Recent from talks
Nothing was collected or created yet.
Position of the Sun
View on Wikipedia
The position of the Sun in the sky is a function of both the time and the geographic location of observation on Earth's surface. As Earth orbits the Sun over the course of a year, the Sun appears to move with respect to the fixed stars on the celestial sphere, along a circular path called the ecliptic.
Earth's rotation about its axis causes diurnal motion, so that the Sun appears to move across the sky in a Sun path that depends on the observer's geographic latitude. The time when the Sun transits the observer's meridian depends on the geographic longitude.
To find the Sun's position for a given location at a given time, one may therefore proceed in three steps as follows:[1][2]
- calculate the Sun's position in the ecliptic coordinate system,
- convert to the equatorial coordinate system, and
- convert to the horizontal coordinate system, for the observer's local time and location. This is the coordinate system normally used to calculate the position of the Sun in terms of solar zenith angle and solar azimuth angle, and the two parameters can be used to depict the Sun path.[3]
This calculation is useful in astronomy, navigation, surveying, meteorology, climatology, solar energy, and sundial design.
Approximate position
[edit]Ecliptic coordinates
[edit]These equations, from the Astronomical Almanac,[4][5] can be used to calculate the apparent coordinates of the Sun, mean equinox and ecliptic of date, to a precision of about 0°.01 (36″), for dates between 1950 and 2050. Similar equations are coded into a Fortran 90 routine in Ref.[3] and are used to calculate the solar zenith angle and solar azimuth angle as observed from the surface of the Earth.
Start by calculating n, the number of days (positive or negative, including fractional days) since Greenwich noon, Terrestrial Time, on 1 January 2000 (J2000.0). If the Julian date for the desired time is known, then
The mean longitude of the Sun, corrected for the aberration of light, is:
The mean anomaly of the Sun (actually, of the Earth in its orbit around the Sun, but it is convenient to pretend the Sun orbits the Earth), is:
Put and in the range 0° to 360° by adding or subtracting multiples of 360° as needed— which is to say, and are really to be evaluated (mod 360).
Finally, the ecliptic longitude of the Sun is:
The ecliptic latitude of the Sun is nearly:
- ,
as the ecliptic latitude of the Sun never exceeds 0.00033° (a little over 1″),[6] and the distance of the Sun from the Earth, in astronomical units, is:
- .
Obliquity of the ecliptic
[edit]Where the obliquity of the ecliptic is not obtained elsewhere, it can be approximated:
Equatorial coordinates
[edit], and form a complete position of the Sun in the ecliptic coordinate system. This can be converted to the equatorial coordinate system by calculating the obliquity of the ecliptic, , and continuing:
- , where is in the same quadrant as ,
To get RA at the right quadrant on computer programs use double argument Arctan function such as ATAN2(y,x)
and declination,
- .
Rectangular equatorial coordinates
[edit]Right-handed rectangular equatorial coordinates in astronomical units are:
- Where axis is in the direction of the March equinox, the axis towards June Solstice, and the axis towards the North celestial pole.[7]
Horizontal coordinates
[edit]Declination of the Sun as seen from Earth
[edit]
The Sun appears to move northward during the northern spring, crossing the celestial equator on the March equinox. Its declination reaches a maximum equal to the angle of Earth's axial tilt (23.44° or 23°26')[8][9] on the June solstice, then decreases until reaching its minimum (−23.44° or -23°26') on the December solstice, when its value is the negative of the axial tilt. This variation produces the seasons.
A line graph of the Sun's declination during a year resembles a sine wave with an amplitude of 23.44°, but one lobe of the wave is several days longer than the other, among other differences.
The following phenomena would occur if Earth were a perfect sphere, in a circular orbit around the Sun, and if its axis were tilted 90°, so that the axis itself is on the orbital plane (similar to Uranus). At one date in the year, the Sun would be directly overhead at the North Pole, so its declination would be +90°. For the next few months, the subsolar point would move toward the South Pole at constant speed, crossing the circles of latitude at a constant rate, so that the solar declination would decrease linearly with time. Eventually, the Sun would be directly above the South Pole, with a declination of −90°; then it would start to move northward at a constant speed. Thus, the graph of solar declination, as seen from this highly tilted Earth, would resemble a triangle wave rather than a sine wave, zigzagging between plus and minus 90°, with linear segments between the maxima and minima.
