Recent from talks
Nothing was collected or created yet.
Himalayas
View on Wikipedia
The Himalayas, or Himalaya (/ˌhɪməˈleɪ.ə, hɪˈmɑːləjə/ HIM-ə-LAY-ə, hih-MAH-lə-yə)[b], is a mountain range in Asia, separating the plains of the Indian subcontinent from the Tibetan Plateau. The range has some of the Earth's highest peaks, including the highest, Mount Everest. More than 100 peaks exceeding elevations of 7,200 m (23,600 ft) above sea level lie in the Himalayas.
Key Information
The Himalayas abut on or cross territories of six countries: Nepal, India, China, Bhutan, Pakistan and Afghanistan. The sovereignty of the range in the Kashmir region is disputed among India, Pakistan, and China.[4] The Himalayan range is bordered on the northwest by the Karakoram and Hindu Kush ranges, on the north by the Tibetan Plateau, and on the south by the Indo-Gangetic Plain. Some of the world's major rivers, the Indus, the Ganges, and the Tsangpo–Brahmaputra, rise in the vicinity of the Himalayas, and their combined drainage basin is home to some 600 million people; 53 million people live in the Himalayas.[5] The Himalayas have profoundly shaped the cultures of South Asia and Tibet. Many Himalayan peaks are sacred in Hinduism and Buddhism. The summits of several—Kangchenjunga (from the Indian side), Gangkhar Puensum, Machapuchare, Nanda Devi, and Kailash in the Tibetan Transhimalaya—are off-limits to climbers.
The Himalayas were uplifted after the collision of the Indian tectonic plate with the Eurasian plate, specifically, by the folding, or nappe-formation of the uppermost Indian crust, even as a lower layer continued to push on into Tibet and add thickness to its plateau; the still lower crust, along with the mantle, however, subducted under Eurasia. The Himalayan mountain range runs west-northwest to east-southeast in an arc 2,400 km (1,500 mi) long.[6] Its western anchor, Nanga Parbat, lies just south of the northernmost bend of the Indus river. Its eastern anchor, Namcha Barwa, lies immediately west of the great bend of the Yarlung Tsangpo River. The Indus-Yarlung suture zone, along which the headwaters of these two rivers flow, separates the Himalayas from the Tibetan plateau; the rivers also separate the Himalayas from the Karakorams, the Hindu Kush, and the Transhimalaya. The range varies in width from 350 km (220 mi) in the west to 151 km (94 mi) in the east.[7]
Etymology
[edit]The name of the range hails from the Sanskrit Himālaya (हिमालय 'abode of snow'[8]), from hima (हिम 'frost/cold'[9]) and ālaya (आलय 'dwelling/house'[10]).[11][12] They are now known as "the Himalaya Mountains", usually shortened to "the Himalayas".
The mountains are known as the Himālaya in Nepali and Hindi (both written हिमालय), Hinvāl (हिंवाळ) in Garhwali, Himāl (हिमाल) in Kumaoni, the Himalaya (ཧི་མ་ལ་ཡ་) or 'The Land of Snow' (གངས་ཅན་ལྗོངས་) in Tibetan, also known as Himālaya in Sinhala (written as හිමාලය), the Himāliya Mountain Range (سلسلہ کوہ ہمالیہ) in Urdu, the Himaloẏ Porbōtmala (হিমালয় পর্বতমালা) in Bengali, and the Ximalaya Mountain Range (simplified Chinese: 喜马拉雅山脉; traditional Chinese: 喜馬拉雅山脉; pinyin: Xǐmǎlāyǎ Shānmài) in Chinese.
The name of the range is sometimes also given as Himavan in older writings, including the Sanskrit epic Mahabharata.[13] Himavat (Sanskrit: हिमवत्) or Himavan Himavān (Sanskrit: हिमवान्) is a Hindu deity who is the personification of the Himalayan Mountain Range. Other epithets include Himaraja (Sanskrit: हिमराज, lit. 'king of snow') or Parvateshwara (Sanskrit: पर्वतेश्वर, lit. 'lord of mountains').
In western literature, some writers refer to it as the Himalaya [14]. This was also previously transcribed as Himmaleh, as in Emily Dickinson's poetry[15] and Henry David Thoreau's essays.[16]
Geography and key features
[edit]



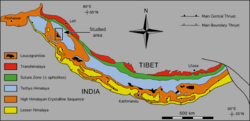
The Himalayas consists of four parallel mountain ranges from south to north: the Sivalik Hills on the south; the Lower Himalayan Range; the Great Himalayas, which is the highest and central range; and the Tibetan Himalayas on the north.[17] The Karakoram are generally considered separate from the Himalayas.
In the middle of the great curve of the Himalayan mountains lie the 8,000 m (26,000 ft) peaks of Dhaulagiri and Annapurna in Nepal, separated by the Kali Gandaki Gorge. The gorge splits the Himalayas into Western and Eastern sections, both ecologically and orographically – the pass at the head of the Kali Gandaki, the Kora La, is the lowest point on the ridgeline between Everest and K2 (the highest peak of the Karakoram range). To the east of Annapurna are the 8,000 m (5.0 miles) peaks of Manaslu and across the border in Tibet, Shishapangma. To the south of these lies Kathmandu, the capital of Nepal and the largest city in the Himalayas. East of the Kathmandu Valley lies the valley of the Bhote/Sun Kosi river which rises in Tibet and provides the main overland route between Nepal and China – the Araniko Highway/China National Highway 318. Further east is the Mahalangur Himal with four of the world's six highest mountains, including the highest: Cho Oyu, Everest, Lhotse, and Makalu. The Khumbu region, popular for trekking, is found here on the south-western approaches to Everest. The Arun river drains the northern slopes of these mountains, before turning south and flowing to the range to the east of Makalu.
In the far east of Nepal, the Himalayas rise to the Kangchenjunga massif on the border with India, the third-highest mountain in the world, the most easterly 8,000 m (26,000 ft) summit and the highest point of India. The eastern side of Kangchenjunga is in the Indian state of Sikkim. Formerly an independent Kingdom, it lies on the main route from India to Lhasa, Tibet, which passes over the Nathu La pass into Tibet. East of Sikkim lies the ancient Buddhist Kingdom of Bhutan. The highest mountain in Bhutan is Gangkhar Puensum, which is also a strong candidate for the highest unclimbed mountain in the world. The Himalayas here are becoming increasingly rugged, with heavily forested steep valleys. The Himalayas continue, turning slightly northeast, through the Indian State of Arunachal Pradesh as well as Tibet, before reaching their easterly conclusion in the peak of Namche Barwa, situated in Tibet, inside the great bend of the Yarlang Tsangpo river. On the other side of the Tsangpo, to the east, are the Kangri Garpo mountains. The high mountains to the north of the Tsangpo, including Gyala Peri, however, are also sometimes included in the Himalayas.
Going west from Dhaulagiri, Western Nepal is somewhat remote and lacks major high mountains, but is home to Rara Lake, the largest lake in Nepal. The Karnali River rises in Tibet but cuts through the centre of the region. Further west, the border with India follows the Sarda River and provides a trade route into China, where on the Tibetan plateau lies the high peak of Gurla Mandhata. Just across Lake Manasarovar from this lies the sacred Mount Kailash in the Kailash Ranges, which stands close to the source of the four main rivers of Himalayas and is revered in Hinduism, Jainism, Buddhism, Sufism and Bonpo. In Uttarakhand, the Himalayas are regionally divided into the Kumaon and Garhwal Himalayas with the high peaks of Nanda Devi and Kamet.[18] The state is also home to the important pilgrimage destinations of Chota Chaar Dhaam, with Gangotri, the source of the holy river Ganges, Yamunotri, the source of the river Yamuna, and the temples at Badrinath and Kedarnath.
The next Himalayan Indian state, Himachal Pradesh, is noted for its hill stations, particularly Shimla, the summer capital of the British Raj, and Dharamsala, the centre of the Tibetan community and government in exile in India. This area marks the start of the Punjab Himalaya and the Sutlej river, the most easterly of the five tributaries of the Indus, cuts through the range here. Further west, the Himalayas form much of the disputed Indian-administered union territory of Jammu and Kashmir where lie the mountainous Jammu region and the renowned Kashmir Valley with the town and lakes of Srinagar. The Himalayas form most of the south-west portion of the disputed Indian-administered union territory of Ladakh. The twin peaks of Nun Kun are the only mountains over 7,000 m (4.3 miles) in this part of the Himalayas. Finally, the Himalayas reach their western end in the dramatic 8000 m peak of Nanga Parbat, which rises over 8,000 m (26,000 ft) above the Indus valley and is the most westerly of the 8000 m summits. The western end terminates at a magnificent point near Nanga Parbat where the Himalayas intersect with the Karakoram and Hindu Kush ranges, in the disputed Pakistani-administered territory of Gilgit-Baltistan. Some portion of the Himalayas, such as the Kaghan Valley, Margalla Hills, and Galyat tract, extend into the Pakistani provinces of Khyber Pakhtunkhwa and Punjab.
Geology
[edit]



Tectonics, the recurring physical changes that affect the arrangement of the Earth's crust, and plate tectonics, the movement of large regions of the Earth's crust in the manner of planar rigid bodies, are key to understanding the formation of the Himalayas.[19] The Earth's crust rests directly on its mantle. Tectonic plates, comprising the crust and the upper portions of their underlying mantle, are moved around by convection in the asthenosphere. The oceanic crust, found beneath oceans, is, on average, 7 km (4.3 mi) thick. It is created from upwelling magma at mid-ocean ridges and predominantly consists of basalt, the principal igneous rock on Earth. In contrast, the continental crust underlying dry land has an average thickness of 35 km (22 mi) and is rich in silica, which is less dense than basalt.[20] It makes the continental tectonic plates more buoyant than the oceanic.[19]
India's defining geologic processes, which began 70 million years ago, had involved India rifting, or splitting away, from Gondwana, and the Indian continental plate along with the Neo-Tethys oceanic plate above it jointly moving northward.[19] As these eventually reached the Eurasian plate, the less buoyant oceanic plate subducted, or slid under Eurasia and was carried into the deeper asthenosphere. In contrast, the Indian continental plate was obstructed because of its thickness and buoyancy. The lateral compression generated by the obstruction caused the plate to be sheared horizontally. Its lower crust and mantle slid under, but one layer of the upper crust piled up in sheets (called nappes) ahead of the subduction zone.[21] Geophysicist Peter Molnar noted that most of the Himalayas are "slices of rock that once were the top part of India's crust."[22] This is the process of mountain building, or orogeny, in the Himalayas.
Before the orogeny, the Eurasian coastline had been similar to today's Central Andes.[23] Along such coastlines, the adjoining oceanic plate subducts and erupts as volcanoes. Magma, which eventually crystallizes into granite, rises into the Earth's crust below the active volcanoes but not to the surface.[23] When India's continental plate pushed against Eurasia, not only did a part of the upper crust fold in nappes, but another stiffer part began to push against (or drag) Eurasia's ancient volcanic mountains farther north.[23] As a result, the crust of this formerly coastal region shortened under compression and thickened to become what is today the Tibetan Plateau.[23] Isostatic equilibrium, or the balance between the gravitational force pulling down on the crust and the force of buoyancy pushing up from the mantle, gives the Tibetan Plateau its notable thickness and altitude.[23]
The Indian plate was not the only landmass that had rifted from Gondwana and drifted northward toward Eurasia.[24] Before the India-Eurasia collision in Middle Paleocene (60 Mya) and subsequent Himalayan orogeny, two other landmasses, the Qiangtang terrane and Lhasa terrane,[d] had drifted up from Gondwana.[24] Qiangtang, a geological region in what is today northern Tibet, had done so in Late Triassic (237–201 Mya).[24] The Lhasa terrane collided with the southern boundary of the Qiangtang in the Early Cretaceous (145–100 Mya).[24] The collision caused the lithospheric mantle of the Lhasa terrane to thicken and shorten, forming a barrier that later prevented the Indian lithosphere from fully subducting under Tibet and leading to further thickening of the Tibetan plateau. The suture zones, or remains of the subduction zone and the terranes that are joined, are found in the Tibetan plateau.[24] The Qiantang and Lhasa terranes were part of the string of microcontinents Cimmeria, today constituting parts of Turkey, Iran, Pakistan, China, Myanmar, Thailand and Malaysia, which had rifted from Gondwana earlier, closing the Paleo-Tethys Ocean above them and opening the Neo-Tethys Ocean between them and Gondwana, eventually colliding with Eurasia, and creating the Cimmerian Orogeny.[26]
After the Lhasa terrane had adjoined Eurasia, an active continental margin opened along its southern flank, below which the Neo-Tethys oceanic plate had begun to subduct. Magmatic activity along this flank produced the Gangdese batholith in what is today the Tibetan trans-Himalaya. Another subduction zone opened to the west, in the ocean basin above the Kohistan-Ladakh island arc. This island arc—formed by one oceanic plate subducting beneath another, its magma rising and creating continental crust—drifted north, closed its ocean basin and collided with Eurasia.[27]
The collision of India with Eurasia closed the Neo-Tethys Ocean.[26] The suture zone (in this instance, the remnants of the Neo-Tethys subduction zone pinched between the two continental crusts), which marks India's welding to Eurasia, is called the Indus-Yarlung suture zone.[26] It lies north of the Himalayas. The headwaters of the Indus River and the Yarlung Tsangpo (later in its course, the Brahmaputra) flow along this suture zone.[26] These two Eurasian rivers, whose courses were continually diverted by the rising Himalayas, define the western and eastern limits, respectively, of the Himalayan mountain range.[26]
During the India-Eurasia collision, two elongated protrusions located on either side of the northern border of the Indian continent generated areas of extreme deformation. A point where mountain ranges with different directions of extension, and thus formed by tectonic forces at varying angles, converge is called a syntaxis (Greek: convergence).[24] The two syntaxes, Nanga Parbat and Namche Barwa, on the northwestern and northeastern corners of the Indian continent, respectively, are characterized by the quick upward movement of land or rocks that were once deeply buried and significantly altered by extreme heat and pressure.[24] Geologists have estimated the rate of uplift of these rocks to be 7 millimetres (0.28 in) per year, or 7 kilometres (4.3 mi) per million years.[24] The protruding regions have some of the highest mountain peaks at 8,125 metres (26,657 ft) and 7,756 metres (25,446 ft), respectively.[24] The regions also have the greatest topographical relief in the interior of a continent, approximately 7,000 metres (23,000 ft) over a horizontal distance of 20–30 kilometres (12–19 mi).[24] Nanga Parbat has a narrow, anticline, or arch-shaped fold whose crest dips sharply to the north, perpendicular to the general direction along which the Himalayas extend.[24] The Indus and Yarlung Tsangpo, which originally emptied into the New-Tethys, now bend around the Nanga Parbat and Namche Barwa, respectively, to eventually empty into the Indian Ocean.
Geologists Wolfgang Frisch, Martin Meschede, and Ronand Blakey write, "India rapidly marched northward towards Asia with a velocity of ca. 20 cm/yr, a plate velocity that exceeds any modern example. This velocity considerably slowed to ca. 5 cm/yr following the collision, yet India continued to protrude into Asia for more than 2000 km. ... The irregular northern margin of the Indian continental crust first came into contact with Eurasia along its northwestern corner, approximately 55 Ma. As a consequence, India underwent a counter-clockwise rotation to close the remaining part of the Neotethys in scissor-like fashion from west to east. The closure of the Neotethys was completed approximately 40 Ma."[24]
Today, the Indian plate continues to be driven horizontally at the Tibetan Plateau, which forces the plateau to continue to move upwards.[28] The Indian plate is moving at 67 mm (2.6 in) per year, and over the next 10 million years, it will travel 1,500 km (930 mi) into Asia. Approximately 20 mm per year of the India–Asia convergence is absorbed by thrusting along the Himalaya southern front. This leads to the Himalayas rising by about 5 mm annually, making them geologically active. The movement of the Indian plate into the Asian plate also makes this region seismically active, leading to earthquakes from time to time.[29]
The Himalayan mountain range consists of three sub-ranges: (1) the Higher- or "Tethys" Himalayas, (2) the Lesser Himalayas, and (3) the Siwaliks. The nappes—large, stacked sheets of rock—found in the Tethys Himalayan mountain range, are primarily composed of sedimentary rocks, such as limestone formed from the accumulation and compression of sediments like sand, mud, and shells deposited in the Neo-Tethys seabed during the Paleogene" (66 Mya–23 Mya).[24] Below the sedimentary rocks in the Higher and Lesser Himalayas is a bottom layer, or basement, composed of metamorphic rock formed much earlier during the Pan-African-Cadomian orogeny between 650 Mya and 550 Mya.[24] The lowest subrange, the Siwaliks, represents the sedimentary rock deposits washed off the rising Himalayas in a foreland basin, a low-lying crustal region, at their foot.[24] It primarily consists of sandstones, shales, and conglomerates formed during the Neogene period (23 Mya to 2.6 Mya).
Geologists Wolfgang Frisch, Martin Meschede, and Ronand Blakey further write, "The Siwaliks are both underlain and overlain by thrusts; they have been overridden by the nappe stack of the Higher and Lesser Himalayas and, in turn, are thrust over more interior parts of the Indian continent. Each of the three mega-units is internally imbricated into several individual nappes. Fensters (windows) and klippen provide important structural information regarding the thrust belts and help document the existence of broad thrust sheets, some of which record thrust distances in excess of 100 km. A fenster or window is an erosional hole through a thrust sheet that exposes a tectonically lower unit framed by a higher unit; a klippe is detached by erosion and forms a remnant of a nappe or higher thrust sheet that rests on top of a lower unit."[27]
Hydrology
[edit]Despite their scale, the Himalayas do not form a major continental divide, and a number of rivers cut through the range, particularly in the eastern part of the range. As a result, the main ridge of the Himalayas is not clearly defined, and mountain passes are not as significant for traversing the range as with other mountain ranges. Himalayas' rivers drain into two large systems:[30]
- The western rivers combine into the Indus Basin. The Indus itself forms the northern and western boundaries of the Himalayas. It begins in Tibet, at the confluence of Sengge and Gar rivers, and flows north-west through India into Pakistan before turning south-west to the Arabian Sea. It is fed by several major tributaries draining the southern slopes of the Himalayas, including the Jhelum, Chenab, Ravi, Beas, and Sutlej rivers, the five rivers of the Punjab.
