Recent from talks
Nothing was collected or created yet.
Cumans
View on WikipediaThe Cumans or Kumans[a][3][4] were a Turkic[3][5][6][7] nomadic people from Central Asia comprising the western branch of the Cuman–Kipchak confederation who spoke the Cuman language. They are referred to as Polovtsians (Polovtsy) in Rus' chronicles, as "Cumans" in Western sources, and as "Kipchaks" in Eastern sources.[8]
Key Information
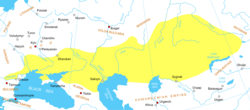
Related to the Pechenegs,[9] they inhabited a shifting area north of the Black Sea and along the Volga River known as Cumania, from which the Cuman–Kipchaks meddled in the politics of the Caucasus and the Khwarazmian Empire.[10]: 7 The Cumans were fierce and formidable nomadic warriors of the Eurasian Steppe who exerted an enduring influence on the medieval Balkans.[11]: 116 [12] They were numerous, culturally sophisticated, and militarily powerful.[13]: 13
Many eventually settled west of the Black Sea, influencing the politics of Kievan Rus', the Galicia–Volhynia Principality, the Golden Horde Khanate, the Second Bulgarian Empire, the Kingdom of Serbia, the Kingdom of Hungary, Moldavia, the Kingdom of Georgia, the Byzantine Empire, the Empire of Nicaea, the Latin Empire, and Wallachia, with Cuman immigrants becoming integrated into each country's elite.[14]: 281 The Cumans played a role in the creation of the Second Bulgarian Empire.[10][15]: 50 Cuman and Kipchak tribes joined politically to create the Cuman–Kipchak confederation.[13]: 7
| History of the Turkic peoples pre–14th century |
|---|
 |
After the Mongol invasion of Kievan Rus' in 1237, many Cumans sought asylum in the Kingdom of Hungary, as many of them had already settled there in the previous decades. The Cumans also played an important role in the Second Bulgarian Empire, the Byzantine Empire, the Latin Empire, and the Nicaea Empire's Anatolia.[10]: 2 [14]: 283 [16][17]
The Cuman language is attested in some medieval documents and is the best-known of the early Turkic languages.[7]: 186 The Codex Cumanicus was a linguistic manual written to help Catholic missionaries communicate with the Cuman people.
Names and etymology
[edit]Cuman
[edit]Cuman appears in ancient Roman texts as the name of a fortress or gate. The Roman natural philosopher Pliny the Elder (who lived in the 1st century AD) mentions "a fortress, the name of which is Cumania, erected for the purpose of preventing the passage of the innumerable tribes that lay beyond" while describing the "Gates of Caucasus" (Derbent, or Darial Gorge).[18] The Greek philosopher Strabo (died c. 24 AD) refers to the Darial Gorge (also known as the Iberian Gates or the Caucasian Gates) as Porta Caucasica and Porta Cumana.[19]
The original meaning of the endonym Cuman is unknown. It is also often unclear whether a particular name refers to the Cumans alone or to both the Cumans and the Kipchaks, as the two tribes often lived side by side.[10]: 6
Most other Turkic-speaking people (as well as most Muslim sources) called the Cumans some variant of "Qipchaqs", while Armenians called them "Xartesk'ns". Qumans were primarily used by Byzantine authors (and a few Arab sources), while the name used in Rus' tended to be "Polovtsian".[20]
In Turkic languages qu, qun, qūn, quman or qoman means "pale, sallow, cream coloured", "pale yellow", or "yellowish grey".[21]: 51 [22] While it is normally assumed that the name referred to the Cumans' hair, Imre Baski—a prominent Turkologist—has suggested that it may have other origins, including:
- the color of the Cumans' horses (i.e. cream tones are found among Central Asian breeds such as the Akhal-Teke);
- a traditional water vessel, known as a quman; or
- a Turkic word for "force" or "power".[23]
Observing that the Hungarian exonym for Cumans—i.e. Kun, Kunok—appeared as Cunus, Cuni in the chronicles and was applied to earlier nomads such as Pechenegs or Oghuzes, György Györffy derived Kun from Huns, instead of Qun, which he kept separate from Kun. However, István Vásáry rejected Györffy's hypothesis and contended that "the Hungarian name of the Cumans must go back to one of their self-appellations, i.e. to Qun." In the Hypatian Codex, a certain individual is called Kuman, while in the parallel account of the Laurentian Codex he is called Kun ("Polovčinu menem Kunui", Vásáry considers this a corruption of Kunu, Russian dative of Kun).[10]: 5
Cumania
[edit]Even after the Cumans were no longer the dominant power in their territory, people still referred to the area as Cumania. The Moroccan traveler, Ibn Battuta (1304 – c. 1369), said of Cumania: "This wilderness is green and grassy with no trees, nor hills, high or low ... there is no means of travelling in this desert except in wagons." The Persian historian Hamdallah Mustawfi (1281–1349) wrote that Cumania has a cold climate and that it has excellent pasturage and numerous cattle and horses.[7]: 40 The 14th-century Travels of Sir John Mandeville, note that Cumania
is one of the great kingdoms in the world, but it is not all inhabited. For at one of the parts there is so great cold that no man may dwell there; and in another part there is so great heat that no man may endure it ... And the principal city of Comania is clept [called] Sarak [Serai], that is one of the three ways for to go into India. But by that way, he may not pass no great multitude of people, but if it be in winter. And that passage men clepe the Derbend. The other way is for to go from the city of Turkestan by Persia, and by that way be many journeys by desert. And the third way is that cometh from Comania and then to go by the Great Sea and by the kingdom of Abchaz ... After that, the Comanians that were in servage in Egypt, felt themselves that they were of great power, they chose them a soldan [sultan] amongst them, the which made him to be clept Melechsalan. And in his time entered into the country of the kings of France Saint Louis, and fought with him; and [the soldan] took him and imprisoned him; and this [soldan] was slain by his own servants. And after, they chose another to be soldan, that they clept Tympieman; and he let deliver Saint Louis out of prison for a certain ransom. And after, one of these Comanians reigned, that hight [was called] Cachas, and slew Tympieman, for to be soldan; and made him be clept Melechmenes.[24]
Polovtsy
[edit]In East Slavic languages (Russian, Ukrainian and Belarusian) the Cumans are known as the Polovtsy, derived from the Slavic root *polvъ "pale; light yellow; blonde".[25][26][failed verification]: 43 Polovtsy or Polovec is often said to be derived from the Old East Slavic polovŭ (половъ) "yellow; pale" by the Rus' people—all meaning "blond".[26][failed verification] The western Cumans, or Polovtsy, were also called Sorochinetses by the Rus'—apparently derived from the Turkic sary chechle "yellow-haired". A similar etymology may have been at work in the name of the Śārī, who also migrated westward ahead of the Qun.[27][full citation needed]
However, according to O. Suleymenov polovtsy may come from a Slavic word for "blue-eyed", i.e. the plȃv (пла̑в) means "blue",[28] but this word also means "fair, blonde" and is a cognate of the above; cf. Eastern Slavic polovŭ.[29] Blonde individuals likely existed among the Kipchaks, yet anthropologically speaking the majority of Turkic peoples had East Asian admixture and generally Kimeks–Kipchaks were dark-haired and brown-eyed.[30] An alternative etymology of Polovtsy is also possible: the Slavic root *pȍlje "field", which would therefore imply that Polovtsy were "men of the field" or "men of the steppe" in contrast to the Lipovtsi.
The Polish term Połowcy was directly borrowed from the neighbouring East Slavic languages, though the term Kumanowie is also common. Both are used interchangeably in Polish-language sources.[2]
Folban, Vallani, Valwe
[edit]In Germanic languages, the Cumans were called Folban, Vallani or Valwe—all derivatives of Proto-Germanic root *falwa- meaning "pale"[7]: 106 (> English "fallow").[31] In the German account by Adam of Bremen, and in Matthaios of Edessa, the Cumans were referred to as the "Blond Ones".[25]
Kipchak
[edit]As stated above, it is unknown whether the name Kipchak referred only to the Kipchaks proper, or to the Cumans as well. The two tribes eventually fused, lived together and probably exchanged weaponry, culture and languages; the Cumans encompassed the western half of the confederation, while the Kipchaks and (presumably) the Kangli/Kankalis (possibly connected to three Pecheneg tribes known collectively as Kangars) encompassed the eastern half. This confederation and their living together may have made it difficult for historians to write exclusively about either nation.[10]: 6
The Kipchaks' folk-etymology posited that their name meant 'hollow tree'; according to them, inside a hollow tree, their original human ancestress gave birth to her son.[32] Németh points to the Siberian qıpčaq "angry, quick-tempered" attested only in the Siberian Sağay dialect.[33] Klyashtorny links Kipchak to qovï, qovuq "unfortunate, unlucky"; yet Golden sees a better match in qïv "good fortune" and adjectival suffix -čāq. Regardless, Golden notes that the ethnonym's original form and etymology "remain a matter of contention and speculation".[34]
Tribes
[edit]Kievan Rus', Mamluk, Hungarian, and Chinese sources preserved the names of many Cuman-Kupchak tribal groupings:
- Altun-oba
- Arslan-opa
- Ay-opa
- Badač
- Barat ~ Beret ~ Baraq,
- Baya(w)ut,
- Burčoğlı (R. Burchebichi; Hg. Borcsol),
- B.zângî ~ B.zânrî (< ? *Buranlı "stormy"),
- Jğrâq ~ Jğrât ~ Jqrâq < Čağraq? ~ Čoğraq? ~ Čağraq? ~ Čoğrat? (< čoğrat- "to boil"),[35]
- Čenegrepa (< Mong. čengkir "light blue, bluish"),
- Čitey(oğlı) (R. Chitѣyebichi),
- Čirtan ~ (*Ozur) Čortan (Hg. Csertan),
- Dorut ~ Dörüt ~ Dört,
- Enčoğlı ~ İlančuglı (Hg. Iloncsuk),
- İt-oğlı,
- Qitan-opa,
- Knn ~ Kyt (either corrupted from Köten, R. Kotianъ, Hg. Kötöny; or from Turkic tribal name Keyit, meaning "to irritate, to annoy"),
- Küčeba ~ Küčoba (R. Kouchebichi < küč "strength"),[36]
- Küčet (< küčet- "to urge to seize"),[37]
- Kor ~ Qor (H. Kór),
- Qara Börklü,
- Qay-opa (R. Kaepiči),[38]
- Qol-oba ~ Qul-oba (R. Kolobichi ~ Kulobichi, Ibn Xaldun: Qᵘlabaoğlı[39]),
- Qmngû/Qumanlu, Qonğuroğlı (H. Kongur),
- Mekrüti ~ Bekrüti ~ Bekürte (< bekürt- "заставлять, укрепить, усилить")[40],
- Mingüzoğlı ,
- Orunqu(t) (< Mong. oroŋğu "small, brown-colored gazelle"),
- Ölberli(ğ) ~ Ölperli(ğ) (Ar. al-b.rlū ~ al-b.rlī, R. Olperliu(i.e.)ve, Olbѣry, Olьbery, Ch. Yuliboli (玉里伯里), Lt. reges Uilperitorum, from Mg. ölöbür "ill, infirm" or Tk. *alp-erlü),[41]
- Ören ~ Uran ~ Oyren ( < cognate ören "bad, wicked, evil"[42] or Mong. oyren "artist, craftsman"[43]),
- Pečeneg,
- Shanmie gumali (苫滅古麻里),
- Tarğıl (R. Targolove < tarğıl- "of cattle or other animals, 'striped'."),[44]
- Tarew (R. Tarьevskyi),
- Terter ~ Teriter-oba (R. Terьterobichi),
- Toqsoba (R. Toksobichi),
- Tğ Yšqût (*Tağ Bašqurt? or Tuğ Bašqurt),
- Ulašoğlı (R. Ulashebichi; Hg. Olás),
- Urus-oba (R. Ourusoba; from endonym *Aoruša of Turkicized Alans, compare Greek: Αορσοι[45] or from Turkic root urus- "to fight," i.e. "soldier" [46] (cf. Middle Turkic uruş "quarrel, fight, battle, war"[47])),
- Yimek ~ Yemek (R. Polovtsi Yemiakove),
- Yete-oba (R. Yetebichi),
- Yuğur,[48]
- Moguty,
- Tatrany,
- Revugy,
- Shelьbiry,
- Topchaki,
- Elьborili,
- Bekoba,
- Quyçı (R. Куичия, Kuichiya, meaning "shepherd"[49]),[50][51]
- etc.
Seven Cuman tribes eventually settled in Hungary, namely:[14]: 280, 511 [52]
- Toqsoba (meaning either "plump leather bottle", "tribe of the dusty steppe", or "nine clans" [compare Toquz Oghuz "nine tribes"]),
- Borcsol ("Pepper Sons"),
- Csertan ("pike"),
- Olás ("union, federation"),
- Kór ~ Kól ("little, few"),
- Iloncsuk ("little snake"), and
- Koncsog ("leather trouser").
Baskakov thought that the Moguty, Tatrany, Revugy, Shelьbiry, and Topchaki belonged to the Chorni Klobuky.[53]
History
[edit]Origins
[edit]
The original homeland of the Cumans is unknown before their eventual settlement in the Eurasian steppe's western part.
Qun
[edit]Chinese authors mentioned a Tiele tribe named 渾 (Mand. Hún (< MC *ɦuon), possibly a transcription of underlying *Qun) located north of the Tuul River.[54][55] The writings of al-Marwazi (c. 1120) state that a Turkic "Qun" people came from the northern Chinese borders—"the land of Qitay" (possibly during a part of a migration from further east). After leaving the lands of the Khitans (possibly due to the Khitans' expansion[56]: 199 ), the Qun entered the territory of the Śari people,[b] whom the Quns expelled. Marwazi wrote that the Qun were Nestorian Christians.[59][10]: 4–5
Golden surmises that these Quns might have sprung "from that same conglomeration of Mongolic peoples from which the Qitañ sprang";[60] however, Golden later suggests that the Quns were Turkic.[61] Despite this, it is possible that certain tribes forming a part of the Cuman–Kipchak conglomerate were of Mongolic origin. Golden considers the Ölberli to have originally been Mongolic-speaking and argues that they were pushed westwards as a result of socio-political changes among the Khitans.[62]
The Syrian historian Yaqut (1179–1229) also mentions the Qun in The Dictionary of Countries, where he notes that "(the sixth iqlim) begins where the meridian shadow of the equinox is seven, six-tenths, and one-sixth of one-tenth of a foot. Its end exceeds its beginning by only one foot. It begins in the homeland of the Qayi, Qun, Khirkhiz, Kimak, at-Tagazgaz, the lands of the Turkomans, Fārāb, and the country of the Khazars."[14]: 279 [63] The Armenian historian, Matthew of Edessa (died 1144), also mentioned the Cumans, using the name χarteš, meaning "blond", "pale", "fair".[64]: 173 [65]
Kipchak relationship
[edit]It cannot be established whether the Cumans conquered the Kipchaks, if the Śari whom the Quns had defeated were to be identified as Kipchaks,[66][67] or whether they simply represent the western mass of largely Kipchak-Turkic speaking tribes.[68] The Quns and Śari (whom Czeglédy (1949:47-48,50) identifies with Yellow Uyghurs[58]) were possibly induced into the Kimek union or took over said union and absorbed the Kimek. As a result, the Kipchaks presumably replaced the Kimeks as the union's dominant group, while the Quns gained ascendancy over the westernmost tribes and became Quman (though difficulties remain with the Qun-Cuman link and how Qun became Cuman, e.g. qun + man "the real Quns"? > *qumman > quman?). Kimeks were still represented amongst the Cuman–Kipchaks as Yimek ~ Yemek.[69]
Potapov writes that:
... during the period from the end of the 800s to 1230 AD [the Cumans] spread their political influence in the broad steppes from Altai to Crimea and Danube. Irtysh with its adjoining steppes (at least below the lake Zaisan) was in the sphere of that confederation. Members of the confederation undoubtedly also were the ancestors of the present Kumandy [in Altai] and Teleuts, which is evidenced by their language that like the language of the Tobol-Irtysh and Baraba Tatars belongs to the Kypchak group.[citation needed]
Conquests
[edit]The Cumans entered the grasslands of the present-day southern Russian steppe in the 11th century AD and went on to assault the Byzantine Empire, the Kingdom of Hungary, the Principality of Pereyaslavl and Kievan Rus'. The Cumans' entry into the area pressed the Oghuz Turks to shift west, which in turn caused the Pechenegs to move to the west of the Dnieper River.[7]: 186 Cuman and Rus' attacks contributed to the departure of the Oghuz from the steppes north of the Black Sea.[7]: 114 Mahmud al-Kashgari, writing in 1076, says that in the east Cuman territory bordered a town near Talas.[14]: 278 The Cumans first entered the Bugeac (Bessarabia) at some point around 1068–1078. They launched a joint expedition with the Pechenegs against Adrianople in 1078. During that same year the Cumans were also fighting the Rus'.[7]: 116 The Russian Primary Chronicle mentions Yemek Cumans who were active in the region of Volga Bulgaria.[14]: 279, 282
Political organization
[edit]The vast territory of the Cuman–Kipchak realm consisted of loosely connected tribal units that represented a dominant military force but were never politically united by a strong central power; the khans acted on their own initiative. The Cuman–Kipchaks never established a state, instead forming a Cuman–Kipchak confederation (Cumania/Desht-i Qipchaq/Zemlja Poloveckaja (Polovcian Land)/Pole Poloveckoe (Polovcian Plain)),[10]: 7 which stretched from the Danube in the west to Taraz, Kazakhstan in the east.[14]: 283 This was possibly due to their facing no prolonged threat before the Mongol invasion, and it may have either prolonged their existence or quickened their destruction.[70]
Robert Wolff states that it was discipline and cohesion that permitted the Cuman–Kipchaks to conquer such a vast territory.[56]: 201 Al-Idrīsī states that Cumania got its name from the city of Cumania; he wrote, "From the city of Khazaria to the city of Kirait is 25 miles. From there to Cumanie, which has given its name to the Cumans, it is 25 miles; this city is called Black Cumania. From the city of Black Cumania to the city of Tmutorakan (MaTlUqa), which is called White Cumania, it is 50 miles. White Cumania is a large inhabited city ... Indeed, in this fifth part of the seventh section there is the northern part of the land of Russia and the northern part of the land of Cumania ... In this sixth part there is a description of the land of Inner Cumania and parts of the land of Bulgaria."[71]
According to the 12th-century Jewish traveler Petachiah of Regensburg "they have no king, only princes and royal families".[70] Cumans interacted with the Rus' principalities, Bulgaria, the Byzantine Empire, and the Wallachian states in the Balkans; with Armenia and the Kingdom of Georgia (see Kipchaks in Georgia) in the Caucasus; and with the Khwarezm Empire in Central Asia. The Cumans–Kipchaks constituted an important element and were closely associated with the Khwarazmian royal house via marital alliances.[72]: 31 The Cumans were also active in commerce with traders from Central Asia to Venice.[73]
The Cumans had a commercial interest in Crimea, where they also took tribute from Crimean cities. A major area of commerce was the ancient city of Sudak, which Ibn al-Air viewed as the "city of the Qifjaq from which (flow) their material possessions. It is on the Khazar Sea. Ships come to it bearing clothes. The Qifjiqs buy from them and sell them slaves. Burtas furs, beaver, squirrels..." Due to their political dominance, the Cuman language became Crimea's lingua franca. Thus the language was adopted by the Karaite Jewish and Crimean Armenian communities (who produced many documents written in Kipchak with the Armenian alphabet[64]: 176 ), where it was preserved for centuries up to the modern day.[72]: 31
Battles in Kievan Rus', in Hungary, and in the Balkans
[edit]
The Cumans first encountered the Rus' in 1055, when they advanced towards the Rus' Pereyaslavl principality, but Prince Vsevolod reached an agreement with them thus avoiding a military confrontation. In 1061, however, the Cumans, under the chieftain Sokal, invaded and devastated the Pereyaslavl principality; this began a war that would go on for 175 years.[7]: 116 [74][75] In 1068 at the Battle of the Alta River, the Cumans defeated the armies of the three sons of Yaroslav the Wise, Grand Prince Iziaslav I of Kiev, Prince Sviatoslav of Chernigov, and Prince Vsevolod of Pereyaslavl. After the Cuman victory, they repeatedly invaded Kievan Rus', devastating the land and taking captives, who became either their slaves or were sold at markets in the south. The most vulnerable regions were the Principality of Pereyaslavl, the Principality of Novgorod-Seversk and the Principality of Chernigov.[75]