If the 90° axial tilt is decreased, then the absolute maximum and minimum values of the declination would decrease, to equal the axial tilt. Also, the shapes of the maxima and minima on the graph would become less acute, being curved to resemble the maxima and minima of a sine wave. However, even when the axial tilt equals that of the actual Earth, the maxima and minima remain more acute than those of a sine wave.
In reality, Earth's orbit is elliptical.[note 1] Earth moves more rapidly around the Sun near perihelion, in early January, than near aphelion, in early July. This makes processes like the variation of the solar declination happen faster in January than in July. On the graph, this makes the minima more acute than the maxima. Also, since perihelion and aphelion do not happen on the exact dates as the solstices, the maxima and minima are slightly asymmetrical. The rates of change before and after are not quite equal. Furthermore, Earth's subsolar point only occurs within the tropics.
The graph of apparent solar declination is therefore different in several ways from a sine wave. Calculating it accurately involves some complexity, as shown below.
Calculations
[edit]The declination of the Sun, δ☉, is the angle between the rays of the Sun and the plane of the Earth's equator. The Earth's axial tilt (called the obliquity of the ecliptic by astronomers) is the angle between the Earth's axis and a line perpendicular to the Earth's orbit. The Earth's axial tilt changes slowly over thousands of years but its current value of about ε = 23.44° is nearly constant, so the change in solar declination during one year is nearly the same as during the next year.
At the solstices, the angle between the rays of the Sun and the plane of the Earth's equator reaches its maximum value of 23.44°. Therefore, δ☉ = +23.44° at the northern summer solstice and δ☉ = −23.44° at the southern summer solstice.
At the moment of each equinox, the center of the Sun appears to pass through the celestial equator, and δ☉ is 0°.
The Sun's declination at any given moment is calculated by:
where EL is the ecliptic longitude (essentially, the Earth's position in its orbit). Since the Earth's orbital eccentricity is small, its orbit can be approximated as a circle which causes up to 1° of error. The circle approximation means the EL would be 90° ahead of the solstices in Earth's orbit (at the equinoxes), so that sin(EL) can be written as sin(90+NDS)=cos(NDS) where NDS is the number of days after the December solstice. By also using the approximation that arcsin[sin(d)·cos(NDS)] is close to d·cos(NDS), the following frequently used formula is obtained:
where N is the day of the year beginning with N=0 at midnight Universal Time (UT) as January 1 begins (i.e. the days part of the ordinal date −1). The number 10, in (N+10), is the approximate number of days after the December solstice to January 1. This equation overestimates the declination near the September equinox by up to +1.5°. The sine function approximation by itself leads to an error of up to 0.26° and has been discouraged for use in solar energy applications.[2] The 1971 Spencer formula[10] (based on a Fourier series) is also discouraged for having an error of up to 0.28°.[11] An additional error of up to 0.5° can occur in all equations around the equinoxes if not using a decimal place when selecting N to adjust for the time after UT midnight for the beginning of that day. So the above equation can have up to 2.0° of error, about four times the Sun's angular width, depending on how it is used.
The declination can be more accurately calculated by not making the two approximations, using the parameters of the Earth's orbit to more accurately estimate EL:[12]
which can be simplified by evaluating constants to:
N is the number of days since midnight UT as January 1 begins (i.e. the days part of the ordinal date −1) and can include decimals to adjust for local times later or earlier in the day. The number 2, in (N-2), is the approximate number of days after January 1 to the Earth's perihelion. The number 0.0167 is the current value of the eccentricity of the Earth's orbit. The eccentricity varies very slowly over time, but for dates fairly close to the present, it can be considered to be constant. The largest errors in this equation are less than ± 0.2°, but are less than ± 0.03° for a given year if the number 10 is adjusted up or down in fractional days as determined by how far the previous year's December solstice occurred before or after noon on December 22. These accuracies are compared to NOAA's advanced calculations[13][14] which are based on the 1999 Jean Meeus algorithm that is accurate to within 0.01°.[15]
(The above formula is related to a reasonably simple and accurate calculation of the Equation of Time, which is described here.)