- The other Himalayan rivers drain the Ganges-Brahmaputra Basin. Its main rivers are the Ganges, the Brahmaputra, and the Yamuna, as well as other tributaries. The Brahmaputra originates as the Yarlung Tsangpo River in western Tibet, and flows east through Tibet and west through the plains of Assam. The Ganges and the Brahmaputra meet in Bangladesh and drain into the Bay of Bengal through the world's largest river delta, the Sunderbans.[31]
The northern slopes of Gyala Peri and the peaks beyond the Tsangpo, sometimes included in the Himalayas, drain into the Irrawaddy River, which originates in eastern Tibet and flows south through Myanmar to drain into the Andaman Sea. The Salween, Mekong, Yangtze, and Yellow River all originate from parts of the Tibetan Plateau that are geologically distinct from the Himalaya mountains and are therefore not considered true Himalayan rivers. Some geologists refer to all the rivers collectively as the circum-Himalayan rivers.[32]
Glaciers
[edit]
The great ranges of central Asia, including the Himalayas, contain the third-largest deposit of ice and snow in the world, after Antarctica and the Arctic.[33] Some even refer to this region as the "Third Pole".[34] The Himalayan range encompasses about 15,000 glaciers, which store about 12,000 km3 (2,900 cu mi), or 3600–4400 Gt (1012 kg)[34] of fresh water.[35] Its glaciers include the Gangotri and Yamunotri (Uttarakhand) and Khumbu glaciers (Mount Everest region), Langtang glacier (Langtang region), and Zemu (Sikkim).
Owing to the mountains' latitude near the Tropic of Cancer, the permanent snow line is among the highest in the world, at typically around 5,500 m (18,000 ft).[36] In contrast, equatorial mountains in New Guinea, the Rwenzoris, and Colombia have a snow line some 900 m (2,950 ft) lower.[37] The higher regions of the Himalayas are snowbound throughout the year, in spite of their proximity to the tropics, and they form the sources of several large perennial rivers.
In recent years, scientists have monitored a notable increase in the rate of glacier retreat across the region as a result of climate change.[38][39] For example, glacial lakes have been forming rapidly on the surface of debris-covered glaciers in the Bhutan Himalaya during the last few decades. Studies have measured an approximately 13% overall decrease in glacial coverage in the Himalayas over the last 40–50 years.[34] Local conditions play a large role in glacial retreat, however, and glacial loss can vary locally from a few m/yr to 61 m/yr.[34] A marked acceleration in glacial mass loss has also been observed since 1975, from about 5–13 Gt/yr to 16–24 Gt/yr.[34] Although the effect of this will not be known for many years, it potentially could mean disaster for the hundreds of millions of people who rely on the glaciers to feed the rivers during the dry seasons.[34][40][41][42] The global climate change will affect the water resources and livelihoods of the Greater Himalayan region.[43]
Lakes
[edit]
The Himalayan region is dotted with hundreds of lakes.[44] Pangong Tso, which is spread across the border between India and China, at the far western end of Tibet, is among the largest with a surface area of 700 km2 (270 sq mi).
South of the main range, the lakes are smaller. Tilicho Lake in Nepal, in the Annapurna massif, is one of the highest lakes in the world. Other lakes include Rara Lake in western Nepal, She-Phoksundo Lake in the Shey Phoksundo National Park of Nepal, Gurudongmar Lake, in North Sikkim, Gokyo Lakes in Solukhumbu district of Nepal, and Lake Tsongmo, near the Indo-China border in Sikkim.[44]
Some of the lakes present the danger of a glacial lake outburst flood. The Tsho Rolpa glacier lake in the Rowaling Valley, in the Dolakha District of Nepal, is rated as the most dangerous. The lake, which is located at an altitude of 4,580 m (15,030 ft), has grown considerably over the last 50 years due to glacial melting.[45][46] The mountain lakes are known to geographers as tarns if they are caused by glacial activity. Tarns are found mostly in the upper reaches of the Himalaya, above 5,500 m (18,000 ft).[47]
Temperate Himalayan wetlands provide important habitat and layover sites for migratory birds. Many mid and low altitude lakes remain poorly studied in terms of their hydrology and biodiversity, like Khecheopalri in the Sikkim Eastern Himalayas.[48]
Climate
[edit]Temperature
[edit]The physical factors determining the climate in any location in the Himalayas include latitude, altitude, and the relative motion of the Southwest monsoon.[49] From north to south, the mountains cover more than eight degrees of latitude, spanning temperate to subtropical zones.[49] The colder air of Central Asia is prevented from blowing down into South Asia by the physical configuration of the Himalayas.[49] This causes the tropical zone to extend farther north in South Asia than anywhere else in the world.[49] The evidence is unmistakable in the Brahmaputra valley as the warm air from the Bay of Bengal bottlenecks and rushes up past Namcha Barwa, the eastern anchor of the Himalayas, and into southeastern Tibet.[49] Temperatures in the Himalayas cool by 2.0 degrees C (3.6 degrees F) for every 300 metres (980 ft) increase of altitude.[49]

As the physical features of mountains are irregular, with broken jagged contours, there can be wide variations in temperature over short distances.[50] Temperature at a location on a mountain depends on the season of the year, the bearing of the sun with respect to the face on which the location lies, and the mass of the mountain, i.e. the amount of matter in the mountain.[50] As the temperature is directly proportional to received radiation from the sun, the faces that receive more direct sunlight also have a greater heat buildup.[50] In narrow valleys—lying between steep mountain faces—there can be dramatically different weather along their two margins.[50] The side to the north with a mountain above facing south can have an extra month of the growing season.[50] The mass of the mountain also influences the temperature, as it acts as a heat island, in which more heat is absorbed and retained than the surroundings, and therefore influences the heat budget or the amount of heat needed to raise the temperature from the winter minimum to the summer maximum.[50]
The immense scale of the Himalayas means that many summits can create their own weather, the temperature fluctuating from one summit to another, from one face to another, and all may be quite different from the weather in nearby plateaus or valleys.[50]
Precipitation
[edit]The Himalayan hydroclimate is crucial for South Asia, where annual summer monsoon floods impact millions.[51]
A critical influence on the Himalayan climate is the Southwest Monsoon. Variability in monsoon rainfall, influenced by local Hadley circulation and tropical sea surface temperatures, is the main factor behind wet and dry years.[52] This is not so much the rain of the summer months as the wind that carries the rain.[50] Different rates of heating and cooling between the Central Asian continent and the Indian Ocean create large differences in the atmospheric pressure prevailing above each.[50] In the winter, a high-pressure system forms and remains suspended above Central Asia, forcing air to flow in the southerly direction over the Himalayas.[50] But in Central Asia, as there is no substantial source for water to be diffused as vapour, the winter winds blowing across South Asia are dry.[50] In the summer months, the Central Asian plateau heats up more than the ocean waters to its south. As a result, the air above it rises higher and higher, creating a thermal low.[50] Off-shore high-pressure systems in the Indian Ocean push the moist summer air inland toward the low-pressure system. When the moist air meets mountains, it rises and upon subsequent cooling, its moisture condenses and is released as rain, typically heavy rain.[50] The wet summer monsoon winds cause precipitation in India and all along the layered southern slopes of the Himalayas. This forced lifting of air is called the orographic effect.[50]

Winds
[edit]The vast size, huge altitude range, and complex topography of the Himalayas mean they experience a wide range of climates, from humid subtropical in the foothills, to cold and dry desert conditions on the Tibetan side of the range. For much of the Himalayas—in the areas to the south of the high mountains, the monsoon is the most characteristic feature of the climate and causes most of the precipitation, while the western disturbance brings winter precipitation, especially in the west. Heavy rain arrives on the southwest monsoon in June and persists until September. The monsoon can seriously impact transport and cause major landslides. It restricts tourism – the trekking and mountaineering season is limited to either before the monsoon in April/May or after the monsoon in October/November (autumn). In Nepal and Sikkim, there are often considered to be five seasons: summer, monsoon, autumn, (or post-monsoon), winter, and spring.[53]
Using the Köppen climate classification, the lower elevations of the Himalayas, reaching in mid-elevations in central Nepal (including the Kathmandu valley), are classified as Cwa, Humid subtropical climate with dry winters. Higher up, most of the Himalayas have a subtropical highland climate (Cwb).[citation needed]
The intensity of the southwest monsoon diminishes as it moves westward along the range, with as much as 2,030 mm (80 in) of rainfall in the monsoon season in Darjeeling in the east, compared to only 975 mm (38.4 in) during the same period in Shimla in the west.[54][55]
The northern side of the Himalayas, also known as the Tibetan Himalaya, is dry, cold, and generally windswept, particularly in the west where it has a cold desert climate. The vegetation is sparse and stunted and the winters are severely cold. Most of the precipitation in the region is in the form of snow during the late winter and spring months.
Local impacts on climate are significant throughout the Himalayas. Temperatures fall by 0.2 to 1.2 °C for every 100 m (330 ft) rise in altitude.[56] This gives rise to a variety of climates, from a nearly tropical climate in the foothills, to tundra and permanent snow and ice at higher elevations. Local climate is also affected by the topography: The leeward side of the mountains receive less rain while the well-exposed slopes get heavy rainfall and the rain shadow of large mountains can be significant, for example, leading to near desert conditions in the Upper Mustang, which is sheltered from the monsoon rains by the Annapurna and Dhaulagiri massifs and has annual precipitation of around 300 mm (12 in), while Pokhara on the southern side of the massifs has substantial rainfall (3,900 mm or 150 in a year). Thus, although annual precipitation is generally higher in the east than in the west, local variations are often more important.[citation needed]
The Himalayas have a profound effect on the climate of the Indian subcontinent and the Tibetan Plateau. They prevent frigid, dry winds from blowing south into the subcontinent, which keeps South Asia much warmer than corresponding temperate regions in the other continents. It also forms a barrier for the monsoon winds, keeping them from traveling northwards, and causing heavy rainfall in the Terai region. The rain shadowing of Himalayas are also believed to play an important part in the formation of Central Asian deserts, such as the Taklamakan and Gobi.[57]
Ecology
[edit]The flora and fauna of the Himalayas vary with climate, rainfall, altitude, and soils. The climate ranges from tropical at the base of the mountains to permanent ice and snow at the highest elevations. The amount of yearly rainfall increases from west to east along the southern front of the range. This diversity of altitude, rainfall, and soil conditions, combined with the very high snow line, supports a variety of distinct plant and animal communities.[44] The extremes of high altitude (low atmospheric pressure), combined with extreme cold, favor extremophile organisms.[58][48]

At high altitudes, the elusive and previously endangered snow leopard is the main predator. Its prey includes members of the goat family grazing on the alpine pastures and living on the rocky terrain, notably the endemic bharal or Himalayan blue sheep. The Himalayan musk deer is also found at high altitudes. Hunted for its musk, it is now rare and endangered. Other endemic or near-endemic herbivores include the Himalayan tahr, the takin, the Himalayan serow, and the Himalayan goral. The critically endangered Himalayan subspecies of the brown bear is found sporadically across the range, as is the Asian black bear. In the mountainous mixed deciduous and conifer forests of the eastern Himalayas, red pandas feed in the dense understories of bamboo. Lower down, the forests of the foothills are inhabited by several different primates, including the endangered Gee's golden langur and the Kashmir gray langur, with highly restricted ranges in the east and west of the Himalayas, respectively.[48]
The unique floral and faunal wealth of the Himalayas is undergoing structural and compositional changes due to climate change. Hydrangea hirta is an example of floral species that can be found in this area. The increase in temperature is shifting various species to higher elevations. The oak forest is being invaded by pine forests in the Garhwal Himalayan region. There are reports of early flowering and fruiting in some tree species, especially rhododendron, apple, and box myrtle. The highest known tree species in the Himalayas is Juniperus tibetica, located at 4,900 m (16,080 ft) in Southeastern Tibet.[59]
Climate-related concerns
[edit]This section may lend undue weight to certain ideas, incidents, or controversies. (February 2025) |
This article may not provide balanced coverage on a geographical region. (February 2025) |
Similar to the mountains, the communities living near the Himalayas are experiencing climate change and its negative impacts significantly more than other parts of the world.[60] Some of the impacts that the communities are facing include erratic rainfall, flooding, rising temperatures, and landslides.[60] These impacts can have extreme negative effects on the villages living in the area especially as the temperatures rise at higher rates than many other places in the world (Alexander et al., 2014). There are more than 1.9 million people who are highly vulnerable due to climate change with an additional 10 million people at risk in Nepal.[60] Nepal is among the top ten most vulnerable Global South countries due to climate change in the world, standing at number 4 as of 2010 according to the climate change risk atlas.[61][62] According to NAPA (National Adaptation Program of Action) of Nepal, many threats including floods, droughts, and landslides are an imminent threat to the glacial lake area.[63] With this in consideration, climate change policy and framework for LAPA (Local Adaptation Plans of Action) were prepared in 2011 primarily focusing on addressing climatic hazards.[63]
Health impacts
[edit]
Local communities are suffering from food scarcity and malnutrition as well as an increasing risk to diseases such as malaria and dengue fever as temperatures rise and allow these diseases to migrate further north.[64] There is also an increasing risk of water borne illnesses accompanied by an increasing lack of safe drinking water.[64] Illness is not the only danger to the communities as temperatures sky rocket. With the climate changing weather patterns are also changing and more extreme weather events are occurring putting local communities more at risk to physical harm and death during erratic weather events.[65] Marginalized groups including children and women are experiencing more severe impacts from climate change and are often more exposed to disease and injury.[64] Over the last couple years these health impacts have gotten increasingly worse and more common. Recent studies have shown that dengue fever has had a consistent pattern of epidemic in Nepal in the years 2010, 2013, 2016, 2017, 2019, 2022 with the largest in terms of severity occurring in 2022.[66] 54,784 reported cases were recorded from all 77 districts in seven provinces.[66] These diseases are simply in addition to other diseases that can be seen with the rise of global temperatures and air pollution. Many vulnerable groups are experiencing an increase in respiratory illness, cardiac illnesses, and asthma.[67] The heat can lead to issues such as a strain on respiratory illnesses, heat stroke, and fever.[67] There is also the increased risk of cancer.[67] Many lower income communities such as the himalayan villages suffer from exposure to more pollution or in some cases exposure to toxic chemicals which has led to an increased rate of cancer in these communities as well as an increased risk of death.[67]
Agricultural impacts
[edit]
The increasing temperatures are also leading to a decrease in territory for local wildlife. This trend has decreased the prey populations of at-risk predators, such as snow leopards. Seeking alternative food sources, snow leopards and other predators attack local farmers' livestock. This livestock consists of yaks, oxen, horses, and goats.[68] Snow leopards have killed about 2.6% of the local livestock per year in response to their shrinking habitat.[68] The overall loss, about a quarter of the average income of local farmers, has had a major impact on the local economy.[68] In retaliation, farmers have begun killing snow leopards, seeking to protect their livestock and their livelihoods.[68]
Policy changes
