Recent from talks
Contribute something
Nothing was collected or created yet.
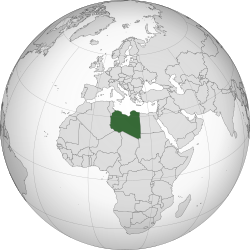
Libya
View on Wikipedia
Libya,[b] officially the State of Libya,[c] is a country in the Maghreb region of North Africa. It borders the Mediterranean Sea to the north, Egypt to the east, Sudan to the southeast, Chad to the south, Niger to the southwest, Algeria to the west, and Tunisia to the northwest. With an area of almost 1.8 million km2 (700,000 sq mi), Libya is the fourth-largest country in Africa and the Arab world, and the 16th-largest in the world.[10] The country claims 32,000 square kilometres of southeastern Algeria, south of the Libyan town of Ghat.[1][11] The capital and largest city is Tripoli, located in the northwest and contains over a million of Libya's 7 million people.[12]
Key Information
Libya has been inhabited by Berbers since the late Bronze Age as descendants from Iberomaurusian and Capsian cultures. In classical antiquity, the Phoenicians established city-states and trading posts in western Libya, while several Greek cities were established in the East. Parts of Libya were variously ruled by Carthaginians, Numidians, Persians, and Greeks before the entire region became a part of the Roman Empire. Libya was an early centre of Christianity. After the fall of the Western Roman Empire, the area of Libya was mostly occupied by the Vandals until the 7th century when invasions brought Islam to the region. From then on, centuries of Arab migration to the Maghreb shifted the demographic scope of Libya in favour of Arabs. In the 16th century, the Spanish Empire and the Knights Hospitaller occupied Tripoli until Ottoman rule began in 1551. Libya was involved in the Barbary Wars of the 18th and 19th centuries. Ottoman rule continued until the Italo-Turkish War in 1911, which resulted in Italy occupying Libya and establishing two colonies: Italian Tripolitania and Italian Cyrenaica, later unified in the Italian Libya colony from 1934 to 1943.[13]
During World War II, Libya was an area of warfare in the North African Campaign. The Italian population then went into decline and Libya became independent as a kingdom in 1951. A bloodless military coup in 1969, initiated by a coalition led by Colonel Muammar Gaddafi, overthrew King Idris I and created a republic. Gaddafi was often described by critics as a dictator, and was one of the world's longest serving non-royal leaders. He ruled for 42 years until being overthrown and killed in the 2011 civil war, which was part of the wider Arab Spring, with authority transferred to the National Transitional Council then to the elected General National Congress.
Since 2011, Libya has been involved in a political and humanitarian crisis, and by 2014, two rival authorities claimed to govern Libya, which led to a second civil war, with parts of Libya split between separate governments, based in Tripoli and Tobruk, as well as various tribal and Islamist militias. The two main warring sides signed a permanent ceasefire in 2020, and a unity government took authority to plan for democratic elections, though political rivalries continue to delay this.[14][15][16][17][18][19][20][21] In March 2022, the House of Representatives ceased recognising the Government of National Unity and proclaimed an alternative government, the Government of National Stability (GNS). Both governments have been functioning simultaneously since then, which has led to dual power in Libya. The international community continues to recognise the unity government as the legitimate government of the country.
Libya is a developing country ranking 115th by HDI, and has the 10th-largest proven oil reserves in the world. Libya has the highest level of greenhouse gas emissions per person in Africa, but has made little progress toward developing climate commitments. Libya is a member of the United Nations, the Non-Aligned Movement, the African Union, the Arab League, the Organisation of Islamic Cooperation, and OPEC. The country's official religion is Islam, with 96.6% of the Libyan population being Sunni Muslims.[1] The official language of Libya is Arabic, with vernacular Libyan Arabic being spoken most widely. The majority of Libya's population is Arab.[22][23][24]
Etymology
[edit]
The origin of the name "Libya" first appeared in an inscription of Ramesses II, written as rbw in hieroglyphic. The name derives from a generalised identity given to a large confederacy of ancient east "Libyan" Berbers, North African people(s) and tribes who lived around the lush regions of Cyrenaica and Marmarica. An army of 40,000 men[25] and a confederacy of tribes known as "Great Chiefs of the Libu" were led by King Meryey who fought a war against pharaoh Merneptah in year 5 (1208 BCE). This conflict was mentioned in the Great Karnak Inscription in the western delta during the 5th and 6th years of his reign and resulted in a defeat for Meryey. According to the Great Karnak Inscription, the military alliance comprised the Meshwesh, the Lukka, and the "Sea Peoples" known as the Ekwesh, Teresh, Shekelesh, and the Sherden.
The Great Karnak Inscription reads:
"... the third season, saying: 'The wretched, fallen chief of Libya, Meryey, son of Ded, has fallen upon the country of Tehenu with his bowmen — Sherden, Shekelesh, Ekwesh, Lukka, Teresh. Taking the best of every warrior and every man of war of his country. He has brought his wife and his children — leaders of the camp, and he has reached the western boundary in the fields of Perire."
The name "Libya" was brought back into use in 1903 by Italian geographer Federico Minutilli. It was intended to supplant terms applied to Ottoman Tripolitania, the coastal region of what is today Libya, having been ruled by the Ottoman Empire from 1551 to 1911 as the Eyalet of Tripolitania.[26]
Libya gained independence in 1951 as the United Libyan Kingdom (المملكة الليبية المتحدة al-Mamlakah al-Lībiyyah al-Muttaḥidah), changing its name to the Kingdom of Libya (المملكة الليبية al-Mamlakah al-Lībiyyah), literally "Libyan Kingdom", in 1963.[27] Following a coup d'état led by Muammar Gaddafi in 1969, the name of the state was changed to the Libyan Arab Republic (الجمهورية العربية الليبية al-Jumhūriyyah al-'Arabiyyah al-Lībiyyah). The official name was "Socialist People's Libyan Arab Jamahiriya" from 1977 to 1986 (الجماهيرية العربية الليبية الشعبية الاشتراكية), and "Great Socialist People's Libyan Arab Jamahiriya"[28] (الجماهيرية العربية الليبية الشعبية الاشتراكية العظمى,[29] al-Jamāhīriyyah al-'Arabiyyah al-Lībiyyah ash-Sha'biyyah al-Ishtirākiyyah al-'Udmá ⓘ) from 1986 to 2011.
The National Transitional Council, established in 2011, referred to the state as simply "Libya". The United Nations (UN) formally recognised the country as "Libya" in September 2011[30] based on a request from the Permanent Mission of Libya citing the Libyan interim Constitutional Declaration of 3 August 2011. In November 2011, the ISO 3166-1 was altered to reflect the new country name "Libya" in English, "Libye (la)" in French.[31]
In December 2017, the Permanent Mission of Libya to the United Nations informed the UN that the country's official name was henceforth the "State of Libya"; "Libya" remained the official short form, and the country continued to be listed under "L" in alphabetical lists.[32]
History
[edit]Ancient Libya
[edit]
The coastal plain of Libya was inhabited by Neolithic peoples from as early as 8000 BC. The Afroasiatic ancestors of the Berber people are assumed to have spread into the area by the Late Bronze Age. The earliest known name of such a tribe was the Garamantes, based in Germa. The Phoenicians were the first to establish trading posts in Libya.[33] By the 5th century BC, the greatest of the Phoenician colonies, Carthage, had extended its hegemony across much of North Africa, where a distinctive civilisation, known as Punic, came into being.
In 630 BC, the ancient Greeks colonised the area around Barca in Eastern Libya and founded the city of Cyrene.[34] Within 200 years, four more important Greek cities were established in the area that became known as Cyrenaica.[35] The area was home to the renowned philosophy school of the Cyrenaics. In 525 BC the Persian army of Cambyses II overran Cyrenaica, which for the next two centuries remained under Persian or Egyptian rule. Alexander the Great ended Persian rule in 331 BC and received tribute from Cyrenaica. Eastern Libya again fell under the control of the Greeks, this time as part of the Ptolemaic Kingdom.

After the fall of Carthage the Romans did not immediately occupy Tripolitania (the region around Tripoli), but left it instead under control of the kings of Numidia, until the coastal cities asked and obtained its protection.[36] Ptolemy Apion, the last Greek ruler, bequeathed Cyrenaica to Rome, which formally annexed the region in 74 BC and joined it to Crete as a Roman province. As part of the Africa Nova province, Tripolitania was prosperous,[36] and reached a golden age in the 2nd and 3rd centuries, when the city of Leptis Magna, home to the Severan dynasty, was at its height.[36]
On the eastern side, Cyrenaica's first Christian communities were established by the time of the Emperor Claudius.[37] It was heavily devastated during the Kitos War[38] and almost depopulated of Greeks and Jews alike.[39] Although repopulated by Trajan with military colonies,[38] from then started its decline.[37] Libya was early to convert to Nicene Christianity and was the home of Pope Victor I; however, Libya was also home to many non-Nicene varieties of early Christianity, such as Arianism and Donatism.
Islamic Libya: 647–1556
[edit]
Under the command of Amr ibn al-As, the Rashidun army conquered Cyrenaica.[40] In 647 an army led by Abdullah ibn Saad took Tripoli from the Byzantines definitively.[40] The Fezzan was conquered by Uqba ibn Nafi in 663. The Berber tribes of the hinterland accepted Islam, however they resisted Arab political rule.[41] For the next several decades, Libya was under the purview of the Umayyad Caliph of Damascus until the Abbasids overthrew the Umayyads in 750, and Libya came under the rule of Baghdad. When Caliph Harun al-Rashid appointed Ibrahim ibn al-Aghlab as his governor of Ifriqiya in 800, Libya enjoyed considerable local autonomy under the Aghlabid dynasty. By the 10th century, the Shiite Fatimids controlled Western Libya, and ruled the entire region in 972 and appointed Bologhine ibn Ziri as governor.[36]
Ibn Ziri's Berber Zirid dynasty ultimately broke away from the Shiite Fatimids, and recognised the Sunni Abbasids of Baghdad as rightful Caliphs. In retaliation, the Fatimids brought about the migration of thousands from mainly two Arab Qaisi tribes, the Banu Sulaym and Banu Hilal to North Africa. This act drastically altered the fabric of the Libyan countryside, and cemented the cultural and linguistic Arabisation of the region.[36]
Zirid rule in Tripolitania was short-lived though, and already in 1001 the Berbers of the Banu Khazrun broke away. Tripolitania remained under their control until 1146, when the region was overtaken by the Normans of Sicily.[42] For the next 50 years, Tripolitania was the scene of numerous battles among Ayyubids, the Almohad rulers and insurgents of the Banu Ghaniya. Later, a general of the Almohads, Muhammad ibn Abu Hafs, ruled Libya from 1207 to 1221 before the later establishment of the Tunisian Hafsid Kingdom[42] independent from the Almohads. In the 14th century, the Banu Thabit dynasty ruled Tripolitania before reverting to direct Hafsid control. By the 16th century, the Hafsids became increasingly caught up in the power struggle between Spain and the Ottoman Empire.
After Abbasid control was weakened, Cyrenaica was under Egypt-based states such as the Tulunids, Ikhshidids, Ayyubids, and Mamluks before Ottoman conquest in 1517. Fezzan acquired independence under Awlad Muhammad dynasty after Kanem rule. Ottomans finally conquered Fezzan between 1556 and 1577.
Ottoman Tripolitania: 1556–1911
[edit]
After a successful invasion of Tripoli by Habsburg Spain in 1510,[42] and its handover to the Knights Hospitaller, the Ottoman admiral Sinan Pasha took control of Libya in 1551.[42] His successor Turgut Reis was named the Bey of Tripoli and later Pasha of Tripoli in 1556. By 1565, administrative authority as regent in Tripoli was vested in a pasha appointed directly by the sultan in Constantinople/Istanbul. In the 1580s, the rulers of Fezzan gave their allegiance to the sultan, and although Ottoman authority was absent in Cyrenaica, a bey was stationed in Benghazi late in the next century to act as agent of the government in Tripoli.[37] European slaves and large numbers of enslaved Blacks transported from Sudan were also a feature of everyday life in Tripoli. In 1551, Turgut Reis enslaved almost the entire population of the Maltese island of Gozo, some 5,000 people, sending them to Libya.[43][44]
In time, real power came to rest with the pasha's corps of janissaries.[42] In 1611 the deys staged a coup against the pasha, and Dey Sulayman Safar was appointed as head of government. For the next hundred years, a series of deys effectively ruled Tripolitania. The two most important Deys were Mehmed Saqizli (r. 1631–49) and Osman Saqizli (r. 1649–72), both also Pasha, who ruled effectively the region.[45] The latter conquered also Cyrenaica.[45]

Lacking direction from the Ottoman government, Tripoli lapsed into a period of military anarchy during which coup followed coup and few deys survived in office more than a year. One such coup was led by Turkish officer Ahmed Karamanli.[45] The Karamanlis ruled from 1711 until 1835 mainly in Tripolitania, and had influence in Cyrenaica and Fezzan as well by the mid-18th century. Ahmed's successors proved to be less capable than himself, however, the region's delicate balance of power allowed the Karamanli. The 1793–95 Tripolitanian civil war occurred in those years. In 1793, Turkish officer Ali Pasha deposed Hamet Karamanli and briefly restored Tripolitania to Ottoman rule. Hamet's brother Yusuf (r. 1795–1832) re-established Tripolitania's independence. In 1816, Yusuf ordered the massacre of the al-Jawazi tribe.[46]

In the early 19th century war broke out between the United States and Tripolitania, and a series of battles ensued in what came to be known as the First Barbary War and the Second Barbary War. By 1819, the various treaties of the Napoleonic Wars had forced the Barbary states to give up piracy almost entirely, and Tripolitania's economy began to crumble. As Yusuf weakened, factions sprung up around his three sons. Civil war soon resulted.[47]
Ottoman Sultan Mahmud II sent in troops ostensibly to restore order, marking the end of both the Karamanli dynasty and an independent Tripolitania.[47] Order was not recovered easily, and the revolt of the Libyan under Abd-El-Gelil and Gûma ben Khalifa lasted until the death of the latter in 1858.[47] The second period of direct Ottoman rule saw administrative changes, and greater order in the governance of the three provinces of Libya. Ottoman rule finally reasserted to Fezzan between 1850 and 1875 for earning income from Saharan commerce.
Italian colonisation and Allied occupation (1911–1951)
[edit]
After the Italo-Turkish War (1911–1912), Italy simultaneously turned the three regions into colonies.[48] From 1912 to 1927, the territory of Libya was known as Italian North Africa. From 1927 to 1934, the territory was split into two colonies, Italian Cyrenaica and Italian Tripolitania, run by Italian governors. Some 150,000 Italians settled in Libya, constituting roughly 20% of the total population.[49]
Omar Mukhtar rose to prominence as a resistance leader against Italian colonisation and became a national hero despite his capture and execution on 16 September 1931.[50] His face is currently printed on the Libyan ten dinar note in memory and recognition of his patriotism. Another prominent resistance leader, Idris al-Mahdi as-Senussi (later King Idris I), Emir of Cyrenaica, continued to lead the Libyan resistance until the outbreak of the Second World War.
The so-called "pacification of Libya" by the Italians resulted in mass deaths of the indigenous people in Cyrenaica, killing approximately one quarter of Cyrenaica's population of 225,000.[51] Ilan Pappé estimates that between 1928 and 1932 the Italian military "killed half the Bedouin population (directly or through disease and starvation in Italian concentration camps in Libya)."[52]

In 1934, Italy combined Cyrenaica, Tripolitania and Fezzan and adopted the name "Libya" (used by the Ancient Greeks for all of North Africa except Egypt) for the unified colony, with Tripoli as its capital.[53] The Italians emphasised infrastructure improvements and public works. In particular, they greatly expanded Libyan railway and road networks from 1934 to 1940, building hundreds of kilometres of new roads and railways and encouraging the establishment of new industries and dozens of new agricultural villages.
In June 1940, Italy entered World War II. Libya became the setting for the hard-fought North African Campaign that ultimately ended in defeat for Italy and its German ally in 1943. From 1943 to 1951, Libya was under Allied occupation. The British military administered the two former Italian Libyan provinces of Tripolitana and Cyrenaïca, while the French administered the province of Fezzan. In 1944, Idris returned from exile in Cairo but declined to resume permanent residence in Cyrenaica until the removal of some aspects of foreign control in 1947. Under the terms of the 1947 peace treaty with the Allies, Italy relinquished all claims to Libya.[54]
Independent Kingdom (1951–1969)
[edit]
A national assembly crafted a constitution that established a monarchy and extended an offer for the throne to Sayyid Idris, the Emir of Cyrenaica.[55] Sayyid Idris held the esteemed position as the leader of the influential Senussi religious brotherhood, which was founded by his grandfather in the preceding century as a response to Western influence in the Arab world.[55] This devout Islamic movement garnered significant support from the desert Bedouin and became a major political force in Libya. During the declining years of the Ottoman Empire, it effectively governed the Libyan interior.[55] Born in an oasis in Cyrenaica in 1890, Sayyid Idris assumed leadership of the Senussi at a young age. He spent a considerable period of exile in Egypt under Italian rule and returned to Libya after the Axis powers were ousted in 1943.[55] On December 24, 1951, as King Idris I, he addressed the nation via radio from Benghazi.[55] On November 21, 1949, the UN General Assembly passed a resolution stating that Libya should become independent before January 1, 1952.[56] Idris represented Libya in the subsequent UN negotiations. By December 24, 1951, Libya declared its independence as the United Kingdom of Libya, a constitutional and hereditary monarchy under King Idris.[57]
However, the new kingdom faced challenging prospects.[55] It lacked significant industry and agricultural resources.[55] The kingdom's primary exports consisted of hides, wool, horses, and ostrich feathers.[55] Despite having one of the lowest income per capita figures globally, it also suffered from one of the highest illiteracy rates.[55] King Idris I, already in his sixties, had no direct heir to succeed him.[55] His cousin, whom he had married in 1932, reportedly experienced numerous miscarriages, and their son, born in 1953, tragically died shortly after birth.[55] Crown Prince Rida, Idris's brother, was the designated heir, but the royal family was riddled with incessant disputes.[55] King Idris's devout Muslim piety, which solidified his support among the Bedouin population, clashed with the modernising and urban intellectual currents in Libya.[55] To address the rivalry between Cyrenaica and Tripolitania, Benghazi and Tripoli alternated as the capital every two years.
The swift emergence of a large number of bureaucrats resulted in a costly royal government.[55] The discovery of significant oil reserves in 1959 and the subsequent income from petroleum sales enabled one of the world's poorest nations to establish an extremely wealthy state.[57] Although oil drastically improved the Libyan government's finances, popular resentment began to build over the increased concentration of the nation's wealth in the hands of King Idris and the national elite.[56][57] This discontent continued to mount with the rise of Nasserism and Arab nationalism throughout North Africa and the Middle East, that inspire many anti-royal coups across the Arab world.[57]
Republic of Libya under Gaddafi (1969–2011)
[edit]On 1 September 1969, a group of rebel military officers led by Muammar Gaddafi launched a coup d'état against King Idris, which became known as the Al Fateh Revolution.[58][59] Gaddafi was referred to as the "Brother Leader and Guide of the Revolution" in government statements and the official Libyan press.[60][59] He began dominating history and politics of Libya for the next four decades.[59] Moving to reduce Italian influence, in October 1970 all Italian-owned assets were expropriated and the 12,000-strong Italian community was expelled from Libya alongside the smaller community of Italian Libyan Jews.[59] The day became a national holiday known as "Day of Revenge";[59] it was later renamed the "Day of Friendship" because of an improvement in Italy–Libya relations.[61]

Libya's increase in prosperity was accompanied by increased internal political repression, and political dissent was made illegal under Law 75 of 1973.[62] Widespread surveillance of the population was carried out through Gaddafi's Revolutionary Committees.[63][62][64] Gaddafi also wanted to ease the strict social restrictions imposed on women by the previous regime, establishing the Revolutionary Women's Formation to encourage reform.[62] In 1970, a law was introduced affirming equality of the sexes and wage parity.[62] In 1971, Gaddafi sponsored the creation of a Libyan General Women's Federation.[62] In 1972, a law was passed criminalising the marriage of girls under the age of sixteen and making the woman's consent a necessary prerequisite for a marriage.[65]
On 25 October 1975, a coup attempt was launched by a group of 20 military officers, mostly from the city of Misrata.[66] This resulted in the arrest and executions of the coup plotters.[67] In March 1977, Libya officially became the "Socialist People's Libyan Arab Jamahiriya".[62] Gaddafi officially passed power to the General People's Committees and henceforth claimed to be no more than a symbolic figurehead.[68][62] The new jamahiriya (Arab for "republic") governance structure he established was officially referred to as "direct democracy".[69] Gaddafi, in his vision of democratic government and political philosophy, published The Green Book in 1975. His short book inscribed a representative mix of utopian socialism and Arab nationalism with a streak of Bedouin supremacy.

