Recent from talks
Nothing was collected or created yet.
Battle of Crete
View on Wikipedia
| Battle of Crete | |||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Part of the Battle of Greece and the Mediterranean theatre | |||||||||
 German Fallschirmjäger landing on Crete, May 1941 | |||||||||
| |||||||||
| Belligerents | |||||||||
|
|
| ||||||||
| Commanders and leaders | |||||||||
|
|
| ||||||||
| Strength | |||||||||
|
United Kingdom: 18,047[1][a] Greece: 10,258[1] – 11,451[2] New Zealand: 7,702[1] Australia: 6,540[1] Total: 42,547[1] |
Germany: 22,000 paratroopers and mountain troops[3] 280 bombers 150 dive bombers 180 fighters 500 transports 80 troop gliders Italy: 2,700 | ||||||||
| Casualties and losses | |||||||||
|
British Commonwealth[4] 3,579+ killed and missing 1,918 wounded 12,254 captured Greece[5] 544+ killed and missing 5,225 captured Material: Royal Navy:[6][b] 12 fleet and 7 auxiliary ships sunk, 22 damaged Royal Air Force: 21 aircraft shot down 12 aircraft destroyed on ground Total: ~23,000 total casualties[7] 4,000 to 6,000 killed[8] (4,000 ground troops, 2,000 sailors) | |||||||||
| Over 500 Greek civilians executed by Axis soldiers. | |||||||||
 | |||||||||
The Battle of Crete (German: Luftlandeschlacht um Kreta, Greek: Μάχη της Κρήτης), codenamed Operation Mercury (German: Unternehmen Merkur), was a major Axis airborne and amphibious operation during World War II to capture the island of Crete. It began on the morning of 20 May 1941, with multiple German airborne landings on Crete. Greek and other Allied forces, along with Cretan civilians, defended the island.[11] After only one day of fighting, the Germans had suffered heavy casualties and the Allied troops were confident that they would defeat the invasion. The next day, through communication failures, Allied tactical hesitation, and German offensive operations, Maleme Airfield in western Crete fell, enabling the Germans to land reinforcements and overwhelm the defensive positions on the north of the island. Allied forces withdrew to the south coast. More than half were evacuated by the British Royal Navy and the remainder surrendered or joined the Cretan resistance. The defence of Crete evolved into a costly naval engagement; by the end of the campaign the Royal Navy's eastern Mediterranean strength had been reduced to only two battleships and three cruisers.[12]
The Battle of Crete was the first occasion where Fallschirmjäger (German paratroops) were used en masse, the first mainly airborne invasion in military history, the first time the Allies made significant use of intelligence from decrypted German messages from the Enigma machine,[13][14] and the first time German troops encountered mass resistance from a civilian population.[15]
Due to the number of casualties and the belief that airborne forces no longer had the advantage of surprise, Hitler became reluctant to authorise further large airborne operations, preferring instead to employ paratroopers as ground troops.[16]
In contrast, the Western allies were impressed by the potential of paratroopers and started to form airborne-assault and airfield-defence regiments.[17]
Background
[edit]British forces had initially garrisoned Crete when the Italians attacked Greece on 28 October 1940,[18] enabling the Greek government to employ the Fifth Cretan Division in the mainland campaign.[19] This arrangement suited the British: Crete could provide the Royal Navy with excellent harbours in the eastern Mediterranean, from which it could threaten the Axis south-eastern flank,[20] and the Ploiești oil fields in Romania would be within range of British bombers based on the island.
The Italians were repulsed, but the subsequent German invasion of April 1941 (Operation Marita), succeeded in overrunning mainland Greece. At the end of the month, 57,000 Allied troops were evacuated by the Royal Navy. Some were sent to Crete to bolster its garrison until fresh forces could be organised, although most had lost their heavy equipment.[21] Winston Churchill, the British prime minister, sent a telegram to the Chief of the Imperial General Staff, General Sir John Dill: "To lose Crete because we had not sufficient bulk of forces there would be a crime."[22]
The German Army High Command (Oberkommando des Heeres, OKH) was preoccupied with finalizing preparations for Operation Barbarossa, the invasion of the Soviet Union, and was largely opposed to a German attack on Crete.[23] However, Hitler remained concerned about attacks in other theatres, in particular on his Romanian fuel supply,[19] and Luftwaffe commanders were enthusiastic about the idea of seizing Crete by a daring airborne attack.[24] The desire to regain prestige after their defeat by the Royal Air Force (RAF) in the Battle of Britain the year before, may also have played a role in their thinking, especially before the advent of the much more important invasion of the Soviet Union.[25] Hitler was won over by the audacious proposal and in Directive 31 he asserted that "Crete... will be the operational base from which to carry on the air war in the Eastern Mediterranean, in co-ordination with the situation in North Africa."[26] The directive also stated that the operation was to be in May[25] and must not be allowed to interfere with the planned campaign against the Soviet Union.[25] Before the invasion, the Germans conducted a bombing campaign to establish air superiority and forced the RAF to move its remaining aeroplanes to Alexandria in Egypt.[27]
Prelude
[edit]Order of battle
[edit]Allied forces
[edit]No RAF units were based permanently at Crete until April 1941, but airfield construction had begun, radar sites had been built and stores delivered. Equipment was scarce in the Mediterranean and in the backwater of Crete. The British forces had seven commanders in seven months. In early April, airfields at Maleme and Heraklion and the landing strip at Rethymno on the north coast were ready and another strip at Pediada-Kastelli was nearly finished. After the German invasion of Greece, the role of the Crete garrison changed from the defence of a naval anchorage to preparing to repel an invasion. On 17 April, Group Captain George Beamish was appointed Senior Air Officer, Crete, taking over from a flight-lieutenant whose duties and instructions had been only vaguely defined. Beamish was ordered to prepare the reception of the Bristol Blenheim bombers of 30 and 203 squadrons from Egypt and the remaining fighter aircraft from Greece, to cover the evacuation of W Force, which enabled the transfer of 25,000 British and Dominion troops to the island, preparatory to their relief by fresh troops from Egypt.[28]
The navy tried to deliver 27,000 long tons (27,000 t) of supplies from 1–20 May 1941, but Luftwaffe attacks forced most ships to turn back, and only 2,700 long tons (2,700 t) were delivered. Only about 3,500 trained British and Greek soldiers were on the island, and the defence devolved to the shaken and poorly equipped troops from Greece, assisted by the last fighters of 33, 80 and 112 squadrons and a squadron of the Fleet Air Arm, once the Blenheims were ordered back to Egypt. In mid-May, the four squadrons had about two dozen aircraft, of which only about twelve were serviceable due to a lack of tools and spares. The unfinished ground at Pediada-Kastelli was blocked with trenches and heaps of soil and all but narrow flight paths were blocked at Heraklion and Rethymno by barrels full of earth. At Maleme, blast pens were built for the aircraft, and barrels full of petrol were kept ready to be ignited by machine-gun fire. Around each ground, a few field guns, anti-aircraft guns, two infantry tanks and two or three light tanks were sited. The three areas were made into independent sectors, but there were only eight QF 3-inch and twenty Bofors 40 mm anti-aircraft guns.[29]

On 30 April 1941, Major-general Bernard Freyberg VC a New Zealand Army officer, was appointed commander of the Allied forces on Crete (Creforce).[30] He was Churchill's personal choice, as the British Prime Minister admired his loyalty and the bravery he had shown during the First World War.[31] By May, the Greek forces consisted of approximately 9,000 troops: three battalions of the 5th Greek Division, which had been left behind when the rest of the unit had been transferred to the mainland against the German invasion; the Cretan Gendarmerie (2,500 men); the Heraklion Garrison Battalion, a defence unit made up mostly of transport and supply personnel; and remnants of the 12th and 20th Greek divisions, which had also escaped from the mainland to Crete and were organised under British command. Cadets from the Gendarmerie academy and recruits from Greek training centres in the Peloponnese had been transferred to Crete to replace the trained soldiers sent to fight on the mainland. These troops were already organised into numbered recruit training regiments, and it was decided to use this structure to organise the Greek troops, supplementing them with experienced men arriving from the mainland.
The British Commonwealth contingent consisted of the original 14,000-man British garrison and another 25,000 British and Commonwealth troops evacuated from the mainland. These evacuees were a combination of intact units, composite units improvised locally, stragglers from every type of army unit, and deserters; most of them lacked heavy equipment. The main formed units were the 2nd New Zealand Division, less the 6th Brigade and division headquarters; the 19th Australian Brigade Group; and the 14th Infantry Brigade of the British 6th Division. There were about 15,000 front-line Commonwealth infantry, augmented by about 5,000 non-infantry personnel equipped as infantry and a composite Australian artillery battery.[32] On 4 May, Freyberg sent a message to the British commander in the Middle East, General Archibald Wavell, requesting the evacuation of about 10,000 unwanted personnel who did not have weapons and had "little or no employment other than getting into trouble with the civil population". As the weeks passed, some 3,200 British, 2,500 Australian and 1,300 New Zealander troops were evacuated to Egypt, but it became evident that it would not be possible to remove all the unwanted troops. Between the night of 15 May and morning of 16 May, the allied forces were reinforced by the 2nd Battalion of the Leicester Regiment, which had been transported from Alexandria to Heraklion by HMS Gloucester and HMS Fiji.[33]
On 17 May, the garrison on Crete included about 15,000 Britons, 7,750 New Zealanders, 6,500 Australians and 10,200 Greeks.[34] On the morning of 19 May, these were augmented by a further 700 men of the Argyll and Sutherland Highlanders, who had been transported from Alexandria to Tymbaki overnight by HMS Glengyle.[33]
Axis forces
[edit]
On 25 April, Hitler signed Directive 28, ordering the invasion of Crete. The Royal Navy retained control of the waters around Crete, so an amphibious assault would have been a risky proposition. With German air superiority assured, an airborne invasion was chosen. This was to be the first big airborne invasion, although the Germans had made smaller parachute and glider-borne assaults in the invasions of Denmark and Norway, Belgium, the Netherlands, France and mainland Greece. In Greece, Fallschirmjäger had been dispatched to capture the bridge over the Corinth Canal, which was being readied for demolition by the Royal Engineers. German engineers landed near the bridge in gliders, while parachute infantry attacked the perimeter defence. The bridge was damaged in the fighting, which slowed the German advance and gave the Allies time to evacuate 18,000 troops to Crete and 23,000 to Egypt, albeit with the loss of most of their heavy equipment.[35]

In May, Fliegerkorps XI moved from Germany to the Athens area, but the destruction wrought during the invasion of Greece forced a postponement of the attack to 20 May. New airfields were built, and 280 long-range bombers, 150 dive-bombers, 90 Bf 109s, 90 Bf 110s and 40 reconnaissance aircraft of Fliegerkorps VIII were assembled, along with 530 Ju 52 transport aircraft and 100 gliders. The Bf 109s and Stuka dive-bombers were based on forward airfields at Molaoi, Melos and Karpathos (then Scarpanto), with Corinth and Argos as base airfields. The Bf 110s were based at airfields near Athens, Argos and Corinth, all within 200 mi (320 km) of Crete, and the bomber or reconnaissance machines were accommodated at Athens, Salonica and a detachment on Rhodes, along with bases in Bulgaria at Sofia and Plovdiv, ten of the airfields being all-weather and 200–250 miles (320–400 km) from Crete. The transport aircraft flew from bases near Athens and southern Greece, including Eleusis, Tatoi, Megara and Corinth. British night bombers attacked the areas in the last few nights before the invasion, and Luftwaffe aircraft eliminated the British aircraft on Crete.[36]

The Germans planned to use Fallschirmjäger to capture important points on the island, including airfields that could then be used to fly in supplies and reinforcements. Fliegerkorps XI was to co-ordinate the attack by the 7th Flieger Division, which would land by parachute and glider, followed by the 22nd Air Landing Division once the airfields were secure. The operation was scheduled for 16 May 1941, but was postponed to 20 May, with the 5th Mountain Division replacing the 22nd Air Landing Division. To support the German attack on Crete, eleven Italian submarines took post off Crete or the British bases of Sollum and Alexandria in Egypt.[37][d]
Intelligence
[edit]British
[edit]Major-General Kurt Student did not add an attack on Crete to Operation Marita until March 1941; supply difficulties delayed the assembly of Fliegerkorps XI and its 500 Ju 52s, then more delays forced a postponement until 20 May 1941. The War Cabinet in Britain had expected the Germans to use paratroops in the Balkans, and on 25 March, British decrypts of Luftwaffe Enigma wireless traffic revealed that Fliegerkorps XI was assembling Ju 52s for glider-towing, and British Military Intelligence reported that 250 aircraft were already in the Balkans. On 30 March, Detachment Süssmann, part of the 7th Fliegerdivision, was identified at Plovdiv. Notice of the target of these units did not arrive, but on 18 April it was found that 250 Ju 52s had been withdrawn from routine operations, and on 24 April it became known that Göring had reserved them for a special operation. The operation turned out to be a descent on the Corinth Canal on 26 April, but then a second operation was discovered and that supplies (particularly of fuel), had to be delivered to Fliegerkorps XI by 5 May; a Luftwaffe message referring to Crete for the first time was decrypted on 26 April.[38]
The British Chiefs of Staff were apprehensive that the target could be changed to Cyprus or Syria as a route into Iraq during the Anglo-Iraqi War (2–31 May 1941) and suspected that references to Crete were a deception, despite having no grounds for this, and on 3 May Churchill thought that the attack might be a decoy. The command in Crete had been informed on 18 April, despite the doubts, and Crete was added to a link from the GC & CS to Cairo, while on 16 and 21 April, intelligence that airborne operations were being prepared in Bulgaria was passed on. On 22 April, the HQ in Crete was ordered to burn all material received through the Ultra link, but Churchill ruled that the information must still be provided. When Freyberg took over on 30 April, the information was disguised as information from a spy in Athens. Remaining doubts about an attack on Crete were removed on 1 May, when the Luftwaffe was ordered to stop bombing airfields on the island and mining Souda Bay and to photograph all of the island. By 5 May it was clear that the attack was not imminent and, next day, 17 May was revealed as the expected day for the completion of preparations, along with the operation orders for the plan from the D-day landings in the vicinity of Maleme and Chania, Heraklion, and Rethymno.[38]
German
[edit]
Admiral Wilhelm Canaris, chief of the Abwehr, originally reported 5,000 British troops on Crete and no Greek forces. It is not clear whether Canaris, who had an extensive intelligence network at his disposal, was misinformed or was attempting to sabotage Hitler's plans (Canaris was killed much later in the war for supposedly participating in the 20 July Plot). Abwehr also predicted the Cretan population would welcome the Germans as liberators, due to their strong republican and anti-monarchist feelings and would want to receive the "... favourable terms which had been arranged on the mainland ..."[39] While Eleftherios Venizelos, the late republican prime minister of Greece, had been a Cretan and support for his ideas was strong on the island, the Germans seriously underestimated Cretan loyalty. King George and his entourage escaped from Greece via Crete with the help of Greek and Commonwealth soldiers, Cretan civilians, and even a band of prisoners who had been released from captivity by the Germans. 12th Army Intelligence painted a less optimistic picture, but also underestimated the number of British Commonwealth forces and the number of Greek troops who had been evacuated from the mainland. General Alexander Löhr, the theatre commander, was convinced the island could be taken with two divisions, but decided to keep 6th Mountain Division in Athens as a reserve.
Weapons and equipment
[edit]This section needs additional citations for verification. (May 2017) |
German
[edit]
The Germans used the new 7.5 cm Leichtgeschütz 40 light gun (a recoilless rifle). At 320 lb (150 kg), it weighed 1⁄10 as much as a standard German 75 mm field gun, yet had 2⁄3 of its range. It fired a 13 lb (5.9 kg) shell more than 3 mi (4.8 km). A quarter of the German paratroops jumped with an MP 40 submachine gun, often carried with a bolt-action Karabiner 98k rifle and most German squads had an MG 34 machine gun.[40] The Germans used colour-coded parachutes to distinguish the canisters carrying rifles, ammunition, crew-served weapons and other supplies. Heavy equipment like the Leichtgeschütz 40 were dropped with a special triple-parachute harness to bear the extra weight.