More complicated algorithms[16][17] correct for changes to the ecliptic longitude by using terms in addition to the 1st-order eccentricity correction above. They also correct the 23.44° obliquity which changes very slightly with time. Corrections may also include the effects of the moon in offsetting the Earth's position from the center of the pair's orbit around the Sun. After obtaining the declination relative to the center of the Earth, a further correction for parallax is applied, which depends on the observer's distance away from the center of the Earth. This correction is less than 0.0025°. The error in calculating the position of the center of the Sun can be less than 0.00015°. For comparison, the Sun's width is about 0.5°.
Atmospheric refraction
[edit]The declination calculations described above do not include the effects of the refraction of light in the atmosphere, which causes the apparent angle of elevation of the Sun as seen by an observer to be higher than the actual angle of elevation, especially at low Sun elevations.[2] For example, when the Sun is at an elevation of 10°, it appears to be at 10.1°. The Sun's declination can be used, along with its right ascension, to calculate its azimuth and also its true elevation, which can then be corrected for refraction to give its apparent position.[2][14][18]
Equation of time
[edit]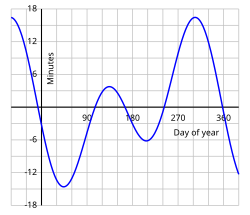
In addition to the annual north–south oscillation of the Sun's apparent position, corresponding to the variation of its declination described above, there is also a smaller but more complex oscillation in the east–west direction. This is caused by the tilt of the Earth's axis, and also by changes in the speed of its orbital motion around the Sun produced by the elliptical shape of the orbit.[2] The principal effects of this east–west oscillation are variations in the timing of events such as sunrise and sunset, and in the reading of a sundial compared with a clock showing local mean time. As the graph shows, a sundial can be up to about 16 minutes fast or slow, compared with a clock. Since the Earth rotates at a mean speed of one degree every four minutes, relative to the Sun, this 16-minute displacement corresponds to a shift eastward or westward of about four degrees in the apparent position of the Sun, compared with its mean position. A westward shift causes the sundial to be ahead of the clock.
Since the main effect of this oscillation concerns time, it is called the equation of time, using the word "equation" in a somewhat archaic sense meaning "correction". The oscillation is measured in units of time, minutes and seconds, corresponding to the amount that a sundial would be ahead of a clock. The equation of time can be positive or negative.
Analemma
[edit]
An analemma is a diagram that shows the annual variation of the Sun's position on the celestial sphere, relative to its mean position, as seen from a fixed location on Earth. (The word analemma is also occasionally, but rarely, used in other contexts.) It can be considered as an image of the Sun's apparent motion during a year, which resembles a figure-8. An analemma can be pictured by superimposing photographs taken at the same time of day, a few days apart for a year.
An analemma can also be considered as a graph of the Sun's declination, usually plotted vertically, against the equation of time, plotted horizontally. Usually, the scales are chosen so that equal distances on the diagram represent equal angles in both directions on the celestial sphere. Thus 4 minutes (more precisely 3 minutes, 56 seconds), in the equation of time, are represented by the same distance as 1° in the declination, since Earth rotates at a mean speed of 1° every 4 minutes, relative to the Sun.
An analemma is drawn as it would be seen in the sky by an observer looking upward. If north is shown at the top, then west is to the right. This is usually done even when the analemma is marked on a geographical globe, on which the continents, etc., are shown with west to the left.
Some analemmas are marked to show the position of the Sun on the graph on various dates, a few days apart, throughout the year. This enables the analemma to be used to make simple analog computations of quantities such as the times and azimuths of sunrise and sunset. Analemmas without date markings are used to correct the time indicated by sundials.[19]
Light-time effects
[edit]We see light from the Sun about 20 angle seconds from where the Sun is when the light is seen. See Solar annual aberration.
See also
[edit]Notes
[edit]- ^ In celestial mechanics, the Earth's orbit would be stated as being a Kepler orbit with an orbital eccentricity of less than 1.
References
[edit]- ^ Meeus, Jean (1991). "Chapter 12: Transformation of Coordinates". Astronomical Algorithms. Richmond, VA: Willmann Bell, Inc. ISBN 0-943396-35-2.