In February 1977, Libya started delivering military supplies to Goukouni Oueddei and the People's Armed Forces in Chad.[62] The Chadian–Libyan War began in earnest when Libya's support of rebel forces in northern Chad escalated into an invasion.[62] Later that same year, Libya and Egypt fought a four-day border war that came to be known as the Egyptian–Libyan War.[62] Both nations agreed to a ceasefire under the mediation of the Algerian president Houari Boumédiène.[70] Hundreds of Libyans lost their lives in the country's support for Idi Amin's Uganda in its war against Tanzania.[62] Gaddafi financed various other groups from anti-nuclear movements to Australian trade unions.[71] On 2 March 1977, Libya officially became the Great Socialist People's Libyan Arab Jamahiriya.[72]
Libya adopted its plain green national flag on 19 November 1977.[62] The country had the only plain-coloured flag in the world until 2011, when Libya adopted its current flag.[citation needed] From 1977 onward, per capita income in the country rose to more than US$11,000, the fifth-highest in Africa,[73] while the Human Development Index became the highest in Africa and greater than that of Saudi Arabia.[74] This was achieved without borrowing any foreign loans, keeping Libya debt-free.[75] The Great Manmade River was also built to allow free access to fresh water across large parts of the country.[74] In addition, financial support was provided for university scholarships and employment programs.[76] Much of Libya's income from oil, which soared in the 1970s, was spent on arms purchases and on sponsoring dozens of paramilitaries and terrorist groups around the world.[77][78][79]
An American airstrike led by then U.S. president Ronald Reagan intended to kill Gaddafi failed in 1986.[62] Libya was finally put under sanctions by the United Nations after the bombing of a commercial flight at Lockerbie in 1988 killed 270 people.[80] In the 1990s, the government's rule was threatened by militant Islamism and an unsuccessful attempt to assassinate Gaddafi.[81] The government responded with repressive measures.[81] Riots and Islamic activisim were crushed by Revolutionary Guard Corps.[81] Nevertheless, Cyrenaica between 1995 and 1998 was politically unstable, due to the tribal allegiances of the local troops.[81] In 2003, Gaddafi announced that all of his regime's weapons of mass destruction were disassembled, and that Libya was transitioning toward nuclear power.[62]
First Libyan Civil War and the fall of Gaddafi (2011)
[edit]
The first civil war came during the Arab Spring movements which overturned the rulers of Tunisia and Egypt. Libya first experienced protests against Gaddafi's regime on 15 February 2011, with a full-scale revolt beginning on 17 February.[82] Libya's authoritarian regime led by Muammar Gaddafi put up much more of a resistance compared to the regimes in Egypt and Tunisia. While overthrowing the regimes in Egypt and Tunisia was a relatively quick process, Gaddafi's campaign posed significant stalls on the uprising in Libya.[83] The first announcement of a competing political authority appeared online and declared the Interim Transitional National Council as an alternative government. One of Gaddafi's senior advisors responded by posting a tweet, wherein he resigned, defected, and advised Gaddafi to flee.[84] By 20 February, the unrest had spread to Tripoli. On 27 February 2011, the National Transitional Council was established to administer the areas of Libya under rebel control. On 10 March 2011, the United States and many other nations recognised the council headed by Mahmoud Jibril as acting prime minister and as the legitimate representative of the Libyan people and withdrawing the recognition of Gaddafi's regime.[85][86]

Pro-Gaddafi forces were able to respond militarily to rebel pushes in Western Libya and launched a counterattack along the coast toward Benghazi, the de facto centre of the uprising.[87] The town of Zawiya, 48 kilometres (30 mi) from Tripoli, was bombarded by air force planes and army tanks and seized by Jamahiriya troops, "exercising a level of brutality not yet seen in the conflict."[88] Organizations of the United Nations, including United Nations Secretary General Ban Ki-moon[89] and the United Nations Human Rights Council, condemned the crackdown as violating international law, with the latter body expelling Libya outright in an unprecedented action.[90][91] On 17 March 2011, the UN Security Council passed Resolution 1973,[92] with a 10–0 vote and five abstentions including Russia, China, India, Brazil and Germany. The resolution sanctioned the establishment of a no-fly zone and the use of "all means necessary" to protect civilians within Libya.[93] On 19 March, the first act of NATO allies to secure the no-fly zone began by destroying Libyan air defences when French military jets entered Libyan airspace on a reconnaissance mission heralding attacks on enemy targets.[94]
In the weeks that followed, U.S. American forces were in the forefront of NATO operations against Libya. More than 8,000 US personnel in warships and aircraft were deployed in the area. At least 3,000 targets were struck in 14,202 strike sorties, 716 of them in Tripoli and 492 in Brega.[95] The U.S. air offensive included flights of B-2 stealth bombers, each bomber armed with sixteen 2000-pound bombs, flying out of and returning to their base in Missouri.[96] The support provided by the NATO air forces contributed to the ultimate success of the revolution.[97] By 22 August 2011, rebel fighters had entered Tripoli and occupied Green Square,[98] which they renamed Martyrs' Square in honour of those killed since 17 February 2011. On 20 October 2011, the last heavy fighting of the uprising came to an end in the city of Sirte. The Battle of Sirte was both the last decisive battle and the last one in general of the First Libyan Civil War where Gaddafi was captured and killed by NATO-backed forces on 20 October 2011. Sirte was the last Gaddafi loyalist stronghold and his place of birth. The defeat of loyalist forces was celebrated on 23 October 2011, three days after the fall of Sirte. At least 30,000 Libyans died in the civil war.[99] In addition, the National Transitional Council estimated 50,000 wounded.[100]
Interwar period and the Second Libyan Civil War (2011–2020)
[edit]
 Tobruk-led Government
Tobruk-led Government  Government of National Accord
Government of National Accord  Petroleum Facilities Guard
Petroleum Facilities Guard  Tuareg tribes
Tuareg tribes  Local forces
Local forces Following the defeat of loyalist forces, Libya was torn among numerous rival, armed militias affiliated with distinct regions, cities and tribes, while the central government had been weak and unable to effectively exert its authority over the country. Competing militias pitted themselves against each other in a political struggle between Islamist politicians and their opponents.[101] On 7 July 2012, Libyans held their first parliamentary elections since the end of the former regime. On 8 August, the National Transitional Council officially handed power over to the wholly elected General National Congress, which was then tasked with the formation of an interim government and the drafting of a new Libyan Constitution to be approved in a general referendum.[102] On 25 August 2012, in what Reuters reported as "the most blatant sectarian attack" since the end of the civil war, unnamed organised assailants bulldozed a Sufi mosque with graves in the centre of the Libyan capital Tripoli. It was the second such razing of a Sufi site in two days.[103] Numerous acts of vandalism and destruction of heritage were carried out by suspected Islamist militias, including the removal of the Nude Gazelle Statue and the destruction and desecration of World War II-era British grave sites near Benghazi.[104][105] Many other cases of heritage vandalism were reported to be carried out by Islamist-related radical militias and mobs that either destroyed, robbed, or looted a number of historic sites.

On 11 September 2012, Islamist militants mounted an attack on the American diplomatic compound in Benghazi,[106] killing the U.S. ambassador to Libya, J. Christopher Stevens, and three others. The incident generated outrage in the United States and Libya.[107] On 7 October 2012, Libya's Prime Minister-elect Mustafa A.G. Abushagur was ousted after failing a second time to win parliamentary approval for a new cabinet.[108][109][110] On 14 October 2012, the General National Congress elected former GNC member and human rights lawyer Ali Zeidan as prime minister-designate.[111] Zeidan was sworn in after his cabinet was approved by the GNC.[112][113] On 11 March 2014, after having been ousted by the GNC for his inability to halt a rogue oil shipment,[114] Prime Minister Zeidan stepped down, and was replaced by Prime Minister Abdullah al-Thani.[115]
The Second Civil War began in May 2014 following fighting between rival parliaments with tribal militias and jihadist groups soon taking advantage of the power vacuum. Most notably, radical Islamist fighters seized Derna in 2014 and Sirte in 2015 in the name of the Islamic State. In February 2015, neighbouring Egypt launched airstrikes against IS in support of the Tobruk government.[116][117][118] In June 2014, elections were held to the House of Representatives, a new legislative body intended to take over from the General National Congress. The elections were marred by violence and low turnout, with voting stations closed in some areas.[119] Secularists and liberals did well in the elections, to the consternation of Islamist lawmakers in the GNC, who reconvened and declared a continuing mandate for the GNC, refusing to recognise the new House of Representatives.[120] Armed supporters of the General National Congress occupied Tripoli, forcing the newly elected parliament to flee to Tobruk.[121][122]

In January 2015, meetings were held with the aim to find a peaceful agreement between the rival parties in Libya. The so-called Geneva-Ghadames talks were supposed to bring the GNC and the Tobruk government together at one table to find a solution of the internal conflict. However, the GNC actually never participated, a sign that internal division not only affected the "Tobruk Camp", but also the "Tripoli Camp". Meanwhile, terrorism within Libya steadily increased, also affecting neighbouring countries. The terrorist attack against the Bardo Museum in Tunisia on 18 March 2015 was reportedly carried out by two Libyan-trained militants.[123] During 2015 an extended series of diplomatic meetings and peace negotiations were supported by the United Nations, as conducted by the Special Representative of the Secretary-General (SRSG), Spanish diplomat Bernardino León.[124][125] UN support for the SRSG-led process of dialogue carried on in addition to the usual work of the United Nations Support Mission in Libya (UNSMIL).[126] In July 2015 SRSG Leon reported to the UN Security Council on the progress of the negotiations, which at that point had just achieved a political agreement on 11 July setting out "a comprehensive framework... includ[ing] guiding principles... institutions and decision-making mechanisms to guide the transition until the adoption of a permanent constitution." Talks, negotiations and dialogue continued on during mid-2015 at various international locations, culminating at Skhirat in Morocco in early September.[127][128]
Also in 2015, as part of the ongoing support from the international community, the UN Human Rights Council requested a report about the Libyan situation[129][130] and the High Commissioner for Human Rights, Zeid Ra'ad Al Hussein, established an investigative body (OIOL) to report on human rights and rebuilding the Libyan justice system.[131] Chaos-ridden Libya emerged as a major transit point for people trying to reach Europe. Between 2013 and 2018, nearly 700,000 migrants reached Italy by boat, many of them from Libya.[132][133] In May 2018 Libya's rival leaders agreed to hold parliamentary and presidential elections following a meeting in Paris.[134] In April 2019, Khalifa Haftar launched Operation Flood of Dignity, in an offensive by the Libyan National Army aimed to seize Western territories from the Government of National Accord (GNA).[135] In June 2019, forces allied to Libya's UN-recognised Government of National Accord successfully captured Gharyan, a strategic town where military commander Khalifa Haftar and his fighters were based. According to a spokesman for GNA forces, Mustafa al-Mejii, dozens of LNA fighters under Haftar were killed, while at least 18 were taken prisoner.[136]
In March 2020, Prime Minister of the GNA Fayez Al-Sarraj commenced Operation Peace Storm. The government initiated the bid in response to the state of assaults carried by Field Marshal Haftar's LNA. "We are a legitimate, civilian government that respects its obligations to the international community, but is committed primarily to its people and has an obligation to protect its citizens," Sarraj said in line with his decision.[137] On 28 August 2020, the BBC Africa Eye and BBC Arabic Documentaries revealed that a drone operated by the United Arab Emirates (UAE) killed 26 young cadets at a military academy in Tripoli, on 4 January. Most of the cadets were teenagers and none of them were armed. The Chinese-made drone Wing Loong II fired Blue Arrow 7 missile, which was operated from UAE-run Al-Khadim Libyan air base. In February, these drones stationed in Libya were moved to an air base near Siwa in the western Egyptian desert.[138] The Guardian probed and discovered the blatant violation of UN arms embargo by the UAE and Turkey on 7 October 2020. As per the reporting, both the nations sent large-scale military cargo planes to Libya in support of their respective parties.[139] On 23 October 2020, a permanent ceasefire was signed to end the war.[140]
Post-civil war years (2020–present)
[edit]In December 2021, the country's first presidential election was scheduled, but was delayed to June 2022[141] and later postponed further.
Fathi Bashagha was appointed prime minister by the parliament in February 2022 to lead a transitional administration, but standing prime minister Abdul Hamid Dbeibeh refused to hand over power as of April 2022. In protest against the Dbeibah government, tribal leaders from the desert town of Ubari shut down the El Sharara oil field, Libya's largest oil field, on 18 April 2022. The shut down threatened to cause oil shortages domestically in Libya, and preclude the state-run National Oil Corp. from exploiting the high oil prices on the international market resulting from the Russian invasion of Ukraine.[142] On 2 July, the House of Representatives was burned down by protesters.[143]
On September 10, 2023, catastrophic floods due to dam failures generated by Storm Daniel devastated the port city of Derna, killing more than 5,900 and possibly as many as 24,000.[144] The floods were the worst natural disaster in Libya's modern history.[145]
In November 2024, the Government of National Unity announced it would instate a morality police to crack-down on "weird haircuts", enforce “modest” clothing, and require male guardians for women.[146]
Geography
[edit]
Libya extends over 1,759,540 square kilometres (679,362 sq mi), making it the 16th-largest nation in the world by size. Libya is bounded to the north by the Mediterranean Sea, the northwest by Tunisia, the west by Algeria, the southwest by Niger, the south by Chad, the southeast by Sudan, and the east by Egypt, as well as maritime borders with Greece, Italy and Malta to the north. Libya lies between latitudes 19° and 34°N, and longitudes 9° and 26°E. Libya comprises three historical regions: Tripolitania, Fezzan, and Cyrenaica.
At 1,770 kilometres (1,100 mi), Libya's coastline is the longest of any African country bordering the Mediterranean.[147][148] The portion of the Mediterranean Sea north of Libya is often called the Libyan Sea. The climate is mostly extremely dry and desertlike in nature. However, the northern regions enjoy a milder Mediterranean climate.[149]
Six ecoregions lie within Libya's borders: Saharan halophytics, Mediterranean dry woodlands and steppe, Mediterranean woodlands and forests, North Saharan steppe and woodlands, Tibesti-Jebel Uweinat montane xeric woodlands, and West Saharan montane xeric woodlands.[150]
Natural hazards come in the form of hot, dry, dust-laden sirocco (known in Libya as the gibli). This is a southern wind blowing from one to four days in spring and autumn. There are also dust storms and sandstorms. Oases can also be found scattered throughout Libya, the most important of which are Ghadames and Kufra.[151]
Libya is highly vulnerable to the effects of climate change and underprepared to deal with them.[152][153] The effects of climate change in Libya, such as desertification, sea level rise, flooding, and irregular weather patterns are already noticeable and are expected to increase.[153] These pose significant threats to Libya's agriculture, food and water security and economic development and sustainability.[154][155]
Libya was a pioneer state in North Africa in species protection, with the creation in 1975 of the El Kouf protected area. The fall of Muammar Gaddafi's regime favoured intense poaching: "Before the fall of Gaddafi even hunting rifles were forbidden. But since 2011, poaching has been carried out with weapons of war and sophisticated vehicles in which one can find up to 200 gazelle heads killed by militiamen who hunt to pass the time. We are also witnessing the emergence of hunters with no connection to the tribes that traditionally practice hunting. They shoot everything they find, even during the breeding season. More than 500,000 birds are killed in this way each year, when protected areas have been seized by tribal chiefs who have appropriated them. The animals that used to live there have all disappeared, hunted when they are edible or released when they are not," explains zoologist Khaled Ettaieb.[156]
Libyan Desert
[edit]

The Libyan Desert, which covers most of Libya, is one of the most arid and sun-baked places on Earth.[58] In places, decades may pass without seeing any rainfall at all, and even in the highlands rainfall seldom happens, once every 5–10 years. At Uweinat, as of 2006[update] the last recorded rainfall was in September 1998.[158]
Likewise, the temperature in the Libyan Desert can be extreme; on 13 September 1922, the town of 'Aziziya, which is located southwest of Tripoli, recorded an air temperature of 58 °C (136.4 °F), considered to be a world record.[159][160][161] In September 2012, however, the world record figure of 58 °C was determined to be invalid by the World Meteorological Organization.[160][161][162]
There are a few scattered uninhabited small oases, usually linked to the major depressions, where water can be found by digging to a few feet in depth. In the west there is a widely dispersed group of oases in unconnected shallow depressions, the Kufra group, consisting of Tazerbo, Rebianae and Kufra.[158] Aside from the scarps, the general flatness is only interrupted by a series of plateaus and massifs near the centre of the Libyan Desert, around the convergence of the Egyptian-Sudanese-Libyan borders.
Slightly further to the south are the massifs of Arkenu, Uweinat, and Kissu. These granite mountains are ancient, having formed long before the sandstones surrounding them. Arkenu and Western Uweinat are ring complexes very similar to those in the Aïr Mountains. Eastern Uweinat (the highest point in the Libyan Desert) is a raised sandstone plateau adjacent to the granite part further west.[158]
The plain to the north of Uweinat is dotted with eroded volcanic features. With the discovery of oil in the 1950s also came the discovery of a massive aquifer underneath much of Libya. The water in the Nubian Sandstone Aquifer System pre-dates the last ice ages and the Sahara Desert itself.[163] This area also contains the Arkenu structures, which were once thought to be two impact craters.[164]
Politics and elections
[edit]

The politics of Libya has been in a tumultuous state since the start of the Arab Spring and the NATO intervention related Libyan Crisis in 2011. The crisis resulted in the collapse of the Libyan Arab Jamahiriya and the killing of Muammar Gaddafi, amidst the First Libyan Civil War and 2011 foreign military intervention.[165][166][167] The crisis was deepened by factional violence in the aftermath of the First Civil War, resulting in the outbreak of the Second Libyan Civil War in 2014.[168] The control over the country is currently split between the House of Representatives (HoR) in Tobruk and the Government of National Unity (GNU) in Tripoli and their respective supporters, as well as various jihadist groups and tribal elements controlling different parts of the country.[169][170]
The former legislature was the General National Congress, which had 200 seats.[171] The General National Congress (2014), a largely unrecognised rival parliament based in the de jure capital of Tripoli, claims to be a legal continuation of the GNC.[172][173] On 7 July 2012, Libyans voted in parliamentary elections, the first free elections in almost 40 years.[174] Around thirty women were elected to become members of parliament.[174] Early results of the vote showed the National Forces Alliance, led by former interim prime minister Mahmoud Jibril, as front runner.[175] The Justice and Construction Party, affiliated with the Muslim Brotherhood, has done less well in Libya than similar parties in Egypt and Tunisia.[176] It won 17 out of 80 seats that were contested by parties; about 60 independents had joined its caucus by 2013.[176] As of January 2013, there was mounting public pressure on the National Congress to set up a constitution-drafting body. Congress had not yet decided whether the members of the body would be elected or appointed.[177] On 30 March 2014, the General National Congress voted to replace itself with a new House of Representatives. The new legislature allocated 30 seats for women, would have 200 seats overall (with individuals able to run as members of political parties), and allowed Libyans of other nationalities to run for office.[178]
Following the 2012 elections, Freedom House improved Libya's rating from Not Free to Partly Free and considered the country an electoral democracy.[179] Gaddafi merged civil and sharia courts in 1973. As of 2013, civil courts employed sharia judges in regular courts of appeal as specialists in sharia appellate cases.[180] Laws regarding personal status are derived from Islamic law as of 2011.[181] At a meeting of the European Parliament Committee on Foreign Affairs on 2 December 2014, UN Special Representative Bernardino León described Libya as a non-state.[182] An agreement to form a national unity government was signed on 17 December 2015.[183] Under the terms of the agreement, a nine-member Presidency Council and a seventeen-member interim Government of National Accord would be formed, with a view to holding new elections within two years.[183] The House of Representatives would continue to exist as a legislature, and an advisory body called the State Council would have members nominated by the General National Congress (2014).[184] The formation of an interim unity government was announced on 5 February 2021, after its members were elected by the Libyan Political Dialogue Forum (LPDF).[185] 74 members of the LPDF cast ballots for four-member slates, which would fill positions including prime minister and the head of the Presidential Council.[185] After no slates reached a 60% vote threshold, the two leading groups competed in a run-off election.[185] Mohamed al-Menfi, a former ambassador to Greece, became head of the Presidential Council.[186]
Meanwhile, the LPDF confirmed that Abdul Hamid Dbeibeh, a businessman, would be the transitional prime minister.[186] All of the candidates who ran in the election, including the members of the winning slate, promised to appoint women to 30% of all senior government positions.[186] The politicians elected to lead the interim government initially agreed not to stand in the national elections scheduled for 24 December 2021.[186] However, Dbeibeh announced his candidacy for president despite the ban in November 2021.[187] The appeals court in Tripoli rejected appeals for his disqualification and allowed Dbeibeh back on the candidates' list, along with a number of other previously disqualified candidates, for the election originally scheduled for December 24.[188] Even more controversially, the court also reinstated Saif al-Islam Gaddafi, a son of the former dictator, as a presidential candidate.[189][190] On 22 December 2021, Libya's Election Commission called for the postponement of the election until 24 January 2022.[191] Earlier, a parliamentary commission said it would be "impossible" to hold the election on 24 December 2021.[192] The UN called on Libya's interim leaders to "expeditiously address all legal and political obstacles to hold elections, including finalising the list of presidential candidates".[192] However, at the last minute, the election was postponed indefinitely and the international community agreed to continue its support and recognition of the interim government headed by Dbeibeh.[193][194] According to new election rules, a new prime minister has 21 days to form a cabinet that must be endorsed by the various governing bodies within Libya.[186] After this cabinet is agreed upon, the unity government will replace all "parallel authorities" within Libya, including the Government of National Accord in Tripoli and the administration led by General Haftar.[186]
Foreign relations
[edit]Libya's foreign policies have fluctuated since 1951. As a kingdom, Libya maintained a definitively pro-Western stance and was recognised as belonging to the conservative traditionalist bloc in the League of Arab States (the present-day Arab League), of which it became a member in 1953.[195] The government was also friendly towards Western countries such as the United Kingdom, United States, France, Italy, and Greece, and established full diplomatic relations with the Soviet Union in 1955.[196] Although the government supported Arab causes, including the Moroccan and Algerian independence movements, it took little active part in the Arab–Israeli conflict or the tumultuous inter-Arab politics of the 1950s and early 1960s. The kingdom was noted for its close association with the West, while it steered a conservative course at home.[197]
After the 1969 coup d'état, Muammar Gaddafi closed American and British bases and partly nationalised foreign oil and commercial interests in Libya. Gaddafi was known for backing a number of leaders viewed as anathema to Westernisation and political liberalism, including Ugandan president Idi Amin,[198] Central African emperor Jean-Bédel Bokassa,[199][200] Ethiopian strongman Haile Mariam Mengistu,[200] Liberian president Charles Taylor,[201] and Yugoslav president Slobodan Milošević.[202]
Relations with the West were strained for most of Gaddafi's rule,[203][204][205] with incidents including the killing of London policewoman Yvonne Fletcher, the bombing of a West Berlin nightclub frequented by U.S. servicemen, and the bombing of Pan Am Flight 103 leading to UN sanctions in the 1990s; by the late 2000s, the United States and other Western powers had normalised relations with Libya.[58] Gaddafi's decision to abandon the pursuit of weapons of mass destruction after the Iraq War saw Iraqi dictator Saddam Hussein overthrown and put on trial led to Libya being hailed as a success for Western soft power initiatives in the War on Terror.[206][207][208] In October 2010, Gaddafi apologised to African leaders on behalf of Arab nations for their involvement in the trans-Saharan slave trade.[209]
Libya is included in the European Union's European Neighbourhood Policy (ENP), which aims at bringing the EU and its neighbours closer. Libyan authorities rejected European Union's plans aimed at stopping migration from Libya.[210][211] In 2017, Libya signed the UN treaty on the Prohibition of Nuclear Weapons.[212]
Military
[edit]This article needs to be updated. (April 2016) |
Libya's previous national army was defeated in the First Libyan Civil War and disbanded. The Tobruk-based House of Representatives, which claims to be the legitimate government of Libya, has attempted to reestablish a military known as the Libyan National Army. Led by Khalifa Haftar, it controls much of eastern Libya.[213] In May 2012, an estimated 35,000 personnel had joined its ranks.[214] The internationally recognised Government of National Accord established in 2015 had its own army that replaced the LNA, consisting largely of undisciplined and disorganised militia groups.
As of November 2012, it was deemed to be still in the embryonic stage of development.[215] President Mohammed Magariaf promised that empowering the army and police force was the government's biggest priority in 2012.[216] President Megarif also ordered that all of the country's militias to come under government authority or disband.[217]
Militias had refused to be integrated into a central security force by February 2013.[218] Many of the militias were disciplined, but the most powerful of them answered only to the executive councils of various Libyan cities.[218] The militias made up the so-called Libya Shield Force, a parallel national force, which operated at the request, rather than at the order, of the defence ministry.[218]
Administrative divisions
[edit]
Historically, the area of Libya was considered three provinces (or states), Tripolitania in the northwest, Barka (Cyrenaica) in the east, and Fezzan in the southwest. The conquest by Italy in the Italo-Turkish War united them into a single political unit.
Since 2007, Libya has been divided into 22 districts (Shabiyat):
In 2022, 18 provinces were declared by the Libyan Government of National Unity (Libyan Observer): the eastern coast, Jabal Al-Akhdar, Al-Hizam, Benghazi, Al-Wahat, Al-Kufra, Al-Khaleej, Al-Margab, Tripoli, Al-Jafara, Al-Zawiya, West Coast, Gheryan, Zintan, Nalut, Sabha, Al-Wadi, and Murzuq Basin.
Human rights
[edit]According to Human Rights Watch annual report 2016, journalists are still being targeted by the armed groups in Libya. The organisation added that Libya ranked very low in the 2015 Press Freedom Index, 154th out of 180 countries.[219] For the 2021 Press Freedom Index its score dropped to 165th out of 180 countries.[220] Homosexuality is illegal in Libya.[221]
Economy
[edit]
The Libyan economy depends primarily upon revenues from the oil sector, which account for over half of GDP and 97% of exports.[222] Libya holds the largest proven oil reserves in Africa and is an important contributor to the global supply of light, sweet crude.[223] During 2010, when oil averaged at $80 a barrel, oil production accounted for 54% of GDP.[224] Apart from petroleum, the other natural resources are natural gas and gypsum.[225] The International Monetary Fund estimated Libya's real GDP growth at 122% in 2012 and 16.7% in 2013, after a 60% plunge in 2011.[222]
In 2023 Libya emitted around 23.77 million tonnes of greenhouse gases, about 0.17% of the world's total emissions. However, the nation ranked as the 21st highest emitter per capita globally and the highest in Africa, at just over 13 tonnes per person.[226] Libya was slow to join climate efforts, signing the United Nations Framework Convention on Climate Change (UNFCCC) in 2016 and the Paris Climate Agreement in 2021.[227] However, as of 2024, Libya has not ratified the Paris Agreement and submitted its Nationally Determined Contributions (NDCs), and has made little progress toward the development of climate change adaptation plans.[228][229]
The World Bank defines Libya as an 'Upper Middle Income Economy', along with only seven other African countries.[230] Substantial revenues from the energy sector, coupled with a small population, give Libya one of the highest per capita GDPs in Africa. Although the government supported Arab causes, including the Moroccan and Algerian independence movements, it took little active part in the Arab–Israeli conflict or the tumultuous inter-Arab politics of the 1950s and early 1960s. The kingdom was noted for its close association with the West, while it steered a conservative course at home.[225] This allowed the Libyan Arab Jamahiriya state to provide an extensive level of social security, particularly in the fields of housing and education.[231]