The troops also carried special strips of cloth to unfurl in patterns to signal to low-flying fighters, to co-ordinate air support and for supply drops. The German procedure was for individual weapons to be dropped in canisters, due to their practice of exiting the aircraft at low altitude. This was a flaw that left the paratroopers armed only with knives, pistols and grenades in the first few minutes after landing. Poor design of German parachutes compounded the problem; the standard German harness had only one riser to the canopy and could not be steered. Even the 25 percent of paratroops armed with sub-machine guns were at a disadvantage, given the weapon's limited range. Many Fallschirmjäger were shot before they reached weapons canisters.
Greek
[edit]Greek troops were armed with Mannlicher–Schönauer 6.5 mm mountain carbines or ex-Austrian 8x56R Steyr-Mannlicher M1895 rifles, the latter a part of post-World War I reparations; about 1,000 Greeks carried antique Fusil Gras mle 1874 rifles. The garrison had been stripped of its best crew-served weapons, which were sent to the mainland; there were twelve obsolescent St. Étienne Mle 1907 light machine-guns and forty miscellaneous LMGs. Many Greek soldiers had fewer than thirty rounds of ammunition but could not be supplied by the British, who had no stocks in the correct calibres. Those with insufficient ammunition were posted to the eastern sector of Crete, where the Germans were not expected in force. The 8th Greek Regiment was under strength and many soldiers were poorly trained and poorly equipped. The unit was attached to 10th New Zealand Infantry Brigade (Brigadier Howard Kippenberger), who placed it in a defensive position around the village of Alikianos where, with local civilian volunteers, they held out against the German 7th Engineer Battalion.
Though Kippenberger had referred to them as "...nothing more than malaria-ridden little chaps...with only four weeks of service," the Greek troops repulsed German attacks until they ran out of ammunition, whereupon they began charging with fixed bayonets, overrunning German positions and capturing rifles and ammunition. The engineers had to be reinforced by two battalions of German paratroops, yet the 8th Regiment held on until 27 May, when the Germans made a combined arms assault by Luftwaffe aircraft and mountain troops. The Greek stand helped to protect the retreat of the Commonwealth forces, who were evacuated at Sfakia. Beevor and McDougal Stewart write that the defence of Alikianos gained at least 24 more hours for the completion of the final leg of the evacuation behind Layforce. The troops who were protected as they withdrew had begun the battle with more and better equipment than the 8th Greek Regiment.[citation needed]
British Commonwealth
[edit]British and Commonwealth troops used the standard Lee–Enfield rifle, Bren light machine gun and Vickers medium machine gun. The British had about 85 artillery pieces of various calibres, many of them captured Italian weapons without sights.[41] Anti-aircraft defences consisted of one light anti-aircraft battery equipped with 20 mm automatic cannon, split between the two airfields. The guns were camouflaged, often in nearby olive groves, and some were ordered to hold their fire during the initial assault to mask their positions from German fighters and dive-bombers. The British had nine Matilda IIA infantry tanks of "B" Squadron, 7th Royal Tank Regiment (7th RTR) and sixteen Light Tanks Mark VIB from "C" Squadron, 3rd King's Own Hussars.[42]
The Matildas had 40 mm Ordnance QF 2 pounder guns, which only fired armour-piercing rounds – not effective anti-personnel weapons. (High explosive rounds in small calibres were considered impractical).[42] The tanks were in poor mechanical condition, as the engines were worn and could not be overhauled on Crete. Most tanks were used as mobile pillboxes to be brought up and dug in at strategic points. One Matilda had a damaged turret crank that allowed it to turn clockwise only. Many British tanks broke down in the rough terrain, not in combat. The British and their allies did not possess sufficient Universal Carriers or trucks, which would have provided the mobility and firepower needed for rapid counter-attacks before the invaders could consolidate.[42]
Strategy and tactics
[edit]Operation Mercury
[edit]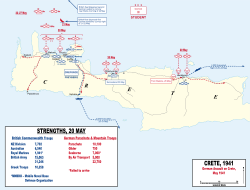
Hitler authorised Unternehmen Merkur (named after the swift Roman god Mercury) with Directive 28; the forces used were to come from airborne and air units already in the area and units intended for Unternehmen Barbarossa were to conclude operations before the end of May, Barbarossa was not to be delayed by the attack on Crete, which had to begin soon or would be cancelled. Planning was rushed and much of Unternehmen Merkur was improvised, including the use of troops who were not trained for airborne assaults.[citation needed] The Germans planned to capture Maleme, but there was debate over the concentration of forces there and the number to be deployed against other objectives, such as the smaller airfields at Heraklion and Rethymno. The Luftwaffe commander, Colonel General Alexander Löhr, and the Kriegsmarine commander, Admiral Karlgeorg Schuster, wanted more emphasis on Maleme, to achieve overwhelming superiority of force.[43] Student wanted to disperse the paratroops more, to maximise the effect of surprise.[43] As the primary objective, Maleme offered several advantages: it was the largest airfield and big enough for heavy transport aircraft, it was close enough to the mainland for air cover from land-based Messerschmitt Bf 109 fighters and it was near the north coast, so seaborne reinforcements could be brought up quickly. A compromise plan by Hermann Göring was agreed, and in the final draft, Maleme was to be captured first, while not ignoring the other objectives.[44]
The invasion force was divided into Kampfgruppen (battlegroups), Centre, West and East, each with a code name following the classical theme established by Mercury; 750 glider-borne troops, 10,000 paratroops, 5,000 airlifted mountain soldiers and 7,000 seaborne troops were allocated to the invasion. The largest proportion of the forces were in Group West. German airborne theory was based on parachuting a small force onto enemy airfields. The force would capture the perimeter and local anti-aircraft guns, allowing a much larger force to land by glider.[45] Freyberg knew this after studying earlier German operations and decided to make the airfields unusable for landing, but was countermanded by the Middle East Command in Alexandria.[46] The staff felt the invasion was doomed now that it had been compromised and may have wanted the airfields intact for the RAF once the invasion was defeated.[46] The Germans were able to land reinforcements without fully operational airfields. One transport pilot crash-landed on a beach, others landed in fields, discharged their cargo and took off again. With the Germans willing to sacrifice some transport aircraft to win the battle, it is not clear whether a decision to destroy the airfields would have made any difference, particularly given the number of troops delivered by expendable gliders.[46]
| Group name | Codename | Commander | Target |
|---|---|---|---|
| Gruppe Mitte (Group Centre) | Mars | Generalmajor Wilhelm Süssmann | Prison Valley, Chania Souda, Rethymno |
| Gruppe West (Group West) | Comet | Generalmajor Eugen Meindl | Maleme |
| Gruppe Ost (Group East) | Orion | Oberst Bruno Bräuer | Heraklion |
Battle
[edit]20 May
[edit]Maleme–Chania sector
[edit]
At 08:00 on 20 May 1941, German paratroopers, jumping out of dozens of Junkers Ju 52 aircraft, landed near Maleme Airfield and the town of Chania. The 21st, 22nd and 23rd New Zealand battalions held Maleme Airfield and the vicinity. The Germans suffered many casualties in the first hours of the invasion: a company of III Battalion, 1st Assault Regiment lost 112 killed out of 126 men, and 400 of 600 men in III Battalion were killed on the first day.[47] Most of the parachutists were engaged by New Zealanders defending the airfield and by Greek forces near Chania. Many gliders following the paratroops were hit by mortar fire seconds after landing, and the New Zealand and Greek defenders almost annihilated the glider troops who landed safely.[47]
Some paratroopers and gliders missed their objectives near both airfields and set up defensive positions to the west of Maleme Airfield and in "Prison Valley" near Chania. Both forces were contained and failed to take the airfields, but the defenders had to deploy to face them.[48] Towards the evening of 20 May, the Germans slowly pushed the New Zealanders back from Hill 107, which overlooked the airfield. Greek police and cadets took part, with the 1st Greek Regiment (Provisional) combining with armed civilians to rout a detachment of German paratroopers dropped at Kastelli. The 8th Greek Regiment and elements of the Cretan forces severely hampered movement by the 95th Reconnaissance Battalion on Kolimbari and Paleochora, where Allied reinforcements from North Africa could be landed.
Rethymno–Heraklion sector
[edit]
A second wave of German transports supported by Luftwaffe and Regia Aeronautica attack aircraft, arrived in the afternoon, dropping more paratroopers and gliders containing assault troops.[49] One group attacked at Rethymno at 16:15 and another attacked at Heraklion at 17:30, where the defenders were waiting for them and inflicted many casualties.
The Rethymno–Heraklion sector was defended by the British 14th Brigade, as well as the 2/4th Australian Infantry Battalion and the Greek 3rd, 7th and "Garrison" (ex-5th Crete Division) battalions. The Greeks lacked equipment and supplies, particularly the Garrison Battalion. The Germans pierced the defensive cordon around Heraklion on the first day, seizing the Greek barracks on the west edge of the town and capturing the docks; the Greeks counter-attacked and recaptured both points. The Germans dropped leaflets threatening dire consequences if the Allies did not surrender immediately. The next day, Heraklion was heavily bombed and the depleted Greek units were relieved and assumed a defensive position on the road to Knossos.[citation needed]

As night fell, none of the German objectives had been secured. Of 493 German transport aircraft used during the airdrop, seven were lost to anti-aircraft fire. The bold plan to attack in four places to maximise surprise, rather than concentrating on one, seemed to have failed, although the reasons were unknown to the Germans at the time.
Among the paratroopers who landed on the first day was former world heavyweight champion boxer Max Schmeling, who held the rank of Gefreiter at the time. Schmeling survived the battle and the war.
21 May
[edit]Overnight, the 22nd New Zealand Infantry Battalion withdrew from Hill 107, leaving Maleme Airfield undefended. During the previous day, the Germans had cut communications between the two westernmost companies of the battalion and the battalion commander, Lieutenant Colonel Leslie Andrew VC, who was on the eastern side of the airfield. The lack of communication was assumed to mean that the battalion had been overrun in the west. With the weakened state of the eastern elements of the battalion and believing the western elements to have been overrun, Andrew requested reinforcement by the 23rd Battalion.[50] Brigadier James Hargest denied the request on the mistaken grounds that the 23rd Battalion was busy repulsing parachutists in its sector. After a failed counter-attack late in the day on 20 May, with the eastern elements of his battalion, Andrew withdrew under cover of darkness to regroup, with the consent of Hargest.[51] Captain Campbell, commanding the westernmost company of the 22nd Battalion, out of contact with Andrew, did not learn of the withdrawal of the 22nd Battalion until early in the morning, at which point he also withdrew from the west of the airfield.[52][53] This misunderstanding, representative of the failings of communication and co-ordination in the defence of Crete, cost the Allies the airfield and allowed the Germans to reinforce their invasion force unopposed.[54] In Athens, Student decided to concentrate on Maleme on 21 May, as this was the area where the most progress had been made and because an early morning reconnaissance flight over Maleme Airfield was unopposed.[51][55] The Germans quickly exploited the withdrawal from Hill 107 to take control of Maleme Airfield, just as a sea landing took place nearby. The Allies continued to bombard the area as Ju 52s flew in units of the 5th Mountain Division at night.[52]
Maleme Airfield counter-attack
[edit]
In the afternoon of 21 May 1941, Freyberg ordered a counter-attack to retake Maleme Airfield during the night of 21/22 May. The 2/7th Battalion was to move 18 miles (29 km) north to relieve the 20th Battalion, which would participate in the attack. The 2/7th Battalion had no transport, and vehicles for the battalion were delayed by German aircraft. By the time the battalion moved north to relieve 20th Battalion for the counter-attack, it was 23:30, and the 20th Battalion took three hours to reach the staging area, with its first elements arriving around 02:45.[52] The counter-attack began at 03:30 but failed because of German daylight air support.[51] (Brigadier George Alan Vasey and Lieutenant-Colonel William Cremor have criticised Freyberg for not properly defending Maleme Airfield.)[56] Hargest also blamed Freyberg for the loss of the airfield.[57]
Axis landing attempt, 21/22 May
[edit]
An Axis convoy of around 20 caïques, escorted by the Italian torpedo boat Lupo, tried to land German reinforcements near Maleme. Force D under Rear-Admiral Irvine Glennie, with three light cruisers and four destroyers, intercepted the convoy before midnight; the convoy turned back with the loss of more than half of its boats, despite Lupo's defence.[58] The attacking British force suffered only slight damage on cruiser HMS Orion caused by friendly fire.[59] About 2⁄3 of the German force of more than 2,000 men was saved by the Italian naval commander, Francesco Mimbelli, against an overwhelmingly superior Allied naval force. A total of 297 German soldiers, two Italian seamen[60] and two British sailors on Orion were killed.[61] Eight caiques were caught and sunk, while at least another six managed to get away,[62] along with three Italian escorting motor-sailing boats.[61] Only one caïque and one cutter from the convoy reached Crete. The caïque landed 3 officers and 110 German soldiers near Cape Spatha, while the cutter arrived safely in Akrotiri, where her crew was engaged by a British Army patrol[63] and took heavy casualties. Of the German soldiers who landed at Akrotiri, only one managed to get through the British lines and join the German paratroopers already fighting for Chania.[64] According to other authors, only one German officer and 35 men from the 100th Regiment landed from the caïque that arrived in Crete.[65]
22 May
[edit]Maleme
[edit]The defending force organised for a night counter-attack on Maleme by two New Zealand battalions, the 20th Battalion of the 4th Brigade and the 28th Maori Battalion of the 5th Brigade. A New Zealand officer present at the battle claimed a long delay ordering the planned counter-attack turned a night attack into a day attack, which led to its failure.[55] Fears of a sea landing meant that a number of units that could have taken part in the attack were left in place, although this possibility was removed by the Royal Navy which arrived too late for the plans to be changed. The delayed counter-attack on the airfield came in daylight on 22 May, when the troops faced Stuka dive bombers, dug-in paratroops and mountain troops. The attack slowly petered out and failed to retake the airfield, which forced the defenders into withdrawals to the eastern end of the island, to avoid being out-flanked.[55]
Axis landing attempt, 22/23 May
[edit]
Admiral Andrew Cunningham sent Force C (three cruisers and four destroyers, commanded by Rear Admiral Edward Leigh Stuart King) into the Aegean Sea through the Kasos Strait, to attack a second flotilla of transports, escorted by the Italian torpedo boat Sagittario. The force sank an isolated caïque at 08:30, saving itself from an air attack that struck the cruiser HMS Naiad as the German pilots tried to avoid killing their troops in the water. The British squadron was under constant air attack and, short of anti-aircraft ammunition, steamed on toward Milos, sighting Sagittario at 10:00. King made the "difficult" decision not to press the attack, despite his overpowering advantage, because of the shortage of ammunition and the severity of the air attacks.[66] The transports were defended by a torpedo charge by Sagittario, which also laid a smoke screen and traded fire with the British force,[67][68] trying to lure them to a different direction. Indeed, King was unaware that a major enemy convoy was ahead of his force until 11:00.[61] Eventually, the convoy and its escort managed to slip away undamaged. King's ships, despite their failure to destroy the German troop transports, had succeeded in forcing the Axis to abort the landing by their mere presence at sea. During the search and withdrawal from the area, Force C suffered many losses to German bombers. Naiad was damaged by near misses and the cruiser HMS Carlisle was hit. Cunningham later criticised King, saying that the safest place during the air attack was amongst the flotilla of caïques.[67][68]
While Force C made its attack on the convoy, Force A1 (Rear Admiral H B Rawlings), Force B (Captain Henry A Rowley) and Glennie's Force D converged west of Antikythera. Concerned about the level of anti-aircraft ammunition available following repeated air attacks, the combined force was ordered to report on their stock of high-angle ammunition at 09:31. Of the cruisers, HMS Ajax had 40 per cent, Orion 38 per cent, Fiji 30 per cent, HMS Dido 25 per cent and Gloucester only 18 per cent. Ajax, Orion and Dido were ordered to return to Alexandria with Glennie's Force D to rearm but Gloucester and Fiji remained with Rawlings' Force A1.[69]
At 12:25 Force A1, stationed 20 to 30 miles west of Antikythera, received a request from King to support the damaged Naiad. Force A1 headed east into the Kythera Channel, rendezvousing with Force C between 13:30 and 14:00. As the more senior admiral, King took command, with air attacks now inflicting damage on both forces. A bomb struck HMS Warspite and the destroyer HMS Greyhound was sunk. King sent HMS Kandahar and HMS Kingston to pick up survivors, while the cruisers Fiji and Gloucester were ordered respectively at 14:02 and 14:07 to provide anti-aircraft support. Writing in despatches after the battle, Cunningham stated that King was unaware of the shortage of anti-aircraft ammunition in Gloucester and Fiji. At 14:13 King and Rawlings exchanged messages about the shortage of ammunition within both Force C and Force A1, with Rawlings expressing concern about the orders given to Gloucester and Fiji. Following this communication, King issued an order to recall both Gloucester and Fiji at 14:57.[69][70]
Between 15:30 and 15:50, while attempting to rejoin Force A1, Gloucester was hit by several bombs and had to be left behind due to the air attacks;[71] the ship was sunk and 22 officers and 700 ratings were killed.[69][72] The air attacks on Force A1 and Force C continued; two bombs hit the battleship HMS Valiant and another hit Fiji, disabling her at 18:45. A Junkers Ju 88 flown by Lieutenant Gerhard Brenner dropped three bombs on Fiji, sinking her at 20:15.[73] Five hundred survivors were rescued by Kandahar and Kingston that night. The Royal Navy had lost two cruisers and a destroyer but had managed to force the invasion fleet to turn round.[74] Royal Navy AA gunners shot down five Junkers Ju 87s and five Ju 88s and damaged sixteen more, some of which crash-landed upon their return to base on the night of 21/22 May.[75]
23–27 May
[edit]
Fighting against fresh German troops, the Allies retreated southward. The 5th Destroyer Flotilla, consisting of HMS Kelly, HMS Kipling, HMS Kelvin, HMS Jackal and HMS Kashmir (Captain, Lord Louis Mountbatten), was ordered to leave Malta on 21 May, to join the fleet off Crete, and arrived after Gloucester and Fiji were sunk. They were sent to pick up survivors and then diverted to attack a German convoy of about fifty ships and caïques off Cape Spatha on Rodopou peninsula, western Crete, on the night of 22/23 May and then shell the Germans at Maleme. Kelvin and Jackal were diverted to another search while Mountbatten, with Kelly, Kashmir and Kipling, was to go to Alexandria.[76]
When rounding the western side of Crete, the three ships were attacked by 24 Ju 87 Stuka dive bombers. Kashmir was hit and sank in two minutes, and Kelly was hit and turned turtle soon after and later sank. Kelly shot down a Stuka before sinking and another was badly damaged and crashed upon returning to base.[77] Kipling survived 83 bombs, while 279 survivors were rescued from the ships. (The Noël Coward film In Which We Serve was based on this action.)[78] The Royal Navy had suffered so many losses from air attacks that on 23 May Admiral Cunningham signalled his superiors that daylight operations could no longer continue, but the Chiefs of Staff demurred.[79] German search-and-rescue aircraft and Italian motor torpedo boats spotted and rescued the 262 survivors from the German light convoy sunk off Cape Spatha.
