Recent from talks
Nothing was collected or created yet.
Comune
View on Wikipedia
| Municipalities of Italy Comuni (Italian) | |
|---|---|
| Category | Regionalised unitary state |
| Location | Italian Republic |
| Number | 7,896 |
| Populations | 33 (Morterone) – 2,751,747 (Rome) |
| Areas | 0.1124 km2 (0.0434 sq mi) (Atrani) – 1,286.7305 km2 (496.8094 sq mi) (Rome) |
| Government |
|
| Subdivisions | |

Regions (black borders)
Provinces (dark gray borders)
Comuni (light grey borders)
A comune (pronounced [koˈmuːne]; pl.: comuni, pronounced [koˈmuːni]) is an administrative division of Italy, roughly equivalent to a township or municipality.[1] It is the third-level administrative division of Italy, after regions (regioni) and provinces (province). The comune can also have the title of città (lit. 'city').[2]
Formed praeter legem according to the principles consolidated in medieval municipalities,[3] the comune is provided for by article 114 of the Constitution of Italy.[4] It can be divided into frazioni, which in turn may have limited power due to special elective assemblies.[5]
In the autonomous region of the Aosta Valley, a comune is officially called a commune in French.
Overview
[edit]The comune provides essential public services: registry of births and deaths, registry of deeds, and maintenance of local roads and public works.[6][7][8] Many comuni have a Polizia Comunale (lit. 'Communal Police'), which is responsible for public order duties.[9] The comune also deal with the definition and compliance with the piano regolatore generale (lit. 'general regulator plan'), a document that regulates the building activity within the communal area.[10]
All communal structures or schools, sports and cultural structures such as communal libraries, theaters, etc. are managed by the comuni.[11] Comuni must have their own communal statute and have a climatic and seismic classification of their territory for the purposes of hazard mitigation and civil protection.[12] Comuni also deal with the waste management.[13]
It is headed by a mayor (sindaco or sindaca) assisted by a legislative body, the consiglio comunale (lit. 'communal council'), and an executive body, the giunta comunale (lit. 'communal committee').[14] The mayor and members of the consiglio comunale are elected together by resident citizens: the coalition of the elected mayor (who needs a relative majority or an absolute majority in the first or second round of voting, depending on the population) gains three fifths of the consiglio's seats.[15]
The giunta comunale is chaired by the mayor, who appoints others members, called assessori, one of whom serves as deputy mayor (vicesindaco).[16] The offices of the comune are housed in a building usually called the municipio, or palazzo comunale (lit. 'town hall').[17]
As of January 2021, there were 7,904 comuni in Italy;[18] they vary considerably in size and population. For example, the comune of Rome, in Lazio, has an area of 1,287.36 km2 (497.05 sq mi) and a population of 2,758,454 inhabitants, and is both the largest and the most populated.[19]

Atrani in the province of Salerno (Campania) is the smallest comune by area, with only 0.1206 km2 (0.0466 sq mi),[20] and Morterone (Lombardy) is the smallest by population.[21] Many present-day comuni trace their roots along timescales spanning centuries and at times millennia.[22][23]
The northernmost comune is Predoi, the southernmost one Lampedusa e Linosa, the westernmost Bardonecchia and the easternmost Otranto.[24] The comune with the longest name is San Valentino in Abruzzo Citeriore,[25] while the comuni with the shortest name are Lu, Ro, Ne, Re and Vo'.[26]
The population density of the comuni varies widely by province and region. The province of Barletta-Andria-Trani, for example, has 381,091 inhabitants in 10 comuni,[27] or over 39,000 inhabitants per comune; whereas the province of Isernia has 81,415 inhabitants in 52 comuni,[28] or 1,640 inhabitants per comune—roughly 24 times more communal units per inhabitant.
The coats of arms of the comuni are assigned by decree of the Prime Minister of Italy by the Office of State Ceremonial and Honors, Honors and Heraldry Service (division of the Presidency of the Council born from the transformation of the Royal Consulta Araldica, eliminated pursuant to the provisions final of the Constitution of Italy).[29]
Subdivisions
[edit]| Year | Number | Population | Pop/Comune |
|---|---|---|---|
| 1861 | 7,720 | 22,171,946 | 2,872 |
| 1871 | 8,383 | 27,295,509 | 3,256 |
| 1881 | 8,260 | 28,951,546 | 3,505 |
| 1901 | 8,263 | 32,963,316 | 3,989 |
| 1911 | 8,324 | 35,841,563 | 4,306 |
| 1921 | 9,195 | 39,396,757 | 4,285 |
| 1931 | 7,311 | 41,043,489 | 5,614 |
| 1936 | 7,339 | 42,398,489 | 5,777 |
| 1951 | 7,810 | 47,515,537 | 6,084 |
| 1961 | 8,035 | 50,623,569 | 6,300 |
| 1971 | 8,056 | 54,136,547 | 6,720 |
| 1981 | 8,086 | 56,556,911 | 6,994 |
| 1991 | 8,100 | 56,885,336 | 7,023 |
| 2001 | 8,101 | 56,995,744 | 7,036 |
| 2011 | 8,092 | 59,433,744 | 7,345 |
| 2021 | 7,904 | 59,236,213 | 7,494 |
Administrative subdivisions within comuni vary according to their population size.
Comuni with at least 250,000 residents are divided into circoscrizioni[31] (roughly equivalent to French arrondissements or London boroughs) to which the comune delegates administrative functions such as the running of schools, social services and waste collection; the delegated functions vary from comune to comune. These bodies are headed by an elected president and a local council.
Smaller comuni usually comprise:
- A main city, town or village, that almost always gives its name to the comune; such a place is referred to as the capoluogo (lit. 'head-place' or 'capital'; cf. the French chef-lieu) of the comune; the word comune is also used in casual speech to refer to the city hall.
- Outlying areas often called frazioni (sg.: frazione, abbreviated: fraz.; lit. 'fraction'), each usually centred on a small town or village. These frazioni usually never had pasts as independent settlements, but occasionally are former smaller comuni consolidated into a larger one. They may also represent settlements which predate the capoluogo. The ancient town of Pollentia (today Pollenzo), for instance, is a frazione of Bra. In recent years the frazioni have become more important due to the institution of the consiglio di frazione (lit. 'fraction council'), a local form of government which can interact with the comune to address local needs, requests and claims. Even smaller places are called località (abbreviated: loc.; lit. 'localities').
- Smaller administrative divisions called municipi,[32] which are similar to districts and neighbourhoods.
Sometimes a frazione might be more populated than the capoluogo; and rarely, owing to unusual circumstances (such as depopulation), the town hall and its administrative functions can be moved to one of the frazioni, but the comune still retains the name of the capoluogo.
In some cases, a comune might not have the same name as the capoluogo. In these cases, it is a comune sparso (lit. 'dispersed municipality') and the frazione which hosts the town hall (municipio) is a sede municipale (compare county seat).
Rione
[edit]Some towns refer to neighborhoods within a comune as a rione (Italian: [riˈoːne]; pl.: rioni) or a contrada (pl.: contrade). The term originated from the administrative divisions of Rome, and is derived from the Latin word regio (pl.: regiones), 'region'. All currently extant rioni are located in Municipio I of Rome.[33] The term has been adopted as a synonym of quartiere in the Italian comuni.[33] Terzieri, quartieri, sestieri, rioni, and their analogues are usually no longer administrative divisions of these towns, but historical and traditional communities, seen especially in towns' annual Palio.
Terziere
[edit]A terziere (pl.: terzieri) is a subdivision of several towns in Italy. The word derives from terzo (lit. 'third') and is thus used only for towns divided into three neighborhoods. Terzieri are most commonly found in Umbria, for example in Trevi, Spello, Narni and Città della Pieve; towns divided into terzieri in other regions include Lucca in Tuscany, and Ancona and Macerata in the Marches. The medieval Lordship of Negroponte, on the island of Euboea, was also divided into three distinct rulerships, which were known as terzieri.
Quartiere
[edit]A quartiere (Italian: [kwarˈtjɛːre]; pl.: quartieri) is a territorial subdivision, properly used, for towns divided into four neighborhoods (quarto; lit. 'fourth') by the two main roads. It has been later used as a synonymous of neighbourhood, and an Italian town can be now subdivided into a larger number of quartieri. The Swiss town of Lugano (in the Italian-speaking canton of Ticino) is also subdivided into quarters.[34]
The English word quarter to mean an urban neighbourhood (e.g. the French Quarter in New Orleans, Louisiana) is derived from the cognate old French word quartier.
