Recent from talks
Nothing was collected or created yet.
Ynone
View on Wikipedia
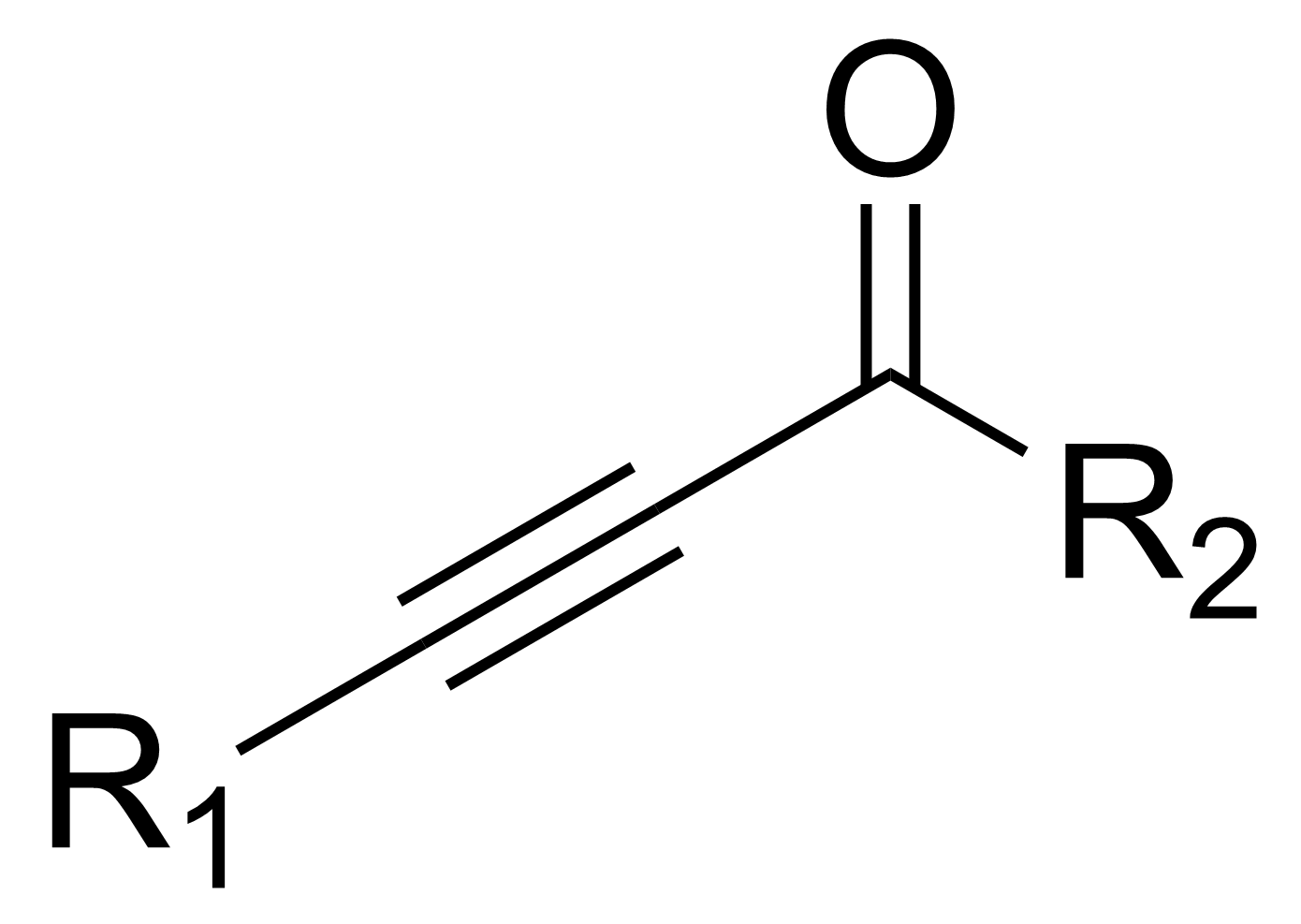
In organic chemistry, an ynone is an organic compound containing a ketone (>C=O) functional group and a C≡C triple bond. Many ynones are α,β-ynones, where the carbonyl and alkyne groups are conjugated. Capillin is a naturally occurring example. Some ynones are not conjugated.
