Recent from talks
Nothing was collected or created yet.
Cosmic ray
View on Wikipedia


Cosmic rays or astroparticles are high-energy particles or clusters of particles (primarily represented by protons or atomic nuclei) that move through space at nearly the speed of light. They originate from the Sun, from outside of the Solar System in the Milky Way,[1] and from distant galaxies.[2] Upon impact with Earth's atmosphere, cosmic rays produce showers of secondary particles, some of which reach the surface, although the bulk are deflected off into space by the magnetosphere or the heliosphere.
Cosmic rays were discovered by Victor Hess in 1912 in balloon experiments, for which he was awarded the 1936 Nobel Prize in Physics.[3]
Direct measurement of cosmic rays, especially at lower energies, has been possible since the launch of the first satellites in the late 1950s. Particle detectors similar to those used in nuclear and high-energy physics are used on satellites and space probes for research into cosmic rays.[4] Data from the Fermi Space Telescope (2013)[5] have been interpreted as evidence that a significant fraction of primary cosmic rays originate from the supernova explosions of stars.[6][better source needed] Based on observations of neutrinos and gamma rays from blazar TXS 0506+056 in 2018, active galactic nuclei also appear to produce cosmic rays.[7][8]
Etymology
[edit]The term ray (as in optical ray) seems to have arisen from an initial belief, due to their penetrating power, that cosmic rays were mostly electromagnetic radiation.[9] Nevertheless, following wider recognition of cosmic rays as being various high-energy particles with intrinsic mass, the term "rays" is consistent with known particles such as cathode rays, canal rays, alpha rays, and beta rays. Meanwhile "cosmic" ray photons, which are quanta of electromagnetic radiation (and so have no intrinsic mass) are known by their common names, such as gamma rays or X-rays, depending on their photon energy.
Composition
[edit]Of primary cosmic rays, which originate outside of Earth's atmosphere, about 99% are the bare nuclei of common atoms (stripped of their electron shells), and about 1% are solitary electrons (that is, one type of beta particle). Of the nuclei, about 90% are simple protons (i.e., hydrogen nuclei); 9% are alpha particles, identical to helium nuclei; and 1% are the nuclei of heavier elements, called HZE ions.[10] These fractions vary highly over the energy range of cosmic rays.[11] A very small fraction are stable particles of antimatter, such as positrons or antiprotons. The precise nature of this remaining fraction is an area of active research. An active search from Earth orbit for anti-alpha particles as of 2019[12] had found no unequivocal evidence.
Upon striking the atmosphere, cosmic rays violently burst atoms into other bits of matter, producing large amounts of pions and muons (produced from the decay of charged pions, which have a short half-life) as well as neutrinos.[13] The neutron composition of the particle cascade increases at lower elevations, reaching between 40% and 80% of the radiation at aircraft altitudes.[14]
Of secondary cosmic rays, the charged pions produced by primary cosmic rays in the atmosphere swiftly decay, emitting muons. Unlike pions, these muons do not interact strongly with matter, and can travel through the atmosphere to penetrate even below ground level. The rate of muons arriving at the surface of the Earth is such that about one per second passes through a volume the size of a person's head.[15] Together with natural local radioactivity, these muons are a significant cause of the ground level atmospheric ionisation that first attracted the attention of scientists, leading to the eventual discovery of the primary cosmic rays arriving from beyond our atmosphere.
Energy
[edit]Cosmic rays attract great interest practically, due to the damage they inflict on microelectronics and life outside the protection of an atmosphere and magnetic field, and scientifically, because the energies of the most energetic ultra-high-energy cosmic rays have been observed to approach 3 × 1020 eV [16] (This is slightly greater than 10 million times the design energy of particles accelerated by the Large Hadron Collider, 7 teraelectronvolts [TeV] (7.0×1012 eV).[17]) One can show that such enormous energies might be achieved by means of the centrifugal mechanism of acceleration in active galactic nuclei. At 50 joules [J] (3.1×1011 GeV),[18] the highest-energy ultra-high-energy cosmic rays (such as the OMG particle recorded in 1991) have energies comparable to the kinetic energy of a 90-kilometre-per-hour [km/h] (56 mph) baseball. As a result of these discoveries, there has been interest in investigating cosmic rays of even greater energies.[19] Most cosmic rays, however, do not have such extreme energies; the energy distribution of cosmic rays peaks at 300 megaelectronvolts [MeV] (4.8×10−11 J).[20]
History
[edit]After the discovery of radioactivity by Henri Becquerel in 1896, it was generally believed that atmospheric electricity, ionization of the air, was caused only by radiation from radioactive elements in the ground or the radioactive gases or isotopes of radon they produce.[21] Measurements of increasing ionization rates at increasing heights above the ground during the decade from 1900 to 1910 could be explained as due to absorption of the ionizing radiation by the intervening air.[22]
Discovery
[edit]
In 1909, Theodor Wulf developed an electrometer, a device to measure the rate of ion production inside a hermetically sealed container, and used it to show higher levels of radiation at the top of the Eiffel Tower than at its base.[23] However, his paper published in Physikalische Zeitschrift was not widely accepted. In 1911, Domenico Pacini observed simultaneous variations of the rate of ionization over a lake, over the sea, and at a depth of 3 metres from the surface. Pacini concluded from the decrease of radioactivity underwater that a certain part of the ionization must be due to sources other than the radioactivity of the Earth.[24]
In 1912, Victor Hess carried three enhanced-accuracy Wulf electrometers[3] to an altitude of 5,300 metres in a free balloon flight. He found the ionization rate increased to twice the rate at ground level.[3] Hess ruled out the Sun as the radiation's source by making a balloon ascent during a near-total eclipse. With the moon blocking much of the Sun's visible radiation, Hess still measured rising radiation at rising altitudes.[3] He concluded that "The results of the observations seem most likely to be explained by the assumption that radiation of very high penetrating power enters from above into our atmosphere."[25] In 1913–1914, Werner Kolhörster confirmed Victor Hess's earlier results by measuring the increased ionization enthalpy rate at an altitude of 9 km.[26][27]

Hess received the Nobel Prize in Physics in 1936 for his discovery.[28][29]

Identification
[edit]Bruno Rossi wrote in 1964:
In the late 1920s and early 1930s the technique of self-recording electroscopes carried by balloons into the highest layers of the atmosphere or sunk to great depths under water was brought to an unprecedented degree of perfection by the German physicist Erich Regener and his group. To these scientists we owe some of the most accurate measurements ever made of cosmic-ray ionization as a function of altitude and depth.[30]
Ernest Rutherford stated in 1931 that "thanks to the fine experiments of Professor Millikan and the even more far-reaching experiments of Professor Regener, we have now got for the first time, a curve of absorption of these radiations in water which we may safely rely upon".[31]
In the 1920s, the term cosmic ray was coined by Robert Millikan who made measurements of ionization due to cosmic rays from deep under water to high altitudes and around the globe. Millikan believed that his measurements proved that the primary cosmic rays were gamma rays; i.e., energetic photons. And he proposed a theory that they were produced in interstellar space as by-products of the fusion of hydrogen atoms into the heavier elements, and that secondary electrons were produced in the atmosphere by Compton scattering of gamma rays. In 1927, while sailing from Java to the Netherlands, Jacob Clay found evidence,[32] later confirmed in many experiments, that cosmic ray intensity increases from the tropics to mid-latitudes, which indicated that the primary cosmic rays are deflected by the geomagnetic field and must therefore be charged particles, not photons. In 1929, Bothe and Kolhörster discovered charged cosmic-ray particles that could penetrate 4.1 cm of gold.[33] Charged particles of such high energy could not possibly be produced by photons from Millikan's proposed interstellar fusion process.[citation needed]
In 1930, Bruno Rossi predicted a difference between the intensities of cosmic rays arriving from the east and the west that depends upon the charge of the primary particles—the so-called "east–west effect".[34] Three independent experiments[35][36][37] found that the intensity is, in fact, greater from the west, proving that most primaries are positive. During the years from 1930 to 1945, a wide variety of investigations confirmed that the primary cosmic rays are mostly protons, and the secondary radiation produced in the atmosphere is primarily electrons, photons and muons. In 1948, observations with nuclear emulsions carried by balloons to near the top of the atmosphere showed that approximately 10% of the primaries are helium nuclei (alpha particles) and 1% are nuclei of heavier elements such as carbon, iron, and lead.[38][39]
During a test of his equipment for measuring the east–west effect, Rossi observed that the rate of near-simultaneous discharges of two widely separated Geiger counters was larger than the expected accidental rate. In his report on the experiment, Rossi wrote "... it seems that once in a while the recording equipment is struck by very extensive showers of particles, which causes coincidences between the counters, even placed at large distances from one another."[40] In 1937, Pierre Auger, unaware of Rossi's earlier report, detected the same phenomenon and investigated it in some detail. He concluded that high-energy primary cosmic-ray particles interact with air nuclei high in the atmosphere, initiating a cascade of secondary interactions that ultimately yield a shower of electrons, and photons that reach ground level.[41]
Soviet physicist Sergei Vernov was the first to use radiosondes to perform cosmic ray readings with an instrument carried to high altitude by a balloon. On 1 April 1935, he took measurements at heights up to 13.6 kilometres using a pair of Geiger counters in an anti-coincidence circuit to avoid counting secondary ray showers.[42][43]
Homi J. Bhabha derived an expression for the probability of scattering positrons by electrons, a process now known as Bhabha scattering. His classic paper, jointly with Walter Heitler, published in 1937 described how primary cosmic rays from space interact with the upper atmosphere to produce particles observed at the ground level. Bhabha and Heitler explained the cosmic ray shower formation by the cascade production of gamma rays and positive and negative electron pairs.[44][45]
Energy distribution
[edit]Measurements of the energy and arrival directions of the ultra-high-energy primary cosmic rays by the techniques of density sampling and fast timing of extensive air showers were first carried out in 1954 by members of the Rossi Cosmic Ray Group at the Massachusetts Institute of Technology.[46] The experiment employed eleven scintillation detectors arranged within a circle 460 metres in diameter on the grounds of the Agassiz Station of the Harvard College Observatory. From that work, and from many other experiments carried out all over the world, the energy spectrum of the primary cosmic rays is now known to extend beyond 1020 eV. A huge air shower experiment called the Auger Project is currently operated at a site on the Pampas of Argentina by an international consortium of physicists. The project was first led by James Cronin, winner of the 1980 Nobel Prize in Physics from the University of Chicago, and Alan Watson of the University of Leeds, and later by scientists of the international Pierre Auger Collaboration. Their aim is to explore the properties and arrival directions of the very highest-energy primary cosmic rays.[47] The results are expected to have important implications for particle physics and cosmology, due to a theoretical Greisen–Zatsepin–Kuzmin limit to the energies of cosmic rays from long distances (about 160 million light years) which occurs above 1020 eV because of interactions with the remnant photons from the Big Bang origin of the universe. Currently the Pierre Auger Observatory is undergoing an upgrade to improve its accuracy and find evidence for the yet unconfirmed origin of the most energetic cosmic rays.
High-energy gamma rays (>50 MeV photons) were finally discovered in the primary cosmic radiation by an MIT experiment carried on the OSO-3 satellite in 1967.[48] Components of both galactic and extra-galactic origins were separately identified at intensities much less than 1% of the primary charged particles. Since then, numerous satellite gamma-ray observatories have mapped the gamma-ray sky. The most recent is the Fermi Observatory, which has produced a map showing a narrow band of gamma ray intensity produced in discrete and diffuse sources in our galaxy, and numerous point-like extra-galactic sources distributed over the celestial sphere.
Solar modulation
[edit]Solar modulation theory explains how the intensity of cosmic rays changes as they travel through the heliosphere, influenced by the solar wind and magnetic field.[49] The solar cycle causes variations in the magnetic field of the solar wind through which cosmic rays propagate to Earth. Solar modulation is a quasiperiodical change in cosmic rays intensity caused by 11- and 22-year cycles of solar activity.[50][51]
Parker transport equation
[edit]The Parker transport equation (also called the Parker equation, for Eugene Parker) is a kinetic equation that describes the acceleration and transport of energetic particles in astrophysical plasmas. The equation comprises diffusion terms both in coordinate space and in momentum space. The equation is used for studying energetic particle transport, and the mechanism of cosmic ray acceleration can be derived from it (diffusive shock acceleration). The equation is also used "to study the acceleration of cosmic rays at supernova remnant shocks, the acceleration and transport of solar energetic particles at shocks driven by coronal mass ejections, and the acceleration and transport of energetic particles at the solar wind termination shock".[52]
The Parker transport equation in one dimension is:[52]
where:
- = omni-directional distribution function of energetic particles
- = plasma (fluid) velocity
- = spatial diffusion coefficient
- = diffusion coefficient in momentum space
- = source term
- = momentum
- = position
- = time
Sources
[edit]Early speculation on the sources of cosmic rays included a 1934 proposal by Baade and Zwicky suggesting cosmic rays originated from supernovae.[53] A 1948 proposal by Horace W. Babcock suggested that magnetic variable stars could be a source of cosmic rays.[54] Subsequently, Sekido et al. (1951) identified the Crab Nebula as a source of cosmic rays.[55] Since then, a wide variety of potential sources for cosmic rays began to surface, including supernovae, active galactic nuclei, quasars, and gamma-ray bursts.[56]

Later experiments have helped to identify the sources of cosmic rays with greater certainty. In 2009, a paper presented at the International Cosmic Ray Conference by scientists at the Pierre Auger Observatory in Argentina showed ultra-high energy cosmic rays originating from a location in the sky very close to the radio galaxy Centaurus A, although the authors specifically stated that further investigation would be required to confirm Centaurus A as a source of cosmic rays.[57] However, no correlation was found between the incidence of gamma-ray bursts and cosmic rays, causing the authors to set upper limits as low as 3.4 × 10−6× erg·cm−2 on the flux of 1 GeV – 1 TeV cosmic rays from gamma-ray bursts.[58]
In 2009, supernovae were said to have been "pinned down" as a source of cosmic rays, a discovery made by a group using data from the Very Large Telescope.[59] This analysis, however, was disputed in 2011 with data from PAMELA, which revealed that "spectral shapes of [hydrogen and helium nuclei] are different and cannot be described well by a single power law", suggesting a more complex process of cosmic ray formation.[60] In February 2013, though, research analyzing data from Fermi revealed through an observation of neutral pion decay that supernovae were indeed a source of cosmic rays, with each explosion producing roughly 3 × 1042 – 3 × 1043 J of cosmic rays.[5][6]

Supernovae do not produce all cosmic rays, however, and the proportion of cosmic rays that they do produce is a question which cannot be answered without deeper investigation.[61] To explain the actual process in supernovae and active galactic nuclei that accelerates the stripped atoms, physicists use shock front acceleration as a plausibility argument (see picture at right).