Sestiere
[edit]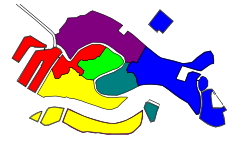
A sestiere (pl.: sestieri) is a subdivision of certain Italian towns and cities. The word is from sesto (lit. 'sixth'), so it is thus used only for towns divided into six districts. The best-known example is the sestieri of Venice, but Ascoli Piceno, Genoa, Milan and Rapallo, for example, were also divided into sestieri. The medieval Lordship of Negroponte, on the island of Euboea, was also at times divided into six districts, each with a separate ruler, through the arbitration of Venice, which were known as sestieri. The island of Crete, a Venetian colony (the Kingdom of Candia) from the Fourth Crusade, was also divided into six parts, named after the sestieri of Venice herself, while the capital Candia retained the status of a comune of Venice. The island of Burano north of Venice is also subdivided into sestieri.
A variation of the word is occasionally found: the comune of Leonessa, for example, is divided into sesti or sixths.
Homonymy
[edit]There are not many perfect homonymous comuni. There are only six cases in 12 comuni:[35]
- Castro: Castro, Apulia and Castro, Lombardy
- Livo: Livo, Lombardy and Livo, Trentino
- Peglio: Peglio, Lombardy and Peglio, Marche
- Samone: Samone, Piedmont and Samone, Trentino
- San Teodoro: San Teodoro, Sardinia and San Teodoro, Sicily
This is mostly due to the fact the name of the province or region was appended to the name of the comune in order to avoid the confusion. Two provincial capitals share the name Reggio: Reggio nell'Emilia, the capital of the province of Reggio Emilia, in the Emilia-Romagna region, and Reggio di Calabria, the capital of the homonymous metropolitan city, in the Calabria region. Many other towns or villages are likewise partial homonyms (e.g. Anzola dell'Emilia and Anzola d'Ossola, or Bagnara Calabra and Bagnara di Romagna).
Title of city
[edit]
The title of città (lit. 'city') in Italy is granted to comuni that have been awarded it by decree of the King of Italy (until 1946) or of the provisional head of state (from 1946 to 1948) or, subsequently, of the President of the Republic (after 1948), on the proposal of the Ministry of the Interior, to which the comune concerned sends an application for a concession, by virtue of their historical, artistic, civic or demographic importance.[2]
The comuni endowed with the title of città usually carry the golden crown above their coat of arms, except with different provisions in the decree approving the coat of arms or in the presence). "The crown of the city ([...]) is formed by a golden circle opened by eight city gates (five visible) with two cordoned walls on the margins, supporting eight towers (five visible) joined by curtain walls, all in gold and black walled."[36]
Statistics
[edit]Largest comuni by area
[edit]The following is a list of the largest comuni in Italy, in descending order of surface area, according to ISTAT data referring to 9 October 2011.[37] The provincial capitals are highlighted in bold.

| Rank | Comune | Region | Province | Area (km2) |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| 1 | Rome | Lazio | Rome | 1,287.36 km2 (497.05 sq mi) |
| 2 | Ravenna | Emilia-Romagna | Ravenna | 653.82 km2 (252.44 sq mi) |
| 3 | Cerignola | Apulia | Foggia | 593.93 km2 (229.32 sq mi) |
| 4 | Noto | Sicily | Syracuse | 554.99 km2 (214.28 sq mi) |
| 5 | Sassari | Sardinia | Sassari | 547.04 km2 (211.21 sq mi) |
| 6 | Monreale | Sicily | Palermo | 530.18 km2 (204.70 sq mi) |
| 7 | Gubbio | Umbria | Perugia | 525.78 km2 (203.00 sq mi) |
| 8 | Foggia | Apulia | Foggia | 509.26 km2 (196.63 sq mi) |
| 9 | L'Aquila | Abruzzo | L'Aquila | 473.91 km2 (182.98 sq mi) |
| 10 | Grosseto | Tuscany | Grosseto | 473.55 km2 (182.84 sq mi) |
| 11 | Perugia | Umbria | Perugia | 449.51 km2 (173.56 sq mi) |
| 12 | Ragusa | Sicily | Ragusa | 444.67 km2 (171.69 sq mi) |
| 13 | Altamura | Apulia | Bari | 431.38 km2 (166.56 sq mi) |
| 14 | Caltanissetta | Sicily | Caltanissetta | 421.25 km2 (162.65 sq mi) |
| 15 | Venice | Veneto | Venice | 415.90 km2 (160.58 sq mi) |
| 16 | Viterbo | Lazio | Viterbo | 406.23 km2 (156.85 sq mi) |
| 17 | Ferrara | Emilia-Romagna | Ferrara | 405.16 km2 (156.43 sq mi) |
| 18 | Andria | Apulia | Barletta-Andria-Trani | 402.89 km2 (155.56 sq mi) |
| 19 | Matera | Basilicata | Matera | 392.09 km2 (151.39 sq mi) |
| 20 | Città di Castello | Umbria | Perugia | 387.32 km2 (149.55 sq mi) |
| 21 | Gravina in Puglia | Apulia | Bari | 384.74 km2 (148.55 sq mi) |
| 22 | Arezzo | Tuscany | Arezzo | 384.70 km2 (148.53 sq mi) |
| 23 | Olbia | Sardinia | Sassari | 383.64 km2 (148.12 sq mi) |
| 24 | Caltagirone | Sicily | Catania | 383.38 km2 (148.02 sq mi) |
| 25 | Manciano | Tuscany | Grosseto | 372.51 km2 (143.83 sq mi) |
| 26 | Enna | Sicily | Enna | 358.75 km2 (138.51 sq mi) |
| 27 | Manfredonia | Apulia | Foggia | 354.54 km2 (136.89 sq mi) |
| 28 | Spoleto | Umbria | Perugia | 348.14 km2 (134.42 sq mi) |
| 29 | Corigliano-Rossano | Calabria | Cosenza | 346.56 km2 (133.81 sq mi) |
| 30 | Cortona | Tuscany | Arezzo | 342.97 km2 (132.42 sq mi) |
Smallest comuni by area
[edit]The following is a list of the smallest comuni in Italy, in ascending order of surface area, according to ISTAT data referring to 9 October 2011.[37]

| Rank | Comune | Region | Province | Area (km2) |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| 1 | Atrani | Campania | Salerno | 0.1206 km2 (0.0466 sq mi) |
| 2 | Miagliano | Piedmont | Biella | 0.6678 km2 (0.2578 sq mi) |
| 3 | Fiorano al Serio | Lombardy | Bergamo | 1.0601 km2 (0.4093 sq mi) |
| 4 | Conca dei Marini | Campania | Salerno | 1.1281 km2 (0.4356 sq mi) |
| 5 | Roccafiorita | Sicily | Messina | 1.1682 km2 (0.4510 sq mi) |
| 6 | Solza | Lombardy | Bergamo | 1.2278 km2 (0.4741 sq mi) |
| 7 | Maslianico | Lombardy | Como | 1.2885 km2 (0.4975 sq mi) |
| 8 | San Lorenzo al Mare | Liguria | Imperia | 1.2886 km2 (0.4975 sq mi) |
| 9 | Crosio della Valle | Lombardy | Varese | 1.4407 km2 (0.5563 sq mi) |
| 10 | Ferrera di Varese | Lombardy | Varese | 1.5265 km2 (0.5894 sq mi) |
| 11 | Casavatore | Campania | Naples | 1.5267 km2 (0.5895 sq mi) |
| 12 | Piario | Lombardy | Bergamo | 1.5451 km2 (0.5966 sq mi) |
| 14 | Vajont | Friuli-Venezia Giulia | Pordenone | 1.5860 km2 (0.6124 sq mi) |
| 15 | Arizzano | Piedmont | Verbano-Cusio-Ossola | 1.5995 km2 (0.6176 sq mi) |
| 16 | Longone al Segrino | Lombardy | Como | 1.6045 km2 (0.6195 sq mi) |
| 17 | Viganò | Lombardy | Lecco | 1.6049 km2 (0.6197 sq mi) |
| 18 | Brunello | Lombardy | Varese | 1.6200 km2 (0.6255 sq mi) |
| 19 | Camparada | Lombardy | Monza e Brianza | 1.6337 km2 (0.6308 sq mi) |
| 20 | Caines | Trentino-Alto Adige | South Tyrol | 1.6345 km2 (0.6311 sq mi) |
| 21 | Curti | Campania | Caserta | 1.6894 km2 (0.6523 sq mi) |
| 22 | Castel Rozzone | Lombardy | Bergamo | 1.7066 km2 (0.6589 sq mi) |
| 23 | Lozza | Lombardy | Varese | 1.7100 km2 (0.6602 sq mi) |
| 24 | Aci Bonaccorsi | Sicily | Catania | 1.7243 km2 (0.6658 sq mi) |
| 25 | Calvignasco | Lombardy | Milan | 1.7272 km2 (0.6669 sq mi) |
| 26 | Ventotene | Lazio | Latina | 1.7454 km2 (0.6739 sq mi) |
| 27 | Lirio | Lombardy | Pavia | 1.7457 km2 (0.6740 sq mi) |
| 28 | Masciago Primo | Lombardy | Varese | 1.8082 km2 (0.6981 sq mi) |
| 29 | Montello | Lombardy | Bergamo | 1.8156 km2 (0.7010 sq mi) |
| 30 | Carzano | Trentino-Alto Adige | Trentino | 1.8202 km2 (0.7028 sq mi) |
Highest comuni by altitude
[edit]The following is a list of the first comuni by altitude, in descending order.[38] The indicated altitude coincides with the height above sea level of the town hall.