The Cumans invaded and plundered the eastern part of the Kingdom of Hungary in 1091.[76] The invading Cumans were leading by chieftain Kapolcs, they broke first in Transylvania, then the territory between the Danube and Tisza rivers. The Cumans tried to leave Hungary with their loot and prisoners, but King Ladislaus I of Hungary reached and defeated them near the Temes river. After the battle, King Ladislaus offered the surviving Cumans a chance to accept Christianity in return for not being sold into slavery. The majority of them accepted, so the king settled them in Jászság. Once the news of the lost battle reached the Cuman camp, the Cumans threatened King Ladislaus with revenge and demanded to free the Cuman prisoners. King Ladislaus marched to the Hungarian border to prevent the next invasion. However, the two armies still clashed near Severin, resulting in a Hungarian victory. During the battle, King Ladislaus killed Ákos, the Cuman chieftain.[77]
The Cumans initially managed to defeat the Grand Prince Vladimir II Monomakh of Kievan Rus' in 1093 at the Battle of the Stugna River, but they were defeated later by the combined forces of Rus principalities led by Monomakh and were forced out of the Rus' borders to the Caucasus. In these battles some Pecheneg and Oghuz groups were liberated from the Cumans and incorporated into the Rus' border-guard system. Khan Boniak launched invasions on Kiev in 1096, 1097, 1105, and 1107.
In 1096, Boniak attacked Kiev and burned down the princely palace in Berestove; he also plundered the Kievan Cave Monastery. Boniak was defeated near Lubny in 1107 by the forces of the Kievan Rus' princes.[78] The Cumans led by Boniak crushed the Hungarian army led by Coloman in 1099 and seized the royal treasury. In 1109, Monomakh launched another raid against the Cumans and captured "1,000 tents".[14]: 282 In 1111, 1113, and 1116, further raids were launched against the Cumans and resulted in the liberation and incorporation of more Pecheneg and Oghuz tribes.
During this time, the Cumans raided the Byzantine Empire and Volga Bulgaria. Volga Bulgaria was attacked again at a later stage, by Khan Ayepa, father-in-law of Grand Prince of Kiev Yuri Dolgorukiy, perhaps at his instigation. The Volga Bulgars in turn poisoned Ayepa "and the other princes; all of them died."[14]: 282 [14]: 240 In 1089, Ladislaus I of Hungary defeated the Cumans after they attacked the Kingdom of Hungary. In 1091, the Pechenegs, a semi-nomadic Turkic people of the prairies of southwestern Eurasia, were decisively defeated as an independent force at the Battle of Levounion by the combined forces of a Byzantine army under Emperor Alexios I Komnenos and a Cuman army under Togortok/Tugorkan and Boniak. Attacked again in 1094 by the Cumans, many Pechenegs were again slain. Some of the Pechenegs fled to Hungary, as the Cumans themselves would do a few decades later. In 1091/1092 the Cumans, under Kopulch, raided Transylvania and Hungary, moving to Bihor and getting as far as the Tisza and Timiș rivers. Loaded with goods and prisoners they then split into three groups, after which they were attacked and defeated by King Ladislaus I.
In 1092, the Cumans resumed their raids against the Rus' and also attacked the Kingdom of Poland:[7]: 121 and reportedly reached northern cities located in Lithuania. In 1094-1095 the Cumans, led by Tugorkan, in support of the exiled Byzantine pretender Constantine Diogenes (as a pretext to plundering), invaded the Balkans and conquered the Byzantine province of Paristrion. The Cumans then advanced all the way to Adrianople and Anchialos but could not conquer them. In the following years, when knights of the First Crusade were passing through the empire, Byzantium offered the Cumans prestige titles and gifts in order to appease them; subsequently good relations ensued.[7]: 122 From 1097 to 1099, Sviatopolk II of Kiev requested help from the Cumans against Coloman, King of Hungary, who was involved in a feud with Volodar of Peremyshl, Prince of Przemyśl. King Coloman and his army crossed the Carpathian Mountains and laid siege on Przemyśl, which prompted David Igorevich, an ally of Volodar Rostislavich, to persuade the Cumans, under Khan Boniak and Altunopa, to attack the Hungarians.[79]
The Hungarian army was soundly crushed by the Cumans; the Illuminated Chronicle mentions that "rarely did Hungarians suffer such slaughter as in this battle."[7]: 124 [80] In 1104 the Cumans were allied with Prince Volodar. In 1106, the Cumans advanced into the Principality of Volhynia, but were repelled by Sviatopolk II. In 1114, the Cumans launched an invasion, from the western Romanian Plain, into the Byzantine Balkans once more. This was followed up by another incursion in 1123/1124. In 1135, the Cumans again invaded the Kingdom of Poland. During the second and third crusades, in 1147 and 1189, crusaders were attacked by Cumans, who were allied to the Asen dynasty of the Second Bulgarian Empire, or who were in Byzantine service.[7]: 124–128
Cumans at that time also resettled in the Kingdom of Georgia and were Christianized. There they achieved prominent positions, helped Georgians to stop the advance of Seljuk Turks, and helped make Georgia the most powerful kingdom of the region (they were referred to as naqivchaqari).[14]: 282 After the death of the warlike Monomakh in 1125, Cumans returned to the steppe along the Rus' borders. Fighting resumed in 1128; Rus' sources mention that Sevinch, son of Khan Boniak, expressed the desire to plant his sword "in the Golden gate of Kiev", as his father had done before him.[14]: 282