- ^ a b c d e Jenkins, Alejandro (2013). "The Sun's position in the sky". European Journal of Physics. 34 (3): 633–652. arXiv:1208.1043. Bibcode:2013EJPh...34..633J. doi:10.1088/0143-0807/34/3/633. S2CID 119282288.
- ^ a b Zhang, T., Stackhouse, P.W., Macpherson, B., and Mikovitz, J.C., 2021. A solar azimuth formula that renders circumstantial treatment unnecessary without compromising mathematical rigor: Mathematical setup, application and extension of a formula based on the subsolar point and atan2 function. Renewable Energy, 172, 1333-1340. DOI: https://doi.org/10.1016/j.renene.2021.03.047
- ^ U.S. Naval Observatory; U.K. Hydrographic Office, H.M. Nautical Almanac Office (2008). The Astronomical Almanac for the Year 2010. U.S. Govt. Printing Office. p. C5. ISBN 978-0-7077-4082-9.
- ^ Much the same set of equations, covering the years 1800 to 2200, can be found at Approximate Solar Coordinates, at the U.S. Naval Observatory website . Graphs of the error of these equations, compared to an accurate ephemeris, can also be viewed.
- ^ Meeus (1991), p. 152
- ^ U.S. Naval Observatory Nautical Almanac Office (1992). P. Kenneth Seidelmann (ed.). Explanatory Supplement to the Astronomical Almanac. University Science Books, Mill Valley, CA. p. 12. ISBN 0-935702-68-7.
- ^ "Selected Astronomical Constants, 2015 (PDF)" (PDF). US Naval Observatory. 2014. p. K6–K7. Archived from the original (PDF) on July 3, 2015.
- ^ "Selected Astronomical Constants, 2015 (TXT)". US Naval Observatory. 2014. p. K6–K7. Archived from the original on March 7, 2015.
- ^ J. W. Spencer (1971). "Fourier series representation of the position of the sun".
{{cite journal}}: Cite journal requires|journal=(help) - ^ Sproul, Alistair B. (2007). "Derivation of the solar geometric relationships using vector analysis". Renewable Energy. 32 (7): 1187–1205. doi:10.1016/j.renene.2006.05.001.
- ^ "SunAlign". Archived from the original on 9 March 2012. Retrieved 28 February 2012.
- ^ "NOAA Solar Calculator". Earth System Research Laboratories. Retrieved 28 February 2012.
- ^ a b "Solar Calculation Details". Earth System Research Laboratories. Retrieved 28 February 2012.
- ^ "Astronomical Algorithms". Retrieved 28 February 2012.
- ^ Blanco-Muriel, Manuel; Alarcón-Padilla, Diego C; López-Moratalla, Teodoro; Lara-Coira, Martín (2001). "Computing the Solar Vector" (PDF). Solar Energy. 70 (5): 431–441. Bibcode:2001SoEn...70..431B. doi:10.1016/s0038-092x(00)00156-0.
- ^ Ibrahim Reda & Afshin Andreas. "Solar Position Algorithm for Solar Radiation Applications" (PDF). Retrieved 28 February 2012.
- ^ "Atmospheric Refraction Approximation". National Oceanic and Atmospheric Administration. Retrieved 28 February 2012.
- ^ Sundial#Noon marks
External links
[edit]- Solar Position Algorithm, at National Renewable Energy Laboratory's Renewable Resource Data Center website.
- Sun Position Calculator, at pveducation.org. An interactive calculator showing the Sun's path in the sky.
- NOAA Solar Calculator, at the NOAA Earth System Research Laboratories's Global Monitoring Division website.
- NOAA's declination and Sun position calculator
- HORIZONS System, at the JPL website. Very accurate positions of Solar System objects based on the JPL DE series ephemerides.
- General ephemerides of the Solar System bodies, at the IMCCE website. Positions of Solar System objects based on the INPOP series ephemerides.
- Solar position in R. Insol package.