Largest comuni by population
[edit]List of the first comuni by population in descending order, according to ISTAT data updated to 28 February 2022.[39] The regional capitals are in bold.

Comuni by demographic ranges
[edit]The data is updated as of 1 January 2021.[40]

| Demographic range | Comuni | Population | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Number | % | Residents | % | |
| more than 500,000 inhab. | 6 | 0.08% | 7,170,310 | 12.10% |
| from 250,000 to 499,999 inhab. | 6 | 0.08% | 1,874,966 | 3.16% |
| from 100,000 to 249,999 inhab. | 32 | 0.40% | 4,749,945 | 8.02% |
| from 60,000 to 99,999 inhab. | 58 | 0.73% | 4,446,634 | 7.50% |
| from 20,000 to 59,999 inhab. | 404 | 5.11% | 13,253,362 | 22.37% |
| from 10,000 to 19,999 inhab. | 698 | 8.83% | 9,662,013 | 16.31% |
| from 5,000 to 9,999 inhab. | 1,179 | 14.92% | 8,331,631 | 14.06% |
| from 3,000 to 4,999 inhab. | 1,087 | 13.75% | 4,222,171 | 7.13% |
| from 2,000 to 2,999 inhab. | 921 | 11.65% | 2,258,907 | 3.81% |
| from 1,000 to 1,999 inhab. | 1,520 | 19.23% | 2,213,443 | 3.74% |
| from 500 to 999 inhab. | 1,101 | 13.93% | 811,919 | 1.37% |
| less than 500 inhab. | 892 | 11.29% | 262,265 | 0.44% |
| Total | 7,904 | 100.00% | 59,257,566 | 100.00% |
Demographic ranges by macroregion
[edit]The data is updated as of 1 January 2021.[40]
| Demographic range | Number of comuni | Resident population | ||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| North | Centre | South | North | Centre | South | |
| more than 500,000 inhab. | 3 | 1 | 2 | 2,804,841 | 2,783,809 | 1,581,660 |
| from 250,000 to 499,999 inhab. | 3 | 1 | 2 | 907,910 | 359,755 | 607,301 |
| from 100,000 to 249,999 inhab. | 17 | 5 | 10 | 2,503,474 | 749,523 | 1,496,948 |
| from 60,000 to 99,999 inhab. | 16 | 16 | 26 | 1,289,906 | 1,253,707 | 1,903,021 |
| from 20,000 to 59,999 inhab. | 158 | 78 | 168 | 4,974,716 | 2,647,385 | 5,631,261 |
| from 10,000 to 19,999 inhab. | 353 | 115 | 230 | 4,824,497 | 1,655,230 | 3,182,286 |
| from 5,000 to 9,999 inhab. | 672 | 155 | 352 | 4,723,268 | 1,139,230 | 2,469,133 |
| from 3,000 to 4,999 inhab. | 620 | 141 | 326 | 2,404,254 | 549,864 | 1,268,053 |
| from 2,000 to 2,999 inhab. | 501 | 100 | 320 | 1,229,705 | 242,581 | 786,621 |
| from 1,000 to 1,999 inhab. | 793 | 182 | 545 | 1,155,222 | 270,306 | 787,915 |
| from 500 to 999 inhab. | 627 | 110 | 364 | 458,324 | 82,312 | 271,283 |
| less than 500 inhab. | 622 | 64 | 206 | 175,415 | 19,431 | 67,419 |
| Total | 4,385 | 968 | 2,551 | 27,451,532 | 11,753,133 | 20,052,901 |
See also
[edit]- Regions of Italy
- Metropolitan cities of Italy
- Provinces of Italy
- List of municipalities of Italy
- List of renamed municipalities in Italy
- Alphabetical list of municipalities of Italy
- Fusion of municipalities of Italy
- Municipalities of Switzerland – those in Italian-speaking areas of the country are called comuni
- Circoscrizione
- Frazione
- Località
- Rioni of Rome
References
[edit]- ^ "Italian communes ordered alphabetically". Retrieved 3 May 2022.
- ^ a b "Testo unico delle leggi sull'ordinamento degli enti locali" (in Italian). Archived from the original on 18 August 2022. Retrieved 4 May 2022.
- ^ "CONSUETUDINE" (in Italian). Retrieved 6 May 2022.
- ^ "La Costituzione - Articolo 114" (in Italian). Retrieved 6 May 2022.
- ^ "DECRETO N. 15 DEL 14/11/2019" (PDF) (in Italian). Archived from the original (PDF) on 14 May 2022. Retrieved 6 May 2022.
- ^ "Gli adempimenti degli uffici Anagrafe" (in Italian). 25 October 2007. Retrieved 3 May 2022.
- ^ "Poteri e compiti degli enti proprietari delle strade" (in Italian). Retrieved 3 May 2022.
- ^ "Settore Lavori pubblici e manutenzione della città" (in Italian). Retrieved 3 May 2022.
- ^ "Cosa fa polizia locale" (in Italian). Retrieved 3 May 2022.
- ^ "Che cos'è un piano regolatore?" (in Italian). Retrieved 6 May 2022.
- ^ "Cultura" (in Italian). Retrieved 3 May 2022.
- ^ "Protezione Civile del Comune di Prato" (in Italian). Retrieved 3 May 2022.
- ^ "I Comuni, per i rifiuti prodotti nel proprio territorio, a quali vincoli normativi sono soggetti in merito a raccolta e trasporto?" (in Italian). Retrieved 6 May 2022.
- ^ "Funzioni e competenze del consiglio comunale" (in Italian). Archived from the original on 26 August 2022. Retrieved 3 May 2022.
- ^ "SISTEMA ELETTORALE COMUNI" (in Italian). Retrieved 3 May 2022.
- ^ "Funzioni della Giunta" (in Italian). Archived from the original on 26 June 2022. Retrieved 3 May 2022.
- ^ "Municipio" (in Italian). Retrieved 3 May 2022.
- ^ a b "Regioni italiane" (in Italian). Retrieved 30 April 2022.
- ^ "Alcune curiosità sui comuni italiani" (in Italian). Retrieved 3 May 2022.
- ^ "Atrani: le tante facce del più piccolo comune italiano" (in Italian). Archived from the original on 8 February 2022. Retrieved 3 May 2022.
- ^ "Comune che "vince" non si cambia: 29 abitanti, Morterone è ancora il più piccolo d'Italia" (in Italian). Retrieved 3 May 2022.
- ^ "I comuni nel Medioevo: nascita e sviluppo tra 1200 e 1300" (in Italian). Retrieved 3 May 2022.
- ^ "Il modello cittadino in epoca romana" (in Italian). Retrieved 3 May 2022.
- ^ "Luoghi d'Italia da primato" (in Italian). 27 November 2017. Retrieved 6 May 2022.
- ^ "Comuni con i nomi più lunghi". Archived from the original on 12 April 2019. Retrieved 1 April 2020.
- ^ "Curiosità e nomi particolari" (in Italian). Retrieved 6 May 2022.
- ^ "Provincia di Barletta-Andria-Trani" (in Italian). Retrieved 3 May 2022.
- ^ "Provincia di Isernia" (in Italian). Retrieved 3 May 2022.
- ^ "Ufficio del cerimoniale di Stato e per le Onorificenze" (in Italian). Retrieved 4 May 2022.
- ^ "Comuni dal 1861". www.comuniverso.it. Retrieved 19 March 2017.
- ^ "Circoscrizioni di decentramento comunale" (in Italian). Retrieved 3 May 2022.
- ^ "L'affluenza, municipio per municipio, a Milano, Roma e Napoli: ecco quali zone hanno votato di più" (in Italian). 10 March 2021. Retrieved 3 May 2022.
- ^ a b (in Italian) The word rione in the Treccani dictionary on-line
- ^ Lugano quartieri
- ^ (in Italian) Complete list and infos on Comuni-italiani.it
- ^ "Caratteristiche tecniche degli emblemi araldici" (in Italian). Retrieved 4 May 2022.
- ^ a b "La superficie dei comuni, delle province e delle regioni italiane" (in Italian). Retrieved 4 May 2022.
- ^ "Comuni italiani per altitudine" (in Italian). Retrieved 4 May 2022.