Libya faces many structural problems including a lack of institutions, weak governance, and chronic structural unemployment.[232] The economy displays a lack of economic diversification and significant reliance on immigrant labour.[233] Libya has traditionally relied on unsustainably high levels of public sector hiring to create employment.[234] In the mid-2000s, the government employed about 70% of all national employees.[233]
Unemployment rose from 8% in 2008 to 21% in 2009, according to the census figures.[235] According to an Arab League report, based on data from 2010, unemployment for women stands at 18% while for the figure for men is 21%, making Libya the only Arab country where there are more unemployed men than women.[236] Libya has high levels of social inequality, high rates of youth unemployment and regional economic disparities.[234] Water supply is also a problem, with some 28% of the population not having access to safe drinking water in 2000.[237]

Two trans-African automobile routes pass through Libya, the Cairo-Dakar Highway and Tripoli-Cape Town Highway. These routes have further contributed in the economic development of Libya.
Libya imports up to 90% of its cereal consumption requirements, and imports of wheat in 2012/13 was estimated at 1 million tonnes.[238] The 2012 wheat production was estimated at 200,000 tonnes.[238] The government hopes to increase food production to 800,000 tonnes of cereals by 2020.[238] However, natural and environmental conditions limit Libya's agricultural production potential.[238] Before 1958, agriculture was the country's main source of revenue, making up about 30% of GDP. With the discovery of oil in 1958, the size of the agriculture sector declined rapidly, accounting for less than 5% GDP by 2005.[239]
The country joined OPEC in 1962.[225] Libya is not a WTO member, but negotiations for its accession started in 2004.[240] In the early 1980s, Libya was one of the wealthiest countries in the world; its GDP per capita was higher than some developed countries.[241]

UN sanctions were lifted in September 2003,[243] and Libya announced in December 2003 that it would abandon programs to build weapons of mass destruction.[citation needed] Other steps have included applying for membership of the World Trade Organization, reducing subsidies, and announcing plans for privatisation.[244]
Authorities privatised more than 100 government-owned companies after 2003 in industries including oil refining, tourism and real estate, of which 29 were 100% foreign owned.[245] Many international oil companies returned to the country, including oil giants Shell and ExxonMobil.[246] After sanctions were lifted there was a gradual increase of air traffic, and by 2005 there were 1.5 million yearly air travellers.[247] Libya had long been a notoriously difficult country for Western tourists to visit due to stringent visa requirements.[248]
In 2007, Saif al-Islam Gaddafi, the second-eldest son of Muammar Gaddafi, was involved in a green development project called the Green Mountain Sustainable Development Area, which sought to bring tourism to Cyrene and to preserve Greek ruins in the area.[249] In August 2011, it was estimated that it would take at least 10 years to rebuild Libya's infrastructure. Even before the 2011 war, Libya's infrastructure was in a poor state due to "utter neglect" by Gaddafi's administration, according to the NTC.[250] By October 2012, the economy had recovered from the 2011 conflict, with oil production returning to near normal levels.[222] Oil production was more than 1.6 million barrels per day before the war. By October 2012, the average oil production has surpassed 1.4 million bpd.[222] The resumption of production was made possible due to the quick return of major Western companies, like TotalEnergies, Eni, Repsol, Wintershall and Occidental.[222] In 2016, an announcement from the company said the company aims 900,000 barrel per day in the next year. Oil production has fallen from 1.6 million barrel per day to 900,000 in four years of war.[251]
The Great Man-Made River is the world's largest irrigation project.[252] The project utilises a pipeline system that pumps fossil water from the Nubian Sandstone Aquifer System from down south in Libya to cities in the populous Libyan northern Mediterranean coast including Tripoli and Benghazi. The water provides 70% of all freshwater used in Libya.[253] During the second Libyan civil war, lasting from 2014 to 2020, the water infrastructure suffered neglect and occasional breakdowns.[254] By 2017, 60% of the Libyan population were malnourished. Since then, 1.3 million people are waiting for emergency humanitarian aid, out of a total population of 7.1 million.[255]
As of March 2024, Libya was actively promoting business development and encouraging both domestic and foreign investment. This strategic initiative is aimed at securing long-term economic stability and prosperity for Libya by diversifying its economic foundation. Embracing green industries like renewable energy, energy efficiency, sustainable agriculture, and eco-tourism holds the potential to generate fresh employment prospects across a spectrum of sectors, thereby addressing unemployment challenges, particularly among the youth demographic.[256]
Demographics
[edit]
Libya is a large country with a relatively small population concentrated very narrowly along the coast.[257] Its population density is about 50 inhabitants per square kilometre (130/sq mi) in the two northern regions of Tripolitania and Cyrenaica, but falls to less than 1 inhabitant per square kilometre (2.6/sq mi) elsewhere. 90% of the people live along the coast in less than 10% of the area.
About 88% of the population is urban, mostly concentrated in the three largest cities, Tripoli, Benghazi and Misrata. Libya has a population of about 6.7 million,[258][259] 27.7% of whom are under the age of 15.[260] In 1984 the population was 3.6 million, an increase from the 1.54 million reported in 1964.[261]
The population of Libya is primarily of Arab ancestry.[262] Arabs account for 92% of the population, while Berbers account for 5%, though other estimates put this percentage at 10%, representing approximately 600,000 people.[263][264] Among the Berber groups are the minority Berber populations of Zuwarah and the Nafusa Mountains. Southern Libya, primarily Sebha, Kufra, Ghat, Ghadamis and Murzuk, is also inhabited by two other ethnic groups; the Tuareg and Toubou. Libya is one of the world's most tribal countries. There are about 140 tribes and clans in Libya.[265] Also living in Libya are an estimated 750,000 Egyptian workers, down from more than 2 million prior to the overthrow of Muammar Gaddafi in 2011.[266]
Family life is important for Libyan families, the majority of whom live in apartment blocks and other independent housing units, with modes of housing depending on their income and wealth. Although the Arab Libyans traditionally lived nomadic Bedouin lifestyles in tents, they have predominately settled in towns and cities.[267] Old ways of life are gradually fading out. A small number of Libyans still live in the desert as their families have done for centuries. Most of the population has occupations in industry and services, and a small percentage is in agriculture.
According to the UNHCR, there were around 8,000 registered refugees, 5,500 unregistered refugees, and 7,000 asylum seekers of various origins in Libya in January 2013. Additionally, 47,000 Libyan nationals were internally displaced and 46,570 were internally displaced returnees.[268]
Health
[edit]In 2010, spending on healthcare accounted for 3.88% of the country's GDP. In 2009, there were 18.71 physicians and 66.95 nurses per 10,000 inhabitants.[269] The life expectancy at birth was 74.95 years in 2011, or 72.44 years for males and 77.59 years for females.[270]
In 2023, the Libyan health ministry announced the launch of the National Strategy for Primary Healthcare 2023–2028 to improve services provided by group clinics and health centres. A unique health number allotted to each citizen will facilitate access to medical records. Before Storm Daniel, the UN Office for the Coordination of Humanitarian Affairs estimated that around 60,000 people were in need of humanitarian aid in Derna and environs. Since the storm many of the hospitals and primary health facilities in Derna and eastern Libya have been rendered partially or completely nonfunctional.[271]
Libya's 2024 Global Hunger Index (GHI) score is 19.2, which indicates a moderate level of hunger. Libya ranks 83rd out of 127 countries.[272]
Education
[edit]
Libya's population includes 1.7 million students, over 270,000 of whom study at the tertiary level.[273] Basic education in Libya is free for all citizens,[274] and is compulsory up to the secondary level. The adult literacy rate in 2010 was 89.2%.[275]
After Libya's independence in 1951, its first university, the University of Libya, was established in Benghazi by royal decree.[276] In the 1975–76 academic year the number of university students was estimated to be 13,418. As of 2004[update], this number has increased to more than 200,000, with another 70,000 enrolled in the higher technical and vocational sector.[273] The rapid increase in the number of students in the higher education sector has been mirrored by an increase in the number of institutions of higher education.
Since 1975 the number of public universities has grown from two to twelve and since their introduction in 1980, the number of higher technical and vocational institutes has grown to 84.[? clarification needed][273] Since 2007 some new private universities such as the Libyan International Medical University have been established. Although before 2011 a small number of private institutions were given accreditation, the majority of Libya's higher education has always been financed by the public budget. In 1998 the budget allocation for education represented 38.2% of Libya's national budget.[276]
In 2024, the Ministry of Education announced the launch of the Full-Day School Project in which 12 schools in different parts of the country will have longer school days. The project aims to provide 800 hours of instruction per year to 3,300 elementary school students.[277]
Ethnicity
[edit]The original inhabitants of Libya belonged predominantly to Berber ethnic groups; however, the long series of foreign invasions and migrations – particularly by Arabs – had a profound and lasting ethnic, linguistic, and cultural influence on Libyan demographics. Centuries of large-scale Arab migration to the Maghreb since the 7th century shifted the demographics of Libya in favour of Arabs. Some Turks settled in Libya during the rule of the Ottoman Empire.
Most of Libya's inhabitants are Arab,[22] with many tracing their ancestry to Bedouin Arab tribes like Banu Sulaym and Banu Hilal, plus Turkish and Berber minorities. The Turkish minority are often called "Kouloughlis" and are concentrated in and around villages and towns.[278] There are some ethnic minorities, such as the Berber Tuareg and the Black African Tebou.[279]
Most Italian settlers, at their height numbering over half a million, left after Italian Libya's independence in 1947. More repatriated in 1970 after the accession of Muammar Gaddafi, but a few hundred returned in the 2000s.[280]
Foreign labour
[edit]As of 2023, the International Organization for Migration (IOM) estimates that approximately 10% of Libya's population (upwards of 700,000 people) constituted foreign labour.[281] Prior to the 2011 revolution, official and unofficial figures of migrant labour ranged from 25% to 40% of the population (between 1.5 and 2.4 million people). Historically, Libya hosted millions of low- and high-skilled Egyptian migrants, in particular.[282]
It is difficult to estimate the total number of immigrants in Libya because the census figures, official counts and typically more accurate unofficial estimates all differ. In the 2006 census, around 359,540 foreign nationals were resident in Libya out of a population of over 5.5 million (6.35% of the population). Almost half of these were Egyptians, followed by Sudanese and Palestinian immigrants.[283] During the 2011 revolution, 768,362 immigrants fled Libya as calculated by the IOM, around 13% of the population at the time, although many more stayed on in the country.[283][284]
If consular records prior to the revolution are used to estimate the immigrant population, as many as 2 million Egyptian migrants were recorded by the Egyptian embassy in Tripoli in 2009, followed by 87,200 Tunisians, and 68,200 Moroccans by their respective embassies. Turkey recorded the evacuation of 25,000 workers during the 2011 uprising.[285] The number of Asian migrants before the revolution were just over 100,000 (60,000 Bangladeshis, 20,000 Filipinos, 18,000 Indians, 10,000 Pakistanis, as well as Chinese, Korean, Vietnamese, Thai and other workers).[286][287] This would put the immigrant population at almost 40% before the revolution and is a figure more consistent with government estimates in 2004 which put the regular and irregular migrant numbers at 1.35 to 1.8 million (25–33% of the population at the time).[283]
Libya's native population of Arabs-Berbers as well as Arab migrants of various nationalities collectively make up 97% of the population as of 2014[update].
Languages
[edit]According to the CIA, the official language of Libya is Arabic.[1] The local Libyan Arabic variety is spoken alongside Modern Standard Arabic. Various Berber languages are also spoken, including Tamasheq, Ghadamis, Nafusi, Suknah and Awjilah.[288] The Libyan Amazigh High Council (LAHC) has declared the Amazigh (Berber or Tamazight) language to be official in the cities and districts inhabited by the Berbers in Libya.[289] In addition, English is widely understood in the major cities,[290] while the former colonial language of Italian is also used in commerce and by the remaining Italian population.[288]
Religion
[edit]
About 97% of the population in Libya are Muslims, most of whom belong to the Sunni branch.[260][291] Small numbers of Ibadi Muslims live in the country.[292][293]
Before the 1930s, the Senussi Sunni Sufi movement was the primary Islamic movement in Libya. This was a religious revival adapted to desert life. Its zawaaya (lodges) were found in Tripolitania and Fezzan, but Senussi influence was strongest in Cyrenaica. Rescuing the region from unrest and anarchy, the Senussi movement gave the Cyrenaican tribal people a religious attachment and feelings of unity and purpose.[294] This Islamic movement was eventually destroyed by the Italian invasion. Gaddafi asserted that he was a devout Muslim, and his government was taking a role in supporting Islamic institutions and in worldwide proselytising on behalf of Islam.[295]
The International Religious Freedom Report 2004 noted that "bishops, priests and nuns wear religious dress freely in public and report virtually no discrimination," while also "enjoying good relations with the Government". The report also indicated that members of minority religions said "they do not face harassment by authorities or the Muslim majority on the basis of their religious practices". The International Christian Concern does not list Libya as a country where there is "persecution or severe discrimination against Christians".[296] Since the fall of Gaddafi, ultra-conservative strains of Islam have reasserted themselves in places. Derna in eastern Libya, historically a hotbed of jihad thought, came under the control of militants aligned with the Islamic State of Iraq and the Levant in 2014.[297] Jihadist elements have also spread to Sirte and Benghazi, among other areas, as a result of the Second Libyan Civil War.[298][299]
Prior to independence, Libya was home to more than 140,000 Christians (mostly of Italian and Maltese ancestry). Many Christian settlers left to Italy or Malta after the independence.[300] Small foreign communities of Christians remained. Coptic Orthodox Christianity, the predominant Christian church of Egypt, is the largest and most historic Christian denomination in Libya. There are about 60,000 Egyptian Copts in Libya.[301] There are three Coptic Churches in Libya, one in Tripoli, one in Benghazi, and one in Misurata.
The Coptic Church has grown in recent years in Libya, due to the growing immigration of Egyptian Copts to Libya. There are an estimated 40,000 Roman Catholics in Libya who are served by two bishops, one in Tripoli (serving the Italian community) and one in Benghazi (serving the Maltese community). There is also a small Anglican community, made up mostly of African immigrant workers in Tripoli which is part of the Anglican Diocese of Egypt. People have been arrested on suspicion of being Christian missionaries, as proselytising is illegal.[302] Christians have also faced the threat of violence from radical Islamists in some parts of the country, with a well-publicised video released by the Islamic State of Iraq and the Levant in February 2015 depicting the mass beheading of Christian Copts.[303][304] Libya was ranked fourth on Open Doors' 2022 World Watch List, an annual ranking of the 50 countries where Christians face the most extreme persecution.[305]
Libya was once the home of one of the oldest Jewish communities in the world, dating back to at least 300 BC.[306] In 1942, the Italian Fascist authorities set up forced labour camps south of Tripoli for the Jews, including Giado (about 3,000 Jews), Gharyan, Jeren, and Tigrinna. In Giado, some 500 Jews died of weakness, hunger, and disease. In 1942, Jews who were not in the concentration camps were heavily restricted in their economic activity and all men between 18 and 45 years were drafted for forced labour. In August 1942, Jews from Tripolitania were interned in a concentration camp at Sidi Azaz. In the three years after November 1945, more than 140 Jews were murdered, and hundreds more wounded, in a series of pogroms.[307] By 1948, about 38,000 Jews remained in the country. Upon Libyan independence in 1951, most of the Jewish community emigrated.
Largest cities
[edit]Culture
[edit]