[edit]Nepal is a part of the Paris agreement and thus is required to have a climate action plan and is being tracked by the Climate Action Tracker.[69] According to the Climate Action Tracker, Nepal is "almost sufficient" on its track to reach the goals set by the Paris Agreement.[69] There are two factors that hold Nepal back from reaching sufficient status and thus stand out.[69] There is no Climate Finance Plan and emissions and temperature rising rate ranking at critically insufficient.[69] Nepal has many goals, however, that are on track with the Paris Agreement.[69] The first of note being a goal of net-zero emissions by 2045.[69] To reach this goal Nepal submitted two separate plans to account for whatever future they experience the first being WAM (with additional measures) and the second being WEM (with existing measures).[69] WEM is based primarily on already existing policies and highlights the energy sector as the main target for CO2 reduction.[69] The WAM scenario introduces a far more ambitious strategy for reducing emissions.[69] In this scenario the focus is primarily on an intervention method and disruption of the energy sector reducing the use of fossil fuels and the incorporation of renewable energy sources. This pathway heavily relies on reducing emissions from energy sources while preserving the carbon-absorbing capacity of the LULUCF (Land Use, Land-Use Change and Forestry) sector.[69] Under this scenario, it is anticipated that net CO2 emissions will remain negative from 2020 to 2030, approach 'zero' between 2035 and 2045, and then revert to negative values by 2050.[69] The goal of this scenario is to accelerate the journey toward achieving carbon neutrality before 2045.[69] These policies along with many more have Nepal on track to stay beneath the 1.5 threshold set by the Paris Agreement.[69]
In May 2025 the representatives of himalayan nations, experts met in Nepal for the first "Sagarmatha Sambaad" (Everest Dialog) about stopping climate change and its effects on the region. Minister Deuba remarked "Climate change is a global crisis transcending national boundaries. Nothing less than a global alliance based on justice and solidarity can hope to make a dent on the existential crisis that climate change brings in its wake".[70] The United Nations leader send a message to the conference in which he reminded that glaciers giving water to rivers are metling in a fast and increasing rate and "reduced water flow in river systems such as the Ganges, Brahmaputra and Indus threatens not only water but also food production for nearly two billion people across South Asia".[71] The conference issued a "Sagarmatha Call for Action" to protect the region from climate change. One of the proposals is a common climate fund for Himalayan nations. Climate experts criticized the outcomes, saying that the real challenge is to implement the decisions. Also the conference only addressed the issue of glacier melt, while in recent times, climate migration due to lack of rainfall also became a major concern.[72]
Local adaptation
[edit]

In recent years many citizens of these Himalayan communities have started to notice the extreme effects of climate change by experiencing nature itself.[73] They have noticed a decrease in precipitation especially in lowland districts, fluctuating temperatures during months of the year that are typically cooler, and changes in weather patterns even compared to early 2000s weather.[73] Many local villagers have identified climate change simply through the availability of certain native plants decreasing or shifting seasons.[73] The concept of climate change has now been aligned with the risk of natural disasters and has increased awareness in the local communities.[73] These impacts of climate change have greatly affected agriculture in the area and has forced farmers to change crops and when they plant them.[73] In response to this rather than push for policy change, citizens have begun to adapt to climate change.[74] According to Dhungana, 91.94% of the respondents experienced drought as major climatic hazards then floods at 83.87%, landslides at 70.97%, and forest fires at 67.74%.[74] In response to this citizens have begun adapting and adopting new practices.[74] As a response to drought at the high altitudes, plantations are planting more protective trees, drought resistant plants, and have begun adopting irrigation practices drawing from nearby streams.[74] In response to flooding, farmers have created more basins, dam construction, and small drainage canals.[74]
The response to landslides includes plantation grasses in previously barren areas, Gabion wall construction, avoiding livestock grazing in landslide-prone areas, and a prohibition on tillage in areas at risk of landslides.[74] To fight the increased rate of forest fires, citizens have begun beating the fires with green branches and mud, construction of fire lines, and are raising awareness about the wildfires.[74] Fire lines are lines of varying width built through the leaf litter of a forest floor down to the soil and minerals to prevent a spread of fire past the line.[75] The main reason for these adaptations is to decrease the risk that climate change poses over these marginalized communities while taking advantage of the moment and allowing for a positive change towards a more sustainable or adaptable future.[74] Major barriers to these adaptations include a lack of funds, a lack of knowledge, a lack of technology, a lack of time, and lack of mandatory policy.[74]
Religions
[edit]There are many cultural and mythological aspects associated with the Himalayas. In Jainism, Mount Ashtapada of the Himalayan mountain range is a sacred place where the first Jain tirthankara, Rishabhanatha, attained moksha. It is believed that after Rishabhanatha attained nirvana, his son, Bharata, had constructed three stupas and twenty four shrines of the 24 tirthankaras with their idols studded with precious stones over there and named it Sinhnishdha.[76][77] For the Hindus, the Himalayas are personified as Himavat, the king of all mountains and the father of the goddess Parvati.[78] The Himalayas are also considered to be the father of the goddess Ganga (the personification of river Ganges).[79] Two of the most sacred places of pilgrimage for the Hindus are the temple complex in Pashupatinath and Muktinath, also known as Shaligrama because of the presence of the sacred black rocks called shaligrams.[80]
The Buddhists also lay a great deal of importance on the Himalayas. Paro Taktsang is the holy place where Buddhism started in Bhutan.[81] The Muktinath is also a place of pilgrimage for the Tibetan Buddhists. They believe that the trees in the poplar grove came from the walking sticks of eighty-four ancient Indian Buddhist magicians or mahasiddhas. They consider the saligrams to be representatives of the Tibetan serpent deity known as Gawo Jagpa.[82] The Himalayan people's diversity shows in many different ways. It shows through their architecture, their languages, and dialects, their beliefs and rituals, as well as their clothing.[82] The shapes and materials of the people's homes reflect their practical needs and beliefs. Another example of the diversity amongst the Himalayan peoples is that handwoven textiles display colors and patterns unique to their ethnic backgrounds. Finally, some people place great importance on jewelry. The Rai and Limbu women wear big gold earrings and nose rings to show their wealth through their jewelry.[82] Several places in the Himalayas are of religious significance in Buddhism, Jainism, Sikhism, Islam and Hinduism. A notable example of a religious site is Paro Taktsang, where Padmasambhava is said to have founded Buddhism in Bhutan.[83]
A number of Vajrayana Buddhist sites are situated in the Himalayas, in Tibet, Bhutan, and in the Indian regions of Ladakh, Sikkim, Arunachal Pradesh, Spiti, and Darjeeling. There were over 6,000 monasteries in Tibet, including the residence of the Dalai Lama.[84] Bhutan, Sikkim, and Ladakh are also dotted with numerous monasteries.[85]
Resources
[edit]The Himalayas are home to a diversity of medicinal resources. Plants from the forests have been used for millennia to treat conditions ranging from simple coughs to snake bites.[80] Different parts of the plants – root, flower, stem, leaves, and bark – are used as remedies for different ailments. For example, a bark extract from an Abies pindrow tree is used to treat coughs and bronchitis. Leaf and stem paste from an Andrachne cordifolia is used for wounds and as an antidote for snake bites. The bark of a Callicarpa arborea is used for skin ailments.[80] Nearly a fifth of the gymnosperms, angiosperms, and pteridophytes in the Himalayas are found to have medicinal properties, and more are likely to be discovered.[80]
Most of the population in some Asian and African countries depends on medicinal plants rather than prescriptions and such.[78] Since so many people use medicinal plants as their only source of healing in the Himalayas, the plants are an important source of income. This contributes to economic and modern industrial development both inside and outside the region.[78] The only problem is that locals are rapidly clearing the forests on the Himalayas for wood, often illegally.[86]
See also
[edit]Notes
[edit]- ^ Sovereignty over the range is contested in several places, most notably in the Kashmir region.[1][2]
- ^ Sanskrit: [ɦɪmaːlɐjɐ]; from Sanskrit himá 'snow, frost' and ā-laya 'dwelling, abode'),[3]
- ^ as seen from a plane approximately above the historic Sawal Dher village, in Khyber Pakhtunkhwa, Pakistan
- ^ Terrane: "A far traveled crustal block accreted to a continent. Due to its remote origin, the terrane shows a different geological evolution compared to adjacent parts of the continent."[25]
References
[edit]- ^ Himalayas (mountains, Asia). Encyclopaedia Britannica. 14 August 2023.
Though India, Nepal, and Bhutan have sovereignty over most of the Himalayas, Pakistan and China also occupy parts of them. In the Kashmir region, Pakistan has administrative control of some 32,400 square miles (83,900 square km) of the range lying north and west of the "line of control" established between India and Pakistan in 1972. China administers some 14,000 square miles (36,000 square km) in the Ladakh region and has claimed territory at the eastern end of the Himalayas within the Indian state of Arunachal Pradesh. Those disputes accentuate the boundary problems faced by India and its neighbours in the Himalayan region.
- ^ Zurick, David; Pocheco, Julsun (2006), Illustrated Atlas of the Himalaya, University Press of Kentucky, p. 8,11,12, ISBN 978-0-8131-7384-9
- ^ "Himalayan". Oxford English Dictionary (Online ed.). Oxford University Press. Retrieved 5 August 2021.
Etymology: < Himālaya (Sanskrit < hima snow + ālaya dwelling, abode) + -an suffix)
(Subscription or participating institution membership required.) - ^ Bishop, Barry. "Himalayas (mountains, Asia)". Encyclopaedia Britannica. Retrieved 30 July 2016.
- ^ A.P. Dimri; B. Bookhagen; M. Stoffel; T. Yasunari (8 November 2019). Himalayan Weather and Climate and their Impact on the Environment. Springer Nature. p. 380. ISBN 978-3-030-29684-1.
- ^ Wadia, D. N. (1931). "The syntaxis of the northwest Himalaya: its rocks, tectonics and orogeny". Record Geol. Survey of India. 65 (2): 189–220.
- ^ Apollo, M. (2017). "Chapter 9: The population of Himalayan regions – by the numbers: Past, present and future". In Efe, R.; Öztürk, M. (eds.). Contemporary Studies in Environment and Tourism. Cambridge Scholars Publishing. pp. 143–159.
- ^ "MW Cologne Scan". www.sanskrit-lexicon.uni-koeln.de. Retrieved 27 March 2022.
- ^ "MW Cologne Scan". www.sanskrit-lexicon.uni-koeln.de. Retrieved 27 March 2022.
- ^ "WIL Cologne Scan". www.sanskrit-lexicon.uni-koeln.de. Retrieved 27 March 2022.
- ^ "BEN Cologne Scan". www.sanskrit-lexicon.uni-koeln.de. Retrieved 27 March 2022.
- ^ "WIL Cologne Scan". www.sanskrit-lexicon.uni-koeln.de. Retrieved 27 March 2022.
- ^ Roshen Dalal (2014). Hinduism: An Alphabetical Guide. Penguin Books. ISBN 978-81-8475-277-9. Entry: "Himavan"
- ^ the Himalaya, Himalayatra, Feel the Soul of Himalaya
- ^ Dickinson, Emily, The Himmaleh was known to stoop.
- ^ Thoreau, Henry David (1849), A Week on the Concord and Merrimack Rivers.
- ^ Bishop, Barry C.; Chatterjee, Shiba P. (14 August 2023). Himalayas. Encyclopedia Britannica.
- ^ Pletcher, Kenneth (13 March 2009). "Kumaun Himalayas". Encyclopedia Britannica.
- ^ a b c Molnar 2015, p. 116.
- ^ Johnson & Harley 2012, p. 2.
- ^ Molnar 2015, p. 117.
- ^ Molnar 2015, p. 118.
- ^ a b c d e Molnar 2015, p. 128.
- ^ a b c d e f g h i j k l m n o Frisch, Meschede & Blakey 2011, p. 174.
- ^ Frisch, Meschede & Blakey 2011, p. 197.
- ^ a b c d e Frisch, Meschede & Blakey 2011, p. 172.
- ^ a b Frisch, Meschede & Blakey 2011, p. 173.
- ^ "Plate Tectonics -The Himalayas". The Geological Society. Retrieved 13 September 2016.
- ^ "Devastating earthquakes are priming the Himalaya for a mega-disaster". Science. 17 January 2019. Retrieved 28 March 2024.
- ^ "Himalayas - Rivers, Glaciers, Peaks | Britannica". www.britannica.com. Retrieved 28 March 2024.
- ^ "Sunderbans the world's largest delta". gits4u.com. Archived from the original on 3 January 2015. Retrieved 3 January 2015.
- ^ Gaillardet, J.; Métivier, F.; Lemarchand, D.; Dupré, B.; Allègre, C.J.; Li, W.; Zhao, J. (2003). "Geochemistry of the Suspended Sediments of Circum-Himalayan Rivers and Weathering Budgets over the Last 50 Myrs" (PDF). Geophysical Research Abstracts. 5: 13,617. Bibcode:2003EAEJA....13617G. Abstract 13617. Archived (PDF) from the original on 9 October 2022. Retrieved 4 November 2006.
- ^ "The Himalayas – Himalayas Facts". Nature on PBS. 11 February 2011. Retrieved 21 January 2014.
- ^ a b c d e f Kulkarni, Anil V.; Karyakarte, Yogesh (2014). "Observed changes in Himalayan Glaciers". Current Science. 106 (2): 237–244. JSTOR 24099804.
- ^ "the Himalayan Glaciers". Fourth assessment report on climate change. IPPC. 2007. Retrieved 22 January 2014.
- ^ Shi, Yafeng; Xie, Zizhu; Zheng, Benxing; Li, Qichun (1978). "Distribution, Feature and Variations of Glaciers in China" (PDF). World Glacier Inventory. Archived from the original (PDF) on 24 April 2013.
- ^ Henderson-Sellers, Ann; McGuffie, Kendal (2012). The Future of the World's Climate: A Modelling Perspective. Elsevier. pp. 199–201. ISBN 978-0-12-386917-3.
- ^ Lee, Ethan; Carrivick, Jonathan L.; Quincey, Duncan J.; Cook, Simon J.; James, William H. M.; Brown, Lee E. (20 December 2021). "Accelerated mass loss of Himalayan glaciers since the Little Ice Age". Scientific Reports. 11 (1): 24284. Bibcode:2021NatSR..1124284L. doi:10.1038/s41598-021-03805-8. ISSN 2045-2322. PMC 8688493. PMID 34931039.
- ^ "Vanishing Himalayan Glaciers Threaten a Billion". Reuters. 4 June 2007. Retrieved 13 March 2018.
- ^ Kaushik, Saurabh; Rafiq, Mohammd; Joshi, P.K.; Singh, Tejpal (April 2020). "Examining the glacial lake dynamics in a warming climate and GLOF modelling in parts of Chandra basin, Himachal Pradesh, India". Science of the Total Environment. 714 136455. Bibcode:2020ScTEn.71436455K. doi:10.1016/j.scitotenv.2019.136455. PMID 31986382. S2CID 210933887.
- ^ Rafiq, Mohammd; Romshoo, Shakil Ahmad; Mishra, Anoop Kumar; Jalal, Faizan (January 2019). "Modelling Chorabari Lake outburst flood, Kedarnath, India". Journal of Mountain Science. 16 (1): 64–76. Bibcode:2019JMouS..16...64R. doi:10.1007/s11629-018-4972-8. ISSN 1672-6316. S2CID 134015944.
- ^ "Glaciers melting at alarming speed". People's Daily Online. 24 July 2007. Archived from the original on 11 October 2017. Retrieved 17 April 2009.
- ^ Himalayan Glaciers: Climate Change, Water Resources, and Water Security. Washington, D.C.: National Academies Press. 2012. doi:10.17226/13449. ISBN 978-0-309-26098-5.
- ^ a b c O'Neill, A. R. (2019). "Evaluating high-altitude Ramsar wetlands in the Sikkim Eastern Himalayas". Global Ecology and Conservation. 20 (e00715): 19. doi:10.1016/j.gecco.2019.e00715.
- ^ "Photograph of Tsho Rolpa".
- ^ Tsho Rolpa
- ^ Drews, Carl. "Highest Lake in the World". Archived from the original on 18 August 2012. Retrieved 14 November 2010.
- ^ a b c O'Neill, Alexander; et al. (25 February 2020). "Establishing Ecological Baselines Around a Temperate Himalayan Peatland". Wetlands Ecology & Management. 28 (2): 375–388. Bibcode:2020WetEM..28..375O. doi:10.1007/s11273-020-09710-7. S2CID 211081106.
- ^ a b c d e f Zurick & Pacheco 2006, p. 50.
- ^ a b c d e f g h i j k l m n Zurick & Pacheco 2006, pp. 50–51.
- ^ Kad, Pratik; Ha, Kyung-Ja (27 November 2023). "Recent Tangible Natural Variability of Monsoonal Orographic Rainfall in the Eastern Himalayas". Journal of Geophysical Research: Atmospheres. 128 (22). AGU. Bibcode:2023JGRD..12838759K. doi:10.1029/2023JD038759.
- ^ Kad, Pratik; Ha, Kyung-Ja (27 November 2023). "Recent Tangible Natural Variability of Monsoonal Orographic Rainfall in the Eastern Himalayas". Journal of Geophysical Research: Atmospheres. 128 (22). AGU. Bibcode:2023JGRD..12838759K. doi:10.1029/2023JD038759.
- ^ "Weather & Season Info of Nepal". Classic Himalaya. Retrieved 28 March 2024.
- ^ "Climate of the Himalayas". Encyclopedia Britannica. Retrieved 18 May 2022.
- ^ Zurick, David; Pocheco, Julsun (2006), Illustrated Atlas of the Himalaya, University Press of Kentucky, p. 52, ISBN 978-0-8131-7384-9
- ^ Romshoo, Shakil Ahmad; Rafiq, Mohammd; Rashid, Irfan (March 2018). "Spatio-temporal variation of land surface temperature and temperature lapse rate over mountainous Kashmir Himalaya". Journal of Mountain Science. 15 (3): 563–576. Bibcode:2018JMouS..15..563R. doi:10.1007/s11629-017-4566-x. ISSN 1672-6316. S2CID 134568990.
- ^ Devitt, Terry (3 May 2001). "Climate shift linked to rise of Himalayas, Tibetan Plateau". University of Wisconsin–Madison News. Retrieved 1 November 2011.
- ^ Hogan, C. Michael (2010). Monosson, E. (ed.). "Extremophile". Encyclopedia of Earth. Washington, DC: National Council for Science and the Environment.
- ^ Miehe, Georg; Miehe, Sabine; Vogel, Jonas; Co, Sonam; Duo, La (May 2007). "Highest Treeline in the Northern Hemisphere Found in Southern Tibet" (PDF). Mountain Research and Development. 27 (2): 169–173. doi:10.1659/mrd.0792. hdl:1956/2482. S2CID 6061587. Archived from the original (PDF) on 6 June 2013.
- ^ a b c Gentle, Popular; Thwaites, Rik; Race, Digby; Alexander, Kim (November 2014). "Differential impacts of climate change on communities in the middle hills region of Nepal". Natural Hazards. 74 (2): 815–836. Bibcode:2014NatHa..74..815G. doi:10.1007/s11069-014-1218-0. hdl:1885/66271. S2CID 129787080.
- ^ Agrawal, A; Perrin, N (2008). Climate adaptation, local institutions and rural livelihoods. University of Michigan, Michigan: IFRI Working Paper # W081-6. pp. 350–367.
- ^ Maple Croft. Climate Risk Dataset.
- ^ a b Government of Nepal. "Climate Change Policy, 2011". Ministry of Environment, Government of Nepal, Kathmandu.
- ^ a b c Devkota, Fidel (1 August 2013). "Climate Change and its socio-cultural impact in the Himalayan region of Nepal – A Visual Documentation". Anthrovision. Vaneasa Online Journal. 1 (2). doi:10.4000/anthrovision.589.
- ^ Devkota, Fidel (2013). "Climate Change and its socio-cultural impact in the Himalayan region of Nepal – A Visual Documentation". Anthrovision. 1 (2). doi:10.4000/anthrovision.589.