On 20 March 1155, Prince Gleb Yuryevich took Kiev with the help of a Cuman army under the Cuman prince Chemgura.[81] By 1160 Cuman raids into Rus' had become an annual event. These attacks put pressure on Rus' and affected trade routes to the Black Sea and Constantinople, in turn leading Rus' to again attempt action. Offenses were halted during 1166–1169, when Grand prince Andrey Bogolyubsky, son of Khan Ayepa's daughter, took control of Kiev in 1169 and installed Gleb as his puppet. Gleb brought in "wild" Cumans as well as Oghuz and Berendei units. Later, the princes of the Principality of Chernigov attempted to use Khan Konchek's army against Kievan Rus' and Suzdal. This Chernigov-Cuman alliance suffered a disastrous defeat in 1180; Elrut, Konchek's brother died in battle. In 1177, a Cuman army that was allied with Ryazan sacked six cities that belonged to the Berendei and Torkil. In 1183, the Rus' defeated a large Cuman army and captured Khan Kobiak (Kobek) as well as his sons and other notables.
Subsequently, Khan Konchek concluded negotiations. Like his son Khan Köten, preceding the Mongol invasion, Khan Konchek was successful in creating a more cohesive force out of the many Cuman groups—he united the western and eastern Cuman–Kipchak tribes. Khan Konchek also changed the old Cuman system of government whereby rulership went to the most senior tribal leader; he instead passed it on to his son Koten.[13]: 21, 22 Igor Svyatoslavich, prince of the Principality of Novgorod-Seversk, attacked the Cumans in the vicinity of the Kayala river in 1185 but was defeated; this battle was immortalized in the Rus' epic poem The Tale of Igor's Campaign, and Alexander Borodin's opera, Prince Igor. The dynamic pattern of attacks and counterattacks between the Rus' and the Cumans indicates that both rarely, if ever, were able to attain the unity needed to deal a fatal blow. The Cuman attacks on the Rus' often had Caucasian and Danubian European implications.[14]: 282
In the Balkans, the Cumans were in contact with all the statal entities. They fought with the Kingdom of Hungary, allied with the Bulgarians of the Second Bulgarian Empire (they were the empire's most effective military component)[26]: 24 and with the Vlachs against the Byzantine Empire. A variant of the oldest Turkic chronicle, Oghuzname (The Oghuz Khan's Tale), mentions the Cumans fighting the Magyars, Rus', Romanians (Ulak), and Bashkirs, who had refused to submit to their authority.[7]: 81

In alliance with the Bulgarians and Vlachs,[82] the Cumans are believed to have played a significant role in the uprising led by brothers Asen and Peter of Tarnovo, resulting in victory over Byzantium and the restoration of Bulgaria's independence in 1185.[83] István Vásáry states that without the active participation of the Cumans, the Vlakho-Bulgarian rebels could never have gained the upper hand over the Byzantines, and ultimately without the military support of the Cumans, the process of Bulgarian restoration could never have been realized.[10]: 73 [84]
The Cuman participation in the creation of the Second Bulgarian Empire in 1185 and thereafter brought about basic changes in the political and ethnic sphere of Bulgaria and the Balkans.[10]: xii The Cumans were allies in the Bulgarian–Latin Wars with emperor Kaloyan of Bulgaria. In 1205, at the Battle of Adrianople (1205), 14,000 Cuman light cavalry contributed to Kaloyan's crushing victory over the Latin Crusaders.[84]
Cuman troops continued to be hired throughout the 13th and 14th century by both the Bulgarians and Byzantines.[85] The Cumans who remained east and south of the Carpathian Mountains established a county named Cumania, which was a strong military base in an area consisting of parts of Moldavia and Wallachia.[15] This is corroborated by archeological findings which show a Cuman presence in the area, mostly in the south part of Moldavia, with their population estimated around 100,000.[86]
Mongol invasions
[edit]

Like most other peoples of medieval Eastern Europe, the Cumans put up a resistance against the relentlessly advancing Mongols led by Jebe and Subutai. The Mongols crossed the Caucasus mountains in pursuit of Muhammad II, the shah of the Khwarezmid Empire, and met and defeated the Cumans in Subcaucasia in 1220. The Cuman khans Danylo Kobiakovych and Yurii Konchakovych died in battle, while the other Cumans, commanded by Khan Köten, managed to get aid from the Rus' princes.[75]
As the Mongols were approaching Russia, Khan Köten fled to the court of his son-in-law, Prince Mstislav the Bold of Galich, where he gave "numerous presents: horses, camels, buffaloes and girls. And he presented these gifts to them, and said the following, 'Today the Mongols took away our land and tomorrow they will come and take away yours'." The Cumans were ignored for almost a year, however, as the Rus' had suffered from their raids for decades. But when news reached Kiev that the Mongols were marching along the Dniester River, the Rus' responded. Mstislav of Galich then arranged a council of war in Kiev, which was attended by Mstislav Romanovich, Prince Yuri II of Vladimir-Suzdal and Mstislav Svyatoslavich of Chernigov.
The princes promised support to Khan Koten's Cumans and an alliance between the Rus' and Cumans was formed. It was decided that the Rus' and Cumans would move east to seek and destroy any Mongols they found. The Rus' princes then began mustering their armies and moved towards the rendezvous point. The army of the alliance of the Rus' and Cumans numbered around 80,000. When the alliance reached Pereyaslavl, they were met by a Mongol envoy that tried to persuade them not to fight. This as well as a second attempt by the Mongols failed; the alliance then crossed the Dnieper River and marched eastward for nine days pursuing a small Mongol contingent, unknowingly being led by a false retreat. The battle took place near the Kalka River in 1223.
Due to confusion and mistakes, and the superb military tactics and fighting-qualities of the Mongols, the Rus' and Cumans were defeated. In the chaos the Cumans managed to retreat, but the Rus' failed to regroup and were crushed.[87]: 74 The Cumans were allied at Kalka River with Wallach warriors named Brodnics, led by Ploscanea.[citation needed] Brodnics' territory was in the lower parts of the Prut river in modern Romania and Moldova. During the second Mongol invasion of Eastern Europe in 1237–1240 the Cumans were defeated again; at this time groups of Cumans went to live with the Volga Bulgars, who had not been attacked yet.[87]: 44
Istvan Vassary states that after the Mongol conquest, "A large-scale westward migration of the Cumans began." Certain Cumans also moved to Anatolia, Kazakhstan and Turkmenistan.[64]: 174 In the summer of 1237 the first wave of this Cuman exodus appeared in Bulgaria. The Cumans crossed the Danube, and this time Tsar Ivan Asen II could not tame them, as he had often been able to do earlier; the only possibility left for him was to let them march through Bulgaria in a southerly direction. They proceeded through Thrace as far as Hadrianoupolis and Didymotoichon, plundering and pillaging the towns and the countryside, just as before. The whole of Thrace became, as Akropolites put it, a "Scythian desert."[10]: 81
A direct attack on Cumania came only in 1238–1239, and encountered serious resistance by various Cuman khans.[88] The final blow came in 1241, when Cuman control over the Pontic steppes ended and the Cuman–Kipchak confederation ceased to exist as a political entity, with the remaining Cuman tribes being dispersed, either becoming subjects and mixing with their Mongol conquerors, as part of what was to be known as the Golden Horde (Kipchak Khanate) and Nogai Horde, or fleeing to the west, to the Byzantine Empire, the Second Bulgarian Empire, and the Kingdom of Hungary, where they integrated into the elite and became kings and nobles with many privileges. Other Cuman captives were sold as slaves, who would go on to become Mamluks in Egypt, who would attain the rank of Sultan or hold regional power as emirs or beys. Some of these Mamluks led by Sultan Baibars would fight the Mongols again, defeating them at the Battle of Ain Jalut and the Battle of Elbistan.[87]: 58 [89]
A group of Cumans under two leaders named Jonas and Saronius, the former of whom was higher in rank, entered the Latin Empire of Constantinople as allies about 1240, probably fleeing the Mongols. The name Saronius (found in Alberic of Trois-Fontaines, who calls the leaders kings) is probably a corruption of the Cuman name Sïčgan, meaning "mouse". They assisted the Emperor Baldwin II in the capture of Tzurullon from the Nicaeans in that year. The following year the Christian daughters of Saronius married two of the leading noblemen of the empire, Baldwin of Hainaut and William of Meri, while Jonas's daughter married Narjot III de Toucy, who had once served as regent of the empire in Baldwin's absence. When Narjot died in 1241, his wife became a nun. Jonas died that same year and was buried in a tumulus outside Constantinople in a pagan ceremony. According to Aubrey, eight volunteer warriors and twenty-six horses were sacrificed at the funeral.[10]: 66
Settlement on the Hungarian plain
[edit]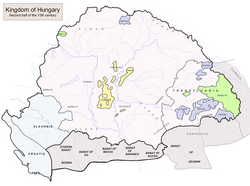
They became one of the important Turkic groups in Desht-i Kipchak region. After Kipchak unity was destroyed by the Mongol attack in 1239, one branch of the Cumans migrated to the Balkans, and another branch went down to the Anatolia. They later came into contact with Georgians, Hungarians and Turks.