Many Arabic speaking Libyans consider themselves as part of a wider Arab community. This was strengthened by the spread of Pan-Arabism in the mid-20th century, and their reach to power in Libya where they instituted Arabic as the only official language of the state. Under Gaddafi's rule, the teaching and even use of indigenous Berber language was strictly forbidden.[308] In addition to banning foreign languages previously taught in academic institutions, leaving entire generations of Libyans with limitations in their comprehension of the English language. Both the spoken Arabic dialects and Berber, still retain words from Italian, that were acquired before and during the Libia Italiana period.
Libyans have a heritage in the traditions of the previously nomadic Bedouin Arabic speakers and sedentary Berber tribes. Most Libyans associate themselves with a particular family name originating from tribal or conquest based heritage.[citation needed]
Reflecting the "nature of giving" (Arabic: الاحسان Ihsan, Berber languages: ⴰⵏⴰⴽⴽⴰⴼ Anakkaf ), amongst the Libyan people as well as the sense of hospitality, the state of Libya made it to the top 20 on Charities Aid Foundation's World Giving Index in 2013.[309] According to Charities Aid Foundation (CAF), in a typical month, almost three-quarters (72%) of all Libyans helped somebody they did not know – the third highest level across all 135 countries surveyed.
There are few theatres or art galleries due to the decades of cultural repression under the Gaddafi regime and lack of infrastructure development under the regime of dictatorship.[310] For many years there have been no public theatres, and only very few cinemas showing foreign films. The tradition of folk culture is still alive and well, with troupes performing music and dance at frequent festivals, both in Libya and abroad.[311]
A large number of Libyan television stations are devoted to political review, Islamic topics and cultural phenomena. A number of TV stations air various styles of traditional Libyan music.[? clarification needed] Tuareg music and dance are popular in Ghadames and the south. Libyan television broadcasts air programs mostly in Arabic though usually have time slots for English and French programs.[? clarification needed] A 1996 analysis by the Committee to Protect Journalists found Libya's media was the most tightly controlled in the Arab world during the country's dictatorship.[312] As of 2012[update] hundreds of TV stations have begun to air due to the collapse of censorship from the old regime and the initiation of "free media".
Many Libyans frequent the country's beach and they also visit Libya's archaeological sites—especially Leptis Magna, which is widely considered to be one of the best preserved Roman archaeological sites in the world.[313] The most common form of public transport between cities is the bus, though many people travel by automobile. There are no railway services in Libya, but these are planned for construction in the near future (see rail transport in Libya).[314]
Libya's capital, Tripoli, has many museums and archives. These include the Government Library, the Ethnographic Museum, the Archaeological Museum, the National Archives, the Epigraphy Museum and the Islamic Museum. The Red Castle Museum located in the capital near the coast and right in the city centre, built in consultation with UNESCO, may be the country's most famous.[315]
Cuisine
[edit]
Libyan cuisine is a mixture of the different Italian, Bedouin and traditional Arab culinary influences.[316] Pasta is the staple food in the Western side of Libya, whereas rice is generally the staple food in the east.
Common Libyan foods include several variations of red tomato sauce based pasta dishes (similar to the Italian Sugo all'arrabbiata dish), rice, usually served with lamb or chicken (typically stewed, fried, grilled, or boiled in-sauce), and couscous, which is steam cooked whilst held over boiling red tomato sauce and meat (sometimes also containing zucchini/courgettes and chickpeas), and typically served along with cucumber slices, lettuce and olives.
Bazeen, a dish made from barley flour and served with red tomato sauce, is customarily eaten communally, with several people sharing the same dish, usually by hand. This dish is commonly served at traditional weddings or festivities. Asida is a sweet version of Bazeen, made from white flour and served with a mix of honey, ghee or butter. Another popular way to serve Asida is with rub (fresh date syrup) and olive oil. Usban is animal tripe stitched and stuffed with rice and vegetables cooked in tomato based soup or steamed. Shurba is a red tomato sauce-based soup, usually served with small grains of pasta.[317]
A very common snack eaten by Libyans is known as khubs bi' tun, literally meaning "bread with tuna fish", usually served as a baked baguette or pita bread stuffed with tuna fish that has been mixed with harissa (chili sauce) and olive oil. Many snack vendors prepare these sandwiches and they can be found all over Libya. Libyan restaurants may serve international cuisine, or may serve simpler fare such as lamb, chicken, vegetable stew, potatoes and macaroni.[318] Due to severe lack of infrastructure, many under-developed areas and small towns do not have restaurants and instead food stores may be the only source to obtain food products. Alcohol consumption is illegal.[319]
There are four main ingredients of traditional Libyan food: olives (and olive oil), dates, grains and milk.[320] Grains are roasted, ground, sieved and used for making bread, cakes, soups and Bazeen. Dates are harvested, dried and can be eaten as they are, made into syrup or slightly fried and eaten with bsisa and milk. After eating, Libyans often drink black tea. This is normally repeated a second time (for the second glass of tea), and in the third round of tea, it is served with roasted peanuts or roasted almonds known as shay bi'l-luz (mixed with the tea in the same glass).[320]
Sport
[edit]Football is the most popular sport in Libya. The country hosted the 1982 African Cup of Nations and almost qualified for the 1986 FIFA World Cup. The national team almost won the 1982 AFCON; they lost to Ghana on penalties 7–6. In 2014, Libya won the African Nations Championship after beating Ghana in the finals. Although the national team has never won a major competition or qualified for a World Cup, there is still lots of passion for the sport and the quality of football is improving.[321] It also participated in many Summer Olympics, such as the 2016 Summer Olympics, the 2008 Summer Olympics and more.
Horse racing is also a popular sport in Libya. It is a tradition of many special occasions and holidays.[322]
See also
[edit]Notes
[edit]- ^ Disputed with Osama Hammad, head of the Government of National Stability, which is recognised by the House of Representatives as the acting Prime Minister of Libya.
- ^ /ˈlɪbiə/ ⓘ LIB-ee-ə; Arabic: ليبيا, romanised: Lībiyā, pronounced [liː.bi.jaː], Libyan Arabic: [ˈliːb.jæ]. All spoken dialects have only two syllables and it's normally pronounced as such.
- ^ Arabic: دولة ليبيا, romanised: Dawlat Lībiyā[8][9][1]
References
[edit]- ^ a b c d e f g "Libya". The World Factbook. Central Intelligence Agency. 7 August 2024. Archived from the original on 9 January 2021. Retrieved 19 August 2024.
- ^ Yakan, Mohamad (30 November 2017). Almanac of African Peoples and Nations. Routledge. p. 62. ISBN 978-1-351-28930-6. Archived from the original on 1 May 2023. Retrieved 6 April 2023.
- ^ "World Economic Outlook Database, April 2025".
- ^ "World Economic Outlook Database, April 2025".
- ^ "World Economic Outlook Database, April 2025".
- ^ "World Economic Outlook Database, April 2025".
- ^ "Human Development Report 2025" (PDF). United Nations Development Programme. 6 May 2025. Archived (PDF) from the original on 6 May 2025. Retrieved 6 May 2025.
- ^ "Member States". United Nations. Archived from the original on 29 June 2021. Retrieved 13 February 2021.
On 22 December 2017, the Permanent Mission of Libya to the United Nations formally notified the United Nations that the government is changing the official name of Libya to 'State of Libya.'
- ^ "Publications Office – Interinstitutional style guide – Annex A5 – List of countries, territories and currencies". Europa (web portal). Archived from the original on 5 August 2013. Retrieved 1 April 2016.
- ^ "Demographic Yearbook (3) Pop., Rate of Pop. Increase, Surface Area & Density" (PDF). United Nations Statistics Division. Archived from the original (PDF) on 14 November 2012. Retrieved 5 February 2013.
- ^ "Libya-Algeria". Sovereign Limits. Archived from the original on 28 September 2023. Retrieved 1 April 2024.
- ^ "Libya Demographics Profile 2014". Indexmundi.com. 30 June 2015. Archived from the original on 4 March 2016. Retrieved 1 April 2016.
- ^ J. Desanges, "The proto-Berbers", pp. 236–245, especially p. 237, in General History of Africa, vol. II: Ancient Civilizations of Africa (UNESCO 1990).
- ^ "Libya — a tale of two governments, again". Arab News. 11 June 2022. Retrieved 28 August 2022.
- ^ "Rival second Libyan assembly chooses own PM as chaos spreads". Reuters. 25 August 2014. Archived from the original on 26 August 2014. Retrieved 25 August 2014.
- ^ Chris Stephen. "Libyan parliament takes refuge in Greek car ferry". The Guardian. Archived from the original on 4 April 2016. Retrieved 1 April 2016.
- ^ "Peace talks between Libyan factions to take place in Geneva". Sun Herald. 7 August 2015. Archived from the original on 14 March 2020. Retrieved 7 August 2015.
- ^ "1969: Bloodless coup in Libya". 1 September 1969. Archived from the original on 20 July 2011. Retrieved 25 October 2018.
- ^ Kafala, Tarik (20 October 2011). "Gaddafi's quixotic and brutal rule". BBC News. Archived from the original on 24 April 2023.
- ^ "Libyan government offensive in Benghazi stalls as Islamists dig in". Reuters. 6 August 2015. Archived from the original on 9 August 2015. Retrieved 7 August 2015.
- ^ "Libyan Civil War: Two warring factions sign 'permanent' ceasefire". The Daily Star. 24 October 2020. Archived from the original on 15 April 2021. Retrieved 5 March 2021.
- ^ a b Britannica Student Encyclopaedia. Encyclopaedia Britannica, Inc. 1 May 2014. ISBN 978-1-62513-172-0.
- ^ "Human Development Report 2023/24" (PDF). United Nations Development Programme. 13 March 2024. Archived (PDF) from the original on 13 March 2024. Retrieved 13 March 2024.
- ^ "World proven crude oil reserves by country, 1980–2004". OPEC. Archived from the original on 11 July 2012. Retrieved 5 February 2013.
- ^ Roberts, Peter (2006). HSC Ancient History. Pascal Press. ISBN 9781741251784. Archived from the original on 31 May 2021. Retrieved 26 May 2020.
- ^ "Bibliografia della Libia"; Bertarelli, p. 177.
- ^ Federal Research Division of the Library of Congress (1987), "Independent Libya" Archived 21 March 2022 at the Wayback Machine, U.S. Library of Congress. Retrieved 14 July 2006.
- ^ "Great Socialist People's Libyan Arab Jamahiriya: Libya". Geographical Names. Archived from the original on 18 January 2012. Retrieved 1 November 2011.
- ^ "الجماهيرية العربية الليبية الشعبية الاشتراكية: Libya". Geographical Names. Archived from the original on 24 July 2014. Retrieved 26 February 2014.
- ^ "United Nations interoffice memorandum dated 16 September 2011 from Desmond Parker, Chief of Protocol, to Shaaban M. Shaaban, Under-Secretary-General for General Assembly and Conference Management, attaching memorandum from Stadler Trengove, Senior Legal Officer". United Nations. 16 September 2011. Archived from the original on 22 January 2013. Retrieved 5 February 2013.
- ^ "ISO 3166-1 Newsletter VI-11: Name change for Libya" (PDF). International Organization for Standardization. 8 November 2011. Archived (PDF) from the original on 17 January 2012. Retrieved 13 December 2011.
- ^ ""State of Libya" in UNTERM (United Nations terminology database)". United Nations. Archived from the original on 5 January 2018. Retrieved 5 January 2018.
- ^ Halsall, Paul (August 1998). "The Histories', Book IV.42–43". Fordham University. Archived from the original on 9 April 2013. Retrieved 5 February 2013.
- ^ "Cyrenaica and the Greeks". Federal Research Division of the Library of Congress. Archived from the original on 22 September 2012. Retrieved 5 February 2013.
- ^ "History of Libya". The History Files. 20 October 2011. Archived from the original on 28 January 2013. Retrieved 5 February 2013.
- ^ a b c d e Bertarelli, p. 202.
- ^ a b c Bertarelli, p. 417.
- ^ a b Rostovtzeff, Michael (1957). Social and Economic History of the Roman Empire (2 ed.). Oxford: Clarendon. p. 364.
- ^ Cassius Dio, lxviii. 32
- ^ a b Bertarelli, p. 278.
- ^ Hourani, Albert (2002). A History of the Arab Peoples. Faber & Faber. p. 198. ISBN 978-0-571-21591-1.
- ^ a b c d e Bertarelli, p. 203.
- ^ Hoppen, Alison (1979). The fortification of Malta by the Order of St. John, 1530–1798. Scottish Academic Press. p. 25.
- ^ Robert C. Davis (5 December 2003). Christian Slaves, Muslim Masters: White Slavery in the Mediterranean, the Barbary Coast, and Italy, 1500–1800. Palgrave Macmillan. ISBN 978-0-333-71966-4. Retrieved 31 May 2012.[page needed]
- ^ a b c Bertarelli, p. 204.
- ^ "Libyan tribe demands to prosecute Turkey for the massacres committed against its people, similar to that of the Armenians". Horizon. 5 October 2016. Archived from the original on 21 December 2019.
- ^ a b c Bertarelli, p. 205.
- ^ "Timeline: Libya". BBC News. 29 January 2013. Archived from the original on 23 October 2011. Retrieved 5 February 2013.
- ^ "Libya". Encyclopædia Britannica. Archived from the original on 30 April 2013. Retrieved 5 February 2013.
- ^ Libya profile – Timeline , BBC News Africa, 1 November 2011
- ^ Mann, Michael (2006). The Dark Side of Democracy: Explaining Ethnic Cleansing. Cambridge University Press. p. 309. ISBN 978-0521538541. Archived from the original on 16 April 2017. Retrieved 1 July 2019.
- ^ Ilan Pappé, The Modern Middle East. Routledge, 2005, ISBN 0-415-21409-2, p. 26.
- ^ Nanjira, Daniel Don (2010). African Foreign Policy and Diplomacy from Antiquity to the 21st Century. ABC-CLIO. p. 207. ISBN 978-0-313-37982-6.
- ^ Tecola W. Hagos (20 November 2004). "Treaty Of Peace With Italy (1947), Evaluation And Conclusion". Ethiopia Tecola Hagos. Archived from the original on 7 December 2012. Retrieved 5 February 2013.
- ^ a b c d e f g h i j k l m n "The Kingdom of Libya is Established". History Today. Retrieved 5 July 2024.
- ^ a b "Libya country profile". BBC News. 15 March 2021. Archived from the original on 6 May 2021. Retrieved 15 March 2021.
- ^ a b c d Schiller, Jon (29 November 2009). Internet View of the Arabic World. CreateSpace. p. 161. ISBN 9781439263266. Archived from the original on 20 March 2018.
- ^ a b c Salak, Kira. "Rediscovering Libya". National Geographic Adventure. Archived from the original on 23 September 2011.
- ^ a b c d e Bearman, Jonathan (1986). Qadhafi's Libya. London: Zed Books. p. 72
- ^ "Libya – History". US Department of State's Background Notes. 15 January 2013. Archived from the original on 4 June 2019. Retrieved 5 February 2013.
- ^ Zoubir, Yahia H. (2009). "Libya and Europe: Economic Realism at the Rescue of the Qaddafi Authoritarian Regime". Journal of Contemporary European Studies. 17 (3): 401–415 [403, 411]. doi:10.1080/14782800903339354. S2CID 153625134.
- ^ a b c d e f g h i j k l m n "Libya: History". /globaledge.msu.edu (via Michigan State University). Archived from the original on 14 August 2011. Retrieved 14 August 2011.
- ^ Eljahmi, Mohamed (2006). "Libya and the U.S.: Gaddafi Unrepentant". Middle East Quarterly. Archived from the original on 2 March 2011.
- ^ "Comparative Criminology – Libya". Crime and Society. Archived from the original on 7 August 2011. Retrieved 24 July 2011.
- ^ Bearman, Jonathan (1986). Qadhafi's Libya. London: Zed Books
- ^ Banégas, Richard (1 January 2012). La Libye révolutionnaire (in French). KARTHALA Editions. p. 69. ISBN 9782811106720. Archived from the original on 20 March 2018.
- ^ Krieger, Joel (2 August 2001). The Oxford Companion to Politics of the World. Oxford University Press, USA. p. 506. ISBN 9780195117394. Archived from the original on 29 June 2014.
- ^ Wynne-Jones, Jonathan (19 March 2011). "Libyan minister claims Gaddafi is powerless and the ceasefire is 'solid'". The Daily Telegraph. London. Archived from the original on 29 October 2011. Retrieved 22 October 2011.
- ^ Robbins, James (7 March 2007). "Eyewitness: Dialogue in the desert". BBC News. Retrieved 22 October 2011.
- ^ "Egypt Libya War 1977". Onwar.com. Archived from the original on 24 March 2012. Retrieved 23 December 2012.
- ^ "A Rogue Returns". AIJAC. February 2003. Archived from the original on 1 March 2003.
- ^ "ICL - Libya - Declaration on the Establishment of the Authority of the People". Archived from the original on 3 March 2016. Retrieved 16 May 2016.
- ^ "African Countries by GDP Per Capita > GDP Per Capita (most recent) by Country". nationmaster.com. Archived from the original on 16 July 2011. Retrieved 24 July 2011.
- ^ a b Azad, Sher (22 October 2011). "Gaddafi and the media". Daily News. Colombo. Archived from the original on 25 October 2011. Retrieved 22 October 2011.
- ^ "Zimbabwe: Reason Wafavarova – Reverence for Hatred of Democracy". The Herald. Harare. 21 July 2011. Archived from the original on 7 November 2011. Retrieved 23 October 2011.
- ^ Shimatsu, Yoichi (21 October 2011). "Villain or Hero? Desert Lion Perishes, Leaving West Explosive Legacy". New America Media. Archived from the original on 22 October 2011. Retrieved 23 October 2011.
- ^ "Endgame in Tripoli". The Economist. London. 24 February 2011. Archived from the original on 7 March 2011.
- ^ Geoffrey Leslie Simons. Libya: the struggle for survival. p. 281.
- ^ St. John, Ronald Bruce (1 December 1992). "Libyan terrorism: the case against Gaddafi". Contemporary Review. Archived from the original on 11 May 2011.
- ^ "Pan Am Flight 103 Bombing – 1988 Lockerbie Bombing Led to Libyan Convictions". Terrorism.about.com. Archived from the original on 2 April 2012. Retrieved 8 July 2012.
- ^ a b c d
- Martínez, Luis (2007). The Libyan Paradox. Columbia University Press. p. 71. ISBN 978-0-231-70021-4.
- Cordesman, Anthony H. (2002). A Tragedy of Arms – Military and Security Developments in the Maghreb. Greenwood Publishing Group. p. 2. ISBN 978-0-275-96936-3.
- ^ "Live Blog – Libya". Al Jazeera. 17 February 2011. Archived from the original on 23 February 2011. Retrieved 23 February 2011.
- ^ Pollack, Kenneth M., ed. (1 January 2011). The Arab awakening: America and the transformation of the Middle East. Washington, DC: Brookings Institution. ISBN 9780815722267. Archived from the original on 15 April 2021. Retrieved 20 November 2016.
- ^ Hussain1 Howard2, Muzammil M.1Philip N.2 (2013). Democracy's Fourth Wave?: Digital Media and the Arab Spring. New York: Oxford University Press. p. 23. ISBN 978-0-19-993697-7.
{{cite book}}: CS1 maint: numeric names: authors list (link) - ^ "The Council"International Recognition". National Transitional Council (Libya). 1 March 2011. Archived from the original on 26 September 2011. Retrieved 23 October 2011.
- ^ "Libya: France recognises rebels as government". BBC News. 10 March 2011. Archived from the original on 23 October 2011. Retrieved 23 October 2011.
- ^ Fahim, Kareem; Kirkpatrick, David D. (9 March 2011). "Qaddafi Forces Batter Rebels in Strategic Refinery Town". The New York Times. Archived from the original on 6 May 2011. Retrieved 9 March 2011.
- ^ The Independent, 9 March 2011 P.4
- ^ "Ban Ki-moon blasts Gaddafi; calls situation dangerous". Hindustan Times. New Delhi. 24 February 2011. Archived from the original on 27 February 2011. Retrieved 26 February 2011.
- ^ "Some backbone at the U.N." Los Angeles Times. 26 February 2011. Archived from the original on 3 March 2011. Retrieved 26 February 2011.
- ^ "Libya Expelled from UN Human Rights Council". Sofia News Agency. 2 March 2011. Archived from the original on 11 May 2011. Retrieved 2 March 2011.
- ^ Jeffrey Scott Shapiro; Kelly Riddell (28 January 2015). "Exclusive: Secret tapes undermine Hillary Clinton on Libyan war". The Washington Times. Archived from the original on 17 February 2015.
- ^ "Security Council authorizes 'all necessary measures' to protect civilians in Libya" (Press release). United Nations. 17 March 2011. Archived from the original on 3 May 2011. Retrieved 30 March 2011.
- ^ Marcus, Jonathan (19 March 2011). "French military jets open fire in Libya". BBC News. Archived from the original on 20 March 2011. Retrieved 20 August 2011.
- ^ "NATO operations in Libya". The Guardian, London, 22 May 2011. 22 May 2011. Archived from the original on 24 June 2014. Retrieved 25 June 2014.
- ^ Tirpak, John "Bombers Over Libya". Archived from the original on 8 June 2014. Air Force Magazine: Journal of the Air Force Association, Vol. 94, No. 7, July 2011. Retrieved 26 June 2014
- ^ "The hidden story of airpower in Libya (and what it means for Syria)". Foreign Policy. 11 February 2013. Archived from the original on 4 March 2016. Retrieved 1 April 2016.
- ^ Richburg, Keith B. (22 August 2011). "Gaddafi's rule crumbling as rebels enter heart of Tripoli". The Washington Post. Archived from the original on 23 January 2012.
- ^ Laub, Karin (8 September 2011). "Libyan estimate: At least 30,000 died in the war". The Guardian. London. Associated Press. Archived from the original on 4 November 2013. Retrieved 25 November 2011.
- ^ Milne, Seumas (26 October 2011). "If the Libyan war was about saving lives, it was a catastrophic failure | Seumas Milne". The Guardian. ISSN 0261-3077. Archived from the original on 1 December 2017. Retrieved 24 November 2017.
- ^ "Armed militias still on the streets in Libya". BBC News. Archived from the original on 30 December 2013.
- ^ Esam Mohamed (8 August 2012). "Libya's transitional rulers hand over power". The Boston Globe. Associated Press. Archived from the original on 8 December 2012. Retrieved 8 August 2012.
- ^ Zargoun, Taha (25 August 2012). "Fighters bulldoze Sufi mosque in central Tripoli". Reuters. Archived from the original on 23 October 2015.
- ^ "Libya's Italian-era gazelle statue disappears in Tripoli". 4 November 2014. Archived from the original on 28 August 2016. Retrieved 19 August 2016.
- ^ Stephen, Chris (4 March 2012). "British war graves in Libya desecrated by Islamist militants". The Guardian. Archived from the original on 13 March 2014. Retrieved 19 August 2016.
- ^ "2012 Benghazi attacks | History, Facts, & Information | Britannica". www.britannica.com. Archived from the original on 30 January 2022. Retrieved 30 January 2022.
- ^ "4 hours of fire and chaos: How the Benghazi attack unfolded". CNN. 12 September 2012. Archived from the original on 21 February 2015. Retrieved 20 February 2015.
- ^ Grant, George (7 October 2012). "Congress dismisses Abushagur". Libya Herald. Archived from the original on 6 August 2013. Retrieved 7 October 2012.
- ^ Zaptia, Sami (7 October 2012). "Abushagur announces a smaller emergency cabinet". Libya Herald. Archived from the original on 9 August 2013. Retrieved 7 October 2012.
- ^ "Libyan Prime Minister Mustafa Abu Shagur to stand down". BBC News. 7 October 2012. Archived from the original on 7 October 2012. Retrieved 7 October 2012.
- ^ Grant, George (14 October 2012). "Ali Zidan elected prime minister". Libya Herald. Archived from the original on 29 September 2013. Retrieved 14 October 2012.
- ^ "Libya congress approves new PM's proposed government". Reuters. 31 October 2012. Archived from the original on 3 November 2012. Retrieved 31 October 2012.
- ^ Zapita, Sami (14 November 2012). "Zeidan government sworn in". Libya Herald. Archived from the original on 6 August 2013. Retrieved 3 June 2013.
- ^ Kirkpatrick, David D (17 March 2014). "U.S. Navy SEALs Take Control of Diverted Oil Tanker". The New York Times. Archived from the original on 21 March 2014. Retrieved 17 March 2014.
- ^ "Libya ex-PM Zeidan 'leaves country despite travel ban'". BBC. 12 March 2014. Archived from the original on 15 March 2014. Retrieved 16 March 2014.
- ^ Kirkpatrick, David (20 February 2015). "Ties to Islamic State Cited by Group in Libya Attacks". The New York Times. Archived from the original on 21 February 2015. Retrieved 20 February 2015.
- ^ Dean, Laura (20 February 2015). "How strong is the Islamic State in Libya?". USA Today. Archived from the original on 22 February 2015. Retrieved 20 February 2015.
- ^ Loveluck, Louisa (20 February 2015). "Isil loyalists claim responsibility for car bombs in Libya, killing at least 40 people". The Daily Telegraph. London. Archived from the original on 21 February 2015. Retrieved 20 February 2015.
- ^ Jawad, Rana (26 June 2014). "Libyan elections: Low turnout marks bid to end political crisis". BBC. Archived from the original on 12 August 2014. Retrieved 22 August 2014.
- ^ "Former Libyan parliament reconvenes, elects Islamist premier". Al Akhbar English. 25 August 2014. Archived from the original on 26 August 2014. Retrieved 25 August 2014.
- ^ "Libya's Islamist militias claim control of capital". The Washington Post. Associated Press. 24 August 2014. Archived from the original on 25 August 2014. Retrieved 26 August 2014.
- ^ Chris Stephen (9 September 2014). "Libyan parliament takes refuge in Greek car ferry". The Guardian. Archived from the original on 16 September 2014. Retrieved 24 September 2014.
- ^ Fanack (22 April 2015). "Terrorism Increases in Libya as Politicians Talk". Fanack.com. Archived from the original on 18 May 2015. Retrieved 13 May 2015.
- ^ Fadel Senna (2 September 2015). "Bernardino Leon, Special Representative and Head of the United Nations Support Mission in Libya, delivers a speech during UN-brokered talks in Skhirat, Morocco, on August 28, 2015 | View photo – Yahoo News". Yahoo! News. Retrieved 1 April 2016.[dead link]