- ^ "Statistiche demografiche ISTAT". Archived from the original on 6 October 2021. Retrieved 3 May 2022.
- ^ a b "Comuni per fasce demografiche" (in Italian). Retrieved 4 May 2022.
Bibliography
[edit]- "Terzière". Enciclopedia Italiana di Scienze, Lettere e Arti (in Italian). Retrieved 2 January 2024.
External links
[edit]- Associazione Nazionale Comuni Italiani (in Italian)
Comune
View on GrokipediaDefinition and Legal Framework
Administrative Role and Equivalence
The comune constitutes Italy's fundamental unit of local administration, operating as the third-level subdivision within the nation's territorial hierarchy, subordinate to 20 regions and approximately 107 provinces or 14 metropolitan cities. This structure positions the comune as the primary interface for implementing national and regional policies at the grassroots level, embodying a principle of decentralization that assigns core public functions to the most proximate authority capable of effective execution. As of recent counts, Italy encompasses 7,904 such entities, ranging from densely populated urban centers to sparsely inhabited rural hamlets.[6] In practical terms, comuni execute central government directives through localized administration, managing essential services including waste collection, maintenance of municipal roads and public spaces, civil registry operations, and basic social welfare provisions. These responsibilities extend to issuing local ordinances on public health and transportation, while also maintaining land registries and facilitating primary education coordination. Grounded in Italy's constitutional framework for subsidiarity—wherein higher tiers intervene only when lower ones prove inadequate—this arrangement aims to tailor governance to local conditions, yet empirical assessments reveal persistent challenges in resource allocation and service delivery uniformity.[7][2] Equivalently, the Italian comune aligns with municipalities or townships in federal systems like the United States, where it parallels entities handling analogous localized competencies, or with German Gemeinden, which similarly decentralize administrative duties. However, Italy's configuration stands out for its pronounced fragmentation, with over 5,700 comuni having fewer than 5,000 residents—a legacy of entrenched local identities that fosters administrative duplication and elevates per-capita costs. Studies attribute resultant inefficiencies to this scale disparity, evidenced by higher operational expenses and suboptimal service outputs in undersized units compared to consolidated peers, prompting ongoing debates on merger incentives despite resistance rooted in communal autonomy.[1][8][9]Constitutional Basis and Hierarchy
The Italian Constitution, promulgated on December 22, 1947, and effective from January 1, 1948, embeds the comuni (municipalities) as foundational elements of the Republic's territorial organization. Article 114 explicitly states that the Republic comprises municipalities, provinces, metropolitan cities, regions, and the state, designating municipalities as autonomous entities with their own statutes, powers, and functions conforming to constitutional norms.[10] This provision underscores the comuni' role in local governance, reflecting a post-World War II commitment to decentralize authority from the central state to foster democratic participation at the grassroots level.[11] Municipal autonomy, as delineated in Article 114, encompasses self-determination in revenue generation, administrative structuring, and expenditure decisions, balanced against national principles of public finance coordination and equitable service provision.[10] Subsequent constitutional amendments, particularly Title V reforms via Constitutional Law No. 3 of 2001, reinforced this by affirming that municipalities exercise functions devolved by state and regional legislation, while adhering to subsidiary principles where higher levels intervene only when local capacities falter.[10] Nonetheless, national laws retain supremacy in conflicts, enabling state overrides to maintain uniform standards across the Republic.[12] In the hierarchical framework, comuni—numbering over 7,900—function at the lowest tier, subject to oversight by the 20 regions and intermediate provincial bodies, including 107 provinces and 14 metropolitan cities established under Law No. 56 of 2014 (Delrio Law).[6] Powers devolved to comuni expanded through the 1970 regional autonomy implementation and 1990s decentralization efforts, such as Law No. 142 of 1990 on municipal and provincial organization and Law No. 59 of 1997 (Bassanini II), which transferred administrative competencies in areas like urban planning and social services from central ministries.[13] These reforms aimed to enhance local efficiency by aligning decision-making with territorial needs, yet persistent central fiscal controls and overlapping jurisdictions between levels have constrained full operational independence, as evidenced by state guardianship (tutela) mechanisms that allow prefects to annul local acts deemed unlawful.[14]Types and Classifications
Italian comuni are categorized primarily by population size for administrative and statistical purposes, revealing stark disparities in scale and capacity. As of 2021, Italy comprised 7,904 comuni, with a significant majority—approximately 70%—having fewer than 5,000 residents, a pattern rooted in the persistence of medieval-era micro-entities rather than optimized modern governance needs.[15][16] Larger comuni, typically those exceeding 100,000 inhabitants, encompass major urban areas and may qualify for enhanced metropolitan status under Legislative Decree 56/2014, which designates 14 metropolitan cities (e.g., Rome, Milan, Naples) to handle supra-municipal coordination in densely populated regions.[17] Special designations confer limited additional privileges or recognitions. The title of città is awarded by presidential decree to select comuni with historical, cultural, or ecclesiastical significance, such as ancient episcopal seats or former regional capitals, symbolizing prestige without altering core competencies.[7] Mountain comuni, often overlapping with small-population categories, benefit from targeted fiscal incentives and support mechanisms under national frameworks like those promoting rural sustainability, aimed at mitigating depopulation and infrastructural deficits in elevated terrains covering about 35% of Italy's land.[18] Coastal and island comuni hold specialized competencies in maritime-territorial planning, including shoreline management and port oversight, delegated under environmental and regional laws to address geographic vulnerabilities like erosion and insular logistics, distinct from inland counterparts.[19][20] These variants underscore how terrain-specific adaptations influence local autonomy, though core municipal functions remain uniform across classifications.Historical Development
Medieval Origins as City-States
The comuni originated in northern and central Italy amid the weakening of feudal hierarchies and the resurgence of long-distance trade in the late 11th century. The earliest documented communes formed in Cremona in 1078 and Pisa in 1081, evolving from episcopal cities where merchants and artisans sought collective self-governance to protect economic interests against rural lords and imperial oversight.[21] By the early 12th century, virtually every major episcopal center in the region, including Milan and Florence, had established consular governments, with elected consules drawn from guild elites managing urban affairs independently of bishops or emperors.[22] This shift was propelled by commercial expansion, as cities positioned along revived Mediterranean trade routes—facilitated by the Crusades and Byzantine contacts—developed proto-capitalist structures like merchant guilds and marketplaces, diminishing feudal obligations and enabling armed resistance to external control.[21][23] Independence was consolidated through military alliances rather than mere negotiation, as communes leveraged their wealth for fortifications and militias. The Lombard League, founded on December 7, 1167, by cities including Milan, Venice, and Bologna, exemplified this strategy, uniting against Holy Roman Emperor Frederick I Barbarossa's campaigns to reimpose imperial authority following his 1154-1155 Italian expedition.[24] Barbarossa's sieges and devastations, such as the 1162 razing of Milan, prompted the League's formation under papal auspices, fostering mutual defense pacts that preserved local sovereignty. The decisive Battle of Legnano on May 29, 1176, where League forces defeated Barbarossa's army, forced concessions in the Peace of Venice (1177), granting communes de facto autonomy and limiting imperial interference for decades.[25] While these institutions promoted economic dynamism—evident in regulated fairs, early banking, and guild monopolies—they were inherently unstable, prone to internal factionalism between pro-papal Guelphs and pro-imperial Ghibellines, which often erupted into violence and podestà appointments to curb elite rivalries.[23] This period's causal dynamics prioritized pragmatic self-interest over egalitarian ideals, with communal oaths binding citizens to collective defense and commerce rather than universal citizenship, laying foundations for territorial expansion into surrounding countrysides by the 13th century.[21]Evolution from Unification to Republic
Following the proclamation of the Kingdom of Italy on March 17, 1861, administrative unification efforts standardized local governance structures, including the comuni, through the Law of Administrative Unification (Legge di Unificazione Amministrativa) enacted on March 20, 1865. This legislation imposed a uniform framework modeled largely on the Piedmontese system, curtailing the diverse autonomies of pre-unification states—such as the elective councils in the Kingdom of the Two Sicilies or the papal territories—and subordinating comuni to oversight by centrally appointed prefects (prefetti).[26] Prefects, as representatives of the Ministry of the Interior, held veto power over municipal decisions, enforced national policies, and suppressed regionalist tendencies to foster national cohesion amid the Risorgimento's centralizing ethos.[27] At unification, the number of comuni stood at approximately 7,720, reflecting a rationalization that eliminated redundancies from fragmented pre-unitary entities without drastic initial mergers.[28] Under the Fascist regime, local autonomy faced further erosion with the royal decree of February 4, 1926, which abolished elected municipal councils and mayors (sindaci), replacing them with appointed podestà.[29] Podestà, selected by the central government often from Fascist Party ranks, exercised executive authority without electoral accountability, centralizing control to align comuni with Mussolini's totalitarian framework and eliminate opposition at the local level.[30] This system suppressed independent decision-making, integrating municipalities into state propaganda and economic directives, such as corporatist policies, while prefects retained supervisory roles to ensure compliance.[29] By 1931, the number of comuni had slightly declined to 7,310 through selective consolidations aimed at administrative efficiency under centralized dictate.[31] The fall of Fascism in 1943 and the 1948 Constitution marked a partial reversal, restoring democratic local governance. Article 114 enshrined comuni as "autonomous entities" with elected bodies responsible for local interests, reinstating mayoral and council elections to decentralize power from the prefectural apparatus.[32] Titles V (Articles 114–133) emphasized subsidiarity, granting comuni legislative and administrative competencies in areas like urban planning and public services, though still under national legal supremacy.[32] Despite efficiency arguments for mergers—given over 70% of comuni had fewer than 5,000 inhabitants—their proliferation endured, rooted in historical fragmentation and resistance to consolidation, maintaining a structure proximate to the 1861 baseline into the republican era.[28]Key Reforms Post-1948
