Recent from talks
Nothing was collected or created yet.
Transcription factor II H
View on Wikipedia
| general transcription factor IIH, polypeptide 1, 62kDa | |||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Identifiers | |||||||
| Symbol | GTF2H1 | ||||||
| Alt. symbols | BTF2 | ||||||
| NCBI gene | 2965 | ||||||
| HGNC | 4655 | ||||||
| OMIM | 189972 | ||||||
| RefSeq | NM_005316 | ||||||
| UniProt | P32780 | ||||||
| Other data | |||||||
| Locus | Chr. 11 p15.1-p14 | ||||||
| |||||||
| general transcription factor IIH, polypeptide 2, 44kDa | |||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Identifiers | |||||||
| Symbol | GTF2H2 | ||||||
| Alt. symbols | BTF2, TFIIH, BTF2P44, T-BTF2P44 | ||||||
| NCBI gene | 2966 | ||||||
| HGNC | 4656 | ||||||
| OMIM | 601748 | ||||||
| RefSeq | NM_001515 | ||||||
| UniProt | Q13888 | ||||||
| Other data | |||||||
| Locus | Chr. 5 q12.2-13.3 | ||||||
| |||||||
| general transcription factor IIH, polypeptide 3, 34kDa | |||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Identifiers | |||||||
| Symbol | GTF2H3 | ||||||
| Alt. symbols | BTF2, TFIIH | ||||||
| NCBI gene | 2967 | ||||||
| HGNC | 4657 | ||||||
| OMIM | 601750 | ||||||
| RefSeq | NM_001516 | ||||||
| UniProt | Q13889 | ||||||
| Other data | |||||||
| Locus | Chr. 12 q24.31 | ||||||
| |||||||
Transcription factor II H (TFIIH) is a multi-subunit protein complex involved in both the transcription of protein-coding genes and the nucleotide excision repair (NER) pathway. TFIIH was first identified in 1989 as general transcription factor-δ or basic transcription factor 2, an essential factor for transcription in vitro. It was subsequently isolated from yeast and officially named TFIIH in 1992.[1][2]
TFIIH is composed of ten subunits. Seven of these—ERCC2/XPD, ERCC3/XPB, GTF2H1/p62, GTF2H4/p52, GTF2H2/p44, GTF2H3/p34, and GTF2H5/TTDA—constitute the core complex. The remaining three subunits—CDK7, MAT1, and cyclin H—form the cyclin-activating kinase (CAK) subcomplex, which is tethered to the core via the XPD protein.[3] Among the core subunits, ERCC2/XPD and ERCC3/XPB possess helicase and ATPase activities and are essential for unwinding DNA to form the transcription bubble. These activities are necessary during transcription in vitro only when the DNA template is not already denatured or is supercoiled.
The CAK subunits, CDK7 and cyclin H, are responsible for the phosphorylation of serine residues in the C-terminal domain of RNA polymerase II, as well as potentially other targets involved in the cell cycle. In addition to its essential role in transcription initiation, TFIIH also plays a critical part in nucleotide excision repair.
History
[edit]Before being designated as TFIIH, the complex was known by several names. It was first isolated in 1989 from rat liver and referred to as transcription factor δ. When identified in cancer cells, it was called basic transcription factor 2, and when isolated from yeast, it was known as transcription factor B. The complex was officially named TFIIH in 1992.[4]
Structure
[edit]TFIIH is a ten‐subunit complex; seven of these subunits comprise the "core" whereas three comprise the dissociable "CAK" (CDK-activating Kinase) module.[5] The core consists of subunits XPB, XPD, p62, p52, p44, p34 and p8 while CAK is composed of CDK7, cyclin H, and MAT1.[5]
Function
[edit]General functions of TFIIH include:
Gene transcription
[edit]TFIIH is a general transcription factor that helps recruit RNA polymerase II (Pol II) to gene promoters. It acts as a DNA translocase, sliding along the DNA while feeding it into the RNA polymerase II cleft, thereby generating torsional strain that facilitates local DNA unwinding.[7] TFIIH also plays a critical role in nucleotide excision repair (NER), where it unwinds DNA at sites of damage following lesion recognition by either the global genome repair (GGR) or transcription-coupled repair (TCR) pathway.[8][9]
DNA repair
[edit]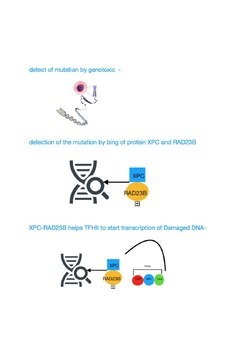
TFIIH participates in nucleotide excision repair (NER) by opening the DNA double helix after damage is initially recognized. NER is a multi-step pathway that removes a wide range of different types of damage that distort normal base pairing, including bulky chemical damage and UV-induced damage. Individuals with mutational defects in genes specifying protein components that catalyze the NER pathway, including the TFIIH components, often display features of premature aging.[10][11]
Clinical significance
[edit]Trichothiodystrophy
[edit]Mutation in genes ERCC3 (XPB), ERCC2 (XPD) or GTF2H5 (TTDA) cause trichothiodystrophy, a condition characterized by photosensitivity, ichthyosis, brittle hair and nails, intellectual impairment, decreased fertility and/or short stature.[10]
Cancer
[edit]Genetic polymorphisms of genes that encode subunits of TFIIH are known to be associated with increased cancer susceptibility in many tissues, e.g. skin tissue, breast tissue and lung tissue. Mutations in the subunits (such as XPD and XPB) can lead to a variety of diseases, including xeroderma pigmentosum (XP) or XP combined with Cockayne syndrome.[12]
Viral infection
[edit]Virus-encoded proteins target TFIIH.[13]
Inhibitors
[edit]Potent, bioactive natural products such as triptolide, which inhibit mammalian transcription by targeting the XPB subunit of the general transcription factor TFIIH, have recently been developed as glucose conjugates to selectively target hypoxic cancer cells with elevated glucose transporter expression.[14]
References
[edit]- ^ Flores O, Lu H, Reinberg D (February 1992). "Factors involved in specific transcription by mammalian RNA polymerase II. Identification and characterization of factor IIH". The Journal of Biological Chemistry. 267 (4): 2786–2793. doi:10.1016/S0021-9258(18)45947-9. PMID 1733973.