The architect of the Georgian-Cuman relations was David IV of Georgia. This event, which was one of the most important military reforms of David's against the Seljuk invaders, took place when a high-level Georgian delegation visited the Cuman headquarters. To strengthen this alliance with the nomads, David married with Cuman King Atrak's daughter Guranduht, and invited her relatives to settle in Georgia.[90] David brokered a truce between the Kipchaks and Alans. Later on he has held some consultations with Vladimir II Monomakh, Grand Duke of Kiev who defeated Atrak in 1109, to ensure free passage of nomadic tribes into Georgia.
King Andrew II of Hungary granted the Burzenland region to the Teutonic Knights in 1211, with the purpose of ensuring security of the southeastern borders of his kingdom against the Cumans. The Teutonic Knights campaigned against the Cumans, on behalf of King Andrew, during the years of 1221–1225.[91][92] However, the Teutonic Knights failed to defeat the Cumans and began to establish a country independent of the King of Hungary. In 1238, after Mongol attacks on Cumania, King Béla IV of Hungary offered refuge to the remainder of the Cuman people under their leader Khan Köten, who in turn vowed to convert his 40,000 families to Christianity. King Béla hoped to use the new subjects as auxiliary troops against the Mongols, who were already threatening Hungary. The Cumans were joined by the Iranian Jasz people, who had been living with the Cumans.[21]: 44 Batu Khan of the Mongols then ordered Bela to stop giving refuge to the Cumans and made a particular point that if attacked the Cumans could easily run away, for they were skilled horseman, but not so for the Hungarians, who were a sedentary nation and had no such luxury. Bela rejected this ultimatum.
Around December 1240, news came that the Mongols were advancing towards Hungary. King Bela then installed front line defenses at the Carpathian Mountains, after which he returned to Buda and called a council of war and ordered unity against the Mongols. The opposite happened, however, as many of the barons were hostile towards the Cumans. The Hungarian barons noted that there were Cumans in the Mongol armies, but they did not realize that this was because they were conscripted into it and had no say in the matter. In particular the barons did not trust Köten, despite the fact that the Mongols had attacked his people for nearly 20 years. This chaos pushed Bela into a corner; feeling he needed to show his strength and keep the rebellious barons on his side, he ordered Köten to be placed under house arrest. This did not placate the barons and had an opposite effect of erroneously seeming to admit that the King harboured doubts about Köten, too. This angered the Cumans, who were far from happy about the actions taken against them, and who had done nothing to invite such actions and hated the Mongols. News arrived on 10 March that the Mongols had attacked the Hungarian defenses at the Carpathian passes. This prompted Bela to send a letter to Duke Frederick of Austria asking for help. Frederick had previously wanted Bela's throne, but Bela responded by amassing a vast army and marching to the gates of Vienna, which forced Frederick to step back. On 14 March, news had arrived that the Carpathian defense forces were defeated by the Mongols. Ironically, given the suspicion of the Cumans, they were the only ones who seemed willing to fight the Mongols, the memory of the fate that had befallen them on the steppes still being fresh in their minds. By this time Bela had lost control of his army and many towns were destroyed. Soon thereafter Frederick arrived, and, wishing to harm the country's defense (in revenge to Bela), he stirred up further feelings against the Cumans.

After crushing defeats and facing complete collapse, the Hungarians engaged in a suicidal betrayal of the Cumans, the people that had done the most in repelling the Mongols. Some of the barons went to Köten's house with the intent of killing him as scapegoat or handing him over to the Mongols, possibly believing the Cuman–Kipchaks were Mongol spies. However, the barons had Köten assassinated in Pest on 17 March 1241.[93][c] When news of this outrage reached the Cuman camp there was an eruption of "Vesuvian intensity". In revenge for this victimization they slaughtered a vast number of Hungarians.[11]: 117 [13]: 22 The Cumans then left for the Balkans and the Second Bulgarian Empire, going on a rampage of destruction through Hungary "equal to that which Europe had not experienced since the incursions of the Mongols".[15]: 37 [94]

With this departure of its only ally and most efficient and reliable military force,[26]: 43 [95] Hungary was now further weakened to attack, and a month later it was destroyed by the Mongols.[15]: 186 [64]: 173 After the invasion, King Béla IV, now penniless and humiliated after the confiscation of his treasury and loss of three of his border areas, begged the Cumans to return to Hungary and help rebuild the country.[15] In return for their military service, Béla invited the Cumans to settle in areas of the Great Plain between the Danube and the Tisza rivers; this region had become almost uninhabited after the Mongol raids of 1241–1242.[96] The Cuman tribes subsequently settled throughout the Great Hungarian Plain, creating two regions incorporating the name Cumania (Kunság in Hungarian): Greater Cumania (Nagykunság) and Little Cumania (Kiskunság). Six of these tribes were the Borchol (Borscol), who settled in county of Temes (the Borchol clan was also active around Rus'; they were also a tribe of the Golden Horde mentioned as Burcoylu); Csertan, who settled in Little Cumania; Olas, who settled in Greater Cumania; Iloncsuk, who settled in Little Cumania; Kor, who settled in the county of Csanad and the sixth being, possibly, Koncsog.[21]: 44 [64]: 174 [96]


As the Cumans came into the kingdom, the Hungarian nobility suspected that the king intended to use the Cumans to strengthen his royal power at their expense.[97]: 80 During the following centuries, the Cumans in Hungary were granted rights and privileges, the extent of which depended on the prevailing political situation. Some of these rights survived until the end of the 19th century, although the Cumans had long since assimilated with Hungarians. The Cumans were different in every way to the local population of Hungary—their appearance, attire, and hairstyle set them apart. In 1270, Elizabeth the Cuman, the daughter of a Cuman chieftain Seyhan,[10]: 99 [98][99] became queen of Hungary. Elizabeth ruled during the minority of her son (future king Ladislaus IV of Hungary) in the years of 1272–1277. A struggle took place between her and the noble opposition, which led to her imprisonment by the rebels; but supporters freed her in 1274.[100] During her reign, gifts of precious clothes, land, and other objects were given to the Cumans with the intent to ensure their continued support, and in particular during the civil war between King Béla IV and Stephen V of Hungary, when both sides tried to gain Cuman support. During this conflict, in 1264, Béla sent Cuman troops commanded by the chieftain Menk to fight his son Stephen.[97]: 82 [101]: 55 Elizabeth married Stephen V; they were parents of six children. Their son, Ladislaus IV became the king of Hungary while her other son, Andrew of Hungary, became Duke of Slavonia. By 1262, Stephen V had taken the title of 'Dominus Cumanorum' and became the Cumans' highest judge. After his enthronement, the Cumans came directly under the power of the king of Hungary and the title of 'Dominus Cumanorum' (judge of the Cumans) had passed to the count palatine, who was the highest official after the king. The Cumans had their own representatives and were exempt from the jurisdiction of county officials.[97]: 82


By the 15th century, the Cumans were permanently settled in Hungary, in villages whose structure corresponded to that of the local population, and they were Christianized. The Cumans did not always ally with the Hungarian kings—they assassinated Ladislaus IV; however, other sources suggest that certain Hungarian barons had a role in his murder, thus Ladislaus fell victim to his political enemies.[101]: 82 The royal and ecclesiastical authorities incorporated, rather than excluded, the Cumans. The Cumans served as light cavalry in the royal army, an obligation since they were granted asylum. Being fierce and capable warriors (as noted by Istvan Vassary), they had an important role in the royal army. The king led them in numerous expeditions against neighbouring countries; most notably they played an important part in the Battle on the Marchfeld between Rudolf of Habsburg and Ottokar II of Bohemia in 1278—King Ladislaus IV and the Cumans (which numbered 16,000)[64]: 173 were on Rudolf's side.
Hungarian kings relied on the Cumans to counterbalance the growing independent power of the nobility.[97]: 81 Royal policy towards the Cumans was determined by their military and political importance. The Hungarian kings continuously hoped to use Cuman military support, the main reason for the invitation to settle and continued royal favors to them. The kings' main aim was to secure Cuman loyalty by various means, including intermarriage between the Cumans and the Hungarian royal family.[97]: 81 Ladislaus IV "the Cuman" (whose mother was Queen Elizabeth the Cuman) was particularly fond of the Cumans and abandoned Hungarian culture and dress for Cuman culture, dress, and hairstyle; he lived with his Cuman entourage and concubines, who were Küpçeç, Mandola, and Ayduva.[64]: 173 [102]
There were clashes between the Hungarians and Cumans in 1280 and 1282. The first involved the king convincing the Cumans not to leave the country, yet a small group still moved to Wallachia. The second was a battle between Cuman rebels and the king's forces.[10]: 106 The Battle of Lake Hód was a battle between the Kingdom of Hungary and the Cumans in 1282 and King Ladislaus IV of Hungary defeated the Cumans. The Cumans initially lived in felt yurts, but as time went by they gradually gave up their nomadic way of life.[64]: 173 The head of Cuman clans served the dual role of a military leader and a judge. The Cumans, having their own jurisdiction, were exempt from Hungarian jurisdiction and appealed to the king only in cases of unsettled disagreements. The Cumans paid 3000 gold bullions a year to the king, as well as other products and animals (since King Béla IV). They had own priests and they were not paying port and custom dues. Cuman villages did not have landlords and thus no manors were established; this meant that the people of these villages bought off statute labour. The royal guard of the Hungarian kings were Cumans, called nyoger. From the 16th century onwards, the Cumans between the Danube and Tisza rivers were referred to as Kiskun, while who lived to the east of the Tisza river were referred to as nagykun.[64]: 173 The majority of Cumans were exterminated during the Great Turkish War.[103]