The establishment of ordinary regions under Constitutional Law No. 1 of 22 October 1963, implemented through Law No. 281 of 16 May 1970, marked the initial phase of post-1948 decentralization, transferring administrative competencies from the central state to regional levels, with subsequent delegation to municipalities in areas such as urban planning and social services.[33] This reform aimed to enhance local responsiveness but often resulted in fragmented implementation, as regions variably devolved powers without uniform capacity building at the municipal level, contributing to uneven service delivery across Italy's approximately 8,000 comuni.[13] In the 1990s, Law No. 142 of 8 June 1990 provided a comprehensive framework for local autonomies, defining the organizational principles for comuni and provinces, including statutes, participatory mechanisms, and expanded roles in public services, while promoting unions of municipalities for joint functions to address inefficiencies in smaller entities.[34] Complementing this, Law No. 81 of 25 March 1993 introduced direct election of mayors and provincial presidents, linking executive and legislative bodies more tightly and aiming to streamline decision-making amid bureaucratic inertia; these changes, part of broader efforts under Minister Franco Bassanini, reduced procedural delays through subsequent laws like No. 59 of 15 March 1997, which further devolved administrative acts to local levels.[35] [36] However, while granting greater fiscal leeway via shared taxes, these reforms exacerbated administrative bloat in under-resourced small comuni, where direct elections sometimes prioritized local patronage over efficiency. The Delrio Law (No. 56 of 7 April 2014) restructured intermediate governance by abolishing elected provincial councils and establishing 10 metropolitan cities alongside reconfigured provinces as non-elective bodies, shifting responsibilities like road maintenance and environmental oversight partly to regions and comuni without commensurate funding or structural support.[37] This devolution sought to rationalize multi-level overlaps but intensified burdens on municipalities, particularly the 5,700 with fewer than 5,000 inhabitants, leading to documented strains on fiscal autonomy amid central spending cuts and persistent fragmentation that hindered economies of scale.[38] Overall, post-1948 reforms advanced subsidiarity in principle but yielded mixed results, with enhanced local decision rights offset by rising per-capita administrative costs and dependency on state transfers, as evidenced by Italy's local debt exceeding 10% of GDP by the mid-2010s.[39]Governance Structure
Elective Bodies and Officials
The mayor (sindaco) is directly elected by residents of the comune and serves as the head of the executive branch, with authority to appoint the giunta and represent the municipality in official capacities.[40] The term of office for the mayor is five years, during which they exercise executive powers subject to council oversight.[3] The municipal council (consiglio comunale) functions as the legislative body, comprising the mayor and a number of elected members determined by population: 10 for comunes with up to 3,000 inhabitants, increasing progressively to 60 for those exceeding one million inhabitants, per Article 37 of the Testo Unico degli Enti Locali (TUEL).[41] Councillors are elected concurrently with the mayor, serving the same five-year term.[3] The executive committee (giunta comunale), chaired by the mayor, includes appointed assessors whose number is capped by population thresholds—typically up to 8 in smaller comunes and 12 in larger ones—and regulated under Article 47 of the TUEL to support executive decision-making.[42] Electoral participation in municipal contests has averaged 50-60% in recent cycles, with declines noted since the early 2000s, signaling voter disengagement that empirically correlates with reduced accountability as officials often derive mandates from slim pluralities of the eligible population.[43] This pattern persists despite direct election mechanisms introduced in 1993, highlighting structural gaps in civic engagement at the local level.[44]Decision-Making Processes
The communal council holds primary responsibility for approving fundamental acts, including the annual budget (bilancio preventivo e consuntivo), urban planning instruments such as the general regulatory plan (piano regolatore generale), and multi-year programs defining strategic priorities.[45] These approvals require a deliberative majority, often necessitating negotiation among diverse political factions in proportionally elected councils, which introduces multiple stages of debate and amendment. For instance, budget proposals originate from the executive junta but must secure council endorsement by year-end, with failure risking provisional administration or fiscal penalties.[45] Consultative referenda serve as a mechanism for citizen input on major issues within communal competence, such as statute modifications or service privatizations, as enabled under Article 8 of the Unified Text on Local Authorities (TUEL, Legislative Decree 267/2000).[46] These are non-binding but can influence council decisions if turnout thresholds are met, typically requiring regulatory frameworks at the local level; however, their use remains sporadic, with low participation often limiting impact. Prefecture oversight enforces legality through preventive checks on specified acts, such as those involving alienations or loans, where the prefect may suspend execution pending review if non-compliance with national norms is evident.[47] Adverse parties or affected citizens can appeal communal decisions to Regional Administrative Tribunals (TAR) within 60 days, enabling judicial annulment for illegitimacy, which adds a further layer of procedural scrutiny.[48] This multi-veto structure—spanning council consensus, prefectural validation, and TAR recourse—causally amplifies local parochial interests, as empirical analyses indicate that Italy's 7,896 municipalities foster fragmented decision chains prone to deadlock.[49] Small-scale communes, numbering over 5,000 with fewer than 3,000 residents, particularly exacerbate delays in infrastructure projects, where NIMBY opposition or coalition bargaining routinely extends timelines beyond those in unitary systems like France's departmental model.[50] International assessments attribute such inefficiencies to veto proliferation, contrasting with streamlined national-level processes and contributing to Italy's lower infrastructure execution rates relative to EU peers.[51] While intended to ensure democratic accountability, this setup empirically prioritizes stasis over expedition, as evidenced by chronic public works overruns exceeding 75% of contracts in municipal portfolios.[52]Accountability Mechanisms
The Autorità Nazionale Anticorruzione (ANAC) exercises oversight over Italian municipalities by monitoring compliance with anti-corruption plans, public procurement processes, and preventive measures against organized crime infiltration, including the power to recommend dissolution of municipal councils in cases of mafia ties..pdf) The Corte dei Conti, as an independent constitutional body, conducts audits of municipal public expenditures and holds officials accountable through judicial proceedings for financial irregularities, with regional sections handling local government cases.[53] These mechanisms aim to enforce fiscal and administrative integrity, yet enforcement often relies on post-facto investigations rather than proactive prevention. Electoral accountability includes provisions for transparency under Italy's 2016 Freedom of Information Act (FOIA, Decreto Legislativo 97/2016), which mandates municipalities to respond to citizen requests for administrative documents and publish logs of such requests, fostering public scrutiny of decision-making.[54] Recall mechanisms, such as revocatory referendums against mayors, are legally possible under regional statutes in limited circumstances but remain rare due to high quorum requirements and low voter turnout, with no widespread national framework for direct recall.[55] Empirical evidence reveals significant enforcement gaps, as mafia organizations like the 'Ndrangheta in Calabria and Cosa Nostra in Sicily have infiltrated southern municipalities, leading to over 100 council dissolutions by prefectural commissioners since 1991 for organized crime associations.[56] High-profile cases, such as the 2020-2023 dissolutions in Calabrian towns like Casapesenna and Platì due to proven mafia control over public contracts and elections, underscore how corruption scandals persist despite ANAC and Corte dei Conti interventions, often requiring central government overrides to restore administration.[57] These failures highlight causal links between weak local institutions and entrenched criminal networks, where formal safeguards prove insufficient against systemic capture.[58]Territorial and Organizational Aspects
Internal Subdivisions