- ^ a b Rublee, Caitlin; Bhatta, Bishnu; Tiwari, Suresh; Pant, Suman (29 November 2023). "Three Climate and Health Lessons from Nepal Ahead of COP28". NAM Perspectives. 11 (29). doi:10.31478/202311f. PMC 11114597. PMID 38784635. S2CID 265597908.
- ^ a b c d Berstrand, s. "Fact Sheet | Climate, Environmental, and Health Impacts of Fossil Fuels (2021) | White Papers | EESI". www.eesi.org.
- ^ a b c d Oli, Madan K.; Taylor, Iain R.; Rogers, M. Elizabeth (1 January 1994). "Snow leopard Panthera uncia predation of livestock: An assessment of local perceptions in the Annapurna Conservation Area, Nepal". Biological Conservation. 68 (1): 63–68. Bibcode:1994BCons..68...63O. doi:10.1016/0006-3207(94)90547-9.
- ^ a b c d e f g h i j k l m "Nepal". climateactiontracker.org.
- ^ Giri, Anil (17 May 2025). "Sagarmatha Sambaad opens with global call for climate action". The Kathmandu Post. Retrieved 19 May 2025.
- ^ Mishra, Vibhu. "'On thin ice': UN chief sounds alarm over rapid Himalayan glacier melt". United Nations. Retrieved 19 May 2025.
- ^ Poudel, Purushottam (19 May 2025). "Sagarmatha Sambaad ends with urgent call to save the mountains". The Kathmandu Post. Retrieved 19 May 2025.
- ^ a b c d e Das, Suraj; Mishra, Anindya Jayanta (1 March 2023). "Climate change and the Western Himalayan community: Exploring the local perspective through food choices". Ambio. 52 (3): 534–545. Bibcode:2023Ambio..52..534D. doi:10.1007/s13280-022-01810-3. PMC 9735043. PMID 36480087.
- ^ a b c d e f g h i Dhungana, Nabin; Silwal, Nisha; Upadhaya, Suraj; Khadka, Chiranjeewee; Regmi, Sunil Kumar; Joshi, Dipesh; Adhikari, Samjhana (1 June 2020). "Rural coping and adaptation strategies for climate change by Himalayan communities in Nepal". Journal of Mountain Science. 17 (6): 1462–1474. Bibcode:2020JMouS..17.1462D. doi:10.1007/s11629-019-5616-3. S2CID 219281555.
- ^ BMP. "Fire Lines and Lanes" (PDF). BMP No. 12, Fire Lines and Lanes.
- ^ Jain, Arun Kumar (2009). Faith & Philosophy of Jainism. Gyan Publishing House. ISBN 978-81-7835-723-2.
- ^ "To heaven and back". The Times of India. 11 January 2012. Archived from the original on 7 July 2012. Retrieved 2 March 2012.
- ^ a b c Gupta, Pankaj; Sharma, Vijay Kumar (2014). Healing Traditions of the Northwestern Himalayas. Springer Briefs in Environmental Science. ISBN 978-81-322-1925-5.
- ^ Dallapiccola, Anna (2002). Dictionary of Hindu Lore and Legend. National Geographic Books. ISBN 978-0-500-51088-9.
- ^ a b c d Jahangeer A. Bhat; Munesh Kumar; Rainer W. Bussmann (2 January 2013). "Ecological status and traditional knowledge of medicinal plants in Kedarnath Wildlife Sanctuary of Garhwal Himalaya, India". Journal of Ethnobiology and Ethnomedicine. 9 (1): 1. doi:10.1186/1746-4269-9-1. PMC 3560114. PMID 23281594.
- ^ Cantor, Kimberly (14 July 2016). "Paro, Bhutan: The Tiger's Nest". Huffington Post. Retrieved 9 June 2018.
- ^ a b c Zurick, David; Julsun, Pacheco; Basanta, Raj Shrestha; Birendra, Bajracharya (2006). Illustrated Atlas of the Himalaya. Lexington: U of Kentucky.
- ^ Pommaret, Francoise (2006). Bhutan Himalayan Mountains Kingdom (5th ed.). Odyssey Books and Guides. pp. 136–137. ISBN 978-962-217-810-6.
- ^ "Tibetan monks: A controlled life". BBC News. 20 March 2008.
- ^ Mehra, P. L. (1960). "Lacunae in the Study of the History of Bhutan and Sikkim". Proceedings of the Indian History Congress. 23: 190–201. ISSN 2249-1937. JSTOR 44137539.
- ^ "Himalayan Forests Disappearing". Earth Island Journal. 21 (4): 7–8. 2006.
Sources
[edit]General
[edit]- Wester, Philippus; Mishra, Arabinda; Mukherji, Aditi; Shrestha, Arun Bhakta, eds. (2019), The Hindu Kush Himalya Assessment: Mountains, Climate Change, Sustainability and People, Springer Open, ICIMOD, HIMAP, ISBN 978-3-319-92287-4, LCCN 2018954855
- Zurick, David; Pacheco, Julsun (2006), Illustrated Atlas of the Himalayas, with Basanta Shrestha and Birendra Bajracharya, Lexington: University Press of Kentucky, ISBN 978-0-8131-2388-2, OCLC 1102237054
Geography
[edit]- Price, Martin F.; Byers, Alton C.; Friend, Donald A.; Kohler, Thomas; Price, Larry W., eds. (2013). Mountain Geography: Physical and Human Dimensions. Berkeley, Los Angeles, and London: University of California Press. ISBN 978-0-520-25431-2. OCLC 841227048.
- Gerrard, John (1990). Mountain environments: an examination of the physical geography of mountains. MIT Press. ISBN 978-0-262-07128-4. OCLC 20637538.
Geology
[edit]- Chakrabarti, B. K. (2016). Geology of the Himalayan Belt: Deformation, Metamorphism, Stratigraphy. Amsterdam and Boston: Elsevier. ISBN 978-0-12-802021-0.
- Davies, Geoffrey F. (2022). Stories from the Deep Earth: How Scientists Figured Out What Drives Tectonic Plates and Mountain Building. Cham, Switzerland: Springer Nature. doi:10.1007/978-3-030-91359-5. ISBN 978-3-030-91358-8. S2CID 245636487.
- Frisch, Wolfgang; Meschede, Martin; Blakey, Ronald (2011). Plate Tectonics: Continental Drift and Mountain Building. Heidelberg: Springer. doi:10.1007/978-3-540-76504-2. ISBN 978-3-540-76503-5.
- Johnson, Michael R. W.; Harley, Simin L. (2012). Orogenesis: The Making of Mountains. Cambridge, UK and New York: Cambridge University Press. ISBN 978-0-521-76556-5.
- Molnar, Peter (2015). Plate Tectonics: A Very Short Introduction. Oxford University Press. ISBN 978-0-19-872826-9.
Climate
[edit]- Clift, Peter D.; Plumb, R. Alan (2008), The Asian Monsoon: Causes, History and Effects, Cambridge and New York: Cambridge University Press, ISBN 978-0-521-84799-5
- Barry, Roger E (2008), Mountain Weather and Climate (3rd ed.), Cambridge and New York: Cambridge University Press, ISBN 978-0-521-86295-0
Ecology
[edit]Society
[edit]Pilgrimage and Tourism
[edit]- Bleie, Tone (2003), "Pilgrim Tourism in the Central Himalayas: The Case of Manakamana Temple in Gorkha, Nepal", Mountain Research and Development, 23 (2), International Mountain Society: 177–184, doi:10.1659/0276-4741(2003)023[0177:PTITCH]2.0.CO;2, S2CID 56120507
- Howard, Christopher A (2016), Mobile Lifeworlds: An Ethnography of Tourism and Pilgrimage in the Himalayas, New York: Routledge, doi:10.4324/9781315622026, ISBN 978-0-367-87798-9
- Humbert-Droz, Blaise (2017), "Impacts of Tourism and Military Presence on Wetlands and Their Avifauna in the Himalayas", in Prins, Herbert H. T.; Namgail, Tsewang (eds.), Bird Migration across the Himalayas Wetland Functioning amidst Mountains and Glaciers, Foreword by H.H. The Dali Lama, Cambridge, UK: Cambridge University Press, pp. 343–358, ISBN 978-1-107-11471-5
- Lim, Francis Khek Ghee (2007), "Hotels as sites of power: tourism, status, and politics in Nepal Himalaya", Journal of the Royal Anthropological Institute, New Series, 13 (3), Royal Anthropological Institute: 721–738, doi:10.1111/j.1467-9655.2007.00452.x
- Nyaupane, Gyan P.; Chhetri, Netra (2009), "Vulnerability to Climate Change of Nature-Based Tourism in the Nepalese Himalayas", Tourism Geographies, 11 (1): 95–119, doi:10.1080/14616680802643359, S2CID 55042146
- Nyaupane, Gyan P.; Timothy, Dallen J., eds. (2022), Tourism and Development in the Himalya: Social, Environmental, and Economic Forces, Routledge Cultural Heritage and Tourism Series, London and New York: Routledge, ISBN 978-0-367-46627-5
- Pati, Vishwambhar Prasad (2020), Sustainable Tourism Development in the Himalya: Constraints and Prospects, Environmental Science and Engineering, Cham, Switzerland: Springer Nature, doi:10.1007/978-3-030-58854-0, ISBN 978-3-030-58853-3, S2CID 229256111
- Serenari, Christopher; Leung, Yu-Fai; Attarian, Aram; Franck, Chris (2012), "Understanding environmentally significant behavior among whitewater rafting and trekking guides in the Garhwal Himalaya, India", Journal of Sustainable Tourism, 20 (5): 757–772, Bibcode:2012JSusT..20..757S, doi:10.1080/09669582.2011.638383, S2CID 153859477
Mountaineering and Trekking
[edit]Further reading
[edit]- Aitken, Bill, Footloose in the Himalaya, Delhi, Permanent Black, 2003. ISBN 81-7824-052-1.
- Berreman, Gerald Duane, Hindus of the Himalayas: Ethnography and Change, 2nd rev. ed., Delhi, Oxford University Press, 1997.
- Edmundson, Henry, Tales from the Himalaya, Vajra Books, Kathmandu, 2019. ISBN 978-9937-9330-3-2.
- Everest, the IMAX movie (1998). ISBN 0-7888-1493-1.
- Fisher, James F., Sherpas: Reflections on Change in Himalayan Nepal, 1990. Berkeley, University of California Press, 1990. ISBN 0-520-06941-2.
- Gansser, Augusto, Gruschke, Andreas, Olschak, Blanche C., Himalayas. Growing Mountains, Living Myths, Migrating Peoples, New York, Oxford: Facts On File, 1987. ISBN 0-8160-1994-0 and New Delhi: Bookwise, 1987.
- Gupta, Raj Kumar, Bibliography of the Himalayas, Gurgaon, Indian Documentation Service, 1981.
- Hunt, John, Ascent of Everest, London, Hodder & Stoughton, 1956. ISBN 0-89886-361-9.
- Isserman, Maurice and Weaver, Stewart, Fallen Giants: The History of Himalayan Mountaineering from the Age of Empire to the Age of Extremes. Yale University Press, 2008. ISBN 978-0-300-11501-7.
- Ives, Jack D. and Messerli, Bruno, The Himalayan Dilemma: Reconciling Development and Conservation. London / New York, Routledge, 1989. ISBN 0-415-01157-4.
- Lall, J.S. (ed.) in association with Moddie, A.D., The Himalaya, Aspects of Change. Delhi, Oxford University Press, 1981. ISBN 0-19-561254-X.
- Nandy, S.N., Dhyani, P.P. and Samal, P.K., Resource Information Database of the Indian Himalaya, Almora, GBPIHED, 2006.
- Swami Sundaranand, Himalaya: Through the Lens of a Sadhu. Published by Tapovan Kuti Prakashan (2001). ISBN 81-901326-0-1.
- Swami Tapovan Maharaj, Wanderings in the Himalayas, English Edition, Madras, Chinmaya Publication Trust, 1960. Translated by T.N. Kesava Pillai.
- Tilman, H. W., Mount Everest, 1938, Cambridge University Press, 1948.
- Turner, Bethan, et al. Seismicity of the Earth 1900–2010: Himalaya and Vicinity. Denver, United States Geological Survey, 2013.
External links
[edit]- The Digital Himalaya research project at Cambridge and Yale (archived)
- Geology of the Himalayan mountains Archived 16 June 2010 at the Wayback Machine
- Birth of the Himalaya
- South Asia's Troubled Waters Journalistic project at the Pulitzer Centre for Crisis Reporting (archived)
- Biological diversity in the Himalayas Encyclopedia of Earth
Himalayas
View on GrokipediaEtymology
Linguistic Origins and Variations
The name Himalaya derives from the Sanskrit compound himālaya (हिमालय), consisting of hima (हिम), meaning 'snow' or 'frost', and ālaya (आलय), meaning 'abode', 'dwelling', or 'place of residence', thus signifying 'abode of snow'. This designation aptly describes the range's high-altitude peaks, which maintain permanent snow cover above approximately 5,500 meters.[6] The term appears in ancient Sanskrit texts, including the Rigveda (composed circa 1500–1200 BCE) and later epics like the Mahabharata, where it refers to the northern mountainous frontier of the Indian subcontinent, often anthropomorphized as Himavat, a deity embodying the snowy mountains.[7] In regional Indo-Aryan languages such as Hindi and Nepali, the name retains the form Himālaya (हिमालय), pronounced similarly and carrying the same semantic weight.[8] Poetic or alternative Sanskrit designations include Himavat or Himavān, emphasizing 'the snowy one', and Himadri, literally 'snow mountain', specifically denoting the Greater Himalayas in classical literature.[9] These variations underscore the term's rootedness in Indo-Aryan linguistic traditions, which dominate the southern flanks of the range. The English plural "Himalayas" represents an anglicization adapted to denote the entire mountain system as a collective chain, with the form first attested in print between 1835 and 1840 during British surveys of the region. In Tibeto-Burman languages like Tibetan, spoken on the northern side, the range lacks an indigenous equivalent to Himālaya; instead, modern usage borrows the Sanskrit-derived transliteration hi ma la ya (ཧི་མ་ལ་ཡ་), while traditional references employ descriptive phrases or local toponyms for subsections, such as gang (mountain ridges).[8] In Chinese, the name is phonetically rendered as Xīmalàyǎ Shān (喜马拉雅山), a transliteration introduced in the 19th century via European cartography, reflecting the term's diffusion beyond its South Asian origins.[10]Physical Geography
Location, Extent, and Topography
The Himalayas constitute a vast mountain system in South Asia, stretching approximately 2,400 kilometers (1,500 miles) from the Indus River gorge near Nanga Parbat in northern Pakistan westward to the Brahmaputra River gorge near Namcha Barwa in eastern India.[11][12] The range spans five countries—Pakistan, India, Nepal, Bhutan, and China (primarily the Tibet Autonomous Region)—and forms a natural barrier between the Tibetan Plateau to the north and the Indo-Gangetic Plain to the south.[12][13] Its width varies between 150 and 400 kilometers (93 to 250 miles), with the southern foothills merging into the alluvial plains of the Indian subcontinent.[1][14] Topographically, the Himalayas are structured into three primary parallel longitudinal divisions from south to north: the Outer Himalayas (also known as the Siwalik Range or Sub-Himalayas), the Lesser Himalayas (or Middle Himalayas), and the Greater Himalayas (Himadri or High Himalayas).[15][11] The Outer Himalayas, the southernmost and geologically youngest zone, rise to elevations of 600 to 1,500 meters and comprise folded and faulted Tertiary sedimentary rocks, including sandstones and shales, often dissected by rivers forming deep gorges known as duns or valleys.[15] Northward, the Lesser Himalayas elevate to 1,500 to 5,000 meters, featuring intensely folded Paleozoic and Mesozoic rocks with structural features like synclines and anticlines, and include prominent valleys such as the Kathmandu Valley.[15] The Greater Himalayas, the core and highest segment, exceed 6,000 meters in average elevation, with peaks surpassing 8,000 meters, characterized by crystalline metamorphic and igneous rocks thrust upward along major faults, perpetual snow cover above the permanent snow line at approximately 5,500 meters, and extensive glacial systems.[11][13] Beyond the Greater Himalayas lies the Trans-Himalayas, including the arid Zaskar and Ladakh ranges, which parallel the main system but are geologically distinct.[15]Major Peaks, Ranges, and Plateaus
The Himalayan mountain system consists of three principal longitudinal divisions running northwest to southeast: the Outer Himalayas (Siwalik Hills), the Lesser Himalayas (Himachal), and the Greater Himalayas (Himadri). [15] The Siwalik Hills, the outermost range, rise to elevations of 900 to 1,200 meters and consist of sedimentary rocks from the Tertiary period. [15] The Lesser Himalayas, situated between the Siwaliks and Greater Himalayas, feature heights of 1,500 to 4,500 meters, with folded structures of older sedimentary and metamorphic rocks. [15] The Greater Himalayas represent the core high-altitude zone, where peaks surpass 6,000 meters, sustained by the perpetual snow line above 5,500 meters. [16] North of the Greater Himalayas lie the Trans-Himalayas, including ranges like the Zaskar and Ladakh, which border high plateaus and basins that grade into the Tibetan Plateau, averaging 4,500 meters in elevation. [16] While the main Himalayan ranges are predominantly folded mountain chains without extensive internal plateaus, elevated intermontane basins such as the Spiti Valley in India reach plateau-like altitudes exceeding 3,500 meters. [16] The Tibetan Plateau, immediately north, functions as a vast elevated block uplifted by the same tectonic forces, spanning over 2.5 million square kilometers at heights generally above 4,000 meters. [2] The Greater Himalayas host the world's highest peaks, including nine of the fourteen mountains exceeding 8,000 meters. [17] These summits result from intense compressional tectonics driving crustal thickening and uplift. [2]| Peak | Height (m) | Location |
|---|---|---|
| Mount Everest | 8,849 | Nepal-China border [17] |
| Kangchenjunga | 8,586 | Nepal-India border [17] |
| Lhotse | 8,516 | Nepal-China border [17] |
| Makalu | 8,485 | Nepal-China border [17] |
| Cho Oyu | 8,188 | Nepal-China border [17] |
| Dhaulagiri | 8,167 | Nepal [17] |
| Manaslu | 8,163 | Nepal [17] |
| Annapurna I | 8,091 | Nepal [17] |
| Shishapangma | 8,027 | China (Tibet) [17] |
Hydrology and Water Systems
The Himalayas serve as the primary hydrological source for several major Asian river systems, including the Indus, Ganges, and Brahmaputra, which collectively drain into basins supporting over 1 billion people. These rivers originate from glacial melt, snowmelt, and monsoon precipitation in the high-altitude ranges, with the Indus flowing northwest through Pakistan, the Ganges southeast into India and Bangladesh, and the Brahmaputra (known as Tsangpo in Tibet) eastward before turning south. Additional transboundary rivers such as the Salween, Mekong, and others also draw from Himalayan headwaters, contributing to the region's "water towers" function by providing consistent dry-season flows through glacial contributions that buffer against seasonal variability.[19][20][21] Glaciers in the Himalaya, Karakoram, and Hindu Kush encompass approximately 55,000 ice bodies, storing vast freshwater reserves equivalent to the largest outside the polar regions, with meltwater comprising a variable but critical portion of river discharge—often up to 40% in upper basins during low-flow periods, though overall annual contributions to major rivers like the Ganges are lower, dominated instead by rainfall. This glacio-hydrological system modulates streamflow, where snowmelt and glacier ablation peak in summer, supplementing monsoon rains that drive the bulk of annual runoff. However, exaggerated claims of dependency, such as 70% of Ganges flow from glaciers, have been refuted, as precipitation remains the dominant source, ensuring river sustainability even amid observed glacial retreat of over 40% since the Little Ice Age.[20][22][23] High-altitude Himalayan lakes, many glacial-carved and situated above 4,000 meters, play a supplementary role in local hydrology, with some exhibiting extreme seasonal water-level fluctuations due to melt input and evaporation, while others contribute to groundwater recharge or minor river inflows. Examples include endorheic basins like Tso Moriri and Tso Kar, where solute dynamics reflect eco-hydrological processes influenced by topography and climate. These lakes and associated wetlands buffer flood risks and sustain alpine ecosystems, though their levels show mixed trends—ten of thirteen monitored lakes rising at 0.173 m/year on average, with salt lakes increasing faster—amid broader climatic shifts.[24][25]Geology
Tectonic Formation and Evolution
