Recent from talks
Nothing was collected or created yet.
Chiropractic
View on Wikipedia
| Alternative medicine | |
|---|---|
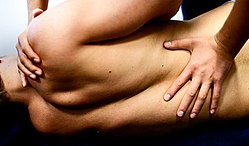
 A chiropractor performing a vertebral adjustment | |
| Claims | Vertebral subluxation, spinal adjustment, Innate Intelligence |
| Risks | Vertebral artery dissection (stroke), compression fracture, death |
| Related fields | Osteopathy, vitalism |
| Original proponents | D. D. Palmer, B. J. Palmer |
| MeSH | D002684 |
| Part of a series on |
| Alternative medicine |
|---|
 |
Chiropractic (/ˌkaɪroʊˈpræktɪk/) is a form of alternative medicine[1] concerned with the diagnosis, treatment and prevention of mechanical disorders of the musculoskeletal system, especially of the spine.[2] The main chiropractic treatment technique involves manual therapy but may also include exercises and health and lifestyle counseling.[3] Most who seek chiropractic care do so for low back pain.[4] Chiropractic is well established in the United States, Canada, and Australia,[5] along with other manual-therapy professions such as osteopathy and physical therapy.[6]
Many chiropractors (often known informally as chiros), especially those in the field's early history, have proposed that mechanical disorders affect general health,[2] and that regular manipulation of the spine (spinal adjustment) improves general health. A chiropractor may have a Doctor of Chiropractic (D.C.) degree and be referred to as "doctor" but is not a Doctor of Medicine (M.D.) or a Doctor of Osteopathic Medicine (D.O.).[7][8] While many chiropractors view themselves as primary care providers,[9][10] chiropractic clinical training does not meet the requirements for that designation.[2] A small but significant number of chiropractors spread vaccine misinformation, promote unproven dietary supplements, or administer full-spine x-rays.[11]
There is no good evidence that chiropractic manipulation is effective in helping manage lower back pain.[12][9] A 2011 critical evaluation of 45 systematic reviews concluded that the data included in the study "fail[ed] to demonstrate convincingly that spinal manipulation is an effective intervention for any condition."[13] Spinal manipulation may be cost-effective for sub-acute or chronic low back pain, but the results for acute low back pain were insufficient.[14] No compelling evidence exists to indicate that maintenance chiropractic care adequately prevents symptoms or diseases.[15]
There is not sufficient data to establish the safety of chiropractic manipulations.[16] It is frequently associated with mild to moderate adverse effects, with serious or fatal complications in rare cases.[17] There is controversy regarding the degree of risk of vertebral artery dissection, which can lead to stroke and death, from cervical manipulation.[18] Several deaths have been associated with this technique[17] and it has been suggested that the relationship is causative,[19][20] a claim which is disputed by many chiropractors.[20]
Chiropractic is based on several pseudoscientific ideas.[21] Spiritualist D. D. Palmer founded chiropractic in the 1890s,[22] claiming that he had received it from "the other world", from a doctor who had died 50 years previously.[23][24] Throughout its history, chiropractic has been controversial.[25][26] Its foundation is at odds with evidence-based medicine, and is underpinned by pseudoscientific ideas such as vertebral subluxation and Innate Intelligence.[27] Despite the overwhelming evidence that vaccination is an effective public health intervention, there are significant disagreements among chiropractors over the subject,[28] which has led to negative impacts on both public vaccination and mainstream acceptance of chiropractic.[29] The American Medical Association called chiropractic an "unscientific cult" in 1966[30] and boycotted it until losing an antitrust case in 1987.[10] Chiropractic has had a strong political base and sustained demand for services. In the last decades of the twentieth century, it gained more legitimacy and greater acceptance among conventional physicians and health plans in the United States.[10] During the COVID-19 pandemic, chiropractic professional associations advised chiropractors to adhere to CDC, WHO, and local health department guidance.[31][32] Despite these recommendations, a small but vocal and influential number of chiropractors spread vaccine misinformation.[11]
Status as fringe healing
[edit]Chiropractic is not regarded as a mainstream branch of medicine.
Origins in "folk medicine"
[edit]Chiropractic's origins lie in the folk medicine of bonesetting,[9] and as it evolved it incorporated vitalism, spiritual inspiration and rationalism.[33] Its founder, D. D. Palmer, called it "a science of healing without drugs".[9] Its early philosophy was based on deduction from irrefutable doctrine, which helped distinguish chiropractic from medicine, provided it with legal and political defenses against claims of practicing medicine without a license, and allowed chiropractors to establish themselves as an autonomous profession.[33] This "straight" philosophy, taught to generations of chiropractors, rejects the inferential reasoning of the scientific method,[33] and relies on deductions from vitalistic first principles rather than on the materialism of science.[34] However, most practitioners tend to incorporate scientific research into chiropractic,[33] and most practitioners are "mixers" who attempt to combine the materialistic reductionism of science with the metaphysics of their predecessors and with the holistic paradigm of wellness.[34] A 2008 commentary proposed that chiropractic actively divorce itself from the straight philosophy as part of a campaign to eliminate untestable dogma and engage in critical thinking and evidence-based research.[35]
Although a wide diversity of ideas exist among chiropractors,[33] they share the belief that the spine and health are related in a fundamental way, and that this relationship is mediated through the nervous system.[36] Some chiropractors claim spinal manipulation can have an effect on a variety of ailments such as irritable bowel syndrome and asthma.[37]
"Subluxation" as a Vitalist concept
[edit]In science-based medicine, the term "subluxation" refers to an incomplete or partial dislocation of a joint, from the Latin luxare for "dislocate".[38][39] Whereas medical doctors use the term exclusively to refer to physical dislocations, Chiropractic founder D. D. Palmer imbued the word subluxation with a metaphysical and philosophical meaning drawn from pseudoscientific traditions such as Vitalism.[40]
Palmer claimed that vertebral subluxations interfered with the body's function and its inborn ability to heal itself.[41] D. D. Palmer repudiated his earlier theory that vertebral subluxations caused pinched nerves in the intervertebral spaces in favor of subluxations causing altered nerve vibration, either too tense or too slack, affecting the tone (health) of the end organ.[40] He qualified this by noting that knowledge of innate intelligence was not essential to the competent practice of chiropractic.[40] This concept was later expanded upon by his son, B. J. Palmer, and was instrumental in providing the legal basis of differentiating chiropractic from conventional medicine.
Vertebral subluxation, a core concept of traditional chiropractic, remains unsubstantiated and largely untested, and a debate about whether to keep it in the chiropractic paradigm has been ongoing for decades.[42] In general, critics of traditional subluxation-based chiropractic (including chiropractors) are skeptical of its clinical value, dogmatic beliefs and metaphysical approach. While straight chiropractic still retains the traditional vitalistic construct espoused by the founders, evidence-based chiropractic suggests that a mechanistic view will allow chiropractic care to become integrated into the wider health care community.[42] This is still a continuing source of debate within the chiropractic profession as well, with some schools of chiropractic still teaching the traditional/straight subluxation-based chiropractic, while others have moved towards an evidence-based chiropractic that rejects metaphysical foundings and limits itself to primarily neuromusculoskeletal conditions.[43][44]
In 2005, the chiropractic subluxation was defined by the World Health Organization as "a lesion or dysfunction in a joint or motion segment in which alignment, movement integrity and/or physiological function are altered, although contact between joint surfaces remains intact.[45] It is essentially a functional entity, which may influence biomechanical and neural integrity."[45] This differs from the medical definition of subluxation as a significant structural displacement, which can be seen with static imaging techniques such as X-rays.[45]
Attorney David Chapman-Smith, Secretary-General of the World Federation of Chiropractic, has stated that "Medical critics have asked how there can be a subluxation if it cannot be seen on X-ray. The answer is that the chiropractic subluxation is essentially a functional entity, not structural, and is therefore no more visible on static X-ray than a limp or headache or any other functional problem."[46] The General Chiropractic Council, the statutory regulatory body for chiropractors in the United Kingdom, states that the chiropractic vertebral subluxation complex "is not supported by any clinical research evidence that would allow claims to be made that it is the cause of disease."[47]
As of 2014, the US National Board of Chiropractic Examiners states "The specific focus of chiropractic practice is known as the chiropractic subluxation or joint dysfunction. A subluxation is a health concern that manifests in the skeletal joints, and, through complex anatomical and physiological relationships, affects the nervous system and may lead to reduced function, disability or illness."[48][27]
Pseudoscience versus spinal manipulation therapy
[edit]While some chiropractors limit their practice to short-term treatment of musculoskeletal conditions, many falsely claim to be able treat myriad other conditions.[49][50] Some dissuade patients from seeking medical care, others have pretended to be qualified to act as a family doctor.[49]
Quackwatch, an alternative medicine watchdog, cautions against seeing chiropractors who:[49][51]
- Treat young children
- Discourage immunization
- Pretend to be a family doctor
- Take full spine X-rays
- Promote unproven dietary supplements
- Are antagonistic to scientific medicine
- Claim to treat non-musculoskeletal problems
Writing for the Skeptical Inquirer, one physician cautioned against seeing even chiropractors who solely claim to treat musculoskeletal conditions:
I think Spinal Manipulation Therapy (SMT) is a reasonable option for patients to try ... But I could not in good conscience refer a patient to a chiropractor... When chiropractic is effective, what is effective is not 'chiropractic': it is SMT. SMT is also offered by physical therapists, DOs, and others. These are science-based providers ... If I thought a patient might benefit from manipulation, I would rather refer him or her to a science-based provider.[49]
Scope of practice
[edit]
Chiropractors emphasize the conservative management of the neuromusculoskeletal system without the use of evidence-based medicines or surgery,[45] with special emphasis on the spine.[2] Back and neck pain are the specialties of chiropractic but many chiropractors treat ailments other than musculoskeletal issues.[9] There is a range of opinions among chiropractors: some believed that treatment should be confined to the spine, or back and neck pain; others disagreed.[52] For example, while one 2009 survey of American chiropractors had found that 73% classified themselves as "back pain/musculoskeletal specialists", the label "back and neck pain specialists" was regarded by 47% of them as a least desirable description in a 2005 international survey.[52] It has been proposed that chiropractors specialize in nonsurgical spine care, instead of attempting to also treat other problems,[35][53] but the more expansive view of chiropractic is still widespread.[54]
Mainstream health care and governmental organizations such as the World Health Organization consider chiropractic to be complementary and alternative medicine (CAM);[1] and a 2008 study reported that 31% of surveyed chiropractors categorized chiropractic as CAM, 27% as integrated medicine, and 12% as mainstream medicine.[55] Many chiropractors believe they are primary care providers,[9][10] including US[56] and UK chiropractors,[57] but the length, breadth, and depth of chiropractic clinical training do not support the requirements to be considered primary care providers,[2] so their role on primary care is limited and disputed.[2][10]
Chiropractic overlaps with several other forms of manual therapy, including massage therapy, osteopathy, physical therapy, and sports medicine.[6][58] In a 2010 article on the history of manipulative therapy, the author opined that "physical therapy emerged and grew alongside osteopathy, chiropractic, and the evolving "scientific" medical profession. However, over the next 100 years, physical therapy, osteopathy, and chiropractic were destined to travel very different paths. In its country of origin, osteopathy would coalesce with the medical profession. Chiropractic would remain autonomous from, and highly competitive with, medicine. Physical therapy, whose roots lay in working alongside and cooperating with medical physicians, continues to do so."[59][needs update]. Osteopathy outside the US remains primarily a manual medical system;[60] physical therapists work alongside and cooperate with mainstream medicine, and osteopathic medicine in the U.S. has merged with the medical profession.[59] Practitioners may distinguish these competing approaches through claims that, compared to other therapists, chiropractors heavily emphasize spinal manipulation, tend to use firmer manipulative techniques, and promote maintenance care; that osteopaths use a wider variety of treatment procedures; and that physical therapists emphasize machinery and exercise.[6]
Chiropractic diagnosis may involve a range of methods including skeletal imaging, observational and tactile assessments, and orthopedic and neurological evaluation.[45] A chiropractor may also refer a patient to an appropriate specialist, or co-manage with another health care provider.[53] Common patient management involves spinal manipulation (SM) and other manual therapies to the joints and soft tissues, rehabilitative exercises, health promotion, electrical modalities, complementary procedures, and lifestyle advice.[3]

A related field, veterinary chiropractic, applies manual therapies to animals and is recognized in many US states,[61] but is not recognized by the American Chiropractic Association as being chiropractic.[62] It remains controversial within certain segments of the veterinary and chiropractic professions.[63]
No single profession "owns" spinal manipulation and there is little consensus as to which profession should administer SM, raising concerns by chiropractors that other medical physicians could "steal" SM procedures from chiropractors.[64] A focus on evidence-based SM research has also raised concerns that the resulting practice guidelines could limit the scope of chiropractic practice to treating backs and necks.[64] Two US states (Washington and Arkansas) prohibit physical therapists from performing SM,[65] some states allow them to do it only if they have completed advanced training in SM, and some states allow only chiropractors to perform SM, or only chiropractors and physicians. Bills to further prohibit non-chiropractors from performing SM are regularly introduced into state legislatures and are opposed by physical therapist organizations.[66]
Treatments
[edit]
Spinal manipulation, which chiropractors call "spinal adjustment" or "chiropractic adjustment", is the most common treatment used in chiropractic care.[67] Spinal manipulation is a passive manual maneuver during which a three-joint complex is taken past the normal range of movement, but not so far as to dislocate or damage the joint.[68] Its defining factor is a dynamic thrust, which is a sudden force that causes an audible release and attempts to increase a joint's range of motion.[68] High-velocity, low-amplitude spinal manipulation (HVLA-SM) thrusts have physiological effects that signal neural discharge from paraspinal muscle tissues, depending on duration and amplitude of the thrust are factors of the degree in paraspinal muscle spindles activation.[69] Clinical skill in employing HVLA-SM thrusts depends on the ability of the practitioner to handle the duration and magnitude of the load.[69] More generally, spinal manipulative therapy (SMT) describes techniques where the hands are used to manipulate, massage, mobilize, adjust, stimulate, apply traction to, or otherwise influence the spine and related tissues.[68]
There are several schools of chiropractic adjustive techniques, although most chiropractors mix techniques from several schools. The following adjustive procedures were received by more than 10% of patients of licensed US chiropractors in a 2003 survey:[67] Diversified technique (full-spine manipulation, employing various techniques), extremity adjusting, Activator technique (which uses a spring-loaded tool to deliver precise adjustments to the spine), Thompson Technique (which relies on a drop table and detailed procedural protocols), Gonstead (which emphasizes evaluating the spine along with specific adjustment that avoids rotational vectors), Cox/flexion-distraction (a gentle, low-force adjusting procedure which mixes chiropractic with osteopathic principles and utilizes specialized adjusting tables with movable parts), adjustive instrument, Sacro-Occipital Technique (which models the spine as a torsion bar), Nimmo Receptor-Tonus Technique, applied kinesiology (which emphasises "muscle testing" as a diagnostic tool), and cranial.[70] Chiropractic biophysics technique uses inverse functions of rotations during spinal manipulation.[71] Koren Specific Technique (KST) may use their hands, or they may use an electric device known as an "ArthroStim" for assessment and spinal manipulations.[72] Insurers in the US and UK that cover other chiropractic techniques exclude KST from coverage because they consider it to be "experimental and investigational".[72][73][74][75] Medicine-assisted manipulation, such as manipulation under anesthesia, involves sedation or local anesthetic and is done by a team that includes an anesthesiologist; a 2008 systematic review did not find enough evidence to make recommendations about its use for chronic low back pain.[76]

Many other procedures are used by chiropractors for treating the spine, other joints and tissues, and general health issues. The following procedures were received by more than one-third of patients of licensed US chiropractors in a 2003 survey: Diversified technique (full-spine manipulation; mentioned in previous paragraph), physical fitness/exercise promotion, corrective or therapeutic exercise, ergonomic/postural advice, self-care strategies, activities of daily living, changing risky/unhealthy behaviors, nutritional/dietary recommendations, relaxation/stress reduction recommendations, ice pack/cryotherapy, extremity adjusting (also mentioned in previous paragraph), trigger point therapy, and disease prevention/early screening advice.[67]
A 2010 study describing Belgian chiropractors and their patients found chiropractors in Belgium mostly focus on neuromusculoskeletal complaints in adult patients, with emphasis on the spine.[77] The diversified technique is the most often applied technique at 93%, followed by the Activator mechanical-assisted technique at 41%.[77] A 2009 study assessing chiropractic students giving or receiving spinal manipulations while attending a United States chiropractic college found Diversified, Gonstead, and upper cervical manipulations are frequently used methods.[78]
Practice guidelines
[edit]Reviews of research studies within the chiropractic community have been used to generate practice guidelines outlining standards that specify which chiropractic treatments are legitimate (i.e. supported by evidence) and conceivably reimbursable under managed care health payment systems.[64] Evidence-based guidelines are supported by one end of an ideological continuum among chiropractors; the other end employs antiscientific reasoning and makes unsubstantiated claims.[2][27][42][79][80] Chiropractic remains at a crossroads, and that in order to progress it would need to embrace science; the promotion by some for it to be a cure-all was both "misguided and irrational".[81] A 2007 survey of Alberta chiropractors found that they do not consistently apply research in practice, which may have resulted from a lack of research education and skills.[82] Specific guidelines concerning the treatment of nonspecific (i.e., unknown cause) low back pain are inconsistent between countries.[83]
Effectiveness
[edit]Numerous controlled clinical studies of treatments used by chiropractors have been conducted, with varied results.[9] There is no conclusive evidence that chiropractic manipulative treatment is effective for the treatment of any medical condition, except perhaps for certain kinds of back pain.[9][13]
Generally, the research carried out into the effectiveness of chiropractic has been of poor quality.[84][85] Research published by chiropractors is distinctly biased: reviews of SM for back pain tended to find positive conclusions when authored by chiropractors, while reviews by mainstream authors did not.[9]
There is a wide range of ways to measure treatment outcomes.[86] Chiropractic care benefits from the placebo response,[87] but it is difficult to construct a trustworthy placebo for clinical trials of spinal manipulative therapy (SMT).[88] The efficacy of maintenance care in chiropractic is unknown.[89]
Available evidence covers the following conditions:
- Low back pain. There is no good evidence chiropractic is effective for helping manage lower back pain.[12]
- Radiculopathy. A 2013 systematic review and meta-analysis found a statistically significant improvement in overall recovery from sciatica following SM, when compared to usual care, and suggested that SM may be considered.[90] There is moderate quality evidence to support the use of SM for the treatment of acute lumbar radiculopathy[91] and acute lumbar disc herniation with associated radiculopathy.[92] There is low or very low evidence supporting SM for chronic lumbar spine-related extremity symptoms and cervical spine-related extremity symptoms of any duration and no evidence exists for the treatment of thoracic radiculopathy.[91]