In 2017, the Pierre Auger Collaboration published the observation of a weak anisotropy in the arrival directions of the highest energy cosmic rays.[62] Since the Galactic Center is in the deficit region, this anisotropy can be interpreted as evidence for the extragalactic origin of cosmic rays at the highest energies. This implies that there must be a transition energy from galactic to extragalactic sources, and there may be different types of cosmic-ray sources contributing to different energy ranges.
Types
[edit]Cosmic rays can be divided into two types:
- galactic cosmic rays (GCR) and extragalactic cosmic rays, i.e., high-energy particles originating outside the solar system, and
- solar energetic particles, high-energy particles (predominantly protons) emitted by the sun, primarily in solar eruptions.
However, the term "cosmic ray" is often used to refer to only the extrasolar flux.

Cosmic rays originate as primary cosmic rays, which are those originally produced in various astrophysical processes. Primary cosmic rays are composed mainly of protons and alpha particles (99%), with a small amount of heavier nuclei (≈1%) and an extremely minute proportion of positrons and antiprotons.[10] Secondary cosmic rays, caused by a decay of primary cosmic rays as they impact an atmosphere, include photons, hadrons, and leptons, such as electrons, positrons, muons, and pions. The latter three of these were first detected in cosmic rays.
Primary cosmic rays
[edit]Primary cosmic rays mostly originate from outside the Solar System and sometimes even outside the Milky Way. When they interact with Earth's atmosphere, they are converted to secondary particles. The mass ratio of helium to hydrogen nuclei, 28%, is similar to the primordial elemental abundance ratio of these elements, 24%.[63] The remaining fraction is made up of the other heavier nuclei that are typical nucleosynthesis end products, primarily lithium, beryllium, and boron. These nuclei appear in cosmic rays in greater abundance (≈1%) than in the solar atmosphere, where they are only about 10−3 as abundant (by number) as helium. Cosmic rays composed of charged nuclei heavier than helium are called HZE ions. Due to the high charge and heavy nature of HZE ions, their contribution to an astronaut's radiation dose in space is significant even though they are relatively scarce.
This abundance difference is a result of the way in which secondary cosmic rays are formed. Carbon and oxygen nuclei collide with interstellar matter to form lithium, beryllium, and boron, an example of cosmic ray spallation. Spallation is also responsible for the abundances of scandium, titanium, vanadium, and manganese ions in cosmic rays produced by collisions of iron and nickel nuclei with interstellar matter.[64]
At high energies the composition changes and heavier nuclei have larger abundances in some energy ranges. Current experiments aim at more accurate measurements of the composition at high energies.
Primary cosmic ray antimatter
[edit]Satellite experiments have found evidence of positrons and a few antiprotons in primary cosmic rays, amounting to less than 1% of the particles in primary cosmic rays. These do not appear to be the products of large amounts of antimatter from the Big Bang, or indeed complex antimatter in the universe. Rather, they appear to consist of only these two elementary particles, newly made in energetic processes.
Preliminary results from the presently operating Alpha Magnetic Spectrometer (AMS-02) on board the International Space Station show that positrons in the cosmic rays arrive with no directionality. In September 2014, new results with almost twice as much data were presented in a talk at CERN and published in Physical Review Letters.[65][66] A new measurement of positron fraction up to 500 GeV was reported, showing that positron fraction peaks at a maximum of about 16% of total electron+positron events, around an energy of 275 ± 32 GeV. At higher energies, up to 500 GeV, the ratio of positrons to electrons begins to fall again. The absolute flux of positrons also begins to fall before 500 GeV, but peaks at energies far higher than electron energies, which peak about 10 GeV.[67] These results on interpretation have been suggested to be due to positron production in annihilation events of massive dark matter particles.[68]
Cosmic ray antiprotons also have a much higher average energy than their normal-matter counterparts (protons). They arrive at Earth with a characteristic energy maximum of 2 GeV, indicating their production in a fundamentally different process from cosmic ray protons, which on average have only one-sixth of the energy.[69]
There is no evidence of complex antimatter atomic nuclei, such as antihelium nuclei (i.e., anti-alpha particles), in cosmic rays. These are actively being searched for. A prototype of the AMS-02 designated AMS-01, was flown into space aboard the Space Shuttle Discovery on STS-91 in June 1998. By not detecting any antihelium at all, the AMS-01 established an upper limit of 1.1 × 10−6 for the antihelium to helium flux ratio.[70]
Secondary cosmic rays
[edit]When cosmic rays enter the Earth's atmosphere, they collide with atoms and molecules, mainly oxygen and nitrogen. The interaction produces a cascade of lighter particles, a so-called air shower secondary radiation that rains down, including x-rays, protons, alpha particles, pions, muons, electrons, neutrinos, and neutrons.[72] All of the secondary particles produced by the collision continue onward on paths within about one degree of the primary particle's original path.
Typical particles produced in such collisions are neutrons and charged mesons such as positive or negative pions and kaons. Some of these subsequently decay into muons and neutrinos, which are able to reach the surface of the Earth. Some high-energy muons even penetrate for some distance into shallow mines, and most neutrinos traverse the Earth without further interaction. Others decay into photons, subsequently producing electromagnetic cascades. Hence, next to photons, electrons and positrons usually dominate in air showers. These particles as well as muons can be easily detected by many types of particle detectors, such as cloud chambers, bubble chambers, water-Cherenkov, or scintillation detectors. The observation of a secondary shower of particles in multiple detectors at the same time is an indication that all of the particles came from that event.
Cosmic rays impacting other planetary bodies in the Solar System are detected indirectly by observing high-energy gamma ray emissions by gamma-ray telescope. These are distinguished from radioactive decay processes by their higher energies above about 10 MeV.
Cosmic-ray flux
[edit]
The flux of incoming cosmic rays at the upper atmosphere is dependent on the solar wind, the Earth's magnetic field, and the energy of the cosmic rays. At distances of ≈94 AU from the Sun, the solar wind undergoes a transition, called the termination shock, from supersonic to subsonic speeds. The region between the termination shock and the heliopause acts as a barrier to cosmic rays, decreasing the flux at lower energies (≤ 1 GeV) by about 90%. However, the strength of the solar wind is not constant, and hence it has been observed that cosmic ray flux is correlated with solar activity.
In addition, the Earth's magnetic field acts to deflect cosmic rays from its surface, giving rise to the observation that the flux is apparently dependent on latitude, longitude, and azimuth angle.
The combined effects of all of the factors mentioned contribute to the flux of cosmic rays at Earth's surface. The following table of participial frequencies reach the planet[74] and are inferred from lower-energy radiation reaching the ground.[75]
In the past, it was believed that the cosmic ray flux remained fairly constant over time. However, recent research suggests one-and-a-half- to two-fold millennium-timescale changes in the cosmic ray flux in the past forty thousand years.[76]
The magnitude of the energy of cosmic ray flux in interstellar space is very comparable to that of other deep space energies: cosmic ray energy density averages about one electron-volt per cubic centimetre of interstellar space, or ≈1 eV/cm3, which is comparable to the energy density of visible starlight at 0.3 eV/cm3, the galactic magnetic field energy density (assumed 3 microgauss) which is ≈0.25 eV/cm3, or the cosmic microwave background (CMB) radiation energy density at ≈0.25 eV/cm3.[77]
Detection methods
[edit]
There are two main classes of detection methods. First, the direct detection of the primary cosmic rays in space or at high altitude by balloon-borne instruments. Second, the indirect detection of secondary particle, i.e., extensive air showers at higher energies. While there have been proposals and prototypes for space and balloon-borne detection of air showers, currently operating experiments for high-energy cosmic rays are ground based. Generally direct detection is more accurate than indirect detection. However the flux of cosmic rays decreases with energy, which hampers direct detection for the energy range above 1 PeV. Both direct and indirect detection are realized by several techniques.
Direct detection
[edit]Direct detection is possible by all kinds of particle detectors at the ISS, on satellites, or high-altitude balloons. However, there are constraints in weight and size limiting the choices of detectors.
An example for the direct detection technique is a method based on nuclear tracks developed by Robert Fleischer, P. Buford Price, and Robert M. Walker for use in high-altitude balloons.[78] In this method, sheets of clear plastic, like 0.25 mm Lexan polycarbonate, are stacked together and exposed directly to cosmic rays in space or high altitude. The nuclear charge causes chemical bond breaking or ionization in the plastic. At the top of the plastic stack the ionization is less, due to the high cosmic ray speed. As the cosmic ray speed decreases due to deceleration in the stack, the ionization increases along the path. The resulting plastic sheets are "etched" or slowly dissolved in warm caustic sodium hydroxide solution, that removes the surface material at a slow, known rate. The caustic sodium hydroxide dissolves the plastic at a faster rate along the path of the ionized plastic. The net result is a conical etch pit in the plastic. The etch pits are measured under a high-power microscope (typically 1600× oil-immersion), and the etch rate is plotted as a function of the depth in the stacked plastic.
This technique yields a unique curve for each atomic nucleus from 1 to 92, allowing identification of both the charge and energy of the cosmic ray that traverses the plastic stack. The more extensive the ionization along the path, the higher the charge. In addition to its uses for cosmic-ray detection, the technique is also used to detect nuclei created as products of nuclear fission.
Indirect detection
[edit]There are several ground-based methods of detecting cosmic rays currently in use, which can be divided in two main categories: the detection of secondary particles forming extensive air showers (EAS) by various types of particle detectors, and the detection of electromagnetic radiation emitted by EAS in the atmosphere.
Extensive air shower arrays made of particle detectors measure the charged particles which pass through them. EAS arrays can observe a broad area of the sky and can be active more than 90% of the time. However, they are less able to segregate background effects from cosmic rays than can air Cherenkov telescopes. Most state-of-the-art EAS arrays employ plastic scintillators. Also water (liquid or frozen) is used as a detection medium through which particles pass and produce Cherenkov radiation to make them detectable.[79] Therefore, several arrays use water/ice-Cherenkov detectors as alternative or in addition to scintillators. By the combination of several detectors, some EAS arrays have the capability to distinguish muons from lighter secondary particles (photons, electrons, positrons). The fraction of muons among the secondary particles is one traditional way to estimate the mass composition of the primary cosmic rays.
An historic method of secondary particle detection still used for demonstration purposes involves the use of cloud chambers[80] to detect the secondary muons created when a pion decays. Cloud chambers in particular can be built from widely available materials and can be constructed even in a high-school laboratory. A fifth method, involving bubble chambers, can be used to detect cosmic ray particles.[81]
More recently, the CMOS devices in pervasive smartphone cameras have been proposed as a practical distributed network to detect air showers from ultra-high-energy cosmic rays.[82] The first app to exploit this proposition was the CRAYFIS (Cosmic RAYs Found in Smartphones) experiment.[83][84] In 2017, the CREDO (Cosmic-Ray Extremely Distributed Observatory) Collaboration[85] released the first version of its completely open source app for Android devices. Since then the collaboration has attracted the interest and support of many scientific institutions, educational institutions, and members of the public around the world.[86] Future research has to show in what aspects this new technique can compete with dedicated EAS arrays.
The first detection method in the second category is called the air Cherenkov telescope, designed to detect low-energy (<200 GeV) cosmic rays by means of analyzing their Cherenkov radiation, which for cosmic rays are gamma rays emitted as they travel faster than the speed of light in their medium, the atmosphere.[87] While these telescopes are extremely good at distinguishing between background radiation and that of cosmic-ray origin, they can only function well on clear nights without the Moon shining, have very small fields of view, and are only active for a few percent of the time.
A second method detects the light from nitrogen fluorescence caused by the excitation of nitrogen in the atmosphere by particles moving through the atmosphere. This method is the most accurate for cosmic rays at highest energies, in particular when combined with EAS arrays of particle detectors.[88] Similar to the detection of Cherenkov-light, this method is restricted to clear nights.
Another method detects radio waves emitted by air showers. This technique has a high duty cycle similar to that of particle detectors. The accuracy of this technique was improved in the last years as shown by various prototype experiments, and may become an alternative to the detection of atmospheric Cherenkov-light and fluorescence light, at least at high energies.
Effects
[edit]Changes in atmospheric chemistry
[edit]Cosmic rays ionize nitrogen and oxygen molecules in the atmosphere, which leads to a number of chemical reactions. Cosmic rays are also responsible for the continuous production of a number of unstable isotopes, such as carbon-14, in the Earth's atmosphere through the reaction:
Cosmic rays kept the level of carbon-14[89] in the atmosphere roughly constant (70 tons) for at least the past 100,000 years,[citation needed] until the beginning of above-ground nuclear weapons testing in the early 1950s. This fact is used in radiocarbon dating.