Italian comuni may incorporate internal subdivisions to facilitate local administration, urban planning, and historical preservation, though these lack autonomous governance and remain subordinate to the municipal council. Such divisions typically serve functional roles in service delivery, zoning regulations, and community organization rather than independent decision-making.[7] In historic urban centers, traditional divisions like rioni, quartieri, terzieri, and sestieri persist primarily for cultural and identificatory purposes, originating from medieval urban layouts. For instance, Rome features 22 rioni established by papal bull in 1586, which delineate central historic areas but hold no administrative authority today, instead informing heritage management and tourism. Venice, uniquely, divides its insular historic core into six sestieri—Cannaregio, Castello, Dorsoduro, San Marco, San Polo, and Santa Croce—dating to the Republic era for neighborhood-based governance and resource allocation, now symbolic yet used in local statistics and events.[7][59] Rural and peri-urban areas often employ frazioni, denoting hamlets or smaller settlements integrated into the comune's territory for statistical and infrastructural tracking. These are formally recognized by ISTAT for census purposes, with populations reported until the 1981 census, aiding in targeted public works like road maintenance without delegating powers. Circoscrizioni, introduced via Law 278/1976 on municipal decentralization, apply mainly to larger comunes (typically over 250,000 inhabitants) to create decentralized zones for citizen consultations and service proximity, such as in Milan's nine circoscrizioni for welfare delegation. Empirical data indicate that formal subdivisions like circoscrizioni are limited to urbanized comunes, while frazioni appear in approximately 40% of Italy's 7,904 comuni as of 2023, predominantly in rural regions for managing dispersed populations.[2][60]Urban and Rural Distinctions
Italian comuni exhibit stark contrasts between urban and rural types, shaped by population density and geographic dispersion. Urban comuni, typically in lowland or coastal plains, manage high-density environments with priorities such as traffic regulation, public transport infrastructure, and preservation of architectural heritage. The Comune of Milan, for instance, had 1,391,498 residents as of January 1, 2023, necessitating extensive urban planning for congestion mitigation and maintenance of sites like the Duomo di Milano. These areas benefit from economies of scale in service provision, enabling efficient delivery of utilities and emergency services due to concentrated demand. In contrast, rural comuni, predominant in mountainous and inland regions, feature sparse populations geared toward agriculture, forestry, and limited tourism. Alpine comuni in regions like Trentino-Alto Adige and Valle d'Aosta often have fewer than 100 residents; examples include Moncenisio with around 10 winter inhabitants and Cervatto with 49, reflecting chronic depopulation exacerbated by harsh terrain.[62] This dispersion causally inflates service delivery costs, as fixed expenses for roads, water supply, and healthcare—spread across vast areas with low taxpayer bases—yield higher per capita outlays; inter-municipal cooperation is frequently required to achieve viable economies, yet remote access still elevates logistics expenses by 20-50% compared to urban counterparts.[63][64] ISTAT data underscore this imbalance: approximately 5,700 comuni (over 70% of the total 7,904) classified as rural or inner areas host only about 20% of Italy's 58.9 million residents as of 2023, while urban and peri-urban comuni—less than 30% of the total—accommodate the remaining 80%, driving national resource allocation toward density-driven challenges. This urban concentration amplifies rural vulnerabilities, including elevated administrative burdens per inhabitant for basic functions like waste management, where low volumes preclude cost-effective centralized processing.[65]Borders and Jurisdictional Overlaps
The territorial boundaries of an Italian comune are defined by regional laws enacted in accordance with Article 133 of the Constitution, which permits modifications to municipal circoscrizioni through procedures involving consultation of affected populations, often via referendums for detachments, aggregations, or fusions, followed by execution via presidential decree proposed by the Minister of the Interior.[66][67] These boundaries, largely inherited from medieval autonomies or the post-unification rearrangements of 1861, frequently exhibit arbitrariness, such as irregular lines shaped by feudal claims or pre-unitary state divisions rather than natural features or functional needs, leading to persistent mismatches with modern settlement patterns.[68] Jurisdictional overlaps commonly arise with supralocal entities like national parks and protected areas, which span multiple comuni without altering municipal borders; for example, parks such as the Gran Paradiso or Stelvio National Parks integrate territories from several adjacent municipalities, requiring park authorities to exercise concurrent competencies over environmental regulation and land use within those bounds. Such configurations demand inter-entity coordination to reconcile local governance with centralized conservation mandates, as park perimeters—delineated by national legislation—impose restrictions that can conflict with municipal planning autonomy. Additionally, unioni di comuni enable voluntary associations to manage shared jurisdictional zones across borders, mitigating fragmentation without formal boundary revisions.[69] Border disputes, though not ubiquitous, highlight the inefficiencies of these historically derived delimitations; conflicts typically stem from unclear demarcations in cadestral records or strategic interests in reallocating tax-generating parcels, with regions empowered only to ascertain existing lines rather than impose new ones, deferring resolutions to administrative decrees or Council of State rulings.[70][71] Politicization occurs when proposed changes prioritize fiscal optimization, such as annexing affluent suburbs, over rational consolidation, perpetuating a system where over 7,900 comuni maintain fragmented perimeters resistant to comprehensive reform despite occasional fusions reducing their number by a few dozen annually.[72] This setup evidences causal persistence of pre-modern territorial logics, complicating unified policy application and fostering occasional litigation that underscores the need for evidence-based boundary rationalization.Functions and Operations
Core Services and Responsibilities
Italian comuni bear primary responsibility for civil registry functions, including the registration of births, marriages, deaths, and citizenship status, as mandated by Legislative Decree No. 267/2000 (TUEL), which assigns to municipalities all administrative tasks concerning local population and territory.[73] These entities also maintain resident population registries (anagrafe), issue identity documents, and oversee electoral operations within their jurisdictions.[73] In public safety, comuni operate municipal police (polizia municipale or locale) for traffic control, urban order enforcement, and administrative policing, distinct from national or provincial forces.[74] Social services constitute a core domain, encompassing welfare assistance, elderly and disability support, family aid, and basic community health coordination, with comuni delivering these through direct provision or delegated networks.[73] Education duties focus on managing nursery schools (asili nido) and primary school facilities, including infrastructure upkeep and auxiliary staff.[73] Infrastructure responsibilities include potable water distribution, sewage systems, solid waste collection and disposal, street lighting, and local road maintenance, all essential for daily habitability.[73] Territorial planning falls under comuni purview, involving zoning regulations (piano regolatore generale), building permit issuance, and land-use oversight to balance development and preservation.[73] Service delivery exhibits marked variance by municipality size: larger comuni (over 10,000 residents) internalize most functions via dedicated departments, achieving higher efficiency in metrics like waste collection coverage (often exceeding 95% in urban areas).[75] Conversely, small comuni—numbering over 5,700 with fewer than 5,000 inhabitants and representing 70% of total municipalities—outsource approximately 40% of services to private or inter-municipal entities due to staffing shortages and fiscal limits, as documented in field studies of local outsourcing practices.[76] This externalization, prevalent in rural waste management and administrative registries, correlates with delivery gaps, such as delayed registry updates in 20-30% of cases for remote hamlets per regional audits.[77]Fiscal and Economic Management
Italian municipalities derive their primary own-source revenues from the Imposta Municipale Unica (IMU), a local property tax levied on the ownership of real estate, excluding primary residences unless classified as luxury properties, with rates typically ranging from 0.46% to 1.06% of the cadastral value as determined by each comune.[78] Additional own revenues include a share of national personal income tax (IRPEF), user fees for services such as waste collection, and minor taxes on economic activities.[17] Central government transfers, including the Fondo di Finanziamento Ordinario and equalization funds, account for approximately 40-44% of total municipal revenues, supplementing local collections to cover essential expenditures.[79] Municipal budgets are required to be balanced, mandating equilibrium between revenues and expenditures within each fiscal year under the principles enshrined in Article 81 of the Italian Constitution and reinforced by domestic fiscal rules.[38] Borrowing is permitted for capital investments but subject to strict debt limits imposed by the Domestic Stability Pact, which caps new indebtedness based on population size and prior fiscal performance to prevent unsustainable accumulation.[80] These constraints aim to ensure fiscal discipline, though enforcement has varied, with smaller comuni often facing tighter effective limits due to limited revenue bases. Per capita operating costs in smaller municipalities—those with fewer than 5,000 inhabitants—tend to exceed those in larger ones by around 20% or more, attributable to fixed administrative overheads and lack of economies of scale in service delivery.[81] This structural disparity elevates spending pressures without proportional revenue growth, potentially constraining investments in infrastructure or business attraction. Moreover, the substantial dependence on central transfers can distort local incentives, fostering reliance on national redistribution rather than aggressive pursuit of endogenous economic development or optimized local taxation, as funding flows are often influenced by political alignments rather than performance metrics.[82]Inter-Municipal Cooperation