- Whiplash and other neck pain. There is no consensus on the effectiveness of manual therapies for neck pain.[93] A 2013 systematic review found that the data suggests that there are minimal short- and long-term treatment differences when comparing manipulation or mobilization of the cervical spine to physical therapy or exercise for neck pain improvement.[94] A 2013 systematic review found that although there is insufficient evidence that thoracic SM is more effective than other treatments, it is a suitable intervention to treat some patients with non-specific neck pain.[95] A 2011 systematic review found that thoracic SM may offer short-term improvement for the treatment of acute or subacute mechanical neck pain; although the body of literature is still weak.[96] A 2010 Cochrane review found low quality evidence that suggests cervical manipulation may offer better short-term pain relief than a control for neck pain, and moderate evidence that cervical manipulation and mobilization produced similar effects on pain, function and patient satisfaction.[97] A 2010 systematic review found low level evidence that suggests chiropractic care improves cervical range of motion and pain in the management of whiplash.[98]
- Headache. There is no good evidence chiropractic helps with migraine.[12]
- Extremity conditions. A 2011 systematic review and meta-analysis concluded that the addition of manual mobilizations to an exercise program for the treatment of knee osteoarthritis resulted in better pain relief than a supervised exercise program alone and suggested that manual therapists consider adding manual mobilization to optimize supervised active exercise programs.[99] There is silver level evidence that manual therapy is more effective than exercise for the treatment of hip osteoarthritis, however this evidence could be considered to be inconclusive.[100] There is a small amount of research into the efficacy of chiropractic treatment for upper limbs,[101] limited to low level evidence supporting chiropractic management of shoulder pain[102] and limited or fair evidence supporting chiropractic management of leg conditions.[103]
- Other. A 2012 systematic review found insufficient low bias evidence to support the use of spinal manipulation as a therapy for the treatment of hypertension.[104] A 2011 systematic review found moderate evidence to support the use of manual therapy for cervicogenic dizziness.[105] There is very weak evidence for chiropractic care for adult scoliosis (curved or rotated spine)[106] and no scientific data for idiopathic adolescent scoliosis.[107] A 2007 systematic review found that few studies of chiropractic care for nonmusculoskeletal conditions are available, and they are typically not of high quality; it also found that the entire clinical encounter of chiropractic care (as opposed to just SM) provides benefit to patients with cervicogenic dizziness, and that the evidence from reviews is negative, or too weak to draw conclusions, for a wide variety of other nonmusculoskeletal conditions, including ADHD/learning disabilities, dizziness, high blood pressure, and vision conditions.[108] Other reviews have found no evidence of significant benefit for asthma,[109][110] baby colic,[111][112] bedwetting,[113] carpal tunnel syndrome,[114] fibromyalgia,[115] gastrointestinal disorders,[116] kinetic imbalance due to suboccipital strain (KISS) in infants,[111][117] menstrual cramps,[118] insomnia,[119] postmenopausal symptoms,[119] or pelvic and back pain during pregnancy.[120] As there is no evidence of effectiveness or safety for cervical manipulation for baby colic, it is not endorsed.[121]
Safety
[edit]
The World Health Organization found chiropractic care in general is safe when employed skillfully and appropriately.[45] There is not sufficient data to establish the safety of chiropractic manipulations.[16] Manipulation is regarded as relatively safe but complications can arise, and it has known adverse effects, risks and contraindications.[45] Absolute contraindications to spinal manipulative therapy are conditions that should not be manipulated; these contraindications include rheumatoid arthritis and conditions known to result in unstable joints.[45] Relative contraindications are conditions where increased risk is acceptable in some situations and where low-force and soft-tissue techniques are treatments of choice; these contraindications include osteoporosis.[45] Although most contraindications apply only to manipulation of the affected region, some neurological signs indicate referral to emergency medical services; these include sudden and severe headache or neck pain unlike that previously experienced.[122] Indirect risks of chiropractic involve delayed or missed diagnoses through consulting a chiropractor.[9]
Spinal manipulation is associated with frequent, mild and temporary adverse effects,[17][122] including new or worsening pain or stiffness in the affected region.[123] They have been estimated to occur in 33% to 61% of patients, and frequently occur within an hour of treatment and disappear within 24 to 48 hours;[16] adverse reactions appear to be more common following manipulation than mobilization.[124] The most frequently stated adverse effects are mild headache, soreness, and briefly elevated pain fatigue.[125] Chiropractic is correlated with a very high incidence of minor adverse effects.[9] Rarely,[45] spinal manipulation, particularly on the upper spine, can also result in complications that can lead to permanent disability or death; these can occur in adults[17] and children.[126] Estimates vary widely for the incidence of these complications,[16] and the actual incidence is unknown, due to high levels of underreporting and to the difficulty of linking manipulation to adverse effects such as stroke, which is a particular concern.[17] Adverse effects are poorly reported in recent studies investigating chiropractic manipulations.[127] A 2016 systematic review concludes that the level of reporting is unsuitable and unacceptable.[128] Reports of serious adverse events have occurred, resulting from spinal manipulation therapy of the lumbopelvic region.[129]
X-rays
[edit]
The use of X-ray imaging in the case of vertebral subluxation exposes patients to harmful ionizing radiation for no evidentially supported reason.[130][131] The 2008 book Trick or Treatment states "X-rays can reveal neither the subluxations nor the innate intelligence associated with chiropractic philosophy, because they do not exist."[132]
Chiropractors sometimes employ diagnostic imaging techniques such as X-rays and CT scans that rely on ionizing radiation.[133] Although there is no clear evidence to justify the practice, some chiropractors still X-ray a patient several times a year.[132] Practice guidelines aim to reduce unnecessary radiation exposure,[133] which increases cancer risk in proportion to the amount of radiation received.[134] Research suggests that radiology instruction given at chiropractic schools worldwide seem to be evidence-based.[131] Although, there seems to be a disparity between some schools and available evidence regarding the aspect of radiography for patients with acute low back pain without an indication of a serious disease, which may contribute to chiropractic overuse of radiography for low back pain.[131] QuackWatch cautions against seeing chiropractors who do full-body x-rays.[49]
Neck manipulation
[edit]Estimates for serious adverse events vary from 5 strokes per 100,000 manipulations to 1.46 serious adverse events per 10 million manipulations and 2.68 deaths per 10 million manipulations, though it was determined that there was inadequate data to be conclusive.[16] Several case reports show temporal associations between interventions and potentially serious complications.[135] The published medical literature contains reports of 26 deaths since 1934 following chiropractic manipulations and many more seem to remain unpublished.[20]
Vertebrobasilar artery stroke (VAS) is statistically associated with chiropractic services in persons under 45 years of age, but it is similarly associated with general practitioner services, suggesting that these associations are likely explained by preexisting conditions.[135][136] Weak to moderately strong evidence supports causation (as opposed to statistical association) between cervical manipulative therapy (CMT) and VAS.[137] There is insufficient evidence to support a strong association or no association between cervical manipulation and stroke.[18] While the biomechanical evidence is not sufficient to support the statement that CMT causes cervical artery dissection (CD), clinical reports suggest that mechanical forces have a part in a substantial number of CDs and the majority of population controlled studies found an association between CMT and VAS in young people.[138] It is strongly recommended that practitioners consider the plausibility of CD as a symptom, and people can be informed of the association between CD and CMT before administering manipulation of the cervical spine.[138] There is controversy regarding the degree of risk of stroke from cervical manipulation.[18] Many chiropractors state that, the association between chiropractic therapy and vertebral arterial dissection is not proven.[20] However, it has been suggested that the causality between chiropractic cervical manipulation beyond the normal range of motion and vascular accidents is probable[20] or definite.[19] There is very low evidence supporting a small association between internal carotid artery dissection and chiropractic neck manipulation.[139] The incidence of internal carotid artery dissection following cervical spine manipulation is unknown.[140] The literature infrequently reports helpful data to better understand the association between cervical manipulative therapy, cervical artery dissection and stroke.[141] The limited evidence is inconclusive that chiropractic spinal manipulation therapy is not a cause of intracranial hypotension.[142] Cervical intradural disc herniation is very rare following spinal manipulation therapy.[143]
A 2012 systematic review concluded that no accurate assessment of risk-benefit exists for cervical manipulation.[18] A 2010 systematic review stated that there is no good evidence to assume that neck manipulation is an effective treatment for any medical condition and suggested a precautionary principle in healthcare for chiropractic intervention even if a causality with vertebral artery dissection after neck manipulation were merely a remote possibility.[20] The same review concluded that the risk of death from manipulations to the neck outweighs the benefits.[20] Chiropractors have criticized this conclusion, claiming that the author did not evaluate the potential benefits of spinal manipulation.[144] Edzard Ernst stated "This detail was not the subject of my review. I do, however, refer to such evaluations and should add that a report recently commissioned by the General Chiropractic Council did not support many of the outlandish claims made by many chiropractors across the world."[144] A 1999 review of 177 previously reported cases published between 1925 and 1997 in which injuries were attributed to manipulation of the cervical spine (MCS) concluded that "The literature does not demonstrate that the benefits of MCS outweigh the risks." The professions associated with each injury were assessed. Physical therapists (PT) were involved in less than 2% of all cases, with no deaths caused by PTs. Chiropractors were involved in a little more than 60% of all cases, including 32 deaths.[145]
A 2009 review evaluating maintenance chiropractic care found that spinal manipulation is associated with considerable harm and no compelling evidence exists to indicate that it adequately prevents symptoms or diseases, thus the risk-benefit is not evidently favorable.[15]
Cost-effectiveness
[edit]A 2012 systematic review suggested that the use of spine manipulation in clinical practice is a cost-effective treatment when used alone or in combination with other treatment approaches.[146] A 2011 systematic review found evidence supporting the cost-effectiveness of using spinal manipulation for the treatment of sub-acute or chronic low back pain; the results for acute low back pain were insufficient.[14]
A 2006 systematic cost-effectiveness review found that the reported cost-effectiveness of spinal manipulation in the United Kingdom compared favorably with other treatments for back pain, but that reports were based on data from clinical trials without placebo controls and that the specific cost-effectiveness of the treatment (as opposed to non-specific effects) remains uncertain.[147] A 2005 American systematic review of economic evaluations of conservative treatments for low back pain found that significant quality problems in available studies meant that definite conclusions could not be drawn about the most cost-effective intervention.[148] The cost-effectiveness of maintenance chiropractic care is unknown.[89][non-primary source needed]
Analysis of a clinical and cost utilization data from the years 2003 to 2005 by an integrative medicine independent physician association (IPA) which looked the chiropractic services utilization found that the clinical and cost utilization of chiropractic services based on 70,274 member-months over a 7-year period decreased patient costs associate with the following use of services by 60% for in-hospital admissions, 59% for hospital days, 62% for outpatient surgeries and procedures, and 85% for pharmaceutical costs when compared with conventional medicine (visit to a medical doctor primary care provider) IPA performance for the same health maintenance organization product in the same geography and time frame.[149]
Education, licensing, and regulation
[edit]Requirements vary between countries. In the U.S. chiropractors obtain a non-medical accredited diploma in the field of chiropractic.[150] Chiropractic education in the U.S. has been criticized for failing to meet generally accepted standards of evidence-based medicine.[151] The curriculum content of North American chiropractic and medical colleges with regard to basic and clinical sciences has little similarity, both in the kinds of subjects offered and in the time assigned to each subject.[152] Accredited chiropractic programs in the U.S. require that applicants have 90 semester hours of undergraduate education with a grade point average of at least 3.0 on a 4.0 scale. Many programs require at least three years of undergraduate education, and more are requiring a bachelor's degree.[153] Canada requires a minimum three years of undergraduate education for applicants, and at least 4200 instructional hours (or the equivalent) of full-time chiropractic education for matriculation through an accredited chiropractic program.[154] Graduates of the Canadian Memorial Chiropractic College (CMCC) are formally recognized to have at least 7–8 years of university level education.[155][156] The World Health Organization (WHO) guidelines suggest three major full-time educational paths culminating in either a DC, DCM, BSc, or MSc degree. Besides the full-time paths, they also suggest a conversion program for people with other health care education and limited training programs for regions where no legislation governs chiropractic.[45]
Upon graduation, there may be a requirement to pass national, state, or provincial board examinations before being licensed to practice in a particular jurisdiction.[157][158] Depending on the location, continuing education may be required to renew these licenses.[159][160] Specialty training is available through part-time postgraduate education programs such as chiropractic orthopedics and sports chiropractic, and through full-time residency programs such as radiology or orthopedics.[161]
In the U.S., chiropractic schools are accredited through the Council on Chiropractic Education (CCE) while the General Chiropractic Council (GCC) is the statutory governmental body responsible for the regulation of chiropractic in the UK.[162][163] The U.S. CCE requires a mixing curriculum, which means a straight-educated chiropractor may not be eligible for licensing in states requiring CCE accreditation.[164] CCEs in the U.S., Canada, Australia and Europe have joined to form CCE-International (CCE-I) as a model of accreditation standards with the goal of having credentials portable internationally.[165] Today, there are 18 accredited Doctor of Chiropractic programs in the U.S.,[166] 2 in Canada,[167] 6 in Australasia,[168] and 5 in Europe.[169] All but one of the chiropractic colleges in the U.S. are privately funded, but in several other countries they are in government-sponsored universities and colleges.[25] Of the two chiropractic colleges in Canada, one is publicly funded (UQTR) and one is privately funded (CMCC). In 2005, CMCC was granted the privilege of offering a professional health care degree under the Post-secondary Education Choice and Excellence Act, which sets the program within the hierarchy of education in Canada as comparable to that of other primary contact health care professions such as medicine, dentistry and optometry.[155][156]
Regulatory colleges and chiropractic boards in the U.S., Canada, Mexico, and Australia are responsible for protecting the public, standards of practice, disciplinary issues, quality assurance and maintenance of competency.[170][171]
Chiropractors often argue that this education is as good as or better than medical physicians', but most chiropractic training is confined to classrooms with much time spent learning theory, adjustment, and marketing.[164] The fourth year of chiropractic education persistently showed the highest stress levels.[172] Every student, irrespective of year, experienced different ranges of stress when studying.[172] The chiropractic leaders and colleges have had internal struggles.[173] Rather than cooperation, there has been infighting between different factions.[173] A number of actions were posturing due to the confidential nature of the chiropractic colleges in an attempt to enroll students.[173][clarification needed]
In 2024, Oregon Public Broadcasting reported on the high debt burden of students who pursued degrees in alternative medicine. Ten different chiropractic programs were ranked among the 47 US graduate programs with highest debt to earnings ratios.[174][175] Analyses by Quackwatch and the Sunlight Foundation found high rates of default on Health Education Assistance Loan (HEAL) student loans used for chiropractic programs.[176][177][178] Among health professionals who were listed as in default on HEAL loans in 2012, 53% were chiropractors.[178]
Ethics
[edit]The chiropractic oath is a modern variation of the classical Hippocratic Oath historically taken by physicians and other healthcare professionals swearing to practice their professions ethically.[179] The American Chiropractic Association (ACA) has an ethical code "based upon the acknowledgement that the social contract dictates the profession's responsibilities to the patient, the public, and the profession; and upholds the fundamental principle that the paramount purpose of the chiropractic doctor's professional services shall be to benefit the patient."[180] The International Chiropractor's Association (ICA) also has a set of professional canons.[181]
A 2008 commentary proposed that the chiropractic profession actively regulate itself to combat abuse, fraud, and quackery, which are more prevalent in chiropractic than in other health care professions, violating the social contract between patients and physicians.[35] According to a 2015 Gallup poll of U.S. adults, the perception of chiropractors is generally favorable; two-thirds of American adults agree that chiropractors have their patient's best interest in mind and more than half also agree that most chiropractors are trustworthy. Less than 10% of US adults disagreed with the statement that chiropractors were trustworthy.[182][183]

Chiropractors, especially in America, have a reputation for unnecessarily treating patients.[132] In many circumstances the focus seems to be put on economics instead of health care.[132] Sustained chiropractic care is promoted as a preventive tool, but unnecessary manipulation could possibly present a risk to patients.[9] Some chiropractors are concerned by the routine unjustified claims chiropractors have made.[9] A 2010 analysis of chiropractic websites found the majority of chiropractors and their associations made claims of effectiveness not supported by scientific evidence, while 28% of chiropractor websites advocate lower back pain care, which has some sound evidence.[186]
The US Office of the Inspector General (OIG) estimated that for calendar year 2013, 82% of payments to chiropractors under Medicare Part B, a total of $359 million, did not comply with Medicare requirements.[187] There have been at least 15 OIG reports about chiropractic billing irregularities since 1986.[187]
In 2009, a backlash to the libel suit filed by the British Chiropractic Association (BCA) against Simon Singh inspired the filing of formal complaints of false advertising against more than 500 individual chiropractors within one 24-hour period,[188][189] prompting the McTimoney Chiropractic Association to write to its members advising them to remove leaflets that make claims about whiplash and colic from their practice, to be wary of new patients and telephone inquiries, and telling their members: "If you have a website, take it down NOW" and "Finally, we strongly suggest you do NOT discuss this with others, especially patients."[188] An editorial in Nature suggested that the BCA may have been trying to suppress debate and that this use of English libel law was a burden on the right to freedom of expression, which is protected by the European Convention on Human Rights.[190] The libel case ended with the BCA withdrawing its suit in 2010.[191][192]
Reception
[edit]Chiropractic is established in the U.S., Canada, and Australia, and is present to a lesser extent in many other countries.[5] It is viewed as a marginal and non-clinically–proven attempt at complementary and alternative medicine, which has not integrated into mainstream medicine.[52]
Australia
[edit]In Australia, there are approximately 2488 chiropractors, or one chiropractor for every 7980 people.[193] Most private health insurance funds in Australia cover chiropractic care, and the federal government funds chiropractic care when the patient is referred by a medical practitioner.[194] In 2014, the chiropractic profession had a registered workforce of 4,684 practitioners in Australia represented by two major organizations – the Chiropractors' Association of Australia (CAA) and the Chiropractic and Osteopathic College of Australasia (COCA).[195] Annual expenditure on chiropractic care (alone or combined with osteopathy) in Australia is estimated to be between AUD$750–988 million with musculoskeletal complaints such as back and neck pain making up the bulk of consultations; and proportional expenditure is similar to that found in other countries.[195] While Medicare (the Australian publicly funded universal health care system) coverage of chiropractic services is limited to only those directed by a medical referral to assist chronic disease management, most private health insurers in Australia do provide partial reimbursement for a wider range of chiropractic services in addition to limited third party payments for workers compensation and motor vehicle accidents.[195]