Reaction products of primary cosmic rays, radioisotope half-lifetime, and production reaction
[edit]- Hydrogen-1 (stable): spallation from nitrogen and oxygen, decay of neutrons from such spallation
- Helium-3 (stable): spallation or from tritium
- Helium-4 (stable): spallation producing alpha rays
- Tritium (12.3 years): 14N(n, 3H)12C (spallation)
- Beryllium-7 (53.3 days)
- Beryllium-10 (1.39 million years): 14N(n,p α)10Be (spallation)
- Carbon-14 (5730 years): 14N(n, p)14C (neutron activation)
- Sodium-22 (2.6 years)
- Sodium-24 (15 hours)
- Magnesium-28 (20.9 hours)
- Silicon-31 (2.6 hours)
- Silicon-32 (101 years)
- Phosphorus-32 (14.3 days)
- Sulfur-35 (87.5 days)
- Sulfur-38 (2.84 hours)
- Chlorine-34 m (32 minutes)
- Chlorine-36 (300,000 years)
- Chlorine-38 (37.2 minutes)
- Chlorine-39 (56 minutes)
- Argon-39 (269 years)
- Krypton-85 (10.7 years)[90]
Role in ambient radiation
[edit]Cosmic rays constitute a fraction of the annual radiation exposure of human beings on the Earth, averaging 0.39 mSv out of a total of 3 mSv per year (13% of total background) for the Earth's population. However, the background radiation from cosmic rays increases with altitude, from 0.3 mSv per year for sea-level areas to 1.0 mSv per year for higher-altitude cities, raising cosmic radiation exposure to a quarter of total background radiation exposure for populations of said cities. Airline crews flying long-distance high-altitude routes can be exposed to 2.2 mSv of extra radiation each year due to cosmic rays, nearly doubling their total exposure to ionizing radiation.
| Radiation | UNSCEAR[91][92] | Princeton[93] | Wa State[94] | MEXT[95] | Remark | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Type | Source | World average |
Typical range | US | US | Japan | |
| Natural | Air | 1.26 | 0.2–10.0a | 2.29 | 2.00 | 0.40 | Primarily from radon, (a)depends on indoor accumulation of radon gas. |
| Internal | 0.29 | 0.2–1.0b | 0.16 | 0.40 | 0.40 | Mainly from radioisotopes in food (40K, 14C, etc.) (b)depends on diet. | |
| Terrestrial | 0.48 | 0.3–1.0c | 0.19 | 0.29 | 0.40 | (c)Depends on soil composition and building material of structures. | |
| Cosmic | 0.39 | 0.3–1.0d | 0.31 | 0.26 | 0.30 | (d)Generally increases with elevation. | |
| Subtotal | 2.40 | 1.0–13.0 | 2.95 | 2.95 | 1.50 | ||
| Artificial | Medical | 0.60 | 0.03–2.0 | 3.00 | 0.53 | 2.30 | |
| Fallout | 0.007 | 0–1+ | – | – | 0.01 | Peaked in 1963 (prior to the Partial Test Ban Treaty) with a spike in 1986; still high near nuclear test and accident sites. For the United States, fallout is incorporated into other categories. | |
| Others | 0.0052 | 0–20 | 0.25 | 0.13 | 0.001 | Average annual occupational exposure is 0.7 mSv; mining workers have higher exposure. Populations near nuclear plants have an additional ≈0.02 mSv of exposure annually. | |
| Subtotal | 0.6 | 0 to tens | 3.25 | 0.66 | 2.311 | ||
| Total | 3.00 | 0 to tens | 6.20 | 3.61 | 3.81 | ||
Figures are for the time before the Fukushima Daiichi nuclear disaster. Human-made values by UNSCEAR are from the Japanese National Institute of Radiological Sciences, which summarized the UNSCEAR data.
Effect on electronics
[edit]Cosmic rays have sufficient energy to alter the states of circuit components in electronic integrated circuits, causing transient errors to occur (such as corrupted data in electronic memory devices or incorrect performance of CPUs) often referred to as "soft errors". This has been a problem in electronics at extremely high-altitude, such as in satellites, but with transistors becoming smaller and smaller, this is becoming an increasing concern in ground-level electronics as well.[96] Studies by IBM in the 1990s suggest that computers typically experience about one cosmic-ray-induced error per 256 megabytes of RAM per month.[97] To alleviate this problem, the Intel Corporation has proposed a cosmic ray detector that could be integrated into future high-density microprocessors, allowing the processor to repeat the last command following a cosmic-ray event.[98] ECC memory is used to protect data against data corruption caused by cosmic rays.
In 2008, data corruption in a flight control system caused an Airbus A330 airliner to twice plunge hundreds of feet, resulting in injuries to multiple passengers and crew members. Cosmic rays were investigated among other possible causes of the data corruption, but were ultimately ruled out as being very unlikely.[99]
In August 2020, scientists reported that ionizing radiation from environmental radioactive materials and cosmic rays may substantially limit the coherence times of qubits if they are not shielded adequately which may be critical for realizing fault-tolerant superconducting quantum computers in the future.[100][101][102]
Significance to aerospace travel
[edit]Galactic cosmic rays are one of the most important barriers standing in the way of plans for interplanetary travel by crewed spacecraft. Cosmic rays also pose a threat to electronics placed aboard outgoing probes. In 2010, a malfunction aboard the Voyager 2 space probe was credited to a single flipped bit, probably caused by a cosmic ray. Strategies such as physical or magnetic shielding for spacecraft have been considered in order to minimize the damage to electronics and human beings caused by cosmic rays.[103][104]
On 31 May 2013, NASA scientists reported that a possible crewed mission to Mars may involve a greater radiation risk than previously believed, based on the amount of energetic particle radiation detected by the RAD on the Mars Science Laboratory while traveling from the Earth to Mars in 2011–2012.[105][106][107]

Flying 12 kilometres (39,000 ft) high, passengers and crews of jet airliners are exposed to at least 10 times the cosmic ray dose that people at sea level receive. Aircraft flying polar routes near the geomagnetic poles are at particular risk.[108][109][110]
Role in lightning
[edit]Cosmic rays have been implicated in the triggering of electrical breakdown in lightning. It has been proposed that essentially all lightning is triggered through a relativistic process, or "runaway breakdown", seeded by cosmic ray secondaries. Subsequent development of the lightning discharge then occurs through "conventional breakdown" mechanisms.[111]
Postulated role in climate change
[edit]A role for cosmic rays in climate was suggested by Edward P. Ney in 1959[112] and by Robert E. Dickinson in 1975.[113] It has been postulated that cosmic rays may have been responsible for major climatic change and mass extinction in the past. According to Adrian Mellott and Mikhail Medvedev, 62-million-year cycles in biological marine populations correlate with the motion of the Earth relative to the galactic plane and increases in exposure to cosmic rays.[114] The researchers suggest that this and gamma ray bombardments deriving from local supernovae could have affected cancer and mutation rates, and might be linked to decisive alterations in the Earth's climate, and to the mass extinctions of the Ordovician.[115][116]
Danish physicist Henrik Svensmark has controversially argued that because solar variation modulates the cosmic ray flux on Earth, it would consequently affect the rate of cloud formation and hence be an indirect cause of global warming.[117][118] Svensmark is one of several scientists outspokenly opposed to the mainstream scientific assessment of global warming, leading to concerns that the proposition that cosmic rays are connected to global warming could be ideologically biased rather than scientifically based.[119] Other scientists have vigorously criticized Svensmark for sloppy and inconsistent work: one example is adjustment of cloud data that understates error in lower cloud data, but not in high cloud data;[120] another example is "incorrect handling of the physical data" resulting in graphs that do not show the correlations they claim to show.[121] Despite Svensmark's assertions, galactic cosmic rays have shown no statistically significant influence on changes in cloud cover,[122] and have been demonstrated in studies to have no causal relationship to changes in global temperature.[123]
Possible mass extinction factor
[edit]A handful of studies conclude that a nearby supernova or series of supernovas caused the Pliocene marine megafauna extinction event by substantially increasing radiation levels to hazardous amounts for large seafaring animals.[124][125][126]
Research and experiments
[edit]There are a number of cosmic-ray research initiatives, listed below.
Ground-based
[edit]- Akeno Giant Air Shower Array
- Chicago Air Shower Array
- CHICOS
- CLOUD
- CRIPT
- GAMMA
- GRAPES-3
- HAWC
- HEGRA
- High Energy Stereoscopic System
- High Resolution Fly's Eye Cosmic Ray Detector
- IceCube
- KASCADE
- MAGIC
- MARIACHI
- Milagro
- NMDB
- Pierre Auger Observatory
- QuarkNet
- Spaceship Earth
- Telescope Array Project
- Tunka experiment
- VERITAS
- Washington Large Area Time Coincidence Array
Satellite
[edit]Balloon-borne
[edit]See also
[edit]- Central nervous system effects from radiation exposure during spaceflight – Space radiation effects on the brain
- Cosmic ray visual phenomena
- Environmental radioactivity – Radioactivity naturally present within the Earth
- Extragalactic cosmic ray – Type of cosmic ray
- Forbush decrease – Decrease in cosmic ray intensity
- Gilbert Jerome Perlow
- Health threat from cosmic rays – Cancer causing exposure to ionizing radiation in spaceflight
- Meter water equivalent – Unit of nuclear and particle physics
- Oh-My-God particle – Ultra-high-energy cosmic ray detected in 1991
- Solar energetic particles – High-energy particles from the Sun
- Track Imaging Cherenkov Experiment
- Ultra-high-energy cosmic ray (UHECR) – Cosmic-ray particle with a kinetic energy greater than 1 EeV
References
[edit]- ^ Sharma, Shatendra (2008). Atomic and Nuclear Physics. Pearson Education India. p. 478. ISBN 978-81-317-1924-4.
- ^ "Detecting cosmic rays from a galaxy far, far away". Science Daily. 21 September 2017. Retrieved 26 December 2017.
- ^ a b c d "Nobel Prize in Physics 1936 – Presentation Speech". Nobelprize.org. 10 December 1936. Retrieved 27 February 2013.
- ^ Cilek, Vaclav, ed. (2009). "Cosmic Influences on the Earth". Earth System: History and Natural Variability. Vol. I. Eolss Publishers. p. 165. ISBN 978-1-84826-104-4.
- ^ a b Ackermann, M.; Ajello, M.; Allafort, A.; Baldini, L.; Ballet, J.; Barbiellini, G.; et al. (15 February 2013). "Detection of the characteristic pion decay-signature in supernova remnants". Science. 339 (6424): 807–811. arXiv:1302.3307. Bibcode:2013Sci...339..807A. doi:10.1126/science.1231160. PMID 23413352. S2CID 29815601.
- ^ a b Pinholster, Ginger (13 February 2013). "Evidence shows that cosmic rays come from exploding stars" (Press release). Washington, DC: American Association for the Advancement of Science.
- ^ Abramowski, A.; et al. (HESS Collaboration) (2016). "Acceleration of petaelectronvolt protons in the Galactic Centre". Nature. 531 (7595): 476–479. arXiv:1603.07730. Bibcode:2016Natur.531..476H. doi:10.1038/nature17147. PMID 26982725. S2CID 4461199.
- ^ Aartsen, Mark; et al. (IceCube Collaboration) (12 July 2018). "Neutrino emission from the direction of the blazar TXS 0506+056 prior to the IceCube-170922A alert". Science. 361 (6398): 147–151. arXiv:1807.08794. Bibcode:2018Sci...361..147I. doi:10.1126/science.aat2890. ISSN 0036-8075. PMID 30002248. S2CID 133261745.
- ^ Christian, Eric. "Are cosmic rays electromagnetic radiation?". NASA. Archived from the original on 31 May 2000. Retrieved 11 December 2012.
- ^ a b "What are cosmic rays?". Goddard Space Flight Center. NASA. Archived from the original on 28 October 2012. Retrieved 31 October 2012."mirror copy, also archived". Archived from the original on 4 March 2016.
- ^ Dembinski, H.; et al. (2018). "Data-driven model of the cosmic-ray flux and mass composition from 10 GeV to 10^11 GeV". Proceedings of Science. ICRC2017: 533. arXiv:1711.11432. doi:10.22323/1.301.0533. S2CID 85540966.
- ^ "Cosmic Rays". Goddard Space Flight Center. imagine.gsfc.nasa.gov. Science Toolbox. National Aeronautics and Space Administration. Retrieved 23 March 2019.
- ^ Resnick, Brian (25 July 2019). "Extremely powerful cosmic rays are raining down on us. No one knows where they come from". Vox Media. Retrieved 14 December 2022.
- ^ Sovilj MP, Vuković B, Stanić D (2020). "Potential benefit of retrospective use of neutron monitors in improving ionising radiation exposure assessment on international flights: issues raised by neutron passive dosimeter measurements and EPCARD simulations during sudden changes in solar activity". Arhiv Za Higijenu Rada I Toksikologiju. 71 (2): 152–157. doi:10.2478/aiht-2020-71-3403. PMC 7968484. PMID 32975102.
- ^ CERN https://home.cern/science/physics/cosmic-rays-particles-outer-space
- ^ Nerlich, Steve (12 June 2011). "Astronomy without a telescope – 'Oh-my-God' particles". Universe Today. Retrieved 17 February 2013.
- ^ "LHC: The guide". Large Hadron Collider. FAQ: Facts and figures. European Organization for Nuclear Research (CERN). 2021. p. 3. Retrieved 9 October 2022.
- ^ Gaensler, Brian (November 2011). "Extreme speed". COSMOS. No. 41. Archived from the original on 7 April 2013.
- ^ Anchordoqui, L.; Paul, T.; Reucroft, S.; Swain, J. (2003). "Ultrahigh energy cosmic rays: The state of the art before the Auger Observatory". International Journal of Modern Physics A. 18 (13): 2229–2366. arXiv:hep-ph/0206072. Bibcode:2003IJMPA..18.2229A. doi:10.1142/S0217751X03013879. S2CID 119407673.
- ^ Nave, Carl R. (ed.). "Cosmic rays". Physics and Astronomy Department. HyperPhysics. Georgia State University. Retrieved 17 February 2013.
- ^ Malley, Marjorie C. (25 August 2011). Radioactivity: A History of a Mysterious Science. Oxford University Press. pp. 78–79. ISBN 978-0-19-976641-3.
- ^ North, John (15 July 2008). Cosmos: An Illustrated History of Astronomy and Cosmology. University of Chicago Press. p. 686. ISBN 978-0-226-59441-5.