After air attacks on Allied positions in Kastelli on 24 May, the 95th Gebirgs Pioneer Battalion advanced on the town.[80] These air attacks enabled the escape of German paratroopers captured on 20 May; the escapees killed or captured several New Zealand officers assigned to lead the 1st Greek Regiment. The Greeks put up determined resistance but, with only 600 rifles and a few thousand rounds of ammunition available for 1,000 ill-trained men, they were unable to repel the German advance.[81] Fighting by the remnants of the 1st Greek Regiment continued in the Kastelli area until 26 May, hampering German efforts to land reinforcements.
Despite the dangers posed by British naval forces, the Kriegsmarine made another attempt to supply the invasion by sea. On 24 May Oberleutnant-zur-See Österlin, who had led the Maleme Flotilla, was given the task of transporting two Panzer II light tanks to Kastelli Kisamou. Österlin commandeered a small wooden lighter at Piraeus and arranged for the tanks to be lowered onto it. At dusk the next day, the lighter, towed by the small harbour tug Kentauros, left Piraeus and headed south towards Crete. Reports of British naval units operating nearby convinced Admiral Schuster to delay the operation and he ordered Österlin to make for a small harbour on the German-occupied island of Kithira.[82][83] At a meeting in Athens on 27 May, Luftwaffe Generals Richthofen, Jeschonnek, and Löhr pressed Schuster to get the tanks delivered somehow before "... the Englander claws himself erect again".[84] One of Richthofen's liaison officers had returned from the island on 26 May; the paratroopers were in poor condition, lacking in discipline, and "at loose ends". He stressed the "absolute and immediate need" for "reinforcement by sea shipment of heavy weaponry if the operation is to get ahead at all."[84]
Awful news from Crete. We are scuppered there, and I'm afraid the morale and material effects will be serious. Certainly the Germans are past-masters in the art of war—and great warriors. If we beat them, we shall have worked a miracle.
— Alexander Cadogan, Diary, 27 May 1941[85]
Schuster issued Österlin new orders to sail for the Gulf of Kissamos, where a landing beach had already been selected and marked out. Upon nearing the shore on 28 May, the lighter was positioned ahead of the tug and firmly beached. A party of engineers then blew the lighter's bow off using demolition charges and the two tanks rolled ashore. They were soon assigned to Advance Detachment Wittman, which had assembled near Prison Valley reservoir the day before. This ad hoc group was composed of a motorcycle battalion, the Reconnaissance Battalion, an anti-tank unit, a motorised artillery troop, and some engineers. General Ringel gave orders for Wittmann to "strike out from Platanos at 03:00 on 28 May in pursuit of the British 'main' via the coastal highway to Rethymno" and thence towards Heraklion.[82] Although they did not play a decisive role, the panzers were useful in helping round up British troops in the Kissamos area, before speeding eastward in support of the German pursuit column.[82]
On the night of 26/27 May, a detachment of some 800 men from No. 7 and No. 50/52 Commandos, as part of Layforce, landed at Souda Bay (Colonel Robert Laycock).[86] Laycock had tried to land the force on 25 May, but had turned back due to bad weather.[86] Although armed mainly with only rifles and a small number of machine guns, they were to carry out rearguard actions in order to buy the garrison enough time to carry out an evacuation.[86]
Troops of the German 141st Mountain Regiment blocked a section of the road between Souda and Chania. On the morning of 27 May, the New Zealand 28th (Māori) Battalion, the Australian 2/7th Battalion and the Australian 2/8th Battalion cleared the road by a bayonet charge (the "Battle of 42nd Street").[87] Command in London decided the cause was hopeless after General Wavell informed the Prime Minister at 0842, 27 May, that the battle was lost, and ordered an evacuation.[88] Freyberg concurrently ordered his troops to withdraw to the south coast to be evacuated.[citation needed]
Italian landing at Sitia
[edit]
On 26 May, in the face of the stalled German advance, senior Wehrmacht officers requested Mussolini to send Italian Army units to Crete in order to help the German forces fighting there.[89][need quotation to verify] On the afternoon of 27 May, an Italian convoy departed from Rhodes with the intention of landing a brigade from the 50th Infantry Division Regina, supported by 13 L3/35 light tanks.[90] Italian participation in the battle of Crete was limited and finally on 28 May, when the campaign was already decided in the Germans' favour and Allied evacuation had begun, an Italian landing force approached the east coast of the island, off Sitia.[91][92][93]
At 13:30 on 28 May, the Italians believed that three cruisers and six destroyers of the Royal Navy were steaming up towards the northern coast of Crete in support of Allied troops, but the Royal Navy was fully occupied evacuating the Crete garrison.[88][90] The Italians assumed that the Royal Navy force would be off Sitia, the planned landing site, by 17:00, and the commander decided that the slowest ship of the convoy would be taken in tow by Lince to increase speed and Crispi was detached to shell the lighthouse at Cape Sideros. The 3,000 men of the division and their equipment were on shore by 17:20 and advanced west mostly unopposed, rendezvousing with the Germans at Ierapetra. The Italian troops later moved their headquarters from Sitia to Agios Nikolaos.[90][94]
Retreat
[edit]
The Germans pushed the British, Commonwealth and Greek forces steadily southward, using aerial and artillery bombardment, followed by waves of motorcycle and mountain troops (the rocky terrain making it difficult to employ tanks). The garrisons at Souda and Beritania gradually fell back along the road to Vitsilokoumos, north of Sfakia. About halfway there, near the village of Askyfou lay a large crater nicknamed "The Saucer", the only place wide and flat enough for a large parachute drop. Troops were stationed about its perimeter, to prevent a landing that might block the retreat. On the evening of the 27th, a small detachment of German troops penetrated Allied lines near Imbros Gorge threatening a column of retreating unarmed Allied forces. The attack was held off by four men, the only ones with weapons.[95] Led by Cpl Douglas Bignal, the men sacrificed themselves,[96]securing the withdrawal of the remainder. Amongst this group was New Zealander Pte Willy Falconer of the Maori battalion, a hero of 42nd Street and Galatas. Also killed were LCpl Philip Stamp and Pte Andrew Payton.[97]
Near Souda, the 5th New Zealand Brigade and the 2/7th Australian Battalion, held off the 141st Mountain Regiment, which had begun a flanking manoeuvre, and on 28 May, at the village of Stylos, the 5th New Zealand Brigade fought a rearguard action. The Luftwaffe was over Rethymno and Heraklion and they were able to retreat down the road.[98]
The retreat of the brigade was covered by two companies of the Māori Battalion under Captain Rangi Royal, who overran the I Battalion, 141st Gebirgsjäger Regiment and halted the German advance. When the main unit was safely to the rear, the Māori retreated 24 miles (39 km), losing only two killed and eight wounded, all of whom were recovered. Layforce was the only big unit in this area to be cut off. Layforce had been sent to Crete by way of Sfakia when it was still hoped that reinforcements could be brought from Egypt to turn the tide of the battle.[86] The battalion-sized force was split up, with a 200-man detachment under Laycock at Souda to cover the retreat of the heavier units. Layforce and three British tanks were joined by the men of the 20th Heavy Anti-Aircraft Battery, who had been assigned to guard Souda docks and refused to believe that an evacuation had been ordered. After a day of battle, Laycock ordered a night retreat to Beritiana, where he was joined by Royal and the Māori, who managed to fight their way out, but Layforce was cut off near the village of Babali Khani (Agioi Pantes). Laycock and his Intelligence Officer, Evelyn Waugh, were able to escape in a tank. Most of the other men of the detachment and the 20th HAA Battery were killed or captured. (By the end of the operation about 600 of the 800 commandos sent to Crete were listed as killed, wounded or missing; only 179 men got off the island.)[99]
Evacuation, 28 May – 1 June
[edit]
From 28 May – 1 June, troops were embarked for Egypt, most being lifted from Sfakia on the south coast. More than 4,000 troops were rescued from Heraklion on the night of 28/29 May but that naval force was attacked for hours by Luftwaffe dive bombers on the voyage back, suffering ships sunk and damaged with numerous casualties among naval personnel and troops. About 6,000 men were withdrawn by cruisers and destroyers from Sfakia on the night of 29 May. Two destroyers carried another 1,400 soldiers away on the night of the 30/31st. During the night of 31 May, Cunningham sent the cruiser Phoebe with four smaller vessels to transport more than 3,500 troops to Alexandria.[100] About 18,600 men of the 32,000 British troops on the island were evacuated; 12,000 British and Dominion troops and thousands of Greeks were still on Crete when the island came under German control on 1 June.[101]
Surrender
[edit]Colonel Campbell, the commander at Rethymno, was forced to surrender his contingent. Rethymno fell and on the night of 30 May, German motorcycle troops linked up with the Italian troops who had landed on Sitia. On 1 June, the remaining 5,000 defenders at Sfakia surrendered.[102] By the end of December, about 500 Commonwealth troops remained at large on the island. While scattered and disorganised, these men and the partisans harassed German troops for long after the withdrawal.
Civilian resistance
[edit]Cretan civilians joined the battle with whatever weapons were at hand.[103] Most civilians went into action armed only with what they could gather from their kitchens or barns and several German parachutists were knifed or clubbed to death in olive groves. In one recorded incident, an elderly Cretan man clubbed a parachutist to death with his walking cane, before the German could disentangle himself from his parachute.[104] In another recorded incident, a local priest and his teenage son broke into a small village museum and took two rifles from the era of the Balkan Wars and sniped at German paratroops at landing zones. The Cretans also used captured German small arms. The Crete civilian actions against the Germans were not limited to harassment; mobs of armed civilians joined in the Greek counter-attacks at Kastelli Hill and Paleochora; the British and New Zealand advisers at these locations were hard pressed to prevent massacres. Civilians also checked the Germans to the north and west of Heraklion and in the town centre.[105]
Massacres of civilians
[edit]
The Battle of Crete was not the first occasion during the Second World War where the German troops encountered widespread resistance from a civilian population, as similar events took place during the invasion of Poland (Kłecko); nevertheless it initially surprised and later outraged them. As most Cretan partisans wore no uniforms or insignia such as armbands or headbands, the Germans felt free of all of the constraints of the Hague Conventions and killed armed and unarmed civilians indiscriminately.[106][e] Even before the end of the battle, civilians were being executed, such as in Missiria. Immediately after Crete fell, collective punishments against civilians intensified. Between 2 June and 1 August, 195 persons from the village of Alikianos and its vicinity were killed in mass shootings known as the Alikianos executions.[107] On 2 June, several male citizens from Kondomari were executed by a firing squad, with the shootings being captured on film by a German army war correspondent. On 3 June, the village of Kandanos was razed to the ground and about 180 of its inhabitants killed. After the war, Student, who ordered the shootings, avoided prosecution for war crimes, despite Greek efforts to have him extradited.[108]
The first resistance movement in Crete was established just two weeks after its capture. Throughout the German occupation in the years that followed, reprisals in retaliation for the involvement of the local population in the Cretan resistance continued. On several occasions, villagers were rounded up and summarily executed. In one of the worst incidents, around 20 villages east of Viannos and west of the Ierapetra provinces were looted and burnt in September 1943, with more than 500 of their inhabitants being massacred.[109] These massacres were among the deadliest during the Axis occupation of Greece during World War II. In August 1944, more than 940 houses in Anogeia were looted and then dynamited. During the same month, nine villages in the Amari Valley were destroyed and 165 people killed in what is now known as the Holocaust of Kedros.[110] All these reprisals were ordered by Generalleutnant Friedrich-Wilhelm Müller, who was nicknamed "The Butcher of Crete". After the war, Müller was tried by a Greek military court and executed.[111] Further assaults on civilians, albeit with lower death tolls, occurred in Vorizia, Kali Sykia, Kallikratis, Skourvoula, and Malathyros.