Of the 2,005 chiropractors who participated in a 2015 survey, 62.4% were male and the average age was 42.1 (SD = 12.1) years.[195] Nearly all chiropractors (97.1%) had a bachelor's degree or higher, with the majority of chiropractor's highest professional qualification being a bachelor or double bachelor's degree (34.6%), followed by a master's degree (32.7%), Doctor of Chiropractic (28.9%) or PhD (0.9%).[195] Only a small number of chiropractor's highest professional qualification was a diploma (2.1%) or advanced diploma (0.8%).[195]
Germany
[edit]In Germany, chiropractic may be offered by medical doctors and alternative practitioners. Chiropractors qualified abroad must obtain a German non-medical practitioner license. Authorities have routinely required a comprehensive knowledge test for this, but in the recent past, some administrative courts have ruled that training abroad should be recognised.[196]
Switzerland
[edit]In Switzerland, only trained medical professionals are allowed to offer chiropractic.[197] Since 1995, chiropractors have been licensed to prescribe a limited set of pharmaceuticals, which were expanded in 2018.[198] A 2010 survey found that 72% of Swiss chiropractors considered their ability to prescribe nonprescription medication as an advantage for chiropractic treatment.[199]
There are approximately 300 chiropractors in Switzerland.[200]
United Kingdom
[edit]Chiropractic is available on the National Health Service in some areas, such as Cornwall, where the treatment is only available for neck or back pain.[201]
A 2010 study by questionnaire presented to UK chiropractors indicated only 45% of chiropractors disclosed to patients the serious risk associated with manipulation of the cervical spine and that 46% believed there was possibility patients would refuse treatment if the risks were correctly explained. However 80% acknowledged the ethical/moral responsibility to disclose risk to patients.[202]
United States and Canada
[edit]In 2025, the American Chiropractic Association reported that 70,000 practitioners were active in the United States.[203] The percentage of the population that utilizes chiropractic care at any given time generally falls into a range from 6% to 12% in the U.S. and Canada,[204] with a global high of 20% in Alberta in 2006.[205] In 2008, chiropractors were reported to be the most common CAM providers for children and adolescents, these patients representing up to 14% of all visits to chiropractors.[206] A 2022 report found 11% of Americans visit a chiropractor.[207][better source needed][full citation needed]
In 2002–03, the majority of those who sought chiropractic did so for relief from back and neck pain and other neuromusculoskeletal complaints;[4] most do so specifically for low back pain.[4][204] The majority of U.S. chiropractors participate in some form of managed care.[10] Although the majority of U.S. chiropractors view themselves as specialists in neuromusculoskeletal conditions, many also consider chiropractic as a type of primary care.[10] In the majority of cases, the care that chiropractors and physicians provide divides the market, however for some, their care is complementary.[10]
In the U.S., chiropractors perform over 90% of all manipulative treatments.[208] Satisfaction rates are typically higher for chiropractic care compared to medical care, with a 1998 U.S. survey reporting 83% of respondents satisfied or very satisfied with their care; quality of communication seems to be a consistent predictor of patient satisfaction with chiropractors.[209]
Utilization of chiropractic care is sensitive to the costs incurred by the co-payment by the patient.[1] The use of chiropractic declined from 9.9% of U.S. adults in 1997 to 7.4% in 2002; this was the largest relative decrease among CAM professions, which overall had a stable use rate.[210] As of 2007 7% of the U.S. population is being reached by chiropractic.[211] They were the third largest medical profession in the US in 2002, following physicians and dentists.[212] Employment of U.S. chiropractors was expected to increase 14% between 2006 and 2016, faster than the average for all occupations.[213]
Since 1972, chiropractic treatment of the spine has been covered by Medicare, the US federal health insurance program in the United States.[214] In 1974 the United States Commissioner of Education officially listed the Council on Chiropractic Education as a "Nationally Recognized Accrediting Agency".[215][216] This allowed for eligibility for federal education and research grants, student eligibility for federal loans, and gave increased legitimacy for chiropractic as a profession overall.[215] In 1980, the American Medical Association revised its code of ethics, allowing members to provide referrals to chiropractors.[217]
Modernly, chiropractors often work in collaboration with primary care physicians and other medical specialists; the American College of Physicians recommends spinal manipulation therapy as an alternative to pain-relieving drugs for low back pain.[218] Most states require insurers to cover chiropractic care, and most HMOs cover these services.[206]
Chiropractors are not normally licensed to write medical prescriptions or perform major surgery in the United States[219] (although New Mexico has become the first US state to allow "advanced practice" trained chiropractors to prescribe certain medications[220][221]). In the US, their scope of practice varies by state, based on inconsistent views of chiropractic care: some states, such as Iowa, broadly allow treatment of "human ailments"; some, such as Delaware, use vague concepts such as "transition of nerve energy" to define scope of practice; others, such as New Jersey, specify a severely narrowed scope.[164] US states also differ over whether chiropractors may conduct laboratory tests or diagnostic procedures, dispense dietary supplements, or use other therapies such as homeopathy and acupuncture; in Oregon they can become certified to perform minor surgery and to deliver children via natural childbirth.[219] A 2003 survey of North American chiropractors found that a slight majority favored allowing them to write prescriptions for over-the-counter drugs.[222]
In 2024, the University of Pittsburgh announced a Doctor of Chiropractic program—the first of its kind at a public research intensive university.[223][224]
History
[edit]
Chiropractic's origins lie in the folk medicine practice of bonesetting, in which untrained practitioners engaged in joint manipulation or resetting fractured bones.[9] Chiropractic was founded in 1895 by Daniel David (D. D.) Palmer in Davenport, Iowa. Palmer, a magnetic healer, hypothesized that manual manipulation of the spine could cure disease.[225] The first chiropractic patient of D. D. Palmer was Harvey Lillard, a worker in the building where Palmer's office was located.[226] He claimed that he had severely reduced hearing for 17 years, which started shortly following a "pop" in his spine.[226] A few days following his adjustment, Lillard claimed his hearing was almost completely restored.[226] Another of Palmer's patients, Samuel Weed, coined the term chiropractic, from Greek χειρο- chiro- 'hand' (itself from χείρ cheir 'hand') and πρακτικός praktikos 'practical'.[227][228] Chiropractic is classified as a field of pseudomedicine.[229]
Chiropractic competed with its predecessor osteopathy, another medical system based on magnetic healing; both systems were founded by charismatic midwesterners in opposition to the conventional medicine of the day, and both postulated that manipulation improved health.[225] Although initially keeping chiropractic a family secret, in 1898 Palmer began teaching it to a few students at his new Palmer School of Chiropractic.[22] One student, his son Bartlett Joshua (B. J.) Palmer, became committed to promoting chiropractic, took over the Palmer School in 1906, and rapidly expanded its enrollment.[22] His son B. J. Palmer helped to expand chiropractic in the early 20th century.[22]
Early chiropractors believed that all disease was caused by interruptions in the flow of innate intelligence, a vitalistic nervous energy or life force that represented God's presence in man; chiropractic leaders often invoked religious imagery and moral traditions.[22] D. D. Palmer said he "received chiropractic from the other world".[23] D. D. and B. J. both seriously considered declaring chiropractic a religion, which might have provided legal protection under the U.S. constitution, but decided against it partly to avoid confusion with Christian Science.[22][23] Early chiropractors also tapped into the Populist movement, emphasizing craft, hard work, competition, and advertisement, aligning themselves with the common man against intellectuals and trusts, among which they included the American Medical Association (AMA).[22]

Chiropractic has seen considerable controversy and criticism.[25][26] Although D. D. and B. J. were "straight" and disdained the use of instruments, some early chiropractors, whom B. J. scornfully called "mixers", advocated the use of instruments.[22] In 1910, B. J. changed course and endorsed X-rays as necessary for diagnosis; this resulted in a significant exodus from the Palmer School of the more conservative faculty and students.[22] The mixer camp grew until by 1924 B. J. estimated that only 3,000 of the United States' 25,000 chiropractors remained straight.[22] That year, B. J.'s invention and promotion of the neurocalometer, a temperature-sensing device, was highly controversial among B. J.'s fellow straights. By the 1930s, chiropractic was the largest alternative healing profession in the U.S.[22]

Chiropractors faced heavy opposition from organized medicine.[226] D. D. Palmer was jailed in 1907 for practicing medicine without a license.[230][full citation needed] Thousands of chiropractors were prosecuted for practicing medicine without a license, and D. D. and many other chiropractors were jailed.[226] To defend against medical statutes, B. J. argued that chiropractic was separate and distinct from medicine, asserting that chiropractors "analyzed" rather than "diagnosed", and "adjusted" subluxations rather than "treated" disease.[226] B. J. cofounded the Universal Chiropractors' Association (UCA) to provide legal services to arrested chiropractors.[226] Although the UCA won their first test case in Wisconsin in 1907, prosecutions instigated by state medical boards became increasingly common and in many cases were successful. In response, chiropractors conducted political campaigns to secure separate licensing statutes, eventually succeeding in all fifty states, from Kansas in 1913 through Louisiana in 1974.[226] The longstanding feud between chiropractors and medical doctors continued for decades.
Chiropractic philosophy includes the following perspectives:[34]
Holism assumes that health is affected by everything in an individual's environment; some sources also include a spiritual or existential dimension.[231] In contrast, reductionism in chiropractic reduces causes and cures of health problems to a single factor, vertebral subluxation.[35] Homeostasis emphasizes the body's inherent self-healing abilities. Chiropractic's early notion of innate intelligence can be thought of as a metaphor for homeostasis.[33]
A large number of chiropractors fear that if they do not separate themselves from the traditional vitalistic concept of innate intelligence, chiropractic will continue to be seen as a fringe profession.[232] A variant of chiropractic called naprapathy originated in Chicago in the early twentieth century.[233][234] It holds that manual manipulation of soft tissue can reduce "interference" in the body and thus improve health.[234]
Straights (Vitalists) versus Mixers (Materialists)
[edit]
By 1914,[235] chiropractors had begun to divide into two groups: "Straights", adherents of the Palmers' supernatural vitalist beliefs, and "Mixers" who sought to integrate Chiropractic into science-based mainstream medicine.[236]: 172
| Perspective attribute | Potential belief endpoints | |
|---|---|---|
| Scope of practice: | narrow ("straight") ← | → broad ("mixer") |
| Philosophic orientation: | vitalistic ← | → materialistic |
| Falsifiability: | untestable Cannot be proven or disproven |
testable Lends itself to scientific inquiry |
| Taken from Mootz & Phillips 1997[34] | ||
Originally, Straight chiropractors adhered to pseudoscientific Vitalist ideas set forth by D. D. and B. J. Palmer, and even modern "straights" often retain metaphysical definitions and vitalistic qualities.[226] Straight chiropractors believed that vertebral subluxation leads to interference with an "innate intelligence" exerted via the human nervous system and is a primary underlying risk factor for many diseases.[226] Straights view the medical diagnosis of patient complaints, which they consider to be the "secondary effects" of subluxations, to be unnecessary for chiropractic treatment.[226] Thus, straight chiropractors are concerned primarily with the detection and correction of vertebral subluxation via adjustment and do not "mix" other types of therapies into their practice style.[226] Their philosophy and explanations were metaphysical in nature, and they preferred to use traditional chiropractic lexicon terminology such as "perform spinal analysis", "detect subluxation", "correct with adjustment".[232] They preferred to remain separate and distinct from mainstream health care.[232] Modernly, "Straights" are a minority among Chiropractors, though "they have been able to transform their status as purists and heirs of the lineage into influence dramatically out of proportion to their numbers."[232]
Mixers, who make up the majority of chiropractors, "mix" chiropractic with diagnostic and treatment approaches from mainstream medical and osteopathic practices.[232] Unlike straight chiropractors, mixers believe subluxation is just one of many causes of disease, and mixers are open to mainstream medicine.[232] Many mixers incorporate mainstream medical diagnostics and employ conventional medical treatments including techniques of physical therapy such as exercise, stretching, massage, ice packs, electrical muscle stimulation, therapeutic ultrasound, and moist heat.[232] But some mixers also use techniques from pseudoscientific alternative medicine, including unnecessary nutritional supplements, acupuncture, homeopathy, herbal remedies, and biofeedback.[232] Author Holly Folk writes that "Few Mixer chiropractors use the term anymore. Today, one is more likely to hear this side described as 'holistic,' 'wellness-oriented,' or 'integrative' practitioners."[236]: 114 Folk argues that "osteopathy underwent a 'Straight-Mixer' debate between traditional vitalists and a faction that embraced the new medical science".: 172
Although mixers are the majority group, many of them retain belief in vertebral subluxation as shown in a 2003 survey of 1,100 North American chiropractors, which found that 88 percent wanted to retain the term "vertebral subluxation complex", and that when asked to estimate the percent of disorders of internal organs that subluxation significantly contributes to, the mean response was 62 percent.[222] A 2008 survey of 6,000 American chiropractors demonstrated that most chiropractors seem to believe that a subluxation-based clinical approach may be of limited utility for addressing visceral disorders, and greatly favored non-subluxation-based clinical approaches for such conditions.[237] The same survey showed that most chiropractors generally believed that the majority of their clinical approach for addressing musculoskeletal/biomechanical disorders such as back pain was based on subluxation.[237] Chiropractors often offer conventional therapies such as physical therapy and lifestyle counseling, and it may for the lay person be difficult to distinguish the unscientific from the scientific.[238]
Restraint of trade decision 1989
[edit]The AMA labeled chiropractic an "unscientific cult" in 1966,[30] and until 1980 advised its members that it was unethical for medical doctors to associate with "unscientific practitioners".[239] This culminated in a landmark 1987 decision, Wilk v. AMA, in which the court found that the AMA had engaged in unreasonable restraint of trade and conspiracy, and which ended the AMA's de facto boycott of chiropractic.[10]
Growing scholarly interest
[edit]Serious research to test chiropractic theories did not begin until the 1970s, and is continuing to be hampered by antiscientific and pseudoscientific ideas that sustained the profession in its long battle with organized medicine.[226] By the mid-1990s there was a growing scholarly interest in chiropractic, which helped efforts to improve service quality and establish clinical guidelines that recommended manual therapies for acute low back pain.[226]
In recent decades chiropractic gained legitimacy and greater acceptance by medical physicians and health plans, and enjoyed a strong political base and sustained demand for services.[10] However, its future seemed uncertain: as the number of practitioners grew, evidence-based medicine insisted on treatments with demonstrated value, managed care restricted payment, and competition grew from massage therapists and other health professions.[10] The profession responded by marketing natural products and devices more aggressively, and by reaching deeper into alternative medicine and primary care.[10]
Public health
[edit]Some chiropractors oppose vaccination and water fluoridation, which are common public health practices.[35] Within the chiropractic community there are significant disagreements about vaccination, one of the most cost-effective public health interventions available.[240] Most chiropractic writings on vaccination focus on its negative aspects,[28] claiming that it is hazardous, ineffective, and unnecessary.[29] Some chiropractors have embraced vaccination, but a significant portion of the profession rejects it, as original chiropractic philosophy traces diseases to causes in the spine and states that vaccines interfere with healing.[29] The extent to which anti-vaccination views perpetuate the current chiropractic profession is uncertain.[28] The American Chiropractic Association and the International Chiropractors Association support individual exemptions to compulsory vaccination laws, and a 1995 survey of U.S. chiropractors found that about a third believed there was no scientific proof that immunization prevents disease.[29] The Canadian Chiropractic Association supports vaccination;[28] a survey in Alberta in 2002 found that 25% of chiropractors advised patients for, and 27% against, vaccinating themselves or their children.[241]
Early opposition to water fluoridation included chiropractors, some of whom continue to oppose it as being incompatible with chiropractic philosophy and an infringement of personal freedom. Other chiropractors have actively promoted fluoridation, and several chiropractic organizations have endorsed scientific principles of public health.[242] In addition to traditional chiropractic opposition to water fluoridation and vaccination, chiropractors' attempts to establish a positive reputation for their public health role are also compromised by their reputation for recommending repetitive lifelong chiropractic treatment.[35]
Controversy
[edit]Throughout its history chiropractic has been the subject of internal and external controversy and criticism.[232][243] According to Daniel D. Palmer, the founder of chiropractic, subluxation is the sole cause of disease and manipulation is the cure for all diseases of the human race.[9][244] A 2003 profession-wide survey[222] found "most chiropractors (whether 'straights' or 'mixers') still hold views of innate intelligence and of the cause and cure of disease (not just back pain) consistent with those of the Palmers."[245] A critical evaluation stated "Chiropractic is rooted in mystical concepts. This led to an internal conflict within the chiropractic profession, which continues today."[9] Chiropractors, including D. D. Palmer, were jailed for practicing medicine without a license.[9] For most of its existence, chiropractic has battled with mainstream medicine, sustained by antiscientific and pseudoscientific ideas such as subluxation.[226] Collectively, systematic reviews have not demonstrated that spinal manipulation, the main treatment method employed by chiropractors, is effective for any medical condition, with the possible exception of treatment for back pain.[9] Chiropractic remains controversial, though to a lesser extent than in past years.[25]
See also
[edit]References
[edit]- ^ a b c Chapman-Smith DA, Cleveland CS III (2005). "International status, standards, and education of the chiropractic profession". In Haldeman S, Dagenais S, Budgell B, et al. (eds.). Principles and Practice of Chiropractic (3rd ed.). McGraw-Hill. pp. 111–34. ISBN 978-0-07-137534-4.
- ^ a b c d e f g Nelson CF, Lawrence DJ, Triano JJ, Bronfort G, Perle SM, Metz RD, Hegetschweiler K, LaBrot T (2005). "Chiropractic as spine care: a model for the profession". Chiropractic & Osteopathy. 13 (1) 9. doi:10.1186/1746-1340-13-9. PMC 1185558. PMID 16000175.
- ^ a b Mootz RD, Shekelle PG (1997). "Content of practice". In Cherkin DC, Mootz RD (eds.). Chiropractic in the United States: Training, Practice, and Research. Rockville, MD: Agency for Health Care Policy and Research. pp. 67–91. OCLC 39856366. AHCPR Pub No. 98-N002.
- ^ a b c Hurwitz EL, Chiang LM (2006). "A comparative analysis of chiropractic and general practitioner patients in North America: findings from the joint Canada/United States Survey of Health, 2002-03". BMC Health Services Research. 6 49. doi:10.1186/1472-6963-6-49. PMC 1458338. PMID 16600038.
- ^ a b Tetrault M (2004). "Global professional strategy for chiropractic" (PDF). Chiropractic Diplomatic Corps. Archived from the original (PDF) on 2008-06-25. Retrieved 2008-04-18.
- ^ a b c Norris P (2001). "How 'we' are different from 'them': occupational boundary maintenance in the treatment of musculo-skeletal problems". Sociology of Health and Illness. 23 (1): 24–43. doi:10.1111/1467-9566.00239.
- ^ "The DC as PCP? Drug Wars Resume – Science-Based Medicine". sciencebasedmedicine.org. 2019-12-18. Archived from the original on 2019-12-18. Retrieved 2020-03-27.
- ^ Bellamy, Jann (December 20, 2018). "Legislative Alchemy 2018: Chiropractors rebranding as primary care physicians continues". sciencebasedmedicine.org. Archived from the original on December 19, 2019. Retrieved 2019-12-18.
- ^ a b c d e f g h i j k l m n o p q r Ernst E (May 2008). "Chiropractic: a critical evaluation". Journal of Pain and Symptom Management. 35 (5): 544–62. doi:10.1016/j.jpainsymman.2007.07.004. PMID 18280103.
- ^ a b c d e f g h i j k l Cooper RA, McKee HJ (2003). "Chiropractic in the United States: trends and issues". Milbank Quarterly. 81 (1): 107–38, table of contents. doi:10.1111/1468-0009.00040. PMC 2690192. PMID 12669653.
- ^ a b MICHELLE R. SMITH, SCOTT BAUER and MIKE CATALINI (October 8, 2021). Anti-vaccine chiropractors rising force of misinformation. Associated Press.