The Cumanians' settlements were destroyed during the Turkish wars in the 16th and 17th centuries; more Cumans than Hungarians were killed.[64]: 176 [105] Around 1702, Cuman and Jasz privileges were lost. The court sold all three districts to the Teutonic Knights, though the lordship of these three regions was returned to Hungary. In 1734, Karcag became a market town, due to the permission to organize fairs. During this time, it had bought off its borders as its own property for 43,200 Rhenish florins. On May 6, 1745, due to the cooperation between the Cumans and Jasz people, as well as their material strength of their communities, they were able to officially buy off their freedom by paying off more than 500,000 Rhenish florins and by arming and sending to camp 1,000 cavalry.[106] At the beginning of the 18th century, the Cumanian territories were resettled by Hungarian-speaking descendants of the Cumans.[107] In the middle of the 18th century, they got their status by becoming free farmers and no longer serfs.[17][108] Here, the Cumans maintained their autonomy, language, and some ethnic customs well into the modern era. According to Pálóczi's estimation, originally 70–80,000 Cumans settled in Hungary. Other estimations are 180–200,000.[64]: 173 [109]: 72

Today there are still villages in Turkey, Kazakhstan and Ukraine founded by Cumans.[110]
This prayer, which was translated into the Cuman language in order to Christianize Shamanist Cumans in Hungary, was recorded in the TRT Documentary Özü Türk program:
| Destroyed Cuman prayer from the original text | The prayer that was rearranged in accordance with the Cuman language because it was damaged | Modern Turkish |
|---|---|---|
| Bezén attamaz ken ze kikte
szénlészen szen ádon dösön szen küklön nitziegén gerde ali kékte bezén akomozne oknémezne ber gézge pitbütör küngön il bézen ménemezne neszem bezdede jermez bezge utro gergenge iltme bezne ol gyamanga kútkor bezne al gyamanna szen borszony bo kacsalli bo tson igyi tengere ammen. |
Bizim atamız kim-sing kökte Şentlensing sening adıng |
Bizim atamız ki sensin gökte Şenlensin senin adın |
Cuman involvement in Serbia
[edit]Cuman involvement in Serbia first occurred as a result of marital ties between Serbia and Hungary. King Stephen V of Hungary gave his daughter, Catherine (whose mother was Queen Elizabeth the Cuman, daughter of the Cuman chieftain Seyhan) in marriage to Stefan Dragutin, son of King Stefan Uroš I of Serbia. King Uroš had promised both his son and King Stephen that he would make Dragutin king during his own lifetime; but he later declined this. Dragutin, in disappointment, requested aid from King Stephen, who said he would lend his Hungarian and Cuman troops. Subsequently, Dragutin set out with his troops and marched on his father. King Uroš had declined once more, and in 1276 Dragutin clashed with his father's army in Gacko, winning the battle. Afterwards, Dragutin took the throne and became king of Serbia. After King Stephen's death, his son, Ladislaus IV the Cuman, continued to support Dragutin, his brother-in-law. From 1270 onwards Cuman mercenaries and auxiliaries were present on both sides of the warring factions, sometimes ignoring the orders of the party they were fighting for, instead acting on their own and looting the countryside. The Cumans had also burned down Žiča, the former see of the archbishopric of the Serbian Church.[10]: 99–101
By 1272, the region of Braničevo in Serbia had become a Hungarian banate, but soon afterwards, its rulers, Kudelin and Darman succeeded in making it an independent state. Kudelin and Darman were either Cuman warriors in Bulgarian service or Bulgarian nobles of Cuman origin. This move to independence had angered Ladislaus IV as well as Dragutin, who wanted to crush the rebellion. Darman and Kudelin were supported by the Tatars of the Golden Horde (Kipchak Khanate) against the Hungarians and Serbs. Subsequently, Dragutin attacked the brothers but failed to defeat them. After this attack the brothers hired Cuman and Tatar mercenaries. Dragutin in turn went to his brother, King Milutin for help. Dragutin battled the brothers again, this time with King Milutin's help as well as support from King Ladislaus IV (Cuman troops), and defeated them. After this King Ladislaus continued negotiations with Darman and Kudelin, but this had failed so he sent Transylvanian and Cuman troops against them. The Cumans had fought on both the Bulgarian and Hungarian-Serbian sides.[10]: 101–106
The Cumans were also involved with the semi-independent Bulgarian Tsardom of Vidin between 1290 and 1300, which had become a target of Serbian expansion. In 1280, a Bulgarian noble of Cuman origin, Shishman, became the ruler of Vidin. He was perhaps granted the position of despot of Vidin soon after the accession of another Bulgarian noble of Cuman origin, the Tsar George Terter I (r. 1280–1292), to the Bulgarian throne in 1280. Shishman was either a close relative or a brother of George Terter I.[112] Shishman may have established his authority over the Vidin region as early as the 1270s, after the death of the previous ruler of that area, Jacob Svetoslav.[113] Danilo, a Serbian archbishop, reported, "At that time in the land of the Bulgars a prince called Shishman emerged. He lived in the town of Vidin, and obtained the adjacent countries and much of the Bulgarian land." Some years after, Shishman invaded Serbia and got as far as Hvosno. After failing to capture Ždrelo, he returned to Vidin, which was subsequently attacked and devastated by King Milutin. However, Milutin replaced him on his throne on the basis that he would become Shishman's ally. In fact, the alliance was strengthened by Shishman marrying the daughter of the Serbian grand župan Dragos. Further security came about when Milutin later gave his daughter Anna as a wife to Shishman's son Michael, who in 1323 became Tsar of Bulgaria.[10]: 107
Golden Horde and Byzantine mercenaries
[edit]
The Cumans who remained scattered in the prairie of what is now southwest Russia joined the Mongol Golden Horde Khanate, and their descendants became assimilated with local populations including the Tatars. The cultural heritage of those Cuman–Kipchaks who remained was transferred to the Mongols, whose élite adopted many of the traits, customs, and language of the Cumans and Kipchaks; the Cumans, Kipchaks, and Mongols finally became assimilated through intermarriage and became the Golden Horde. Those Cumans, with the Turko-Mongols, adopted Islam in the second half of the 13th and the first half of the 14th century.[75]
The Cuman-Kipchaks, who were first seen in Byzantine resources in 1078, began to serve as mercenaries in the Byzantine army from the reign of Emperor Alexios I Komnenos.[114] In 1086 Cumans devastated Byzantine settlements in the Balkans. Later the Cumans joined the Pechenegs and the former Hungarian king, Salomon, in plundering the Byzantine Balkan provinces. Subsequent to this, the Cumans gave aid to Tatos, the chief of Distra. In 1091 there was a disagreement in plunder shares between the Cumans and Pechenegs, which resulted in a breach between the two peoples; this contributed to the Cumans (led by Togortok/Tugorkan and Boniak, who had repeatedly raided Kievan Rus') joining Alexios I Komnenos against the Pechenegs in the Battle of Levounion.[7]: 120
The Cumans invaded the Balkans a couple of weeks after the Battle of Kalka River large groups[115] Cumans invaded Thrace where they pillaged towns that had recently come under the control of the Nicaean Empire. This continued until 1242 when Nicaean emperor John III Doukas Vatatzes, in response to the situation, won their favour with "gifts and diplomacy". Later, he succeeded in settling a group of Cumans in Anatolia, in the Meander valley and the region east of Philadelphia, and another group in the regions of Anatolia near Constantinople.[116]
Cumans had served as mercenaries in the armies of the Byzantine Empire since the reign of Alexios I Komnenos (1081–1118)[6] and were one of the most important elements of the Byzantine army until the mid-14th century. They served as light cavalry (horse-archers) and as standing troops;[6] those in the central army were collectively called Skythikoi/Skythikon.[115] Other Cumans lived a more dangerous life as highlanders on the fringes of the empire, possibly being involved in a mixture of agriculture and transhumance, acting as a buffer between Nicaean farmers and Turkic nomads.
These Cumans were frequently mustered for Byzantine campaigns in Europe.[6] In 1242 they were employed by Vatatzes in his siege of Thessaloniki. In 1256 emperor Theodore II Laskaris left a force of 300 Cumans with the Nicaean governor of Thessaloniki. In 1259, 2000 Cuman light cavalry fought for the Nicaean Empire at the Battle of Pelagonia. Cumans were again involved in 1261, where the majority of the 800 troops under Alexios Strategopoulos that retook Constantinople, were Cumans. Large Cuman contingents were also part of the Byzantine Emperor Michael VIII Palaiologos' European campaigns of 1263–1264, 1270–1272 and 1275. Cumans were again employed by emperor Andronikos II Palaiologos in 1292, in his campaign against the Despotate of Epirus. The Cumans, together with Turk mercenaries, terminated the campaign by an unauthorized retreat.
In contrast to their light cavalry counterparts, Cuman standing troops appear as a distinct group only once, albeit very significantly.
An example of this influential group was Sytzigan (known as Syrgiannes after baptism), who before 1290 became Megas Domestikos (Commander-in-Chief of the Army) under Emperor Andronikos II.[115] His son, Syrgiannes Palaiologos, attained the title of Pinkernes and was a friend of Andronikos III Palaiologos and John Kantakouzenos. An act from the archive of the Lavra of Athanasios mentions Cuman Stratioti (mercenaries from the Balkans) in the region of Almopia who received two douloparoikoi in 'pronoia' (a Byzantine form of feudalism based on government assignment of revenue-yielding property to prominent individuals in return for military service) some time before 1184.[6][117]
Traces of Cumans in Anatolia
[edit]In 1239–1240, large groups of Cumans fleeing from the Mongols crossed the Danube. These groups wandered for a long time to find a suitable place to settle in Thrace. John III Doukas Vatatzes who wanted to prevent Cumans invasion of Empire of Nicaea lands and to benefit from their military capabilities invited Cumans in Empire of Nicaea service. He settled some of them in Thrace and Macedonia, and some in Anatolia to the Meander (Menderes) valley and some to the Phrygia and Bithynia.[116][118][119][120] These Cumans preserved their identity after the Ottomans conquered the lands they lived in.[121][122][123][124] It is accepted that some of the Cumans who settled in West Anatolia during the reign of Emperor John III Dukas Vatatzes of Nicaea are the ancestors of a part of the community called Manavs living in Northwest Anatolia today.[125][121][126][127][128][122][120][129][130]
Traces of Cumans in Romania
[edit]Toponyms pointing at a Cuman presence were preserved in names of villages and places in the Wallachian Plain, for example: Comana, Comanca, Câmpia Comancei and Valea Comancei in Olt County, Comanii Vechi, Comăneanca (Prahova County), Vadul Cumanilor (near Calafat).[131]
Culture
[edit]Horses were central to Cuman culture and way of life,[25] and their main activity was animal husbandry. The knight Robert de Clari described the Cumans as nomadic warriors who raised horses, sheep, goats, camels, and cattle. They moved north with their herds in summer and returned south in winter. Some of the Cumans led a semi-settled life and took part in trading and farming, as well as blacksmithing, furriery, shoe making, saddle making, bow making, and clothes making.[132] They mainly sold and exported animals, mostly horses, and animal products. They attached feeding sacks to the bridles of their horses, allowing them to cover great distances. They could go on campaign with little baggage and carry everything they needed. They wore sheepskin and were armed with composite bows and arrows. They prayed to the first animal they saw in the morning.[133][134] Like the Bulgars, the Cumans were known to drink blood from their horse (they would cut a vein) when they ran out of water far from an available source. Their traditional diet consisted of soup with millet and meat and included beer, curdled mare's milk, kumis, and bread (though bread could be rare depending on location).[25]
The fundamental unit of Cuman society was the family, made up of blood relatives.[135] A group of families formed a clan, led by a chief; a group of clans formed a tribe, led by a khan. A typical Cuman clan was named after an object, animal, or a leader of the clan. The names of the leaders of clans or tribes sometimes ended in "apa/aba". Cuman names were descriptive and represented a personal trait or an idea. Clans lived together in movable settlements named 'Cuman towers' by Kievan Rus' chroniclers.
The Cuman–Kipchak tribes formed sub-confederations governed by charismatic ruling houses—they acted independently of each other and had opposing policies. The territory controlled distinguished each Cuman tribe: the "seashore" Cuman tribes lived in the steppes between the mouths of the Dnieper and the Dniester; the "coastal" tribes lived on the coast of the Sea of Azov; the "Dnieper" tribes lived on both banks of the bend in the Dnieper Valley; and the "Don" Cumans lived in the Don River Valley.[135] D. A. Rasovskii notes five separate independent Cuman groups: the central Asiatic, the Volga-Yayik (or Ural), the Donets-Don (between the Volga and the Dnieper), the lower course of the Dnieper, and the Danube.[56]: 200
The Rus' grouped the Cuman–Kipchaks into two categories: the Non Wild Polvcians—'civilized' Cumans of the western part of the Cuman–Kipchak confederation who had friendly relations with Kievan Rus'—and the Wild Polvcians —who formed the eastern part of the confederation and who had hostile relations with Kievan Rus'.[13]: 13 As the Cuman–Kipchaks gained more territory, they drove off or dominated many tribes—such as the Oghuz, various Iranian and Finno-Ugric tribes, Pechenegs, and Slavs. They also raided the Byzantine Empire and a few times joined the Normans from southern Italy and the Hungarians in doing so. Over the course of time feudalism would take over the traditional social structure of the Cumans, and this led to the changing of identity from kinship to territory-based. Some of the Cumans eventually settled and led sedentary lives involved in agriculture and crafts such as leather and iron working and weapon making. Others became merchants and traded from their towns along the ancient trade routes to regions such as the Orient, Middle East, and Italy.[25]
The Cumans also played the role of middlemen in trade between Byzantium and the East, which passed through the Cuman- controlled ports of Sudak (Surozh), Oziv, and Saksyn. Several land routes between Europe and the Near East ran through Cuman territories: the Zaloznyi, the Solianyi, and the Varangian. Cuman towns—Sharukan, Suhrov/Sugrov, and Balin—appeared in the Donets River Basin; they were also inhabitted by other peoples besides the Cumans. Due to the practice of Cuman towns being named after their khans, town names changed over time—the town of Sharukan appears as Osenev, Sharuk, and Cheshuev. Rock figures called stone babas, which are found throughout southern Ukraine and other areas on the steppes of Russia, were closely connected with the Cuman religious cult of shamanism.
The Cumans tolerated all religions, and Islam and Christianity spread quickly among them. As they were close to the Kievan Rus' principalities, Cuman khans and important families began to slavicize their names—for example, Yaroslav Tomzakovych, Hlib Tyriievych, Yurii Konchakovych, and Danylo Kobiakovych. Ukrainian princely families were often connected by marriage with Cuman khans, lessening wars and conflicts. Sometimes the princes and khans waged joint campaigns; for example, in 1221 they attacked the trading town of Sudak on the Black Sea, which was held by the Seljuk Turks and which interfered with Rus'-Cuman trade.[75]