Aftermath
[edit]Analysis
[edit]
The German Air Ministry was shocked by the number of transport aircraft lost in the battle, and Student, reflecting on the casualties suffered by the paratroopers, concluded after the war that Crete was the death of the airborne force. Hitler, believing airborne forces to be a weapon of surprise which had now lost that advantage, concluded that the days of the airborne corps were over and directed that paratroopers should be employed as ground-based troops in subsequent operations in the Soviet Union.[16]
The battle for Crete delayed Operation Barbarossa but not directly.[112] The start date for Barbarossa (22 June 1941) had been set several weeks before the Crete operation was considered and the directive by Hitler for Operation Mercury made it plain that preparations for Merkur must not interfere with Barbarossa.[25] Units assigned to Merkur were intended for Barbarossa and were forced to redeploy to Poland and Romania by the end of May. Movement of surviving units from Greece was not delayed. The transfer of Fliegerkorps VIII north, ready for Barbarossa, eased the Royal Navy evacuation of the defenders. The delay of Operation Barbarossa was exacerbated also by the late spring and floods in Poland.[113]
The Air operation impact of the Battle of Crete to Operation Barbarossa was direct.[114] The considerable losses of the Luftwaffe during the operation Mercury, specifically regarding troop carrier planes, affected the capacity of air power operations at the start of the Russian campaign. Additionally, with German parachute troops being decimated in Crete, there was an insufficient number of men that were qualified to carry out the huge-scale airborne operations that were necessary at the beginning of the invasion. Furthermore, the delay of the whole Balkan campaign, including the Battle of Crete, did not allow for exploiting the strategic advantages that German forces had gained in the Eastern Mediterranean. With the VIII Air Corps ordered to Germany for refitting before Crete was secured, significant command and communication issues hampered redeployment of the whole formation as the ground personnel was directly redeployed to their new bases in Poland.[114]
The sinking of the German battleship Bismarck on 27 May distracted British public opinion but the loss of Crete, particularly as a result of the failure of the Allied land forces to recognise the strategic importance of the airfields, led the British government to make changes.[115][116] Only six days before the initial assault, the Vice Chief of Air Staff presciently wrote: "If the Army attach any importance to air superiority at the time of an invasion then they must take steps to protect our aerodromes with something more than men in their first or second childhood". Shocked and disappointed with the Army's inexplicable failure to recognise the importance of airfields in modern warfare, Churchill made the RAF responsible for the defence of its bases and the RAF Regiment was formed on 1 February 1942.[117] Allied commanders at first worried the Germans might use Crete as a springboard for further operations in the Mediterranean East Basin, possibly for an airborne attack on Cyprus or a seaborne invasion of Egypt, in support of Axis forces operating from Libya. Operation Barbarossa made it apparent that the occupation of Crete was a defensive measure to secure the Axis southern flank.[118]
Ultra
[edit]
For a fortnight, Enigma intercepts described the arrival of Fliegerkorps XI around Athens, the collection of 27,000 registered tons of shipping and the effect of air attacks on Crete, which began on 14 May 1941. A postponement of the invasion was revealed on 15 May, and on 19 May, the probable date was given as the next day. The German objectives in Crete were similar to the areas already being prepared by the British, but foreknowledge increased the confidence of the local commanders in their dispositions. On 14 May, London warned that the attack could come any time after 17 May, which information Freyberg passed on to the garrison. On 16 May the British authorities expected an attack by 25,000 to 30,000 airborne troops in 600 aircraft and by 10,000 troops transported by sea. (The real figures were 15,750 airborne troops in 520 aircraft and 7,000 by sea; late decrypts reduced uncertainty over the seaborne invasion.) The British mistakes were smaller than those of the Germans, who estimated the garrison to be only a third of the true figure. (The after-action report of Fliegerkorps XI contained a passage recounting that the operational area had been so well prepared that it gave the impression that the garrison had known the time of the invasion.[119])
The Germans captured a message from London marked "Personal for General Freyberg" which was translated into German and sent to Berlin. Dated 24 May and headed "According to most reliable source" it said where German troops were on the previous day (which could have been from reconnaissance) but also specified that the Germans were next going to "attack Suda Bay". This could have indicated that Enigma messages were compromised.[120]
Antony Beevor in 1991 and P. D. Antill in 2005 wrote that Allied commanders knew of the invasion through Ultra intercepts. Freyberg, informed of the air component of the German battle plan, had started to prepare a defence near the airfields and along the north coast. He had been hampered by a lack of modern equipment, and the lightly armed paratroopers had about the same firepower as the defenders, if not more. Ultra intelligence was detailed but was taken out of context and misinterpreted.[121][122] While emphasis was placed on the airborne assault, the German messages also mentioned seaborne operations; Freyberg, expecting an amphibious landing, garrisoned the coast – which reduced the number of men available to defend the airfield at Maleme, the principal German objective.[123] In 1993, F. H. Hinsley, the official historian of British intelligence during the war, wrote that the Germans had more casualties in the conquest of Crete than in the rest of the Greek campaign; the 7th Fliegerdivision was decimated, leaving the Germans with a crippled airborne arm. It was the only unit of its kind and was not rebuilt.[124]
Hinsley wrote that it was difficult to measure the influence of intelligence gained during the battle, because although Ultra revealed German situation reports, reinforcement details and unit identifications, and although more intelligence was gleaned from prisoners and captured documents, it was not known how swiftly the information reached Freyberg or how he used it. The German parachute warfare manual had been captured in 1940, and after the war Student said that he would have changed tactics had he known this. Field-signals intelligence was obtained, including bombing instructions and information from the Fliegerkorps XI tactical code. Lack of air cover prevented much British air reconnaissance north of Crete, but on 21 May signals intelligence enabled an aircraft to spot a convoy. After midnight the navy sank twelve ships and the rest scattered, which led to a second invasion convoy being called back. The second convoy was intercepted during the morning of 22 May, despite the cost to the navy of a daylight operation, and no more seaborne attempts were made.[125]
Casualties
[edit]




Official German casualty figures are contradictory due to minor variations in documents produced by German commands on various dates. Davin estimated 6,698 losses, based upon an examination of various sources.[126] Davin wrote that his estimate might exclude lightly wounded soldiers.[127]
Reports of German casualties in British reports are in almost all cases exaggerated and are not accepted against the official contemporary German returns, prepared for normal purposes and not for propaganda.
— Davin[128]
In 1956, Playfair and the other British official historians, gave figures of 1,990 Germans killed, 2,131 wounded, 1,995 missing, a total of 6,116 men "compiled from what appear to be the most reliable German records".[129]
Exaggerated reports of German casualties began to appear after the battle had ended. In New Zealand, The Press on 12 June 1941 reported that
The Germans lost at least 12,000 killed and wounded, and about 5,000 drowned.
— Taylor[130]
Churchill claimed that the Germans must have suffered well over 15,000 casualties. Buckley, based on British intelligence assumptions of two enemies wounded for every one killed, gave an estimate of 16,800 casualties. The United States Army Center of Military History, citing a report of the Historical Branch of the British Cabinet Office, concluded that military historians accept estimates from 6,000 to 7,000 German casualties.[131] The Australian Graves Commission counted about 4,000 German graves in the Maleme–Souda Bay area, and about 1,000 more at Rethymno and Heraklion, that would have included deaths during the German occupation due to sickness, accidents, or fighting with partisan forces.[132]
The official historians recorded 147 Luftwaffe aircraft destroyed and 64 damaged beyond repair by enemy action, with 73 destroyed due to extensive non-combat damage, for a total of 284 aircraft. Another 84 planes had repairable non-combat damage. In 1987, Shores, Cull, and Malizia recorded losses of 220 aircraft destroyed and 64 written off due to damage, a total of 284 aircraft between 13 May and 1 June: 147 in combat, 73 non-combat, 64 written-off, and 125 damaged but repairable.[129][10] A total of 311 Luftwaffe aircrew were listed as killed or missing and 127 were wounded.[10] In a 1948 RAF staff publication, Luftwaffe losses were given as about 4,500 parachute and glider troop casualties and about 170 Ju 52s lost or severely damaged; losses in fighter and bomber units were small due to the lack of air opposition.[133]
The British lost 1,742 killed, 1,737 wounded, and 11,835 taken prisoner from a garrison of slightly more than 32,000 men; and there were 1,828 dead and 183 wounded Royal Navy personnel.[129] Of a force of more than 10,000 men, 5,255 Greek troops were captured.[134] After the war, the Allied graves from the four burial grounds that had been established by the Germans were moved to Souda Bay War Cemetery. A large number of civilians were killed in the crossfire or died fighting as partisans. Many Cretan civilians were shot by the Germans in reprisal during the battle and in the occupation.[135] One Cretan source puts the number of Cretans killed by Germans at 6,593 men, 1,113 women, and 869 children. German records put the number of Cretans executed by firing squad as 3,474 and at least 1,000 civilians were killed in massacres late in 1944.[136]
The Luftwaffe sank the cruisers HMS Gloucester, HMS Fiji, and HMS Calcutta and the destroyers Kelly, Greyhound and Kashmir from 22 May – 1 June. Italian bombers from 41° Gruppo sank the destroyer HMS Juno on 21 May and on 28 May damaged another destroyer, HMS Imperial, beyond repair.[137][138] The British also lost the destroyer HMS Hereward on 29 May, when she was attacked by German Junkers Ju 87 "Stuka" dive-bombers.[139]
Damage to the aircraft carrier HMS Formidable, the battleships HMS Warspite and HMS Barham, the cruisers HMS Ajax, HMS Dido, HMS Orion, and HMAS Perth, the submarine HMS Rover, the destroyers HMS Kelvin and HMS Nubian, kept them out of action for months. At anchor in Souda Bay, northern Crete, the heavy cruiser HMS York was disabled by Italian explosive motor boats and beached on 26 March; and was later wrecked by demolition charges when Crete was evacuated in May.[140] By 1 June, the eastern Mediterranean strength of the Royal Navy had been reduced to two battleships and three cruisers, against four battleships and eleven cruisers of the Italian Navy.[12] For the British, the Battle of Crete was the costliest naval engagement of the entire war.[141]
Royal Navy shipborne anti-aircraft gun claims for the period of 15–27 May amounted to: "Twenty enemy aircraft ... shot down for certain, with 11 probables. At least 15 aircraft appeared to have been damaged ..."; from 28 May – 1 June, another two aircraft were claimed shot down and six more damaged, for a total of 22 claimed destroyed, 11 probably destroyed and 21 damaged.[142]
| Crete Military Casualties[f] | Killed | Missing (presumed dead) |
Total Killed and Missing | Wounded | Captured | Total |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| British Commonwealth | 3,579 [143]
|
3,579 [4]
|
1,918 [4]
|
12,254 [144]
|
17,754 [145]
| |
| German[9] | 1,353
|
2,421
|
3,774
|
2,120
|
5,894
| |
| Greek[5] | 426
|
118
|
544
|
5,225
|
5,769
|
Occupation
[edit]For the German occupation of Crete, see Fortress Crete.
See also
[edit]- Military history of Greece during World War II
- Battle of Maleme
- Invasion of Yugoslavia
- The 11th Day: Crete 1941 – documentary containing eyewitness accounts of participants in battle and resistance movement
- Fallschirmjäger memorial
- Von Blücher brothers
- Greek resistance
- Cretan resistance
- Crete Cuff Title
Notes
[edit]- a The following forces were present on Crete as of 20 May 1941: Armed Forces: 15,063; Royal Navy: 425; Royal Marines: 1,941; Royal Air Force: 618.[1]
- b From 20 May to 2 June: 4 Cruisers, 8 Destroyers, 2 Minesweepers, 5 Motor torpedo boats were sunk and 3 Battleships, 1 Aircraft Carrier, 7 Cruisers, 9 Destroyers and 2 assault ships were damaged.[6][146]
- c Between 13 May to 1 June 147 in combat, 73 non-combat, 64 written-off and 125 damaged.[10]
- d Italian submarines: Nereide, Tricheco, Uarsciek, Fisalia, Topazio, Adua, Dessie, Malachite, Squalo, Smeraldo, and Sirena.[37]
- e After the King had escaped to Crete on 22 April and issued a defiant memorandum to the Germans, Hitler responded by attacking him in a speech on 4 May. The British feared a propaganda coup if a sovereign monarch under their protection were to be captured, and helped him to escape.[147]
- f Participants on the battle included David Coke • Roald Dahl • Roy Farran • Bernard Freyberg • Clive Hulme • Robert Laycock • Patrick Leigh Fermor • John Pendlebury • George Psychoundakis • Max Schmeling • Theodore Stephanides • Evelyn Waugh (the battle forms an important episode in Waugh's novel Officers and Gentlemen, part of the Sword of Honour trilogy) • Lawrence Durrell • Charles Upham • Geoffrey Cox • Dan Davin (New Zealand Official Historian of the battle)
References
[edit]- ^ a b c d e f Daniel M. Davin (1953). "The Official History of New Zealand in the Second World War 1939–1945". Victoria University of Wellington. p. 480. Archived from the original on 5 October 2018. Retrieved 22 November 2018.
- ^ "(Greek) page 10, retrieved on 27.5.2010: 474 officers and 10,977 soldiers" (PDF). Archived from the original (PDF) on 17 July 2011. Retrieved 27 May 2010.
- ^ "Air War for Yugoslavia Greece and Crete 1940–41" p. 402
- ^ a b c Davin, p. 486 and Playfair, p.147, for RN Casualties.
- ^ a b Αγώνες και νεκροί του Ελληνικου Στρατού κατά το Δεύτερο Παγκόσμιο Πόλεμο 1940–1945 [Struggles and Dead of the Greek Army during the Second World War 1940–1945] (in Greek). Athens: Γενικό Επιτελειο Στρατού, Διεύθυνση Ιστορίας Στρατού [General Staff of the Army, Army History Directorate]. 1990. pp. 15–16.
- ^ a b See Casualties Section
- ^ "How British Bungling Lost the Battle for Crete in WWII". www.thenationalherald.com. Archived from the original on 2 March 2018. Retrieved 2 March 2018.
- ^ a b c "The Historical Combat Effectiveness of Lighter-Weight Armored Forces" (PDF). The Dupuy Institute. 2001. p. 84. Archived (PDF) from the original on 15 October 2019. Retrieved 19 November 2018.
- ^ a b c d Shores, Cull & Malizia 1987, p. 403
- ^ "The Battle for Crete". www.nzhistory.net.nz. Archived from the original on 21 April 2009. Retrieved 17 May 2009.
- ^ a b Pack 1973, p. 91.
- ^ Paul Collier (6 June 2014). The Second World War (4): The Mediterranean 1940–1945. Bloomsbury Publishing. p. 74. ISBN 978-1-4728-0990-2. Archived from the original on 28 September 2019. Retrieved 19 July 2017.
The first convincing demonstration of this potential in operational conditions came in May 1941, when the entire plan for the German airborne capture of Crete was decrypted two weeks before the invasion took place.
- ^ Beevor 1992, p. [page needed]
- ^ Maloney, Shane (July 2006). "Bogin, Hopit". The Monthly. Archived from the original on 4 September 2009. Retrieved 11 March 2010.
- ^ a b Beevor 1991, pp. 229–230
- ^ i.e. see also Operation Overlord, Operation Market Garden and Operation Varsity.
- ^ Long 1953, p. 203
- ^ a b Beevor 1991, p. 11
- ^ Murfett 2008, p. 114
- ^ Long 1953, p. 205.
- ^ Churchill & Gilbert 1983, p. 898
- ^ Pack 1973, p. 21.
- ^ Spencer 1962, p. 95.
- ^ a b c d Schreiber, Stegemann & Vogel 1995, pp. 530–531
- ^ Brown 2002, pp. 1–2
- ^ Vick 1995, p. 27
- ^ Richards 1974, pp. 324–325.
- ^ Richards 1974, pp. 325–327.
- ^ Playfair et al. 1956, p. 126.
- ^ Peponas, Emmanouil (April–May 2021). "Winston Churchill and the Battle of Crete (1941)". Electronic Journal of Social and Strategic Studies. 2 (1): 78–90. doi:10.47362/ejsss.2021.2112. ISSN 0975-6299.
- ^ Long 1953, pp. 218–219.
- ^ a b Cunningham, Section 2 paragraph 5
- ^ Long 1953, pp. 210–213
- ^ Antill 2005, p. 13.
- ^ Air 2001, p. 124.
- ^ a b Bertke, Smith & Kindell 2012, p. 505.
- ^ a b Hinsley 1994, pp. 81–82.
- ^ Buckley 1952, p. 163.
- ^ Antill 2005, p. 25.
- ^ MacDonald 1995, p. 153.
- ^ a b c Antill 2005, p. 24.
- ^ a b c Kavanaugh 2010, p. 38
- ^ Kavanaugh 2010, p. 39
- ^ Antill 2005, p. 32
- ^ a b c Vick 1995
- ^ a b Keegan 2011, p. 135
- ^ Keegan 2011, pp. 135–138
- ^ Germany and the Second World War, Volume 3, Militärgeschichtliches Forschungsamt, p. 546, Oxford University Press, 1995
- ^ Donald, Haddon; Hutching, Megan (2000). "Haddon Donald describes defending Maleme airfield, Crete". New Zealand History online. Archived from the original on 20 August 2011. Retrieved 3 June 2012.