- ^ Kim TK, Ebright RH, Reinberg D (May 2000). "Mechanism of ATP-dependent promoter melting by transcription factor IIH". Science. 288 (5470). New York, N.Y.: 1418–1422. Bibcode:2000Sci...288.1418K. doi:10.1126/science.288.5470.1418. PMID 10827951.
- ^ Lee TI, Young RA (2000). "Transcription of eukaryotic protein-coding genes". Annual Review of Genetics. 34: 77–137. doi:10.1146/annurev.genet.34.1.77. PMID 11092823.
- ^ Rimel JK, Taatjes DJ (June 2018). "The essential and multifunctional TFIIH complex". Protein Science. 27 (6): 1018–1037. doi:10.1002/pro.3424. PMC 5980561. PMID 29664212.
- ^ a b Drapkin R, Reardon JT, Ansari A, Huang JC, Zawel L, Ahn K, et al. (April 1994). "Dual role of TFIIH in DNA excision repair and in transcription by RNA polymerase II". Nature. 368 (6473): 769–772. Bibcode:1994Natur.368..769D. doi:10.1038/368769a0. PMID 8152490. S2CID 4363484.
- ^ a b Compe E, Egly JM (May 2012). "TFIIH: when transcription met DNA repair". Nature Reviews. Molecular Cell Biology. 13 (6): 343–354. doi:10.1038/nrm3350. PMID 22572993. S2CID 29077515.
- ^ Fishburn J, Tomko E, Galburt E, Hahn S (2015). "Double-stranded DNA translocase activity of transcription factor TFIIH and the mechanism of RNA polymerase II open complex formation". Proceedings of the National Academy of Sciences of the United States of America. 112 (13): 3961–3966. Bibcode:2015PNAS..112.3961F. doi:10.1073/pnas.1417709112. PMC 4386358. PMID 25775526.
- ^ Hoogstraten D, Nigg AL, Heath H, Mullenders LH, van Driel R, Hoeijmakers JH, et al. (November 2002). "Rapid switching of TFIIH between RNA polymerase I and II transcription and DNA repair in vivo". Molecular Cell. 10 (5): 1163–1174. doi:10.1016/s1097-2765(02)00709-8. PMID 12453423.
- ^ Assfalg R, Lebedev A, Gonzalez OG, Schelling A, Koch S, Iben S (January 2012). "TFIIH is an elongation factor of RNA polymerase I". Nucleic Acids Research. 40 (2): 650–659. doi:10.1093/nar/gkr746. PMC 3258137. PMID 21965540.
- ^ a b Theil AF, Hoeijmakers JH, Vermeulen W (November 2014). "TTDA: big impact of a small protein". Experimental Cell Research. 329 (1): 61–68. doi:10.1016/j.yexcr.2014.07.008. PMID 25016283.
- ^ Edifizi D, Schumacher B (August 2015). "Genome Instability in Development and Aging: Insights from Nucleotide Excision Repair in Humans, Mice, and Worms". Biomolecules. 5 (3): 1855–1869. doi:10.3390/biom5031855. PMC 4598778. PMID 26287260.
- ^ Oh KS, Khan SG, Jaspers NG, Raams A, Ueda T, Lehmann A, et al. (November 2006). "Phenotypic heterogeneity in the XPB DNA helicase gene (ERCC3): xeroderma pigmentosum without and with Cockayne syndrome". Human Mutation. 27 (11): 1092–1103. doi:10.1002/humu.20392. PMID 16947863. S2CID 22852219.
- ^ Le May N, Dubaele S, Proietti De Santis L, Billecocq A, Bouloy M, Egly JM (February 2004). "TFIIH transcription factor, a target for the Rift Valley hemorrhagic fever virus". Cell. 116 (4): 541–550. doi:10.1016/s0092-8674(04)00132-1. PMID 14980221. S2CID 14312462.
- ^ Datan E, Minn I, Peng X, He QL, Ahn H, Yu B, et al. (Sep 2020). "A Glucose-Triptolide Conjugate Selectively Targets Cancer Cells under Hypoxia". iScience. 23 (9) 101536. Bibcode:2020iSci...23j1536D. doi:10.1016/j.isci.2020.101536. PMC 7509213. PMID 33083765.
External links
[edit]- Transcription+Factor+TFIIH at the U.S. National Library of Medicine Medical Subject Headings (MeSH)