In Italy, inter-municipal cooperation addresses the administrative fragmentation caused by over 7,900 municipalities, many of which are small and face resource constraints, through formal associations that enable joint provision of services without merging entities. The primary mechanism is the unione di comuni, a stable institutional body comprising two or more municipalities that collectively exercises specific administrative functions, as regulated by Legislative Decree 267/2000 (Testo Unico degli Enti Locali). These unions typically focus on shared areas such as planning, social services, and environmental management, allowing smaller entities to pool expertise and infrastructure while retaining individual autonomy. Consortia (consorzi), another form, involve temporary or project-specific collaborations for targeted initiatives like waste management or tourism promotion, offering flexibility but less permanence than unions.[83] Legislation has encouraged or mandated cooperation for efficiency, particularly for municipalities under 5,000 inhabitants, which constitute about 70% of Italian communes but only 16-17% of the population. Under Article 14 of Decree-Law 78/2010, such small municipalities were required to exercise fundamental functions associatively via unions or conventions, with minimum thresholds of 10,000 inhabitants overall (or 3,000 in disadvantaged areas like mountains or islands). Although constitutional challenges and subsequent abrogations have softened the strict obligation—such as rulings questioning its enforceability—many regions retain incentives or regional mandates to promote associations, reflecting a pragmatic adaptation to scale economies amid fiscal pressures. As of 2023, approximately 437 unions exist, encompassing 2,823 municipalities (36% of the total) and serving 10.5 million residents, or roughly 18% of Italy's population.[84][85][86] Empirical outcomes of these arrangements are mixed, with evidence of cost efficiencies offset by coordination challenges. Analyses indicate that unions can reduce per-capita expenditure on shared functions by leveraging economies of scale, enabling reallocations to service improvements or tax relief, though gains vary by union size and function type. For instance, joint procurement and administrative streamlining have yielded measurable savings in operational budgets. However, the added layer of inter-municipal governance often introduces decision-making delays and overlapping bureaucracies, as consensus requirements among disparate local interests can slow responsiveness compared to standalone operations. These trade-offs highlight cooperation as a partial remedy to fragmentation's inefficiencies, though not a full substitute for structural consolidation.[87][88]Demographic and Geographic Statistics
Population Distributions
As of January 1, 2025, Italy's 7,904 municipalities exhibit stark population disparities, with Rome holding the largest at approximately 2.75 million residents, followed by Milan at 1.37 million and Naples at 909,000.[89][90] In contrast, over 5,700 municipalities—more than 70% of the total—have fewer than 1,000 inhabitants, many of which are rural hamlets in the Apennines or islands with populations under 500, underscoring the fragmented nature of local governance. Only 44 municipalities exceed 100,000 residents, while 136 surpass 50,000, concentrating over half of Italy's 58.97 million people in fewer than 2% of administrative units.[91][89] Population trends reveal ongoing declines in many smaller municipalities, driven by net emigration and aging demographics, with national resident figures dropping by about 60,000 in 2023 alone and projections indicating an average annual loss approaching 100,000 amid low fertility rates of 1.2 births per woman.[92][91] Emigration outflows reached 191,000 to foreign countries in 2024, up 20.5% from the prior year, disproportionately affecting southern and inland areas where young residents migrate to urban centers or abroad, exacerbating depopulation in over 4,000 municipalities with negative natural balance.[92] This has led to imbalances, with 20% of municipalities losing more than 5% of their population per decade, particularly those under 5,000 residents.[93] Regionally, northern macroregions like Lombardy and Veneto host denser clusters of mid-sized municipalities, with average densities exceeding 400 inhabitants per square kilometer in urbanized provinces, attracting internal migrants and sustaining growth in 15% of northern units.[94] Southern regions, including Sicily and Calabria, feature sparser distributions, where over 80% of municipalities remain below 5,000 residents and densities often fall under 100 per square kilometer, amplifying vulnerabilities to further outflows and contributing to a decade-long loss of 1 million residents primarily in the Mezzogiorno.[93] Central areas bridge this divide but show similar small-unit declines outside metropolitan hubs like Florence.[94]Area and Elevation Extremes
The largest comune in Italy by surface area is Rome, encompassing 1,285 square kilometers that include expansive urban, suburban, and rural zones, necessitating coordinated management of diverse land uses from historical centers to peripheral agricultural districts.[95] In contrast, the smallest is Atrani in Campania, covering just 0.12 square kilometers along the Amalfi Coast, where steep terrain and coastal constraints amplify pressures on limited space for housing, roads, and utilities.[96] These area disparities challenge standardized administrative policies, as vast comuni like Rome require broad-scale infrastructure investments for water distribution and waste management across heterogeneous landscapes, while minuscule ones like Atrani contend with capacity limits for emergency services and public works amid high topographic constraints. Elevation extremes further complicate uniform governance. The highest-elevation comune is Sestriere in Piedmont, situated at 2,035 meters above sea level, where severe alpine conditions—including heavy snowfall, avalanche risks, and short growing seasons—demand specialized adaptations for road maintenance, heating systems, and seasonal population fluxes from tourism.[97] Alpine comuni such as Livigno, with its main settlement at approximately 1,816 meters, face analogous issues, including isolation during winter closures and reliance on cross-border supply chains due to high-altitude logistics.[98] At the opposite end, low-lying coastal and deltaic comuni like Jolanda di Savoia in Emilia-Romagna include terrain dipping to -3.44 meters below sea level in the Po Valley, heightening vulnerability to flooding and subsidence that strain dike systems and drainage infrastructure beyond what flatter inland policies can address.[99] Such vertical variations underscore the need for tailored local responses, as national guidelines on environmental planning and disaster preparedness often fail to account for site-specific geophysical realities, leading to inefficiencies in resource allocation.| Extreme Category | Comune Example | Value | Administrative Implication |
|---|---|---|---|
| Largest Area | Rome | 1,285 km² | Extensive multi-zone coordination for services like transport and zoning.[95] |
| Smallest Area | Atrani | 0.12 km² | Intensified infrastructure strain in confined, sloped spaces.[96] |
| Highest Elevation | Sestriere | 2,035 m | Specialized handling of winter isolation and tourism surges.[97] |
| Lowest Elevation Point | Jolanda di Savoia | -3.44 m | Elevated flood defense requirements in subsiding deltas.[99] |
Trends in Size and Density
Since the 2011 census, Italy's resident population has decreased from 59,433,744 to 58,971,230 by the end of 2023, reflecting broader demographic pressures including low fertility rates and net migration outflows from rural areas.[100][101] This national trend manifests unevenly across comuni, with 57.8% of the approximately 7,900 municipalities experiencing population loss in 2023 compared to 2022, driven primarily by internal migration toward urban centers and a negative natural balance in peripheral regions.[101] Rural and inner-area comuni, often characterized by aging populations and limited economic opportunities, have seen more pronounced shrinkage, exacerbating the fragmentation of administrative units. Population density has risen in metropolitan areas amid ongoing urbanization, where inflows from smaller comuni concentrate residents in higher-density zones; for instance, northern and central urban agglomerations have absorbed much of the internal migration, increasing local densities while rural comuni densities decline.[102] Approximately 25% of Italian comuni—around 2,023 entities—had fewer than 1,000 inhabitants as of recent counts, rendering them particularly vulnerable to further depopulation due to insufficient tax bases and service provision challenges.[103] These small entities, concentrated in southern and Apennine regions, face causal factors such as youth out-migration for employment and a fertility rate below replacement levels, leading to sustained size contraction without countervailing immigration. ISTAT projections indicate continued population redistribution, with urban areas projected to mitigate overall decline through relative stability (e.g., only 1.8% drop in highly urbanized zones over the next decade), while small comuni endure heightened consolidation pressures from demographic unsustainability.[104] This dynamic underscores a causal shift toward larger, denser administrative cores, as low-density rural units struggle with viability amid persistent negative growth rates exceeding 5 per 1,000 in inner Mezzogiorno municipalities.[105]Challenges and Criticisms
Bureaucratic Inefficiencies and Costs
Italian communes exhibit pronounced bureaucratic inefficiencies, particularly in permitting processes, where obtaining construction permits averages 132 days nationwide, exceeding the EU average of 91 days by approximately 44%.[106] This stems from an average of 14 procedures per permit, with regional disparities amplifying delays—northern cities like Milan require 105 days, while southern ones like Reggio Calabria demand 326 days.[106] Associated costs reach 4.6% of warehouse value on average, double the EU's 1.9%, reflecting layered approvals and compliance verifications.[106] Overregulation fosters defensive bureaucracy, wherein officials, fearing personal liability under opaque and proliferating rules, defer decisions or impose extraneous checks, inflating administrative overheads.[107] Italy's legal complexity alone imposes €110 billion annually in economic costs, equivalent to over 5% of GDP, through stifled investment and duplicated efforts at the municipal level.[108] In small communes, mandatory staffing for core functions—despite low populations—yields elevated per capita administrative burdens, as fixed-rule compliance lacks economies of scale, per indices assessing personnel per 1,000 inhabitants. These dynamics causally impede productivity, with OECD estimates attributing 0.3-0.5% annual GDP growth losses to excessive public sector red tape and procedural rigidity in local administrations.[109] Empirical studies confirm that rule accumulation, rather than mere volume of staff, drives this drag by prioritizing procedural safeguards over outcomes.[110]Fragmentation and Localism Drawbacks