Robert de Clari reported that the Cumans often wore a sleeveless sheepskin vest, usually worn in conjunction with bracers.[25] Underneath the vest was worn a short or long sleeved tunic/tabard, extended to the mid calf, splitting in the front and back between the legs. Men wore trousers and a kaftan, each fastened by a belt, which was the traditional costume.
The women also wore caftans, as well as pants, dresses, and tunics shorter than those worn by men, sometimes split along the front, back, and sides. Clothes were commonly coloured deep crimson for decoration. Cuman men wore distinguishing conical felt or leather hats, pointed at the top with a broad brim (if made of felt) or a fur trim around the base (if made of leather). The brim of the hat formed a sharp angle at the front and upturned on the rear and at the sides. Women wore a large variety of head dresses and also wore conical hats but with a felt top and a cloth veil extending down the back.
This veil only covered the back neck and not the hair or face; another source states that it did cover the hair and that sometimes one or two braids were visible. Women wore a variety of jewellery, such as torques, a type of neck ornament consisting of one or several metal strands attached to a ribbon or necklace and hung around the neck, and head dresses that were made of a series of silver rings on a solid, cylindrically shaped material that was fastened at the temples. The men shaved the top of their head, while the rest of the hair was plaited into several braids; they also had prominent moustaches. Other Cumans also wore their hair very long, without shaving the top. The women had their hair loose or braided with buns twisting at the side. Both men and women followed a tradition of braiding coloured ribbons into their hair. For footwear, Cuman men and women wore long leather or felt boots with support straps connected to their belt. Both men and women wore cloth or metal arm bands.[25][109]: 255 [115]: 43