Position of the Sun
View on GrokipediaCelestial Coordinate Systems
Ecliptic Coordinates
Ecliptic coordinates describe the position of celestial objects relative to the ecliptic plane, which is the apparent annual path of the Sun across the celestial sphere. In this system, the ecliptic longitude (λ) is measured eastward from the vernal equinox along the ecliptic, ranging from 0° to 360°, while the ecliptic latitude (β) is measured northward or southward from the ecliptic plane, ranging from -90° to +90°. For the Sun, the ecliptic latitude remains near 0° because the ecliptic is defined by its mean orbital path.[6] The Sun's ecliptic latitude is essentially 0°, varying by up to about 9 arcseconds due to small perturbations in Earth's orbit caused by gravitational influences from other planets, which cause minor deviations from the ideal ecliptic plane. These variations are negligible for most observational purposes, keeping the Sun's path effectively confined to the ecliptic.[7] Historically, ecliptic coordinates have been fundamental for describing solar positions since antiquity; in the Ptolemaic geocentric model, Claudius Ptolemy utilized them in the Almagest (2nd century CE) to track the Sun's motion along the zodiac, simplifying predictions of its position relative to fixed stars. Similarly, in the Copernican heliocentric system of the 16th century, Nicolaus Copernicus retained ecliptic coordinates to model the Sun as the center, with Earth's orbit projecting the apparent solar path.[8][6] The mean ecliptic longitude of the Sun provides a simplified approximation of its position, ignoring short-term perturbations. It can be calculated using the formula where is the number of days elapsed since the J2000.0 epoch (January 1, 2000, 12:00 TT). This formula yields the geometric mean longitude, which advances approximately 360° over the course of a year, reflecting the Sun's uniform circular motion in the mean orbital model.[8] From a heliocentric perspective, the Sun's geocentric position in ecliptic coordinates is the direct projection of Earth's position in its orbit around the Sun onto the celestial sphere, reversed in direction; as Earth moves counterclockwise along its orbit, the Sun appears to move clockwise along the ecliptic from Earth's viewpoint. This relationship underscores the ecliptic system's utility for solar system dynamics, as it aligns with the plane of Earth's orbit.[9]Equatorial Coordinates
The equatorial coordinate system specifies the position of the Sun on the celestial sphere using two angular coordinates: right ascension (α or RA) and declination (δ or Dec). Right ascension measures the eastward angular distance from the vernal equinox along the celestial equator, analogous to longitude, and is expressed in hours (0 to 24 h), where 1 hour corresponds to 15°. Declination measures the north-south angular distance from the celestial equator, analogous to latitude, ranging from -90° at the south celestial pole to +90° at the north celestial pole.[10] These coordinates are particularly useful for aligning telescopes with Earth's rotational axis and tracking apparent solar motion relative to the fixed stars.[10] Annually, the Sun's position traces the ecliptic in equatorial coordinates, causing systematic variations in both RA and Dec. The right ascension increases at an average rate of approximately 4 minutes per day, reflecting the Sun's mean orbital motion of about 360° per 365.25 days relative to the stars, or roughly 0.986° per day in ecliptic longitude, which projects onto the equatorial frame.[11] The declination oscillates between a minimum of about -23.44° near the winter solstice and a maximum of +23.44° near the summer solstice (for Northern Hemisphere observers), with the amplitude determined by the obliquity of the ecliptic (ε ≈ 23.44°), the tilt of Earth's rotational axis relative to its orbital plane.[8] This range arises because the ecliptic is inclined to the celestial equator by ε, confining the Sun's path within these limits.[8] Converting the Sun's position from ecliptic coordinates—primarily ecliptic longitude λ (with ecliptic latitude β ≈ 0°)—to equatorial coordinates involves accounting for the obliquity ε. The declination is computed as yielding δ directly via the arcsine function. The right ascension α is then derived from with the quadrant determined by the signs of the numerator and denominator to ensure α falls in the correct range (0° to 360° or 0 h to 24 h). These formulas stem from the spherical geometry of rotating the ecliptic frame by ε around the line of nodes (the vernal equinox).[8] For the modern value of ε, an approximation is ε = 23.439° - 0.00000036° × D, where D is the number of days from J2000.0.