The Himalayas originated from the collision between the northern margin of the Indian tectonic plate and the southern edge of the Eurasian plate, initiating the ongoing Himalayan orogeny approximately 50 million years ago during the Eocene epoch.[26] Prior to this, the Indian plate had separated from the Gondwanan supercontinent around 180 million years ago and drifted northward at rates of 15-20 centimeters per year, driven by mantle convection and seafloor spreading in the Indian Ocean.[2] The initial contact slowed the Indian plate's northward velocity to 4-6 centimeters per year, as evidenced by paleomagnetic and stratigraphic records marking the closure of the Neo-Tethys Ocean.[26] This oblique convergence has resulted in over 2,000 kilometers of crustal shortening, manifested through the development of a series of south-verging thrust faults and fold belts that stack Indian continental crust northward.[2] Key structural elements include the Main Frontal Thrust, Main Boundary Thrust, and Main Central Thrust, which accommodate ongoing deformation by thrusting older rocks over younger sediments.[27] The collision thickened the crust beneath the Himalayas and adjacent Tibetan Plateau to 70-80 kilometers, far exceeding typical continental thicknesses of 30-40 kilometers, primarily through ductile thickening and magmatic underplating rather than simple piling of sediments.[2] The orogeny's evolution features episodic phases of intensified uplift, with major rapid exhumation occurring during the Miocene around 23-10 million years ago, coinciding with a partial slowdown in plate convergence.[28] Current convergence rates between the plates measure about 4-5 centimeters per year, sustaining uplift at 5-10 millimeters per year in high-relief zones like Nanga Parbat, balanced against erosion rates that locally exceed 10 millimeters per year.[2] This dynamic equilibrium underscores the causal role of sustained plate tectonics in maintaining the range's elevation, with no evidence for alternative drivers like isostatic rebound dominating the process. Estimates of collision onset vary between 40-59 million years ago based on differing interpretations of sedimentary and paleontological data, reflecting complexities in reconstructing diachronous initial contact along the arcuate collision zone.[29][30]Seismic Activity and Hazards
The Himalayan region exhibits high seismic activity primarily due to the ongoing convergence between the Indian and Eurasian tectonic plates, which collide at a rate of 40–50 mm per year.[31] [32] This continental collision, initiated approximately 40–50 million years ago, continues to uplift the range at about 5 mm annually while generating frequent earthquakes along major thrust faults such as the Main Himalayan Thrust.[2] [33] Seismicity is distributed broadly, with earthquakes occurring at shallow to intermediate depths, reflecting strain accumulation from plate motion.[34] The region records thousands of minor events annually, alongside infrequent great earthquakes exceeding magnitude 8. Historical records indicate eight events between magnitude 7 and 8 since 1600, six of which occurred after 1900, including the 1905 Kangra (Mw 7.8), 1934 Bihar-Nepal (Mw 8.4, over 10,500 fatalities), and 1950 Assam (Mw 8.5–8.7) earthquakes.[35] [36] [37] More recent examples include the 2015 Gorkha earthquake (Mw 7.8) in Nepal, which caused over 8,000 deaths and extensive damage.[38]| Date | Location | Magnitude (Mw) | Fatalities | Notes |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| January 15, 1934 | Bihar-Nepal | 8.4 | 10,500+ | Destroyed infrastructure across Nepal and India.[36] |
| August 15, 1950 | Assam | 8.5–8.7 | ~1,500 | Largest instrumentally recorded in the region; altered river courses.[37] |
| April 25, 2015 | Gorkha, Nepal | 7.8 | ~9,000 | Triggered avalanches on Mount Everest; damaged heritage sites.[38] |
Mineral Composition and Resources
The Himalayan orogen comprises a diverse array of rock types shaped by prolonged tectonic deformation, including low- to high-grade metamorphic rocks such as schists, gneisses, and marbles derived from Proterozoic to Cenozoic sedimentary protoliths, alongside ophiolitic ultramafics, granitic intrusions, and Quaternary glacial sediments. Heavy mineral assemblages in Neogene foreland sediments feature amphiboles, epidote, and tourmaline, sourced from eroding Higher Himalayan crystalline complexes, indicating a polymetallic provenance influenced by subduction-related magmatism.[45] Leucogranites, emplaced during Miocene crustal melting, host accessory rare metals including beryl, tourmaline, and spodumene, with beryllium first documented near Mount Everest in 1922.[46] Mineral resources in the Himalayas include base and precious metals concentrated in ophiolitic mélanges, sedimentary-hosted deposits, and skarn systems, though extraction is constrained by steep topography, seismic risks, and limited infrastructure. In Nepal, metallic ores occur at over 107 copper sites (e.g., Gyazi in Gorkha District), 57 lead-zinc prospects (e.g., Ganesh Himal with 2 million metric tons at 13% Pb+Zn), and 88 iron localities (e.g., Thoshe with 15.9 million metric tons at 45.3% Fe), yet no large-scale production exists as of 2019, with only prospecting licenses active.[47] Placer gold is recovered from rivers like the Kali Gandaki, while primary gold and associated tungsten-molybdenum appear in Higher Himalayan veins.[47] In Pakistan's northwestern Himalayan extensions, including Karakoram and Kohistan, chromite pods and lenses in ophiolites (e.g., Chilas and Jijal Complexes) form economically viable deposits, contributing to national output from podiform occurrences linked to Mesozoic seafloor spreading.[48] Copper mineralization, often with gold, occurs in porphyry and volcanogenic massive sulfide settings within island-arc sequences, as at Saindak (440 million metric tons at 0.41% Cu).[49] Lead-zinc and antimony deposits in the Tethyan belt reflect Mississippi Valley-type and orogenic processes.[50] India's Himalayan states (e.g., Himachal Pradesh, Jammu & Kashmir) host copper, lead-zinc, chromite, and nickel in Proterozoic to Cenozoic sequences, with potential in lesser-explored shear zones, though major reserves lie in peripheral cratons.[51] Eastern Himalayan sectors in China feature large sedimentary-hosted polymetallic deposits, such as the Eocene Xiwu Pb-Zn-Ag system (second-largest in Tibet, with substantial tonnage undisclosed but indicative of basin-scale mineralization).[52] Bhutan and Arunachal Pradesh show graphite and dolomite prospects, but systematic surveys indicate modest endowments compared to global standards. Non-metallic resources like limestone (over 1.3 billion metric tons in Nepal) support regional cement production, exceeding 6.6 million metric tons annually as of 2018.[47] Overall, the range's metallogenic potential stems from collisional recycling of Tethyan oceanic crust, yet underexplored due to accessibility challenges.[53]Climate
Regional Climatic Zones
The Himalayas feature pronounced vertical climatic zonation driven by elevation gradients, orographic precipitation, and the barrier effect against the South Asian monsoon, resulting in a transition from tropical conditions in the foothills to perpetual ice at summit levels. These zones generally align with vegetation belts, though exact elevation thresholds vary regionally due to latitude, aspect, and local topography—typically higher in the eastern sectors where warmer temperatures and greater moisture allow upslope shifts in biomes.[54] In the tropical zone, spanning roughly 0–1,000 meters in elevation, particularly in the Siwalik foothills and Indo-Gangetic plains adjacent to the range, summers are hot and humid with temperatures often exceeding 30°C and influenced by pre-monsoon thunderstorms, while winters remain mild; this zone supports moist and dry deciduous forests dominated by species like Shorea robusta.[54] The subtropical zone, from approximately 1,000–1,800 meters (extending higher, up to 2,000 meters eastward), experiences warmer temperate conditions with distinct wet summers and dry winters, fostering montane subtropical broadleaf and pine forests including Pinus roxburghii and Quercus incana.[54] The temperate zone occupies mid-elevations of 1,800–3,600 meters, where mean annual temperatures drop to 5–15°C, supporting monsoon-influenced montane temperate forests of oaks, maples, and conifers such as Abies pindrow and Cedrus deodara; subalpine extensions reach 3,500–4,200 meters with denser fir and spruce stands before the tree line.[54] Above the tree line, the alpine zone (generally >3,600 meters, up to 5,500–6,000 meters) features cold, short growing seasons with heavy snowfall and temperatures often below freezing for much of the year, sustaining herbaceous meadows, shrubs like Juniperus species, and alpine scrub; the nival zone beyond this comprises arctic-like deserts of ice, snow, and sparse lichens, with minimal precipitation mostly as snow and extreme diurnal temperature swings.[54] Regional east-west contrasts overlay this vertical structure, with the southeastern Himalayas (e.g., Arunachal Pradesh, Bhutan) exhibiting humid to semi-humid conditions and 6–12 wet months annually due to effective monsoon orographic lift, yielding annual rainfall exceeding 2,000–10,000 mm in windward slopes and supporting denser vegetation.[55] In contrast, the northwestern sectors (e.g., Kashmir, Himachal Pradesh) are drier and semi-arid, receiving precipitation primarily from winter westerlies rather than the attenuated summer monsoon, with fewer wet months, lower humidity, and adjacent arid Tibetan plateaus north of the range; this aridity intensifies rain shadows, limiting forest cover and promoting steppes at comparable elevations.[55]Precipitation Patterns and Monsoons
The Himalayan range profoundly influences regional precipitation through orographic lift, where moist air masses ascending the southern slopes condense and release heavy rainfall, while the northern slopes experience a pronounced rain shadow effect, resulting in arid conditions. During the summer monsoon season (June to September), the southwest monsoon from the Indian Ocean delivers the majority of annual precipitation to the southern flanks, with outer ranges receiving up to 3,000–4,000 mm annually in some eastern and central pockets due to forced uplift.[56] In contrast, northern inner valleys, such as those in Mustang and Dolpo, receive minimal monsoon moisture, often classified as cold deserts with annual totals below 500 mm.[57] This south-north gradient arises from the barrier effect of the high peaks, which deflect moist flows southward while depriving leeward areas.[55] Monsoon precipitation exhibits spatial variability along the arc of the range, with heavier totals in the eastern Himalayas compared to the west, forming an arc-shaped rain belt driven by the interaction of large-scale monsoon flows and diurnal cycles.[58] [59] Pre-monsoon rains (March–May) contribute over 25% of annual totals in upper central Himalayan valleys, often enhanced by surface heating that promotes convection along southern slopes.[60] Elevation plays a key role, with precipitation peaking at mid-slopes before declining at higher altitudes; for instance, monsoonal rates decrease from 5–35 mm/day on lower southern slopes to 1–21 mm/day in high northern Himalayan zones.[61] Locations like Dharamshala record extreme monthly peaks, such as 765 mm in July alone, underscoring the intensity of orographic enhancement.[62] Winter precipitation, primarily from western disturbances—extratropical cyclones originating in the Mediterranean—provides a secondary but critical moisture source, especially in the western Himalayas, where they account for about 80% of non-monsoonal totals.[63] These systems, occurring 6–7 times per month during December–February, deliver moderate rainfall or snowfall, often as embedded convection rather than widespread deluge, sustaining river flows and agriculture in rain-shadow areas.[64] Recent observations at high elevations, such as Pheriche (4,260 m) with 463 mm annually (17% as snow) and Pyramid (5,035 m) with 587 mm (23% as snow), highlight how winter events supplement monsoon deficits at altitude.[65] Overall, annual precipitation gradients reflect topographic forcing, with southern sub-alpine zones averaging 1,000–1,500 mm and multiple dry months even in wetter sectors.[66]Temperature Variations and Extremes
The Himalayan region's temperatures exhibit pronounced variations driven primarily by elevation, with an average environmental lapse rate of approximately 6.5°C per kilometer of ascent, though local effects such as inversion layers and föhn winds can modify this.[67] At lower elevations like the foothills near 1,000 meters, daytime temperatures in summer can reach 25–35°C, while high-altitude valleys such as Leh experience extremes from -35°C in winter to 35°C in summer.[57] Summit temperatures on peaks exceeding 8,000 meters, including Mount Everest, remain below freezing year-round, averaging -19°C in summer and dropping to -36°C or lower in winter.[68] [69] Seasonal extremes underscore the range's climatic severity: winter minima at high elevations like the Everest summit have reached -60°C, influenced by clear skies and radiative cooling, while base camp areas record -30°C to -25°C.[70] The lowest verified air temperature in the broader Himalayan zone, including Ladakh's Drass at 3,234 meters, hit -45°C, reflecting the arid, high-plateau conditions amplifying nocturnal cooling.[71] Summer maxima at comparable altitudes rarely exceed 10–15°C during the day, with the warmest recorded summit air temperature on Everest at -2.5°C on July 13, 2019.[72] Diurnal temperature ranges are exceptionally large, often 15–20°C or more at elevations above 3,000 meters, due to intense solar heating by day and rapid heat loss at night under low humidity and sparse vegetation; this range increases with altitude in winter over western sectors, showing positive trends of up to 0.1°C per decade in some analyses.[73] Northern slopes display greater sensitivity to cooling seasons, with temperature drops exceeding southern counterparts by 0.2–0.6°C over multi-decadal periods like 1934–1975 in Kathmandu records.[74] [67] These patterns arise from topographic blocking of moist air masses, fostering continental aridity north of the range and enhancing inversion-driven stability.[75]Ecology and Biodiversity
Flora and Vegetation Zones
The flora of the Himalayas is stratified into distinct vegetation zones primarily driven by altitudinal gradients, with temperature decreasing by approximately 0.6–0.7°C per 100 m rise and varying precipitation influencing species distribution. These zones transition from tropical broadleaf forests in the lowlands to sparse alpine communities near the permanent snowline at around 5,500–6,000 m, supporting roughly 10,000 vascular plant species across the region.[76] Eastern sectors exhibit wetter conditions fostering denser evergreen forests, while western areas are drier with more coniferous dominance.[77]| Zone | Elevation Range (m) | Dominant Flora |
|---|---|---|
| Tropical | Up to ~700 | Shorea robusta (sal), Senegalia catechu (khair), Bombax ceiba (silk-cotton), Dalbergia sissoo (Indian rosewood); grasslands with over 100 grass species.[77] |
| Subtropical | ~700–1,800 (east); ~700–1,400 (west) | Pinus roxburghii (chir pine), Schima wallichii, Castanopsis spp., Olea cuspidata; tree ferns (Cyathea spinulosa).[77] |
| Temperate | ~1,400–3,500 | Quercus spp. (oaks), Pinus wallichiana (blue pine), Abies spectabilis (silver fir), Rhododendron arboreum; dense epiphytes including orchids and ferns.[77][78] |
| Subalpine | ~3,000–4,200 | Betula utilis (Himalayan birch), Juniperus spp. (junipers), dwarf rhododendrons; understorey of Arundinaria and Thamnocalamus bamboos.[77][78] |
| Alpine | ~3,700–5,500+ | Dwarf shrubs (juniper, rhododendron), herbs (Meconopsis spp., Primula spp., Leontopodium); lichens dominant above treeline; highest vascular plant at ~6,180 m (Arenaria bryophylla on Everest).[77] |
Fauna and Wildlife
The Himalayan fauna exhibits remarkable diversity, encompassing approximately 300 mammal species across its altitudinal gradients from subtropical foothills to alpine zones above 5,000 meters.[80] This variation supports specialized adaptations, with species distributions influenced by elevation, vegetation, and climate. In protected areas like the Great Himalayan National Park Conservation Area, records include 31 mammals, 209 birds, 12 reptiles, and 9 amphibians, highlighting the region's ecological richness.[81] Prominent mammals include the snow leopard (Panthera uncia), an apex predator inhabiting high-altitude trans-Himalayan landscapes from 3,000 to 6,000 meters. Nepal's snow leopard population is estimated at 397 individuals, with densities averaging 1 per 100 km² in surveyed regions.[82] In India's Himachal Pradesh, recent surveys confirm 83 snow leopards, with densities ranging from 0.16 to 0.53 per 100 km², concentrated in trans-Himalayan areas.[83] The species faces threats from habitat fragmentation and human-wildlife conflict, though protected areas host significant portions of the population.[84] Other notable mammals are the red panda (Ailurus fulgens), endemic to Eastern Himalayan temperate forests with dense bamboo understories at 2,600–3,600 meters, where it prefers steep slopes and north-facing aspects.[85] Nearly 50% of its global habitat lies in the Eastern Himalayas, spanning countries like Nepal and Bhutan.[86] The endangered Himalayan musk deer (Moschus chrysogaster) and Asiatic black bear (Ursus thibetanus) occupy mid-elevation forests, while the Himalayan tahr (Hemitragus jemlahicus), endemic to the western Himalayas, thrives in rugged alpine meadows.[87] Avian diversity features over 200 species in key reserves, including endangered ones like the black-necked crane (Grus nigricollis), which breeds in high-altitude wetlands of Ladakh during summer migrations.[88] In the Eastern Himalayas, 28 bird species are threatened, alongside 19 mammals among 163 globally threatened taxa.[89] Reptiles and amphibians are less diverse due to harsh conditions but include species adapted to montane streams and forests. Overall, anthropogenic pressures such as poaching and habitat loss challenge conservation, with endemic and endangered species concentrated in biodiversity hotspots.[90]Endemic Species and Biodiversity Hotspots
The Himalayan biodiversity hotspot supports around 10,000 plant species, of which approximately 3,160 are endemic, along with 71 endemic genera.[80] Among vertebrates, about 300 mammal species occur in the region, including roughly a dozen endemics such as the endangered golden langur (Trachypithecus geei), restricted to forests in Bhutan and northeast India.[80] Other notable endemic mammals in the eastern portion include the hispid hare (Caprolagus hispidus), pygmy hog (Porcula salvania), and Namdapha flying squirrel (Biswamoyopterus biswasi).[91] In Nepal alone, 312 flowering plant species are endemic, with concentrations at elevations of 3,800–4,200 meters.[92] The rhododendron genus exemplifies floral endemism, with numerous species like Rhododendron niveum unique to Himalayan slopes.[93] The Eastern Himalayas stand out as a subregion of exceptional richness, hosting 300 mammal species, 977 birds, 176 reptiles, 105 amphibians, and 269 freshwater fish, many with high endemism levels; for instance, 3,500 of its roughly 9,000 plant species are endemic.[91] The broader Himalaya qualifies as one of 36 global biodiversity hotspots, characterized by elevated species diversity under threat from habitat loss.[94] This status underscores the region's role in harboring rare taxa, including 163 globally threatened species across taxa, driven by its topographic and climatic gradients that foster speciation.[89] Conservation efforts target these hotspots, particularly the Eastern Himalayas spanning Nepal, Bhutan, and northeast India, where endemism peaks due to isolation and varied ecosystems from subtropical to alpine zones.[5]Human History and Settlement