- ^ a b c Urits I, Schwartz RH, Orhurhu V, Maganty NV, Reilly BT, Patel PM, Wie C, Kaye AD, Mancuso KF, Kaye AJ, Viswanath O (January 2021). "A Comprehensive Review of Alternative Therapies for the Management of Chronic Pain Patients: Acupuncture, Tai Chi, Osteopathic Manipulative Medicine, and Chiropractic Care". Adv Ther (Review). 38 (1): 76–89. doi:10.1007/s12325-020-01554-0. PMC 7854390. PMID 33184777.
- ^ a b Posadzki P, Ernst E (2011). "Spinal manipulation: an update of a systematic review of systematic reviews". The New Zealand Medical Journal. 124 (1340): 55–71. PMID 21952385.
- ^ a b Lin CW, Haas M, Maher CG, Machado LA, van Tulder MW (2011). "Cost-effectiveness of guideline-endorsed treatments for low back pain: a systematic review". European Spine Journal. 20 (7): 1024–38. doi:10.1007/s00586-010-1676-3. PMC 3176706. PMID 21229367.
- ^ a b Ernst E (2009). "Chiropractic maintenance treatment, a useful preventative approach?". Preventive Medicine. 49 (2–3): 99–100. doi:10.1016/j.ypmed.2009.05.004. PMID 19465044.
- ^ a b c d e Gouveia LO, Castanho P, Ferreira JJ (2009). "Safety of chiropractic interventions: a systematic review" (PDF). Spine. 34 (11): E405–13. doi:10.1097/BRS.0b013e3181a16d63. PMID 19444054. S2CID 21279308. Archived (PDF) from the original on 2016-09-19.
- ^ a b c d e Ernst E (2007). "Adverse effects of spinal manipulation: a systematic review". Journal of the Royal Society of Medicine. 100 (7): 330–38. doi:10.1177/014107680710000716. PMC 1905885. PMID 17606755. Archived from the original on 2010-05-16.
- Christian Nordqvist (2007-07-02). "Spinal Manipulation Should Not Be Routinely Used, New Study Warns". Med News Today.
- ^ a b c d Haynes MJ, Vincent K, Fischhoff C, Bremner AP, Lanlo O, Hankey GJ (2012). "Assessing the risk of stroke from neck manipulation: a systematic review". International Journal of Clinical Practice. 66 (10): 940–47. doi:10.1111/j.1742-1241.2012.03004.x. PMC 3506737. PMID 22994328.
- ^ a b Ernst E (2010). "Vascular accidents after neck manipulation: cause or coincidence?". International Journal of Clinical Practice. 64 (6): 673–77. doi:10.1111/j.1742-1241.2009.02237.x. PMID 20518945. S2CID 38571730.
- ^ a b c d e f g Ernst E (2010). "Deaths after chiropractic: a review of published cases". International Journal of Clinical Practice. 64 (8): 1162–65. doi:10.1111/j.1742-1241.2010.02352.x. PMID 20642715. S2CID 45225661.
- ^ For an explanation regarding the description of chiropractic as a pseudoscience, see:
- Singh, Simon; Ernst, Edzard (2008). "The Truth About Chiropractic Therapy". Trick or Treatment? Alternative Medicine on Trial. London: Bantam Press. ISBN 978-0-593-06129-9. OCLC 190777228.
- Good R, Slezak P (2011). "Introductory Comments on Pseudoscience in Society and School". Science & Education. Springer. pp. 401–409. doi:10.1007/s11191-010-9331-2.
The uncritical habits of mind that allow pseudosciences like subluxation chiropractic, astrology, intelligent design, and countless 'new age' medical cures to flourish are an important indication that science education needs to be changed.
- Hansson, Sven Ove (2017-06-01). "Science denial as a form of pseudoscience". Studies in History and Philosophy of Science Part A. 63: 39–47. Bibcode:2017SHPSA..63...39H. doi:10.1016/j.shpsa.2017.05.002. ISSN 0039-3681. PMID 28629651.
- Ernst, Edzard (2009-04-01). "Complementary/alternative medicine: engulfed by postmodernism, anti-science and regressive thinking". The British Journal of General Practice. 59 (561): 298–301. doi:10.3399/bjgp09X420482. ISSN 0960-1643. PMC 2662117. PMID 19341568.
- Hall, Harriet (May 2020). "Applied kinesiology and other chiropractic delusions". Skeptical Inquirer. 44 (3): 21–23.
- Novella, Steven (March 22, 2017). "Cracking Down on Chiropractic Pseudoscience". sciencebasedmedicine.org. New England Skeptical Society. Archived from the original on December 19, 2019. Retrieved 2019-12-19.
- Williams, William F. (2000). Encyclopedia of Pseudoscience: From Alien Abductions to Zone Therapy. Facts on File Inc. p. 51. ISBN 1-57958-207-9
- ^ a b c d e f g h i j k Martin SC (October 1993). "Chiropractic and the social context of medical technology, 1895-1925". Technology and Culture. 34 (4): 808–34. doi:10.2307/3106416. JSTOR 3106416. PMID 11623404. S2CID 23423922.
- ^ a b c "D. D. Palmer's Religion of Chiropractic" – Letter from D. D. Palmer to P. W. Johnson, D.C., May 4, 1911. In the letter, he often refers to himself with royal third person terminology and also as "Old Dad".
- ^ Lazarus, David (June 30, 2017). Column: Chiropractic treatment, a $15-billion industry, has its roots in a ghost story. Archived July 19, 2020, at the Wayback Machine --- "Daniel David Palmer, the 'father' of chiropractic who performed the first chiropractic adjustment in 1895, was an avid spiritualist. He maintained that the notion and basic principles of chiropractic treatment were passed along to him during a seance by a long-dead doctor. 'The knowledge and philosophy given me by Dr. Jim Atkinson, an intelligent spiritual being ... appealed to my reason,' Palmer wrote in his memoir The Chiropractor, which was published in 1914 after his death in Los Angeles. Atkinson had died 50 years prior to Palmer's epiphany." Los Angeles Times. Retrieved: September 25, 2019.
- ^ a b c d DeVocht JW (2006). "History and overview of theories and methods of chiropractic: a counterpoint". Clinical Orthopaedics and Related Research. 444: 243–49. doi:10.1097/01.blo.0000203460.89887.8d. PMID 16523145. S2CID 35775630.
- ^ a b Homola S (2006). "Chiropractic: history and overview of theories and methods". Clinical Orthopaedics and Related Research. 444: 236–42. doi:10.1097/01.blo.0000200258.95865.87. PMID 16446588.
- ^ a b c Joseph C. Keating Jr.; Cleveland CS III; Menke M (2005). "Chiropractic history: a primer" (PDF). Association for the History of Chiropractic. Archived from the original (PDF) on 19 June 2013. Retrieved 2008-06-16.
A significant and continuing barrier to scientific progress within chiropractic are the anti-scientific and pseudo-scientific ideas (Keating 1997b) which have sustained the profession throughout a century of intense struggle with political medicine. Chiropractors' tendency to assert the meaningfulness of various theories and methods as a counterpoint to allopathic charges of quackery has created a defensiveness which can make critical examination of chiropractic concepts difficult (Keating and Mootz 1989). One example of this conundrum is the continuing controversy about the presumptive target of DCs' adjustive interventions: subluxation (Gatterman 1995; Leach 1994).
- ^ a b c d Busse JW, Morgan L, Campbell JB (2005). "Chiropractic antivaccination arguments". Journal of Manipulative and Physiological Therapeutics. 28 (5): 367–73. doi:10.1016/j.jmpt.2005.04.011. PMID 15965414.
- ^ a b c d Campbell JB, Busse JW, Injeyan HS (2000). "Chiropractors and vaccination: a historical perspective". Pediatrics. 105 (4) e43. doi:10.1542/peds.105.4.e43. PMID 10742364.
- ^ a b Johnson C, Baird R, Dougherty PE, Globe G, Green BN, Haneline M, Hawk C, Injeyan HS, Killinger L, Kopansky-Giles D, Lisi AJ, Mior SA, Smith M (2008). "Chiropractic and public health: current state and future vision". Journal of Manipulative and Physiological Therapeutics. 31 (6): 397–410. doi:10.1016/j.jmpt.2008.07.001. PMID 18722194.
- ^ WFC Public Health Committee and WFC Research Committee (March 17, 2020). COVID-19 Advice for Chiropractors World Federation of Chiropractic.
- ^ Robert C. Jones, et al. Not Business as Usual: A Safe, Responsible Response to COVID-19 American Chiropractic Association
- ^ a b c d e f Keating JC Jr (2005). "Philosophy in chiropractic". In Haldeman S, Dagenais S, Budgell B, et al. (eds.). Principles and Practice of Chiropractic (3rd ed.). McGraw-Hill. pp. 77–98. ISBN 978-0-07-137534-4.
- ^ a b c d Mootz RD, Phillips RB (1997). "Chiropractic belief systems". In Cherkin DC, Mootz RD (eds.). Chiropractic in the United States: Training, Practice, and Research. Rockville, MD: Agency for Health Care Policy and Research. pp. 9–16. OCLC 39856366. AHCPR Pub No. 98-N002.
- ^ a b c d e f Murphy DR, Schneider MJ, Seaman DR, Perle SM, Nelson CF (Aug 2008). "How can chiropractic become a respected mainstream profession? The example of podiatry". Chiropractic & Osteopathy. 16 10. doi:10.1186/1746-1340-16-10. PMC 2538524. PMID 18759966.
- ^ Gay RE, Nelson CF (2003). "Chiropractic philosophy". In Wainapel SF, Fast A (eds.). Alternative Medicine and Rehabilitation: a Guide for Practitioners. New York: Demos Medical Publishing. ISBN 978-1-888799-66-8.
- ^ "Chiropractic". NHS Choices. 20 August 2014. Retrieved 19 September 2016.
- ^ "Subluxation". Merriam-Webster. Retrieved January 4, 2018.
- ^ "luxation (n.)". Online Etymology Dictionary. Archived from the original on 2019-05-01. Retrieved July 28, 2021.
- ^ a b c Keating, J. C. Jr (1995). "D. D. Palmer's forgotten theories of chiropractic" (PDF). Association for the History of Chiropractic. Archived (PDF) from the original on 2007-07-10. Retrieved 2008-05-14.
- ^ Keating JC Jr (2005). "A brief history of the chiropractic profession". In Haldeman S, Dagenais S, Budgell B, et al. (eds.). Principles and Practice of Chiropractic (3rd ed.). McGraw-Hill. pp. 23–64. ISBN 978-0-07-137534-4.
- ^ a b c Keating JC, Charlton KH, Grod JP, Perle SM, Sikorski D, Winterstein JF (August 2005). "Subluxation: dogma or science?". Chiropractic & Osteopathy. 13 17. doi:10.1186/1746-1340-13-17. PMC 1208927. PMID 16092955.
- ^ Rose KA, Adams A (2000). "A survey of the use of evidence-based health care in chiropractic college clinics" (PDF). Journal of Chiropractic Education. 14 (2): 71–77. doi:10.7899/1042-5055-14.2.71. Archived from the original (PDF) on 2008-10-02.
- ^ Homola S (2006). "Can chiropractors and evidence-based manual therapists work together? an opinion from a veteran chiropractor" (PDF). Journal of Manual & Manipulative Therapy. 14 (2): E14–18. CiteSeerX 10.1.1.366.2817. doi:10.1179/jmt.2006.14.2.14E. S2CID 71826135. Archived (PDF) from the original on 2007-07-10.
- ^ a b c d e f g h i j k World Health Organization (2005). WHO guidelines on basic training and safety in chiropractic (PDF). World Health Organization. ISBN 978-92-4-159371-7. Archived from the original (PDF) on 2022-03-13. Retrieved 2008-02-29.
- ^ David Chapman-Smith (2000). "Principles and Goals of Chiropractic Care". The Chiropractic Profession: Its Education, Practice, Research and Future Directions. NCMIC Group. p. 160. ISBN 978-1-892734-02-0.
- ^ "Guidance on claims made for the chiropractic vertebral subluxation complex" (PDF). General Chiropractic Council. Archived from the original (PDF) on 2011-04-16. Retrieved 2010-09-30.
- ^ NBCE (2014), About Chiropractic, National Board of Chiropractic Examiners, archived from the original on June 19, 2015, retrieved February 1, 2015
- ^ a b c d e Hall, Harriet (June 1, 2017). "Chiropractors: Pro and Con". Skeptical Inquirer. Archived from the original on 2020-08-23. Retrieved July 28, 2021.
- ^ Benedetti, Paul; MacPhail, Wayne (2002). Spin Doctors: The Chiropractic Industry Under Examination. Toronto: Dundurn Group. p. 198. ISBN 1-55002-406-X.
- ^ "Chirobase". Quackwatch. 7 May 2019. Archived from the original on 2020-06-10. Retrieved July 28, 2021.
- ^ a b c Villanueva-Russell Y (June 2011). "Caught in the crosshairs: identity and cultural authority within chiropractic". Social Science & Medicine. 72 (11): 1826–37. doi:10.1016/j.socscimed.2011.03.038. PMID 21531061.
- ^ a b Meeker WC, Haldeman S (2002). "Chiropractic: a profession at the crossroads of mainstream and alternative medicine". Annals of Internal Medicine. 136 (3): 216–27. CiteSeerX 10.1.1.694.4126. doi:10.7326/0003-4819-136-3-200202050-00010. PMID 11827498. S2CID 16782086.
- ^ Gleberzon BJ, Cooperstein R, Perle SM (2005). "Can chiropractic survive its chimerical nature?". The Journal of the Canadian Chiropractic Association. 49 (2): 69–73. PMC 1840015. PMID 17549192.
- ^ Redwood D, Hawk C, Cambron J, Vinjamury SP, Bedard J (2008). "Do chiropractors identify with complementary and alternative medicine? results of a survey". The Journal of Alternative and Complementary Medicine. 14 (4): 361–68. doi:10.1089/acm.2007.0766. PMID 18435599.
- ^ Bellamy, Jann J (2010). "Legislative alchemy: the US state chiropractic practice acts". Focus on Alternative and Complementary Therapies. 15 (3): 214–22. doi:10.1111/j.2042-7166.2010.01032.x.
- ^ Jones-Harris, Amanda R (October 2010). "Are chiropractors in the uk primary healthcare or primary contact practitioners?: a mixed methods study". Chiropractic & Osteopathy. 18 (28) 28. doi:10.1186/1746-1340-18-28. PMC 3161390. PMID 20979615.
- ^ Theberge N (January 2008). "The integration of chiropractors into healthcare teams: a case study from sport medicine". Sociology of Health & Illness. 30 (1): 19–34. doi:10.1111/j.1467-9566.2007.01026.x. PMID 18254831.
- ^ a b Pettman E (2007). "A history of manipulative therapy". Journal of Manual & Manipulative Therapy. 15 (3): 165–74. doi:10.1179/106698107790819873. PMC 2565620. PMID 19066664.
- ^ Baer HA (2006). "The drive for legitimization by osteopathy and chiropractic in Australia: between heterodoxy and orthodoxy". Complementary Health Practice Review. 11 (2): 77–94. doi:10.1177/1533210106292467.
- ^ "Scope of Practice: Complementary and alternative veterinary medicine (CAVM) and other practice act exemptions". American Veterinary Medical Association. May 2019. Archived from the original on April 4, 2016. Retrieved April 1, 2016.
- ^ ACA House of Delegates (1994). "'Veterinary' chiropractic". American Chiropractic Association. Archived from the original on May 17, 2008. Retrieved 2008-07-05.
- ^ Kamen, Daniel (June 18, 2001). "Politics and technique". Dynamic Chiropractic. Vol. 19, no. 13.
- ^ a b c Villanueva-Russell Y (2005). "Evidence-based medicine and its implications for the profession of chiropractic". Social Science & Medicine. 60 (3): 545–61. doi:10.1016/j.socscimed.2004.05.017. PMID 15550303.
- ^ Anderson, Chantal (2009-01-22). "Physical therapists, chiropractors square off over bill". The Seattle Times. Archived from the original on 2010-09-22. Retrieved 2010-09-23.
- ^ Hilliard JW, Johnson ME (2004). "State practice acts of licensed health professions: scope of practice". DePaul Journal of Health Care Law. 8 (1): 237–61.
- ^ a b c Christensen MG, Kollasch MW (2005). "Professional functions and treatment procedures" (PDF). Job Analysis of Chiropractic (PDF). Greeley, CO: National Board of Chiropractic Examiners. pp. 121–38. ISBN 978-1-884457-05-0. Archived from the original (PDF) on 2008-09-10. Retrieved 2008-08-25.
- ^ a b c Winkler K, Hegetschweiler-Goertz C, Jackson PS, et al. (2003). "Spinal manipulation policy statement" (PDF). American Chiropractic Association. Archived from the original (PDF) on 2011-07-20. Retrieved 2008-05-24.
- ^ a b Pickar JG, Sung PS, Kang YM, Ge W (2007). "Response of lumbar paraspinal muscles spindles is greater to spinal manipulative loading compared with slower loading under length control". The Spine Journal. 7 (5): 583–95. doi:10.1016/j.spinee.2006.10.006. PMC 2075482. PMID 17905321.
- ^ Cooperstein R, Gleberzon BJ (2004). Technique Systems in Chiropractic. Churchill Livingstone. ISBN 978-0-443-07413-4.[page needed]
- ^ Harrison DD, Janik TJ, Harrison GR, Troyanovich S, Harrison DE, Harrison SO (1996). "Chiropractic biophysics technique: a linear algebra approach to posture in chiropractic". Journal of Manipulative and Physiological Therapeutics. 19 (8): 525–35. PMID 8902664.
- ^ a b "Provider Manual for Chiropractic Services" (PDF). North Dakota Department of Human Services. State of North Dakota. Archived from the original (PDF) on 2016-04-08. Retrieved 2016-04-14.
- ^ NHS Leeds West CCG Assurance Committee (2014-01-02). "Complementary and Alternative Therapies Evidence Based Decision Making Framework" (PDF). leedswestccg.nhs.uk. Archived from the original (PDF) on 2016-03-04. Retrieved 2015-06-30.
- ^ "Chiropractic Services - Policy", Aetna, archived from the original on 24 March 2016, retrieved 29 March 2016
- ^ "Chiropractic Policy" (PDF). Oklahoma State University Health Plan. 1 April 2016. Archived from the original (PDF) on 5 January 2017. Retrieved 14 April 2016.
- ^ Dagenais S, Mayer J, Wooley JR, Haldeman S (2008). "Evidence-informed management of chronic low back pain with medicine-assisted manipulation". The Spine Journal. 8 (1): 142–49. doi:10.1016/j.spinee.2007.09.010. PMID 18164462.
- ^ a b Ailliet L, Rubinstein SM, de Vet HC (October 2010). "Characteristics of chiropractors and their patients in Belgium". Journal of Manipulative and Physiological Therapeutics. 33 (8): 618–25. doi:10.1016/j.jmpt.2010.08.011. PMID 21036284.
- ^ Ndetan HT, Rupert RL, Bae S, Singh KP (February 2009). "Prevalence of musculoskeletal injuries sustained by students while attending a chiropractic college". Journal of Manipulative and Physiological Therapeutics. 32 (2): 140–48. doi:10.1016/j.jmpt.2008.12.012. PMID 19243726.
