also
[edit]References
[edit]- ^ a b "Ontario Time Zone – Ontario Current Local Time – Daylight Saving Time". TimeTemperature.com. Retrieved 1 February 2015.
- ^ a b c d e f g "Time Zones of the United States". Statoids. Retrieved 25 August 2012.
- ^ a b "Time zone map (spring)" (PDF). Indiana State. 13 March 2011. Archived from the original (PDF) on 10 May 2012. Retrieved 14 July 2012.
- ^ a b "Michigan Time Zone – Michigan Current Local Time – Daylight Saving Time". TimeTemperature.com. Retrieved 25 August 2012.
- ^ a b "Hora Oficial en los Estados Unidos Mexicanos" (in Spanish). Centro Nacional de Metrologîa. 2 April 2023. Retrieved 21 October 2023.
- ^ "Kentucky County Map". Kentucky Map Collection. Geology.com. Retrieved 6 October 2012.
- ^ "Tennessee County Map". Tennessee Map Collection. Geology.com. Retrieved 6 October 2012.
- ^ "Brazil: Acre and parts of Amazonas switch time zones". Time and Date. 31 October 2013 [9 October 2013]. Retrieved 17 November 2013.
- ^ "Navassa Island". WorldTimeZone. Retrieved 6 October 2012.
External links
[edit] Media related to UTC−05:00 at Wikimedia Commons
Media related to UTC−05:00 at Wikimedia Commons