Prehistoric Inhabitation and Migration
The foothills of the Himalayas, particularly the Siwalik ranges in northern India and Nepal, contain some of the earliest evidence of human occupation in the region, with Lower Paleolithic Acheulian assemblages representing open-air sites characterized by handaxes and cleavers.[95] These artifacts indicate early hominin activity tied to the exploitation of riverine environments, likely by mobile hunter-gatherers adapting to subtropical to temperate zones during the Pleistocene.[96] In the Sub-Himalayan tracts of Himachal Pradesh, such as along the Sir Khad tributary, Late Acheulian to Middle Paleolithic sites yield hafted tools, including wood-working implements and those for large-game processing, suggesting intensified resource use and technological diversification by archaic populations around 100,000 to 50,000 years ago.[97] Higher elevations presented greater barriers due to altitude, cold, and oxygen scarcity, delaying permanent inhabitation until the late Pleistocene or early Holocene. Footprints and handprints preserved in hot spring sediments on the Tibetan Plateau, at elevations exceeding 4,000 meters, demonstrate year-round human presence by approximately 12,600 years ago, predating previously estimated colonization timelines and implying seasonal or adaptive foraging strategies.[98] Ancient DNA from mid-elevation sites in Nepal's Mustang District and adjacent areas reveals genetic continuity with southern Asian populations, with admixture events involving early highland groups traceable to migrations before and after the Last Glacial Maximum around 20,000 years ago.[99] Rock engravings—tens of thousands documented across Ladakh, Mustang, Spiti, and western Tibet—further attest to symbolic and territorial behaviors by these groups, with motifs depicting hunters, animals, and geometric patterns dated stylistically to the Upper Paleolithic or Epipaleolithic.[100] Migration patterns into the core Himalayan ranges involved incremental advances from lowland corridors, with the mountains functioning as both a formidable geographic filter—restricting gene flow to transverse valleys and passes—and a conduit for bidirectional exchange between the Indian subcontinent and Central Asian steppes.[101] Genomic analyses of ancient individuals from Nepal's southern Tibetan fringe indicate multiple influxes, including South Asian-derived lineages admixing with high-altitude adapted groups around 3,000 to 5,000 years ago, facilitating Neolithic transitions evidenced by microlithic tools and early pastoralism in sites like those in Ladakh's Indus Valley above 3,000 meters.[99] These movements were driven by climatic amelioration post-glaciation, resource pursuit, and possibly population pressures from expanding plains networks, though direct evidence remains sparse due to erosion, glaciation, and limited surveys in remote terrains.[102] Mesolithic sites in Nepal's Siwalik hills, featuring refined microliths, bridge Paleolithic foraging to incipient sedentism, underscoring gradual altitudinal colonization rather than rapid invasion.[103]Ancient Civilizations and Trade Routes
The Indus Valley Civilization, flourishing from approximately 3300 to 1300 BCE in the northwestern regions of the Indian subcontinent, maintained indirect connections to the Himalayan region through river systems originating in the mountains, such as the Indus River, which sourced from Tibetan plateaus and facilitated early agricultural and urban development in adjacent plains.[104] [105] Archaeological evidence indicates that major Indus settlements like those near the Ghaggar-Hakra (ancient Sarasvati) river thrived on remnant channels influenced by Himalayan glacial melt, though a key river shifted eastward prior to the civilization's peak urban phase around 2600 BCE, suggesting adaptation to stabilized water sources rather than direct perennial Himalayan flows.[106] This proximity enabled resource exchanges, including timber and minerals from Himalayan foothills, supporting the civilization's bronze-age metallurgy and trade networks extending toward Central Asia.[107] In the Kathmandu Valley, one of the few habitable intermontane basins within the Himalayas, early settlements by Kirati peoples date to around 800 BCE, marking some of the region's earliest organized societies with rudimentary agriculture and pastoralism adapted to high-altitude constraints.[108] These were succeeded by the Licchavi dynasty, ruling from circa 450 to 750 CE, which established a centralized kingdom fostering inscriptional records, temple architecture, and governance influenced by Indian Gupta styles.[109] The Licchavis promoted trans-Himalayan commerce, leveraging passes to connect with Tibetan plateau societies and northern Indian plains, evidenced by royal inscriptions detailing land grants and trade guilds; their era saw Nepal emerge as a conduit for goods like wool, salt, and borax from Tibet exchanged for Indian spices, textiles, and metals.[110] Key figures like Amshuverma (r. circa 605–621 CE) expanded routes northward, allying through marriage—such as his daughter Bhrikuti's union with Tibetan king Songtsen Gampo—facilitating Buddhist iconography and mercantile ties that bolstered Kathmandu's prosperity.[111] Himalayan trade routes integrated into broader Eurasian networks by the 1st century CE following the Kushan Empire's expansion, branching from the Silk Road via high passes like those in Kashmir and Ladakh to link Indian subcontinental markets with Central Asian and Chinese interiors.[112] These paths, including the Zoji La and Shipki La crossings, traversed elevations exceeding 4,000 meters, carrying silk, horses, and lapis lazuli northward while returning with Tibetan salt, musk, and gold, with caravans of yaks and mules navigating seasonal closures due to snow.[113] In western sectors, routes like the Sumsan Sumba connected Spiti Valley to Tibetan enclaves, sustaining local economies through barter systems documented in medieval traveler accounts, though risks from avalanches and raids limited volumes to essential commodities rather than bulk goods.[114] The Kali Gandaki Valley in central Nepal served as a pivotal corridor, channeling trade between the Gangetic plains and Tibetan highlands, with archaeological finds of Roman coins and Chinese silks underscoring multidirectional exchanges predating Islamic era disruptions.[115] Such routes not only disseminated technologies like ironworking but also cultural elements, including early Buddhist manuscripts, across the barrier-like range.[116]Colonial Era and Modern Demographic Shifts
During the early 19th century, British East India Company forces engaged in the Anglo-Nepalese War from November 1814 to March 1816 against the expanding Gorkha Kingdom, which had incorporated Himalayan territories including Kumaon, Garhwal, and parts of Sikkim.[117] The conflict concluded with the Treaty of Sugauli in 1816, under which Nepal ceded approximately one-third of its territory—over 10,000 square miles—to British India, including the aforementioned regions and access to the Terai lowlands, while retaining internal autonomy as a buffer state.[118] This treaty also initiated Gurkha recruitment into British forces, with over 200,000 Nepali soldiers serving by World War II, fostering economic ties but limiting Nepal's external relations.[119] Similar dynamics unfolded in Bhutan and Sikkim, where British interventions through wars and treaties in the 1860s and 1770s established suzerainty over foreign affairs while allowing nominal independence.[120] In Bhutan, the Treaty of Sinchula in 1865 ended hostilities by ceding the Duar passes and territories amounting to 1,300 square miles after Anglo-Bhutanese conflicts. Sikkim, annexed as a protectorate in 1890 following disputes over trade routes, saw British infrastructure like roads and tea plantations introduced, altering local economies. In the western Himalayas, British paramountcy over princely states such as Jammu and Kashmir from 1846 onward secured strategic borders, with surveys mapping over 2,000 miles of frontier by the Great Trigonometrical Survey. These policies prioritized frontier security against Russian and Chinese influences, establishing hill stations like Shimla (founded 1819) and Darjeeling (annexed 1835) as administrative and climatic retreats, drawing European settlers and spurring limited demographic influxes of administrators and laborers.[121] Post-independence from Britain in 1947, Himalayan demographics underwent pronounced shifts driven by national policies, economic pressures, and geopolitical upheavals. In Nepal and Indian Himalayan states like Uttarakhand and Himachal Pradesh, large-scale outmigration accelerated from the 1970s, with rural youth departing for urban centers in the Indo-Gangetic plains or abroad; by 2014, projections indicated that 20% annual youth emigration could halve highland populations within decades, exacerbating aging demographics and birth rate declines below replacement levels in regions like Sikkim.[122] This outflux, fueled by limited arable land (only 10-15% cultivable) and education-driven aspirations, led to labor shortages, farmland abandonment, and increased female-headed households, with remittances constituting up to 25% of Nepal's GDP by 2020.[123][124] In the Tibetan Plateau under Chinese administration since 1951, policies promoting Han Chinese settlement have inverted ethnic compositions; by the 2020 census, Tibet Autonomous Region's population reached 3.6 million, with Han migrants comprising an estimated 10-20% in urban areas like Lhasa, up from negligible pre-1950 figures, alongside infrastructure projects facilitating influxes.[125] Tibetan refugee outflows peaked after the 1959 uprising, with over 80,000 fleeing to India and Nepal, establishing settlements like Dharamshala (population ~15,000 Tibetans by 2020), though new arrivals have dwindled to under 1,000 annually since 2008 due to tightened borders.[126] In Bhutan, citizenship policies in the 1980s-1990s expelled or denationalized up to 100,000 Lhotshampa (Nepali-origin) residents, reducing their share from 45% to under 25%, amid cultural preservation drives. These shifts reflect causal pressures from modernization, state policies, and resource constraints, often prioritizing security and assimilation over indigenous stability.[127]Cultures and Religions
Indigenous Ethnic Groups and Languages
The Himalayas are inhabited by a diverse array of indigenous ethnic groups, many adapted to high-altitude environments through generations of residence. These populations primarily consist of Tibeto-Burman-speaking peoples who migrated from Tibetan plateaus and Central Asia over centuries, alongside indigenous hill tribes predating Indo-Aryan expansions. In Nepal, key groups include the Sherpas, concentrated in the eastern high valleys like Solukhumbu, numbering around 150,000 and known for physiological adaptations to low oxygen levels; the Gurungs and Magars in the central and western hills, with populations exceeding 500,000 each, traditionally involved in agriculture and military service; and the Tamangs, numbering over 1.5 million, residing near Kathmandu with distinct shamanistic and Buddhist practices.[128][129][108] In the Indian Himalayas, including Sikkim and Ladakh, the Lepchas—considered autochthonous to Sikkim with a population of about 50,000—preserve animist traditions blended with Buddhism, while Bhutias, of Tibetan origin, number around 100,000 and dominate higher elevations. Western sectors feature Balti people in Gilgit-Baltistan, practicing Shia Islam and speaking a Tibetic dialect, with communities sustaining terraced farming. Bhutanese groups include Ngalops (also called Bhote), comprising 50% of the population at roughly 400,000, who speak Dzongkha, and Sharchops in the east, Tibeto-Burman speakers maintaining matrilineal customs. Indo-Aryan Khas groups, such as Kshetri and Bahun, prevail in lower Nepalese and Indian foothills, influencing demographics through historical migrations.[108][130][131] Linguistically, the region hosts over 100 languages, predominantly from the Tibeto-Burman branch of the Sino-Tibetan family, reflecting ethnic fragmentation and isolation by terrain. Sherpa, Gurung, Magar, Tamang, and Lepcha languages belong to this family, often tonal and agglutinative, with limited mutual intelligibility despite shared roots; for instance, Sherpa derives from Central Tibetan dialects introduced by 16th-century migrants. Tibetic languages like Ladakhi and Balti extend across the trans-Himalaya, while Dzongkha serves as Bhutan's official tongue. Indo-European languages, notably Nepali (a Khas derivative spoken by 45% of Nepalis as a first language), dominate foothills and act as lingua francas, overlaying Tibeto-Burman substrates in multilingual communities. This diversity, with some languages endangered due to urbanization and Nepali dominance, underscores the Himalayas' role as a linguistic hotspot, though documentation remains incomplete for remote dialects.[108][132][130]Religious Traditions and Sacred Sites
The Himalayas are central to several religious traditions, particularly Hinduism and Tibetan Buddhism, which view the range's peaks, valleys, and water bodies as abodes of deities and sites of spiritual attainment. In Hinduism, mountains symbolize divine manifestation, with the region embodying the cosmic axis connecting earth and heaven. Tibetan Buddhism, prevalent in Nepal's Khumbu, India's Ladakh and Sikkim, and Bhutan's highlands, integrates local animist beliefs into monastic practices centered on meditation, tantric rituals, and circumambulation of sacred landscapes. Bon, the indigenous Tibetan faith predating Buddhism, reveres the Himalayas as realms of elemental spirits, while Jainism identifies specific peaks with liberation events.[133] [134] [135] Mount Kailash, at 6,638 meters in China's Tibetan region, stands as the paramount sacred site, embodying Shiva's throne for Hindus and the axis mundi in Buddhist and Bon cosmologies; Jains regard it as proximate to Ashtapad, where the first tirthankara Rishabhanatha achieved moksha around the 7th century BCE per tradition. Pilgrims perform the 52-kilometer kora, a clockwise circuit yielding spiritual merit equivalent to vast lifetimes of practice, drawing thousands annually despite arduous high-altitude conditions. Adjacent Lake Manasarovar, at 4,590 meters, amplifies sanctity as a site for ritual bathing, believed to purify karma across these faiths.[136] [137] [138] In India's Garhwal Himalayas, the Chota Char Dham circuit—Yamunotri (Yamuna source temple, opened annually around April 2025), Gangotri (Ganges origin shrine), Kedarnath (Shiva Jyotirlinga at 3,583 meters, site of 2013 floods killing thousands), and Badrinath (Vishnu abode)—forms a sequential Hindu pilgrimage from Haridwar, spanning 1,000 kilometers over 10-15 days and attracting over 3 million visitors yearly during the May-October season when passes are accessible. These sites, established between the 8th and 16th centuries CE, underscore the Himalayas' role in Vedic and Puranic narratives of river origins and ascetic penance.[139] [140] Buddhist sacred sites proliferate in the trans-Himalayan belt, with gompas (monasteries) like Nepal's Tengboche (founded 1916, housing ancient relics) and India's Hemis (established 1672, venue for annual festivals) serving as repositories of thangkas, statues, and texts for Vajrayana practices. Mustang's Kagbeni and hidden beyuls (sanctuary valleys) in Bhutan preserve esoteric lineages, where lamas guide retreats amid glacial lakes and chortens (stupas) inscribed with mantras. Sacred waters, such as Sikkim's Gurudongmar Lake at 5,430 meters—touched by Guru Padmasambhava per legend—draw devotees for blessings of longevity and clarity.[141] [142] [143] Jain traditions focalize on Ashtapad, an 18,000-foot peak near Kailash, symbolizing the eightfold path to nirvana and inaccessible since the 1950s due to geopolitical restrictions, limiting pilgrimages to circum-Kailash proxies. These sites' endurance reflects causal ties between altitude-induced isolation and preserved orthodoxy, unmarred by lowland syncretism, though modern tourism strains ecological and ritual integrity.[144] [145]Cultural Practices and Festivals
The Himalayan region's cultural practices reflect adaptations to high-altitude exigencies, including transhumant yak herding that supplies milk, meat, wool for textiles, and dung for fuel, with herds migrating seasonally across altitudes in a system tied to ethnic rituals and economic survival across Nepal, India, Bhutan, and Tibetan areas.[146] [147] Fraternal polyandry, where brothers share a wife, has persisted in Tibetan and adjacent Himalayan communities such as those in Nepal's Humla and Mustang districts, primarily to avert land fragmentation and curb population growth amid scarce arable resources and arable plateaus limited to about 5-10% of terrain.[148] [149] Indigenous Bon shamanism, predating Buddhism, endures through practitioners known as pawo or lhapa who perform exorcisms, healings, and invocations to local deities via trance states and offerings, particularly in eastern Tibetan and Nepali Himalayan pockets.[150] [151] Festivals integrate these practices, serving as occasions for communal rites, masked performances, and feasts that honor deities, ensure harvests, and fortify social ties among ethnic groups like Sherpas, Gurungs, and Tibetans.- Lhosar (Tibetan New Year): Celebrated variably as Gyalpo Lhosar by Sherpas, Sonam Lhosar by Gurungs, and Tamu Lhosar by Tamangs in late February or early March per the lunar calendar, it features thorough home cleanings symbolizing renewal, erection of prayer flags, offerings of tsampa (roasted barley flour), feasts with chang (barley beer), and line dances; preparations span 15 days, emphasizing family gatherings and expulsion of misfortunes.[152] [153]
- Mani Rimdu: A 19-day Buddhist rite culminating in three days of public masked dances at monasteries such as Tengboche, Chiwong, and Thame in Nepal's Everest region during October-November, it dramatizes Guru Rinpoche (Padmasambhava)'s eighth-century subjugation of demons through choreography with thunderbolt props and fire rituals, followed by communal blessings and khapse (fried dough) distributions to avert calamities.[154] [155]