- ^ Joseph C. Keating Jr. (1997). "Chiropractic: science and antiscience and pseudoscience side by side". Skeptical Inquirer. 21 (4): 37–43.
- ^ Phillips RB (2005). "The evolution of vitalism and materialism and its impact on philosophy". In Haldeman S, Dagenais S, Budgell B, et al. (eds.). Principles and Practice of Chiropractic (3rd ed.). McGraw-Hill. pp. 65–76. ISBN 978-0-07-137534-4.
- ^ Reggars JW (2011). "Chiropractic at the crossroads or are we just going around in circles?". Chiropractic & Manual Therapies. 19 11. doi:10.1186/2045-709X-19-11. PMC 3119029. PMID 21599991.
- ^ Suter E, Vanderheyden LC, Trojan LS, Verhoef MJ, Armitage GD (February 2007). "How important is research-based practice to chiropractors and massage therapists?". Journal of Manipulative and Physiological Therapeutics. 30 (2): 109–15. doi:10.1016/j.jmpt.2006.12.013. PMID 17320731.
- ^ Murphy AY, van Teijlingen ER, Gobbi MO (September 2006). "Inconsistent grading of evidence across countries: a review of low back pain guidelines". Journal of Manipulative and Physiological Therapeutics. 29 (7): 576–81, 581.e1–2. doi:10.1016/j.jmpt.2006.07.005. PMID 16949948.
- ^ Ernst E, Canter PH (April 2006). "A systematic review of systematic reviews of spinal manipulation". Journal of the Royal Society of Medicine. 99 (4): 192–96. doi:10.1177/014107680609900418. PMC 1420782. PMID 16574972.
- "Back treatment 'has few benefits'". BBC News. March 22, 2006.
- ^ Johnston BC, da Costa BR, Devereaux PJ, Akl EA, Busse JW (April 2008). "The use of expertise-based randomized controlled trials to assess spinal manipulation and acupuncture for low back pain: a systematic review". Spine. 33 (8): 914–18. doi:10.1097/BRS.0b013e31816b4be4. PMID 18404113. S2CID 28092478.
- ^ Khorsan R, Coulter ID, Hawk C, Choate CG (June 2008). "Measures in chiropractic research: choosing patient-based outcome assessments". Journal of Manipulative and Physiological Therapeutics. 31 (5): 355–75. doi:10.1016/j.jmpt.2008.04.007. PMID 18558278.
- ^ Kaptchuk TJ (June 2002). "The placebo effect in alternative medicine: can the performance of a healing ritual have clinical significance?". Annals of Internal Medicine. 136 (11): 817–25. CiteSeerX 10.1.1.694.4848. doi:10.7326/0003-4819-136-11-200206040-00011. PMID 12044130. S2CID 207535762.
- ^ Hancock MJ, Maher CG, Latimer J, McAuley JH (2006). "Selecting an appropriate placebo for a trial of spinal manipulative therapy". Australian Journal of Physiotherapy. 52 (2): 135–38. doi:10.1016/S0004-9514(06)70049-6. PMID 16764551.
- ^ a b Leboeuf-Yde C, Hestbaek L (2008). "Maintenance care in chiropractic – what do we know?". Chiropractic & Osteopathy. 16 3. doi:10.1186/1746-1340-16-3. PMC 2396648. PMID 18466623.
- ^ Lewis RA, Williams NH, Sutton AJ, Burton K, Din NU, Matar HE, Hendry M, Phillips CJ, Nafees S, Fitzsimmons D, Rickard I, Wilkinson C (2013). "Comparative clinical effectiveness of management strategies for sciatica: systematic review and network meta-analyses" (PDF). The Spine Journal. 15 (6): 1461–77. doi:10.1016/j.spinee.2013.08.049. PMID 24412033.
- ^ a b Leininger B, Bronfort G, Evans R, Reiter T (February 2011). "Spinal manipulation or mobilization for radiculopathy: a systematic review". Physical Medicine and Rehabilitation Clinics of North America. 22 (1): 105–25. doi:10.1016/j.pmr.2010.11.002. PMID 21292148.
- ^ Hahne AJ, Ford JJ, McMeeken JM (May 2010). "Conservative management of lumbar disc herniation with associated radiculopathy: a systematic review". Spine. 35 (11): E488–504. doi:10.1097/BRS.0b013e3181cc3f56. PMID 20421859. S2CID 19121111.
- ^ Vernon H, Humphreys BK (2007). "Manual therapy for neck pain: an overview of randomized clinical trials and systematic reviews" (PDF). Europa Medicophysica. 43 (1): 91–118. PMID 17369783.
- ^ Schroeder J, Kaplan L, Fischer DJ, Skelly AC (2013). "The Outcomes of Manipulation or Mobilization Therapy Compared with Physical Therapy or Exercise for Neck Pain: A Systematic Review". Evidence-Based Spine-Care Journal. 4 (1): 30–41. doi:10.1055/s-0033-1341605. PMC 3699243. PMID 24436697.
- ^ Huisman PA, Speksnijder CM, de Wijer A (January 2013). "The effect of thoracic spine manipulation on pain and disability in patients with non-specific neck pain: a systematic review". Disability and Rehabilitation. 35 (20): 1677–85. doi:10.3109/09638288.2012.750689. PMID 23339721. S2CID 12159586.
- ^ Cross KM, Kuenze C, Grindstaff TL, Hertel J (September 2011). "Thoracic spine thrust manipulation improves pain, range of motion, and self-reported function in patients with mechanical neck pain: a systematic review". Journal of Orthopaedic & Sports Physical Therapy. 41 (9): 633–42. doi:10.2519/jospt.2011.3670. PMID 21885904.
- ^ Gross A, Miller J, D'Sylva J, Burnie SJ, Goldsmith CH, Graham N, Haines T, Brønfort G, Hoving JL (August 2010). "Manipulation or mobilisation for neck pain: a Cochrane Review". Manual Therapy. 15 (4): 315–33. doi:10.1016/j.math.2010.04.002. PMID 20510644.
- ^ Shaw L, Descarreaux M, Bryans R, Duranleau M, Marcoux H, Potter B, Ruegg R, Watkin R, White E (2010). "A systematic review of chiropractic management of adults with Whiplash-Associated Disorders: recommendations for advancing evidence-based practice and research". Work. 35 (3): 369–94. doi:10.3233/WOR-2010-0996. PMID 20364057.
- ^ Jansen MJ, Viechtbauer W, Lenssen AF, Hendriks EJ, de Bie RA (2011). "Strength training alone, exercise therapy alone, and exercise therapy with passive manual mobilisation each reduce pain and disability in people with knee osteoarthritis: a systematic review". Journal of Physiotherapy. 57 (1): 11–20. doi:10.1016/S1836-9553(11)70002-9. PMID 21402325.
- ^ French HP, Brennan A, White B, Cusack T (April 2011). "Manual therapy for osteoarthritis of the hip or knee - a systematic review". Manual Therapy. 16 (2): 109–17. doi:10.1016/j.math.2010.10.011. PMID 21146444.
- ^ McHardy A, Hoskins W, Pollard H, Onley R, Windsham R (February 2008). "Chiropractic treatment of upper extremity conditions: a systematic review". Journal of Manipulative and Physiological Therapeutics. 31 (2): 146–59. doi:10.1016/j.jmpt.2007.12.004. PMID 18328941.
- ^ Pribicevic M, Pollard H, Bonello R, de Luca K (2010). "A systematic review of manipulative therapy for the treatment of shoulder pain". Journal of Manipulative and Physiological Therapeutics. 33 (9): 679–89. doi:10.1016/j.jmpt.2010.08.019. PMID 21109059.
- ^ Brantingham, James W.; Bonnefin, Debra; Perle, Stephen M.; Cassa, Tammy Kay; Globe, Gary; Pribicevic, Mario; Hicks, Marian; Korporaal, Charmaine (2012). "Manipulative Therapy for Lower Extremity Conditions: Update of a Literature Review". Journal of Manipulative and Physiological Therapeutics. 35 (2): 127–66. doi:10.1016/j.jmpt.2012.01.001. PMID 22325966.
- ^ Mangum K, Partna L, Vavrek D (2012). "Spinal manipulation for the treatment of hypertension: a systematic qualitative literature review". Journal of Manipulative and Physiological Therapeutics. 35 (3): 235–43. doi:10.1016/j.jmpt.2012.01.005. PMID 22341795.
- ^ Lystad RP, Bell G, Bonnevie-Svendsen M, Carter CV (2011). "Manual therapy with and without vestibular rehabilitation for cervicogenic dizziness: a systematic review". Chiropractic & Manual Therapies. 19 (1) 21. doi:10.1186/2045-709X-19-21. PMC 3182131. PMID 21923933.
- ^ Everett CR, Patel RK (September 2007). "A systematic literature review of nonsurgical treatment in adult scoliosis". Spine. 32 (19 Suppl): S130–34. doi:10.1097/BRS.0b013e318134ea88. PMID 17728680. S2CID 9339782.
- ^ Romano M, Negrini S (2008). "Manual therapy as a conservative treatment for adolescent idiopathic scoliosis: a systematic review". Scoliosis. 3 2. doi:10.1186/1748-7161-3-2. PMC 2262872. PMID 18211702.
- ^ Hawk C, Khorsan R, Lisi AJ, Ferrance RJ, Evans MW (June 2007). "Chiropractic care for nonmusculoskeletal conditions: a systematic review with implications for whole systems research". The Journal of Alternative and Complementary Medicine. 13 (5): 491–512. doi:10.1089/acm.2007.7088. PMID 17604553.
- ^ Ernst E (December 2009). "Spinal manipulation for asthma: a systematic review of randomised clinical trials". Respiratory Medicine. 103 (12): 1791–95. doi:10.1016/j.rmed.2009.06.017. PMID 19646855.
- ^ Hondras MA, Linde K, Jones AP (2005). "Manual therapy for asthma". Cochrane Database of Systematic Reviews (2) CD001002. doi:10.1002/14651858.CD001002.pub2. PMID 15846609.
- ^ a b Gotlib A, Rupert R (2008). "Chiropractic manipulation in pediatric health conditions--an updated systematic review". Chiropractic & Osteopathy. 16 11. doi:10.1186/1746-1340-16-11. PMC 2553791. PMID 18789139.
- ^ Baby colic:
- Ernst E (2009). "Chiropractic spinal manipulation for infant colic: a systematic review of randomised clinical trials". International Journal of Clinical Practice. 63 (9): 1351–53. doi:10.1111/j.1742-1241.2009.02133.x. PMID 19691620. S2CID 36131261.
- Husereau D, Clifford T, Aker P, Leduc D, Mensinkai S (2003). Spinal Manipulation for Infantile Colic (PDF). Technology report no. 42. Ottawa: Canadian Coordinating Office for Health Technology Assessment. ISBN 978-1-894978-11-8. Archived from the original (PDF) on 2008-12-17. Retrieved 2008-10-06.
- ^ Huang, Tao; Shu, Xu; Huang, Yu Shan; Cheuk, Daniel KL; Huang, Tao (2011). "Complementary and miscellaneous interventions for nocturnal enuresis in children". Cochrane Database of Systematic Reviews (12) CD005230. doi:10.1002/14651858.CD005230.pub2. PMID 22161390.
- ^ O'Connor D, Marshall S, Massy-Westropp N, Pitt V (2003). "Non-surgical treatment (other than steroid injection) for carpal tunnel syndrome". Cochrane Database of Systematic Reviews. 2003 (1) CD003219. doi:10.1002/14651858.CD003219. PMC 6486195. PMID 12535461.
- ^ Fibromyalgia:
- Sarac AJ, Gur A (2006). "Complementary and alternative medical therapies in fibromyalgia". Current Pharmaceutical Design. 12 (1): 47–57. doi:10.2174/138161206775193262. PMID 16454724.
- Schneider M, Vernon H, Ko G, Lawson G, Perera J (2009). "Chiropractic management of fibromyalgia syndrome: a systematic review of the literature". Journal of Manipulative and Physiological Therapeutics. 32 (1): 25–40. doi:10.1016/j.jmpt.2008.08.012. PMID 19121462.
- Ernst E (2009). "Chiropractic treatment for fibromyalgia: a systematic review". Clinical Rheumatology. 28 (10): 1175–78. doi:10.1007/s10067-009-1217-9. PMID 19544042. S2CID 25339207.
- ^ Ernst E (2011). "Chiropractic treatment for gastrointestinal problems: A systematic review of clinical trials". Canadian Journal of Gastroenterology. 25 (1): 39–49. doi:10.1155/2011/910469. PMC 3027333. PMID 21258667.
- ^ Brand PL, Engelbert RH, Helders PJ, Offringa M (2005). "[Systematic review of the effects of therapy in infants with the KISS-syndrome (kinetic imbalance due to suboccipital strain)]". Nederlands Tijdschrift voor Geneeskunde (in Dutch). 149 (13): 703–07. PMID 15819137.
- ^ Proctor ML, Hing W, Johnson TC, Murphy PA, Brown J (2006). "Spinal manipulation for primary and secondary dysmenorrhoea". The Cochrane Database of Systematic Reviews. 3 (3) CD002119. doi:10.1002/14651858.CD002119.pub3. PMC 6718213. PMID 16855988.
- ^ a b Goto, Viviane; Frange, Cristina; Andersen, Monica L.; Júnior, José M. S.; Tufik, Sergio; Hachul, Helena (May 2014). "Chiropractic intervention in the treatment of postmenopausal climacteric symptoms and insomnia: A review". Maturitas. 78 (1): 3–7. doi:10.1016/j.maturitas.2014.02.004. PMID 24656717.
- ^ Liddle, Sarah D.; Pennick, Victoria (2015-09-30). "Interventions for preventing and treating low-back and pelvic pain during pregnancy". Cochrane Database of Systematic Reviews. 2015 (9) CD001139. doi:10.1002/14651858.CD001139.pub4. PMC 7053516. PMID 26422811.
- ^ Camilleri M, Park SY, Scarpato E, Staiano A (2017). "Exploring hypotheses and rationale for causes of infantile colic". Neurogastroenterology & Motility (Review). 29 (2) e12943. doi:10.1111/nmo.12943. PMC 5276723. PMID 27647578.
- ^ a b Anderson-Peacock E, Blouin JS, Bryans R, Danis N, Furlan A, Marcoux H, Potter B, Ruegg R, Stein JG, White E (2005). "Chiropractic clinical practice guideline: evidence-based treatment of adult neck pain not due to whiplash". The Journal of the Canadian Chiropractic Association. 49 (3): 158–209. PMC 1839918. PMID 17549134.
• Anderson-Peacock E, Bryans R, Descarreaux M, Marcoux H, Potter B, Ruegg R, Shaw L, Watkin R, White E (2008). "A Clinical Practice Guideline Update from The CCA•CFCREAB-CPG" (PDF). The Journal of the Canadian Chiropractic Association. 52 (1): 7–8. PMC 2258235. PMID 18327295. Archived from the original (PDF) on 2010-09-05. - ^ Thiel HW, Bolton JE, Docherty S, Portlock JC (2007). "Safety of chiropractic manipulation of the cervical spine: a prospective national survey". Spine. 32 (21): 2375–78. doi:10.1097/BRS.0b013e3181557bb1. PMID 17906581. S2CID 42353750.
- ^ Hurwitz EL, Morgenstern H, Vassilaki M, Chiang LM (July 2005). "Frequency and clinical predictors of adverse reactions to chiropractic care in the UCLA neck pain study". Spine. 30 (13): 1477–84. doi:10.1097/01.brs.0000167821.39373.c1. PMID 15990659. S2CID 45678522.
- ^ "Safety and regulation of chiropractic". NHS Choices. 20 August 2014. Retrieved 22 September 2016.
- ^ Vohra S, Johnston BC, Cramer K, Humphreys K (2007). "Adverse events associated with pediatric spinal manipulation: a systematic review". Pediatrics. 119 (1): e275–83. doi:10.1542/peds.2006-1392. PMID 17178922. S2CID 43683198.
- ^ Ernst E, Posadzki P (2012). "Reporting of adverse effects in randomised clinical trials of chiropractic manipulations: a systematic review". The New Zealand Medical Journal. 125 (1353): 87–140. PMID 22522273.
- ^ Gorrell LM, Engel RM, Brown B, Lystad RP (2016). "The reporting of adverse events following spinal manipulation in randomized clinical trials-a systematic review". The Spine Journal (Systematic Review). 16 (9): 1143–51. doi:10.1016/j.spinee.2016.05.018. PMID 27241208.
- ^ Hebert JJ, Stomski NJ, French SD, Rubinstein SM (2013). "Serious Adverse Events and Spinal Manipulative Therapy of the Low Back Region: A Systematic Review of Cases". Journal of Manipulative and Physiological Therapeutics. 38 (9): 677–91. doi:10.1016/j.jmpt.2013.05.009. PMID 23787298.
- ^ Jenkins, H. J. (5 October 2016). "Awareness of radiographic guidelines for low back pain: a survey of Australian chiropractors". Chiropractic & Manual Therapies. 24 39. doi:10.1186/s12998-016-0118-7. PMC 5051064. PMID 27713818.
- ^ a b c Ammendolia C, Taylor JA, Pennick V, Côté P, Hogg-Johnson S, Bombardier C (2008). "Adherence to radiography guidelines for low back pain: A survey of chiropractic schools worldwide". Journal of Manipulative and Physiological Therapeutics. 31 (6): 412–18. doi:10.1016/j.jmpt.2008.06.010. PMID 18722195.
- ^ a b c d Singh, S.; Ernst, E. (2008). "The truth about chiropractic therapy". Trick or Treatment: The Undeniable Facts about Alternative Medicine. W. W. Norton. pp. 145–90. ISBN 978-0-393-06661-6.
- ^ a b Bussières AE, Taylor JA, Peterson C (2008). "Diagnostic imaging practice guidelines for musculoskeletal complaints in adults – an evidence-based approach – part 3: spinal disorders". Journal of Manipulative and Physiological Therapeutics. 31 (1): 33–88. doi:10.1016/j.jmpt.2007.11.003. PMID 18308153.
- ^ Committee to Assess Health Risks from Exposure to Low Levels of Ionizing Radiation: Board on Radiation Effects Research" US National Research Council (2006). Health Risks from Exposure to Low Levels of Ionizing Radiation: BEIR VII Phase 2. Washington, DC: The National Academies Press. doi:10.17226/11340. ISBN 978-0-309-09156-5.
- ^ a b Hurwitz EL, Carragee EJ, van der Velde G, Carroll LJ, Nordin M, Guzman J, Peloso PM, Holm LW, Côté P, Hogg-Johnson S, Cassidy JD, Haldeman S (2008). "Treatment of neck pain: noninvasive interventions: results of the Bone and Joint Decade 2000–2010 Task Force on Neck Pain and Its Associated Disorders". Spine. 33 (4 Suppl): S123–52. doi:10.1097/BRS.0b013e3181644b1d. PMID 18204386. S2CID 27261997.
- ^ Paciaroni M, Bogousslavsky J (2009). "Cerebrovascular complications of neck manipulation". European Neurology. 61 (2): 112–18. doi:10.1159/000180314. PMID 19065058.