- ^ "Video: Remarks by SRSG Bernardino Leon on Talks". 27 January 2015. Archived from the original on 4 March 2016. Retrieved 9 September 2015.
- ^ "OHCHR in Libya". Ohchr.org. 17 September 2012. Archived from the original on 24 April 2016. Retrieved 1 April 2016.
- ^ "15 July 2015, Security Council briefing on the situation in Libya, Special Representative of the Secretary-General for Libya Bernardino Leon | Department of Political Affairs". United Nations. 15 July 2015. Archived from the original on 23 October 2015. Retrieved 1 April 2016.
- ^ Miles, Tom (4 September 2015). "U.N. sees Libya talks entering final mile, eyes Sept. 20 deal". Reuters. Archived from the original on 23 October 2015. Retrieved 1 April 2016.
- ^ "United Nations Official Document". United Nations. Archived from the original on 4 June 2016. Retrieved 1 April 2016.
- ^ "Human Rights Council adopts eight resolutions and closes twenty-eighth session". Ohchr.org. Archived from the original on 24 April 2016. Retrieved 1 April 2016.
- ^ "OHCHR Investigation on Libya". Ohchr.org. 1 January 2014. Archived from the original on 1 April 2016. Retrieved 1 April 2016.
- ^ "African migrants fear for future as Italy struggles with surge in arrivals". Reuters. 18 July 2017. Archived from the original on 2 April 2019. Retrieved 29 August 2018.
- ^ "What will Italy's new government mean for migrants?". The Local Italy. 21 May 2018. Archived from the original on 1 April 2019. Retrieved 29 August 2018.
- ^ "Libya's rival leaders agree to hold elections in December". Al Jazeera. Archived from the original on 18 September 2020. Retrieved 1 July 2018.
- ^ "Clashes erupt south of Libyan capital". 20 April 2019. Archived from the original on 26 May 2021. Retrieved 20 April 2019.
- ^ "Libya government forces capture key town from Haftar's fighters". The Defense Post. 27 June 2019. Archived from the original on 26 May 2021. Retrieved 27 June 2019.
- ^ "Sarraj announces launch of Operation Peace Storm in response to Haftar attacks". The Union Journal. Archived from the original on 23 June 2021. Retrieved 27 March 2020.
- ^ "UAE implicated in lethal drone strike in Libya". BBC News. 28 August 2020. Archived from the original on 11 December 2020. Retrieved 28 August 2020.
- ^ "Turkey and UAE openly flouting UN arms embargo to fuel war in Libya". The Guardian. 7 October 2020. Archived from the original on 27 June 2021. Retrieved 7 October 2020.
- ^ Nebehay, Stephanie; McDowall, Angus (23 October 2020). Jones, Gareth; Maclean, William (eds.). "Warring Libya rivals sign truce but tough political talks ahead". Reuters. Archived from the original on 3 February 2021. Retrieved 21 April 2021.
- ^ "Why Libya's election got postponed: A quick guide". Al Jazeera. 23 December 2021. Archived from the original on 28 April 2022. Retrieved 28 April 2022.
- ^ Magdy, Samy (18 April 2022). "Libya's largest oil field closed as turmoil intensifies". ABC News. Archived from the original on 19 April 2022. Retrieved 18 April 2022.
- ^ "Libya protesters storm parliament building in Tobruk". BBC News. 2 July 2022. Archived from the original on 4 July 2022. Retrieved 4 July 2022.
- ^ "A year on, rebuilding Libya's flood-hit Derna plagued by politics". Al-Monitor. 7 September 2024. Retrieved 8 September 2024.
- ^ Ndebele, Lenin. "A storm caused devastation in Libya, but politics may be its biggest problem in the aftermath". News24. Archived from the original on 4 October 2023. Retrieved 4 October 2023.
- ^ "Libyan Government reinstates morality police". Middle East Eye. Retrieved 12 November 2024.
- ^ "Libya Background". Education Libya. 30 March 2004. Archived from the original on 26 April 2004.
- ^ "Field Listings – Coastlines". The World Factbook. Archived from the original on 16 July 2017. Retrieved 5 February 2013.
- ^ "Weather and Climate in Libya". Southtravels.com. Archived from the original on 5 June 2013. Retrieved 23 December 2012.
- ^ Dinerstein, Eric; et al. (2017). "An Ecoregion-Based Approach to Protecting Half the Terrestrial Realm". BioScience. 67 (6): 534–545. doi:10.1093/biosci/bix014. ISSN 0006-3568. PMC 5451287. PMID 28608869.
- ^ "Old Town of Ghadames (1986) Libyan Arab Jamahirya". World Cultural Heritage. 20 July 2006. Archived from the original on 10 August 2016. Retrieved 10 August 2016.
- ^ University of Notre Dame (2022). "ND-GAIN Country Index". Notre Dame Global Adaptation Initiative. Retrieved 5 March 2025.
- ^ a b UNDP; UNICEF; IOM UN Migration; COP 27 (October 2022). "UN Climate Change Fact Sheet: Libya" (PDF).
{{cite web}}: CS1 maint: numeric names: authors list (link) - ^ UNDP. "Libya: Environment and Climate Change". UNDP. Retrieved 5 March 2025.
- ^ World Bank Climate Change Knowledge Portal. "Libya". climateknowledgeportal.worldbank.org. Retrieved 5 March 2025.
- ^ "Le Maghreb prend conscience du déclin de sa biodiversité". 4 August 2020. Archived from the original on 15 April 2021. Retrieved 13 October 2020.
- ^ "Libya". reports.unocha.org. 26 August 2021. Archived from the original on 5 April 2023. Retrieved 19 July 2023.
- ^ a b c András Zboray. "Flora and Fauna of the Libyan Desert". Fliegel Jezerniczky Expeditions. Archived from the original on 8 December 2012. Retrieved 5 February 2013.
- ^ "How Hot is Hot?". Extreme Science. Archived from the original on 2 February 2013. Retrieved 5 February 2013.
- ^ a b "World: Highest Temperature". World Weather / Climate Extremes Archive. Arizona State University. 2012. Archived from the original on 4 January 2013. Retrieved 15 January 2013.
- ^ a b El Fadli, KI; et al. (September 2012). "World Meteorological Organization Assessment of the Purported World Record 58 °C Temperature Extreme at El Azizia, Libya (13 September 1922)". Bulletin of the American Meteorological Society. 94 (2): 199. Bibcode:2013BAMS...94..199E. doi:10.1175/BAMS-D-12-00093.1. ISSN 0003-0007.
- ^ Westcott, Tom (15 September 2012). "Libya loses 'world's hottest place' record". Libya Herald. Archived from the original on 20 August 2013.
- ^ "Fossil Water in Libya". NASA. Archived from the original on 18 February 2013. Retrieved 5 February 2013.
- ^ Cigolini, C, C Laiolo, and M Rossetti (2012) Endogenous and nonimpact origin of the Arkenu circular structures (al-Kufrah basin-SE Libya) Meteoritics & Planetary Science. 47(11):1772–1788.
- ^ "Libya mired in chaos 10 years after Arab Spring". France 24. 10 February 2021. Archived from the original on 10 February 2021. Retrieved 14 February 2022.
- ^ "10 years since Kadhafi death, stability still eludes Libya". France 24. 19 October 2021. Archived from the original on 19 October 2021. Retrieved 14 February 2022.
- ^ "Feature: Libyans struggling in poverty, chaos 10 years after NATO intervention". Xinhua News Agency. 7 May 2021. Archived from the original on 14 February 2022. Retrieved 14 February 2022.
- ^ "Libya's Second Civil War: How did it come to this?". Conflict News. Archived from the original on 20 March 2015. Retrieved 22 March 2015.National Post View (24 February 2015). "National Post View: Stabilizing Libya may be the best way to keep Europe safe". National Post. Archived from the original on 17 March 2015. Retrieved 22 March 2015.
- ^ Pelham, Nicolas (February 2015). "Libya Against Itself". The New York Review of Books. Archived from the original on 14 October 2022. Retrieved 18 February 2015.
- ^ Fadel, L. "Libya's Crisis: A Shattered Airport, Two Parliaments, Many Factions". Archived 2015-04-26 at the Wayback Machine
- ^ "Legislative Branch". The World Factbook. Archived from the original on 11 October 2017.
- ^ "Libya's ex-parliament reconvenes, appoints Omar al-Hasi as PM". Reuters. 25 August 2014. Archived from the original on 2 April 2015. Retrieved 4 March 2015.
- ^ "Egypt reiterates support for 'Libya's legitimate institutions' amid deepening crisis". Daily News Egypt. 28 December 2014. Archived from the original on 8 April 2015. Retrieved 4 March 2015.
- ^ a b "Encouraging Libyan women to play a greater role in politics". Radio France Internationale. 4 February 2013. Archived from the original on 1 May 2013.
- ^ Stephen, Chris (10 July 2012). "Muslim Brotherhood fell 'below expectations' in Libyan elections". The Guardian. London. Archived from the original on 9 November 2013. Retrieved 5 February 2013.
- ^ a b "The knack of organisation". The Economist. London. 12 January 2013. Archived from the original on 8 January 2018.
- ^ "In Libya, New Government Has Expressed Determination to Tackle Major Internal Problems, Including Precarious Security Situation, Security Council Told" (Press release). United Nations. 29 January 2013. Archived from the original on 12 December 2013. Retrieved 28 June 2017.
- ^ "Congress votes to replace itself with new House of Representatives". Libya Herald. 30 March 2014. Archived from the original on 31 March 2014. Retrieved 1 April 2014.
- ^ "Libya". Freedom in the World 2013. Freedom House. 9 January 2013. Archived from the original on 3 February 2013.
- ^ "Libya". Law.emory.edu. Archived from the original on 12 February 2013. Retrieved 18 February 2013.
- ^ "Libya Gender Equality Profile" (PDF). Unicef. Archived (PDF) from the original on 2 May 2013.
- ^ "Libya moved from dictatorship to non-state: U.N. envoy". Al Arabiya News. 2 December 2014. Archived from the original on 16 December 2014. Retrieved 4 December 2014.
- ^ a b Kingsley, Patrick. "Libyan politicians sign UN peace deal to unify rival governments". The Guardian. Archived from the original on 17 December 2015. Retrieved 1 April 2016.
- ^ "Libyan deal on course, but who is on board?". Al Arabiya. 25 December 2015. Archived from the original on 28 January 2016. Retrieved 1 April 2016.
- ^ a b c "UN-led Libya forum selects new interim government". www.aljazeera.com. Archived from the original on 20 February 2021. Retrieved 5 February 2021.
- ^ a b c d e f "Libya crisis: Vote to unite splintered nation". BBC News. 5 February 2021. Archived from the original on 15 April 2021. Retrieved 5 February 2021.
- ^ "Interim leader Abdul Hamid Dbeibah to run for Libyan presidency". www.aljazeera.com. Archived from the original on 23 November 2021. Retrieved 19 December 2021.
- ^ "Tripoli Appeals Court reinstates Dbeibah as presidential candidate | The Libya Observer". www.libyaobserver.ly. Archived from the original on 2 December 2021. Retrieved 19 December 2021.
- ^ "Libyan court reinstates Saif Gaddafi as presidential candidate". www.aljazeera.com. Archived from the original on 24 September 2023. Retrieved 21 December 2021.
- ^ "Saif Al-Islam Gaddafi back in Libya presidential election race | The Libya Observer". www.libyaobserver.ly. Archived from the original on 6 December 2021. Retrieved 21 December 2021.
- ^ "Libya elections: Delay called for in presidential poll". BBC News. 22 December 2021. Archived from the original on 2 July 2023. Retrieved 23 December 2021.
- ^ a b "Fears of Libya violence as UN races to manage election postponement". the Guardian. 21 December 2021. Archived from the original on 4 April 2023. Retrieved 23 December 2021.
- ^ "UK's ambassador drawn into Libyan political crisis after elections called off". the Guardian. 26 December 2021. Archived from the original on 24 August 2023. Retrieved 28 December 2021.
- ^ "Libyan parliament delays next move amid election chaos". Reuters. 27 December 2021. Archived from the original on 3 April 2023. Retrieved 28 December 2021.
- ^ "Independent Libya". Federal Research Division of the Library of Congress. Archived from the original on 22 September 2012. Retrieved 5 February 2013.
- ^ Zoubir, Yahia (2009). "Libya and Europe: Economic Realism at the Rescue of the Qaddafi Authoritarian Regime". Journal of Contemporary European Studies. 17 (3): 401–415. doi:10.1080/14782800903339354. S2CID 153625134.
- ^ Abadi, Jacob (2000). "Pragmatism and Rhetoric in Libya's Policy Toward Israel". The Journal of Conflict Studies: Volume XX Number 1 Fall 2000, University of New Brunswick. Archived from the original on 30 March 2012. Retrieved 5 February 2013.
- ^ Idi Amin; Benoni Turyahikayo-Rugyema (1998). Idi Amin speaks: an annotated selection of his speeches. African Studies Program, University of Wisconsin-Madison. ISBN 978-0-942615-38-8.
- ^ Joseph T. Stanik (2003). El Dorado Canyon: Reagan's undeclared war with Qaddafi. Naval Institute Press. ISBN 978-1-55750-983-3.
- ^ a b Lee Davis, Brian (1990). Qaddafi, terrorism, and the origins of the U.S. attack on Libya. Bloomsbury Academic. p. 16. ISBN 9780275933029.
- ^ "How the mighty are falling". The Economist. London. 5 July 2007. Archived from the original on 12 October 2007. Retrieved 17 July 2007.
- ^ "Gaddafi Given Yugoslavia's Top Medal By Milosevic". Reuters. 26 October 1999. Archived from the original on 15 May 2011.
- ^ Rayner, Gordon (28 August 2010). "Yvonne Fletcher killer may be brought to justice". The Daily Telegraph. London. Archived from the original on 31 August 2010.
- ^ Lee Davis, Brian. Qaddafi, terrorism, and the origins of the U.S. attack on Libya. p. 183.
- ^ President Ronald Reagan (10 March 1982). "Proclamation 4907 – Imports of Petroleum". US Office of the Federal Register. Archived from the original on 6 March 2008.
- ^ "Blair hails new Libyan relations". BBC News. 25 March 2004. Archived from the original on 7 March 2013. Retrieved 5 February 2013.
- ^ Marcus, Jonathan (15 May 2006). "Washington's Libyan fairy tale". BBC News. Archived from the original on 16 January 2013. Retrieved 5 February 2013.
- ^ Leverett, Flynt (23 January 2004). "Why Libya Gave Up on the Bomb". The New York Times. Archived from the original on 1 April 2011. Retrieved 24 February 2011.
- ^ "Gaddafi warns Sudan secession would be dangerous for Africa". France 24. 10 October 2010. Archived from the original on 28 June 2021. Retrieved 25 June 2021.
- ^ "Libya rejects EU plans for migrant centers on its territory". Reuters. 20 July 2018. Archived from the original on 29 August 2018. Retrieved 29 August 2018.
- ^ "Libyan authorities oppose EU migrant plans". EUobserver. 8 February 2017. Archived from the original on 26 May 2021. Retrieved 29 August 2018.
- ^ "Chapter XXVI: Disarmament – No. 9 Treaty on the Prohibition of Nuclear Weapons". United Nations Treaty Collection. 7 July 2017. Archived from the original on 6 August 2019. Retrieved 16 August 2019.
- ^ Allahoum, Ramy (9 September 2018). "Q&A: What's next for Libya?". Al Jazeera. Archived from the original on 3 August 2020. Retrieved 9 September 2018.
- ^ Worth, Robert F. (13 May 2012). "In Libya, the Captors Have Become the Captive". The New York Times. Archived from the original on 24 May 2012. Retrieved 24 May 2012.
- ^ "US-backed force in Libya face challenges". The Guardian. London. 13 November 2012. Archived from the original on 27 December 2016.
- ^ "Libyans lament their missing army". Al Jazeera. 19 October 2012. Archived from the original on 24 January 2013.
- ^ Mohamed, Esam; Alfitory, Osama (23 September 2012). "Libya orders 'illegitimate' militias to disband". Yahoo! News. Associated Press. Archived from the original on 5 March 2016.
- ^ a b c "The party and the hangover". The Economist. London. 23 February 2013. Archived from the original on 22 February 2013. Retrieved 21 February 2013.
- ^ "Libya: Events of 2015". Libya. Human Rights Watch. 11 January 2016. Archived from the original on 16 December 2016.
- ^ "2021 World Press Freedom Index". Reporters Sans Frontieres. Archived from the original on 27 April 2022. Retrieved 28 April 2022.
- ^ "Here are the 10 countries where homosexuality may be punished by death". The Washington Post. 16 June 2016. Archived from the original on 11 November 2016.
- ^ a b c d e "Oil production boosts Libya economy, instability hampers reconstruction". The Daily Star. 20 October 2012. Archived from the original on 9 February 2013.
- ^ "Libya – Analysis". U.S. Energy Information Administration. Archived from the original on 9 December 2012.
- ^ "Oil rents (% of GDP) - Libya | Data". data.worldbank.org. Archived from the original on 30 January 2018.
- ^ a b c "Libya facts and figures". OPEC. Archived from the original on 19 May 2014.
- ^ Jones, Matthew W.; Peters, Glen P.; Gasser, Thomas; Andrew, Robbie M.; Schwingshackl, Clemens; Gütschow, Johannes; Houghton, Richard A.; Friedlingstein, Pierre; Pongratz, Julia (13 November 2024), National contributions to climate change due to historical emissions of carbon dioxide, methane and nitrous oxide, doi:10.5281/zenodo.14054503, retrieved 5 March 2025
- ^ UNICEF (September 2022). "UNICEF Libya Water Scarcity and Climate Change: an analysis on WASH enabling environment in Libya". UNICEF Middle East and North Africa. Retrieved 14 November 2024.
- ^ "Climate Vulnerability in Libya: Building Resilience Through Local Empowerment". Carnegie Endowment for International Peace. Retrieved 14 November 2024.
- ^ "Environment and Climate Change". UNDP. Retrieved 5 March 2025.
- ^ "Upper Middle Income Economies". World Bank. Archived from the original on 24 May 2008. Retrieved 5 February 2013.
- ^ "Libyan Arab Jamahiriya Report". United Nations High Commissioner for Human Rights. Archived from the original on 14 September 2013. Retrieved 5 February 2013.
- ^ "Libya on Recovery Path but Faces Long Rebuilding Effort". IMF. 2012. Archived from the original on 5 February 2013.
- ^ a b "Libya". International Labour Organization. Archived from the original on 24 December 2012.
- ^ a b "Libya". African Economic Outlook. Archived from the original on 26 March 2013.
- ^ "Libya's Jobless Rate at 20.7 Percent". Reuters Africa. 2 March 2009. Archived from the original on 20 October 2012. Retrieved 5 February 2013.
- ^ "More men unemployed than women in Libya: report". Al Arabiya. 18 March 2012. Archived from the original on 2 May 2012. Retrieved 5 February 2013.
- ^ "Safe Drinking Water" (PDF). WHO/UNIADF Joint Monitoring Programme. 2000. Archived (PDF) from the original on 14 November 2012. Retrieved 5 February 2013.
- ^ a b c d "Country Brief on Libya". FAO Global Information and Early Warning System on Food and Agriculture. Archived from the original on 11 November 2012.
- ^ "Olive Oil – Libya's Other Oil Economy". VOA News. Archived from the original on 6 August 2012. Retrieved 5 February 2013.
- ^ "Libya – Trade". European Commission. Archived from the original on 13 February 2013.
- ^ Philips' Modern School Atlas, 1987, 1983 GNP per capita figures are quoted in a list.
- ^ "In a pure coincidence, Gaddafi impeded U.S. oil interests before the war" Archived 27 July 2011 at the Wayback Machine, Glenn Greenwald. Salon. 11 June 2011. Retrieved 11 June 2011
- ^ "Libya". The World Factbook. 17 September 2025. Retrieved 20 October 2025.
{{cite web}}: CS1 maint: url-status (link) - ^ "WTO go-ahead for Libya talks". BBC. 27 July 2004. Archived from the original on 17 June 2013. Retrieved 21 May 2012.
- ^ Cohn, Carolyn (24 July 2009). "Libya expects nearly $2 bln in new FDI". Reuters Africa. Archived from the original on 20 October 2012. Retrieved 5 February 2013.
- ^ "Shell returns to Libya with gas exploration pact". Oil & Gas News. 9–15 May 2005. Archived from the original on 13 May 2005.
- ^ Jawad, Rana (31 May 2006). "Libyan aviation ready for take-off". BBC News. Archived from the original on 10 April 2013. Retrieved 5 February 2013.
- ^ Bangs, Richard; Ammar Mabrouk Eltaye. "Libya sees thriving tourism industry ahead". NBC News. Archived from the original on 24 September 2020. Retrieved 10 October 2007.
- ^ Rosenthal, Elisabeth (16 October 2007). "A Green Resort Is Planned to Preserve Ruins and Coastal Waters". The New York Times. Archived from the original on 27 December 2016.
- ^ "Libyan sovereign wealth fund 'missing $2.9bn'". BBC News. 26 August 2011. Archived from the original on 18 January 2013. Retrieved 5 February 2013.
- ^ "As The Power Struggle Endures, Libya Eyes 900,000 Bpd Oil Output". Archived from the original on 9 December 2016.
- ^ Guinness World Records 2008 Book Archived 24 September 2015 at the Wayback Machine. ISBN 978-1-904994-18-3
- ^ Moutaz Ali (2017). "The Eighth Wonder of the World?". Quantara.de. Archived from the original on 19 December 2021. Retrieved 18 July 2021.
- ^ In battle for Libya's oil, water becomes a casualty Archived 18 July 2021 at the Wayback Machine. Reuters. 2 July 2019.
- ^ "Libye : Les terribles séquelles de l'intervention de l'OTAN". 11 November 2019. Archived from the original on 21 April 2021. Retrieved 13 October 2020.
- ^ "Expert in Design a green investment framework for Libya (H/F)". expertise-france.gestmax.fr. Archived from the original on 27 March 2024. Retrieved 27 March 2024.
- ^ Zakaria, Fareed (25 February 2011). "Gadhafi's brutal regime can't survive". CNN. Archived from the original on 3 December 2013.
- ^ "World Population Prospects 2022". United Nations Department of Economic and Social Affairs, Population Division. Retrieved 17 July 2022.
- ^ "World Population Prospects 2022: Demographic indicators by region, subregion and country, annually for 1950–2100" (XSLX) ("Total Population, as of 1 July (thousands)"). United Nations Department of Economic and Social Affairs, Population Division. Retrieved 17 July 2022.
- ^ a b "Libya". The World Factbook. Archived from the original on 9 January 2021. Retrieved 5 February 2013.
- ^ "Libya". Countrystudies.us. Archived from the original on 26 August 2013. Retrieved 5 February 2013.
- ^ "Population of Libya". Fanack.com. Archived from the original on 26 February 2021. Retrieved 27 June 2019.
- ^ Yakan, Mohamad (30 November 2017). Almanac of African Peoples and Nations. Routledge. ISBN 978-1-351-28930-6. Archived from the original on 1 May 2023. Retrieved 6 April 2023.
- ^ Zurutuza, Karlos. "Berbers fear ethnic conflict". www.aljazeera.com. Archived from the original on 29 January 2023. Retrieved 20 October 2022.
- ^ "Uprising in Libya: 'Survival Hinges on Tribal Solidarity'". Der Spiegel. 23 February 2011. Archived from the original on 24 May 2012. Retrieved 5 February 2013.
- ^ Ahmed, Nadia (20 February 2015). "Why Egyptians are risking their lives to work in Libya". The Guardian. ISSN 0261-3077. Retrieved 14 July 2023.
- ^ Al-Hawaat, Ali. "The Family and the work of women, A study in the Libyan Society". National Center for Research and Scientific Studies of Libya. Archived from the original on 3 April 2003. Retrieved 5 February 2013.
- ^ "UNHCR Global Appeal 2013 Update". UNHCR. Archived from the original on 7 November 2014. Retrieved 16 December 2014.
- ^ "Health". SESRIC. Archived from the original on 23 October 2014. Retrieved 5 February 2013.
- ^ "Demography". SESRIC. Archived from the original on 23 October 2014. Retrieved 5 February 2013.
- ^ "Rebuilding Libya's health system". 7 November 2023. Archived from the original on 2 May 2024. Retrieved 2 May 2024.
- ^ "Global Hunger Index Scores by 2024 GHI Rank". Global Hunger Index (GHI) - peer-reviewed annual publication designed to comprehensively measure and track hunger at the global, regional, and country levels. Retrieved 24 December 2024.
- ^ a b c Clark, Nick (July 2004). "Education in Libya". World Education News and Reviews, Volume 17, Issue 4. Archived from the original on 8 February 2013. Retrieved 5 February 2013.
- ^ "Education of Libya". Federal Research Division of the Library of Congress. Archived from the original on 21 September 2012. Retrieved 5 February 2013.
- ^ "National adult literacy rates (15+), youth literacy rates (15–24) and elderly literacy rates (65+)". UNESCO Institute for Statistics. Archived from the original on 29 October 2013.
- ^ a b El-Hawat, Ali (8 January 2013). "Country Higher Education Profiles – Libya". International Network for Higher Education in Africa. Archived from the original on 5 June 2010. Retrieved 5 February 2013.
- ^ "Libya Launches Full Day School". Archived from the original on 2 May 2024. Retrieved 2 May 2024.
- ^ "Libya". Encyclopedia Britannica. Encyclopædia Britannica Online. 2012. Archived from the original on 22 November 2012.
- ^ Dupree, Louis (1958). "The Non-Arab Ethnic Groups of Libya". Middle East Journal. 12 (1): 33–44.
- ^ "Libya – Italian colonization". Britannica. Archived from the original on 5 August 2011. Retrieved 20 August 2011.
- ^ "Libya — Migrant Report 46 (January - February 2023)". IOM. 21 November 2023. Archived from the original on 21 November 2023. Retrieved 21 November 2023.
{{cite web}}: CS1 maint: bot: original URL status unknown (link) - ^ Tsourapas, Gerasimos (17 March 2015). "The Politics of Egyptian Migration to Libya". Middle East Research and Information Project. Archived from the original on 11 November 2016. Retrieved 4 December 2016.
- ^ a b c "Migration Facts Libya" (PDF). Migrationpolicycentre.eu. Archived (PDF) from the original on 4 March 2016. Retrieved 1 April 2016.
- ^ Brachet, Julien (2016). "Policing the Desert: The IOM in Libya Beyond War and Peace". Antipode. 48 (2): 272–292. Bibcode:2016Antip..48..272B. doi:10.1111/anti.12176.[permanent dead link]
- ^ Abdusamee, Mohammed; Hacaoglu, Selcan (17 June 2020). "Top Turkish Ministers Meet UN Backed Libyan Government". Bloomberg. Archived from the original on 11 August 2020.
- ^ "Libya, Tunisia: Migrants – Migration News | Migration Dialogue". Migration.ucdavis.edu. Archived from the original on 5 March 2016. Retrieved 1 April 2016.
- ^ "Libya Herald, Updated: 2,000 Filipino workers in Libya, 126 infected and 6 died of Coronavirus". libyaherald.com. 30 January 2021. Archived from the original on 15 April 2021. Retrieved 1 February 2021.
- ^ a b "Libya". CIA. Archived from the original on 9 January 2021. Retrieved 16 December 2014.
- ^ "Tamazight declared official language in Amazigh-peopled districts". Life. 22 February 2017. Archived from the original on 17 March 2017. Retrieved 22 February 2017.
- ^ "The Importance Of English As A Foreign Language In Libya". Archived from the original on 15 April 2021. Retrieved 20 December 2020.
- ^ Chivvis, Christopher S.; Martini, Jeffrey (18 March 2014). Libya After Qaddafi: Lessons and Implications for the Future. Rand Corporation. p. 49. ISBN 978-0-8330-8489-7. Archived from the original on 26 May 2021. Retrieved 30 December 2018.