- Tiji: Held over three days in mid-May at Lo Manthang in Nepal's Upper Mustang, this Vajrayana festival reenacts the deity Dorje Jono's mythical victory over a demon causing famine and drought, with lamas in ornate masks performing ritual dances, horse races, and invocations to invoke rain and prosperity for the arid kingdom's 2,000 residents.[156] [157]
- Dumje: A post-monsoon Sherpa harvest festival in September-October in Nepal's Khumbu valley villages, involving monastic invocations for familial and agricultural bounty, archery contests, butter lamp lightings, and shared meals of yak-derived products, reinforcing clan solidarity through participatory rituals excluding tourists.[158] [159]
Exploration and Mountaineering
Early European Expeditions
Following the Anglo-Nepalese War of 1814–1816, British forces annexed the regions of Kumaon and Garhwal, opening these western Himalayan territories to systematic European surveys for mapping and resource assessment.[162] William Webb, a British surveyor, conducted detailed measurements in Kumaon from 1816 to 1820, including an altitude determination of Nanda Devi at 25,669 feet—later refined but indicative of early trigonometric efforts amid challenging terrain and local resistance.[162] The Great Trigonometrical Survey of India, initiated in 1802 by William Lambton under East India Company auspices, extended northward into Himalayan foothills by the 1820s, employing chain triangulation to measure vast arcs with unprecedented precision for the era, ultimately aiding in peak height calculations.[163] George Everest, superintendent from 1823, oversaw advancements that reached Himalayan extremities, prioritizing geometric accuracy over direct ascents due to logistical barriers and political restrictions in Nepal and Tibet.[164] Independent explorer William Moorcroft, a veterinarian dispatched by the East India Company to procure superior horse breeds, led expeditions from 1819 to 1825, traversing Punjab into the trans-Himalaya and becoming the first European to reach Leh in Ladakh on September 1820 via the Spiti route after delays including consultations with Maharaja Ranjit Singh.[165] Earlier, in 1812, Moorcroft had disguised himself as a Hindu pilgrim to survey Manasarovar Lake's hydrography, gathering intelligence on trade routes and wool sources amid Russian influences in the region; his travels yielded detailed accounts of Ladakh's geography and economy before his death in Bukhara in 1825.[166] In the mid-1840s, British Army officers Henry Strachey and Richard Strachey extended explorations from Kumaon toward western Tibet, with Henry reaching Manasarovar and Rakastal lakes in 1846 via Spiti passes, followed by Richard's 1848 journey confirming hydrological connections and collecting geological data under orders blending scientific and strategic aims.[162] These efforts built on Moorcroft's paths but faced Tibetan frontier hostilities, yielding maps that informed boundary delineations.[167] Botanist Joseph Dalton Hooker conducted the era's premier natural history expedition from 1847 to 1851, basing in Darjeeling to penetrate Sikkim's eastern Himalayan ranges, amassing over 3,000 plant species including rhododendrons, while navigating local intrigue and imprisonment by Sikkimese authorities before diplomatic release.[168] Hooker's routes, documented in his Himalayan Journals, emphasized altitudinal zonation and floristic richness, contrasting with prior surveys' focus on geodesy and contributing foundational data on biodiversity gradients driven by orographic uplift.[169]20th-Century Ascents and Milestones
The first successful ascent of an 8000-meter peak occurred on Annapurna I (8,091 meters) on June 3, 1950, by a French expedition led by Maurice Herzog. Louis Lachenal and Herzog reached the summit without supplemental oxygen, enduring extreme conditions that resulted in severe frostbite requiring amputations for both climbers upon descent. This achievement marked a breakthrough in high-altitude mountaineering, demonstrating the feasibility of summiting such elevations despite logistical challenges in Nepal's remote terrain.[170] On July 3, 1953, Austrian climber Hermann Buhl completed the first ascent of Nanga Parbat (8,126 meters) solo via the Rakhiot Face during a German-Austrian expedition organized by Karl Herrligkoffer. Buhl, climbing without oxygen after separating from his team, spent over 40 hours on the final push, bivouacking en route due to fatigue and weather. This solo effort on the notoriously dangerous "Killer Mountain," which had claimed numerous lives in prior attempts, highlighted individual endurance limits at extreme altitudes.[171] The most iconic milestone came on May 29, 1953, when New Zealand's Edmund Hillary and Nepalese Sherpa Tenzing Norgay summited Mount Everest (8,848 meters), the world's highest peak, as part of the British expedition led by John Hunt. Utilizing supplemental oxygen and fixed ropes, they traversed the South Col route from Nepal, overcoming the Khumbu Icefall and Hillary Step. This ascent, following multiple failed expeditions since the 1920s, symbolized human triumph over the Himalayas' greatest challenge and spurred global interest in high-altitude climbing.[172] Subsequent years saw rapid progress with first ascents of other major Himalayan peaks. Kangchenjunga (8,586 meters), the third-highest, was summited on May 25, 1955, by a British team including Joe Brown, George Band, Norman Hardie, and Charles Evans via the Southwest Face. Cho Oyu (8,188 meters) followed in October 1954 by a Austro-German-Swiss group led by Herbert Tichy, notable for minimal oxygen use. These climbs, often relying on large teams and Sherpa support, established patterns for tackling the remaining 8000ers, though with ongoing risks of avalanche and altitude sickness.[173]Contemporary Challenges and Records
Overcrowding on Himalayan peaks, particularly Mount Everest, has intensified safety risks during peak climbing seasons, with 2024 seeing approximately 900 climbers on the mountain and 12 confirmed deaths, marking one of the deadliest years on record.[174] This congestion often results in bottlenecks at key points like the Hillary Step, exacerbating exposure to avalanches, exhaustion, and acute mountain sickness among climbers, many of whom lack sufficient experience due to the proliferation of guided commercial expeditions.[174] In response, Nepalese authorities have introduced measures such as requiring climbers to use GPS trackers and limiting team sizes starting in 2025, though enforcement remains inconsistent amid high permit fees generating substantial revenue.[175] Commercialization has democratized access to 8,000-meter peaks but amplified hazards, as novice climbers supported by supplemental oxygen and Sherpa assistance contribute to higher fatality rates; for instance, Everest's overall death toll exceeded 330 by mid-2025, with over 200 bodies still unrecovered due to logistical difficulties.[176] Climate change compounds these issues by altering ice and snow conditions, leading to more unstable seracs and unpredictable weather patterns that have made routes like the Khumbu Icefall increasingly treacherous and extended the "climbing window" variability.[177] Pollution from expeditions, including discarded gear and human waste, further degrades the environment, with Mount Everest accumulating tons of trash annually despite cleanup efforts.[178] Notable records persist amid these challenges, highlighting elite mountaineering prowess; Kami Rita Sherpa achieved his 31st Everest summit on May 27, 2025, surpassing previous benchmarks for repeat ascents.[179] On K2, at least 41 summits were recorded in 2025 under harsh conditions, including high winds and jet stream interference, underscoring the peak's enduring lethality compared to Everest.[180] Speed records include Phunjo Lama's fastest female ascent of Everest in 2024, while autumn expeditions in 2025 featured a ski descent from Everest's summit and multiple Manaslu records, demonstrating adaptive techniques in variable terrain.[181][182]Economy and Resources
Natural Resource Extraction
The Himalayan range harbors diverse mineral deposits formed through tectonic processes, including metallic ores such as copper, iron, lead, zinc, and gold, as well as non-metallic resources like limestone, dolomite, and magnesite.[49] Extraction activities remain limited across much of the region due to high-altitude inaccessibility, fragile ecosystems, and inadequate infrastructure, with mining output constituting less than 1% of GDP in countries like Nepal.[183] In Nepal, documented reserves include approximately 1 million tons of copper ore and significant iron ore deposits exceeding 50 million tons, primarily in the lesser Himalayan zones, though commercial-scale operations are nascent and focused on small artisanal mines.[184] Gemstone mining targets corundum varieties embedded in metamorphic marbles, notably in east-central Nepal's Ganesh Himal and Langtang areas, where gem-quality rubies (often with purple fluorescence) and fancy sapphires (blue to violet hues) have been extracted since systematic discoveries in the mid-1990s, yielding crystals up to several carats despite challenges from overburden removal at elevations over 4,000 meters.[185] Other semi-precious stones, including kyanite from high-grade schist deposits and tourmaline from pegmatites, support localized artisanal operations in Nepal's mid-hills, contributing to exports valued at under $1 million annually as of recent assessments.[186] In India's Himalayan states, such as Arunachal Pradesh and Sikkim, dolomite and graphite mining occurs on a modest scale, with annual production figures around 100,000 tons for construction aggregates.[187] Under Chinese administration in the Tibetan Plateau's Himalayan fringes, large-scale extraction targets copper porphyry deposits (e.g., Yulong belt with over 10 million tons of reserves), lithium brines, and rare earth elements, with operations like the Qulong mine producing 100,000 tons of copper concentrate yearly by 2020, often employing open-pit methods that exacerbate dust pollution and water diversion.[188] These activities, valued at billions in strategic minerals including gold and uranium, have intensified since 2010, prompting concerns over transboundary environmental impacts into India and Nepal.[189] Timber harvesting from subtropical to alpine forests supplies species like pine, oak, and rhododendron, sustaining local construction and fuel needs for over 50 million residents, but commercial logging has driven net forest loss of nearly 10,000 km² between 1992 and 2018, concentrated in Nepal and India at mid-elevations (2,000–3,000 meters).[190] Historical data indicate a 30% regional deforestation rate over the prior three decades, primarily from unmanaged commercial felling rather than subsistence fuelwood alone, with annual losses averaging 0.8% in monitored Bhutanese and Nepalese tracts.[191] Predominant techniques involve selective cutting and slope-based extraction, amplifying landslide risks in seismically active zones.[192] Illegal operations, particularly in India's northeastern Himalayas, have depleted over 20% of protected forest cover in select reserves since 2010, underscoring enforcement gaps.[193]Hydropower Development and Infrastructure
The Himalayan region harbors substantial hydropower potential, estimated at 882 gigawatts (GW) across countries including India, Nepal, Bhutan, and China, yet only about 6% of this capacity has been harnessed as of 2025.[194] Development has accelerated since the late 20th century, driven by the steep gradients and glacial-fed rivers of the Indus, Ganges, and Brahmaputra basins, which provide reliable seasonal flows for run-of-river and storage projects. In India, hydroelectric capacity in Himalayan states is projected to rise significantly, with national hydro output expected to expand from 42 GW to 67 GW by 2031-32, supported by over 80 large projects exceeding 25 MW operational or under construction as of 2022.[195] [196] Nepal relies heavily on hydropower for nearly all its 3,422 MW installed capacity as of March 2025, while Bhutan has achieved energy self-sufficiency through exports to India, targeting 25 GW total capacity by 2040.[194] [197] Infrastructure encompasses high-head dams, extensive tunneling for diversion, and transmission lines navigating rugged terrain. In Nepal, projects like the 144 MW Kali Gandaki A, operational since 2002, feature concrete gravity dams with sluicing gates to manage sediment from monsoon floods.[198] Bhutan's cascade developments, including the Tala and Chukha plants, integrate storage reservoirs with run-of-river designs, exporting surplus power via Indian grid interconnections.[197] India has initiated upgrades to reservoir capacities at Kashmir projects in 2025 to enhance peaking power amid suspended treaties, while China's Tibetan Plateau initiatives involve large-scale dams on transboundary rivers like the Yarlung Tsangpo (Brahmaputra), raising downstream flow concerns.[199] [200] These systems often require blasting and deforestation for access roads and tunnels, exacerbating slope instability in tectonically active zones.[201]| Project | Country | Capacity (MW) | Operational Year |
|---|---|---|---|
| Kali Gandaki A | Nepal | 144 | 2002[198] |
| Tanahu | Nepal | 140 | Under construction (expected ~2027)[202] |
| Tala (representative of Bhutan cascade) | Bhutan | 1,020 | 2007 (phased)[197] |
Tourism, Trekking, and Local Economies
Tourism centered on trekking forms a cornerstone of economic activity in the Himalayan region, particularly in Nepal and northern Indian states like Uttarakhand and Himachal Pradesh. In Nepal, international tourist arrivals totaled 1,147,567 in 2024, reflecting a 13.1% rise from 2023, with a substantial portion directed toward Himalayan trekking destinations such as the Everest, Annapurna, and Langtang areas.[209] These visitors contribute through trekking permits, accommodations in teahouses, and hiring of local guides and porters, channeling funds into remote high-altitude communities. Key trekking routes, including the Annapurna Circuit and Everest Base Camp trails, draw international adventurers seeking proximity to peaks like Annapurna I and Mount Everest. The Everest region has seen visitor numbers surge by more than 70% in recent post-pandemic years relative to prior periods.[210] Seasonality confines peak activity to spring (March-May) and autumn (September-November), aligning with favorable weather for high passes and base camp approaches. Sherpa and other indigenous groups in Nepal's Khumbu Valley exhibit high economic dependence on trekking tourism, with livelihoods tied to roles as guides, porters, and lodge proprietors.[211] This sector accounts for 8-15% of GDP in Himalayan nations and employs around 7.3 million people regionally, fostering infrastructure like trails and sanitation while enabling investments in education and healthcare.[212] [213] In India, trekking sustains rural economies in Himalayan districts by generating jobs in hospitality and guiding, contributing to poverty alleviation through direct and multiplier effects such as capital accumulation and skill development.[214] However, reliance on tourism exposes communities to volatility; off-season periods and events like earthquakes or pandemics trigger income shortfalls, often resulting in food insecurity without agricultural diversification.[215] Precarious employment structures further limit long-term stability, underscoring the need for balanced development to distribute benefits beyond elite guiding roles.[216]Geopolitical Significance
Border Disputes and Conflicts
The Himalayan region encompasses several unresolved border disputes primarily involving India with China, Pakistan, Nepal, and Bhutan, stemming from ambiguous colonial-era demarcations and post-independence territorial claims. These conflicts center on the Line of Actual Control (LAC) between India and China, spanning approximately 3,488 kilometers across the western (Aksai Chin) and eastern (Arunachal Pradesh) sectors, as well as high-altitude zones like the Siachen Glacier between India and Pakistan. Tensions arise from differing interpretations of historical treaties, strategic military advantages, and resource control, leading to military standoffs, incursions, and occasional fatalities without formal resolution.[217][218] The Sino-Indian border dispute escalated into full-scale war from October 20 to November 21, 1962, when Chinese forces advanced into Aksai Chin—a barren plateau India claims as part of Ladakh—and the North-East Frontier Agency (now Arunachal Pradesh), capturing key positions before unilaterally withdrawing from the eastern sector while retaining control of Aksai Chin, which China views as vital for linking Xinjiang and Tibet. India maintains that Aksai Chin was historically part of Jammu and Kashmir, while China asserts sovereignty based on traditional boundaries, rejecting the McMahon Line in the east as an invalid colonial imposition. Subsequent clashes include the 1967 Nathu La and Cho La incidents in Sikkim, where artillery exchanges resulted in hundreds of casualties on both sides, and the 1975 Tulung La ambush killing four Indian soldiers. More recently, the June 15, 2020, Galwan Valley clash along the LAC in Ladakh saw hand-to-hand combat kill 20 Indian troops and an undisclosed number of Chinese personnel, marking the deadliest confrontation in decades and prompting infrastructure buildup on both sides.[219][218][220] In the northwest Himalayas, the Siachen Glacier dispute pits India against Pakistan over a 70-kilometer-long glacier at altitudes exceeding 6,000 meters, the world's highest battlefield. The conflict originated from the 1949 Karachi Agreement and 1972 Simla Agreement, which demarcated the ceasefire line up to NJ9842 but left the glacier's status undefined; Pakistan interpreted it to extend northward, while India launched Operation Meghdoot on April 13, 1984, securing the glacier's dominating ridges and passes like Sia La and Bilafond La before Pakistani forces could respond. Since then, India has maintained control despite extreme conditions causing more deaths from avalanches and hypoxia than combat, with a ceasefire holding since 2003 amid periodic violations. Pakistan contests Indian presence as an occupation of its territory, but India's preemptive action prevented Pakistani dominance over strategic heights overlooking the region.[221][222][223] Tri-junction disputes further complicate the landscape, as seen in the 2017 Doklam standoff at the Bhutan-India-China border, where Chinese construction of a road on the Doklam plateau—claimed by Bhutan but asserted by China as part of its territory—prompted Indian troop intervention on June 16, 2017, to protect Bhutan's sovereignty and the Siliguri Corridor. The 73-day face-off ended with mutual disengagement on August 28, 2017, without altering positions, though China has continued incremental encroachments. Similarly, the India-Nepal dispute over Kalapani, Lipulekh, and Limpiyadhura involves a 370-square-kilometer area along the Kali River in the western Himalayas; Nepal claims it based on the 1816 Treaty of Sugauli, arguing the river's source lies at Limpiyadhura, while India administers the region since establishing a post during the 1962 Sino-Indian War and inaugurated a road through Lipulekh Pass in May 2020, prompting Nepal to amend its constitution with a new map incorporating the territories. These disputes persist without demarcation, exacerbated by China's growing influence in Nepal and Bhutan.[224][225][226][227]Strategic Military Infrastructure