- ^ Wulf, Theodor (1910). "Beobachtungen über die Strahlung hoher Durchdringungsfähigkeit auf dem Eiffelturm" [Observations of radiation of high penetration power at the Eiffel tower]. Physikalische Zeitschrift (in German). 11: 811–813.
- ^ Pacini, D. (1912). "La radiazione penetrante alla superficie ed in seno alle acque". Il Nuovo Cimento. 3 (1): 93–100. arXiv:1002.1810. Bibcode:1912NCim....3...93P. doi:10.1007/BF02957440. S2CID 118487938.: Translated with commentary in de Angelis, A. (2010). "Penetrating Radiation at the Surface of and in Water". Il Nuovo Cimento. 3 (1): 93–100. arXiv:1002.1810. Bibcode:1912NCim....3...93P. doi:10.1007/BF02957440. S2CID 118487938.
- ^ Hess, V.F. (1912). "Über Beobachtungen der durchdringenden Strahlung bei sieben Freiballonfahrten" [On observations of penetrating radiation during seven free balloon flights]. Physikalische Zeitschrift (in German). 13: 1084–1091. arXiv:1808.02927.
- ^ Kolhörster, Werner (1913). "Messungen der durchdringenden Strahlung im Freiballon in größeren Höhen" [Measurements of the penetrating radiation in a free balloon at high altitudes]. Physikalische Zeitschrift (in German). 14: 1153–1156.
- ^ Kolhörster, W. (1914). "Messungen der durchdringenden Strahlungen bis in Höhen von 9300 m." [Measurements of the penetrating radiation up to heights of 9300 m.]. Verhandlungen der Deutschen Physikalischen Gesellschaft (in German). 16: 719–721.
- ^ Hess, V.F. (1936). "The Nobel Prize in Physics 1936". The Nobel Foundation. Retrieved 11 February 2010.
- ^ Hess, V.F. (1936). "Unsolved Problems in Physics: Tasks for the Immediate Future in Cosmic Ray Studies". Nobel Lectures. The Nobel Foundation. Retrieved 11 February 2010.
- ^ Rossi, Bruno Benedetto (1964). Cosmic Rays. New York: McGraw-Hill. ISBN 978-0-07-053890-0.
{{cite book}}: ISBN / Date incompatibility (help) - ^ Geiger, H.; Rutherford, Lord; Regener, E.; Lindemann, F.A.; Wilson, C.T.R.; Chadwick, J.; et al. (1931). "Discussion on Ultra-Penetrating Rays". Proceedings of the Royal Society of London A. 132 (819): 331. Bibcode:1931RSPSA.132..331G. doi:10.1098/rspa.1931.0104.
- ^ Clay, J. (1927). "Penetrating Radiation" (PDF). Proceedings of the Section of Sciences, Koninklijke Akademie van Wetenschappen te Amsterdam. 30 (9–10): 1115–1127. Archived (PDF) from the original on 6 February 2016.
- ^ Bothe, Walther; Werner Kolhörster (November 1929). "Das Wesen der Höhenstrahlung". Zeitschrift für Physik. 56 (11–12): 751–777. Bibcode:1929ZPhy...56..751B. doi:10.1007/BF01340137. S2CID 123901197.
- ^ Rossi, Bruno (August 1930). "On the Magnetic Deflection of Cosmic Rays". Physical Review. 36 (3): 606. Bibcode:1930PhRv...36..606R. doi:10.1103/PhysRev.36.606.
- ^ Johnson, Thomas H. (May 1933). "The Azimuthal Asymmetry of the Cosmic Radiation". Physical Review. 43 (10): 834–835. Bibcode:1933PhRv...43..834J. doi:10.1103/PhysRev.43.834.
- ^ Alvarez, Luis; Compton, Arthur Holly (May 1933). "A Positively Charged Component of Cosmic Rays". Physical Review. 43 (10): 835–836. Bibcode:1933PhRv...43..835A. doi:10.1103/PhysRev.43.835.
- ^ Rossi, Bruno (May 1934). "Directional Measurements on the Cosmic Rays Near the Geomagnetic Equator". Physical Review. 45 (3): 212–214. Bibcode:1934PhRv...45..212R. doi:10.1103/PhysRev.45.212.
- ^ Freier, Phyllis; Lofgren, E.; Ney, E.; Oppenheimer, F.; Bradt, H.; Peters, B.; et al. (July 1948). "Evidence for Heavy Nuclei in the Primary Cosmic radiation". Physical Review. 74 (2): 213–217. Bibcode:1948PhRv...74..213F. doi:10.1103/PhysRev.74.213.
- ^ Freier, Phyllis; Peters, B.; et al. (December 1948). "Investigation of the Primary Cosmic Radiation with Nuclear Photographic Emulsions". Physical Review. 74 (12): 1828–1837. Bibcode:1948PhRv...74.1828B. doi:10.1103/PhysRev.74.1828.
- ^ Rossi, Bruno (1934). "Misure sulla distribuzione angolare di intensita della radiazione penetrante all'Asmara". Ricerca Scientifica. 5 (1): 579–589.
- ^ Auger, P.; et al. (July 1939), "Extensive Cosmic-Ray Showers", Reviews of Modern Physics, 11 (3–4): 288–291, Bibcode:1939RvMP...11..288A, doi:10.1103/RevModPhys.11.288.
- ^ J.L. DuBois; R.P. Multhauf; C.A. Ziegler (2002). The Invention and Development of the Radiosonde (PDF). Smithsonian Studies in History and Technology. Vol. 53. Smithsonian Institution Press. Archived (PDF) from the original on 5 June 2011.
- ^ S. Vernoff (1935). "Radio-Transmission of Cosmic Ray Data from the Stratosphere". Nature. 135 (3426): 1072–1073. Bibcode:1935Natur.135.1072V. doi:10.1038/1351072c0. S2CID 4132258.
- ^ Bhabha, H. J.; Heitler, W. (1937). "The Passage of Fast Electrons and the Theory of Cosmic Showers" (PDF). Proceedings of the Royal Society A: Mathematical, Physical and Engineering Sciences. 159 (898): 432–458. Bibcode:1937RSPSA.159..432B. doi:10.1098/rspa.1937.0082. ISSN 1364-5021. Archived (PDF) from the original on 2 January 2016.
- ^ Braunschweig, W.; et al. (1988). "A study of Bhabha scattering at PETRA energies". Zeitschrift für Physik C. 37 (2): 171–177. doi:10.1007/BF01579904. S2CID 121904361.
- ^ Clark, G.; Earl, J.; Kraushaar, W.; Linsley, J.; Rossi, B.; Scherb, F.; Scott, D. (1961). "Cosmic-Ray Air Showers at Sea Level". Physical Review. 122 (2): 637–654. Bibcode:1961PhRv..122..637C. doi:10.1103/PhysRev.122.637.
- ^ "The Pierre Auger Observatory". Auger Project. Archived from the original on 3 September 2018.
- ^ Kraushaar, W. L.; et al. (1972). "(none)". The Astrophysical Journal. 177: 341. Bibcode:1972ApJ...177..341K. doi:10.1086/151713.
- ^ Cummings, A. C.; Stone, E. C. (1998). "Anomalous Cosmic Rays and Solar Modulation". Space Science Reviews. 83 (1–2): 51–62. doi:10.1023/A:1005057010311.
- ^ Tomassetti, Nicola; Bertucci, Bruna; Fiandrini, Emanuele (2022). "Temporal evolution and rigidity dependence of the solar modulation lag of Galactic cosmic rays". Physical Review D. 106 (10) 103022. arXiv:2210.05693. Bibcode:2022PhRvD.106j3022T. doi:10.1103/PhysRevD.106.103022.
- ^ Potgieter, Marius (2013). "Solar Modulation of Cosmic Rays". Living Reviews in Solar Physics. 10 (1): 3. arXiv:1306.4421. Bibcode:2013LRSP...10....3P. doi:10.12942/lrsp-2013-3.
- ^ a b Zimbardo, G.; Perri, S.; Effenberger, F.; Fichtner, H. (1 November 2017). "Fractional Parker equation for the transport of cosmic rays: steady-state solutions". Astronomy & Astrophysics. 607: A7. Bibcode:2017A&A...607A...7Z. doi:10.1051/0004-6361/201731179 – via www.aanda.org.
- ^ Baade, W.; Zwicky, F. (1934). "Cosmic rays from super-novae". Proceedings of the National Academy of Sciences of the United States of America. 20 (5): 259–263. Bibcode:1934PNAS...20..259B. doi:10.1073/pnas.20.5.259. JSTOR 86841. PMC 1076396. PMID 16587882.
- ^ Babcock, H. (1948). "Magnetic variable stars as sources of cosmic rays". Physical Review. 74 (4): 489. Bibcode:1948PhRv...74..489B. doi:10.1103/PhysRev.74.489.
- ^ Sekido, Y.; Masuda, T.; Yoshida, S.; Wada, M. (1951). "The Crab Nebula as an observed point source of cosmic rays". Physical Review. 83 (3): 658–659. Bibcode:1951PhRv...83..658S. doi:10.1103/PhysRev.83.658.2.
- ^ Gibb, Meredith (3 February 2010). "Cosmic rays". Imagine the Universe. NASA Goddard Space Flight Center. Retrieved 17 March 2013.
- ^ Hague, J.D. (July 2009). "Correlation of the Highest Energy Cosmic Rays with Nearby Extragalactic Objects in Pierre Auger Observatory Data" (PDF). Proceedings of the 31st ICRC, Łódź 2009. International Cosmic Ray Conference. Łódź, Poland. pp. 6–9. Archived from the original (PDF) on 28 May 2013. Retrieved 17 March 2013.
- ^ Hague, J.D. (July 2009). "Correlation of the highest energy cosmic rays with nearby extragalactic objects in Pierre Auger Observatory data" (PDF). Proceedings of the 31st ICRC, Łódź, Poland 2009 – International Cosmic Ray Conference: 36–39. Archived from the original (PDF) on 28 May 2013. Retrieved 17 March 2013.
- ^ Moskowitz, Clara (25 June 2009). "Source of cosmic rays pinned down". Space.com. Tech Media Network. Retrieved 20 March 2013.
- ^ Adriani, O.; Barbarino, G.C.; Bazilevskaya, G.A.; Bellotti, R.; Boezio, M.; Bogomolov, E.A.; et al. (2011). "PAMELA measurements of cosmic-ray proton and helium spectra". Science. 332 (6025): 69–72. arXiv:1103.4055. Bibcode:2011Sci...332...69A. doi:10.1126/science.1199172. hdl:2108/55474. PMID 21385721. S2CID 1234739.
- ^ Jha, Alok (14 February 2013). "Cosmic ray mystery solved". The Guardian. London, UK: Guardian News and Media Ltd. Retrieved 21 March 2013.
- ^ Pierre Auger Collaboration; Aab, A.; Abreu, P.; Aglietta, M.; Al Samarai, I.; Albuquerque, I. F. M.; Allekotte, I.; Almela, A.; Alvarez Castillo, J.; Alvarez-Muñiz, J.; Anastasi, G. A.; Anchordoqui, L.; Andrada, B.; Andringa, S.; Aramo, C.; Arqueros, F.; Arsene, N.; Asorey, H.; Assis, P.; Aublin, J.; Avila, G.; Badescu, A. M.; Balaceanu, A.; Barbato, F.; Barreira Luz, R. J.; Beatty, J. J.; Becker, K. H.; Bellido, J. A.; Berat, C.; et al. (The Pierre Auger Collaboration) (2017). "Observation of a large-scale anisotropy in the arrival directions of cosmic rays above 8×1018 eV". Science. 357 (6357): 1266–1270. arXiv:1709.07321. Bibcode:2017Sci...357.1266P. doi:10.1126/science.aan4338. PMID 28935800. S2CID 3679232.
- ^ Mewaldt, Richard A. (1996). "Cosmic Rays". California Institute of Technology. Archived from the original on 30 August 2009. Retrieved 26 December 2012.
- ^ Koch, L.; Engelmann, J. J.; Goret, P.; Juliusson, E.; Petrou, N.; Rio, Y.; Soutoul, A.; Byrnak, B.; Lund, N.; Peters, B. (October 1981). "The relative abundances of the elements scandium to manganese in relativistic cosmic rays and the possible radioactive decay of manganese 54". Astronomy and Astrophysics. 102 (11): L9. Bibcode:1981A&A...102L...9K.
- ^ Accardo, L.; et al. (AMS Collaboration) (18 September 2014). "High statistics measurement of the positron fraction in primary cosmic rays of 0.5–500 GeV with the alpha magnetic spectrometer on the International Space Station" (PDF). Physical Review Letters. 113 (12) 121101. Bibcode:2014PhRvL.113l1101A. doi:10.1103/PhysRevLett.113.121101. PMID 25279616. Archived (PDF) from the original on 17 October 2014.
- ^ Schirber, Michael (2014). "Synopsis: More dark matter hints from cosmic rays?". Physical Review Letters. 113 (12) 121102. arXiv:1701.07305. Bibcode:2014PhRvL.113l1102A. doi:10.1103/PhysRevLett.113.121102. hdl:1721.1/90426. PMID 25279617. S2CID 2585508.
- ^ "New results from the Alpha Magnetic$Spectrometer on the International Space Station" (PDF). AMS-02 at NASA. Archived (PDF) from the original on 23 September 2014. Retrieved 21 September 2014.
- ^ Aguilar, M.; Alberti, G.; Alpat, B.; Alvino, A.; Ambrosi, G.; Andeen, K.; et al. (2013). "First result from the Alpha Magnetic Spectrometer on the International Space Station: Precision measurement of the positron fraction in primary cosmic rays of 0.5–350 GeV" (PDF). Physical Review Letters. 110 (14) 141102. Bibcode:2013PhRvL.110n1102A. doi:10.1103/PhysRevLett.110.141102. PMID 25166975. Archived (PDF) from the original on 13 August 2017.