[8] In rectangular (Cartesian) form, the equatorial coordinates represent the Sun's direction as a unit vector from Earth's center, with the x-axis pointing toward the vernal equinox, the z-axis toward the north celestial pole, and the y-axis completing the right-handed system. These are given by This transformation facilitates vector-based computations in celestial mechanics, such as orbital perturbations or alignments in space missions.[10] Over long timescales, Earth's axial precession causes the vernal equinox to drift westward along the ecliptic at about 50.3 arcseconds per year, gradually shifting the reference frame for equatorial coordinates. For the Sun, whose apparent position is tied to the geocentric ecliptic, this results in secular changes to RA and Dec when expressed in a fixed epoch like J2000. The IAU 2006 precession model updates the classical precession parameters with improved dynamical consistency, incorporating a revised frame bias and precession rates in longitude (ψ_A) and obliquity (θ_A) for epochs from 1900 to 2100, achieving sub-arcsecond accuracy for solar ephemerides.[12] This model is implemented in modern astronomical software to adjust coordinates for precession effects beyond short-term observations.[12]Horizontal Coordinates
The horizontal coordinate system describes the position of the Sun as seen from a specific location on Earth, using two angles: altitude and azimuth. Altitude is the angular height of the Sun above the horizon, ranging from 0° at the horizon to 90° at the zenith directly overhead.[13] Azimuth is the horizontal direction to the Sun, measured clockwise from true north (0°) to 360°.[13] These coordinates depend on the observer's latitude and the local time of day, providing a local-frame view that accounts for Earth's rotation. To compute the Sun's horizontal coordinates from its equatorial coordinates, the declination (δ) and right ascension (α) are transformed using the observer's latitude (φ) and local sidereal time (LST). The hour angle (H) is first calculated as H = LST - α, representing the angular offset from the observer's meridian. The altitude (alt) is then given by the formula: This equation derives from spherical trigonometry on the celestial sphere.[14] The azimuth can be derived similarly, though it requires additional trigonometric adjustments for the full direction.[14] The Sun's daily path in horizontal coordinates traces an arc across the sky, rising near the east (azimuth ≈90°), reaching maximum altitude at solar noon, and setting near the west (azimuth ≈270°). The path's length and peak height vary with latitude and the Sun's declination; at the equator, the path is nearly overhead year-round, while at higher latitudes, it is lower and shorter in winter.[13] Solar noon occurs when the hour angle H = 0°, at which point the maximum altitude is 90° - |φ - δ|.[15] These coordinates are essential for practical applications, such as orienting solar panels to maximize energy capture by aligning with the Sun's altitude and azimuth throughout the day.[16] Similarly, horizontal sundials rely on the Sun's azimuth and altitude to project shadows for timekeeping, with the gnomon's angle matched to the local latitude.[17]Apparent Motion and Variations
Declination of the Sun
The declination of the Sun (δ) is its angular position north or south of the celestial equator in the equatorial coordinate system, varying annually due to Earth's axial tilt relative to its orbital plane around the Sun. This variation causes the Sun's apparent path to shift between the tropics of Cancer and Capricorn, influencing the length of daylight and the progression of seasons on Earth. The maximum extent of this shift is determined by the obliquity of the ecliptic (ε), the angle between Earth's equatorial plane and its orbital plane, which is approximately 23.44° but subject to long-term changes from precession and short-term perturbations from nutation. The Sun's declination reaches its extremes at the solstices: +23.44° at the June summer solstice (northern hemisphere) and -23.44° at the December winter solstice, corresponding to the Sun's highest and lowest positions relative to the equator. These values stem directly from Earth's axial tilt of about 23.44°, which tilts the celestial equator relative to the ecliptic by the same amount. At the equinoxes, δ = 0°, when the Sun crosses the celestial equator; these occur approximately on March 20 (vernal equinox) and September 22 (autumnal equinox) in the Gregorian calendar for the northern hemisphere. The declination's sinusoidal variation over the year drives seasonal contrasts, with higher δ values leading to longer days and more direct sunlight in the summer hemisphere, and lower