- ^ Miley ML, Wellik KE, Wingerchuk DM, Demaerschalk BM (2008). "Does cervical manipulative therapy cause vertebral artery dissection and stroke?". Neurologist. 14 (1): 66–73. doi:10.1097/NRL.0b013e318164e53d. PMID 18195663. S2CID 18062970.
- ^ a b Biller, J.; Sacco, R. L.; Albuquerque, F. C.; Demaerschalk, B. M.; Fayad, P.; Long, P. H.; Noorollah, L. D.; Panagos, P. D.; Schievink, W. I.; Schwartz, N. E.; Shuaib, A.; Thaler, D. E.; Tirschwell, D. L. (2014). "Cervical Arterial Dissections and Association With Cervical Manipulative Therapy: A Statement for Healthcare Professionals From the American Heart Association/American Stroke Association". Stroke. 45 (10): 3155–74. doi:10.1161/STR.0000000000000016. PMID 25104849.
- ^ Church, Ephraim W; Sieg, Emily P; Zalatimo, Omar; Hussain, Namath S; Glantz, Michael; Harbaugh, Robert E (2016). "Systematic Review and Meta-analysis of Chiropractic Care and Cervical Artery Dissection: No Evidence for Causation". Cureus. 8 (2) e498. doi:10.7759/cureus.498. PMC 4794386. PMID 27014532.
- ^ Chung CL, Côté P, Stern P, L'espérance G (2014). "The Association Between Cervical Spine Manipulation and Carotid Artery Dissection: A Systematic Review of the Literature". Journal of Manipulative and Physiological Therapeutics. 38 (9): 672–6. doi:10.1016/j.jmpt.2013.09.005. PMID 24387889.
- ^ Wynd S, Westaway M, Vohra S, Kawchuk G (2013). "The quality of reports on cervical arterial dissection following cervical spinal manipulation". PLOS ONE. 8 (3) e59170. Bibcode:2013PLoSO...859170W. doi:10.1371/journal.pone.0059170. PMC 3604043. PMID 23527121.
- ^ Tuchin, P. (2014). "A systematic literature review of intracranial hypotension following chiropractic". International Journal of Clinical Practice. 68 (3): 396–402. doi:10.1111/ijcp.12247. PMID 24372942. S2CID 5315779.
- ^ Yang, Hwan-Seo; Oh, Young-Min; Eun, Jong-Pil (2016). "Cervical Intradural Disc Herniation Causing Progressive Quadriparesis After Spinal Manipulation Therapy". Medicine. 95 (6) e2797. doi:10.1097/MD.0000000000002797. PMC 4753938. PMID 26871842.
- ^ a b E Ernst (2011). "Response to critiques of deaths after chiropractic". International Journal of Clinical Practice. 65 (1): 106. doi:10.1111/j.1742-1241.2010.02568.x. S2CID 72845939.
- ^ Di Fabio, Richard P (January 1, 1999). "Manipulation of the Cervical Spine: Risks and Benefits". Physical Therapy. 79 (1). doi:10.1093/ptj/79.1.50. Retrieved November 1, 2021.
Although the risk of injury associated with MCS appears to be small, this type of therapy has the potential to expose patients to vertebral artery damage that can be avoided with the use of mobilization (nonthrust passive movements). The literature does not demonstrate that the benefits of MCS outweigh the risks. Several recommendations for future studies and for the practice of MCS are discussed.
- ^ Michaleff ZA, Lin CW, Maher CG, van Tulder MW (2012). "Spinal manipulation epidemiology: Systematic review of cost effectiveness studies". Journal of Electromyography and Kinesiology. 22 (5): 655–62. doi:10.1016/j.jelekin.2012.02.011. PMID 22429823.
- ^ Canter PH, Coon JT, Ernst E (2006). "Cost-Effectiveness of Complementary Therapies in the United Kingdom – A Systematic Review†". Evidence-Based Complementary and Alternative Medicine. 3 (4): 425–32. doi:10.1093/ecam/nel044. PMC 1697737. PMID 17173105. Archived from the original on 2008-05-11.
- ^ van der Roer N, Goossens ME, Evers SM, van Tulder MW (2005). "What is the most cost-effective treatment for patients with low back pain? a systematic review". Best Practice & Research Clinical Rheumatology. 19 (4): 671–84. doi:10.1016/j.berh.2005.03.007. PMID 15949783.
- ^ Sarnat RL, Winterstein J, Cambron JA (May 2007). "Clinical Utilization and Cost Outcomes From an Integrative Medicine Independent Physician Association: An Additional 3-Year Update". Journal of Manipulative and Physiological Therapeutics. 30 (4): 263–69. doi:10.1016/j.jmpt.2007.03.004. PMID 17509435. S2CID 613004.
- ^ "Glossary". National Center for Education Statistics, U.S. Dept. of Education. Archived from the original on 2009-06-04. Retrieved 2009-06-05.
- ^ Marcus DM, McCullough L (2009). "An evaluation of the evidence in 'evidence-based' integrative medicine programs". Academic Medicine. 84 (9): 1229–34. doi:10.1097/ACM.0b013e3181b185f4. PMID 19707062.
- ^ Coulter I, Adams A, Coggan P, Wilkes M, Gonyea M (September 1998). "A comparative study of chiropractic and medical education". Alternative Therapies in Health and Medicine. 4 (5): 64–75. PMID 9737032.
- ^ "Prospective students". Association of Chiropractic Colleges. Archived from the original on 2009-08-14. Retrieved 2009-07-23.
- ^ "Standards for Accreditation of Doctor of Chiropractic Programmes" (PDF). Canadian Federation of Chiropractic Regulatory and Educational Accrediting Boards. 2011-11-26. Archived from the original (PDF) on 2015-09-23. Retrieved 2014-08-02.
- ^ a b "CMCC Backgrounder 2015" (PDF). Canadian Memorial Chiropractic College. Archived (PDF) from the original on 2019-02-26. Retrieved 26 February 2019.
- ^ a b "Degree Authority in Ontario". Ontario Ministry of Training, Colleges and Universities. Retrieved 2010-12-14.
- ^ "State chiropractic licensure". Life University. 2008. Archived from the original on 2009-08-01. Retrieved 2009-06-05.
- ^ "Becoming a chiropractor". Canadian Federation of Chiropractic Regulatory and Educational Accrediting Boards. Archived from the original on 2009-06-15. Retrieved 2009-06-05.
- ^ Grod JP (2006). "Continuing health education in Canada". The Journal of the Canadian Chiropractic Association. 50 (1): 14–17. PMC 1839972. PMID 17549163.
- ^ Stuber KJ, Grod JP, Smith DL, Powers P (2005). "An online survey of chiropractors' opinions of Continuing Education". Chiropractic & Osteopathy. 13 (1) 22. doi:10.1186/1746-1340-13-22. PMC 1282582. PMID 16242035.
- ^ Coulter ID, Adams AH, Sandefur R (1997). "Chiropractic training" (PDF). In Cherkin DC, Mootz RD (eds.). Chiropractic in the United States: Training, Practice, and Research (PDF). Rockville, MD: Agency for Health Care Policy and Research. pp. 17–28. OCLC 39856366. Archived from the original on 2008-06-25. Retrieved 2008-05-11. AHCPR Pub No. 98-N002.
- ^ "The Council on Chiropractic Education (CCE)". The Council on Chiropractic Education. Retrieved 2008-07-05.
- ^ "The General Chiropractic Council". Retrieved 2020-05-02.
- ^ a b c Morrison P (2009). "Adjusting the role of chiropractors in the United States: why narrowing chiropractor scope of practice statutes will protect patients". Health Matrix. 19 (2): 493–537. PMID 19715143.
- ^ "About Us". Councils on Chiropractic Education International. Archived from the original on 2010-11-18. Retrieved 2010-09-30.
- ^ "Accredited Doctor of Chiropractic programs". The Council on Chiropractic Education. Archived from the original on 2008-02-14. Retrieved 2008-02-22.
- ^ "Accreditation of educational programmes". Canadian Federation of Chiropractic Regulatory and Educational Accrediting Boards. Archived from the original on 2009-05-18. Retrieved 2009-06-05.
- ^ "Program Accreditation Status". Council on Chiropractic Education Australasia. Archived from the original on 2011-02-17. Retrieved 2010-09-30.
- ^ "Institutions holding Accredited Status with the ECCE". European Council On Chiropractic Education. 2010-11-01. Archived from the original on 2014-07-22. Retrieved 2014-08-02.
- ^ "Canadian Chiropractic Association FAQs". Canadian Chiropractic Association. Archived from the original on 2009-08-17. Retrieved 2010-10-02.
- ^ "Federation of Chiropractic Licensing Boards FAQ". Federation of Chiropractic Licensing Boards. Retrieved 2010-10-02.
- ^ a b Hester H, Cunliffe C, Hunnisett A (2013). "Stress in chiropractic education: a student survey of a five-year course". Journal of Chiropractic Education. 27 (2): 147–51. doi:10.7899/JCE-13-4. PMC 3791907. PMID 23957319.
- ^ a b c Johnson C (December 2010). "Reflecting on 115 years: the chiropractic profession's philosophical path". Journal of Chiropractic Humanities. 17 (1): 1–5. doi:10.1016/j.echu.2010.11.001. PMC 3342796. PMID 22693471.
- ^ Camhi, Tiffany (30 August 2024). "Oregon alternative medicine students face a long road to loan forgiveness". OPB. Retrieved 28 October 2024.
- ^ U.S. Department of Education. "Most Recent Data by Field of Study". U.S. Department of Education College Scorecard. Archived from the original on 9 September 2024.
- ^ Rosiak, Luke (12 January 2010). "Chiropractics lobbied for special student loans, defaulted in droves: Sunlight Foundation". Sunlight Foundation. Retrieved 29 October 2024.
- ^ Mirtz, DC, Timothy (23 April 2003). "The Student Loan Mess: Why Chiropractic Is in Trouble". Quackwatch. Retrieved 29 October 2024.
- ^ a b "Chiropractic Student Loan Default Rates (1999 to 2012)". Quackwatch. 12 March 2018. Retrieved 29 October 2024.
- ^ Simpson JK, Losco B, Young KJ (2010). "Development of the murdoch chiropractic graduate pledge". Journal of Chiropractic Education. 24 (2): 175–86. doi:10.7899/1042-5055-24.2.175. PMC 2967342. PMID 21048880.
- ^ Staff. "Code of Ethics". American Chiropractic Association. Archived from the original on 2014-02-22. Retrieved 2014-02-11.
- ^ Staff. "ICA code of Ethics". International Chiropractor's Association. Archived from the original on 2014-04-05.
- ^ "Majority in U.S. Say Chiropractic Works for Neck, Back Pain". Gallup Inc. 8 September 2015. Retrieved 2015-09-13.
- ^ Weeks, William B; Goertz, Christine M; Meeker, William C; Marchiori, Dennis M (2015-01-01). "Public Perceptions of Doctors of Chiropractic: Results of a National Survey and Examination of Variation According to Respondents' Likelihood to Use Chiropractic, Experience With Chiropractic, and Chiropractic Supply in Local Health Care Markets". Journal of Manipulative and Physiological Therapeutics. 38 (8): 533–44. doi:10.1016/j.jmpt.2015.08.001. PMID 26362263.
- ^ "A pivotal moment for free speech in Britain". The Guardian. April 15, 2010.
- ^ "The BHA re-publishes Simon Singh's article on chiropractic therapy". British Humanist Association. July 29, 2009.
- ^ Ernst E, Gilbey A (2010). "Chiropractic claims in the English-speaking world". The New Zealand Medical Journal. 123 (1312): 36–44. PMID 20389316.
- ^ a b Stephen Barrett (2017-01-02). "Medicare Overpayments to Chiropractors Are Widespread". American Council on Science and Health.
- ^ a b Lucas Laursen. "The Great Beyond: Chiropractic group advises members to 'withdraw from the battleground'". Nature.com. Retrieved 20 June 2009.
- ^ Lucas Laursen. "The Great Beyond: Complaints converge on chiropractors". Nature.com. Retrieved 20 June 2009.
- ^ "Unjust burdens of proof". Nature. 459 (7248): 751. June 2009. Bibcode:2009Natur.459Q.751.. doi:10.1038/459751a. PMID 19516290.
- ^ Pallab Ghosh (2010-04-15). "Case dropped against Simon Singh". BBC News.
- ^ Mark Henderson (2010-04-16). "Science writer Simon Singh wins bitter libel battle". Times Online. London. Archived from the original on June 11, 2011.
- ^ Leach, Matthew J. (2013-08-01). "Profile of the complementary and alternative medicine workforce across Australia, New Zealand, Canada, United States and United Kingdom". Complementary Therapies in Medicine. 21 (4): 364–378. doi:10.1016/j.ctim.2013.04.004. ISSN 0965-2299. PMID 23876568.
- ^ Xue CC, Zhang AL, Lin V, Myers R, Polus B, Story DF (2008). "Acupuncture, chiropractic and osteopathy use in Australia: a national population survey". BMC Public Health. 8 105. doi:10.1186/1471-2458-8-105. PMC 2322980. PMID 18377663.
- ^ a b c d e f Adams, Jon; Lauche, Romy; Peng, Wenbo; Steel, Amie; Moore, Craig; Amorin-Woods, Lyndon G.; Sibbritt, David (2017). "A workforce survey of Australian chiropractic: the profile and practice features of a nationally representative sample of 2,005 chiropractors". BMC Complementary and Alternative Medicine. 17 (1): 14. doi:10.1186/s12906-016-1542-x. ISSN 1472-6882. PMC 5217252. PMID 28056964.
 This article incorporates text by Jon Adams, Romy Lauche, Wenbo Peng, Amie Steel, Craig Moore, Lyndon G. Amorin-Woods, and David Sibbritt available under the CC BY 4.0 license.
This article incorporates text by Jon Adams, Romy Lauche, Wenbo Peng, Amie Steel, Craig Moore, Lyndon G. Amorin-Woods, and David Sibbritt available under the CC BY 4.0 license.
- ^ "Freedom of Profession for Chiropractors in Germany". ACLANZ. aclanz Rechtsanwälte. Retrieved 16 June 2023.
- ^ Dunning, James R.; Rosner, Anthony L.; Perle, Stephen M.; Kawchuk, Greg (2011). "Osteopathic Manipulative Treatment for Low Back Pain: A Systematic Review and Meta-Analysis of Randomized Controlled Trials". Journal of Manipulative and Physiological Therapeutics. 34 (3): 183–190. doi:10.1016/j.jmpt.2010.11.006. PMID 21419335.
- ^ Emary, Peter C.; Oremus, Mark; Houweling, Taco A. W.; Wangler, Martin; Akhtar-Danesh, Noori (October 20, 2020). "Attitudes, beliefs, and practices among Swiss chiropractors regarding medication prescribing for musculoskeletal conditions: a national Q-methodology study". Chiropractic & Manual Therapies. 28 (1): 54. doi:10.1186/s12998-020-00341-6. PMC 7574492. PMID 33076943.
- ^ Wangler M, Zaugg B, Faigaux E (2010). "Medication Prescription: A Pilot Survey of Bernese Doctors of Chiropractic Practicing in Switzerland". Journal of Manipulative and Physiological Therapeutics. 33 (3): 231–237. doi:10.1016/j.jmpt.2010.01.013. PMID 20350678.
- ^ "ChiroSuisse - Organisation". www.chirosuisse.ch (in German). Schweizerische Gesellschaft für Chiropraktik. Retrieved 16 June 2023.
- ^ "Chiropractic treatment available on NHS in Cornwall". BBC News. August 13, 2013. Retrieved August 18, 2013.
- ^ Langworthy JM, Forrest L (2010). "Withdrawal rates as a consequence of disclosure of risk associated with manipulation of the cervical spine". Chiropractic & Osteopathy. 18 27. doi:10.1186/1746-1340-18-27. PMC 3161389. PMID 20977721.
- ^ "Key Facts". ACA Today.
- ^ a b Lawrence DJ, Meeker WC (2007). "Chiropractic and CAM utilization: a descriptive review". Chiropractic & Osteopathy. 15 2. doi:10.1186/1746-1340-15-2. PMC 1784103. PMID 17241465.
- ^ Crownfield PW (2007). "Chiropractic in Alberta: a model of consumer utilization and satisfaction". Dynamic Chiropractic. Vol. 25, no. 6.
- ^ a b Kemper KJ, Vohra S, Walls R (December 2008). "American Academy of Pediatrics. The use of complementary and alternative medicine in pediatrics". Pediatrics. 122 (6): 1374–1386. doi:10.1542/peds.2008-2173. PMID 19047261.
- ^ "Chiropractic: In Depth".
- ^ Cherkin, Daniel C.; Mootz, Robert D. (2010). "Chiropractic in the United States:Training, Practice, and Research". Chirobase. Retrieved 2010-10-01.
- ^ Gaumer G (2006). "Factors associated with patient satisfaction with chiropractic care: survey and review of the literature". Journal of Manipulative and Physiological Therapeutics. 29 (6): 455–462. doi:10.1016/j.jmpt.2006.06.013. PMID 16904491.
- ^ Tindle HA, Davis RB, Phillips RS, Eisenberg DM (2005). "Trends in use of complementary and alternative medicine by US adults: 1997–2002". Alternative Therapies in Health and Medicine. 11 (1): 42–49. PMID 15712765.
- ^ Stanley, G. (2007). "The Sustainability of Chiropractic". Dynamic Chiropractic. Vol. 25, no. 19.
- ^ Eric J. Bailey (2002). African American Alternative Medicine: Using Alternative Medicine to Prevent and Control Chronic Diseases. Greenwood Publishing Group. pp. 26ff. ISBN 978-0-89789-747-1.
- ^ "Chiropractors". U.S. Bureau of Labor Statistics. 2007. Retrieved 2008-07-05.
- ^ "7 Years of Lobbying Finally Brings Chiropractic Under Umbrella of Medicare (Published 1972)". The New York Times. 19 November 1972.
- ^ a b Peterson, Dennis; Wiese, Glenda (1995). Chiropractic: An Illustrated History. Mosby. p. 205. ISBN 978-0-8016-7735-9.
- ^ Wyatt, LH; Perle, SM; et al. (2005). "The necessary future of chiropractic education: a North American perspective". Chiropractic & Osteopathy. 13 10. doi:10.1186/1746-1340-13-10. PMC 1181629. PMID 16001976.
- ^ Agocs, S. (2011). "Chiropractic's Fight for Survival". AMA Journal of Ethics. 13 (6): 384–388. doi:10.1001/virtualmentor.2011.13.6.mhst1-1106. PMID 23131408.
- ^ "Chiropractic care for pain relief". 16 February 2015.
- ^ a b Parkman CA (2004). "Issues in credentialing CAM providers". The Case Manager. 15 (4): 24–27. doi:10.1016/j.casemgr.2004.05.004. PMID 15247891.
- ^ "Occupational And Professional Licensing, Chiropractic Practitioners, Chiropractic Advanced Practice Certification Registry". State of New Mexico. Archived 2010-03-17 at the Wayback Machine. Retrieved 2010-05-03.
- ^ "Occupational And Professional Licensing, Chiropractic Practitioners, Chiropractic Advanced Practice Certification Registry" (PDF). State of New Mexico. Retrieved 2010-05-03.