India and China have significantly expanded military infrastructure along the Line of Actual Control (LAC) in the Himalayas since the 2020 Galwan Valley clash, driven by the need for rapid troop deployment and logistics in extreme high-altitude conditions exceeding 15,000 feet.[200] India's Border Roads Organisation (BRO) has constructed over 4,700 kilometers of strategic roads, tunnels, airstrips, and helipads across Ladakh, Uttarakhand, Sikkim, and Arunachal Pradesh to counterbalance China's advances, enabling faster mobilization of artillery, tanks, and infantry.[228] These developments reflect a mutual escalation where infrastructure serves dual civilian-military purposes but primarily enhances forward positioning amid unresolved border claims spanning approximately 3,488 kilometers.[229] India's key projects include the Sela Tunnel, a 2.6-kilometer all-weather passage at 13,000 feet on the Tezpur-Tawang road in Arunachal Pradesh, inaugurated in March 2024 to provide year-round access to forward bases near the LAC despite heavy snowfall.[230] In Ladakh, the BRO completed a motorable road at Mig La Pass in October 2025, reaching 19,400 feet—the world's highest—to support logistics for troops overlooking the LAC.[231] Additional tunnels, such as the planned Shinku La project at 16,580 feet linking Zanskar Valley to Himachal Pradesh, aim to bypass vulnerable passes like Zoji La, reducing travel time from days to hours for reinforcements.[232] These efforts sustain around 90,000 troops with systems like K9 Vajra howitzers, addressing logistical challenges where oxygen scarcity and sub-zero temperatures historically limited operations to seasonal windows.[229] China's People's Liberation Army (PLA) has pursued a "gray-zone" strategy on the Tibetan Plateau, constructing hundreds of xiaokang (well-off) villages since 2020 along the LAC, which double as potential military outposts with rapid-access roads and helipads for troop surges.[233] A new railway line, operational by late 2025, connects Tibet's interior to areas near Lhasa and the LAC, facilitating armored vehicle transport and supply lines over terrain where prior infrastructure lagged, though still constrained by thin air and permafrost.[234] High-altitude airfields and upgraded highways in Tibet enable PLA reinforcements, as seen in 2024 incursions up to 37 miles into disputed areas, underscoring Beijing's aim to dominate logistics while avoiding full-scale conflict.[235] In the western Himalayas, the Siachen Glacier—controlled by India since Operation Meghdoot in 1984—hosts the world's highest battlefield, with Indian posts on the Saltoro Ridge at altitudes up to 22,000 feet preventing Pakistan-China territorial linkage.[236] Infrastructure includes a base camp at 12,000 feet in Partapur, extensive track networks, all-terrain vehicle bridges developed by DRDO, and heavy-lift helicopter pads for sustaining 102 Infantry Brigade amid avalanches and -50°C temperatures.[236] Recent upgrades, including 4G/5G connectivity rolled out in January 2025, enhance real-time command while BRO roads bolster access, maintaining strategic denial despite high operational costs estimated at millions daily.[237][238]Regional Power Dynamics and Alliances
The Himalayan region serves as a critical geopolitical fault line, primarily defined by the rivalry between India and China, with territorial disputes spanning over 3,500 kilometers of contested borders. In the western sector, China administers approximately 38,000 square kilometers of Aksai Chin, claimed by India as part of Ladakh, a legacy of the 1962 Sino-Indian War where Chinese forces advanced through the area to secure a strategic road link to Xinjiang.[217] Further east, China asserts claims over Arunachal Pradesh, which India administers and views as integral territory, renaming places within it in 2023 to reinforce sovereignty amid ongoing incursions.[239] These disputes escalated in 2020 with the Galwan Valley clash, resulting in over 20 Indian and an undetermined number of Chinese casualties, prompting troop buildups and infrastructure races, though partial disengagements occurred by October 2024.[239] Pakistan's alignment with China amplifies tensions in the northwest Himalayas, particularly through the China-Pakistan Economic Corridor (CPEC), a component of China's Belt and Road Initiative that traverses the Karakoram range via Gilgit-Baltistan, a territory disputed between India and Pakistan. CPEC includes upgrades to the Karakoram Highway, with China investing around $2 billion by 2019 to rebuild a 160-mile stretch, enhancing connectivity but raising Indian concerns over encirclement and sovereignty violations in Kashmir.[240] This axis allows China access to the Arabian Sea, bypassing the Malacca Strait, while Pakistan gains infrastructure, though projects have strained its economy and environment in fragile Himalayan ecosystems.[241] India perceives this as a dual threat, combining Pakistan's historical Kashmir claims with China's expansionism. In the eastern Himalayas, smaller states navigate great-power pressures, with Bhutan maintaining a defense alliance with India under a 2007 treaty that obligates consultation on foreign policy and security, positioning Bhutan as a buffer against Chinese advances in areas like Doklam, where a 2017 standoff saw Indian troops intervene to prevent road construction.[242] Nepal, historically closer to India via open borders and trade, has pursued hedging strategies, accepting Chinese investments in hydropower and railways while protesting Indian maps incorporating disputed territories like Lipulekh in 2020, reflecting Kathmandu's efforts to assert sovereignty amid economic dependencies on both neighbors.[243] China's outreach, including proposals for a "Himalayan Quad" with Nepal, Pakistan, and Afghanistan, aims to counter Indian influence, though Nepal's terrain limits rapid integration.[244] These dynamics underscore the Himalayas' role in water security and military positioning, with rivers originating there sustaining over 1.9 billion people downstream.[245]Environmental Changes and Debates
Glacier Retreat and Mass Balance Data
The Hindu Kush-Himalaya (HKH) region contains approximately 55,000 glaciers covering over 60,000 km², though estimates vary due to mapping challenges in rugged terrain.[246] Empirical observations from satellite altimetry and in-situ measurements indicate heterogeneous glacier mass balance, with overall negative trends but regional anomalies. Geodetic mass balance assessments using ICESat and ASTER data for the period 2000–2016 reveal an average ice mass loss of about 16.3 ± 3.5 Gt/year across High Mountain Asia, equivalent to roughly -0.36 m water equivalent (w.e.) per year when normalized by glacier area.[247] In the central and eastern Himalayas, mass loss rates often exceed -0.5 m w.e./a, while the Karakoram range shows near-equilibrium or slight mass gains in some sub-periods, attributed to increased winter precipitation.[248] In-situ glaciological measurements on benchmark glaciers provide direct mass balance series. For instance, the Chhota Shigri Glacier in the western Himalaya recorded cumulative negative mass balances averaging -0.47 m w.e./a from 2002–2022, with reanalysis confirming nonlinear responses to temperature and precipitation variability.[249] Similarly, Pensilungpa Glacier in the Zanskar range exhibited an average annual mass balance of -0.46 m w.e. from 2016–2022, accompanied by terminus retreat of 6.4 m/a and equilibrium line altitude rise of 20 m.[250] Lake-terminating glaciers like Gepang Gath in the Chandra basin show amplified mass loss due to calving and subaqueous melting, with rates up to -1.0 m w.e./a in recent decades, exacerbated by proglacial lake expansion.[251] These measurements highlight that debris-covered tongues, common in the Himalaya, experience suppressed ablation at low elevations but overall contribute to net loss through reduced accumulation zones. Long-term reconstructions indicate accelerated mass loss since the Little Ice Age maximum around 1850, with Himalayan glaciers forfeiting at least 40% of their area and 390–586 Gt of ice volume by 2020, contributing 0.92–1.38 mm to sea-level rise.[252] However, retreat rates have decelerated in some monitored glaciers, such as Gangotri, from historical highs to 10–15 m/a in recent years, challenging narratives of uniform acceleration.[253] GRACE/GRACE-FO gravimetry data, adjusted for hydrological leakage, confirm post-2000 mass losses of 4–8 Gt/year in the Nepal Himalaya, though uncertainties persist from groundwater signals and model assumptions.[254] Regional syntheses underscore that while eastern sectors face higher deglaciation risks, western anomalies persist, with mass balance sensitivities varying by elevation and monsoon influence.[255]Land Use Changes and Deforestation
Forest cover across the Himalayan region has exhibited heterogeneous changes, with satellite-based assessments revealing net stability from 1992 to 2018 amid localized losses totaling nearly 10,000 km², predominantly in Nepal and India. [190] Between 1998 and 2008, forest area expanded by 4,983.65 km², largely through conversion from shrubland and cropland, but contracted by 4,732.71 km² from 2008 to 2018, reflecting cycles influenced by policy interventions and human pressures. [256] In the Nepalese Lesser Himalayas, community forestry programs have driven forest recovery, increasing extent and density over the past three decades, with over 80% of streamflow in the region tied to these recovering watersheds. [257] Deforestation rates vary by country and management status, with unprotected temperate forests experiencing annual losses of 0.5% in Bhutan and 0.6% in Nepal from 2000 to 2014, compared to higher rates in India and China. [258] In Bhutan's case, constitutional mandates require at least 60% forest cover, contributing to sustained low degradation. [259] Eastern Himalayan foothills in India lost 581.92 km² of forest from 1990 to 2024, driven by encroachment and agriculture, while the Garhwal region saw annual forest cover decline rates of 0.22% (1976–1998) and 0.27% (1998–2014). [260] [261] Primary drivers include population growth fueling fuelwood collection and agricultural expansion, alongside infrastructure development; for instance, in Pakistan's western Himalayas, biotic pressures like grazing and illicit logging have fragmented forests, with shrubland-to-forest transitions accounting for 68.8% of gains since 2000 in Nepal. [262] [263] Glacial retreat has amplified land use shifts, increasing barren land by 30% and grasslands by 10% (totaling 3,433 km²) in higher elevations, often converting former ice-covered areas unsuitable for forests. [264] These changes have heightened fragmentation, with 32,323 ha lost overall in studied management regimes at an annual rate of 2,938 ha (0.8%). [259]Attribution to Natural Variability vs. Anthropogenic Factors
Himalayan glaciers have exhibited retreat since the end of the Little Ice Age around 1850, with mass loss rates accelerating in recent decades, though long-term context reveals fluctuations tied to natural climate variability rather than solely unprecedented anthropogenic forcing. Studies indicate that while contemporary retreat averages 10-15 meters per year regionally, satellite observations show the majority of glaciers stable, a minority shrinking, and some advancing, challenging narratives of uniform catastrophic melt. This variability aligns with historical patterns, including advances during cooler periods and retreats during warmer interstadials, suggesting a component of natural recovery from the Little Ice Age's cooler conditions. Attribution models incorporating North Atlantic sea surface temperature anomalies, linked to multidecadal ocean oscillations, explain significant portions of mass balance variability in the northeastern Tibetan Plateau, underscoring the role of internal climate modes over external forcings alone.[253][265][252][266] Anthropogenic factors contribute through regional warming, estimated at 1-2°C since pre-industrial times, amplified in high elevations, but causal chains are complicated by local pollutants like black carbon (BC) from biomass burning and industrial emissions in South Asia. BC deposition reduces snow albedo, accelerating melt by absorbing solar radiation, with studies attributing up to 39% of glacier mass loss in the Tibetan Plateau to this short-lived aerosol, comparable to or exceeding CO2's radiative impact in the region due to its direct surface forcing. Unlike long-lived greenhouse gases, BC's atmospheric lifetime of weeks allows for rapid mitigation via emission controls, yet mainstream attributions often prioritize global CO2 narratives, potentially downplaying these proximal, human-sourced drivers amid institutional biases favoring systemic climate models over localized empirical forensics. Empirical data from ice cores and modeling reveal BC's effects compound with dust, altering seasonal runoff independent of broader tropospheric warming.[267][268][269] Debates persist due to data gaps and modeling uncertainties, with some analyses showing glacier numbers increasing by ~11% in Nepal from 1980 to 2010 via fragmentation rather than wholesale disappearance, and retreat rates varying by subregion—faster in monsoon-influenced western Himalayas but stable or surging in others. First-principles assessment favors disentangling forcings: while anthropogenic GHGs elevate baseline temperatures, natural variability (e.g., solar irradiance cycles, monsoon dynamics) and episodic events like cloudbursts explain much intermittency, with overreliance on equilibrium climate sensitivity models risking conflation of correlation with causation. Sources emphasizing anthropogenic dominance, often from academia with documented left-leaning institutional pressures, warrant scrutiny against satellite-derived mass balance records that reveal no uniform "tipping point" but rather heterogeneous responses modulated by topography and precipitation shifts. Integrated assessments highlight that reducing regional BC could yield faster glacier stabilization than CO2 cuts alone, prioritizing actionable causality over aggregated global attributions.[270][271][272]Conservation Efforts
Protected Areas and National Parks
The Himalayas encompass a network of protected areas, including national parks, conservation areas, and biosphere reserves, spanning India, Nepal, Bhutan, Pakistan, and China, which collectively cover approximately 40% of the Hindu Kush Himalaya region's land area and safeguard critical habitats for endemic species amid rapid environmental pressures. These designations, often managed by national governments with international oversight from bodies like UNESCO, prioritize habitat preservation, biodiversity monitoring, and sustainable resource use, though enforcement varies due to geopolitical tensions and local livelihoods dependent on grazing and collection. Transboundary initiatives, such as the Kangchenjunga Conservation Area linking Nepal and India, exemplify cooperative efforts to address shared ecosystems.[273][274] In Nepal, Sagarmatha National Park, established on July 19, 1976, spans 1,148 km² in the Khumbu region and includes Mount Everest (8,848 m), glaciers, and alpine valleys, serving as a core zone for snow leopard and Himalayan tahr conservation while designated a UNESCO World Heritage Site in 1979 for its outstanding universal value in geological and biological features.[275][276] The Annapurna Conservation Area, Nepal's largest at 7,629 km² and established in 1992, integrates community-based management under the National Trust for Nature Conservation, protecting diverse elevations from subtropical forests to high-altitude meadows and supporting over 100,000 residents through ecotourism revenues that fund anti-poaching and habitat restoration.[277][278] Other Nepalese sites include Langtang National Park (1,710 km², central Himalayas) and Kanchenjunga Conservation Area (2,035 km²), focusing on rhododendron forests and transboundary wildlife corridors.[279] India's protected areas feature the Great Himalayan National Park Conservation Area in Himachal Pradesh, inscribed as a UNESCO World Heritage Site in 2014, covering 754.5 km² of core temperate forests and hosting 805 vascular plant species alongside rare fauna like the western tragopan pheasant, with strict no-development zones to maintain ecological integrity.[280] Nanda Devi National Park, established in 1982 and part of a UNESCO World Heritage Site since 1988 (expanded to include Valley of Flowers), encompasses 630 km² around the 7,817 m Nanda Devi peak, functioning as a biosphere reserve core for over 300 bird species and endangered mammals such as the musk deer, though access restrictions limit human impact.[281][282] In the eastern sector, Khangchendzonga National Park (1,784 km², Sikkim) links with Nepalese areas to protect the world's third-highest peak and associated biodiversity hotspots.[283] Bhutan's Himalayan parks, such as Jigme Dorji National Park (4,789 km², established 1974), integrate sacred sites with conservation to preserve black-necked cranes and takin, emphasizing low-impact governance aligned with Gross National Happiness principles. Pakistan's Khunjerab National Park in the Karakoram-Himalaya transition guards ibex and Marco Polo sheep across 2,261 km², while China's Qomolangma (Everest) National Park mirrors Sagarmatha efforts on the Tibetan side. These areas collectively mitigate deforestation and poaching but face challenges from climate-driven shifts, requiring evidence-based adaptive management over ideologically driven policies.[284]| Protected Area | Country | Area (km²) | Establishment Year | Key Features |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Sagarmatha National Park | Nepal | 1,148 | 1976 | Mount Everest, UNESCO site, snow leopard habitat[275] |
| Annapurna Conservation Area | Nepal | 7,629 | 1992 | Largest in Nepal, community-managed, diverse elevations[277] |
| Great Himalayan National Park | India | 754.5 (core) | 1984 (park), 2014 (UNESCO) | Temperate forests, 805 plant species[280] |
| Nanda Devi National Park | India | 630 | 1982 | Biosphere core, high-altitude biodiversity, restricted access[281] |
| Jigme Dorji National Park | Bhutan | 4,789 | 1974 | Sacred landscapes, endemic ungulates[284] |