values resulting in shorter days and oblique incidence in winter. The declination can be calculated using the formula: where ε is the obliquity of the ecliptic and λ is the Sun's ecliptic longitude, which increases roughly uniformly from 0° at the vernal equinox to 360° over the year. This approximation assumes a mean ecliptic longitude but can be refined for precision. The ecliptic longitude λ is determined from the Earth's orbital position, often using Keplerian elements or ephemerides. The obliquity ε is not constant; it decreases slowly due to the gravitational torques from the Moon and Sun causing Earth's precession and nutation. In 2000 (epoch J2000.0), ε was 23°26'21.406" (approximately 23.439281°), and it declines by about 0.47 arcseconds per year as part of the ~26,000-year precession cycle. A more precise expression is ε ≈ 23.439281° - 0.013° × t, where t is the time in Julian centuries from J2000.0; this accounts for the secular decrease from precession.[8] Nutation introduces small periodic variations: the principal term from lunar orbital precession adds up to ±9.2 arcseconds to the longitude and ±6.9 arcseconds to the obliquity, resulting in δ fluctuations of up to about ±10 arcseconds over an 18.6-year cycle, incorporated via the nutation in obliquity (Δε) in refined formulas like ε_true = ε_mean + Δε.[18] These effects are critical for high-precision astronomy, such as satellite operations or eclipse predictions.Equation of Time
The equation of time quantifies the discrepancy between apparent solar time, as indicated by the position of the Sun in the sky, and mean solar time, which assumes a uniform daily motion of the Sun across the sky. Defined as apparent solar time minus mean solar time, this difference arises primarily from two astronomical effects and varies annually between approximately -16 minutes and +14 minutes.[19] The two main components contributing to the equation of time are the eccentricity effect and the obliquity effect. The eccentricity effect stems from Earth's elliptical orbit around the Sun, with an eccentricity of about 0.0167, causing the Sun's apparent angular speed to vary; this component alone produces a variation of up to ±7.66 minutes, peaking around early September and early March. The obliquity effect results from the 23.44° tilt of Earth's rotational axis relative to its orbital plane, which affects the projection of Earth's rotation onto the orbital plane and contributes up to ±9.87 minutes, with zero values at the equinoxes and solstices. These effects combine to produce the overall annual variation in .[19] An approximation for the equation of time, derived from Fourier series representations of solar position, is given by where is in minutes and is the mean solar anomaly in radians (often computed as , with as the day of the year). This formula provides sufficient accuracy for many engineering and astronomical applications, with errors typically under 0.5 minutes.[20] The equation of time reaches its positive peak of about +14 minutes in mid-February, when apparent solar time is ahead of mean solar time, and its negative peak of about -16 minutes in early November, when apparent solar time lags behind. The following table summarizes key annual values based on standard astronomical computations:| Date (approximate) | Equation of Time (minutes) |
|---|---|
| February 11 | +14.0 |
| May 14 | +3.7 |
| July 26 | -6.3 |
| November 3 | -16.4 |
,_Phang_Nga_Bay,_Thailand.jpg/250px-Sunrise,_Koh_Yao_Noi_(island),_Phang_Nga_Bay,_Thailand.jpg)
,_Phang_Nga_Bay,_Thailand.jpg/2000px-Sunrise,_Koh_Yao_Noi_(island),_Phang_Nga_Bay,_Thailand.jpg)























![{\displaystyle \delta _{\odot }=\arcsin \left[\sin \left(-23.44^{\circ }\right)\cdot \sin \left(EL\right)\right]}](https://wikimedia.org/api/rest_v1/media/math/render/svg/88a08dc771b0aad640193a7c3ef372bb8f41140d)
![{\displaystyle \delta _{\odot }=-23.44^{\circ }\cdot \cos \left[{\frac {360^{\circ }}{365}}\cdot \left(N+10\right)\right]}](https://wikimedia.org/api/rest_v1/media/math/render/svg/eae7c990d26a9bb3d2f5a7a88768d28be0628fc2)
![{\displaystyle \delta _{\odot }=\arcsin \left[\sin \left(-23.44^{\circ }\right)\cdot \cos \left({\frac {360^{\circ }}{365.24}}\left(N+10\right)+{\frac {360^{\circ }}{\pi }}\cdot 0.0167\sin \left({\frac {360^{\circ }}{365.24}}\left(N-2\right)\right)\right)\right]}](https://wikimedia.org/api/rest_v1/media/math/render/svg/11d079f081b428348b4a17de9515fdc031088d48)
![{\displaystyle \delta _{\odot }=-\arcsin \left[0.39779\cos \left(0.98565^{\circ }\left(N+10\right)+1.914^{\circ }\sin \left(0.98565^{\circ }\left(N-2\right)\right)\right)\right]}](https://wikimedia.org/api/rest_v1/media/math/render/svg/583fa421f34aaf0bc31729bebc784ed8d17d9742)