- ^ Moskalenko, I.V.; Strong, A.W.; Ormes, J.F.; Potgieter, M.S. (January 2002). "Secondary antiprotons and propagation of cosmic rays in the Galaxy and heliosphere". The Astrophysical Journal. 565 (1): 280–296. arXiv:astro-ph/0106567. Bibcode:2002ApJ...565..280M. doi:10.1086/324402. S2CID 5863020.
- ^ Aguilar, M.; Alcaraz, J.; Allaby, J.; Alpat, B.; Ambrosi, G.; Anderhub, H.; et al. (AMS Collaboration) (August 2002). "The Alpha Magnetic Spectrometer (AMS) on the International Space Station: Part I – Results from the test flight on the space shuttle". Physics Reports. 366 (6): 331–405. Bibcode:2002PhR...366..331A. doi:10.1016/S0370-1573(02)00013-3. hdl:2078.1/72661. S2CID 122726107.
- ^ "EGRET detection of gamma rays from the Moon". GSFC. NASA. 1 August 2005. Retrieved 11 February 2010.
- ^ Morison, Ian (2008). Introduction to Astronomy and Cosmology. John Wiley & Sons. p. 198. Bibcode:2008iac..book.....M. ISBN 978-0-470-03333-3.
- ^ "Extreme Space Weather Events". National Geophysical Data Center. Archived from the original on 22 May 2012. Retrieved 19 April 2012.
- ^ "How many?". Auger.org. Cosmic rays. Pierre Auger Observatory. Archived from the original on 12 October 2012. Retrieved 17 August 2012.
- ^ "The mystery of high-energy cosmic rays". Auger.org. Pierre Auger Observatory. Archived from the original on 8 March 2021. Retrieved 15 July 2015.
- ^ Lal, D.; Jull, A.J.T.; Pollard, D.; Vacher, L. (2005). "Evidence for large century time-scale changes in solar activity in the past 32 Kyr, based on in-situ cosmogenic 14C in ice at Summit, Greenland". Earth and Planetary Science Letters. 234 (3–4): 335–349. Bibcode:2005E&PSL.234..335L. doi:10.1016/j.epsl.2005.02.011.
- ^ Castellina, Antonella; Donato, Fiorenza (2012). "Astrophysics of Galactic charged cosmic rays". In Oswalt, T.D.; McLean, I.S.; Bond, H.E.; French, L.; Kalas, P.; Barstow, M.; Gilmore, G.F.; Keel, W. (eds.). Planets, Stars, and Stellar Systems (1 ed.). Springer. ISBN 978-90-481-8817-8.
- ^ R.L. Fleischer; P.B. Price; R.M. Walker (1975). Nuclear tracks in solids: Principles and applications. University of California Press. Bibcode:1975ucb..book.....F.
- ^ "What are cosmic rays?" (PDF). Michigan State University National Superconducting Cyclotron Laboratory. Archived from the original (PDF) on 12 July 2012. Retrieved 23 February 2013.
- ^ "Cloud Chambers and Cosmic Rays: A Lesson Plan and Laboratory Activity for the High School Science Classroom" (PDF). Cornell University Laboratory for Elementary-Particle Physics. 2006. Archived (PDF) from the original on 6 June 2013. Retrieved 23 February 2013.
- ^ Chu, W.; Kim, Y.; Beam, W.; Kwak, N. (1970). "Evidence of a Quark in a High-Energy Cosmic-Ray Bubble-Chamber Picture". Physical Review Letters. 24 (16): 917–923. Bibcode:1970PhRvL..24..917C. doi:10.1103/PhysRevLett.24.917.
- ^ Timmer, John (13 October 2014). "Cosmic ray particle shower? There's an app for that". Ars Technica.
- ^ Collaboration website Archived 14 October 2014 at the Wayback Machine
- ^ CRAYFIS detector array paper. Archived 14 October 2014 at the Wayback Machine
- ^ "CREDO". credo.science.
- ^ "CREDO's first light: The global particle detector begins its collection of scientific data". EurekAlert!.
- ^ "The Detection of Cosmic Rays". Milagro Gamma-Ray Observatory. Los Alamos National Laboratory. 3 April 2002. Archived from the original on 5 March 2013. Retrieved 22 February 2013.
- ^ Letessier-Selvon, Antoine; Stanev, Todor (2011). "Ultrahigh energy cosmic rays". Reviews of Modern Physics. 83 (3): 907–942. arXiv:1103.0031. Bibcode:2011RvMP...83..907L. doi:10.1103/RevModPhys.83.907. S2CID 119237295.
- ^ Trumbore, Susan (2000). J. S. Noller; J. M. Sowers; W. R. Lettis (eds.). Quaternary Geochronology: Methods and Applications. Washington, D.C.: American Geophysical Union. pp. 41–59. ISBN 978-0-87590-950-9. Archived from the original on 21 May 2013. Retrieved 28 October 2011.
- ^ "Natürliche, durch kosmische Strahlung laufend erzeugte Radionuklide" (PDF) (in German). Archived from the original (PDF) on 3 February 2010. Retrieved 11 February 2010.
- ^ UNSCEAR "Sources and Effects of Ionizing Radiation" page 339 retrieved 29 June 2011
- ^ Japan NIRS UNSCEAR 2008 report page 8 retrieved 29 June 2011
- ^ Princeton.edu "Background radiation" Archived 9 June 2011 at the Wayback Machine retrieved 29 June 2011
- ^ Washington state Dept. of Health "Background radiation" Archived 2 May 2012 at the Wayback Machine retrieved 29 June 2011
- ^ Ministry of Education, Culture, Sports, Science, and Technology of Japan "Radiation in environment" Archived 22 March 2011 at the Wayback Machine retrieved 29 June 2011
- ^ "IBM experiments in soft fails in computer electronics (1978–1994)". In "Terrestrial cosmic rays and soft errors", IBM Journal of Research and Development, Vol. 40, No. 1, 1996. Retrieved 16 April 2008.
- ^ Scientific American (21 July 2008). "Solar Storms: Fast Facts". Nature Publishing Group.
- ^ "Intel plans to tackle cosmic ray threat". BBC News, 8 April 2008. Retrieved 16 April 2008.
- ^ "In-flight upset, 154 km west of Learmonth, Western Australia, 7 October 2008, VH-QPA, Airbus A330-303" Archived 5 May 2022 at the Wayback Machine (2011). Australian Transport Safety Bureau.
- ^ "Quantum computers may be destroyed by high-energy particles from space". New Scientist. Retrieved 7 September 2020.
- ^ "Cosmic rays may soon stymie quantum computing". phys.org. Retrieved 7 September 2020.
- ^ Vepsäläinen, Antti P.; Karamlou, Amir H.; Orrell, John L.; Dogra, Akshunna S.; Loer, Ben; Vasconcelos, Francisca; Kim, David K.; Melville, Alexander J.; Niedzielski, Bethany M.; Yoder, Jonilyn L.; Gustavsson, Simon; Formaggio, Joseph A.; VanDevender, Brent A.; Oliver, William D. (August 2020). "Impact of ionizing radiation on superconducting qubit coherence". Nature. 584 (7822): 551–556. arXiv:2001.09190. Bibcode:2020Natur.584..551V. doi:10.1038/s41586-020-2619-8. ISSN 1476-4687. PMID 32848227. S2CID 210920566. Retrieved 7 September 2020.
- ^ Globus, Al (10 July 2002). "Appendix E: Mass Shielding". Space Settlements: A Design Study. NASA. Archived from the original on 31 May 2010. Retrieved 24 February 2013.
- ^ Atkinson, Nancy (24 January 2005). "Magnetic shielding for spacecraft". The Space Review. Retrieved 24 February 2013.
- ^ a b Kerr, Richard (31 May 2013). "Radiation Will Make Astronauts' Trip to Mars Even Riskier". Science. 340 (6136): 1031. Bibcode:2013Sci...340.1031K. doi:10.1126/science.340.6136.1031. PMID 23723213.
- ^ a b Zeitlin, C.; Hassler, D. M.; Cucinotta, F. A.; Ehresmann, B.; Wimmer-Schweingruber, R.F.; Brinza, D. E.; Kang, S.; Weigle, G.; et al. (31 May 2013). "Measurements of Energetic Particle Radiation in Transit to Mars on the Mars Science Laboratory". Science. 340 (6136): 1080–1084. Bibcode:2013Sci...340.1080Z. doi:10.1126/science.1235989. PMID 23723233. S2CID 604569.
- ^ a b Chang, Kenneth (30 May 2013). "Data Point to Radiation Risk for Travelers to Mars". The New York Times. Retrieved 31 May 2013.
- ^ Phillips, Tony (25 October 2013). "The Effects of Space Weather on Aviation". Science News. NASA. Archived from the original on 28 September 2019. Retrieved 12 July 2017.
- ^ "Converting Cosmic Rays to Sound During a Transatlantic Flight to Zurich" on YouTube
- ^ "NAIRAS Real-time radiation Dose". sol.spacenvironment.net.
- ^ "Runaway Breakdown and the Mysteries of Lightning", Physics Today, May 2005.
- ^ Ney, Edward P. (14 February 1959). "Cosmic Radiation and the Weather". Nature. 183 (4659): 451–452. Bibcode:1959Natur.183..451N. doi:10.1038/183451a0. S2CID 4157226.
- ^ Dickinson, Robert E. (December 1975). "Solar Variability and the Lower Atmosphere". Bulletin of the American Meteorological Society. 56 (12): 1240–1248. Bibcode:1975BAMS...56.1240D. doi:10.1175/1520-0477(1975)056<1240:SVATLA>2.0.CO;2.
- ^ "Ancient Mass Extinctions Caused by Cosmic Radiation, Scientists Say". National Geographic. 2007. Archived from the original on 23 April 2007.
- ^ Melott, A. L.; Thomas, B. C. (2009). "Late Ordovician geographic patterns of extinction compared with simulations of astrophysical ionizing radiation damage". Paleobiology. 35 (3): 311–320. arXiv:0809.0899. Bibcode:2009Pbio...35..311M. doi:10.1666/0094-8373-35.3.311. S2CID 11942132.
- ^ "Did Supernova Explosion Contribute to Earth Mass Extinction?". Space.com. 11 July 2016.
- ^ Long, Marion (25 June 2007). "Sun's Shifts May Cause Global Warming". Discover. Retrieved 7 July 2013.
- ^ Svensmark, Henrik (1998). "Influence of Cosmic Rays on Earth's Climate" (PDF). Physical Review Letters. 81 (22): 5027–5030. Bibcode:1998PhRvL..81.5027S. CiteSeerX 10.1.1.522.585. doi:10.1103/PhysRevLett.81.5027. Archived (PDF) from the original on 9 August 2017.
- ^ Plait, Phil (31 August 2011). "No, a new study does not show cosmic-rays are connected to global warming". Discover. Kalmbach. Archived from the original on 12 January 2018. Retrieved 11 January 2018.
- ^ Benestad, Rasmus E. (9 March 2007). "'Cosmoclimatology' – tired old arguments in new clothes". Retrieved 13 November 2013.
- ^ Peter Laut, "Solar activity and terrestrial climate: an analysis of some purported correlations", Journal of Atmospheric and Solar-Terrestrial Physics 65 (2003) 801–812
- ^ Lockwood, Mike (16 May 2012). "Solar Influence on Global and Regional Climates". Surveys in Geophysics. 33 (3–4): 503–534. Bibcode:2012SGeo...33..503L. doi:10.1007/s10712-012-9181-3.
- ^ Sloan, T.; Wolfendale, A. W. (7 November 2013). "Cosmic rays, solar activity and the climate". Environmental Research Letters. 8 (4) 045022. Bibcode:2013ERL.....8d5022S. doi:10.1088/1748-9326/8/4/045022.
- ^ Melott, Adrian L.; Marinho, F.; Paulucci, L. (2019). "Muon Radiation Dose and Marine Megafaunal Extinction at the end-Pliocene Supernova". Astrobiology. 19 (6): 825–830. arXiv:1712.09367. doi:10.1089/ast.2018.1902. PMID 30481053. S2CID 33930965.
- ^ Benitez, Narciso; et al. (2002). "Evidence for Nearby Supernova Explosions". Physical Review Letters. 88 (8) 081101. arXiv:astro-ph/0201018. Bibcode:2002PhRvL..88h1101B. doi:10.1103/PhysRevLett.88.081101. PMID 11863949. S2CID 41229823.
- ^ Fimiani, L.; Cook, D. L.; Faestermann, T.; Gómez-Guzmán, J. M.; Hain, K.; Herzog, G.; Knie, K.; Korschinek, G.; Ludwig, P.; Park, J.; Reedy, R. C.; Rugel, G. (2016). "Interstellar 60Fe on the Surface of the Moon". Physical Review Letters. 116 (15) 151104. Bibcode:2016PhRvL.116o1104F. doi:10.1103/PhysRevLett.116.151104. PMID 27127953.
Further references
[edit]- De Angelis, Alessandro; Pimenta, Mario (2018). Introduction to particle and astroparticle physics (multimessenger astronomy and its particle physics foundations). Springer. doi:10.1007/978-3-319-78181-5. ISBN 978-3-319-78181-5.
- R.G. Harrison and D.B. Stephenson, Detection of a galactic cosmic ray influence on clouds, Geophysical Research Abstracts, Vol. 8, 07661, 2006 SRef-ID: 1607-7962/gra/EGU06-A-07661
- Anderson, C. D.; Neddermeyer, S. H. (1936). "Cloud Chamber Observations of Cosmic Rays at 4300 Meters Elevation and Near Sea-Level" (PDF). Phys. Rev. 50 (4): 263–271. Bibcode:1936PhRv...50..263A. doi:10.1103/physrev.50.263.
- Boezio, M.; et al. (2000). "Measurement of the flux of atmospheric muons with the CAPRICE94 apparatus". Phys. Rev. D. 62 (3) 032007. arXiv:hep-ex/0004014. Bibcode:2000PhRvD..62c2007B. doi:10.1103/physrevd.62.032007.