- ^ a b c McDonald WP, Durkin KF, Pfefer M, et al. (2003). How Chiropractors Think and Practice: The Survey of North American Chiropractors. Ada, Ohio: Institute for Social Research, Ohio Northern University. ISBN 978-0-9728055-5-1.[page needed]
- ^ "Breaking the Cycle: How Health Sciences Teams Are Tackling the Overdose Crisis and Opioid Addiction | Health Sciences | University of Pittsburgh".
- ^ "Pitt to create doctor of chiropractic program". Pittsburgh Post-Gazette. 20 February 2024. pp. A10.
- ^ a b Baer HA (1987). "Divergence and convergence in two systems of manual medicine: osteopathy and chiropractic in the United States". Medical Anthropology Quarterly. 1 (2): 176–193. doi:10.1525/maq.1987.1.2.02a00030.
- ^ a b c d e f g h i j k l m n o Keating, J. C. Jr; Cleveland, C. S. III; Menke, M. (2005). "Chiropractic history: a primer" (PDF). Association for the History of Chiropractic. Archived from the original (PDF) on 2014-04-24. Retrieved 2008-06-16.
- ^ "chiropractic". Oxford English Dictionary. Oxford University Press. 2014. Archived from the original on May 3, 2013.
- ^ "chiro-". Oxford English Dictionary. Oxford University Press. 2014. Archived from the original on August 12, 2014.
- ^ Swanson ES (2015). "Pseudoscience". Science and Society: Understanding Scientific Methodology, Energy, Climate, and Sustainability. Springer. p. 65. ISBN 978-3-319-21987-5.
- ^ [1] — Chiro.org
- ^ Freeman J (February 2005). "Towards a definition of holism". The British Journal of General Practice. 55 (511): 154–55. PMC 1463203. PMID 15720949.
- ^ a b c d e f g h i Kaptchuk TJ, Eisenberg DM (November 1998). "Chiropractic: origins, controversies, and contributions". Archives of Internal Medicine. 158 (20): 2215–24. doi:10.1001/archinte.158.20.2215. PMID 9818801.
- ^ Martin Gardner (1 June 1957). Fads and Fallacies in the Name of Science. Courier Corporation. pp. 227–. ISBN 978-0-486-20394-2.
{{cite book}}: ISBN / Date incompatibility (help) - ^ a b Raso J (1997). "Dictionary of Metaphysical Healthcare – Glossary". Quackwatch. Retrieved 12 February 2016.
- ^ "Straight Chiropractic". Wausau Pilot. Wausau, Wisconsin. Jun 23, 1914. p. 5 – via Newspapers.com.
- ^ a b Folk, Holly (March 13, 2017). The Religion of Chiropractic: Populist Healing from the American Heartland. UNC Press Books. ISBN 978-1-4696-3280-3 – via Google Books.
- ^ a b Smith M, Carber LA (2008). "Survey of US Chiropractor Attitudes and Behaviors about Subluxation" (PDF). Journal of Chiropractic Humanities. 15: 19–26. doi:10.1016/s1556-3499(13)60166-7. Archived from the original (PDF) on 2012-04-25.
- ^ Benedetti, Paul; MacPhail, Wayne (2002-01-01). Spin Doctors: The Chiropractic Industry Under Examination. Dundurn. p. 18. ISBN 978-1-55002-406-7.
- ^ Cherkin D (November 1989). "AMA policy on chiropractic". American Journal of Public Health. 79 (11): 1569–70. doi:10.2105/AJPH.79.11.1569-a. PMC 1349822. PMID 2817179.
- ^ Wardle, Jon; Frawley, Jane; Steel, Amie; Sullivan, Elizabeth (2016). "Complementary medicine and childhood immunisation: A critical review". Vaccine. 34 (38): 4484–4500. doi:10.1016/j.vaccine.2016.07.026. PMID 27475472.
- ^ Russell ML, Injeyan HS, Verhoef MJ, Eliasziw M (2004). "Beliefs and behaviours: understanding chiropractors and immunization". Vaccine. 23 (3): 372–379. doi:10.1016/j.vaccine.2004.05.027. PMID 15530683.
- ^ Jones RB, Mormann DN, Durtsche TB (1989). "Fluoridation referendum in La Crosse, Wisconsin: contributing factors to success". American Journal of Public Health. 79 (10): 1405–1408. doi:10.2105/AJPH.79.10.1405. PMC 1350185. PMID 2782512.
- ^ Jaroff, Leon (27 February 2002). "Back Off, Chiropractors!". Time. Retrieved 7 June 2009.
- ^ Palmer DD (1910). The Chiropractor's Adjuster: Text-book of the Science, Art and Philosophy of Chiropractic for Students and Practitioners. Portland, Oregon: Portland Printing House Co. OCLC 17205743.
A subluxated vertebra ... is the cause of 95 percent of all diseases ... The other five percent is caused by displaced joints other than those of the vertebral column.
- ^ Gunther Brown, Candy (July 7, 2014). "Chiropractic: Is it Nature, Medicine or Religion?". HuffPost.
Further reading
[edit]- Long PH (2013). Barrett S (ed.). Chiropractic Abuse: An Insider's Lament. American Council on Science & Health. ISBN 978-0-9727094-9-1.
- Homola S (2002). "Chiropractic: Conventional or Alternative Healing?". In Shermer M (ed.). The Skeptic Encyclopedia of Pseudoscience. Vol. 1. ABC-CLIO. pp. 308–. ISBN 978-1-57607-653-8.
- Menke JM (January 2014). "Do Manual Therapies Help Low Back Pain?: A Comparative Effectiveness Meta-Analysis". Spine (Meta-analysis). 39 (7): E463–72. doi:10.1097/BRS.0000000000000230. PMID 24480940. S2CID 25497624.
External links
[edit]Chiropractic
View on GrokipediaDefinition and Core Principles
Philosophical Foundations
Chiropractic philosophy originates from the ideas of Daniel David Palmer, who founded the discipline in 1895 in Davenport, Iowa. Palmer articulated a worldview rooted in vitalism, positing that a universal intelligence—described as the organizing principle present in all matter and equated by him to "God, the Eternal, the All-Wise"—underlies natural laws and animates living systems. This universal intelligence manifests within organisms as innate intelligence, an inherent, adaptive force that directs bodily functions, maintains homeostasis, and facilitates self-healing without external material intervention.[11][12] Central to this philosophy is the 33 principles codified by B.J. Palmer, D.D. Palmer's son, which formalize innate intelligence as the vital entity distinguishing living from non-living matter. Principle 1 states: "The Major Premise: There is an Intelligence in all matter and matter takes its character from this Intelligence, which is universal in its nature." Principle 20 elaborates: "There is a substance of life, which we call Innate Intelligence, present in every organism, which is the animating force." Principle 6, the Principle of Time, states that there is no process that does not require time, emphasizing the need for time in bodily organization, coordination, and adaptation of forces. Principle 23 specifies that innate intelligence adapts universal forces and matter for bodily use, ensuring all parts work in harmony. These principles frame health as the optimal expression of innate intelligence, with dis-ease—intentionally hyphenated by both D.D. and B.J. Palmer to signify "lack of ease" or disharmony in the body, distinct from "disease" (which implies external pathology)—arising from its interference rather than external pathogens alone, underscoring chiropractic's emphasis on restoring innate harmony rather than merely treating symptoms.[13][14][15] Palmer's concepts drew from 19th-century influences including mesmerism, spiritualism, and teleological metaphors, evolving through his writings from 1896 to 1913. While early formulations emphasized moral and metaphysical dimensions—such as innate intelligence's role in ethical living—later chiropractic thinkers debated interpretations, with some viewing it as a deductive major premise for clinical reasoning and others critiquing its vitalistic elements as incompatible with empirical science. Nonetheless, these foundations distinguish chiropractic from biomedical models by prioritizing the body's self-regulating capacity over symptom suppression.[11][12] Professional organizations such as the World Federation of Chiropractic describe chiropractic as a holistic health profession that employs a biopsychosocial model of care. This approach treats the patient as a whole, taking into account biomedical, psychological, and social components of health, including the patient's needs, beliefs, preferences, full medical history, lifestyle, and personal circumstances, rather than focusing solely on isolated symptoms. Chiropractors emphasize the body's innate ability to heal, supported through manual therapies including spinal adjustments that address the nervous system and musculoskeletal system, while incorporating patient education, advice on exercise and lifestyle, promotion of self-efficacy, rehabilitation, and multicomponent interventions aimed at overall health and well-being. The American Chiropractic Association similarly characterizes chiropractic as a holistic approach to health care that generally excludes drugs or surgery.[16][2]Vertebral Subluxation Theory
The vertebral subluxation theory forms a cornerstone of traditional chiropractic philosophy, asserting that partial displacements or dysfunctions of vertebrae, known as subluxations, compress or irritate spinal nerves, thereby interfering with the transmission of vital nerve impulses from the brain to bodily tissues and organs. This disruption is claimed to impair the body's innate self-healing capacity, resulting in a wide array of health conditions beyond mere musculoskeletal disorders, including visceral diseases.[17] The theory posits that chiropractic adjustments to correct these subluxations restore proper nerve flow and health.[18] Daniel David Palmer originated the concept in 1895 during his adjustment of Harvey Lillard, a Davenport, Iowa janitor deaf for 17 years following a vertebral popping sensation in his upper back. Palmer identified a subluxation at the atlas vertebra, adjusted it, and Lillard reportedly regained hearing, which Palmer interpreted as evidence of subluxation-induced nerve impingement preventing auditory function.[19] Drawing from magnetic healing and anatomical observations, Palmer formalized the idea that 95% of diseases stem from spinal misalignments affecting nerves, as detailed in his later writings.[20] The term "subluxation," borrowed from earlier medical literature denoting minor joint displacements, was adapted by Palmer to encompass not just mechanical shifts but functional lesions causing systemic pathology.[21] The theory evolved through Palmer's son, Bartlett Joshua Palmer, who amplified its scope, establishing "straight" chiropractic schools emphasizing subluxation detection and correction via X-rays and instrumentation for non-symptomatic care.[22] Proponents, including the International Chiropractors Association, define vertebral subluxation as a "potentially reversible or preventable alteration of spinal motion segments from normal alignment or function," central to practice.[23] However, internal chiropractic divisions emerged, with "mixer" practitioners incorporating broader therapies and evidence-based approaches, often de-emphasizing unsubstantiated subluxation claims for visceral disease causation.[24] Scientific scrutiny reveals no empirical support for the theory's core assertions. Anatomical studies fail to demonstrate that minor vertebral displacements produce nerve compression sufficient to cause distant organ dysfunction, and clinical trials show spinal manipulation benefits limited to low back pain and related conditions, not systemic diseases.[25] Reviews characterize the concept as implausible, lacking validation through controlled experiments or imaging confirmation of causal links to non-musculoskeletal ailments.[24] Critics, including former chiropractors, argue it perpetuates pseudoscientific foundations incompatible with modern physiology, where disease etiologies involve complex multifactorial processes rather than singular nerve interference from spinal misalignment.[26] Despite this, subluxation remains doctrinally entrenched in segments of the profession, contributing to ongoing debates over chiropractic's scientific legitimacy.[27]Historical Development
Origins and Early Pioneers
Daniel David Palmer, born on March 7, 1845, in Pickering, Ontario, Canada, immigrated to the United States around 1865 and later practiced as a magnetic healer in Davenport, Iowa, starting in 1888.[28] [29] Palmer, who held spiritualist beliefs and experimented with energy-based healing, sought to differentiate his methods from conventional medicine by emphasizing spinal manipulation to address disease causes.[30] On September 18, 1895, Palmer performed what is regarded as the first chiropractic adjustment on Harvey Lillard, a janitor in the same building who had lost hearing in one ear following a back strain 17 years earlier.[19] [31] According to Palmer's account, Lillard reported restored hearing after the manipulation of a vertebral subluxation, which Palmer theorized impinged on nerves supplying the auditory system, thereby interrupting vital force transmission—a concept he termed "innate intelligence" flowing through the nervous system.[32] [33] This event, documented in Palmer's writings and corroborated by chiropractic historical records, marked the empirical origin of chiropractic as a distinct practice, though the hearing recovery remains an unverified anecdotal claim central to its foundational narrative.[19] [34] Palmer formalized chiropractic by establishing the Palmer School of Chiropractic (initially the Palmer Infirmary and Chiropractic Institute) in Davenport in 1897, training the first students in spinal adjustment techniques to correct subluxations and restore health without drugs or surgery.[28] He published foundational texts outlining the philosophy, asserting that 95% of diseases stemmed from spinal misalignments disrupting nerve function, a view derived from his observations rather than controlled experimentation.[29] Palmer's son, Bartlett Joshua (B.J.) Palmer, born in 1882, took over the school in 1906 after purchasing it from his father, transforming it into a major institution and earning recognition as chiropractic's "Developer."[35] [36] B.J. Palmer expanded the profession through aggressive promotion, introducing neurocalometer technology in the 1920s for detecting subluxations via heat differentials and advocating the "Big Idea" that innate intelligence self-heals when unobstructed, influencing early chiropractic philosophy and practice standardization.[37] [38] Under his leadership, enrollment grew, and chiropractic spread internationally, though internal debates over mixing therapies persisted.[39]Evolution and Internal Divisions
Following D.D. Palmer's death in 1913, chiropractic experienced profound internal evolution characterized by ideological schisms that shaped its professional trajectory for over a century.[40] The primary division emerged between "straights," who adhered strictly to the founder's vitalistic philosophy of correcting vertebral subluxations exclusively through spinal adjustments to restore innate intelligence, and "mixers," who expanded practices to include adjunctive therapies like physiotherapy, diet, and massage, viewing chiropractic as a broader drugless healing art.[40] This conflict intensified during the Era of Prosecution (1900–1950), with over 15,000 legal actions against practitioners, 20% resulting in imprisonment, as straights like B.J. Palmer defended a "separate and distinct" identity against medical assimilation.[41] B.J. Palmer, D.D. Palmer's son, solidified the straight faction through innovations like the neurocalometer in 1924 and leadership of the Universal Chiropractors' Association, which evolved into the International Chiropractors Association (ICA) founded in 1926 to promote principle-based subluxation care.[40] [42] Mixers, seeking legitimacy via eclectic methods, established the American Chiropractic Association in 1922 as an alternative to Palmer's group, reorganizing into its modern form in 1963 to advocate expanded scope amid ongoing external persecution, including the American Medical Association's Committee on Quackery formed in 1962.[43] [44] These divisions manifested in organizational rivalries, with the ICA upholding traditional vitalism while the ACA pursued evidence-informed integration, contributing to fragmented unity during licensure battles and the Wilk v. AMA antitrust victory in 1987.[41] Professionalization efforts further exacerbated tensions, as the Council on Chiropractic Education (CCE), recognized by the U.S. Department of Education in 1974, imposed standards favoring mixer curricula with diagnostic training and basic sciences, prompting straight-aligned schools like Sherman College to file antitrust lawsuits against the CCE, ACA, and National Board of Chiropractic Examiners in 1986.[40] Similar litigation, including Life University v. CCE in 2003, highlighted disputes over accreditation's doctrinal bias toward broad-scope practice, limiting straight institutions' federal student aid eligibility until settlements.[40] Despite partial convergence in the Era of Legitimation (1960–present), where chiropractic gained licensure in 90 global jurisdictions and university-based education, the straight-mixer schism endures, impeding consensus on core identity—subluxation-centric vitalism versus musculoskeletal evidence-based care—and mainstream healthcare integration, as evidenced by persistent low public trust rankings.[41][45]Legal and Professional Milestones
Early chiropractors encountered significant legal opposition from medical authorities, who prosecuted practitioners for operating without a medical license under statutes prohibiting unlicensed medical practice. Daniel David Palmer, chiropractic's founder, was imprisoned for 23 days in Scott County Jail, Iowa, in 1906 after refusing to pay a fine for such an offense.[46] A pivotal early victory occurred in the 1907 Morikubo case in Wisconsin, where chiropractor Shegataro Morikubo was acquitted after demonstrating that his adjustments did not constitute drugless healing under the state's medical practice act, establishing a legal precedent distinguishing chiropractic from general medical practice.[30] The Universal Chiropractors' Association formed in 1906 primarily to defend members against legal prosecutions and advocate for statutory recognition.[47] Kansas enacted the first U.S. state law specifically licensing chiropractors in 1913, requiring examination and registration while exempting the profession from broader medical licensing requirements.[2] By 1923, all Canadian provinces except Quebec had licensed chiropractic, with Alberta passing the first such legislation in 1923.[47] The American Chiropractic Association (originally the United Chiropractors of America, later renamed) was established in 1922 to represent broad-scope practitioners and advance professional standards.[48] The International Chiropractors Association followed in 1926, emphasizing chiropractic's foundational principles.[42] Licensure expanded unevenly across U.S. states amid ongoing conflicts with organized medicine; by 1974, Louisiana became the final state to enact chiropractic licensing laws, achieving universal regulation in all 50 states, the District of Columbia, and U.S. territories.[2] The National Board of Chiropractic Examiners was founded in 1963 to standardize examinations, administering its first national tests in 1965 to facilitate interstate practice mobility.[49] A landmark antitrust case, Wilk et al. v. American Medical Association et al., filed in 1976, alleged a conspiracy to eliminate chiropractic competition; in 1987, a federal court ruled in favor of the chiropractors, finding the AMA guilty of unreasonable restraint of trade and invalidating its ethical ban on physician-chiropractor collaboration, which had portrayed chiropractic as unscientific.[35] This decision marked a turning point in professional acceptance, though chiropractic organizations maintain it preserved autonomy against medical dominance rather than endorsing efficacy claims.[35]Education, Training, and Regulation
Professional Education
Professional education for chiropractors centers on obtaining a Doctor of Chiropractic (DC) degree from an accredited institution, which serves as the primary qualification for entry into the profession. Admission typically requires completion of at least 90 semester hours of undergraduate coursework, including foundational sciences such as biology, chemistry, and physics, with a minimum cumulative GPA ranging from 2.25 to 3.0 depending on the program; some institutions mandate a full bachelor's degree or equivalent.[50][51][52] DC programs generally span 3.5 to 4 years, encompassing a minimum of 4,200 instructional hours that integrate didactic, laboratory, and clinical components; accelerated options can reduce this to approximately 3 years and 4 months for qualified entrants.[51][53][54] The curriculum is structured progressively: the initial 1.5 to 2 years emphasize basic biomedical sciences like anatomy, physiology, biochemistry, pathology, and radiology, akin to those in medical schools, followed by advanced studies in chiropractic-specific techniques, diagnosis, and patient management.[50][55] Subsequent phases incorporate hands-on training in spinal manipulation, adjunctive therapies, and clinical internships where students treat patients under supervision, often accumulating thousands of hours in outpatient settings.[56][57] Accreditation of DC programs is overseen by the Council on Chiropractic Education (CCE) in the United States, which establishes standards for curriculum rigor, faculty qualifications, facilities, and clinical competencies to ensure graduates meet professional benchmarks.[58][59] These standards require integration of evidence-informed practices alongside traditional chiropractic principles, though programs vary in emphasis on research literacy and interprofessional collaboration. A point of professional debate is the emphasis on active rehabilitation, such as therapeutic exercises, in chiropractic education. CCE standards include therapeutic exercise, but National Board of Chiropractic Examiners (NBCE) exams focus primarily on sciences and adjustment techniques, with no dedicated active-rehabilitation domain—unlike Doctor of Physical Therapy (DPT) curricula, which make it central.[60][61] The World Federation of Chiropractic’s (WFC) 2019 Rehabilitation Competency Framework encouraged greater integration of evidence-informed rehabilitation skills worldwide, welcomed by many educators.[62] The International Chiropractors Association (ICA) and subluxation-focused (“straight”) practitioners, however, express philosophical reservations, viewing a heavy rehabilitation emphasis as potentially diluting chiropractic’s traditional vitalistic identity and its historic core objective of detecting and correcting vertebral subluxations—a concept that remains central to their philosophy but which systematic reviews have found lacks scientific evidence of existence as a detectable clinical entity capable of causing visceral disease or requiring specific correction for general health.[63][64][65][66] Critics of this vitalistic model argue that limited entry-level training in active rehabilitation can foster patient dependency on repeated passive care, as clinical evidence from guidelines for musculoskeletal disorders like low back pain indicates that passive manual therapies alone may lead to less optimal long-term outcomes compared to multimodal approaches incorporating therapeutic exercises, which reduce recurrence and enhance patient self-management.[67][68] Internationally, similar bodies like the Councils on Chiropractic Education International (CCEI) harmonize requirements across countries, with over 20 nations hosting accredited programs as of 2022.[69] Graduates must subsequently pass national board examinations, such as those from the National Board of Chiropractic Examiners (NBCE), prior to state licensure, but this formal education phase equips practitioners with skills for diagnosing and managing primarily musculoskeletal conditions through manual therapies.[70][71]Licensing and Scope of Practice