- ^ a b c "The battle: days 1–3 – The Battle for Crete". New Zealand History online. 2011. Archived from the original on 2 February 2012. Retrieved 3 June 2012.
- ^ a b c Long 1953, pp. 221–255.
- ^ Πέπονας, Εμμανουήλ (2019). Η μάχη της Κρήτης (1941) (Master thesis) (in Greek). University of Ioannina. doi:10.26268/heal.uoi.9746.
- ^ "The controversies – The Battle for Crete". NZHistory. Archived from the original on 16 December 2008. Retrieved 24 November 2015.
- ^ a b c Donoghue, Tim (2011). "Officer breaks rank over the Battle of Crete". stuff.co.nz. Archived from the original on 2 July 2012. Retrieved 27 April 2012.
- ^ "Battle of Crete: Greece sacrificed much for the greater good – Neos Kosmos". 30 May 2010. Archived from the original on 15 March 2015. Retrieved 15 March 2015.
- ^ "Battle of Crete". www.lawrencewattskiwiwarhistory.wordpress.com. Archived from the original on 15 March 2015. Retrieved 15 March 2015.
- ^ Pack 1973, p. 32.
- ^ Roskill 1957, p. 441.
- ^ Greene & Massignani 1998, p. 170.
- ^ a b c Bilalis, Aris (2019). "The German convoys to Crete". Naftiki Ellas. Archived from the original on 5 November 2021. Retrieved 2 November 2021 – via Academia.edu.
- ^ O'Hara 2009, pp. 119
- ^ Beevor 1991, p. 164
- ^ Shores, Cull & Malizia 1987, pp. 357
- ^ Stewart, Ian McDougall Guthrie (1966). The Struggle for Crete, 10 May--1 June 1941. Oxford U.P. p. 281. ISBN 978-0-608-13736-0. Archived from the original on 16 April 2023. Retrieved 15 November 2021.
- ^ Cunningham, Section 1, paragraph 5.
- ^ a b Greene & Massignani 1998, p. 172.
- ^ a b Beevor 1991, p. 167
- ^ a b c Otter 2001, Chapter 14
- ^ Cunningham, Section 1, paragraph 8, and Section 2, paragraphs 30-35.
- ^ Cunningham, Section 2, paragraph 35.
- ^ Roskill 1957, p. 442.
- ^ Cunningham, Section 2, paragraph 38.
- ^ Beevor 1991, pp. 166–168.
- ^ Shores, Cull & Malizia 1987, pp. 357–9
- ^ Roskill 1957, p. 443.
- ^ Shores, Cull & Malizia 1987, p. 358.
- ^ Beevor 1991, pp. 170–171.
- ^ Roskill 1957, pp. 443–444.
- ^ Davin 1953, pp. 289–292.
- ^ Davin 1953, pp. 71–72
- ^ a b c Ansel 1972, pp. 401–402.
- ^ Schenk, p.25
- ^ a b Ansel 1972, pp. 401–402
- ^ Cadogan, Alexander (1972). The Diaries of Sir Alexander Cadogan 1938–1945: Edited by David Dilks, G. P. Putnam's Sons, New York. Page 381.
- ^ a b c d Saunders 1959, p. 55
- ^ Davin 1953, pp. 377–379
- ^ a b Forty, George, The Battle of Crete Ian Allan, London, 2001, p. 129
- ^ Germany and the Second World War, Volume 3, Militärgeschichtliches Forschungsamt, p. 549, Oxford University Press, 1995
- ^ a b c Cocchia, Aldo (1980). The Hunters and the Hunted. Naval Institute Press, pp. 59–69. ISBN 978-0-405-13030-4
- ^ Airborne Invasion Of Crete, 1941. Pickle Partners Publishing. 15 August 2014. p. 55. ISBN 978-1-78289-318-9. Archived from the original on 16 April 2023. Retrieved 20 May 2022.
- ^ Palazzo, Albert (1 July 2010). The Battle of Crete. Simon and Schuster. p. 76. ISBN 978-1-921941-24-5. Archived from the original on 16 April 2023. Retrieved 27 May 2022.
- ^ Tucker, Spencer C. (6 September 2016). World War II: The Definitive Encyclopedia and Document Collection [5 volumes]: The Definitive Encyclopedia and Document Collection. ABC-CLIO. p. 477. ISBN 978-1-85109-969-6. Archived from the original on 16 April 2023. Retrieved 27 May 2022.
- ^ "Egeo in Guerra – Lo sbarco italiano a Creta del maggio 1941". Archived from the original on 3 February 2011. Retrieved 6 January 2021.
- ^ "Battle of Crete". Operations & Codenames of WWII. Retrieved 9 June 2024.
- ^ "Battle of Crete". Operations & Codenames of WWII. Retrieved 9 June 2024.
- ^ "Battle of Crete". Operations & Codenames of WWII. Retrieved 9 June 2024.
- ^ Playfair et al. 1956, p. 144.
- ^ Chappell 1996, p. 16
- ^ Ian Stewart The Struggle for Crete 1966, pp. 457-472
- ^ Roskill 1957, pp. 444–446.
- ^ Playfair et al. 1956, pp. 142, 146.
- ^ Beevor 1991, pp. 116–117
- ^ MacDonald 1995, pp. 176–178.
- ^ MacDonald 1995, p. 195.
- ^ Beevor 1991, pp. 342, 235–248.
- ^ Kiriakopoulos 1995, pp. 32–34.
- ^ Beevor 1991, pp. 236, 342.
- ^ Beevor 1991, pp. 292, 165.
- ^ Beevor 1991, pp. 231.
- ^ Stein, Stuart. "Noteworthy War Criminals". University of the West of England. Archived from the original on 1 April 2012. Retrieved 21 May 2016.
- ^ Willmott 2008, pp. 128–129.
- ^ Germany and the Second World War, Volume IV, The Attack on the Soviet Union, Militärgeschichtliches Forschungsamt ed, (1995), see especially p.376; McDonald, C. (1995) The Lost Battle: Crete 1941, pp. 63–84.
- ^ a b "PART FIVE THE RELATIONSHIP BETWEEN THE CAMPAIGNS IN THE BALKANS AND". history.army.mil. Archived from the original on 24 June 2021. Retrieved 6 June 2021.
- ^ Pack 1973, p. 57
- ^ Vick 1995, p. 21
- ^ "A Brief History of the RAF Regiment". Ministry of Defence. 2012. Archived from the original on 6 April 2012. Retrieved 29 May 2012.
- ^ Playfair et al. 1956, pp. 148–149.
- ^ Hinsley 1994, pp. 82–84.
- ^ Sebag-Montefiore, Hugh (2017) [2000]. Enigma: The Battle for the Code. London: Weidenfeld & Nicolson. p. 181. ISBN 978-1-4746-0832-9.
- ^ Beevor 1991, Appendix C.
- ^ Handel, Michael I. (1990). Handel, Michael (ed.). Intelligence and Military Operations. Studies in Intelligence. Abingdon, Oxfordshire: Routledge (published 2013). p. 47. ISBN 978-1-135-17934-2. Archived from the original on 28 September 2019. Retrieved 23 July 2018.
It appears that General Freyberg was introduced to Ultra only shortly before the battle of Crete began and therefore had no time to become familiar with its proper interpretation. This situation was exacerbated by the fact that 'he was forbidden to show it (the information derived from Ultra) to anyone or to discuss it with his intelligence staff.' [...] Moreover, tight security regulations prohibiting him from taking action on the basis of uncorroborated Ultra evidence limited its value.
- ^ Antill 2005, p. 36.
- ^ Hinsley 1994, p. 84.
- ^ Hinsley 1994, pp. 84–85.
- ^ Davin 1953, pp. 486–488.
- ^ Davin 1953, p. 488.
- ^ Davin 1953, p. 486.
- ^ a b c Playfair et al. 1956, p. 147.
- ^ Taylor 1986, p. 299.
- ^ Anon 1952, pp. 139–141.
- ^ Davin 1953, pp. 486–487.
- ^ Air 2001, p. 125.
- ^ Long 1953, p. 316.
- ^ "Οι ωμότητες των Γερμανών στην Κρήτη". www.patris.gr. Archived from the original on 19 July 2011. Retrieved 10 April 2009.
- ^ MacDonald 1995, p. 303.
- ^ Higham 2006, p. 166
- ^ Cloutier 2013, p. 71
- ^ English 1993, p. 107
- ^ Whitley 1999, p. 94.
- ^ "How British Bungling Lost the Battle for Crete in WWII". www.thenationalherald.com. Archived from the original on 2 March 2018. Retrieved 2 March 2018.
- ^ Cunningham, Paragraph 78 and Paragraphs 1–54 of the last section
- ^ Davin, p. 486 and Playfair, p.147, for RN Casualties. This number includes those missing in action.
- ^ Davin, p. 486. The total number excludes several hundred RN PoWs.
- ^ Davin, p. 486 and Playfair, p.147, for RN Casualties. The total number excludes several hundred RN PoWs.
- ^ David A. Thomas (1972). "The Naval Battle for Crete". National Museum of the Royal New Zealand Navy. Archived from the original on 21 December 2018. Retrieved 20 December 2018.
- ^ Buckley 1952, p. 211
Sources
[edit]- Ansel, Walter (1972). Hitler and the Middle Sea. Duke University Press. ISBN 978-0-8223-0224-7.
- Antill, Peter D. (2005). Crete 1941: Germany's lightning airborne assault. Campaign series. Oxford; New York: Osprey Publishing. ISBN 978-1-84176-844-1.
- Beevor, Antony (1991). Crete: The Battle and the Resistance. London: John Murray. ISBN 978-0-7195-4857-4.
- Beevor, Antony (1992). Crete: The Battle and the Resistance. London: Penguin. ISBN 978-0-14-016787-0.
- Bertke, Donald A.; Smith, Gordon; Kindell, Don (2012). World War II Sea War: The Royal Navy is Bloodied in the Mediterranean. Vol. III. Lulu. ISBN 978-1-937470-01-2. [self-published source?]
- Brown, David (2002). The Royal Navy and the Mediterranean: November 1940 – December 1941. Whitehall Histories. Vol. II. London: Whitehall History in association with Frank Cass. ISBN 978-0-7146-5205-4.
- Buckley, Christopher (1952). Greece and Crete 1941. Second World War, 1939–1945; a popular military history. London: HMSO.
- Chappell, Mike (1996). Army Commandos 1940–1945. Elite. London: Osprey. ISBN 978-1-85532-579-1.
- Churchill, Randolph Spencer; Gilbert, Martin (1983). Winston S. Churchill: Finest hour, 1939–1941. Houghton Mifflin. ISBN 978-0-395-34402-6.
- Cloutier, Patrick (2013). Regio Esercito: The Italian Royal Army in Mussolini's Wars, 1935–1943. Lulu. ISBN 978-0-557-08181-3. [self-published source?]
- "Cunningham, A. B., The Battle of Crete, Despatch to the Lord Commissioners of the Admiralty, 4 August 1941". The London Gazette (Supplement). No. 38296. 21 May 1948. pp. 3103–3119.
- Davin, Daniel Marcus (1953). Crete. The Official History of New Zealand in the Second World War 1939–1945 (New Zealand Electronic Text Collection online ed.). Wellington, NZ: Historical Publications Branch, Department of Internal Affairs, Government of New Zealand. OCLC 1252361. Archived from the original on 18 March 2012. Retrieved 4 November 2015.
- English, John (1993). Amazon to Ivanhoe: British Standard Destroyers of the 1930s. Kendal, England: World Ship Society. ISBN 978-0-905617-64-0.
- Gill, George Hermon (1957). Royal Australian Navy, 1939–1942. Australia in the War of 1939–1945 (2). Vol. I. Canberra, ACT: Australian War Memorial. OCLC 848228. Archived from the original on 9 January 2016. Retrieved 24 November 2015.
- Greene, Jack; Massignani, Alessandro (1998). The Naval War in the Mediterranean 1940–1943. London: Chatham Publishing. ISBN 978-1-86176-057-9.
- Higham, Robin (2006). Why Air Forces Fail: The Anatomy of Defeat. Lexington, Kentucky: University Press of Kentucky. ISBN 978-0-81317-174-6.
- Hill, Maria (2010). Diggers and Greeks: The Australian Campaigns in Greece and Crete. UNSW Press. ISBN 978-1-74223-245-4.
- Hinsley, F. H. (1994) [1993]. British Intelligence in the Second World War. Its influence on Strategy and Operations. History of the Second World War. abr. (2nd rev. ed.). London: HMSO. ISBN 978-0-11-630961-7.
- H. M. Ships Damaged or Sunk by Enemy Action, 1939–1945 (PDF). No ISBN. London: Admiralty: Director of Naval Construction. 1952. Archived from the original (PDF) on 10 June 2016. Retrieved 24 November 2013.
{{cite book}}: CS1 maint: publisher location (link) - Kavanaugh, Stephen (2010). Hitler's Malta Option: A Comparison of the Invasion of Crete (Operation Merkur) and the Proposed Invasion of Malta (Operation Hercules). Nimble Books. ISBN 978-1-60888-030-0.
- Keegan, John (2011). The Second World War. Random House. ISBN 978-1-4464-9649-7.
- Kiriakopoulos, G. C. (1995). The Nazi Occupation of Crete: 1941–1945. Santa Babara, CA: Praeger. ISBN 978-0-275-95277-8.
- Long, Gavin (1953). Greece, Crete and Syria. Australia in the War of 1939–1945. Series One – Army. Vol. II (1st ed.). Canberra: Australian War Memorial. OCLC 3134080. Archived from the original on 11 July 2015. Retrieved 4 November 2015.
- MacDonald, Callum (1995). The Lost Battle – Crete 1941. Papermac. ISBN 978-0-333-61675-8.
- Murfett, Malcolm H. (2008). Naval Warfare 1919–1945: An Operational History of the Volatile War at Sea. London: Taylor & Francis. ISBN 978-0-415-45804-7.
- Naval Operations in the Battle of Crete, 20th May – 1st June 1941. Naval Staff History, Second World War. Battle Summary (rev. ed.). London: Admiralty Historical Section. 1960 [194]. OCLC 224008525. BR 1732 (2).
- O'Hara, Vincent P. (2009). Struggle for the Middle Sea: The Great Navies at War in the Mediterranean Theater, 1940–1945. Annapolis, MD: Naval Institute Press. ISBN 978-1-59114-648-3.
- Otter, Ken (2001) [1999]. HMS Gloucester: The Untold Story (2nd ed.). Durham, UK: G.A.M. Books. ISBN 978-0-9522194-2-2. OCLC 59524624.
- Pack, S.W.C. (1973). The Battle for Crete. Annapolis, MD: Naval Institute Press. ISBN 978-0-87021-810-1.
- Playfair, Major-General I.S.O.; Flynn, Captain F.C.; Molony, Brigadier C.J.C. & Toomer, Air Vice-Marshal S.E. (2004) [1st. pub. HMSO 1956]. Butler, J.R.M (ed.). The Mediterranean and Middle East: The Germans come to the help of their Ally (1941). History of the Second World War, United Kingdom Military Series. Vol. II. Naval & Military Press. ISBN 978-1-84574-066-5. Archived from the original on 27 October 2012. Retrieved 30 May 2012.
- Richards, Denis (1974) [1953]. Royal Air Force 1939–1945: The Fight at Odds. Vol. I (paperback (online) ed.). London: HMSO. ISBN 978-0-11-771592-9. Archived from the original on 24 September 2015. Retrieved 4 November 2015.
- Roskill, S. W. (1957) [1954]. Butler, J. R. M (ed.). War at Sea. History of the Second World War United Kingdom Military Series. Vol. I (4th impr. ed.). London: HMSO. OCLC 881709135. Archived from the original on 9 November 2015. Retrieved 4 November 2015.
- Saunders, Hilary St. George (1959) [1949]. The Green Beret: The Commandos at War. Four Square Books. London: Landsborough. OCLC 503725176.
- Shores, Christopher; Cull, Brian; Malizia, Nicola (1987). Air War For Yugoslavia, Greece, and Crete 1940–41. London: Grub Street. ISBN 978-0-948817-07-6.