- R. Clay and B. Dawson, Cosmic Bullets, Allen & Unwin, 1997. ISBN 1-86448-204-4
- T. K. Gaisser, Cosmic Rays and Particle Physics, Cambridge University Press, 1990. ISBN 0-521-32667-2
- P. K. F. Grieder, Cosmic Rays at Earth: Researcher's Reference Manual and Data Book, Elsevier, 2001. ISBN 0-444-50710-8
- A. M. Hillas, Cosmic Rays, Pergamon Press, Oxford, 1972 ISBN 0-08-016724-1
- Kremer, J.; et al. (1999). "Measurement of Ground-Level Muons at Two Geomagnetic Locations". Phys. Rev. Lett. 83 (21): 4241–4244. Bibcode:1999PhRvL..83.4241K. doi:10.1103/physrevlett.83.4241.
- Neddermeyer, S. H.; Anderson, C. D. (1937). "Note on the Nature of Cosmic-Ray Particles" (PDF). Phys. Rev. 51 (10): 884–886. Bibcode:1937PhRv...51..884N. doi:10.1103/physrev.51.884.
- M. D. Ngobeni and M. S. Potgieter, Cosmic ray anisotropies in the outer heliosphere, Advances in Space Research, 2007.
- M. D. Ngobeni, Aspects of the modulation of cosmic rays in the outer heliosphere, MSc Dissertation, Northwest University (Potchefstroom campus) South Africa 2006.
- D. Perkins, Particle Astrophysics, Oxford University Press, 2003. ISBN 0-19-850951-0
- C. E. Rolfs and S. R. William, Cauldrons in the Cosmos, The University of Chicago Press, 1988. ISBN 0-226-72456-5
- B. B. Rossi, Cosmic Rays, McGraw-Hill, New York, 1964.
- Martin Walt, Introduction to Geomagnetically Trapped Radiation, 1994. ISBN 0-521-43143-3
- Taylor, M.; Molla, M. (2010). "Towards a unified source-propagation model of cosmic rays". Publ. Astron. Soc. Pac. 424: 98. Bibcode:2010ASPC..424...98T.
- Ziegler, J. F. (1981). "The Background in Detectors Caused By Sea Level Cosmic Rays". Nuclear Instruments and Methods. 191 (1): 419–424. Bibcode:1981NIMPR.191..419Z. doi:10.1016/0029-554x(81)91039-9.
- TRACER Long Duration Balloon Project: the largest cosmic ray detector launched on balloons.
- Carlson, Per; De Angelis, Alessandro (2011). "Nationalism and internationalism in science: the case of the discovery of cosmic rays". European Physical Journal H. 35 (4): 309–329. arXiv:1012.5068. Bibcode:2010EPJH...35..309C. doi:10.1140/epjh/e2011-10033-6. S2CID 7635998.
External links
[edit]Cosmic ray
View on GrokipediaDefinition and Properties
Etymology and Basic Characteristics
The term "cosmic rays" denotes high-energy ionizing radiation originating from extraterrestrial sources and penetrating Earth's atmosphere. It was coined in 1925 by American physicist Robert A. Millikan, who conducted extensive measurements of atmospheric ionization at various altitudes and depths, initially interpreting the phenomenon as electromagnetic gamma radiation generated by atomic processes in interstellar space.[7][8] Millikan's naming reflected his hypothesis that these "rays" arose from the "birth cries of infant atoms" in the cosmos, a view later revised as evidence showed they consist primarily of charged particles rather than photons.[9] The discovery of cosmic rays predates the terminology, traced to Austrian physicist Victor F. Hess's balloon experiments in 1911–1912. Using electroscopes to measure ionization rates, Hess observed that radiation intensity increased with altitude up to about 5 kilometers, contradicting expectations of solely terrestrial radioactive decay and indicating an influx from above the atmosphere.[10][2] These findings, confirmed by subsequent flights including one during a solar eclipse on August 17, 1912, established cosmic rays as penetrating radiation of extraterrestrial origin, earning Hess the 1936 Nobel Prize in Physics (shared with Carl D. Anderson for muon discovery).[11] Cosmic rays fundamentally comprise relativistic charged particles, predominantly protons (approximately 89–90% of the flux), followed by helium nuclei (alpha particles, about 9–10%), and trace amounts of heavier atomic nuclei, electrons, positrons, and photons.[1][12] These primaries arrive nearly isotropically at Earth with energies spanning over 12 orders of magnitude, from roughly 10^8 electronvolts (eV) for typical galactic cosmic rays to exceeding 10^20 eV for ultra-high-energy events, far surpassing energies achievable in terrestrial accelerators.[13] Upon collision with atmospheric nuclei, primary cosmic rays generate extensive air showers of secondary particles, including muons, electrons, and neutrinos, which constitute the observable radiation at sea level.[1] The charged nature of most cosmic rays subjects them to deflection by galactic and solar magnetic fields during propagation, while their high velocities—approaching the speed of light—enable minimal interaction en route until atmospheric entry.[14]Chemical Composition
Primary cosmic rays, as measured at Earth after accounting for solar modulation and heliospheric effects, consist primarily of atomic nuclei, with protons (hydrogen nuclei) accounting for approximately 87% of the particle flux by number, helium nuclei (alpha particles) about 12%, and heavier nuclei (elements from lithium to trans-iron) the remaining 1%.[4] Electrons and positrons make up a smaller fraction, typically ≤1% combined, with their spectra exhibiting distinct hardening features above several hundred GeV due to propagation and potential nearby sources.[4] These proportions are derived from direct measurements by space-based detectors, which resolve particle charge and rigidity to identify elemental species.[15] The heavier nuclear component, though minor in abundance, provides critical insights into acceleration and propagation processes, as its isotopic and elemental ratios deviate from solar system values. Experiments such as the Alpha Magnetic Spectrometer (AMS-02) on the International Space Station have precisely measured fluxes of key species like carbon, oxygen, neon, magnesium, silicon, and iron from ~2 GV to several TV, revealing two distinct spectral groups: one including helium, carbon, oxygen, and iron with identical rigidity dependence above ~60 GV, and another comprising neon, magnesium, silicon, and sulfur that hardens similarly but shows independent behavior at lower energies.[15] Nitrogen and lighter secondaries like lithium and beryllium exhibit mixed primary-secondary origins, with boron-to-carbon ratios decreasing as R^{-0.333} (where R is rigidity) above 65 GV, indicating diffusive propagation in the Galaxy.[15] Ultra-heavy elements (Z > 30) are rarer, with abundances measured by balloon-borne instruments like SuperTIGER, showing enhancements relative to solar system compositions for refractory elements locked in dust grains during acceleration.[16]| Element Group | Approximate Abundance (% by number) | Key Measurements |
|---|---|---|
| Protons (H) | 87 | AMS-02, PAMELA [4] |
| Helium (He) | 12 | AMS-02 fluxes to 60 GV [15] |
| Light nuclei (Li-Be-B, C-N-O) | ~0.5 | AMS-02 secondary/primary ratios [15] |
| Medium-heavy (Ne-Mg-Si-S) | ~0.3 | AMS-02 group spectra [15] |
| Heavy (Fe and beyond) | ~0.2 | AMS-02, HEAO-3 [4] |
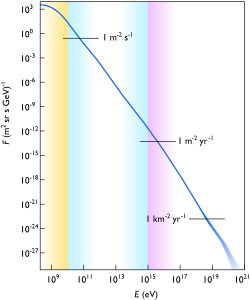
Energy Spectrum and Flux
The energy spectrum of cosmic rays at Earth is characterized by the differential flux , where for energies from approximately eV to the knee at around eV.[18] [4] This power-law form arises from acceleration mechanisms in astrophysical sources, with the flux decreasing steeply as energy increases, such that the integral flux above 1 GeV/nucleon is on the order of particles m s sr.[19] Measurements of this spectrum rely on direct detection via satellites and balloons for energies below eV and indirect air-shower observations for higher energies.[4] At the knee, located near 4 PeV ( eV), the spectral index steepens to , marking a transition potentially linked to the maximum energy achievable by galactic accelerators or changes in propagation. [18] Above the knee, the spectrum continues as a steeper power law until the ankle feature around eV, where the index flattens to , indicating a possible dominance shift to extragalactic contributions.[20] [4] These features have been precisely mapped by observatories like the Pierre Auger Observatory, which report the ankle rollover at eV with a hardening from to .[20] Flux at ultra-high energies, such as above eV, drops to below m s sr, requiring large-scale arrays for detection.[21] Solar modulation suppresses the flux at low rigidities ( GV), varying with the 11-year solar cycle, while geomagnetic effects influence trajectories at Earth.[4] The observed spectrum reflects primarily protons and light nuclei at lower energies, with heavier composition inferred above the knee from air-shower depth profiles.[22] Recent measurements confirm no significant deviations from the power-law envelope beyond established features up to the highest observed energies exceeding eV.[4]Historical Development
Initial Discovery (1912–1930s)
In 1911 and 1912, Austrian physicist Victor Hess conducted a series of manned balloon ascents to investigate the sources of atmospheric ionization, which had been observed to persist beyond explanations from terrestrial radioactivity.[2] During these flights, Hess employed electroscopes to measure ionization rates at varying altitudes. On August 7, 1912, amid a total solar eclipse, Hess reached an altitude of approximately 5,300 meters, where measurements revealed that ionization initially decreased with height but then markedly increased, indicating a penetrating radiation originating from beyond Earth's atmosphere rather than from below.[23][3] This counterintuitive finding suggested an extraterrestrial origin, as daytime measurements ruled out solar contributions and the eclipse conditions minimized potential ultraviolet interference.[11] Hess's results were independently corroborated by Italian physicist Domenico Pacini, who performed similar underwater and lake-based experiments in 1911 and 1912, detecting reduced ionization at depth that aligned with an influx of high-altitude radiation.[24] Further confirmation came from Werner Kolhörster's balloon flights in 1913–1914, which extended measurements to over 9,000 meters and affirmed the upward trend in ionization intensity.[25] These early experiments established the existence of a pervasive, penetrating radiation component, though its particulate or electromagnetic nature remained debated amid World War I interruptions.[26] By the mid-1920s, American physicist Robert Millikan resumed systematic investigations using high-altitude balloons and mountain expeditions, confirming the extraterrestrial source through ionization profiles from sea level to 15,500 meters.[8] Millikan coined the term "cosmic rays" in 1925, interpreting the phenomenon as high-energy gamma radiation from interstellar atomic processes, a view that influenced early nomenclature despite later evidence favoring charged particles.[7] Through the 1920s and into the 1930s, expeditions to equatorial and polar regions revealed latitude-dependent variations attributable to Earth's magnetic field deflection, prompting initial theories on charged particle trajectories and energization mechanisms, though source identification awaited particle physics advances.[27][28]Particle Identification and Early Experiments (1930s–1950s)
In 1932, Carl D. Anderson detected the positron while studying cosmic ray tracks in a cloud chamber equipped with a strong magnetic field, observing particles with electron mass but opposite curvature to electrons, thus confirming the existence of antimatter as predicted by Paul Dirac's 1928 relativistic quantum equation.[29][30] This discovery, made at Caltech under Robert Millikan's guidance, marked the first experimental verification of an antiparticle and earned Anderson the 1936 Nobel Prize in Physics shared with Victor Hess.[29][31] Cloud chambers, pioneered by C.T.R. Wilson, allowed visualization of ionizing paths, enabling charge and momentum estimation from track curvature in magnetic fields up to 15,000 gauss.[32] By the mid-1930s, experiments revealed a penetrating component in cosmic rays beyond electrons and positrons, leading Anderson and Seth Neddermeyer to identify particles with masses approximately 200 times that of the electron in 1936, using cloud chambers with lead absorbers to measure penetration depths.[33] These muons, initially termed "mesotrons" or heavy electrons, were confirmed in 1937 by George Street and Edward Stevenson via independent cloud chamber measurements showing consistent intermediate masses and weak ionization.[34] Unlike expected Yukawa mesons mediating nuclear forces, muons exhibited minimal interaction with matter, penetrating thick lead shields while curving like charged leptons in fields, distinguishing them from protons or neutrons.[34] Bruno Rossi's coincidence counter circuits, developed from 1930 onward, facilitated timing correlations of multiple detectors, quantifying muon flux at sea level around 1 per cm² per minute and revealing directional isotropy.[35] Photographic nuclear emulsions emerged as a key tool in the 1940s, offering higher resolution for decay events than cloud chambers. In 1947, Cecil Powell's Bristol group exposed emulsions at high altitudes via balloons, capturing V-shaped tracks from pion decays into muons, confirming Hideki Yukawa's 1935 prediction of pi-mesons with masses near 140 and 270 electron masses for charged and neutral variants, respectively.[36][37] Pions, produced in atmospheric collisions of primary cosmic protons with nuclei, decayed rapidly (lifetime ~10^{-8} seconds), explaining muon origins as secondaries.[37] Powell received the 1950 Nobel Prize for this identification, which resolved the mesotron puzzle by distinguishing weakly interacting muons from strongly interacting pions.[36] Mid-1940s experiments by G.D. Rochester and C.C. Butler using triggered cloud chambers at Manchester detected anomalous V- and K-particle decays, revealing "strange" particles like kaons and lambda hyperons with lifetimes around 10^{-10} seconds and masses exceeding protons.[37][38] These findings, from events at energies unattainable in early accelerators, spurred parity violation studies and strangeness conservation, with cosmic ray fluxes enabling rare event statistics despite low event rates.[37] By the 1950s, as particle accelerators reached GeV energies, cosmic rays remained vital for ultra-relativistic studies, though emulsion and counter arrays shifted focus to air showers and composition.[39][40]Advances in Energy Measurement and Source Theories (1960s–Present)
