Recent from talks
Nothing was collected or created yet.
Dioxirane
View on Wikipedia
| |||
 | |||
| Names | |||
|---|---|---|---|
| Preferred IUPAC name
Dioxirane | |||
| Systematic IUPAC name
Dioxacyclopropane | |||
| Other names
1,2-Dioxacyclopropane
Methylene peroxide Peroxymethane | |||
| Identifiers | |||
3D model (JSmol)
|
|||
| ChemSpider | |||
PubChem CID
|
|||
CompTox Dashboard (EPA)
|
|||
| |||
| |||
| Properties | |||
| CH2O2 | |||
| Molar mass | 46.03 g/mol | ||
Except where otherwise noted, data are given for materials in their standard state (at 25 °C [77 °F], 100 kPa).
| |||
In chemistry, dioxirane (systematically named dioxacyclopropane, also known as methylene peroxide or peroxymethane) is an organic compound with formula CH
2O
2. The molecule consists of a ring with one methylene and two oxygen atoms. It is of interest as the smallest cyclic organic peroxide, but otherwise it is of little practical value.
Synthesis
[edit]Dioxirane is highly unstable and the majority of studies of it have been computational; it has been detected during the low temperature (–196 °C) reaction of ethylene and ozone,[1] although even at these temperatures such a mixture can be explosive.[2] Its formation is thought to be radical in nature, preceding via a Criegee intermediate. Microwave analysis has indicated C-H, C-O and O-O bond lengths of 1.090, 1.388 and 1.516 Å respectively.[2] The very long and weak O-O bond (cf. hydrogen peroxide O-O = 1.47 Å) is the origin of its instability.
Other dioxiranes
[edit]Beyond the parent dioxirane, which is mainly of theoretical interest, more common dioxiranes are dimethyldioxirane (DMD or DMDO) and trifluoromethyl-methyldioxirane (TFD). DMDO and the still more reactive methyl(trifluoromethyl)dioxirane have seen some use in organic synthesis,[3] These dioxiranes may be produced through the action of KHSO5 on carbonyl compounds. Because of their low-lying σ*O-O orbital, they are highly electrophilic oxidants and react with unsaturated functional groups, Y-H bonds (yielding oxygen insertion products), and heteroatoms.[4] (1)
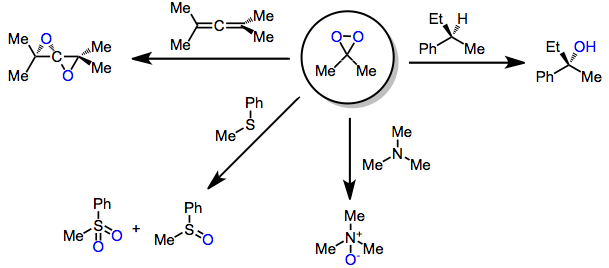
Dioxiranes are intermediate in the Shi epoxidation reaction. The latter is effective for chemoselective oxidations of C-H and Si-H bonds.[5] Although this class of reagents is most famous for the epoxidation of alkenes, dioxiranes have been used extensively for other kinds of oxidations as well.
Difluorodioxirane, which boils at about –80 to –90 °C, is one of the very few dioxirane derivatives that is stable in pure form at room temperature and is thermodynamically stable (ΔH° = –104 kcal/mol).[6][7] Dimesityldioxirane is another relatively stable derivative which has been characterized by X-ray crystallography.[8]
See also
[edit]References
[edit]- ^ Lovas, F.J.; Suenram, R.D. (November 1977). "Identification of dioxirane (H2) in ozone-olefin reactions via microwave spectroscopy". Chemical Physics Letters. 51 (3): 453–456. Bibcode:1977CPL....51..453L. doi:10.1016/0009-2614(77)85398-0.
- ^ a b Suenram, R. D.; Lovas, F. J. (August 1978). "Dioxirane. Its synthesis, microwave spectrum, structure, and dipole moment". Journal of the American Chemical Society. 100 (16): 5117–5122. Bibcode:1978JAChS.100.5117S. doi:10.1021/ja00484a034.
- ^ Ruggero Curci; Anna Dinoi; Maria F. Rubino (1995). "Dioxirane oxidations: Taming the reactivity-selectivity principle" (PDF). Pure Appl. Chem. 67 (5): 811–822. doi:10.1351/pac199567050811. S2CID 44241053.
- ^ Adam, W.; Curci, R.; Edwards, J. O. Acc. Chem. Res. 1989, 22, 205.
- ^ Asensio, G.; González-Núñez, M. E.; Biox Bernardini, C.; Mello, R.; Adam, W. J. Am. Chem. Soc. 1993, 115, 7250.
- ^ Kraka, Elfi; Konkoli, Zoran; Cremer, Dieter; Fowler, Joseph; Schaefer, Henry F. (1996-01-01). "Difluorodioxirane: An Unusual Cyclic Peroxide". Journal of the American Chemical Society. 118 (43): 10595–10608. Bibcode:1996JAChS.11810595K. doi:10.1021/ja961983w. ISSN 0002-7863.
- ^ Russo, Antonio; DesMarteau, Darryl D. (1993). "Difluorodioxirane". Angewandte Chemie International Edition in English. 32 (6): 905–907. doi:10.1002/anie.199309051. ISSN 0570-0833.
- ^ Sander, Wolfram; Schroeder, Kerstin; Muthusamy, Sengodagounder; Kirschfeld, Andreas; Kappert, Wilhelm; Boese, Roland; Kraka, Elfi; Sosa, Carlos; Cremer, Dieter (1997-08-01). "Dimesityldioxirane". Journal of the American Chemical Society. 119 (31): 7265–7270. Bibcode:1997JAChS.119.7265S. doi:10.1021/ja964280n. ISSN 0002-7863.