In the United States, chiropractors must obtain licensure from state boards to practice legally, with all 50 states, the District of Columbia, and several territories requiring a Doctor of Chiropractic (D.C.) degree from a Council on Chiropractic Education (CCE)-accredited institution, passage of the National Board of Chiropractic Examiners (NBCE) examinations (Parts I-IV), and often a bachelor's degree or equivalent undergraduate credits.[72][73] Additional state-specific requirements may include jurisprudence exams, background checks, and limited clinical experience, while most states mandate continuing education for renewal, typically 12-40 hours biennially focused on clinical competency and ethics.[74][75] The scope of practice for U.S. chiropractors centers on the diagnosis, treatment, and management of neuromusculoskeletal disorders, primarily through spinal manipulation and manual therapies, though it varies by state statute.[76][77] In broader jurisdictions, such as Texas, chiropractors may perform physical therapy modalities (e.g., ultrasound, electrical stimulation), order diagnostic imaging, and conduct minor procedures like needle use for non-surgical purposes, but they are prohibited from prescribing medications, performing surgery, or practicing outside musculoskeletal conditions unless explicitly authorized.[78][79] Narrower scopes in some states restrict practice to spinal adjustments and associated conditions, reflecting historical debates over expanding beyond vertebral subluxation theory, with the Federation of Chiropractic Licensing Boards (FCLB) promoting model acts that emphasize evidence-informed care within defined limits to ensure public safety.[80][81] Internationally, chiropractic licensing and scope exhibit significant variation, with statutory regulation in 42 countries as of 2019, often requiring degrees from accredited programs (typically 4-5 years) and national exams akin to U.S. standards.[82] In nations like the United Kingdom and Australia, regulated under bodies such as the General Chiropractic Council, practitioners hold full practice rights for spinal manipulation and musculoskeletal care but face restrictions on diagnostics or therapeutics overlapping with medicine, emphasizing title protection and mandatory registration.[83][84] Countries without formal regulation, such as many in Africa and Asia, permit practice under general health laws but lack standardized licensing, leading to inconsistent scopes that may include or exclude adjunctive therapies based on local legislation rather than unified professional standards.[85] The World Federation of Chiropractic tracks these differences, noting that while core manipulation remains universal, expansions into physiotherapy or nutrition are jurisdiction-dependent and subject to interprofessional turf disputes.[83]International Variations
Chiropractic is statutorily regulated in approximately 50 countries, with legal status categorized by the World Federation of Chiropractic as fully regulated under specific legislation, practiced under general health laws, unclear or de facto tolerated, or facing risk of prosecution.[83] North America and the Western Pacific exhibit robust regulation, including mandatory licensing and defined scopes of practice, whereas Africa and Asia display greater variability, with many nations lacking formal recognition and exposing practitioners to legal uncertainties.[83] In Europe, 13 countries including Denmark, France, Switzerland, and the United Kingdom maintain specific statutory frameworks, while others like Germany and the Netherlands operate under broader health regulations, contributing to inconsistencies in cross-border practice recognition.[83][86] Educational requirements also diverge internationally, though the World Health Organization's guidelines advocate a minimum of 4,200 hours of instruction across biomedical sciences, chiropractic principles, and clinical training.[87] In Canada, candidates must complete at least three years of undergraduate prerequisites before a four-year Doctor of Chiropractic program, followed by passing the Canadian Chiropractic Examining Board examinations for provincial registration, totaling around seven years of post-secondary education.[88][89] Australia mandates a five-year accredited university program, typically structured as a bachelor's degree in health sciences followed by a master's in chiropractic, with registration requiring assessment by the Chiropractic Board of Australia.[90] In the United Kingdom, the General Chiropractic Council approves four- to five-year integrated master's programs (MChiro or equivalent), demanding A-level qualifications or equivalents for entry and emphasizing clinical competency.[91][92] Scope of practice varies correspondingly; regulated nations like those in North America often permit diagnosis, spinal manipulation, and adjunctive therapies within musculoskeletal bounds, while unregulated areas may restrict activities to avoid prosecution risks.[83] The European Council on Chiropractic Education seeks to standardize competencies across the continent, but national differences persist, with some countries tying licensure to medical oversight and others granting autonomous status.[93] In Latin America and the Middle East/North Africa, regulation is emerging in select countries like Mexico and Israel, but training often relies on imported standards from accredited international programs, leading to potential gaps in local adaptation.[83] The World Federation of Chiropractic promotes harmonization through policy advocacy, aiming to elevate global standards amid these disparities to mitigate risks from unqualified practice.[94]Clinical Practice and Techniques
Spinal Manipulation and Adjustment
Spinal manipulation, commonly referred to as chiropractic adjustment, consists of applying a targeted, controlled force to individual spinal joints using the hands or a specialized instrument to enhance joint motion and reduce associated discomfort.[95] This manual therapy targets hypo-mobile segments identified through physical palpation and assessment of spinal alignment and range of motion.[96] The predominant method employs high-velocity, low-amplitude (HVLA) thrusts, delivering a swift impulse—typically 220–889 Newtons over 75–225 millimeters—directed perpendicular to the joint plane at the end range of passive motion, without exceeding anatomical limits.[96] Patients are positioned supine, prone, or side-lying on a padded treatment table, with the chiropractor stabilizing adjacent structures while imparting the thrust, frequently eliciting an audible "pop" from synovial fluid cavitation as gas bubbles collapse within the joint capsule.[95][97] Post-adjustment, joint mobility is re-evaluated to confirm improved function.[96] Several variations exist within chiropractic practice. The diversified technique, utilized in over 70% of adjustments, relies on direct manual HVLA thrusts tailored to specific vertebral levels.[97] Drop-table methods, such as the Thompson terminal point technique, incorporate a segmented table that yields slightly under the thrust to amplify segmental motion without increasing force amplitude.[96][97] For patients intolerant to HVLA, low-force alternatives include spinal mobilization via sustained oscillatory pressures or the Activator Method, which uses a handheld, spring-loaded mallet to deliver precise impulses.[97] Flexion-distraction employs a specialized table to induce gentle, rhythmic flexion and traction, decompressing intervertebral discs and facets primarily for lumbar applications.[97] These approaches prioritize patient comfort while aiming to address joint restrictions empirically observed in musculoskeletal complaints like acute low back pain.[96]Adjunctive Therapies
Chiropractors frequently employ adjunctive therapies alongside spinal manipulation to address musculoskeletal conditions, aiming to enhance pain relief, reduce inflammation, and improve mobility. These procedures, often drawn from physical therapy modalities, include soft tissue techniques such as massage and myofascial release, which target muscle adhesions and trigger points to alleviate tension and promote healing.[98][99] Other common interventions encompass cryotherapy or thermotherapy for modulating inflammation and pain, as well as ultrasound to deliver deep heat and facilitate tissue repair in conditions like tendonitis.[100][101] Electrotherapeutic modalities, including transcutaneous electrical nerve stimulation (TENS) and interferential current, are utilized to interrupt pain signals and stimulate endorphin release, particularly for acute injuries or chronic low back pain.[98] Patient education on therapeutic exercises, posture correction, and lifestyle modifications serves as a non-invasive adjunct, with studies indicating that combining such active rehabilitation with manipulation yields better short-term outcomes for low back pain than manipulation alone.[102] Nutritional counseling and custom orthotics may also be recommended to address contributing factors like dietary inflammation or biomechanical imbalances, though their integration varies by practitioner scope.[98] Evidence for these adjunctive approaches remains supportive rather than definitive; a Cochrane review found moderate benefits from massage for subacute and chronic back pain, comparable to other conservative treatments, but emphasized the need for larger trials.[103] Techniques like Active Release Therapy (ART) and extracorporeal shockwave therapy show promise in reducing soft tissue restrictions, yet randomized controlled trials often highlight patient expectations and placebo effects as contributors to perceived efficacy over specific mechanisms.[98][102] Usage prevalence is high, with surveys reporting that over 90% of chiropractors incorporate soft tissue work and physiotherapeutic agents, reflecting a multimodal approach aligned with evidence-based guidelines for nonspecific musculoskeletal disorders.[104]Evidence-Based Guidelines
Evidence-based guidelines for chiropractic care emphasize spinal manipulative therapy (SMT) as a nonpharmacologic option primarily for acute and subacute nonspecific low back pain, where it provides modest short-term pain relief and functional improvement comparable to other conservative interventions such as exercise or analgesics, though evidence quality is often moderate to low.[105] [106] The American College of Physicians (ACP) 2017 guideline recommends clinicians offer SMT alongside superficial heat, massage, or acupuncture as initial treatments for acute or subacute low back pain lasting less than 12 weeks, prioritizing these over pharmacologic options due to lower risk of adverse effects, with decisions guided by patient preferences and clinician expertise.[105] [107] For chronic low back pain exceeding 12 weeks, the ACP advises against routine SMT as a standalone therapy, favoring multimodal approaches including exercise, psychological interventions, and multidisciplinary rehabilitation, as SMT shows no clinically superior long-term benefits over sham or inert treatments in systematic reviews.[105] [108] The UK's National Institute for Health and Care Excellence (NICE) 2016 guideline on low back pain and sciatica similarly endorses manual therapies like SMT within a self-management framework for persistent pain, recommending up to nine sessions of specialist input including manipulation for those not improving after initial advice, exercise, and pharmacological trials, but cautions against its use in isolation and stresses shared decision-making to address psychological factors.[109] For neck pain, best-practice recommendations from chiropractic-focused reviews, informed by randomized trials, suggest SMT combined with exercise and mobilization for acute nonspecific cases, aiming to reduce pain and disability in the short term, though evidence is limited by small sample sizes and heterogeneity in techniques.[110] Cochrane analyses indicate SMT yields similar outcomes to physical therapy or analgesics for acute low back pain but lacks high-quality proof of superiority over placebo for chronic or radicular symptoms, highlighting the need for patient-specific predictors like symptom duration under 16 days or no leg pain for better response.[111] [68] Guidelines universally advise against routine imaging or advanced diagnostics for uncomplicated musculoskeletal complaints, reserving SMT for cases without red flags like progressive neurological deficits, and integrate it into broader care pathways emphasizing education, activity maintenance, and risk stratification to minimize harms such as transient soreness.[112] Independent syntheses, including those from the ACP and Cochrane, prioritize empirical trial data over anecdotal or theoretical claims, noting that while chiropractic organizations like the American Chiropractic Association endorse SMT for headaches and extremity conditions based on lower-quality evidence, mainstream bodies limit endorsements to back-related disorders due to insufficient comparative effectiveness data elsewhere.[113] [114] Overall, these frameworks promote chiropractic as adjunctive rather than primary care, with efficacy tied to contextual factors like provider training and patient selection, rather than unsubstantiated vertebral subluxation paradigms.[103]Scientific Evidence and Effectiveness
Efficacy for Musculoskeletal Disorders
Spinal manipulative therapy (SMT), the primary intervention in chiropractic care, demonstrates modest efficacy for pain relief and functional improvement in acute low back pain (LBP), with effects comparable to other recommended conservative treatments such as exercise or analgesics. A 2017 meta-analysis of 26 randomized controlled trials (RCTs) involving 1,717 participants found that SMT was associated with small, short-term improvements in pain (mean difference -10 on a 100-point scale) and function at up to 6 weeks, though no benefits were observed beyond this period.[115] Similarly, a Cochrane review of 15 RCTs concluded that SMT provides no clinically relevant advantage over other therapies for acute LBP, supported by low-quality evidence indicating equivalent outcomes to usual care or sham manipulation.[116] For chronic LBP, evidence supports SMT as an effective option for symptom management, yielding similar reductions in pain and disability to evidence-based alternatives like physical therapy or medication, but outperforming non-recommended interventions such as bed rest. A 2019 systematic review and meta-analysis of 47 RCTs reported moderate-quality evidence that SMT reduces pain intensity (standardized mean difference -0.28) and improves function, with effects persisting up to 6 months in some cases.[117] The 2011 Cochrane review of 26 RCTs further affirmed high-quality evidence of no significant differences in outcomes between SMT and other active treatments for chronic LBP, positioning it as a viable non-pharmacological approach. In neck pain, SMT shows potential for short-term pain reduction and increased range of motion, particularly in acute nonspecific cases, though results are inconsistent compared to mobilization or exercise. A 2025 systematic review and meta-analysis of RCTs indicated that SMT significantly lowers pain and disability in acute neck pain patients, with low risk of adverse events.[118] However, earlier reviews, including a best evidence synthesis, found insufficient high-quality data to confirm superiority over conventional physical therapy for chronic neck pain.[119] Across musculoskeletal disorders, clinical practice guidelines from organizations like the American College of Physicians endorse SMT as a first-line non-drug treatment for acute and chronic LBP, reflecting accumulated RCT evidence of comparable efficacy to other modalities without superior long-term benefits. Limitations include reliance on self-reported outcomes, potential placebo contributions, and variable study quality, with few trials isolating chiropractic-specific techniques from adjunctive care.[120] Overall, while SMT addresses symptoms effectively in select spinal conditions, causal mechanisms beyond biomechanical effects remain unproven, emphasizing its role in multimodal conservative management rather than standalone cure.Safety Considerations
Mild adverse events following chiropractic spinal manipulation are common, occurring in 23% to 83% of treatments, typically manifesting as transient soreness, stiffness, headache, or fatigue, often similar to post-exercise soreness, lasting 24 to 48 hours.[121][122][123] Serious adverse events, such as vertebrobasilar stroke, disc herniation, or cauda equina syndrome, are rare, with incidence rates estimated at approximately 0.21 per 100,000 manipulations based on retrospective analyses of clinical records.[124][125] Systematic reviews of randomized controlled trials indicate that while reporting of adverse events has improved, severe complications remain infrequent and often underreported due to reliance on voluntary submissions rather than mandatory surveillance.[126] Cervical spinal manipulation carries a particular risk of vertebral or carotid artery dissection leading to ischemic stroke, with the association potentially involving primarily the aggravation of pre-existing dissections rather than initiation of new ones, as suggested by biomechanical and epidemiological evidence; case-control studies show a small but statistically significant association, though causality is not definitively established.[127] Population-based studies estimate this risk at about 1 in 1 to 5 million cervical manipulations, comparable to or lower than risks from everyday activities like rapid head turning or certain medical procedures, but higher than for lumbar manipulation.[128][129] Reviews of multiple studies express mixed conclusions on overall safety, with 46% deeming spinal manipulation safe, 13% highlighting harms, and the remainder neutral, underscoring the need for patient-specific risk assessment, especially in those with vascular risk factors.[130] In comparison to alternative therapies for musculoskeletal pain, chiropractic manipulation demonstrates a similar safety profile to physical therapy or mobilization techniques, with no excess serious events in head-to-head trials, though all manual therapies share risks of minor transient effects.[131][132] Contraindications include acute inflammatory conditions, severe osteoporosis, or known arterial fragility, and practitioners are advised to screen for red flags like unexplained neurological symptoms to mitigate rare but potentially catastrophic outcomes.[8] Empirical data supports informed consent emphasizing these probabilities over absolute safety claims.[118]Cost-Effectiveness and Comparative Outcomes
Studies evaluating the cost-effectiveness of chiropractic care for spine-related musculoskeletal disorders, such as low back pain (LBP), have generally found lower overall healthcare expenditures compared to usual medical management, particularly when chiropractic serves as the initial treatment modality. A 2015 systematic review of 13 cost-comparison studies, including data from private health insurance and workers' compensation plans, reported that healthcare costs were lower for patients receiving chiropractic care, with reductions attributed to decreased utilization of advanced imaging, pharmaceuticals, and emergency services.[133] This pattern held across acute and chronic cases, though the review noted variability due to differences in study designs and populations. A 2024 systematic review of 14 studies involving adults with spine-related pain similarly concluded that costs were generally lower under chiropractic management, with effect sizes indicating savings of 20-40% in total claims expenditures in multiple analyses, despite limitations like observational data and potential confounding from patient self-selection.[134] Comparative outcomes against medical care show chiropractic spinal manipulation providing equivalent or modestly superior short-term pain relief and functional improvements for nonspecific LBP, often at reduced cost. For instance, an analysis of commercial health plan data from 2005-2008 found average per-episode costs for back pain were $289 for chiropractic-covered patients versus $399 for those without such coverage, a 28% reduction linked to fewer opioid prescriptions and specialist referrals.[135] In a randomized trial augmenting usual medical care with chiropractic for active-duty military personnel with LBP, the addition yielded moderate improvements in pain intensity and disability at 6 weeks, with no significant cost escalation beyond the intervention itself.[136] However, a pragmatic economic evaluation of LBP treatment in Switzerland reported chiropractic care as slightly more expensive than medical care for acute cases (adjusted mean difference of $63 at 12 months), though costs converged for chronic LBP with comparable health gains.[137]| Study/Source | Condition | Key Cost Finding | Outcome Comparison |
|---|---|---|---|
| Hurwitz et al. (2015 systematic review)[133] | Spine pain (acute/chronic) | 20-40% lower total costs vs. medical care | Similar pain relief; reduced ancillary services |
| Whedon et al. (2024 systematic review)[134] | Spine-related pain | Lower claims costs with chiropractic initiation | Modest long-term savings; variable quality of evidence |
| Legorreta et al. (2004 claims analysis)[135] | Back pain episodes | $289 vs. $399 per episode (28% lower) | Fewer hospitalizations and drug claims |
| Goertz et al. (2018 RCT)[136] | Acute/chronic LBP | No added cost burden from augmentation | Better short-term pain/disability scores |