In the 1960s, large-scale ground-based arrays for detecting extensive air showers enabled measurements of cosmic rays up to energies of eV, with John Linsley's 1962 detection at Volcano Ranch marking the first such event using scintillator tanks spaced over several kilometers.[41] Subsequent arrays like Haverah Park, operational from 1967 with over 200 water-Cherenkov detectors spanning 12 km², improved flux statistics and energy reconstruction for events above eV by correlating particle arrival times and densities.[41] Balloon-borne and early satellite experiments, such as those in the 1970s, complemented ground data by directly sampling primary spectra, revealing the "knee" feature around eV where flux steepens, attributed to the maximum rigidity of galactic acceleration sites.[42] The 1990s saw fluorescence telescopes, like the Fly's Eye detector, provide calorimetric energy measurements by observing nitrogen de-excitation light in air showers, yielding the 1991 "Oh-My-God" particle at approximately eV, equivalent to a baseball's kinetic energy.[43] Ground arrays such as AGASA reported similar ultra-high-energy events up to eV, though with systematic uncertainties in shower size-to-energy calibration exceeding 20%.[41] The Pierre Auger Observatory, commencing operations in 2004, introduced hybrid detection combining fluorescence telescopes with 1,660 surface water-Cherenkov detectors over 3,000 km², achieving energy resolution below 20% and systematic uncertainties around 14% for events above eV through cross-calibration of shower profiles and lateral distributions.[44] This precision confirmed the spectral "ankle" at eV and a suppression beyond eV, aligning with predictions.[45] Theoretical advances intertwined with measurements, as the 1966 Greisen-Zatsepin-Kuzmin (GZK) limit predicted a cutoff near eV from proton interactions with cosmic microwave background photons, confining ultra-high-energy cosmic ray (UHECR) sources to within 100 Mpc.[41] Observations by HiRes in 2008 and Pierre Auger confirmed this suppression at 5-6 sigma, supporting extragalactic propagation models over exotic explanations for pre-cutoff fluxes.[45] For lower energies, diffusive shock acceleration in supernova remnants (SNRs) gained empirical support; Fermi Gamma-ray Space Telescope data from 2013 revealed pion-decay signatures in remnants like IC 443 and W44, indicating protons accelerated to PeV energies produce observed gamma rays.[46] UHECR source models evolved toward active galactic nuclei and gamma-ray bursts, bolstered by Pierre Auger's 2007 correlation of events above eV with nearby AGN, though refined analyses emphasize composition-dependent propagation.[41] Recent dipole anisotropy measurements, with amplitudes of 6-7% above 8 EeV pointing toward Centaurus, further evidence extragalactic dominance and coherent galactic outflow.[47] Ongoing upgrades like AugerPrime enhance muon detection for composition discrimination, probing source transitions empirically.[44]Propagation and Modulation
Interstellar and Heliospheric Transport
Cosmic rays originating from galactic sources propagate through the interstellar medium primarily via spatial diffusion, resulting from resonant scattering by Alfvén waves and magnetic turbulence associated with the galactic magnetic field, which has a strength of approximately 3–5 μG.[48] This process is anisotropic, with parallel diffusion coefficients exceeding perpendicular ones by factors of 10–100, depending on turbulence levels above 5% of the ordered field.[49] Convection, driven by large-scale galactic winds at velocities of 10–50 km/s, also contributes to outward transport, particularly for lower-rigidity particles, while adiabatic energy losses occur during expansion in low-density regions.[50] The effective diffusion coefficient scales with particle rigidity as , inferred from secondary-to-primary ratios like boron-to-carbon, which constrain propagation parameters.[51] Residence times in the Galaxy range from to years for GeV–TeV nuclei, as determined from the decay of radioactive isotopes such as (half-life 1.4 Myr) relative to stable .[52] The local interstellar spectrum (LIS), representing the flux just beyond the heliopause, has been directly measured by Voyager 1 since its crossing on August 25, 2012, at approximately 122 AU, revealing intensities for protons above 200 MeV/nuc about 10–20% higher than at 1 AU during solar minimum, with greater suppression for lower energies due to prior heliospheric effects.[53] Voyager 2 confirmed similar spectra after its 2018 crossing at 119 AU, providing complementary data on electrons and heavier nuclei down to 3 MeV/nuc.[54] These measurements validate models where interstellar cosmic rays, upon entering the heliosphere—a plasma bubble extending roughly 100–120 AU carved by the solar wind at 300–800 km/s—undergo reduced flux via multiple mechanisms: diffusive scattering on interplanetary magnetic field fluctuations (turbulence level ~5–10%), convection outward with the solar wind, gradient and curvature drifts (polarity-dependent over the 22-year solar cycle), and adiabatic deceleration during radial expansion.[55] Heliospheric modulation is energy- and charge-sign dependent, suppressing fluxes below ~10 GeV/nuc by factors of 2–10 relative to the LIS, with the effect quantified by the modulation potential in force-field approximations during solar minimum to maximum, respectively.[56] Protons experience stronger modulation than electrons due to differing diffusion coefficients and drift efficiencies, as evidenced by Voyager's observed spectral hardening beyond the heliopause.[57] The heliospheric current sheet's wavy structure enhances drift for positively charged particles during A>0 polarity epochs (e.g., 1990–2000, 2013–present), allowing access to polar regions and reducing overall suppression.[58] These processes ensure that observed Earth fluxes reflect a filtered subset of the interstellar population, with minimal alteration for ultra-high-energy cosmic rays above 100 GeV, where gyroradii exceed heliospheric scales.[59]Solar Cycle Modulation Effects
The flux of galactic cosmic rays (GCRs) at Earth is modulated by solar activity primarily through the heliospheric magnetic field (HMF) embedded in the solar wind, which scatters, drifts, and convects charged particles away from the inner heliosphere.[60] This modulation is most pronounced for particles with rigidities below approximately 10 GV, corresponding to energies of a few GeV per nucleon, where diffusion and drift effects dominate over the weaker influence at higher energies.[60] During periods of high solar activity, enhanced solar wind speeds (up to 800 km/s or more) and increased HMF strength (from ~3-5 nT at solar minimum to 5-7 nT at maximum) amplify these effects, reducing GCR intensities by 20-30% at 1 GV rigidity compared to solar minimum levels.[61] Observations from ground-based neutron monitors and space instruments, such as the Advanced Composition Explorer (ACE) satellite, confirm an anticorrelation between GCR intensity and the 11-year sunspot cycle, with minima in flux occurring near solar maximum (e.g., reduced intensities during the 2014 solar maximum compared to the 2009 minimum).[61] For instance, over solar cycles 23 and 24 (1996-2019), proton fluxes at ~1 GeV showed variations of up to 50% between minima and maxima, with cycle 24 exhibiting weaker modulation due to lower overall solar activity.[61] Data from the Alpha Magnetic Spectrometer (AMS-02) on the International Space Station further reveal that this 11-year variation superimposes on a longer 22-year Hale cycle tied to HMF polarity reversals, which alter drift patterns: positively charged particles drift inward more efficiently toward the heliospheric current sheet during positive polarity epochs (A>0, like 1990s-2010s), leading to higher fluxes at Earth during those minima.[55] The energy spectrum of modulation shows a steeper decline in flux at lower rigidities during solar maximum, flattening toward higher energies where GCRs penetrate more readily; for example, helium nuclei fluxes measured by AMS-02 decreased by factors of 2-3 at 1 GV from 2011 (deep solar minimum) to 2014 (maximum), but only ~10% at 10 GV.[62] This is often parameterized using the force-field approximation, where the modulation potential φ (in MV) peaks at ~600-900 MV during solar maximum and drops to ~300-500 MV at minimum, effectively describing the average suppression as an electrostatic barrier scaled by particle charge-to-mass ratio (φ = (Z/A) ϕ).[63] Empirical fits to AMS-02 proton and helium data from 2011-2023 validate this approach, with φ tracking sunspot numbers but revealing residual asymmetries from drifts not fully captured by the simple model.[64] Solar cycle modulation also exhibits spatial gradients, with higher GCR fluxes at higher heliographic latitudes due to reduced turbulence away from the wavy current sheet during maximum; Voyager spacecraft data from the 1980s-2000s showed latitudinal differences of 10-20% in intensities.[60] Recent analyses of cycle 24 (2008-2019) indicate weaker overall modulation than cycle 23, attributed to subdued HMF growth and slower solar wind recovery post-2009 minimum, resulting in prolonged high fluxes that persisted into 2013.[65] These variations influence secondary particle production in Earth's atmosphere but diminish rapidly beyond ~10 AU, where local interstellar spectra dominate.[60]Mathematical Modeling via Parker Equation
The Parker transport equation, derived by Eugene N. Parker in 1965, mathematically describes the phase-space evolution of cosmic ray particles in expanding solar wind flows, such as those in the heliosphere, by balancing convective, diffusive, and energetic particle interactions.[66] This partial differential equation underpins most numerical models of galactic cosmic ray (GCR) modulation, capturing how the solar wind's outward flow and turbulent magnetic fields reduce GCR intensities observed at Earth compared to interstellar values.[67] The equation assumes gyrotropic particle distributions and isotropic pitch-angle scattering, deriving from the Boltzmann equation under quasi-linear approximations for pitch-angle diffusion.[68] In its standard spherical coordinate form for steady-state, radial symmetry in the heliosphere, the equation for the omnidirectional distribution function (proportional to the cosmic ray intensity ) is: where is the solar wind velocity (typically ~400–800 km/s radially outward), is the spatial diffusion tensor (dominated by parallel components ~10^{20}–10^{22} cm²/s at GeV energies, dependent on magnetic turbulence), represents stochastic momentum diffusion from second-order Fermi processes or drifts (often ~10^{-6}–10^{-3} per solar wind crossing time), and is a source term for local injection (negligible for GCRs but relevant near shocks).[69] [70] The convection term drives particle outflow, diffusion enables inward propagation against the wind, the adiabatic term accounts for cooling from spherical expansion (with at heliocentric distance ), and momentum diffusion introduces energy-dependent drifts.[71] Solutions to the equation, often obtained via finite-difference numerics or stochastic differential equations, reproduce observed GCR spectral hardening below ~10 GeV and the ~20–30% intensity variation over the 11-year solar cycle, with minima during solar maximum due to enhanced diffusion suppression from stronger heliospheric current sheet waviness and magnetic turbulence.[72] [73] Boundary conditions typically set to local interstellar spectrum values (e.g., ~4.5 × 10^{-3} (E/1 GeV)^{-2.7} particles cm^{-2} s^{-1} sr^{-1} GeV^{-1} at 1 AU equivalent) at the heliopause (~120–150 AU), while inner boundary fluxes at ~0.3 AU incorporate drift effects from the interplanetary magnetic field polarity reversal every ~11 years.[65] Extensions include time-dependence for drift modulations, 3D geometry for current sheet tilt (increasing from ~10° at minimum to ~60° at maximum), and turbulence models linking to observed solar wind Alfvénic fluctuations. Validation against neutron monitor data (e.g., Climax or Oulu stations recording ~10% annual flux changes) and spacecraft measurements (e.g., Voyager 1 crossing the heliopause on August 25, 2012, revealing a ~10% intensity jump) confirms the model's causal fidelity, though discrepancies at ultra-high energies (>100 GeV) highlight needs for improved pitch-angle scattering theories.[74] [75]Origins and Types
Primary Cosmic Rays
Primary cosmic rays are high-energy charged particles and nuclei accelerated at astrophysical sources outside the solar system, which propagate through interstellar and interplanetary space before entering Earth's upper atmosphere.[76] These particles constitute the initial component of cosmic radiation observed at Earth, distinct from secondaries produced by atmospheric interactions.[77] Their composition by particle number is dominated by protons, comprising approximately 89%, followed by helium nuclei (alpha particles) at about 10%, with the remaining ~1% consisting of heavier atomic nuclei (such as carbon, oxygen, and iron), electrons, positrons, and other leptons.[78] This distribution reflects enrichment in refractory elements compared to solar system abundances, consistent with acceleration mechanisms favoring ions from stellar ejecta.[19] Energies of primary cosmic rays range from ~10^9 eV (1 GeV) to over 10^20 eV, with the differential flux following a steep power-law spectrum, J(E) ∝ E^{-2.7} for energies between 10^{11} eV and 10^{15} eV, flattening slightly at higher energies near the "knee" around 3–5 × 10^{15} eV.[79] [19] At the top of the atmosphere, the integrated flux for particles above 1 GeV/nucleon is approximately 1 particle per cm² per second, decreasing inversely with energy.[80] Galactic primaries up to the knee are primarily accelerated via diffusive shock acceleration in supernova remnants, while ultra-high-energy examples likely originate from extragalactic processes such as active galactic nuclei or gamma-ray bursts, though exact mechanisms remain under investigation.[76] Measurements from balloon-borne and space-based detectors, including AMS-02 on the International Space Station, confirm these compositional and spectral features with high precision, revealing subtle deviations attributable to propagation effects like spallation and energy losses.[81]Secondary Cosmic Rays
Secondary cosmic rays consist of particles generated through interactions between primary cosmic rays and nuclei in Earth's atmosphere. These interactions initiate extensive air showers, where high-energy primaries, predominantly protons, collide with atmospheric constituents such as nitrogen and oxygen, producing a cascade of lighter particles.[82] The process begins at altitudes of approximately 20-30 km, with particle multiplicity peaking around 10-15 km before attenuation through further interactions and decays.[12] The primary mechanisms involve hadronic interactions yielding pions and kaons, which promptly decay into muons and neutrinos, alongside electromagnetic cascades from photons and electrons generating further pairs via bremsstrahlung and pair production. Neutral pions decay into gamma rays, contributing to the electromagnetic component, while charged pions and kaons produce muons that dominate the penetrating radiation reaching sea level due to their weak interactions and relativistic speeds minimizing energy loss.[83] Neutrinos, produced copiously in pion and kaon decays, traverse the atmosphere undetected by conventional ground-based detectors.[84] At sea level, the flux of secondary cosmic rays is characterized by muons comprising about 70-80% of charged particles, with an integrated flux exceeding 1 muon per cm² per minute and a mean energy of approximately 4 GeV. Electrons and positrons, arising mainly from muon decays and atmospheric interactions, constitute roughly 10%, alongside minor contributions from hadrons and gamma rays. The muon flux for momenta above 1 GeV/c measures around 60-70 m⁻² s⁻¹ sr⁻¹, varying with zenith angle and modulated by atmospheric density.[85] [86] This composition reflects selective survival: muons penetrate deeply owing to their long lifetime dilated by Lorentz factors, whereas electrons and hadrons are absorbed higher up.[77] These secondaries enable indirect probing of primary cosmic ray properties, as ground-level detectors capture the shower remnants rather than primaries, which rarely reach the surface. Air shower arrays exploit the lateral distribution of charged secondaries to reconstruct primary energies, often exceeding 10¹⁸ eV.[12] Variations in secondary fluxes, influenced by geomagnetic fields and solar activity, provide insights into propagation effects, though atmospheric production efficiencies depend on primary spectra and interaction cross-sections measured in accelerator experiments.[83]Ultra-High-Energy Cosmic Rays and Antimatter