When the Cuman–Kipchaks swore oaths, it was done with swords in the hands that touched the body of a dog cut in two. The Italian Franciscan friar, traveler, and historian, John of Plano Carpini, says that when the Hungarian prince married the Cuman princess, ten Cumans swore over a dog cut in half with a sword that they would defend the Kingdom of Hungary. The Christian writer and historian of the crusades, Jean de Joinville (c. 1224–c. 1317), mentions that when the Cumans and Byzantines made an alliance, the Cumans made a dog pass between both sides and cut it with a sword, obliging the Byzantines to do the same; the Cumans said that both they and the Byzantines should be cut in pieces if they failed each other. Joinville described a Cuman noble's funeral: he was buried seated on a chair whilst his best horse and best sergeant were placed beside him alive.
Prior to this the sergeant was given a large sum of money by the Cuman leaders for the purpose of handing it back to them when they too would come into the afterlife. The Cuman khan also gave a letter of recommendation to the sergeant, which was addressed to the first king of the Cumans, in which the present king testified to the sergeant's good character. After these proceedings a huge mound was raised above the tomb. Cumans were buried in their warrior outfits.[109]: 255 [136] Wolves were greatly respected by the Cuman–Kipchaks, and they would sometimes howl along with them in commune. The personal bodyguard of the khan were called Bori (wolf in Turkic). Like other nomadic nations, the Cuman–Kipchaks initiated blood bonds (with the purpose of symbolically cementing a bond) by the drinking or mixing of each other's blood. Amongst the Cuman–Kipchaks ethnic names often became personal names—this was also practiced amongst the Mongols. This practice involved naming newborns after the names of conquered tribes and people. Names such as 'Baskord' (from the Bashkirs), 'Imek' (from the Kimeks), 'Kitan' (from the Mongol Khitan people), and 'Urus' were used by the Cumans.[10]: 28
Friar William of Rubruck, a Franciscan traveler who visited the Mongols in 1253–55, provides another account of Cuman customs. He mentions that Cumans built statues for dead notables, facing east and holding a cup (these statues are not to be confused with the balbals, which represent the enemies that were killed by him). He also notes that for richer notables, the Cumans built tombs in the form of houses. Rubruk gives an eyewitness account of a man who had recently died: the Cumans had hung up sixteen horses' hides, in groups of four, between high poles, facing the four points of the compass. The mourners then also placed kumis for the dead man to consume. Other graves had plenty of stones statues placed around them (balbals), with four tall ones placed to face the points of the compass.
Rubrick also wrote "Here the Cumans, who are called Chapchat [Kipchak] used to pasture their flocks, but the Germans call them Valans and their province Valania, and Isidorus calls (the region stretching) from the river Don as far as the Azov Sea and the Danube, Alania. And this land stretches from the Danube as far as the Don, the borderline of Asia and Europe; one can reach there in two months with quick riding as the Tatars ride.... and this country which extends from the Danube to the Tanais [Don] was all inhabited by the Chapcat Comans, and even further from the Don to the Volga, which rivers are at a distance of ten days' journey...And in the territory between these two rivers [i.e. the Don and the Volga] where we continued our way, the Cuman Kipchaks lived."[10]: 6 [136][137]
For many years before the Mongol invasion, the Cuman–Kipchaks were in ambiguous relationships with their neighbours (often through marital and martial alliances), the Kwarizmians, Byzantines, Georgians, and the Rus'; at a given time they could be at peace with one, at war with another.[138] The Byzantine Empire hesitated to go to war with the Cuman–Kipchaks north of the Danube River; instead, like the Hungarians, they chose to bribe them. Since Kwarizm had more important enemies, they hired the Cuman–Kipchaks for garrison duty.[25] There were numerous ways the Cuman–Kipchaks could make a living as nomadic warriors. One could partake in questing and raiding with their tribe and subsequently keep the spoils. Another avenue was to seek employment as a mercenary in exchange for the guarantee of loot. One could serve in a garrison, although this caused those Cumans to eventually forget their light cavalry skills and become poor infantry. This was fully exploited when the Mongol army destroyed the Cuman–Kipchak garrison in Samarkand.[139] Cuman–Kipchak women fought beside their fellow male warriors. Women were shown great respect and would often ride on a horse or wagon while the men walked.[25][132][140]: 52
In their travels, the Cumans used wagons to transport supplies as well as weapons such as mangonels and ballistas. Light felt tents with a frame consisting of wooden laths could be carried on top of wagons and easily be placed on the ground. The windows of the tents were "grilled" in such a way that it was difficult to see in but easy to see out. As the Cumans became more settled, they constructed forts for defence and settlement purposes.[25] The Cuman–Kipchaks used dung for fires when firewood was not available. The Cumans had very strict rules (taboos) against theft, and thus would, without prohibition, loosen their horses, camels, and livestock (sheep, oxen) without shepherds or guards when they were stationary. The law of blood vengeance was common among the Cuman–Kipchaks.[132] The Cuman calendar was atypical, as it showed neither specific Christian influences nor any trace of the Chinese–Turkic twelve-year animal cycle; it appeared to be an archaic system.[72]: 51
Military tactics
[edit]
Up until the late 11th and early 12th centuries, the Cumans fought mainly as light cavalry, later developing heavy cavalry. The main weapons of the Cumans were the recurved and, later, the composite bow (worn on the hip with the quiver), and the javelin, curved sword (a sabre less curved than a scimitar), mace, and heavy spear for lancing. Due to European influence, some of the later period Cumans wielded war hammers and axes. For defense they used a round or almond shaped shield, short sleeved mail armour, consisting of commonly alternating solid and riveted rows, Lamellar armour (iron or leather), leather cuirass, shoulder spaulders, conical or dome shaped iron helmet with a detachable iron or bronze anthropomorphic face plate (gold for princes and khans), and at times a camail suspended from the helmet, consisting of chain or leather.
The armour was strengthened by leather or felt disks that were attached to the chest and back. The items suspended from the belts were a bow case with bow, a quiver, a knife and a comb. They also wore elaborate masks in battle, shaped like and worn over the face. The Cuman Mamluks in Egypt were, in general, more heavily armed than Mongol warriors, sometimes having body armour and carrying a bow and arrow, axe, club, sword, dagger, mace, shield, and a lance. The Cuman Mamluks rode on larger Arabian horses in comparison to steppe ones.[25][141][109]: 255
The commonly employed Cuman battle tactic was repeated attacks by light cavalry archers, facing and shooting to the rear of the horse, then a feigned retreat and skilled ambush. To maintain this tactic to optimum efficiency, the Cumans kept a large number of reserve horses (10–12 remounts) to replace fatigued ones, so that a fresh horse was available at all times. The horsemen used oval shaped stirrups and employed a large bridle for their horses. Another important accessory was a small whip attached to the rider's wrist. Tribal banners were either made of cloth with tribal emblems or dyed horse hair—with more tails signifying greater importance of the warrior or group. Some of the Cumans who moved west were influenced by Western heraldry, and they eventually displayed hybridized European-Cuman heraldry.[115]
Niketas Choniates, while describing a Battle of Beroia in the late 12th century, gave an interesting description of the nomadic battle techniques of the Cumans:
They [The Cumans] fought in their habitual manner, learnt from their fathers. They would attack, shoot their arrows and begin to fight with spears. Before long they would turn their attack into flight and induce their enemy to pursue them. Then they would show their faces instead of their backs, like birds cutting through the air, and would fight face to face with their assailants and struggle even more bravely. This they would do several times, and when they gained the upper hand over the Romans [Byzantines], they would stop turning back again. Then they would draw their swords, release an appalling roar, and fall upon the Romans quicker than a thought. They would seize and massacre those who fought bravely and those who behaved cowardly alike."[10]: 55–56
Robert de Clari gave another description:
Each one has at least ten or twelve horses, and they have them so well-trained that they follow them wherever they want to take them, and they mount first on one and then on another. When they are on a raid, each horse has a bag hung on his nose, in which his fodder is put, and he feeds as he follows his master, and they do not stop going by night or by day. And they ride so hard that they cover in one day and one night fully six days' journey or seven or eight. And while they are on the way they will not seize anything or carry it along, before their return, but when they are returning, then they seize plunder and make captives and take anything they can get. Nor do they go armed, except that they wear a garment of sheepskin and carry bows and arrows.[56]: 200
Religion
[edit]The Cuman people practiced the shamanistic religion of Tengrism. Their belief system had animistic and shamanistic elements; they celebrated their ancestors and provided the dead with objects whose lavishness was considered an indicator to the recipient's social rank.
The Cumans referred to their shamans as Kam (female: kam katun); their activities were referred to as qamlyqet, meaning "to prophesy". The Cumans used Iranian words to designate certain concepts: uchuchmak (a native Turkic word cognate with Turkish uçuşmak) meaning "fly away, paradise" and keshene meaning "nest" (an Iranian borrowing; the concept was that the soul has the form of a bird).[136]
Funerals for important members involved firstly creating a mound, then placing the dead inside, along with various items deemed useful in the afterlife, a horse (like the Bulgars), and sometimes a servant or slave.[25]
Cuman divination practices used animals, especially the wolf and dog. The dog "It/Kopec" was sacred to the Cuman–Kipchaks, to the extent that an individual, tribe, or clan would be named after the dog or type of dog. Cumans had shamans who communicated with the spirit world; they were consulted for questions of outcomes.[102]
The Cumans in Christian territories were baptized in 1227 by Robert, Archbishop of Esztergom, in a mass baptism in Moldavia on the orders of Bortz Khan,[142] who swore allegiance to King Andrew II of Hungary.[101]: 48
Codex Cumanicus
[edit]The Codex Cumanicus, which was written by Italian merchants and German missionaries between 1294 and 1356,[64]: 173 was a linguistic manual for the Turkic Cuman language of the Middle Ages, designed to help Catholic missionaries communicate with the Cumans.[136] It consisted of a Latin–Persian–Cuman glossary, grammar observations, lists of consumer goods and Cuman riddles.[64]: 176 [136] The first copy was written in the monastery of St. John near Saray. A later copy (1330–1340) is thought to have been written in a Franciscan friary. Later, different sections of the codex, such as the Interpreter's Book (which was for commercial, merchant use) and the Missionaries' Book (which contains sermons, psalms and other religious texts along with Cuman riddles) were combined.[143]
The Interpreter's Book consists of 110 pages; pages 1–63 contain alphabetically arranged verbs in Latin, Persian and Cuman. The Missionaries' Book contains vocabulary listings, grammatical notes, Cuman riddles, religious texts and some Italian verses. The Cuman riddles are the oldest documented material of Turkic riddles and constitute Turkic folklore. Some of the riddles have almost identical modern equivalents (for example Kazakh). The Codex Cumanicus is composed of several Cuman–Kipchak dialects.[143]
The Cumans' language was a form of Kipchak Turkic and was, until the 14th century, a lingua franca over much of the Eurasian steppes.[144][145] A number of Cuman–Kipchak–Arabic grammar glossaries appeared in Mamluk lands in the 14th and 15th centuries. It is supposed that the Cumans had their own writing system (mentioned by the historian Gyárfás), which could have been a runic script. The supposition that the Cumans had a runic script is also suggested by the academic Hakan Aydemir, who mentioned a buckle with runic writing from a Cuman grave[64]: 176 There was also some Khazar Jewish linguistic influence upon the Cumans—the Cuman words shabat and shabat kun (meaning Saturday) are related to the Hebrew word Shabbat (meaning Sabbath). These Hebrew influences in the language may have resulted from contact or intermarriage between Khazars and some of the Cumans in the mid-11th century.[143][146]
Cuman leaders
[edit]- Iskal or Eskel (compare OTrk 𐰔𐰏𐰠 Izgil, the endonym of a Western Turkic Nushibi tribe who would later join and be assimilated into the Volga Bulgars) who were mentioned by Ahmad ibn Fadlan after visiting Volga region in 921–922. They also were mentioned by Abu Saʿīd Gardēzī in his Zayn al-Akhbār. According to Bernhard Karlgren, Eskels became the Hungarian people Székelys. Yury Zuev thought that Iskal who is mentioned in the Laurentian Codex about the first military encounter of Cumans against the Ruthenians on February 2, 1061, is personification of a tribal name.
- Sharukan/Sharagan (also known as Sharukan the Elder), grand father of Konchak. He was another Polovotsian khan who was victorious against the Ruthenian army of Yaroslavichi at the Alta river (Battle of the Alta River). According to the Novgorod First Chronicle Sharukan was taken as prisoner by Svyatoslav II of Kiev in 1068, while no such information is provided in the Laurentian Codex. In May 1107 along with Bonyak, Sharukan raided a couple of Ruthenian cities (Pereyaslav and Lubny); however, already in August of the same year the collective Ruthenian army led by Svyatoslav carried out a devastating defeat to the Cuman Horde forcing Sharukan to flee.
- Bonyak/Maniak,[147] Cuman khan who was actively involved in civil conflicts of Ruthenia. He had a brother Taz who perished at the battle on the Sula River in 1107. Bonyak was last mentioned in 1167 when he was defeated by Oleg of Siveria. Bonyak was a leader of the Cuman tribe Burchevichi that resided in steppes of the East Ukraine between modern cities of Zaporizhia and Donetsk.
- Tugorkan (1028–1096), was mentioned in essays of the Byzantine Princess Anna Komnene along with his compatriot Bonyak. He perished with his son at the battle on the Trubizh River against the Ruthenian army.
- Syrchan, a son of Sharukan. He was a leader of a Cuman tribe that lived on the right banks of Siversky Donets. Chronicles mentioned that after the death of Vladimir II Monomakh, grand prince of Kiev, Syrchan sent out an emissary and a singer Orev to Georgia after his brother Atrak/Otrok (who, with 40,000 Cuman troops, was in Georgia at the time), urging him to return. Khan Otrok agreed (giving up the fame and security he had won in Georgia), after smelling eyevshan, the grass of his native steppe.[14]: 281 Syrchan was mentioned in the poem of Apollon Maykov (1821–1897) "Emshan".
- Otrok/Atrak, a son of Sharukan and a brother of Syrchan. In 1111 he, along with his brother, withdrew to the Lower Don region after losing a battle against the Ruthenians. There Atrak's horde joined the local Alans. In 1117 his army sacked Sarkel and 5 other cities belonging to the Torkils and Berendei forcing the local Pechenegs, Berendei and Torkils to flee to Ruthenia. Around the same time Atrak invaded the Northern Caucasus where he entered into conflict with local Circassians pushing them beyond the Kuban River. The conflict was settled by a Georgian King David IV of Georgia who offered military service to Atrak against Seljuks in 1118. David also married the daughter of Atrak—Gurandukht. After withdrawal of Atrak away from the Don region, the Alan's duchy in East Ukraine was liquidated in 1116–17. Atrak returned after the death of Vladimir Monomakh in 1125.
- Khan Konchek/Konchak/Kumcheg (meaning 'trousers'), grandson of Sharukan, son of Khan Otrok. He united the tribes of the eastern Cumans in the later half of the 12th century, after which in the 1170s and 1180s he launched a number of particularly destructive attacks on the settlements in the Duchy of Kiev, the Principality of Chernigov and the Principality of Pereyaslavl. Konchak gave aid to the princes of the Principality of Novgorod-Seversk in their struggle for control with the other Rus' princes. Along with Khan Kobiak/Kobek, Khan Konchak was routed on the Khorol River in 1184 during an assault on Kievan Rus'. In 1185, he defeated the army of Ihor Sviatoslavych, who was taken as a prisoner. Later, Konchak laid siege to Pereiaslav and ravaged the Chernihiv and Kyiv areas. His daughter married prince Vladimir Igorevich of Putivl (Igor's son). It is hypothesized that Konchek was with the Cumans who helped Riurik Rostislavovich seize and sack of Kiev in 1202.[14]: 283 Khan Konchek is credited with certain technological advancements, such as Greek fire and a special bow that needed 50 men to operate.[14]: 283 Konchek was noted by the Rus' to be "greater than all the Cumans".[14]: 283 He died in a skirmish that preceded the Battle of Kalka River. The struggle to repel Khan Konchak and his army by Ihor Sviatoslavych and the Rus' princes is immortalized in the epic The Tale of Igor's Campaign ("Slovo o polku Ihorevi)."
- Syrgiannés/Sıçğan It is seen that some of the Cumans, who were on the way to prevent the Seljuk Turks expansion and were taken into Byzantine service after a Mongolian invasion, also served in the imperial palace and rose to high positions in time. As a matter of fact, Syrgiannés (Sytzigan: Sıçğan: Rat), who was the son of one of the Cuman begs, was baptized and married a woman from the Palaiologos family, and later received the title of Megas Domestic. The presence of his descendants in the Byzantine Empire continued for nearly 100 years. The last representative of this The Cuman Family, which was later assimilated into Byzantine Culture was also named Syrgiannés, just like the first member of the family. Syrgiannés, who was the governor of Macedonia and Thrace, was the elder emperor II. After participating in the struggles between Andronikos and his grandson that started in 1320, he fell out of favor and led a dull life until he was killed by the emperor's men in 1334.[121][130][148]
Appearance
[edit]The craniometric and genetic data, as well as contemporary art, support the image of a people highly heterogenous in appearance. Skulls with East Asian features are often found in burials associated with the Cumans and Pechenegs in Europe.[149]
The genetic material is mixed, albeit that European matrilineal DNA predominates[150] (see also below). Unlike the written sources, paintings and miniatures from between the 12th and 14th century (close in time to the settlement of Cumans to Central Europe) tend to support the picture of a mixed population that is suggested by the craniometric and genetic analyses. In the Anjou Legendarium Cumans are depicted with East Asian features and dark hair, while a fresco in the Kraskovo church in Slovakia depicts Cumans with Caucasian features.[151]
There are also depictions of Cumans with Caucasian features, but dark complexion (e.g. in the Képes Krónika Pictum). Notably, all of these phenotypes can be traced to groups described in Chinese and Arab sources, that are assumed to have later merged in the Cuman–Kipchak confederation. Fair complexion, e.g. red hair and blue or green eyes, were already noted by the Chinese among the Qincha (Kipchak), while the Tiele (to whom the Qun belonged) were not described as foreign looking, i.e. they were likely East Asian in appearance.[151] A dark complexion was attributed to the Pechenegs by Ibn Fadlan, who did not specify, however, if their features are European or Asian.[152] The Kipchak, Qun and Pechenegs all assimilated into the Cuman–Kipchak confederation, eventually.
Legacy
[edit]
As the Cumans ceased to have a state of their own, they were gradually absorbed into Eurasian populations (certain families in Hungary, Bulgaria, North Macedonia, Turkey, Romania, Georgia, Kazakhstan, Tatars in Crimea).[15] The Cumans in Dobruja were assimilated into Bulgarian and Romanian people.[64]: 176 Traces of the Cumans can still be found in placenames stretching from China to the Balkans, such as:
- the city of Kumanovo in North Macedonia;
- the abandoned village of Barakli in Valandovo, Yugoistochen, North Macedonia;
- a Slavic village named Kumanichevo in the Kastoria region of Greece (renamed to Lithia in 1928);
- a Slavic village named Kumanich in the Drama region of Greece (renamed to Dasoto in 1927);
- Comăneşti in Romania;
- Kuman, a city in Xinjiang, China;
- Polovtsy, a town in Smolensk Oblast, Russia;
- Polovtsy in Mogilev Region, Belarus;
- the steppes north of the Caucasus Mountains, referred to as Kuban as well as the Kuban River;
- the village of Kumane in Serbia;
- the subdivision of Kumanitsa in the municipality of Ivanjica, Serbia;
- Komani, a historical tribe and region in Montenegro;
- the municipality of Kuman in the Fier District, Fier County, southwestern Albania;
- Comana in Northern Dobruja (also Romania);
- the small village of Kumanite in Bulgaria;
- Kuman, a town in Qashqadaryo, Uzbekistan;
- Debrecen in Hungary;
- the village of Bugac in Hungary;
- the counties of Bács-Kiskun and Jász-Nagykun-Szolnok as well as the cities Kiskunhalas and Kunszentmiklós in Hungary;
- Karcag district, located in Jász-Nagykun-Szolnok county, Hungary;
- the village of Kunmadaras in Greater Cumania, Hungary;
- Turkey, Kırkağaç district of Manisa province, Yortan neighbourhood, (name changed to Bostancı);
- Turkey, Gölcük district of Kocaeli province, Ulaşlı neighbourhood;
- Turkey, Kandıra district of Kocaeli province, Burhanlı neighbourhood;
- Turkey, Gelibolu district of Çanakkale province, Burhanlı village;
- Turkey, Kastamonu province, Burhanlı village;
- Turkey, Meriç district of Edirne province, Saruhanlu village, (name changed to Adasarhanlı);
- Turkey, Manisa province, Saruhanlı district;
- Turkey, Tire district of İzmir province, Saruhanlı neighbourhood;
- Turkey, Nilüfer district of Bursa province, Kayapa neighbourhood;
- Turkey, Büyükorhan district of Bursa province, Kayapa neighbourhood;
- Turkey, Geyve district of Sakarya province, Bayat neighbourhood;
- Turkey, Gölpazarı district of Bilecik province, Bayat neighbourhood;
- Turkey, Ereğli district of Zonguldak province, Bayat village;
- Turkey, Kütahya province, Bayat village;
- Turkey, Aslanapa district, Kütahya province, Bayat village;
- Turkey, Kütahya province, Aslanapa (Old Arslanapa township) district;
- Turkey, Altıeylül district of Balıkesir province, Bayat neighbourhood;
- Turkey, İvrindi district of Balıkesir province, Kayapa neighbourhood;
- Turkey, Edirne province, Kayapa village;
- Turkey, Hisarcık district of Kütahya province, Ulaşlar village;
- Turkey, Gerede district of Bolu province, Ulaşlar village;
- Turkey, Dikmen district of Sinop province, Yortan village, (name changed to Şeyhhüseyin);
- Turkey, Karabük province, Yortan village, (name changed to Güneşli);
- Turkey, Akyazı district of Sakarya province, Yortan neighbourhood, (name changed to Çıldırlar);
- Turkey, Söke district of Aydın province, Yortan location;
- and the town of Kumaniv in Khmelnytskyi Oblast, Ukraine;
- Turkey, Yalova province, Saruhanlu village (name changed to Elmalık)[155];
- Turkey, Yalova province, Yortan village (name changed to Kazımiye)[156];
- Turkey, Gönen district of Balıkesir province, Yortan village, (name changed to Bostancı);
- Turkey, Kütahya province, Karsak village;
- Turkey, Polatlı district of Ankara province, Karsaklı village, (name changed to Türkkarsak);
- Turkey, Orhangazi district of Bursa province, Karsak village.[157]
Some famous Crimean Tatar historians such as Halil Inalcik and Ilber Ortayli refused to use the term Tatar, Crimean Tatars are direct descendants of Cumans who were settled in Pontic Steppes before the Tatar migration.[158][159] Historically, Cuman language is considered the direct ancestor of the current language of the Crimean Tatars with possible incorporations of the other languages, like Crimean Gothic.[160][161][162][163]