- Spencer, John H. (1962). Battle for Crete. London: Heinemann. OCLC 2517566.
- Schreiber, Gerhard; Stegemann, Bernd; Vogel, Detlef (1995). Germany and the Second World War: The Mediterranean, South-east Europe, and North Africa, 1939–1941. Vol. III. London: Oxford University Press. ISBN 978-0-19-822884-4.
- Taylor, Nancy Margaret (2004) [1986]. "8 Blood is Spilt". The Home Front. The Official History of New Zealand in the Second World War 1939–1945. Vol. I (New Zealand Electronic Text Centre (online) ed.). Wellington, NZ: Historical Publications Branch, Department of Internal Affairs, Government of New Zealand. OCLC 226971019. Archived from the original on 20 December 2020. Retrieved 4 November 2015.
- The German Campaigns in the Balkans (Spring 1941). Dept of the Army Pamphlet. Washington, DC: Dept. of the Army, Office of the Chief of Military History. 1952. OCLC 43416304. Archived from the original on 4 March 2016. Retrieved 4 November 2015.
- The Rise and Fall of the German Air Force. Air 41/10 (Public Record Office War Histories ed.). Richmond, Surrey: Air Ministry. 2001 [1948]. ISBN 978-1-903365-30-4.
- Vick, Alan (1995). Snakes in the Eagle's Nest: A History of Ground Attacks on Air Bases. Rand Corporation. ISBN 978-0-8330-1629-4.
- Whitley, M. J. (1999). Cruisers of World War II. London: Brockhampton Press. ISBN 978-1-86019-874-8.
- Willmott, H. P. (2008). The Great Crusade: A New Complete History of the Second World War (rev. ed.). Washington, DC: Potomac Books. ISBN 978-1-61234-387-7.
Further reading
[edit]- Books
- Badsey, Stephen (2000). The Hutchinson Atlas of World War II Battle Plans: Before and After. London: Taylor & Francis. ISBN 978-1-57958-265-4.
- Barber, Laurie; Tonkin-Covell, John (1990). Freyberg: Churchill's Salamander. London: Hutchinson. ISBN 978-1-86941-052-0.
- Beevor, Antony (1991). Crete: The Battle and the Resistance. London: Penguin Books. ISBN 978-0-14-016787-0.
- Brown, David (2002). The Royal Navy and the Mediterranean: November 1940 – December 1941. Whitehall Histories. Vol. II. London: Whitehall History in association with Frank Cass. ISBN 978-0-7146-5205-4.
- Churchill, Winston Spencer (1985). The Second World War: The Grand Alliance. Vol. III. New York: Houghton Mifflin Harcourt. ISBN 978-0-395-41057-8.
- Clark, Alan (1989) [1962]. The Fall of Crete. London: Anthony Blond. ISBN 978-960-226-090-6.
- Cody, J. F. (2004) [1956]. 28 Maori Battalion. The Official History of New Zealand in the Second World War 1939–1945 (New Zealand Electronic Text Centre [online] ed.). Wellington: Historical Publications Branch. OCLC 173284168. Archived from the original on 25 October 2015. Retrieved 5 November 2015.
- Comeau, M. G. (2000). Operation Mercury: Airmen in the Battle of Crete. J & K. H. Publishing. ISBN 978-1-900511-79-7.
- Elliot, Murray (1992) [1987]. Vasili: The Lion of Crete. London, Australia, South Africa (Greek pbk. Efstathiadis Group ed.). New Zealand: Century Hutchinson. ISBN 978-960-226-348-8.
- Ewer, Peter (2008). Forgotten Anzacs: The Campaign in Greece, 1941. Carlton North, Vic.: Scribe. ISBN 978-1-921215-29-2. OCLC 457093199.
- Guard, Julie (2007). Airborne: World War II Paratroopers in Combat. Osprey. ISBN 978-1-84603-196-0.
- Hadjipateras, Costas; Fafalios, Maria (1989). Crete 1941, Eyewitnessed. Efstathiadis Group. ISBN 978-960-226-184-2.
- Harokopos, George (1993). Spilios Menounos (ed.). The Fortress Crete 1941–1944 The Secret War 1941–1944: Espionage and Counter-Espionage in Occupied Crete. English translation: B. Giannikos (Greek paperback ed.). Seagull. ISBN 978-960-7296-35-1.
- Hellenic Army General Staff (1997). An Abridged History of the Greek-Italian and Greek-German War, 1940–1941 (Land Operations). Athens: Army History Directorate Editions. ISBN 978-960-7897-01-5. OCLC 45409635.
- Hill, Maria (2010). Diggers and Greeks. UNSW Press. ISBN 978-1-74223-014-6.
- Kershaw, Robert (2024). The Hill: The Brutal Fight for Hill 107 in the Battle of Crete. Bloomsbury Publishing. ISBN 978-147-2864-52-9.
- Kiriakopoulos, G. C. (1985). Ten Days to Destiny: The Battle for Crete, 1941. ISBN 978-0-380-70102-5.
- Kokonas M. D., N. A. (1993). Leigh Fermor, P. (ed.). The Cretan Resistance 1941–1945: The Official British Report of 1945 Together with Comments by British Officers who took part in the Resistance (Greek pbk ed.). London. ISBN 978-960-85329-0-8.
{{cite book}}: CS1 maint: location missing publisher (link) - Lind, Lew (1991). Flowers of Rethymno: Escape from Crete. Kangaroo Press. ISBN 978-0-86417-394-2.
- Mazower, Mark (1993). Inside Hitler's Greece: The Experience of Occupation 1941–44. New Haven and London: Yale University Press. ISBN 978-0-300-05804-8.
- Moorehead, Alan (1941). Mediterranean Front. London: Hamish Hamilton. OCLC 21896524.
- Stanley Moss, W. (1950). Ill Met By Moonlight: The Story of the Kidnapping of General Karl Kreipe, the German Divisional Commander in Crete. New York: MacMillan. OCLC 1027344.
- Nasse, Jean-Yves (2002). Fallschirmjager in Crete, 1941: The Merkur Operation. Histoire & Collections. ISBN 978-2-913903-37-1.
- Nigl, Alfred (2007). Silent Wings Savage Death: Saga of the 82nd Airborne's Glider Artillery in World War II. Santa Ana, CA: Graphic Publishers. ISBN 978-1-882824-31-1.
- Palazzo, Albert (2007). The Battle of Crete. Australian Army Campaigns. Canberra, Australia: Australian Military History Publications. ISBN 978-0-9757669-1-0.
- Psychoundakis, George (1991) [1955]. Patrick Leigh Fermor (ed.). The Cretan Runner: His History of the German Occupation (in Greek). Athens: Efstathiadis Group. ISBN 978-960-226-013-5.
- Richter, Heinz A. (2011). Operation Merkur. Die Eroberung der Insel Kreta im Mai 1941 [Operation Mercury. The Conquest of the Island Crete in May, 1941] (in German). Rutzen. ISBN 978-3-447-06423-1.
- Ross, A. (2004) [1959]. 23 Battalion. The Official History of New Zealand in the Second World War 1939–1945 (New Zealand Electronic Text Centre [online] ed.). Wellington: Historical Publications Branch. OCLC 173284126. Archived from the original on 28 October 2015. Retrieved 5 November 2015.
- Sadler, John (2007). Op Mercury, The Fall of Crete 1941. Pen & Sword Books. ISBN 978-1-84415-383-1.
- Saunders, Tim (2007). Crete. Barnsley: Pen and Sword. ISBN 978-1-84415-557-6.
- Schenk, Peter (2000). Kampf um die Ägäis: die Kriegsmarine in den griechischen Gewässern 1941–1945 [Battle for the Aegean Sea, the Navy in Greek waters 1941–1945] (in German). Mittler & Sohn. ISBN 978-3-8132-0699-9.
- Spencer, John Hall (2008). Battle for Crete. Barnsley: Pen and Sword. ISBN 978-1-84415-770-9.
- Taylor, A. J. P. (1965). English history, 1914–1945. Oxford History of England. London: Oxford University Press. ISBN 978-0-19-821715-2.
- Thomas, D. A. (1980) [1972]. Crete 1941: The Battle at Sea (Greek pbk edition (in English): Efstathiadis Group, Athens ed.). London: Andre Deutsch. OCLC 11023583.
- Willingham, Matthew (2005). Perilous Commitments: The Battle for Greece and Crete 1940–1941. Spellmount. ISBN 978-1-86227-236-1.
- Websites
- Power, Graham. "The Battle of Pink Hill". Power Publishing. Archived from the original on 25 May 2010. Retrieved 13 June 2010.
- Power, Graham. "The ANZACs at 42nd Street" (PDF). Power Publishing. Archived from the original (PDF) on 15 May 2016. Retrieved 29 May 2016.
External links
[edit]- HMS Ajax at Crete Archived 29 December 2019 at the Wayback Machine
- New Zealand History Second World War
- Australian War Memorial Second World War Official Histories
- H.M. Ships Damaged or Sunk by Enemy Action, 1939–1945
- Landing in the bay of Sitia 28 May 1941 r. (PL)
- Battle of Crete Photo and Documents Archive
- John Dillon's Battle of Crete site
- Stoker Harold Siddall Royal Navy, his capture on Crete and life as a POW
- Admiral Sir A. B. Cunningham, The Battle of Crete
- Charles Prestidge-King, The Battle of Crete: A Re-evaluation
- James Cagney, 2011, Animated Maps of The Battle of Crete Archived 1 May 2013 at the Wayback Machine
- The 11th Day: Crete 1941 Archived 7 October 2013 at the Wayback Machine
Battle of Crete
View on GrokipediaBackground
Strategic Context in the Mediterranean Theater
The Mediterranean Theater emerged as a critical arena in World War II following Italy's entry into the war on June 10, 1940, where Benito Mussolini aimed to challenge British naval dominance and secure supply lines to North Africa. Italy's subsequent invasion of Greece on October 28, 1940, through Albania sought to exploit perceived British weakness after the fall of France but faltered due to harsh terrain, Greek resistance, and logistical strains, resulting in Italian forces being pushed back by early November.[7] This setback threatened Axis prestige and exposed vulnerabilities in the Balkans, prompting Adolf Hitler to intervene to stabilize the front and prevent British consolidation.[7] Germany's Directive 18, issued on November 12, 1940, outlined plans to secure Romania's oil fields and support Italy in Greece, culminating in Operation Marita, the invasion of Yugoslavia and Greece launched on April 6, 1941. German forces, leveraging blitzkrieg tactics, overran Yugoslav defenses by April 17 and captured Athens on April 27, forcing British Expeditionary Forces to evacuate over 50,000 troops to Crete by May 1.[8] This Balkan diversion delayed preparations for Operation Barbarossa, the invasion of the Soviet Union, by approximately five weeks, yet it eliminated immediate threats to Axis flanks in southeastern Europe.[9] Crete held pivotal strategic value as the largest island in the Aegean Sea, offering airfields and harbors that could extend Axis reconnaissance and bombing range over the eastern Mediterranean, directly supporting Erwin Rommel's Afrika Korps in Libya and threatening the British-held Suez Canal and Middle Eastern oil routes.[1] For the Allies, under British command, Crete served as a forward base for the Royal Navy to interdict Axis convoys and maintain pressure on Italian shipping, but its loss would cede air superiority to the Luftwaffe, hampering naval operations amid ongoing attrition in North Africa.[10] Control of Crete was thus essential for Axis ambitions to achieve temporary naval supremacy in the central and eastern Mediterranean, facilitating reinforcements to Axis armies facing British counteroffensives like Operation Compass.[11]Fall of Mainland Greece and Allied Retreat to Crete
The Italian invasion of Greece, launched on 28 October 1940, encountered strong resistance and stalled, with Greek forces advancing into Albania by early 1941.[12] In response, Adolf Hitler initiated Operation Marita on 6 April 1941, deploying the German 12th Army—comprising approximately 14 divisions, over 600 tanks, and more than 1,000 aircraft—to invade Greece and Yugoslavia simultaneously, aiming to secure the southern flank for the planned invasion of the Soviet Union and relieve pressure on Italian forces.[13] [14] The Germans exploited the Monastir Gap, bypassing the fortified Metaxas Line, and captured Thessaloniki on 9 April after Allied forces under Lieutenant General Henry Maitland Wilson withdrew to avoid encirclement.[13] British, Australian, New Zealand, and other Commonwealth troops, totaling around 57,000 in W Force, had been dispatched to Greece at Prime Minister Winston Churchill's insistence starting in March 1941, despite warnings from commanders like General Archibald Wavell about insufficient resources.[14] German advances overwhelmed Allied positions, with breakthroughs at the Battle of Vevi on 12 April and the Servia Pass, forcing a general retreat southward through the rugged Greek terrain.[13] The Greek Army of Epirus, facing encirclement after successes in Albania, capitulated on 20 April, prompting King George II to flee Athens on 25 April as German forces entered the capital on 27 April.[13] [14] On 21 April, Allied commanders ordered the evacuation of remaining forces, initiating Operation Demon on 24 April under Vice Admiral Henry Pridham-Wippell.[15] The Royal Navy, utilizing over 70 ships including destroyers and cruisers, extracted approximately 50,000 troops from ports in the Peloponnese such as Nafplion, Monemvasia, and Kalamata over the next five days, with many directed to Crete as a forward defensive position.[16] [15] The operation succeeded in minimizing naval losses despite Luftwaffe attacks that sank several vessels, but the hasty withdrawal left behind most artillery, vehicles, and supplies, while around 11,000 Allied personnel were captured.[16] [17] Evacuees arriving on Crete—numbering roughly 32,000 British Commonwealth troops—were fatigued, lightly armed, and dispersed, complicating subsequent defensive preparations against an anticipated Axis assault.[17]Geographical and Logistical Challenges of Crete
Crete's geography posed significant obstacles to both defenders and invaders during the 1941 battle. The island's rugged, mountainous terrain, including the White Mountains in the west exceeding 2,000 meters and the central Ida massif with peaks up to 2,456 meters, fragmented the landscape into steep ravines, craggy hills, and thick olive groves that hindered rapid troop movements and concentrations. Limited road infrastructure, primarily confined to a single coastal highway along the northern shore, restricted internal logistics and reinforcements, while the narrow coastal plains—varying from 12 to 60 kilometers in width—concentrated key assets such as the three principal airfields at Maleme, Rethymno, and Heraklion, as well as ports like Suda Bay, within vulnerable proximity to potential assault zones facing German-held Greece approximately 100 kilometers north.[18][5] These features amplified logistical challenges for Allied forces, who, following chaotic evacuations from mainland Greece in April 1941, arrived depleted of heavy equipment, vehicles, and ample ammunition, relying on improvised defenses and personal weapons amid poor infrastructure and dependence on Royal Navy convoys for resupply—convoys that faced severe interdiction from Axis air superiority. The island's isolation, situated about 450 miles from British bases in Egypt, further strained air support, placing Crete at the edge of fighter range and exposing supply lines to Luftwaffe attacks from surrounding Axis aerodromes. Defensive dispositions were thus stretched across dispersed sectors, with inadequate mobile reserves like trucks or carriers delaying counterattacks against airborne threats.[18][5] For the German airborne assault under Operation Mercury, the terrain exacerbated vulnerabilities inherent to paratroop operations. Drops on 20 May 1941 scattered lightly equipped Fallschirmjäger across rocky, walled fields and ravines, resulting in heavy initial casualties—estimated at over 25 percent in the first wave due to landing injuries and immediate counterfire—while the fragmented landscape delayed unit cohesion and access to heavier weapons or reinforcements until airfields could be secured for sustained supply flights. Initial reliance on imprecise airdrops for ammunition and equipment proved inadequate against determined resistance, compounded by British naval dominance that precluded early seaborne support, forcing the invaders into a precarious foothold dependent on rapid airfield captures amid the island's natural defensive barriers.[5][19]Prelude
Axis Planning and Operation Mercury
Following the Axis conquest of mainland Greece in late April 1941, German planners identified Crete as a critical objective to eliminate the last Allied foothold in the Aegean, secure supply lines to North Africa, and safeguard the southern flank for the impending invasion of the Soviet Union. General Kurt Student, commander of the XI Fliegerkorps and pioneer of German airborne doctrine, proposed a bold airborne assault as the primary means of capture, leveraging paratroopers and gliders to seize key airfields without relying on naval forces vulnerable to British Royal Navy dominance. Hermann Göring, head of the Luftwaffe, endorsed the plan despite Hitler's initial reluctance, prioritizing it over preparations for Barbarossa.[1][20] Operation Mercury, codenamed Unternehmen Merkur, was formalized in early May 1941 under Student's direction, with the invasion scheduled for 20 May to exploit favorable weather and surprise. The assault force totaled around 22,000 troops, primarily from the 7th Flieger-Division's Fallschirmjäger regiments (FJR 1, 2, 3, and 4), reinforced by glider infantry from Sturmabteilung Koch and air-landed mountain troops from the 5th Gebirgs-Division in subsequent waves. These were organized into three Kampfgruppen: West under Generalmajor Meindl targeting Maleme airfield; Center under Generalmajor Süßmann for Chania and Rethymno; and East under Generalmajor Ramcke for Heraklion. Supporting air power from Luftflotte 4 under Generaloberst Alexander Löhr included over 1,000 aircraft for transport, bombing, and fighter cover, but no initial seaborne element was planned due to assessed risks from Allied naval interdiction.[21][20] Italian involvement was peripheral; Benito Mussolini granted permission for German use of bases but demurred on major commitments, citing naval concerns, with Italian forces limited to token air and later amphibious support starting 28 May. German planning assumed rapid airfield seizure within hours to enable reinforcement by Ju 52 transports, underestimating Allied strength—later revealed as around 32,000 troops—and local civilian resistance. Intelligence failures, including dismissal of Ultra decrypts indicating Allied awareness, compounded risks, yet Student pressed ahead, viewing Crete as a validation of airborne tactics proven in prior operations like Eben Emael. The operation's high command structure placed Student in tactical control, with Löhr overseeing broader air operations from Greece.[1][4]Allied Forces, Command, and Defenses