Ultra-high-energy cosmic rays (UHECRs) are charged particles, primarily protons and heavier atomic nuclei, with kinetic energies exceeding electronvolts (EeV), far surpassing the highest energies achievable in terrestrial particle accelerators like the Large Hadron Collider, which reaches approximately eV per proton.[87] Their flux is exceedingly low, dropping to about particles per square kilometer per steradian per year above eV, necessitating vast detector arrays spanning hundreds of square kilometers for observation. The most energetic event recorded, dubbed the "Oh-My-God" particle, attained roughly eV in 1991 by the Fly's Eye detector, equivalent to the kinetic energy of a baseball thrown at 100 km/h concentrated in a single proton.[87] UHECRs are detected indirectly through the extensive air showers they induce upon entering Earth's atmosphere, where a single primary particle generates cascades of up to secondary particles, including muons, electrons, and photons, spanning several kilometers across the ground. Hybrid observatories like the Pierre Auger Observatory in Argentina, covering 3000 km² with over 1600 water-Cherenkov surface detectors and 27 fluorescence telescopes, measure shower profiles via the depth of maximum development () and muon content to infer primary composition and energy. Recent data from Telescope Array in Utah confirmed a 240 EeV event on May 27, 2024, highlighting ongoing detections despite rarity.[5] Composition analyses indicate a mix dominated by protons (light elements) at the highest energies, transitioning toward heavier nuclei like helium or iron at lower UHE thresholds, consistent with extragalactic acceleration mechanisms such as shocks in active galactic nuclei or gamma-ray bursts, constrained by the Greisen-Zatsepin-Kuzmin (GZK) limit that attenuates fluxes above eV due to photopion production on cosmic microwave background photons.[87] No primary antimatter components, such as antiprotons or anti-nuclei, have been identified among UHECRs, with composition studies showing no anomalous signals in shower observables that would indicate annihilation products or differing interaction profiles.[87] Antimatter in cosmic rays is predominantly secondary, arising from pair production or spallation in interstellar medium interactions of lower-energy primaries, with antiproton fluxes measured at ~1% of protons below 100 GeV by experiments like AMS-02 on the International Space Station, but diminishing at UHE scales due to energy-dependent production thresholds and propagation losses.[88] Primordial or source-originated UHE antimatter would face severe attenuation: charged antiparticles propagating through the Milky Way encounter hydrogen densities of ~1 cm^{-3}, yielding annihilation optical depths of order unity over galactic scales (~10 kpc), rendering distant extragalactic antimatter fluxes negligible compared to observed matter-dominated UHECRs. Searches for antihelium or heavier anti-nuclei, which could signal antimatter domains, yield upper limits below relative to matter nuclei even at TeV energies, with no extension to UHECR regimes due to detection challenges in air showers, where matter and antimatter primaries produce visually indistinguishable hadronic cascades.[89] Theoretical models invoking extragalactic UHE antiparticles predict contributions below detectable thresholds, consistent with the absence of gamma-ray signatures from large-scale matter-antimatter interfaces, which would emit diffuse annihilation radiation unobserved by Fermi-LAT. Thus, UHECR observations reinforce a baryon-asymmetric universe, with antimatter confined to fleeting secondary productions rather than primary fluxes.[87]Detection Methods
Direct Detection Techniques
Direct detection techniques measure primary cosmic rays before they interact significantly with Earth's atmosphere, requiring instruments at high altitudes or in space to capture incoming particles with high fidelity. These methods typically involve multi-layer detectors that identify particle species through charge (Z) via energy loss (dE/dx) measurements in gaseous or solid trackers, momentum via curvature in magnetic fields (rigidity R = pc/Ze), velocity via time-of-flight (TOF) or Cherenkov radiation, and total energy via electromagnetic or hadronic calorimetry.[90] Transition radiation detectors (TRD) and ring-imaging Cherenkov (RICH) systems further distinguish leptons from hadrons by exploiting relativistic effects.[91] Such setups achieve particle identification efficiencies exceeding 90% for protons and helium up to TeV energies, though acceptance is limited by detector area (typically ~1 m²) and exposure time.[92] High-altitude balloon platforms, reaching ~40 km, enable direct sampling with reduced atmospheric overburden (~5 g/cm² residual), facilitating long-duration flights (up to weeks) via superpressure or zero-pressure designs, often launched from Antarctica for polar circulation. The Balloon-borne Experiment with a Superconducting Spectrometer (BESS) employed a 0.8 T superconducting magnet, drift chambers, and TOF scintillators to measure proton and helium spectra below 1 TeV/nucleus during flights like BESS-Polar II in 2007-2008, yielding fluxes precise to ~5% and setting stringent limits on antihelium (<10^{-6} relative to helium).[93] Similarly, the Cosmic Ray Energetics and Mass (CREAM) experiment, with silicon charge detectors and a tungsten/sampling calorimeter, accumulated 161 days of exposure across multiple Antarctic flights from 2004-2015, extending composition measurements of nuclei up to iron to ~10^{15} eV.[94] These balloon missions provide critical data on spectral indices and cutoff features but suffer from variable exposure and geomagnetic effects at lower rigidities (<10 GV).[95] Satellite and space station-based instruments offer stable, long-term operation above the atmosphere, with the International Space Station (ISS) providing a unique low-Earth orbit platform. The Payload for Antimatter Matter Particle Astrophysics (PAMELA), operational from June 2006 to 2016 on the Resurs-DK1 satellite, used a permanent magnet (0.43 T), silicon trackers, and neutron detector to map proton and helium rigidities from 1 GV to 1.2 TV, revealing a spectral hardening above 200 GV inconsistent with simple power-law models.[96] The Alpha Magnetic Spectrometer-02 (AMS-02), deployed on the ISS in May 2011, integrates a 0.86 T superconducting magnet, nine-layer silicon tracker, TRD, RICH, and dual-sided calorimeter, amassing over 230 billion proton events and 7 billion helium events by 2023, with precision enabling detection of flux break structures at 300 GV for protons and 200 GV for helium, alongside searches for primordial antimatter.[97] AMS-02's ~0.5 m² sr acceptance and continuous data stream surpass prior missions, though radiation damage to silicon layers necessitates redundancy.[98] These techniques probe cosmic ray origins, acceleration, and propagation up to ~PeV energies, where fluxes drop to ~1 particle/m²/s/sr, but cannot access ultra-high energies (>10^{17} eV) due to rarity and finite apertures, necessitating hybrid approaches with indirect ground arrays. Data from direct detectors reveal deviations from expected diffusive propagation models, such as rigidity-dependent hardening, attributed to source spectra or propagation effects rather than instrumental bias, as cross-verified across missions.[92] Ongoing upgrades, like AMS-02's tracker augmentation in 2025, aim to boost acceptance by 50% for extended antimatter and dark matter indirect searches.[99]Indirect Detection and Air Shower Arrays
High-energy cosmic rays, particularly those exceeding 10^{15} eV, interact with atmospheric nuclei to produce extensive air showers (EAS), cascades of secondary particles including electrons, photons, muons, and hadrons that can span kilometers.[100] These showers enable indirect detection since primaries rarely reach ground level due to low flux at ultra-high energies.[101] EAS detection infers primary energy, direction, and composition by sampling the shower front at Earth's surface or optically imaging its development.[102] Surface detector arrays form the core of ground-based EAS observatories, deploying spaced particle counters to measure the lateral distribution, density, and arrival times of charged secondaries.[103] Plastic scintillation detectors excel in precise timing and muon identification via pulse shape analysis, while water Cherenkov tanks capture both direct particle signals and isotropic Cherenkov light generated in water, offering robust all-weather operation.[104] Reconstruction algorithms fit observed patterns to simulations, estimating primary energy from total charged particles (scaling as ~1.1 times electromagnetic energy) and composition from muon-to-electron ratios.[105] Optical methods complement particle detection by viewing the shower longitudinally. Fluorescence telescopes record ultraviolet emission from excited nitrogen molecules, providing calorimetric energy measurement via total track light yield, though limited to moonless nights and clear skies.[106] Air Cherenkov techniques detect forward-beamed light from relativistic shower particles, sensitive to early shower stages and useful for distinguishing gamma-ray primaries from hadronic cosmic rays via shower morphology.[107] Hybrid systems integrate these for enhanced precision, cross-validating surface timing with optical profiles to reduce systematics.[108] The Pierre Auger Observatory, spanning 3,000 km² in Argentina, pioneered large-scale hybrid detection with 1,660 water Cherenkov surface stations and 27 fluorescence telescopes, probing cosmic rays above 3 \times 10^{17} eV.[104] It has measured the spectrum up to 10^{20} eV, identified dipole anisotropy, and constrained composition toward heavier nuclei at highest energies.[108] Complementing in the Northern Hemisphere, the Telescope Array covers 700 km² in Utah with 507 scintillator detectors and fluorescence units, detecting events above 10^{18} eV including a record 2.4 \times 10^{20} eV particle in May 2021.[5] [109] These arrays achieve ~10% energy resolution and map arrival directions over steradians, aiding source searches despite atmospheric attenuation uncertainties.[110] Facilities like the High-Altitude Water Cherenkov (HAWC) Observatory in Mexico, with 300 water Cherenkov tanks at 4,100 m elevation, extend indirect detection to TeV-scale showers, primarily for gamma rays but also cosmic-ray muons, enhancing multi-messenger studies.[111] Ongoing upgrades, such as AugerPrime's scintillator tops for muon counting, aim to refine mass discrimination amid debates on shower universality and modeling biases.[101]Terrestrial and Astrophysical Effects
Atmospheric Interactions and Secondary Production
Primary cosmic rays, predominantly protons with energies exceeding 100 MeV, collide inelastically with nuclei such as nitrogen and oxygen in Earth's upper atmosphere, typically at depths of 15-20 g/cm², initiating extensive air showers through hadronic interactions.[19] These collisions produce a spray of secondary particles, including pions (π⁺, π⁻, π⁰), kaons, and other hadrons, via processes like charge exchange and fragmentation, with the leading particle continuing forward while secondaries branch out.[82] Neutral pions decay rapidly (lifetime ~10⁻¹⁶ s) into two gamma rays, which initiate electromagnetic cascades through pair production and bremsstrahlung, generating electrons, positrons, and photons that multiply until reaching critical energy (~80 MeV in air), after which ionization dominates and the shower attenuates.[112] Charged pions and kaons decay primarily into muons and neutrinos (π⁺ → μ⁺ + ν_μ; similar for π⁻), with muons, due to their weak interactions and relativistic speeds, penetrating deeply with minimal energy loss from ionization, radiation, or nuclear interactions.[19] The cascade reaches a maximum intensity, known as the Pfotzer maximum, at altitudes of 10-20 km, where particle production peaks before absorption.[113] At sea level, the secondary flux is dominated by muons, comprising about 70% of detected particles, with a vertical intensity of approximately 1 muon per cm² per minute for energies above 1 GeV and a mean energy of ~4 GeV.[85] Electromagnetic components (electrons, positrons) and hadronic remnants constitute the remainder but are largely absorbed higher in the atmosphere, while neutrinos escape detection at ground level due to low cross-sections.[19] The overall secondary spectrum reflects the primary spectrum softened by atmospheric attenuation, with production yields modeled via Monte Carlo simulations like CORSIKA, accounting for interaction cross-sections measured at accelerators.[114]Radiation Exposure and Biological Implications
Cosmic rays constitute a component of the natural ionizing radiation background to which humans are exposed on Earth, primarily via secondary particles such as muons that penetrate the atmosphere. At sea level, the average annual effective dose from cosmic radiation is approximately 0.3 to 0.4 millisieverts (mSv), representing about 10% of the total natural background dose of around 3 mSv per year.[115][116] This exposure increases significantly with altitude, as thinner atmosphere provides less shielding; for instance, at 10 km altitude typical for commercial flights, doses can reach 5-10 microsieverts (µSv) per hour.[117] Aircrew and frequent flyers receive elevated doses due to prolonged time at high altitudes and latitudes, where geomagnetic shielding is weaker. Occupational exposure for airline pilots and cabin crew averages 1.2 to 5 mSv per year, depending on flight patterns, with long-haul polar routes yielding higher values up to 2.2 mSv annually for captains.[118][119] These levels approach or exceed regulatory limits for radiation workers in some cases, prompting monitoring recommendations, though epidemiological studies show no clear excess cancer risk beyond baseline after accounting for confounders like lifestyle.[120][121] In space beyond low-Earth orbit, cosmic rays—particularly galactic cosmic rays (GCR) and solar particle events—pose substantial risks due to unshielded high-energy ions. Astronauts on missions like those to Mars could accumulate 300-1000 mSv over 2-3 years, far exceeding Earth's annual background and increasing lifetime cancer risk by 3-5% or more, alongside potential central nervous system effects, cardiovascular damage, and degenerative diseases.[122][123] Biological impacts stem from the high linear energy transfer (LET) of heavy ions, which produce dense ionization tracks causing clustered DNA double-strand breaks that are inefficiently repaired, leading to mutations, genomic instability, and non-targeted effects like persistent inflammation.[124][125] Acute effects are rare given the low flux, but stochastic risks dominate, with animal models indicating accelerated aging-like processes including fibrosis and cognitive deficits.[126][127] NASA limits career exposures to constrain risks to acceptable levels, emphasizing the need for improved shielding and countermeasures.[128]