Synthesis of α,β-ynones
[edit]One method for synthesizing ynones is the acyl substitution reaction of an alkynyldimethylaluminum with an acyl chloride. An alkynyldimethylaluminum compound is the reaction product of trimethylaluminum and a terminal alkyne.[1]

An alternative is the direct coupling of an acyl chloride with a terminal alkyne, using a copper-based nanocatalyst:[2]

Other methods utilize an oxidative cleavage of an aldehyde, followed by reaction with a hypervalent alkynyl iodide, using a gold catalyst.[3]
An alternative but longer synthetic method involves the reaction of an alkynyllithium compound with an aldehyde. The reaction produces a secondary alcohol that then can be oxidized via the Swern oxidation.
Synthesis of β,γ- and γ,δ-ynones
[edit]Terminal alkynes add across α,β-unsaturated ketones in the presence of palladium catalysts. The reaction affords γ,δ-ynones.[4] Terminal alkynes add across epoxides to given yneols, which can be oxidized to give β,γ-ynones.[5]
Further reading
[edit]- Bis-ynones can undergo an intramolecular cycloaddition to form furan derivatives.[6]
See also
[edit]References
[edit]- ^ Wang, Baomin; Bonin, Martine; Micouin, Laurent (June 22, 2005). "A Straightforward Synthesis of Ynones by Reaction of Dimethylalkynylaluminum Reagents with Acid Chlorides". J. Org. Chem. 70 (15): 6126–6128. doi:10.1021/jo050760y. PMID 16018717.
- ^ Weijiang, Sun; Wang, Yan; Wua, Xuan; Yao, Xiaoquan (2013). "Palladium-, ligand-, and solvent-free synthesis of ynones by the coupling of acyl chlorides and terminal alkynes in the presence of a reusable copper nanoparticle catalyst". Green Chemistry. 15 (9): 2356–2360. doi:10.1039/c3gc40980e.
- ^ Wang, Zhaofeng; Li, Li; Yong, Huang (August 18, 2014). "A General Synthesis of Ynones from Aldehydes via Oxidative C–C bond Cleavage under Aerobic Conditions". J. Am. Chem. Soc. 136 (35): 12233–12236. doi:10.1021/ja506352b. PMID 25133731.
- ^ Feng Zhou, Liang Chen, Chao-Jun Li (2014). "Palladium-catalyzed 1,4-Addition of Terminal Alkynes to Conjugated Enones". Organic Syntheses. 91: 72. doi:10.15227/orgsyn.091.0072.
{{cite journal}}: CS1 maint: multiple names: authors list (link) - ^ Adam Sniady, Marco S. Morreale, Roman Dembinski (2007). "Electrophilic Cyclization with N-Iodosuccinimide: Preparation of 5-(4-Bromophenyl)-3-Iodo-2-(4-Methyl-Phenyl)Furan". Organic Syntheses. 84: 199. doi:10.15227/orgsyn.084.0199.
{{cite journal}}: CS1 maint: multiple names: authors list (link) - ^ Wills, M.S.B.; Danheiser, R.L. (August 28, 1998). "Intramolecular [4 + 2] Cycloaddition Reactions of Conjugated Ynones. Formation of Polycyclic Furans via the Generation and Rearrangement of Strained Heterocyclic Allenes". J. Am. Chem. Soc. 120 (36): 9378–9379. doi:10.1021/ja9819209.
External links
[edit] Media related to Ynones at Wikimedia Commons
Media related to Ynones at Wikimedia Commons