- ^ "Minority Muslim Groups". Islamopedia Online. Archived from the original on 15 April 2016. Retrieved 1 April 2016.
- ^ "Pakistani Ahmedis Held". Libya Herald. Tripoli. 16 January 2013. Archived from the original on 31 May 2014. Retrieved 5 June 2014.
- ^ "The Sanusis". Federal Research Division of the Library of Congress. Archived from the original on 21 September 2012. Retrieved 5 February 2013.
- ^ "Islam in Revolutionary Libya". Federal Research Division of the Library of Congress. Archived from the original on 21 September 2012. Retrieved 5 February 2013.
- ^ "Libya: Situation of Muslims who have converted to Christianity; treatment by society and the authorities". refworld. Archived from the original on 15 September 2023. Retrieved 5 February 2013.
- ^ "Derna: An Islamic State emirate on Egypt's borders". Egypt Independent. 15 October 2014. Archived from the original on 21 February 2015. Retrieved 20 February 2015.
- ^ Faucon, Benoît; Bradley, Matt (17 February 2015). "Islamic State Gained Strength in Libya by Co-Opting Local Jihadists". The Wall Street Journal. Archived from the original on 21 February 2015. Retrieved 20 February 2015.
- ^ Moore, Jack (29 January 2015). "Al-Qaeda 'Islamic Police' on Patrol in Libyan City Contested With ISIS". Newsweek. Archived from the original on 20 February 2015. Retrieved 20 February 2015.
- ^ Greenberg, Udi; A. Foster, Elizabeth (2023). Decolonization and the Remaking of Christianity. Pennsylvania: University of Pennsylvania Press. p. 105. ISBN 9781512824971.
- ^ "Christian Communities". Islamopedia Online. Archived from the original on 26 March 2016. Retrieved 1 April 2016.
- ^ "Foreigners held in Libya on suspicion of proselytising". BBC News. 16 February 2013. Archived from the original on 17 February 2013.
- ^ Fadel, Leila (17 February 2015). "ISIS Beheadings in Libya Devastate An Egyptian Village". NPR. Archived from the original on 19 February 2015. Retrieved 20 February 2015.
- ^ Malsin, Jared (20 February 2015). "'We want our sons back': fears grow for Egyptians missing in Libya". The Guardian. Archived from the original on 20 February 2015. Retrieved 20 February 2015.
- ^ "Serving Persecuted Christians Worldwide - Libya - Open Doors UK & Ireland". Open Doors UK & Ireland. Opendoorsuk.org. Archived from the original on 24 June 2022. Retrieved 24 June 2022.
- ^ "History of the Jewish Community in Libya". University of California at Berkeley. Archived from the original on 25 April 2013. Retrieved 5 February 2013.
- ^ Harris, David A. (2000). In the Trenches: Selected Speeches and Writings of an American Jewish Activist, 1979–1999. KTAV Publishing House, Inc. pp. 149–150. ISBN 978-0-88125-693-2.
- ^ Lane, Edwin (23 December 2011). "After Gaddafi, Libya's Amazigh demand recognition". BBC News. Archived from the original on 20 December 2016.
- ^ "CAF America- a global grantmaking organization". Archived from the original on 15 July 2014. Retrieved 7 July 2014.
- ^ "Libya looking at economic diversification". Alexander's Gas & Oil Connections. 17 September 1999. Archived from the original on 9 December 2000.
- ^ "Libyan Dance Schools in Libya, Dancewear Suppliers, Dancing Organizations, Libyan National Commission for UNESCO, M. A. Oraieth". Bangkokcompanies.com. Archived from the original on 15 May 2007. Retrieved 8 July 2012.
- ^ "North Korea Tops CPJ list of '10 Most Censored Countries". Committee to Protect Journalists. 1996. Archived from the original on 8 July 2008. Retrieved 5 February 2013.
- ^ Donkin, Mike (23 July 2005). "Libya's tourist treasures". BBC News. Archived from the original on 10 April 2013. Retrieved 5 February 2013.
- ^ "Libya and Russia viewing resumption of railway projects". 1 October 2018. Archived from the original on 26 May 2021. Retrieved 1 November 2019.
- ^ Bouchenaki, Mounir. "Museum Architecture: beyond the <> and ... beyond" (PDF). UNESCO. Archived from the original (PDF) on 2 May 2013. Retrieved 5 February 2013.
- ^ "Enjoy a taste of Libya's traditional dishes | The Libya Observer". www.libyaobserver.ly. Archived from the original on 12 June 2021. Retrieved 25 May 2021.
- ^ Fabricant, Florence (4 January 2006). "In Libya, for Starters, It's the Soup". The New York Times. ISSN 0362-4331. Archived from the original on 13 October 2022. Retrieved 13 October 2022.
- ^ "Libya - Culture - Libyan Cuisine". www.liquisearch.com. Retrieved 5 September 2025.
- ^ "Alcohol poisoning kills 51 in Libya". BBC News. 11 March 2013. Archived from the original on 9 April 2023. Retrieved 6 April 2023.
- ^ a b "Libyan Food". Temehu Tourism Services. 24 June 2010. Archived from the original on 6 August 2011. Retrieved 20 August 2011.
- ^ "Libya – Political process". Encyclopedia Britannica. Archived from the original on 28 November 2011. Retrieved 5 October 2020.
- ^ "Sports in Libya". Fanack.com. Archived from the original on 19 September 2020. Retrieved 5 October 2020.
Bibliography
[edit]![]() This article incorporates public domain material from The World Factbook. CIA.
This article incorporates public domain material from The World Factbook. CIA.![]() This article incorporates public domain material from U.S. Bilateral Relations Fact Sheets. United States Department of State.
This article incorporates public domain material from U.S. Bilateral Relations Fact Sheets. United States Department of State.
External links
[edit]Government
[edit]- Information Portal – Official Libya Information Portal
- Government – official website of Government of National Unity of Libya
- Prime Minister – official website of the prime minister of Libya
- House of Representatives Archived 4 May 2020 at the Wayback Machine – official website of the Libyan House of Representatives
- Statistics and Census – official website of Bureau of Statistics and Census
History
[edit]- "History" – Libyan History at Embassy of the State of Libya in Washington
Tourism
[edit]- Ministry of Tourism and Handcrafts – official website of the Ministry of Tourism and Handcrafts
Maps
[edit] Wikimedia Atlas of Libya
Wikimedia Atlas of Libya Geographic data related to Libya at OpenStreetMap
Geographic data related to Libya at OpenStreetMap
Libya
View on GrokipediaLibya, officially the State of Libya (دولة ليبيا, Dawlat Lībiyā), is a North African country bordering the Mediterranean Sea to the north, with land borders shared with Algeria, Chad, Egypt, Niger, Sudan, and Tunisia; it spans 1,759,540 square kilometers, making it the fourth-largest country in Africa by area, and has an estimated population of 7,361,263 as of 2024, predominantly composed of Arab and Amazigh (Berber) ethnic groups.[1][1] The capital and largest city is Tripoli, situated on the northwestern coast, while the country features vast desert interiors dominated by the Sahara, with limited arable land confined to coastal regions and oases.[1] Historically, Libya's territory has been a crossroads of civilizations, from ancient Phoenician and Roman settlements—evidenced by UNESCO sites like Leptis Magna—to Ottoman suzerainty in the 16th century, Italian colonization from 1911 to 1943, and independence as the United Kingdom of Libya in 1951 under King Idris I.[1] A 1969 military coup led by Muammar Gaddafi established a revolutionary regime that nationalized oil resources, pursued Arab socialist policies, and maintained authoritarian control until his overthrow in 2011 amid the Arab Spring uprisings, which escalated into NATO-backed intervention and subsequent civil conflict.[1] This event precipitated a power vacuum, reviving tribal and regional divisions absent under Gaddafi's centralized rule, resulting in ongoing fragmentation between rival administrations, such as the UN-recognized Government of National Unity in Tripoli and the Libyan National Army in the east, with militias controlling key territories and delaying national elections.[1] Economically, Libya possesses Africa's largest proven oil reserves, accounting for over 95% of export revenues and about 60% of GDP, with crude production averaging around 1.3-1.4 million barrels per day in recent years despite intermittent shutdowns due to political disputes; the 2024 GDP is estimated at $90.6 billion, though per capita figures remain low amid corruption, infrastructure decay, and reliance on hydrocarbons without diversified sectors.[1][2][3] Growth projections for 2025 hover at 6.2%, driven by oil recovery, but systemic governance failures—exacerbated by foreign meddling and internal factionalism—have hindered institutional renewal and human development, positioning Libya as a major transit point for irregular migration to Europe and a site of proxy influences.[4][1][5]
Names and Etymology
Etymology
The name "Libya" derives from the ancient Egyptian term rbw (or variants like Libu or Rebu), referring to Berber-speaking tribal groups inhabiting regions west of the Nile River, as attested in Egyptian inscriptions from the reign of Ramesses II (c. 1279–1213 BCE).[6][7] These terms denoted nomadic or semi-nomadic peoples in North Africa, distinct from Egyptian domains, and appear in records describing military encounters or migrations during the New Kingdom period.[8] Ancient Greeks adopted and adapted the name as Libyē (Λιβύη), initially applying it to coastal territories immediately west of Egypt but later expanding its scope to encompass much of the known African continent beyond the Nile, as noted by Herodotus in the 5th century BCE.[6][9] This broader usage reflected Greek perceptions of a vast, unified "Libyan" expanse inhabited by indigenous groups, though internal divisions among tribes like the Libu, Meshwesh, and Tehenu were recognized in Egyptian sources.[7] The ethnonym's persistence into classical antiquity underscores its role in denoting non-Egyptian North African identities, without a confirmed Indo-European or Semitic root, though speculative links to words meaning "heart" or "zeal" lack primary evidential support.[10] In modern usage, the sovereign state established in 1951 adopted "Libya" to evoke this ancient regional nomenclature, aligning with post-colonial naming conventions that reference pre-Islamic heritage amid diverse ethnic compositions including Arab, Berber, and Tuareg populations.[6] The term's application to the unified nation-state post-Italian colonial rule (1911–1943) and United Nations trusteeship thus bridges ancient tribal designations with contemporary geopolitical boundaries.[8]Historical and Official Names
The name "Libya" derives from ancient Greek usage, where it referred broadly to the North African region west of Egypt, encompassing Berber-inhabited lands, but it was not applied as a unified political entity until the 20th century.[11] Prior to Italian unification, the territory consisted of distinct Ottoman provinces: Tripolitania (centered on Tripoli), Cyrenaica (Barqa), and Fezzan (in the southwest), which were semi-autonomous vilayets with varying degrees of central control from Istanbul.[12] Under Italian colonial rule, the area was initially designated as Italian North Africa from 1912 to 1927, following the Italo-Turkish War, before being reorganized into separate colonies of Italian Tripolitania and Italian Cyrenaica; Fezzan was administered separately.[11] In 1934, Italy consolidated these into a single colony officially named Libya, reviving the ancient term for administrative purposes while suppressing local resistance.[13] Upon independence on December 24, 1951, under United Nations supervision, the federation of the three provinces became the United Kingdom of Libya (al-Mamlaka al-Lībiyya al-Muttaḥida), a constitutional monarchy led by King Idris I; this was shortened to Kingdom of Libya (al-Mamlaka al-Lībiyya) in 1963 after the abolition of federal structures.[14] The 1969 coup by Muammar Gaddafi's Free Officers Movement established the Libyan Arab Republic (al-Jumhūriyyah al-ʿArabiyyah al-Lībiyyah) on September 1, reflecting pan-Arab nationalist ideology and the overthrow of the monarchy.[15] In 1977, following Gaddafi's "Third Universal Theory" outlined in the Green Book, the name was changed to the Socialist People's Libyan Arab Jamahiriya (al-Jamāhīriyyah al-ʿArabiyyah al-Lībiyyah al-Shaʿbiyyah al-Ishtirākiyyah), a neologism coined by Gaddafi to denote a "state of the masses" governed through people's committees rather than traditional republican institutions.[16] This cumbersome title persisted until the 2011 civil war and Gaddafi's overthrow, after which the United Nations recognized the interim National Transitional Council as representing "Libya" on September 16, 2011. Post-2011, the official name was simplified to State of Libya (Dawlat Libyā) by the General National Congress in 2013, emphasizing a return to a concise designation amid ongoing factional divisions between rival governments in Tripoli and Tobruk.[17] This name aligns with the 2011 Constitutional Declaration and subsequent drafts, though de facto control remains fragmented, with entities like the Government of National Unity using it nominally since 2021.[16]| Period | Official Name | Key Context |
|---|---|---|
| 1934–1951 | Libya (colony) | Italian unification of provinces into one entity.[11] |
| 1951–1963 | United Kingdom of Libya | Federal monarchy post-independence.[14] |
| 1963–1969 | Kingdom of Libya | Centralized monarchy.[13] |
| 1969–1977 | Libyan Arab Republic | Post-coup republic under Gaddafi.[15] |
| 1977–2011 | Great Socialist People's Libyan Arab Jamahiriya | Gaddafi's ideological "mass state" system.[16] |
| 2011–present | State of Libya | Transitional name after revolution.[17] |
History
Prehistoric and Ancient Periods
Evidence of human presence in the region of modern Libya dates to the Paleolithic era, with some of the earliest artifacts including stone tools and rock engravings found in the Messak Plateau and Tadrart Acacus Mountains in the southwest.[18] These engravings, primarily from the Archaic period, depict large wild animals and are estimated to originate around 12,000 years ago, reflecting a hunter-gatherer lifestyle in a once-lusher Sahara environment.[19] The Tadrart Acacus sites contain thousands of paintings and engravings spanning multiple phases, from the "Round Head" style around 10,000–6,000 BC showing abstract human figures, to later pastoral scenes with cattle and herders indicating a shift to Neolithic animal domestication by approximately 6000 BC.[20] This rock art illustrates climatic changes and cultural adaptations, as the region transitioned from a savanna supporting bovine pastoralism to increasing aridity, with camel introductions appearing in depictions after 1000 BC.[21] Berber ancestors, proto-Amazigh peoples, likely began permanent settlements around 8000 BC, exploiting Mediterranean coastal fertility for early farming and herding.[22] In ancient times, indigenous Berber tribes organized in loose confederations dominated the territory, engaging in agriculture, trade, and intermittent warfare. Phoenician settlers from the Levant established coastal outposts in Tripolitania (western Libya) by around 1000 BC, founding cities such as Leptis Magna, Sabratha, and Oea (modern Tripoli), which grew under Carthaginian oversight as Punic emporia focused on olive oil, grain, and maritime commerce.[23] These settlements expanded influence inland but faced resistance from Berber groups, culminating in alliances during the Punic Wars (264–146 BC), after which Rome dismantled Carthaginian power in North Africa.[24] Eastern Libya, or Cyrenaica, saw Greek colonization starting with Cyrene's founding circa 631 BC by Dorian settlers from Thera, leading to the Pentapolis (five cities: Cyrene, Apollonia, Ptolemais, Arsinoe, and Berenice) that formed a prosperous Hellenistic kingdom exporting silphium and horses.[25] Persian conquest in 525 BC briefly interrupted Greek autonomy, followed by integration into Alexander's empire in 331 BC and Ptolemaic Egypt until Roman annexation of Cyrenaica in 74 BC.[26] In the south, the Garamantes Berbers developed a kingdom in Fezzan around 400 BC, utilizing subterranean aqueducts (foggara) for irrigation to farm oases and control trans-Saharan trade routes in salt, gold, and slaves, often clashing with Roman expeditions.[24] Roman rule unified Libya as provinces of Creta et Cyrenaica (east) and later Africa Proconsularis extending into Tripolitania, fostering urban growth and infrastructure; Leptis Magna, refounded as a colonia under Trajan, peaked under native emperor Septimius Severus (r. 193–211 AD), who enhanced its harbors, basilica, and triumphal arch with Severan dynasty funds.[26] Provincial prosperity relied on Berber labor and taxation, though nomadic raids and the Garamantes' resistance—subdued by Cornelius Balbus in 19 BC—highlighted ongoing tensions between sedentary Roman centers and pastoral tribal dynamics.[24] By the 3rd century AD, Christianity spread via coastal cities, but Vandal invasions in 429 AD and Byzantine reconquest marked the decline of classical antiquity in the region.[23]Islamic and Ottoman Eras (647–1911)
The Arab Muslim conquest of Libya's coastal regions, particularly Tripolitania and Cyrenaica, commenced in 647 CE with raids led by Abd Allah ibn Sa'd ibn Abi Sarh following the fall of Egypt in 642 CE.[27] These expeditions targeted Byzantine-held territories, imposing tribute and gradually incorporating the area into the expanding Rashidun and later Umayyad Caliphate, though full subjugation required multiple campaigns amid Berber resistance.[28] By 670 CE, Uqba ibn Nafi established a military base at Kairouan in modern Tunisia, facilitating further advances into Tripolitania, where Arab forces defeated local Byzantine and Berber coalitions, securing Tripoli by the early 8th century.[29] Fezzan in the south remained largely autonomous under Berber tribes, with intermittent Arab influence via trans-Saharan trade routes. Under Umayyad rule from Damascus (661–750 CE), administration focused on coastal garrisons and tax collection, with Arab settlers intermarrying local Berbers and promoting Islam through incentives like reduced jizya for converts.[30] Berber Kharijite revolts, fueled by egalitarian doctrines rejecting Umayyad Arab supremacy, erupted in the 740s, establishing short-lived Ibadi states in Tripolitania's hinterlands, such as under Abi al-Khattab in 760 CE.[27] The Abbasid overthrow of the Umayyads in 750 CE shifted the caliphal center to Baghdad, weakening direct control; Libya devolved into semi-independent emirates under local Arab-Berber elites, with Abbasid governors nominally overseeing Tripoli but struggling against autonomous tribal confederations in Cyrenaica and Fezzan.[30] Economic life centered on Mediterranean trade in olive oil, grains, and slaves, alongside pastoralism, though arid conditions limited large-scale agriculture. The Fatimid Caliphate, an Ismaili Shia dynasty originating among Berber Kutama tribes in modern Algeria, extended its reach into Libya by 909 CE, using Tripolitania as a staging ground for eastward expansion.[30] Fatimid forces under Abu Abdallah al-Shi'i captured Tripoli in 908–909 CE, establishing fortified bases like the qasr at Ajdabiya in Cyrenaica to project power, though Bedouin unrest and logistical challenges hindered sustained interior control.[31] By 969 CE, after conquering Egypt and founding Cairo as their capital, the Fatimids delegated Libya to Zirid governors, Sunni Berber allies who nominally upheld Fatimid suzerainty but increasingly asserted autonomy, leading to revolts like the Banu Hilal Arab migrations in the 1050s that disrupted agriculture and urban life.[30] Subsequent Hafsids in Tunis exerted intermittent influence over western Tripolitania from the 13th century, fostering trade hubs but facing challenges from Spanish incursions, including the 1510 seizure of Tripoli by Knights Hospitaller. Ottoman forces under Admiral Turgut Reis (Dragut) captured Tripoli from the Knights of St. John on August 15, 1551, after a month-long siege involving 1,200 Ottoman troops and corsair allies against a garrison of 200 knights and 2,500 mercenaries, establishing the Regency of Tripoli as an Ottoman eyalet.[32] Administered by a pasha appointed triennially from Istanbul, the regency integrated diverse ethnic groups—Arabs, Berbers, Turks, and Kouloughlis (Turkish-Berber offspring)—through a military-bureaucratic system reliant on janissary corps and tribal subsidies, while corsair fleets under pasha command raided European shipping, generating revenue from captives and tribute estimated at 200,000–300,000 Spanish dollars annually by the 18th century.[33] Cyrenaica operated as a sanjak under the pasha's oversight, with the Senussi order emerging in 1837 at Bayda to promote religious revivalism among Bedouins, countering Ottoman secular influences. In 1711, Ahmed Karamanli, a Kouloughli cavalry officer, overthrew the Ottoman pasha in a coup, founding a dynasty that ruled autonomously until 1835, paying nominal tribute to the sultan while controlling trans-Saharan caravan trade in gold, ivory, and slaves from Fezzan.[32] The Karamanlis centralized power in Tripoli, expanding date palm cultivation and fortifications, but faced succession crises, including Yusuf Karamanli's 1795 fratricide of his brother Ahmad and civil wars in the 1830s that weakened the dynasty amid European pressures like the U.S. Barbary Wars (1801–1805), where American forces bombarded Tripoli to end tribute demands.[34] Ottoman direct rule resumed in 1835 under Mahmud II's Tanzimat reforms, imposing conscription and land taxes that sparked tribal revolts, such as the 1836 Misrata uprising, while suppressing the Karamanli remnants; administration emphasized Istanbul-appointed governors and garrisons, fostering urban growth in Tripoli's population to 20,000 by 1900, sustained by pilgrimage routes and olive exports.[34] Ottoman control persisted until the Italo-Turkish War erupted in 1911, marking the era's close.[33]Italian Colonialism and World War II (1911–1951)
Italy declared war on the Ottoman Empire on September 29, 1911, initiating the Italo-Turkish War to seize control of the Ottoman provinces of Tripolitania and Cyrenaica, which Italy termed Libya.[35] Italian naval forces bombarded Tripoli on the same day, landing troops that captured the city by October 23, 1911, after initial resistance from local Ottoman and Arab forces.[36] The conflict expanded to include aerial bombings—the first in history—and Italian advances into the interior, though guerrilla resistance persisted. The war concluded with the Treaty of Lausanne (also known as the Treaty of Ouchy) on October 18, 1912, by which the Ottoman Empire ceded Libya to Italy, though effective control remained limited to coastal areas amid ongoing local opposition.[35] Under Benito Mussolini's fascist regime from the 1920s, Italy pursued aggressive pacification and settlement policies to consolidate rule. Italian forces, led by generals such as Rodolfo Graziani, conducted brutal campaigns against indigenous resistance, particularly the Senussi Order in Cyrenaica, employing concentration camps, forced deportations, and mass executions.[37] By the late 1920s, an estimated 10,000 to 20,000 Libyans were interned in camps like those at Suluq and Agedabia, where mortality rates exceeded 10% due to disease and starvation.[38] Italy facilitated the settlement of approximately 110,000 Italian colonists by 1940, establishing agricultural ventures and infrastructure such as the Via Balbia coastal highway to support demographic colonization.[37] These efforts displaced native populations and aimed to create a "Fourth Shore" for Italy, though they fueled prolonged insurgency. The most prominent resistance leader was Omar al-Mukhtar, a Senussi sheikh who commanded guerrilla forces in Cyrenaica from 1911, organizing hit-and-run attacks that inflicted significant casualties on Italian troops.[39] Mukhtar's forces, leveraging desert terrain and tribal alliances, sustained the Second Italo-Senussi War from 1923 until his capture on September 11, 1931, at age 73.[40] Tried by an Italian military tribunal, he was publicly hanged on September 16, 1931, in Suluq concentration camp before 20,000 witnesses, an event intended to demoralize the population but which instead solidified his status as a national symbol.[41] Italian estimates place Libyan deaths from the reconquest at around 20,000 combatants and civilians, though higher figures from indigenous accounts suggest up to 60,000, reflecting the campaign's severity.[37] Libya became a major theater in World War II's North African Campaign, beginning with Italy's invasion of Egypt on September 13, 1940, from bases in Tripolitania, involving 250,000 troops under Marshal Rodolfo Graziani.[42] British Commonwealth forces countered with Operation Compass in December 1940, capturing 130,000 Italians and pushing to El Agheila by February 1941. German intervention via the Afrika Korps under Erwin Rommel in March 1941 reversed gains, with Axis forces besieging Tobruk from April to December 1941 and advancing to El Alamein near Alexandria by mid-1942.[42] Allied victories at the First and Second Battles of El Alamein (July-October 1942) halted the Axis, followed by Operation Torch landings in November 1942 and the capture of Tripoli on January 23, 1943. Axis remnants surrendered in Tunisia on May 13, 1943, ending organized fighting in North Africa.[42] Following Axis defeat, Allied forces administered Libya: Britain controlled Tripolitania and Cyrenaica from 1943, while France oversaw Fezzan.[43] Italian settlers, numbering about 110,000, faced repatriation pressures, with over 20,000 leaving by 1947 amid economic hardship and political uncertainty. The 1947 Paris Peace Treaty stripped Italy of sovereignty, placing Libya under temporary UN trusteeship.[44] Debates in the UN General Assembly culminated in Resolution 289 (IV) on November 21, 1949, endorsing independence by January 1, 1952, under Emir Mohammed Idris al-Senussi of Cyrenaica. Libya achieved sovereignty as the United Kingdom of Libya on December 24, 1951, marking the end of colonial rule.[43]Kingdom of Libya (1951–1969)