Italy maintains approximately 7,904 municipalities, a structure characterized by significant fragmentation despite fewer total units than France's roughly 35,000 communes.[3][111] This proliferation of small entities—many with populations under 1,000—inhibits economies of scale, as fixed administrative and service provision costs, such as staffing for public utilities and planning, escalate on a per capita basis in low-density areas.[112] OECD analysis indicates that such municipal fragmentation correlates with reduced economic performance in regions reliant on coordinated infrastructure and investment, where small units duplicate efforts in areas like waste management and transport without achieving cost efficiencies available to larger consolidations.[113] Localism exacerbates these issues by fostering resistance to mergers, often rooted in preserving entrenched patronage networks that sustain political influence at the micro-level. Italian municipalities have undergone the fewest consolidations in Europe since the 2000s, despite legislative incentives like financial bonuses, as local elites prioritize autonomy over collective gains. This parochialism empirically hampers development, with studies showing that unmerged small comuni exhibit lower administrative capacity and stalled infrastructure projects, diverting resources from growth-oriented initiatives to maintain fragmented governance.[114] In contrast, more consolidated systems, such as the United Kingdom's approximately 300 principal local authorities, demonstrate superior outcomes in service standardization and fiscal efficiency, enabling better leveraging of scale for economic cohesion.[115] Italy's fragmentation thus undermines national priorities, privileging hyper-local identities that fragment policy coherence and impede unified responses to challenges like depopulation and regional disparities.[116]Corruption and Governance Failures
Mafia organizations, particularly the 'Ndrangheta in Calabria, have infiltrated numerous Italian comuni, leading to state capture at the municipal level through control over local administration, public procurement, and political appointments.[117] Between 1991 and 2023, the Italian government dissolved over 200 municipalities due to verified mafia infiltrations, with more than 100 cases linked to southern regions where 'Ndrangheta clans dominate, enabling them to siphon public funds and rig contracts.[118] These dissolutions, mandated by anti-mafia laws, reveal systemic capture risks in smaller, resource-poor comuni vulnerable to organized crime's coercive tactics. Clientelism thrives in Italy's fragmented municipal system, where small-scale governance—over 70% of the 7,900 comuni have fewer than 5,000 residents—facilitates personalized exchanges of favors, jobs, and votes for loyalty, distorting resource allocation.[119] Judicial data from the Court of Cassation highlight corruption among mayors as a key vector, with analyses of judgments from 2005 to 2015 documenting widespread abuse of office, bribery, and embezzlement in local executive roles.[120] Transparency International's Corruption Perceptions Index scores Italy at 56 out of 100 in 2023, reflecting entrenched public sector issues, including at the local level where irregular payments in services pose moderate to high risks.[121][122] Such governance failures divert municipal budgets from infrastructure and services to illicit networks, eroding public trust and perpetuating economic stagnation, particularly in the South.[123] Regional panel analyses confirm corruption's negative causal impact on long-term growth, as it undermines the efficiency of public expenditures and deters investment by inflating costs and risks.[124] In infiltrated areas, this manifests in persistent underdevelopment, with mafia-controlled comunes exhibiting lower GDP per capita and higher unemployment compared to unaffected peers.[125]Reforms and Future Prospects
Recent Legislative Changes
In response to the earthquakes beginning on August 24, 2016, in central Italy, the government enacted Decreto-Legge n. 189/2016, establishing special reconstruction offices (Uffici Speciali per la Ricostruzione) in the affected regions of Abruzzo, Lazio, Marche, and Umbria to oversee urban planning, permit issuance, and derogations from standard procedures for the 62 initially impacted municipalities.[126] [127] This legislation centralized certain administrative powers, allowing these offices to bypass typical municipal timelines for repairs and rebuilding, with municipalities required to transmit certifications while the offices handled final approvals to accelerate recovery amid over 300 deaths and widespread destruction.[128] Subsequent ordinances extended these provisions to additional seismic events through 2017, aiming to address devolution-induced delays in fragmented local responses. The 2020s saw a national push for digital administration under the Piano Nazionale di Ripresa e Resilienza (PNRR), with over €6 billion allocated via Mission 1, Component 1 for municipalities to implement online citizen services, interoperability platforms, and data management systems by 2026.[129] This included Measure 1.4.1 targeting enhanced public service experiences, surpassing early milestones like platform adoption in larger entities but revealing devolution's shortfalls in uniform execution across Italy's 7,896 municipalities as of 2025.[130] Outcomes have been mixed, with aggregate PNRR digital targets achieved by mid-2025, yet empirical data show uneven digitization: larger urban comuni advanced in service portals and AI integration, while smaller, rural ones—comprising over 70% of entities—faced persistent gaps in skills, infrastructure, and interoperability due to local capacity limits and fragmentation.[131] [132] These disparities underscore causal inefficiencies from decentralized autonomy, prompting ongoing central monitoring via the Mappa dei Comuni Digitali to enforce standardization despite resistance from local variances.[133][134]Merger Initiatives and Resistance
Between 2010 and 2016, Italian national legislation introduced financial incentives to encourage voluntary mergers among small municipalities, including one-time grants and ongoing contributions equivalent to up to 40% of state transfers for a decade, as stipulated in updates to the Consolidated Text on Local Authorities (TUEL).[135][136] These measures built on earlier frameworks like Law 142/1990 but intensified post-2014 with the Delrio Law (56/2014), aiming to rationalize administrative structures amid fiscal pressures.[137] The initiatives yielded approximately 140 mergers by the late 2010s, abolishing 329 municipalities and creating fewer, larger entities, though adoption remained limited to regions like Piedmont and Veneto with supportive local policies.[138][139] Merged communes often realized net administrative cost reductions in 91% of examined cases, excluding incentives, through consolidated staffing and services, with empirical analyses estimating average savings of 10-20% in per-capita expenditures.[138] Merger proposals frequently encountered resistance via mandatory local referendums, where approval requires a simple majority but turnout and opposition reflect entrenched localism; of 274 referendums held nationwide since 1990, only 55% succeeded, with failure rates exceeding 50% in regions like Tuscany.[140][141] Voters prioritize campanilismo—fierce attachment to municipal identity, symbols, and autonomy—over efficiency gains, viewing mergers as threats to self-governance despite evidence of fiscal benefits.[142] Consequently, mergers account for under 5% of Italy's roughly 8,000 communes, perpetuating fragmentation.[139]Comparative Efficiency Assessments
Italy's subnational governments, including over 7,800 communes, account for about 15.5% of GDP in expenditure as of 2020, below the OECD average of 17.1%, yet this decentralization is marked by elevated per capita administrative costs due to the prevalence of small-scale municipalities with populations under 5,000.[17] In comparison, Germany's subnational entities, structured around 16 Länder and around 11,000 municipalities but with greater consolidation at intermediate levels, manage roughly 22% of GDP in expenditure, benefiting from economies of scale that reduce unit costs despite similar numbers of local units.[143] This results in Italy's local spending per capita exceeding Germany's by factors linked to fixed overheads in tiny communes, where administrative expenses can consume up to 40% of budgets in entities under 1,000 residents, versus under 20% in larger German counterparts.[116] OECD assessments highlight Italy's subnational efficiency challenges, with the country ranking 30th out of 38 OECD members in overall government effectiveness (score of 0.61 on a -2.5 to 2.5 scale) as of 2023, reflecting perceptions of suboptimal public service delivery and civil service quality at local levels.[144] World Bank indicators corroborate this, placing Italy below peers like Germany (score 1.45) in subnational fiscal management and service provision efficiency, attributing gaps to fragmentation that dilutes bargaining power, inflates procurement costs, and hampers professionalization.[145] Empirical studies on Italian municipalities demonstrate that efficiency gains correlate with scale, with smaller communes exhibiting 10-20% higher operational costs per service unit compared to consolidated EU counterparts in France or Spain, where fewer, larger units achieve better resource allocation.[116] While advancements in digital governance and AI-driven tools—such as automated permitting systems trialed in select Italian provinces—promise to offset some inefficiencies by reducing paperwork and enabling predictive budgeting, these measures alone cannot address underlying scale diseconomies without structural rationalization like voluntary mergers.[146] OECD analyses emphasize that peers achieving high subnational performance, such as Denmark post-2007 reforms consolidating to 98 municipalities, realized 15-25% cost savings and improved service outcomes, underscoring the need for Italy to prioritize amalgamation over incremental tech adoption for sustainable efficiency.References
- https://www.regione.[emilia-romagna](/page/Emilia-Romagna).it/idf/numeri/2017/1-2017/massarenti.pdf/%40%40download/file/Massarenti.pdf