Lieutenant General Bernard Freyberg, commander of the 2nd New Zealand Expeditionary Force, was appointed overall commander of Allied forces on Crete on 30 April 1941, with authority over British, Commonwealth, and Greek troops.[22] This decision by Prime Minister Winston Churchill elevated Freyberg despite his primary responsibility to New Zealand forces, reflecting confidence in his World War I experience and leadership during the Greek campaign evacuation.[23] Freyberg reported to General Archibald Wavell in Middle East Command, but operational control on the island was hampered by poor communications and incomplete integration of disparate units rushed from mainland Greece.[24] The Allied garrison comprised approximately 32,000 British Commonwealth troops, including remnants of the 14th, 16th, and 42nd British Brigades, the 4th New Zealand Brigade (about 6,100 men), and the 19th Australian Brigade (around 3,000 men), supplemented by base troops and artillery units.[5] An additional 11,500 Greek troops, primarily from the 5th and 8th Divisions' remnants and local garrison units, were under Freyberg's command, though poorly equipped and demoralized after defeats on the mainland.[25] Many soldiers arrived fatigued and without heavy equipment, having abandoned most vehicles, tanks, and supplies during the April-May 1941 evacuation from Greece, leaving the force reliant on light infantry weapons and limited captured Italian artillery.[20] Defenses centered on protecting the island's three operational airfields at Maleme, Retimo, and Heraklion, with forces dispersed in brigade groups: the west under New Zealand control around Maleme and Suda Bay, central Retimo held by Australians, and eastern Heraklion by British and Greeks.[26] Freyberg prioritized airfield security against potential airborne threats while maintaining mobile reserves for anticipated seaborne landings at key ports like Suda and Heraklion, but thin troop densities—often one battalion per sector—left positions vulnerable.[24] Artillery support was meager, totaling 49 field guns and fewer than 30 anti-aircraft pieces, with no armored vehicles or effective air cover, as the Royal Air Force had withdrawn its squadrons by early May due to Luftwaffe dominance.[9] Fortifications consisted mainly of hasty trenches and pillboxes around airfields, exacerbated by logistical shortages and intelligence emphasis on naval invasion over paratroop assault.[1]Intelligence: Ultra Decrypts and German Deception
British codebreakers at Bletchley Park, through decryption of German Enigma-encrypted communications known as Ultra, obtained detailed foreknowledge of Operation Mercury, the planned airborne invasion of Crete scheduled for 20 May 1941.[27] Ultra intercepts revealed the German order of battle, including approximately 22,000 Fallschirmjäger paratroopers and glider troops from the 7th Flieger Division and 22nd Luftlande Division, targeted drop zones at Maleme airfield, Chania, Rethymno, and Heraklion, and the intention to secure airfields for subsequent reinforcements.[28] These decrypts, disseminated to Allied commander Lieutenant General Bernard Freyberg by mid-May, confirmed the primacy of airborne assault over any immediate seaborne effort, with naval landings envisioned only as a follow-on after establishing secure lodgments.[5] Despite this precision, Freyberg prioritized defenses against a perceived massive seaborne invasion, allocating scarce reserves and artillery to beach fortifications while under-preparing mobile counterattacks against paratroop concentrations.[29] This emphasis stemmed partly from Prime Minister Winston Churchill's directive to safeguard Ultra's secrecy by avoiding actions that implied exact foreknowledge of airborne details, instead amplifying plausible but secondary threats like amphibious landings to mask the intelligence source.[5] Consequently, key assets such as the New Zealand 22nd Battalion at Maleme were held back from immediate reinforcement of overrun positions, allowing German paratroops to consolidate despite high initial casualties and scattered drops.[9] German deception efforts aimed to obscure preparations for Crete by simulating continued planning for Operation Sea Lion, the aborted invasion of Britain, including beach assault training in the Balkans and radio traffic suggesting buildup against the UK or Soviet targets.[21] Tactically, the Luftwaffe conducted routine bombing raids on Allied positions in the days before 20 May to feign normal operations rather than invasion prelude, while transport aircraft assembled under cover of exercises mimicking other objectives.[21] These measures achieved limited strategic surprise, as Ultra nullified much of the misdirection, though German intelligence failures—relying on outdated Abwehr estimates of only 5,000 weakly armed Allied troops on Crete—compounded Allied advantages that were ultimately squandered through defensive misprioritization.[21]Weapons, Equipment, and Tactical Doctrines
German forces in Operation Mercury relied on specialized airborne equipment to execute the invasion. Fallschirmjäger paratroopers jumped from Junkers Ju 52 transport aircraft armed initially only with pistols or knives, as their primary weapons—Karabiner 98k rifles, MP 38/40 submachine guns, MG 34 machine guns, and light mortars—were container-dropped separately to reduce load weight and allow for heavier supply parachutes.[30] Glider units using DFS 230 assault gliders transported heavier items, including 37mm PaK 36 anti-tank guns, 75mm infantry guns, and additional machine guns, enabling small teams to seize fortified positions like bridges or airfields with immediate firepower support.[31] This equipment mix prioritized mobility over sustained firepower, with resupply dependent on capturing airfields for subsequent airlifts of ammunition and mountain infantry divisions. Allied defenders, comprising British, Australian, New Zealand, and Greek troops under Creforce, utilized conventional infantry armaments adapted for island defense. Commonwealth units were equipped with .303 Lee-Enfield rifles, Bren light machine guns, and Vickers .303 medium machine guns, providing suppressive fire capabilities but limited anti-tank options beyond Boys anti-tank rifles and captured Italian 47mm guns.[32] Anti-aircraft defenses included approximately eight QF 3-inch guns and twenty Bofors 40 mm guns, insufficient to counter the Luftwaffe's volume of sorties, while Greek contingents fielded a patchwork of older rifles, light machine guns, and scarce artillery from pre-occupation stocks.[3] Overall, Allied forces suffered from shortages of heavy weapons, radios for coordination, and entrenching tools, constraining their ability to fortify positions effectively against airborne threats.[18] German tactical doctrine extended Blitzkrieg principles to airborne warfare, emphasizing surprise mass drops on multiple objectives to paralyze command and seize airfields for rapid reinforcement, as outlined in General Kurt Student's plan for Mercury, which allocated three airborne divisions to capture Maleme, Rethymno, and Heraklion simultaneously on 20 May 1941.[31] Glider elements were tasked with precision strikes on strongpoints, while paratroopers fought in ad hoc groups to consolidate gains before seaborne and airlifted follow-ups, though the separation of weapons from troops created initial vulnerabilities exploited by defenders.[33] This approach succeeded at Maleme due to incomplete Allied counterattacks but incurred 4,000 casualties on the first day, prompting Hitler to restrict future large-scale paratroop assaults.[34] Allied doctrine under Lieutenant General Bernard Freyberg prioritized a perimeter defense against anticipated seaborne invasion, informed by Ultra intelligence, with interior forces held in reserve for counterattacks; however, emphasis on beach defenses over airfield protection allowed German paratroops to establish footholds despite foreknowledge of the airborne threat.[5] Terrain was leveraged for ambushes and enfilade fire against scattered drops, bolstered by Cretan civilians using knives and farm tools, but fragmented command, minimal wireless sets, and delayed reinforcements undermined cohesive tactical execution across sectors.[35] The battle highlighted doctrinal mismatches, with Allies relying on static attrition warfare ill-suited to fluid airborne incursions, contributing to the evacuation of 17,000 troops by 1 June 1941.[36]The Battle
Initial Airborne Landings: 20 May 1941
Operation Mercury's airborne phase opened around 07:00 on 20 May 1941, following preliminary Luftwaffe bombing and strafing runs on Allied positions across northern Crete. German forces, primarily from the 7th Flieger Division under XI Flieger Corps command, deployed paratroopers via approximately 500 Junkers Ju 52 transport aircraft and DFS 230 gliders, targeting four key sectors to capture airfields essential for resupply. The assault involved roughly 10,000 paratroopers and 750 glider troops in the initial waves, marking the largest airborne operation attempted to date.[37][1][21] Landings concentrated on Maleme airfield in the west, where the 3rd Fallschirmjäger Regiment dropped west of the field, facing immediate counterfire from New Zealand's 22nd Battalion entrenched on nearby Hill 107; simultaneous drops occurred near Chania and Suda Bay by elements of the 3rd Regiment's assault groups, aiming to link up and secure the port. Further east, the 2nd Fallschirmjäger Regiment targeted Rethymno airfield against Australian defenders, while the 1st Regiment assaulted Heraklion airfield, opposed by Australian, British, and Greek troops. German plans called for synchronized drops in waves every 15 minutes, but navigational errors, strong winds, and Allied anti-aircraft fire—supplemented by small arms from ground troops—dispersed many paratroopers, with significant numbers killed mid-descent or upon landing unarmed, as weapons containers often landed separately.[21][1][20] Initial outcomes were largely disastrous for the Germans, with isolated pockets struggling against organized Allied resistance and spontaneous Cretan civilian attacks using improvised weapons; by evening, no airfield was firmly in German hands, and estimates place first-day casualties at over 4,000, including many officers, representing about 40% of committed airborne forces. Luftwaffe losses included at least seven Ju 52s destroyed in the first wave alone, hampering further drops. However, in the Maleme sector, a critical gap emerged when New Zealand forces temporarily withdrew from Hill 107 overlooking the airfield, allowing surviving paratroopers under Lieutenant Colonel Richard Heidrich to regroup and prepare a counter-push, setting the stage for subsequent reinforcements. This near-failure underscored the risks of airborne assaults against alerted defenders, as empirical evidence from the descent phase revealed vulnerabilities in paratrooper dispersal and equipment recovery amid contested terrain.[21][38][1]Western Sector Engagements: Maleme and Chania
The western sector of Crete, encompassing Maleme airfield and the port of Chania, became the focal point of the initial German airborne assault on 20 May 1941, where elements of the 7th Flieger Division targeted key infrastructure to establish a bridgehead. Maleme airfield, defended primarily by the New Zealand 22nd Battalion under Lieutenant Colonel Leslie Andrew, represented a strategic objective due to its suitability for rapid reinforcement by transport aircraft. German paratroopers from Fallschirmjäger Regiment 3 and glider-borne Sturmregiment troops landed west of the airfield and in adjacent dry riverbeds, suffering immediate heavy casualties from Allied anti-aircraft fire and small-arms fire from entrenched New Zealand positions on Hill 107 (also known as Point 107).[39] [38] In the Chania area, additional glider landings aimed to seize the town and Suda Bay but encountered fierce resistance from New Zealand's 19th Battalion and local Greek forces, resulting in the failure to capture these objectives and the death of the 7th Flieger Division's commander, General Wilhelm Süßmann.[39] Initial German assaults on Hill 107 were repulsed by the 22nd Battalion, which maintained control of the airfield perimeter despite intense close-quarters fighting and the loss of up to two-thirds of one German battalion in the sector. A limited New Zealand counterattack involving two British light tanks and a platoon supported by the 23rd Battalion faltered due to mechanical breakdowns and lack of coordination, as Brigadier James Hargest denied further reinforcements to avoid overextension. In Prison Valley near Chania, scattered paratroop drops established a tenuous foothold threatening Allied communications, prompting a counterthrust by the 19th Battalion that achieved no decisive gains and withdrew under pressure. These engagements inflicted disproportionate casualties on the Germans, with dispersed drops and lack of heavy equipment exacerbating their vulnerability during the landing phase.[39] [38] Overnight from 20 to 21 May, Lieutenant Colonel Andrew, perceiving Hill 107 as untenable amid reports of German consolidation, ordered the withdrawal of his battalion's troops from the feature to a rear ridge without fully coordinating with higher command, leaving the position lightly held by two isolated companies that later extricated under fire. This decision, approved by Hargest, allowed German forces to occupy Hill 107 unopposed by dawn on 21 May, enabling them to secure Maleme airfield and commence landings of reinforcements from the 5th Gebirgs Division despite ongoing Allied artillery fire. Allied commander Lieutenant General Bernard Freyberg planned a counteroffensive with the 20th and 28th (Māori) Battalions of the 4th New Zealand Brigade, but delays arising from Australian relief operations, rough terrain, and incomplete intelligence prevented its execution in strength, permitting German mountain troops—approximately 650 arriving by evening—to solidify their hold.[39] [38] The loss of Maleme marked a pivotal shift in the western sector, as the airfield facilitated the influx of over 12,000 German troops by subsequent days, overwhelming local Allied defenses around Chania through sustained air superiority and incremental advances. German casualties in the 7th Flieger Division for the operation exceeded 4,000, with Maleme accounting for a significant portion due to the intensity of ground resistance, while New Zealand forces in the sector endured heavy but unquantified losses in personnel and materiel. This outcome underscored the causal impact of tactical hesitation and communication lapses on Allied fortunes, contrasting with the Germans' exploitation of the secured lodgment despite their initial numerical and logistical disadvantages.[39] [38]Central and Eastern Sector Fighting: Rethymno and Heraklion
The central and eastern sectors of Crete, encompassing Rethymno and Heraklion, saw intense airborne assaults by German paratroopers on 20 May 1941 as part of Operation Mercury.[26] In the Rethymno area, Australian forces from the 2/11th Battalion (Western Australians) and 2/1st Battalion (New South Welshmen) defended the airfield and surrounding positions against scattered German landings.[26] These units, part of four Australian battalions and a field artillery regiment holding the line from Georgiopolis to Rethymno, repelled initial drops and conducted counterattacks to prevent the establishment of a bridgehead.[26] German paratroopers at Rethymno faced severe containment, with Australian defenders denying access to the airstrip through close-quarters fighting from 20 May onward.[40] Between 22 and 26 May, Australians launched repeated assaults on German positions west of Perivolia airfield and east of the aerodrome, inflicting heavy losses on the invaders.[41] Over 11 days of combat, the Australians suffered 286 casualties while effectively destroying the German forces that had landed in the sector, though ammunition shortages and lack of reinforcements eventually forced their surrender on 1 June.[42] At Heraklion, the airfield came under attack by mid-afternoon on 20 May following Luftwaffe bombings, with German parachute and glider troops targeting the port and runway.[26] The sector was held by Brigadier Brian Chappell's 14th British Infantry Brigade, reinforced by Australian and Greek units, who engaged in brutal defensive actions against the 3rd Fallschirmjäger Regiment.[9] Fighting persisted from 20 to 29 May, marked by fierce resistance that delayed German consolidation despite air superiority, contributing to high Axis losses in the overall campaign where paratroopers suffered approximately 3,352 killed or missing from an assault force of 22,000.[20] Allied forces at Heraklion maintained control longer than in western sectors but were compelled to withdraw during the general evacuation by 1 June amid mounting pressure from German advances linking up from Maleme.[1]Critical Reinforcements and Counterattacks: 21-23 May