The Kingdom of Libya was established on December 24, 1951, as a constitutional and hereditary monarchy under King Idris I, marking the first instance of an African nation attaining independence through United Nations mediation rather than conflict. December 24 is celebrated as Libya's Independence Day, commemorating the achievement of independence in 1951 from post-colonial administrations under UN supervision.[45] Initially structured as a federal system comprising three provinces—Cyrenaica, Tripolitania, and Fezzan—the kingdom's constitution emphasized Islamic principles, with the king holding significant executive powers including veto authority over legislation and command of the armed forces.[46] The federal arrangement reflected the diverse tribal and regional identities forged under prior colonial divisions, but it was abolished in 1963 via constitutional amendment, transitioning Libya to a unitary state to centralize administration and resource management.[47][46] At independence, Libya's economy was underdeveloped, with per capita income among the lowest globally and heavy reliance on foreign aid from the United States and United Kingdom, supplemented by revenues from hosting military installations such as the U.S. Wheelus Air Base and British facilities.[48] Oil exploration concessions granted in the mid-1950s yielded the kingdom's first major discovery in 1959 near Zliten in Cyrenaica, spurring commercial production by 1961 and catapulting government petroleum revenues from approximately $40 million in 1962 to $800 million by 1968.[49][50] This windfall enabled infrastructure investments, including roads, schools, and ports, while diversifying exports beyond subsistence agriculture and fostering urban growth, though wealth distribution favored Cyrenaica due to the concentration of oil fields there.[51] Foreign policy under King Idris prioritized alignment with Western powers, maintaining military bases that provided economic stability pre-oil but fueled domestic resentment amid rising Arab nationalism and perceptions of subservience.[52][48] Internally, the regime faced challenges from tribal favoritism toward the Sanusi order, allegations of corruption among officials, and socioeconomic inequalities exacerbated by uneven oil benefits and limited political liberalization, which suppressed opposition and bred discontent among youth and military officers.[53] These tensions culminated in a bloodless coup on September 1, 1969, executed by the Free Officers Movement led by Muammar Gaddafi while the king was abroad for medical treatment, dissolving the monarchy and proclaiming the Libyan Arab Republic.[54]Gaddafi Era: Achievements, Policies, and Repression (1969–2011)
Muammar Gaddafi, leading the Free Officers Movement, seized power in a bloodless coup on September 1, 1969, overthrowing King Idris I and establishing the Libyan Arab Republic. Gaddafi, then 27, became chairman of the Revolutionary Command Council, consolidating control through purges of rivals and royalist elements. His regime pursued Arab socialist policies, nationalizing foreign-owned oil companies between 1970 and 1973, which increased state revenues from petroleum exports and funded extensive public works.[2] By the mid-1970s, Libya's GDP per capita had risen from approximately $300 in 1969 to over $10,000 by the 1980s, driven by oil windfalls, though much of this wealth was centralized under Gaddafi's direct oversight.[55] Gaddafi outlined his Third Universal Theory in The Green Book, published starting in 1975, advocating a system of direct democracy through people's committees and congresses, rejecting representative parliaments as exploitative. In 1977, he declared the Great Socialist People's Libyan Arab Jamahiriya, or "state of the masses," ostensibly empowering local committees to manage affairs, but in practice, these bodies served as instruments of regime loyalty, with ultimate authority residing in Gaddafi and his inner circle. Social policies emphasized redistribution: education and healthcare became free, contributing to literacy rates climbing from under 25% in 1969 to around 88% by 2010, and life expectancy increasing from about 51 years in 1969 to 74 years by 2011.[56][57] The Great Man-Made River project, initiated in 1984, tapped fossil aquifers in the Sahara to pipe over 6 million cubic meters of water daily to coastal cities and farms, costing an estimated $25 billion and enabling agricultural expansion despite Libya's arid conditions.[58] Despite these developments, Gaddafi's rule was marked by severe repression to maintain power. The regime operated a pervasive security apparatus, including the Internal Security Agency and Revolutionary Committees, which monitored dissent, enforced ideological conformity, and conducted arbitrary arrests. Political opposition was criminalized; thousands of suspected Islamists, liberals, and tribal rivals were imprisoned or executed, with no independent judiciary or free press allowed.[59] A notorious example was the Abu Salim prison massacre on June 28, 1996, where security forces killed at least 1,200 inmates—many political prisoners—during a riot suppression, with families denied information for years.[60][61] Externally, Gaddafi's policies included support for militant groups, exporting repression through state-sponsored terrorism. Libya provided arms and training to the IRA and Palestinian factions, and was implicated in the 1988 Lockerbie bombing of Pan Am Flight 103, which killed 270 people; Libyan agents were convicted, and the regime accepted responsibility in 2003, paying $2.7 billion in compensation.[62][63] These actions led to UN sanctions from 1992 to 1999, isolating Libya economically until Gaddafi renounced terrorism and weapons programs in 2003. While social indicators improved via oil-funded universal services, the absence of accountable governance fostered corruption and inefficiency, with achievements overshadowed by systemic human rights abuses that stifled civil society.[64][59]2011 Revolution, NATO Intervention, and Gaddafi's Fall
Protests against Muammar Gaddafi's regime erupted on February 15, 2011, in Benghazi, sparked by the arrest of human rights activist Fathi Terbil and inspired by uprisings in Tunisia and Egypt.[65] Demonstrations quickly spread to other cities, including Tripoli, where protesters gathered in Green Square on February 17, demanding Gaddafi's resignation.[66] Although initially peaceful, the unrest turned violent as security forces opened fire on demonstrators, killing at least 24 in the first days according to Human Rights Watch reports.[67] Gaddafi responded defiantly, refusing to step down and vowing on February 22, 2011, to fight protesters "house by house" and die as a martyr rather than relinquish power.[68] [66] By late February, rebels had seized control of Benghazi and eastern Libya, forming the National Transitional Council (NTC) on February 27 in Benghazi to coordinate the opposition and seek international recognition as Libya's legitimate representatives.[69] Gaddafi's loyalist forces launched counteroffensives, recapturing western cities like Zawiya and advancing toward Benghazi by early March, prompting fears of a massacre in the rebel stronghold.[70] On March 17, 2011, the UN Security Council adopted Resolution 1973, authorizing member states to enforce a no-fly zone and take "all necessary measures" to protect civilians from attacks, short of foreign occupation, in response to reports of regime atrocities.[71] NATO launched Operation Unified Protector on March 19, conducting airstrikes against Gaddafi's military assets, which halted the advance on Benghazi and shifted momentum to the rebels.[70] The intervention, involving over 26,000 sorties by NATO forces, targeted command-and-control centers, armor, and supply lines, enabling NTC fighters to push westward despite their disorganized state and reliance on defected military units.[72] Rebels captured Tripoli on August 21, 2011, after NATO strikes weakened defenses, forcing Gaddafi to flee to his hometown of Sirte.[73] Intense fighting ensued in Sirte, with NATO providing close air support until October 2011. On October 20, Gaddafi's convoy attempting to escape was struck by a NATO airstrike, after which he was captured alive by NTC fighters, beaten, and killed by gunshot wounds to the head and abdomen, as documented by witnesses and forensic evidence.[74] [75] His death marked the end of 42 years of rule, though the NTC's victory came amid mutual atrocities by both sides, with post-conflict investigations revealing war crimes including executions and indiscriminate bombings.[76] The intervention's expansion beyond civilian protection to facilitating regime change drew criticism for exceeding the resolution's mandate, contributing to Libya's subsequent instability despite initial aims to avert humanitarian disaster.[77]Civil Wars and Fragmentation (2011–2020)
Following Muammar Gaddafi's overthrow in October 2011, Libya experienced rapid fragmentation as hundreds of revolutionary militias retained weapons and asserted local control, undermining the interim National Transitional Council and creating a power vacuum. Armed groups besieged government ministries in Tripoli by 2013, paralyzing central authority and exacerbating regional and tribal divisions over resource allocation, particularly oil revenues. The failure to integrate or disband these militias, rooted in the unstructured NATO-supported rebellion, allowed Islamist factions like Ansar al-Sharia to gain footholds, exemplified by their role in the September 11, 2012, attack on the U.S. consulate in Benghazi, which killed Ambassador J. Christopher Stevens and three other Americans.[78] Elections in July 2012 established the General National Congress (GNC), intended as a transitional body, but Islamist-leaning members dominated political isolation laws, alienating secular rivals and fueling unrest. Tensions escalated in 2014 when the GNC rejected results of June parliamentary elections for the House of Representatives (HoR), citing low turnout amid violence; in response, Misrata-based militias under Operation Dawn captured Tripoli in July, reinstating the GNC and forming a rival National Salvation Government. The elected HoR fled eastward to Tobruk and allied with General Khalifa Haftar, whose Operation Dignity—launched in May 2014 to clear Islamists from Benghazi—evolved into the Libyan National Army (LNA), pitting eastern forces against western coalitions including Libya Dawn and later the UN-backed Government of National Accord (GNA). This schism initiated the second civil war, characterized by proxy battles for territory and oil facilities, with jihadist groups like the Islamic State exploiting chaos to seize Sirte in February 2015 before Misrata brigades, with U.S. airstrikes, recaptured it in January 2016.[78][79] The UN-mediated Libyan Political Agreement of December 2015 aimed to unify institutions by creating the GNA in Tripoli, endorsed internationally but rejected by the HoR, which retained de facto control in the east under Haftar. Haftar's forces seized the "oil crescent" ports in September 2016, controlling much of Libya's hydrocarbon output and deepening economic divides. Foreign interventions intensified the conflict: Turkey and Qatar supplied arms and advisors to the GNA and allied Islamist groups to counter regional rivals, while the United Arab Emirates, Egypt, France, and Russia backed Haftar's LNA with drones, mercenaries (including Wagner Group), and logistics to combat jihadism and secure Mediterranean stability. In April 2019, Haftar's LNA captured southern oil fields and launched an offensive on Tripoli, sparking urban warfare that displaced over 200,000 and caused hundreds of civilian deaths, but Turkish drone support enabled GNA counteroffensives, halting the advance by mid-2020.[78][79][79] A nationwide ceasefire in October 2020, brokered by the UN, paused large-scale fighting after years of attrition that left Libya divided into rival administrations, with militias entrenched and central institutions ineffective. The wars resulted in thousands of combatant and civilian casualties, widespread human rights abuses by all factions, and the proliferation of arms that sustained fragmentation beyond 2020. UN officials described the civilian toll as "incalculable," with intensified suffering from indiscriminate shelling and militia abuses during the 2019-2020 Tripoli battles.[78][80][79]Ongoing Division and Crises (2020–Present)
Following the 2020 ceasefire, Libya experienced a tenuous halt to large-scale fighting, but underlying factional rivalries persisted between the UN-recognized Government of National Unity (GNU) in Tripoli and the Libyan National Army (LNA) under Khalifa Haftar in the east. On October 23, 2020, representatives from both sides signed a permanent ceasefire agreement in Geneva, committing to withdraw forces from frontline positions, unify military structures, and end foreign mercenary deployments, which largely held despite sporadic violations.[81][82] This paved the way for the formation of the interim GNU on March 10, 2021, led by Prime Minister Abdul Hamid Dbeibeh, which was approved by the House of Representatives on March 15 and tasked with organizing national elections by December 2021 while consolidating state institutions.[83][84] However, the GNU's mandate has been undermined by Dbeibeh's refusal to step down, creating parallel governance with Haftar's eastern administration, which controls key oil facilities and rejects Tripoli's authority.[79][85] National elections, initially scheduled for December 24, 2021, were indefinitely postponed amid disputes over electoral laws, candidate eligibility—including Haftar's potential run—and constitutional basis, with the High National Elections Commission citing unresolved issues.[86][87] By 2025, no presidential or parliamentary polls have occurred, though limited municipal elections in August 2025 saw 71% turnout in 26 western municipalities, boycotted by eastern authorities aligned with Haftar, highlighting geographic splits.[88][89] These delays stem from elite power struggles, militia vetoes, and foreign backers prioritizing influence over unification, perpetuating a de facto partition where the GNU holds Tripoli but lacks effective control over the east and south.[90][91] Economic instability has intensified due to oil revenue disputes, which constitute approximately 93% of government funding and are frequently weaponized in factional conflicts. Blockades at ports and fields, such as those in April 2022 and August 2024, halted production—dropping output below 500,000 barrels per day at times—and led to billions in lost revenue, exacerbating inflation, subsidies shortfalls, and liquidity crises.[92][93] Disputes over Central Bank leadership and revenue distribution between east and west prompted outflows of $6 billion in reserves by mid-2025, despite total oil income reaching $14.65 billion in the first nine months of the year.[94][95] Militia control over facilities enables extortion, with production volatility tied to political feuds rather than market factors.[96][97] Humanitarian crises compound the fragmentation, exemplified by the September 10–11, 2023, floods in Derna triggered by Storm Daniel's extreme rainfall, which overwhelmed two poorly maintained dams, causing their collapse and killing over 11,000 people while displacing tens of thousands.[98][99] The disaster's severity—flood surges 20 times higher than modeled without dam failures—was worsened by years of neglect, corruption, and conflict-eroded infrastructure under LNA oversight, with warnings ignored since 2007.[100][101] Rescue efforts exposed governance voids, as militias restricted access and aid diversion occurred, underscoring how divided authority hampers disaster response.[102] Foreign powers sustain the stalemate through proxy support: Turkey bolstered the GNU with drones, troops, and bases post-2020, reversing Haftar's advances, while Russia deploys Africa Corps mercenaries (successors to Wagner) to the LNA, securing oil sites and training forces.[103][104] Egypt and the UAE provide Haftar with arms and logistics, motivated by border security and anti-Islamist aims, creating a balance of external deterrents that prevents outright war but entrenches non-state actors.[105][106] As of October 2025, militia clashes in Tripoli and threats of renewed blockades signal escalating risks, with UN efforts stalled by vetoes from entrenched elites.[107][108]Geography
Physical Features and Topography
Libya spans approximately 1,760,000 square kilometers, with a Mediterranean coastline extending nearly 1,800 kilometers.[109] The country's topography is dominated by the vast Libyan Desert, a flat to undulating plateau forming part of the Sahara, covering about 90% of the land area and characterized by sand dunes, rocky plateaus, and gravel plains.[110] This desert terrain rises gradually southward from the coast, with elevations typically ranging from 500 to 1,000 meters, though it includes significant variations such as depressions and mountain spurs.[111] Libya's landscape divides into three main historical regions: Tripolitania in the northwest, Cyrenaica in the northeast, and Fezzan in the southwest. Tripolitania features the Al-Jifarah (Gefara) coastal plain, a lowland strip averaging 50-100 km wide and fertile due to rainfall and aquifers, backed by the Nafūsah Plateau, an eastward-trending limestone escarpment rising to about 1,000 meters with steep northern faces and gentler southern slopes leading to the desert.[112] Cyrenaica includes a narrower coastal plain, the Marj Plain, and the elevated Jabal al-Akhdar (Green Mountains), a dissected limestone plateau reaching up to 865 meters, supporting terraced agriculture before descending to the arid interior.[113] Fezzan consists of a series of basins and depressions with wadis (seasonal riverbeds) and oases, interspersed with mobile sand dunes up to 150 meters high, and includes the northern extension of the Tibesti Mountains where Bikku Bitti, Libya's highest point at 2,267 meters, is located near the Chad border.[113][114] The lowest elevation is Sabkhat Ghuzayyil at -47 meters below sea level, a salt flat in the central-western desert.[115] No permanent rivers exist, but numerous wadis drain sporadically toward the coast or inland depressions, underscoring the arid nature shaped by hyper-arid conditions and episodic flash floods.[109] The central region around the Gulf of Sidra features the flat Syrtis Desert, a transitional steppe zone between the coastal areas.[112]Climate and Desertification
Libya's climate is predominantly hot desert (BWh in the Köppen-Geiger classification), encompassing approximately 95% of the country's land area, characterized by extreme aridity, high daytime temperatures, and minimal precipitation.[116] Coastal regions along the Mediterranean exhibit a more temperate arid Mediterranean climate (Csa), featuring hot, dry summers with average highs of 30–35°C (86–95°F) in July and August, and mild winters with lows around 10–15°C (50–59°F), though inland areas experience greater diurnal temperature swings and summer peaks exceeding 45°C (113°F).[117] Annual precipitation averages 56 mm nationwide, with over 93% of the territory receiving less than 100 mm, primarily during sporadic winter rains influenced by Mediterranean cyclones; the northeastern Jebel Akhdar highlands receive the highest amounts at 400–700 mm, enabling limited olive and fruit cultivation, while the southern Sahara zones often record under 50 mm.[118][119][120] These climatic conditions, driven by the subtropical high-pressure belt and the rain shadow of the Atlas Mountains to the west, contribute directly to widespread desertification, defined as land degradation in arid, semi-arid, and dry sub-humid areas resulting from climatic variations and human activities. Approximately 90% of Libya is already classified as desert, with the remaining 10%—primarily semi-arid rangelands and coastal plains—at high risk of further encroachment due to expanding sand dunes, soil erosion, and salinization.[121] Key causal factors include chronic low rainfall and rising temperatures, which reduce soil moisture and vegetation cover, compounded by anthropogenic pressures such as overgrazing by livestock, unregulated groundwater extraction for agriculture, and deforestation for fuelwood, leading to a loss of up to 1–2% of arable land annually in vulnerable zones.[122][123] Desertification impacts are multifaceted, severely limiting agricultural productivity—Libya imports over 80% of its food despite fossil water-dependent irrigation from the Great Man-Made River project—and exacerbating water scarcity, with per capita renewable water resources below 100 cubic meters annually, far under the global water stress threshold of 1,700 m³. Dust storms and shifting dunes further degrade infrastructure and croplands, while intensified flash floods from rare heavy rains erode topsoil in denuded areas, as evidenced by the 2023 Derna disaster where upstream desertified wadis amplified downstream flooding. Conflict since 2011 has hindered mitigation, disrupting reforestation and soil conservation programs, though pre-2011 efforts under the Gaddafi regime, including the planting of over 20 million trees via the "Green Belt" initiative, demonstrated partial success in stabilizing dunes around oases.[124][125][126] Projections from climate models indicate a 10–20% precipitation decline by 2050 under moderate emissions scenarios, accelerating desertification rates unless countered by improved land management and reduced reliance on unsustainable irrigation.[127]Libyan Desert and Sahara Influence
The Libyan Desert forms the core of Libya's geography, comprising over 90% of the nation's 1,759,540 square kilometers and representing the northeastern extension of the Sahara Desert system.[128] [129] This expanse includes vast sand seas such as the Calanscio and Rebiana, gravel-covered plateaus, and rocky highlands like the Tibesti Mountains' eastern flanks, with elevations reaching up to 2,000 meters in some areas. The desert's hyper-arid conditions stem from its position within the Sahara's rain shadow, where subtropical high-pressure systems suppress precipitation, resulting in annual rainfall typically under 25 mm in interior zones.[130] [131] The Sahara's climatic dominance profoundly shapes Libya's environmental dynamics, fostering extreme diurnal temperature swings—often exceeding 30°C between day and night—and recurrent dust storms known as gibli or chergui, which carry fine particulate matter across the country. These storms, intensified by wind erosion over denuded surfaces, degrade air quality, disrupt transportation, and contribute to respiratory health issues, with events in 2023 alone affecting visibility to near zero in multiple regions. Desertification accelerates under this influence, as wind-driven sand encroachment threatens arable fringes and oases, reducing vegetative cover and exacerbating soil loss at rates estimated to advance dunes by several meters annually in vulnerable areas like Sabha.[132] [133][134] Human settlement patterns reflect the desert's constraining influence, confining over 90% of Libya's population to the northern Mediterranean coastal strip, while interior oases such as Awjila and Ghadames sustain sparse communities through groundwater-dependent agriculture and pastoralism. Historically, this aridity supported nomadic Tuareg and Tebu lifestyles adapted to trans-Saharan trade routes, but modern reliance on fossil aquifers for irrigation has depleted resources, with overexploitation in oases leading to land degradation and reduced palm yields. Economically, the desert's subsurface basins harbor Libya's primary oil and gas reserves, discovered in the 1950s in formations like the Sirte Basin, underpinning export revenues that constitute over 90% of government income despite the harsh surface conditions limiting diversification.[135] [136][137] Environmental challenges from Sahara expansion include biodiversity loss in isolated wadis and playas, where episodic flash floods briefly support acacia groves and migratory fauna, but persistent aridity favors extremophiles over diverse ecosystems. Mitigation efforts, such as dune stabilization with marram grass or petroleum-based barriers, have yielded mixed results, with sand mobility posing ongoing risks to infrastructure in southern provinces. Climate projections indicate further Sahara southward creep into Libya's semi-arid zones, potentially displacing marginal farming by mid-century without adaptive water management.[125] [138][123]Coastal Regions and Water Resources
Libya possesses a Mediterranean coastline spanning approximately 1,800 kilometers, characterized by a narrow coastal plain varying in width from 10 to 50 kilometers, which contrasts sharply with the arid interior and hosts over 90% of the population.[109] This plain, particularly in the western Tripolitania region, includes marshy areas interspersed with sandy stretches, lagoons, and oases that enable limited agriculture such as olive and citrus cultivation through irrigation.[139] Eastern Cyrenaica features similar low-lying coastal terrain supporting barley and vegetable farming, though productivity remains constrained by soil salinity and irregular rainfall averaging under 250 millimeters annually along the shore.[109] Water resources in these coastal zones are severely limited, with overexploitation of shallow aquifers leading to intrusion of seawater and depletion rates exceeding recharge by factors of 10 to 20 times in populated areas like Tripoli and Benghazi.[140] Libya's per capita renewable freshwater availability stands below 100 cubic meters per year, far under the global water scarcity threshold of 1,000 cubic meters, necessitating reliance on non-renewable fossil groundwater and artificial supply systems.[141] The Great Man-Made River (GMMR) project, operational since the 1980s, addresses this by extracting water from deep Nubian Sandstone Aquifer wells—often exceeding 500 meters in depth—in the Sahara and piping up to 6.5 million cubic meters daily to coastal cities for urban consumption and irrigation.[58] This $25 billion infrastructure, comprising over 1,300 wells and extensive pipelines, has sustained coastal agriculture but draws from finite reserves projected to last 20 to 50 years at current extraction rates without replenishment.[142][143] Desalination supplements GMMR supplies, with 21 operational plants along the coast producing about 525,680 cubic meters per day as of recent assessments, primarily via reverse osmosis and multi-stage flash distillation technologies adopted since 1964.[144] These facilities, concentrated in cities like Tripoli and Misrata, provide potable water but face high energy demands—up to 4 kilowatt-hours per cubic meter for reverse osmosis—and environmental drawbacks including brine effluent that exacerbates coastal salinity.[145] Post-2011 civil unrest has compounded vulnerabilities through pipeline sabotage, plant damage, and uneven maintenance, reducing GMMR output by up to 30% in affected segments and straining desalination capacity amid population pressures.[142] Sustainable management requires integrating wastewater reuse for irrigation—currently underutilized despite potential to recycle 200 million cubic meters annually—and curbing agricultural over-irrigation, which consumes 80% of supplies, though institutional fragmentation hinders coordinated reforms.[146][147]Biodiversity and Environmental Challenges
Libya's biodiversity is constrained by its predominantly hyper-arid climate and vast desert expanses, which cover over 90% of the country's land area, limiting species diversity primarily to coastal zones, oases, and scattered mountainous regions. Flora consists of approximately 1,750 species, with about 4% endemic to Libya and a phytogeographic profile dominated by Mediterranean elements such as hardy shrubs, grasses, and acacia trees adapted to low rainfall.[148] Fauna includes desert-adapted mammals like the fennec fox and sand cat, various reptiles, and insects, while marine environments host around 1,500 species, including 560 types of algae.[149][150] Assessments of 239 plant and 862 animal species indicate threats to nine plants, 11 mammals, and eight birds, reflecting habitat pressures from aridity and human activity.[151] Coastal areas support monk seal colonies and diverse avifauna, though populations have declined due to overexploitation.[152] Protected areas aim to conserve these ecosystems, with key sites including El-Kouf National Park, Karabolli National Park, and nature reserves such as Benghazi, Zellaf, and Sorman (established in 1992 for coastal protection).[153][149] In 2011, marine protected areas were designated at Farwa Lagoon and Ain Al-Ghazalah to safeguard lagoon habitats.[154] As of August 2025, plans to establish 16 additional nature reserves nationwide seek to expand coverage amid biodiversity loss.[155] However, enforcement remains inconsistent due to political fragmentation, limiting effectiveness against poaching and encroachment.[156] Environmental challenges exacerbate biodiversity decline, with desertification advancing at high rates, consuming arable land and promoting sand dune encroachment that reduces habitat for endemic species.[157] Water scarcity, driven by reliance on the Nubian Sandstone Aquifer System and the Great Man-Made River project initiated in 1984, ranks Libya as the sixth most water-stressed country globally as of 2019, intensifying competition for resources in oases and coastal farms.[158] Oil extraction and post-2011 civil wars have caused spills and infrastructure damage, polluting soils and oases with hydrocarbons and methane emissions, as documented in leaks affecting surface soils since 2023.[159][160] Conflict-induced loss of regulatory oversight has worsened air and water pollution from gas flaring and untreated waste, while climate-driven droughts and floods—such as the September 2023 Derna disaster—highlight vulnerabilities amplified by governance failures.[161][124] These factors, compounded by salinization and habitat fragmentation, threaten long-term ecological stability without coordinated resource management.[147]Governance and Politics
Administrative Structure
Libya's administrative structure is formally organized as a unitary state divided into 22 governorates (sha'biyat), which constitute the primary subnational divisions responsible for coordinating local services, development, and governance. These governorates include Al Butnan, Al Jabal al Akhdar, Al Jabal al Gharbi, Al Jafarah, Al Jufrah, Al Kufrah, Al Marj, Al Marqab, Al Wahat, An Nuqat al Khams, Az Zawiyah, Banghazi (Benghazi), Darnah, Ghat, Misratah, Murzuq, Nalut, Sabha, Surt, Tarabulus (Tripoli), Wadi al Hayat, and Wadi ash Shati.[1] This framework originated from a 2007 reorganization that consolidated prior subdivisions into 22 units, a structure that has remained nominally in place following the 2011 revolution despite political instability.[162] Each governorate is further subdivided into baladiyat (municipalities), smaller units that handle day-to-day administration such as public services, infrastructure maintenance, and community affairs, often through elected or appointed local councils.[162] Municipal elections have been conducted in phases since 2013, with over 80 councils established by 2014 in areas under varying degrees of central oversight, though implementation has been inconsistent due to security challenges and resource constraints.[163] At the national level, the executive branch—currently embodied in the Government of National Unity (GNU)—exercises nominal authority over governorate appointments and policy directives, while legislative input from the House of Representatives influences broader administrative laws.[1] In practice, however, local autonomy prevails in many regions, with municipalities frequently negotiating directly with international aid providers or operating independently amid weak central enforcement mechanisms.[164]Current Political Division: GNU vs. LNA
The Government of National Unity (GNU), established in March 2021 through a UN-facilitated Libyan Political Dialogue Forum process, serves as the internationally recognized interim executive authority based in Tripoli, controlling western Libya including the capital and surrounding areas, which constitute approximately one-third of the country's northern territory.[165][85] Led by Prime Minister Abdul Hamid Dbeibeh, the GNU was intended as a transitional body to organize national elections within one year, but Dbeibeh has refused to relinquish power absent a popular vote, leading the House of Representatives to vote on August 13, 2024, to terminate his government's term in favor of a new administration.[166] This standoff has perpetuated a de facto partition, with the GNU reliant on alliances with western militias such as the Stability Support Apparatus and backed by Turkish military support, while facing internal clashes, including those between the 444th Infantry Brigade and rival forces in Tripoli on May 12, 2025.[167][168] Opposing the GNU is the Libyan National Army (LNA), commanded by Field Marshal Khalifa Haftar and aligned with the Tobruk-based House of Representatives (HoR), which exercises legislative authority over eastern and southern Libya.[169] The LNA controls over 70% of Libyan territory, including key oil-producing regions in the east and south such as Sirte, Jufra, and border areas with Sudan, Chad, and Niger, enabling it to influence national revenue through production shutdowns and blockades, as seen in repeated disruptions since 2020.[170][171] Haftar's forces, supported by Egypt, the United Arab Emirates, and Russian Wagner Group mercenaries (with a noted expansion of Russian presence in eastern bases by 2025), have consolidated power through operations neutralizing Islamist groups and securing borders, though this has involved dynastic appointments like son Saddam Haftar's promotion to a senior military role in August 2025.[172][173] The core division manifests in competing claims over unified institutions, particularly the Central Bank of Libya and the National Oil Corporation, where GNU control of financial flows from Tripoli clashes with LNA demands for equitable revenue sharing, exacerbating economic paralysis.[91] National elections, originally scheduled for December 24, 2021, remain indefinitely postponed due to disputes over electoral laws, candidate eligibility (including Haftar's presidential bid), and base constitutions, with the HoR's passage of a no-confidence motion against the GNU in September 2021 underscoring irreconcilable governance visions.[79] Recent de-escalation efforts, such as the October 2, 2025, agreement between GNU head Dbeibeh and UN envoy Abdoulaye Bathily's successor on phased Tripoli security measures, have yielded limited progress amid ongoing militia skirmishes and foreign proxy influences.[174] Local municipal elections commenced in 16 areas on October 18, 2025, after an August delay, but these exclude national unification and highlight the entrenched stalemate as of late 2025.[175][165]Elections, Reforms, and Stalled Democratization
Following the 2011 overthrow of Muammar Gaddafi, Libya held its first post-revolutionary parliamentary elections on July 7, 2012, for the 200-seat General National Congress (GNC), with voter turnout exceeding 60 percent and a secular-leaning National Forces Alliance securing around 40 percent of seats amid widespread participation.[176] These elections marked an initial step toward institutionalizing governance, though underlying tribal, regional, and militia divisions persisted without resolution. The GNC tasked a constituent assembly with drafting a constitution, but progress stalled due to competing Islamist and federalist demands, exacerbating factional tensions.[177] Elections for the House of Representatives (HoR) on June 25, 2014, replaced the GNC but were undermined by violence, including attacks on polling stations and a boycott by federalist groups in eastern Libya seeking greater autonomy, resulting in turnout below 30 percent.[176] The HoR, dominated by anti-Islamist factions, relocated to Tobruk after Islamist-aligned militias seized Tripoli, prompting the defunct GNC's revival as a rival body and igniting the Second Libyan Civil War (2014–2020). United Nations mediation efforts, including the 2015 Skhirat Agreement establishing the UN-backed Government of National Accord (GNA) in Tripoli, aimed to unify institutions but faced rejection from the HoR and eastern commander Khalifa Haftar's Libyan National Army (LNA), perpetuating parallel governance structures.[78] Reforms during this period, such as central bank unification in 2018 and oil facility reopenings under UN pressure, provided temporary economic stabilization but failed to address core power-sharing disputes, as militias retained de facto control over territories and revenues.[88] In March 2021, the UN-facilitated Libyan Political Dialogue Forum selected Abdul Hamid Dbeibeh as prime minister of the Government of National Unity (GNU), intended as a transitional body to organize national elections by December 24, 2021, including simultaneous presidential and parliamentary votes. Preparatory electoral laws were enacted in Tripoli, but controversies over candidate eligibility—such as disqualifications of figures like Saif al-Islam Gaddafi and debates on Haftar's dual military-political role—along with unresolved constitutional bases for the presidency, led to the High National Elections Commission's dissolution of poll committees on December 21, 2021, postponing the vote indefinitely.[87][178] Dbeibeh's refusal to relinquish power post-mandate expiration in 2022 prompted the HoR to nominate rival prime ministers, including Fathi Bashagha and later Osama Hammad, entrenching the Tripoli-based GNU against the HoR-aligned Government of National Stability (GNS) in the east.[179] Democratization efforts since 2021 have remained stalled amid elite-level obstructions, with UN roadmaps for constitutional and electoral frameworks repeatedly derailed by disagreements on power distribution, militia disarmament, and foreign influences supporting proxies—Turkey backing western militias, Russia and Egypt aligning with Haftar.[88][180] Limited progress occurred in local governance, such as municipal elections on August 16, 2025, in 26 western municipalities with 71 percent turnout, hailed as a democratic test but boycotted in HoR/GNS areas and excluding national unification.[88] By October 2025, the UN envoy warned that absent compromise on a unified government and electoral laws, Libya's transition risks indefinite paralysis, as entrenched factions prioritize control over revenues and territory, yielding no national polls since 2014 and perpetuating militia dominance over state institutions.[180] Youth-led protests in 2024–2025 against blackouts and stagnation underscored public frustration, yet without coercive unification or external incentives overriding domestic spoilers, reforms have yielded fragmented, legitimacy-deficient governance rather than consolidated democracy.[181]Foreign Relations and External Influences
Following the 2011 overthrow of Muammar Gaddafi, Libya's political fragmentation has been exacerbated by competing foreign interventions, transforming the country into a proxy battleground for regional and global powers seeking influence over its oil resources, migration routes, and strategic location. Turkey has provided decisive military support to the UN-recognized Government of National Unity (GNU) in Tripoli, deploying drones, Syrian mercenaries, and troops during the 2019-2020 offensive by Khalifa Haftar's Libyan National Army (LNA), which halted Haftar's advance on the capital.[182] In July 2025, Turkey and the GNU signed agreements enhancing military cooperation, including advanced training, expertise exchange, and logistical aid, with Turkish forces' presence extended to 2026.[183] [184] [185] Opposing this, Russia has backed Haftar's LNA in eastern Libya since 2018 through the Wagner Group (rebranded as Africa Corps after 2023 leadership changes), deploying approximately 2,000 mercenaries for ground operations, air defense, and training, alongside offers of resource concessions in exchange for basing rights.[186] [187] The United Arab Emirates (UAE) has supplied Haftar with air support, including Chinese-made drones from bases in eastern Libya, while Egypt has provided logistical and border security assistance to counter Islamist threats and refugee flows, viewing Haftar as a bulwark against instability spilling into its territory.[188] [79] These interventions have prolonged the stalemate, with foreign actors prioritizing geopolitical gains over Libyan unification, as evidenced by arms flows violating UN embargoes.[88] [189] The United Nations Support Mission in Libya (UNSMIL) has led mediation efforts, facilitating dialogues like the 2020 ceasefire and pushing for elections delayed since 2021, but progress stalled amid rival governments' intransigence and external vetoes.[190] In June 2025, international follow-up committees reaffirmed commitment to UN processes under Security Council resolutions, yet foreign military presences—estimated at thousands of troops and contractors—continue to undermine central authority.[191] The United States has maintained limited engagement, focusing on counterterrorism and migration, while the European Union supports UN mediation but faces criticism for migration pacts with Libyan coast guard units linked to abuses, providing vessels and training that enable interdictions returning migrants to detention centers.[185] [192] [179] As of mid-2025, these dynamics have entrenched divisions, with no unified foreign policy emerging despite sporadic de-escalations in Tripoli.[193]Military, Militias, and Security Apparatus
Following the 2011 overthrow of Muammar Gaddafi, Libya's centralized military structure dissolved amid unsecured stockpiles of weapons, leading to widespread proliferation that armed revolutionary groups and subsequent militias.[194] These non-state actors filled the security vacuum, controlling territories, ports, oil facilities, and even state institutions, often integrating into formal apparatuses while retaining operational independence and engaging in extortion, smuggling, and human trafficking.[195] By 2025, no unified national army exists; instead, forces align with rival governments—the UN-recognized Government of National Unity (GNU) in Tripoli and the Libyan National Army (LNA) in the east and south—exacerbated by militia infighting and foreign proxies.[196] The LNA, commanded by General Khalifa Haftar since 2014, functions as the primary military force in eastern and southern Libya, comprising regular units, tribal militias, Salafist factions, and foreign mercenaries including Sudanese and Chadian fighters alongside Russian Wagner Group (now Africa Corps) personnel.[197] It draws from Gaddafi-era stockpiles, including over 1,000 T-54/55 tanks, hundreds of T-62s and T-72s, artillery systems, and aircraft like MiG-23s, supplemented by recent acquisitions such as Russian BM-30 Smerch rocket launchers, Tor-M2 air defenses, and Mi-26 helicopters displayed in 2025 exercises.[198] The LNA's advances, such as capturing oil crescent facilities in 2019, rely on UAE-supplied drones and Egyptian logistical support, enabling control over key economic assets despite UN arms embargoes.[88] In western Libya, the GNU oversees a loose coalition of militias formalized as security bodies, including the 444th Infantry Brigade, the Special Deterrence Force (RADA), and the Stability Support Apparatus (SSA), which handle internal policing, detentions, and border control but frequently clash over influence and resources.[107] These groups, backed by Turkish military aid including Bayraktar drones and troop deployments since 2020, defend Tripoli against LNA incursions and manage urban security, yet their autonomy fosters cycles of violence, as seen in May 2025 clashes between the 444th Brigade and SSA that killed dozens and displaced civilians.[199] GNU Prime Minister Abdul Hamid Dbeibah has described militia elimination as an "ongoing project," but integration efforts reward abusive actors with salaries and legitimacy, perpetuating impunity.[200][201] Foreign interventions sustain this apparatus: Russia's Africa Corps provides LNA training and air support from bases like Al-Jufra, countering Turkish bases in Misrata that bolster GNU-aligned forces, while UAE and Egyptian aid to Haftar offsets Qatari and Turkish influence in the west.[202][104] These proxies enforce a fragile 2020 ceasefire but deepen divisions, with 2025 militia buildups in Tripoli signaling risks of renewed escalation absent unified command.[167] Tribal militias, such as those from Zintan or Tebu groups, further complicate control, leveraging local loyalties for leverage in oil revenue sharing and smuggling routes.[203] Overall, the security landscape prioritizes factional power over national defense, hindering disarmament and professionalization efforts.[204]Human Rights: Historical and Contemporary Issues
Under Muammar Gaddafi's rule from 1969 to 2011, Libya's government systematically repressed political opposition through arbitrary arrests, torture, and extrajudicial killings, affecting thousands of citizens suspected of dissent.[205] Security forces routinely suppressed protests, such as student demonstrations in the 1970s, with mass executions and disappearances; for instance, in 1976, over 100 prisoners were publicly hanged in Tripoli and other cities for alleged opposition activities.[205] The regime also targeted ethnic groups, including forced relocations and abuses during the Chadian border conflict in the 1980s, where Libyan forces committed documented killings and rapes.[205] A pivotal event was the Abu Salim prison massacre on June 29, 1996, when guards in Tripoli's Abu Salim facility opened fire on approximately 1,700 prisoners during a riot sparked by demands for better conditions and family visits, killing an estimated 1,270 inmates over several hours through shootings, beatings, and denial of medical care.[206] Families received no official information for years, fueling widespread grief and contributing to unrest that culminated in the 2011 uprising; as of 2024, accountability remains elusive despite protests by victims' relatives.[207] Following Gaddafi's overthrow in 2011, Libya's descent into civil conflict fragmented authority among militias, enabling unchecked abuses including war crimes such as the ethnic cleansing of Tawergha town by Misrata-based militias, displacing over 30,000 dark-skinned residents in August 2011 amid killings, rapes, and arson.[208] Armed groups on all sides committed torture, arbitrary detentions, and summary executions during the 2014-2020 war, with Human Rights Watch documenting over 100 cases of militias executing Gaddafi loyalists in 2011 alone.[209] Contemporary violations persist amid political division between the Government of National Unity and Libyan National Army factions, with militias controlling detention centers where torture—including beatings, electric shocks, and sexual violence—is rampant, leading to dozens of custody deaths in 2024 alone from ill-treatment and neglect.[210] Migrants and refugees face acute risks, exemplified by open-air slave auctions in 2017 where sub-Saharan African men were sold for $400 each in Tripoli, as verified by CNN footage and prompting UN Security Council condemnation; such practices continue in unofficial markets tied to smuggling networks.[211][212] In 2024-2025, UN reports noted over 700,000 migrants detained in facilities with forced labor and extortion, while Libyan activists endure enforced disappearances and targeted killings for criticizing abuses.[213] Impunity endures as militias integrate into state structures without prosecution, exacerbating a cycle where post-2011 instability has sustained repression without Gaddafi's centralized control.[214]Economy
Resource Base: Oil and Natural Gas
Libya holds Africa's largest proven crude oil reserves, totaling 48 billion barrels as of early 2024, which represent 41% of the continent's reserves and about 3% of the global total.[215] These reserves are predominantly light, sweet crude with low sulfur content, concentrated in the Sirte Basin in the north-central region, which accounts for over 80% of the country's output, supplemented by smaller contributions from the Murzuq, Ghadames, and Tripolitania offshore basins.[215] Key fields include Sharara (the largest, with capacity exceeding 300,000 barrels per day), El Feel, Bouri (offshore), Waha, and Sirte.[215] Proven natural gas reserves stood at 53 trillion cubic feet in early 2024, ranking fifth in Africa behind Nigeria, Algeria, Egypt, and Angola, with significant associated gas from oil fields and non-associated reserves in the offshore Greenstream area.[215] Commercial oil production began in 1961 following the 1959 discovery at the Zelten field in the Sirte Basin, initially developed by foreign concessions under Esso (now ExxonMobil) and others.[215] The National Oil Corporation (NOC), founded in 1970 as a state entity, progressively nationalized foreign assets through the 1970s, gaining majority stakes by 1973 and full control by the early 1980s, thereby centralizing upstream and downstream operations under government oversight.[216] Production peaked at 1.75 million barrels per day in 2008 after sanctions were lifted in 2003, enabling foreign investment recovery, but civil unrest from 2011 onward caused repeated shutdowns, dropping output to near zero at times and averaging below 500,000 barrels per day through much of the 2010s.[217] As of late 2024 into 2025, oil production has stabilized around 1.2 to 1.4 million barrels per day, with January 2025 output at 1.277 million barrels per day amid efforts to reach 1.6 million by year-end, though militia blockades and political rivalries—such as those between the Tripoli-based Government of National Unity and eastern forces—continue to enforce force majeure declarations and halt fields like Sharara intermittently.[217][218] Natural gas production reached 67,730 terajoules in 2023, primarily for domestic power generation and reinjection to maintain oil field pressures, with exports via the Greenstream pipeline to Italy averaging about 8 billion cubic meters annually before disruptions; however, output has declined since 2020 due to underinvestment and conflict-related maintenance issues.[219] The NOC maintains joint ventures with international firms like Eni, TotalEnergies, and Repsol for exploration and enhanced recovery, but chronic instability has limited new drilling, leaving potential reserves—estimated at up to 18 billion barrels in unexplored blocks—untapped.[215] Oil and gas revenues constitute over 90% of export earnings and government income, underscoring the sector's dominance despite representing less than 1% of global supply.[215]| Year | Average Oil Production (million bpd) | Key Events |
|---|---|---|
| 2008 | 1.75 | Pre-Arab Spring peak post-sanctions lift[217] |
| 2011 | ~0.5 (sharp drop) | Civil war onset, field shutdowns[215] |
| 2020 | ~0.3 | COVID-19 and blockades[217] |
| 2024 | ~1.2 | Recovery with fluctuations[215] |
| 2025 (Jan) | 1.28 | Aiming for 1.6 by year-end[217][218] |