On 21 May 1941, German forces exploited the New Zealand 22nd Battalion's withdrawal from Hill 107 overlooking Maleme airfield during the previous night, advancing to seize the airfield by midday.[39] This development enabled the first landings of transport aircraft, including Junkers Ju 52s, which delivered initial reinforcements such as infantry and light equipment from the 5th Mountain Division directly onto the captured field, bolstering the beleaguered paratroopers who had suffered heavy losses on 20 May.[20][1] Lieutenant General Bernard Freyberg, recognizing the airfield's strategic value for further German build-up, ordered the 2nd New Zealand Division to counterattack and retake Maleme that night, assigning the 20th Battalion and 28th (Māori) Battalion to lead the assault supported by other elements.[24][43] However, delays arose from communication breakdowns, incomplete troop concentrations, and navigational issues in the darkness, postponing the attack until dawn on 22 May.[39][44] The daylight counteroffensive exposed the New Zealanders to intense Luftwaffe bombing and strafing, which disrupted formations and inflicted significant casualties, while additional German glider reinforcements and consolidated defenses repelled the advance.[39][45] By midday, the assault collapsed short of the airfield, allowing Germans to maintain control and continue receiving airlifted troops, including artillery and assault guns, which shifted the balance in the western sector.[24][46] On 23 May, with German strength augmented by thousands of flown-in reinforcements over the prior days, assaults pressed Allied lines near Maleme, compelling New Zealand and British units to withdraw eastward to a new defensive position at Platanias to avoid encirclement.[47] Freyberg's forces, hampered by ammunition shortages and relentless air superiority, could mount no effective riposte, as German mountain troops began probing toward Chania, underscoring the critical failure to neutralize the airfield foothold promptly.[9][24]Final Phases and Italian Landings: 23-27 May
By 23 May, German forces, having secured Maleme airfield, intensified airlifts of reinforcements including elements of the 5th Gebirgs Division, enabling advances toward Chania while Allied troops under Brigadier Howard Kippenberger withdrew to defensive positions around Galatas to avoid encirclement.[48] German Kampfgruppe Ramcke repelled counterattacks by New Zealand's 28th (Maori) Battalion at Platanias Bridge, consolidating control over the western plain and freeing the airfield from artillery threat.[48] On 24 May, German patrols from the 85th and 100th Gebirgsjäger Regiments probed the Galatas frontline, while additional paratroops dropped southwest of Heraklion to support stalled assaults there; Allied RAF strikes destroyed 24 Junkers Ju 52 transports at Maleme, though Luftwaffe dominance limited further air operations.[48] The next day, 25 May, Fallschirmjäger of Kampfgruppe Ramcke launched a dusk assault on Galatas, overrunning positions held by New Zealand's 18th Battalion amid close-quarters fighting; a subsequent Allied counterattack, featuring bayonet charges by New Zealand and British troops supported by Cretan irregulars, temporarily restored parts of the line before pressure forced withdrawal.[48] The 26 May breakthrough along the Chania-Galatas line saw Ramcke's group advance along the coast road, compelling New Zealand's 21st Battalion to fall back toward Suda Bay; concurrent southern thrusts by the 3rd Fallschirmjäger Regiment strained Allied reserves, prompting Lieutenant General Bernard Freyberg to order a general retreat to Sphakia for potential evacuation amid mounting shortages of ammunition and water.[49] In the east, garrisons at Rethymno and Heraklion remained isolated but defiant, with Australian and Greek forces repelling probing attacks despite encirclement risks.[49] On 27 May, German battlegroups encircled Allied Force Reserve near Chania, but a counterattack at the improvised "42nd Street" defense line—led by New Zealand's 28th Maori Battalion and Australia's 2/7th Battalion with fixed bayonets—halted the 141st Gebirgsjäger Regiment, inflicting approximately 200 casualties and buying time for withdrawal; British Layforce commandos arrived at Suda Bay, while General Freyberg and Middle East Command deemed the position untenable, formalizing evacuation plans.[50] Italian naval forces, operating under Admiral Francesco Mimbelli, provided limited support but avoided direct confrontation with Royal Navy elements; German high command, facing attrition, requested Mussolini's assistance with army units to bolster the faltering advance, though significant Italian landings in the west did not materialize until after Allied departures.[10] Eastern sectors at Rethymno and Heraklion held firm against intensified German pressure, with no breakthroughs by day's end.[49]Allied Evacuation and German Victory Consolidation
By late May 1941, with German forces advancing across Crete and Allied positions collapsing in the west and center, General Bernard Freyberg ordered a general withdrawal toward the southern port of Sfakia on 26 May to facilitate evacuation by the Royal Navy.[1] [9] The retreat involved disorganized marches through rugged terrain, with Commonwealth units like the New Zealand 2nd Division and Australian 6th Division covering the rear against pursuing Fallschirmjäger and Gebirgsjäger.[51] [26] Evacuation operations commenced on the night of 28-29 May, focusing on Sfakia due to its relative isolation from German-held airfields, though Heraklion saw limited earlier lifts.[26] Royal Navy destroyers and cruisers, operating under constant Luftwaffe attacks, transported approximately 16,000 Allied troops to Egypt between 28 May and 1 June, including 6,000 on the first night alone; vessels like HMS Gloucester and HMS Greyhound were sunk during these runs, contributing to the loss of three cruisers and six destroyers overall.[1] [16] Despite these efforts, around 9,000-11,000 troops remained ashore by 31 May, either captured during the final German push or choosing guerrilla resistance, as shipping capacity and air cover proved insufficient.[51] [3] As Allied forces disengaged, German units under General Kurt Student consolidated gains by securing key airfields at Maleme and Heraklion, enabling the airlift of over 20,000 reinforcements from the 5th Mountain Division by 30 May, which shifted the battle from airborne desperation to ground dominance.[4] Italian naval forces attempted landings at Sitia and Kastelli on 28-31 May, committing about 5,000 troops, but these were marginal and placed under German operational control, with Axis command declaring the island secured on 1 June 1941.[52] German patrols mopped up pockets of resistance in the White Mountains, capturing stragglers and executing suspected partisans, while establishing garrisons in Chania and Rethymno to enforce occupation amid heavy casualties that numbered 6,700 total for the Wehrmacht.[4] This victory provided Germany unchallenged access to the Aegean but at a cost that prompted Adolf Hitler to restrict future large-scale paratroop operations.[31]Civilian Resistance and Reprisals
Cretan Participation in the Defense
Cretan civilians mobilized en masse following the German airborne landings on 20 May 1941, spontaneously taking up arms against the invading paratroopers in a display of fierce, improvised resistance that caught the attackers off guard. Armed primarily with traditional implements such as knives, axes, scythes, and farm tools, local inhabitants—predominantly men but including women and adolescents—targeted isolated or descending Fallschirmjäger units, often charging them during the chaos of dispersal across the island's rugged terrain.[53] [54] This grassroots uprising was not orchestrated by Allied command but arose from a cultural ethos of martial tradition and immediate revulsion toward the unannounced assault on their homeland.[53] In the western sector around Maleme and Chania, Cretans supplemented the outnumbered New Zealand and Greek regular forces, forming ad hoc groups that ambushed German elements attempting to consolidate bridgeheads and seize airfields. Local gendarmerie units, numbering several thousand, integrated civilian fighters into defensive lines, particularly in urban areas where close-quarters fighting neutralized the paratroopers' initial advantages in surprise.[34] [2] Reports from the period indicate that such participation extended to the central and eastern sectors, including Rethymno and Heraklion, where villagers repelled early probes by Fallschirmjäger and reinforced garrisons holding key positions against follow-on glider reinforcements.[54] The scale of involvement was substantial, with estimates suggesting thousands of non-combatants actively engaged over the battle's initial days, though precise figures remain elusive due to the decentralized nature of the effort.[53] This civilian involvement persisted through the battle's duration, even as Allied organized resistance waned, with Cretans conducting hit-and-run attacks on supply lines and stragglers amid the 21-23 May counteroffensives. Their actions often blurred lines between combatants and non-combatants under international norms, as fighters discarded civilian attire post-engagement to evade reprisals, a tactic rooted in the island's guerrilla heritage rather than formal irregular warfare doctrine.[53] German after-action assessments later acknowledged the unforeseen ferocity of this response, attributing operational disruptions in part to the population's unanticipated belligerence, which compounded the paratroopers' vulnerabilities during landing phases.[53]Effectiveness Against German Forces
Cretan civilians, largely unarmed or equipped with rudimentary tools such as rocks, shovels, pitchforks, scythes, and outdated shotguns, mounted fierce close-quarters attacks against German paratroopers immediately following the airborne landings on 20 May 1941. These actions targeted isolated and disorganized Fallschirmjäger units, who were vulnerable due to scattered drops, heavy anti-aircraft fire, and lack of immediate heavy support. In villages like Modhion, civilians inflicted 60% casualties on the German 10th Company, while at Gerani, only 14 out of 126 paratroopers survived assaults by local fighters. Individual acts of resistance, such as that of Nicholas Manolakakis, who reportedly killed 40 Germans before being executed, underscored the personal scale of engagement.[53] The effectiveness stemmed from Cretan cultural traditions of hospitality turned to vengeance, local terrain knowledge enabling ambushes, and the element of surprise, as German planners had underestimated civilian hostility based on assumptions of Mediterranean sympathy toward the Axis. Women participated actively, sniping from Chania rooftops and joining sieges, amplifying the psychological shock to elite troops unaccustomed to such irregular warfare. This resistance delayed German consolidation in key sectors, buying time for Allied counterattacks and contributing to the invaders' high attrition rates on the first day, when paratrooper losses exceeded 1,000.[53] Quantitative assessments indicate civilians caused approximately one-third of total German casualties, estimated at around 1,955 of the 6,580 overall losses (including 3,400 paratrooper deaths), primarily through presumed killings of missing troops. While exact figures remain elusive due to incomplete records and the chaos of combat, historical analyses attribute this disproportionate impact to the civilians' role in exploiting the airborne operation's inherent weaknesses, such as prolonged exposure during descent and assembly. The ferocity prompted German commanders to report "fanatical" opposition, with units like Oberleutnant Toschka's suffering near annihilation from civilian onslaughts.[53] Overall, civilian efforts rendered the German victory pyrrhic, as the casualties—combined with Allied resistance—led Adolf Hitler to prohibit future large-scale airborne assaults, reshaping Axis doctrine. However, their impact waned after 21 May as German reinforcements arrived via sea and air, allowing organized advances; civilians shifted to guerrilla harassment but could not alter the strategic outcome of Allied evacuation by 1 June. This phase highlighted causal vulnerabilities in airborne tactics against motivated irregulars, though reprisals later exacted a heavy toll on the population.[53][31]German Response: Executions and Massacres
In retaliation for the active participation of Cretan civilians in combat operations that contributed to heavy German casualties during the Battle of Crete, German airborne forces under General Kurt Student implemented immediate reprisal policies targeting villages involved in resistance. These measures included summary executions of male civilians, often by ad hoc firing squads, as a deterrent against further irregular warfare, with directives from higher command establishing a ratio of ten Cretan executions per German soldier killed or wounded.[55][53] On 24 May 1941, amid ongoing fighting in the western sector, paratroopers from units engaged near Chania conducted mass executions at Alikianos, targeting men from the village and adjacent areas for their role in ambushing and killing dropped troops shortly after the airborne landings. Survivors and local accounts indicate dozens were shot, with bodies left unburied as a warning.[56] The most documented reprisal occurred on 2 June 1941 at Kondomari, two days after the island's surrender, where Fallschirmjäger rounded up and executed approximately 60 male villagers by firing squad for prior attacks on isolated paratroopers. The operation was photographed by German war correspondent Franz-Peter Weixler, whose images, later recovered from archives, captured the assembly of victims and the execution process, providing direct evidence of the systematic nature of the killings ordered by Student.[55] On 3 June 1941, German forces razed the village of Kandanos, executing around 180 inhabitants—including women and elderly—in response to local defenders who had delayed advances toward Chania for two days using improvised weapons and terrain knowledge. Troops dynamited homes and erected a sign stating the destruction punished "the bloody, barbaric retaliation against our warriors," marking an escalation to collective punishment beyond individual combatants.[57] These early actions resulted in hundreds of civilian deaths across western Crete, establishing a pattern of terror to secure compliance during the initial occupation phase, though they failed to fully suppress subsequent guerrilla activity.[58][59]Aftermath and Analysis
Casualties, Losses, and Pyrrhic Victory Debate
The German airborne assault on Crete from 20 to 31 May 1941 inflicted severe casualties on the Fallschirmjäger divisions, with official Wehrmacht records reporting 2,124 killed, 1,917 missing (presumed dead), and 2,640 wounded, totaling approximately 6,681 casualties out of an initial airborne force of around 22,000 paratroopers and glider troops.[60] These losses represented over 30% of the assault force, disproportionately affecting elite units like the 7th Flieger-Division, where entire companies were decimated on the first day due to scattered drops, lack of heavy weapons, and fierce ground resistance.[1] German material losses compounded the human toll, including over 220 transport aircraft destroyed or damaged, primarily Junkers Ju 52s, which strained Luftwaffe resources already committed to the Eastern Front buildup.[1] Allied ground forces suffered around 3,000 killed or missing and 15,000 captured from an initial strength of approximately 42,000 troops, including British, New Zealand, Australian, and Greek contingents, with many captured during the disorganized evacuation from 28-31 May.[61] The Royal Navy, crucial for evacuation and interdiction, lost three cruisers and six destroyers sunk, with over 2,000 sailors killed in air attacks, alongside damage to major warships like HMS Warspite and Barham.[61] Cretan civilians and irregulars, numbering in the thousands who took up arms spontaneously, incurred heavy losses estimated at 2,000-3,000 killed, often in close-quarters fighting or subsequent reprisals, though exact figures remain disputed due to incomplete records.[53] The battle's outcome sparked debate over whether it constituted a Pyrrhic victory for Germany, given the tactical success in seizing the island against numerical superiority but at the cost of irreplaceable elite airborne troops and aircraft that could not be readily rebuilt amid broader war demands.[4] Adolf Hitler, citing the "butcher's bill," reportedly declared the paratrooper's era over in a 21 May 1941 directive, effectively halting large-scale airborne operations thereafter, as seen in the scaled-back role of Fallschirmjäger in later campaigns like Crete's occupation or Arnhem.[62] Proponents of the Pyrrhic label, including post-war analyses, emphasize that the high attrition—equivalent to two regiments annihilated—weakened Germany's ability to conduct similar high-risk assaults, while the strategic gain of denying Crete as an Allied base proved marginal, as Axis forces lacked the naval power to exploit it fully against British Mediterranean operations.[4] Counterarguments note that exaggerated Allied intelligence on German losses (initially claimed at 15,000-20,000) influenced perceptions, and the victory secured the Aegean flank for Operation Barbarossa, but empirical evidence of doctrinal abandonment and resource diversion supports the consensus of a costly triumph that eroded German qualitative edges without proportional strategic returns.[62]| Belligerent | Killed/Missing | Wounded | Captured | Key Material Losses |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Germany | ~4,041 | 2,640 | Minimal | 220+ aircraft |
| Allies (Ground) | ~3,000 | Unknown | ~15,000 | N/A |
| Royal Navy | ~2,000 | Unknown | N/A | 3 cruisers, 6 destroyers sunk |
| Cretan Civilians | ~2,000-3,000 | Unknown | N/A | N/A |