By the end of the 15th century, the main prerequisites that led to the formation of an independent Crimean Tatar ethnic group were created: the political dominance of the Crimean Khanate was established in Crimea, the Turkic languages (Cuman–Kipchak on the territory of the khanate) became dominant, and Islam acquired the status of a state religion throughout the Peninsula. By a preponderance Cumanian population of the Crimea acquired the name "Tatars", the Islamic religion and Turkic language, and the process of consolidating the multi-ethnic conglomerate of the Peninsula began, which has led to the emergence of the Crimean Tatar people.[164] Over several centuries, on the basis of Cuman language with a noticeable Oghuz influence, the Crimean Tatar language has developed.[165][166][167][168]
The flower, Kumoniga (melilot), is also a relic of the Cumans.[84] The Gagauz people are believed by some historians to be descendants of the Cumans; the name Qipcakli occurs as a modern Gagauz surname.[21]: 47 [84] The etymology of the Sea of Azov is popularly said to derive from a certain Cuman prince named Azum or Asuf, who was killed defending a town in this region in 1067.[169]
As the Mongols pushed westward and devastated their state, most of the Cumans fled to Hungary, as well as the Second Bulgarian Empire since they were major military allies. The Cuman participation in the creation of the Second Bulgarian Empire in 1185 and thereafter brought about basic changes in the political and ethnic sphere of Bulgaria and the Balkans.[10] Bulgarian Tsar Ivan-Asen II was descended from Cumans and settled them in the southern parts of the country, bordering the Latin Empire and the Despotate of Thessalonica.[84] Those territories are in present-day Turkish Europe, Bulgaria, and North Macedonia.

The Cumans who settled in Hungary had their own self-government in a territory that bore their name, Kunság, that survived until the 19th century. Two regions—Little Cumania and Greater Cumania—exist in Hungary. The name of the Cumans (Kun) is preserved in county names Bács-Kiskun and Jász-Nagykun-Szolnok and several municipalities such as Kunbaja or Kunhegyes. The Cumans were organized into four tribes in Hungary: Kolbasz/Olas in upper Cumania around Karcag and the other three in lower Cumania.

The Cuman language disappeared from Hungary in the 17th or 18th century, possibly following the Turkish occupation. The last person who was able to speak some Cumanian on a decaying level was István Varró from Karcag, who died in 1770. During the 1740s, when Cuman was no longer spoken, a Cuman version of the Lord's Prayer suddenly surfaced. It was taught in schools in Greater Cumania and Little Cumania until the mid-20th century, in turn becoming a cornerstone of Cuman identity. In the 20th century enthusiastic self-styled Cumans collected 'Cuman folklore', which consisted of elements such as a traditional Cuman dance, Cuman characteristics such as pride and staunch Calvinism[clarification needed] (by religion, as may be seen by figures for religion in Hungary, the Kiskunság is almost entirely Roman Catholic, whereas in Nagykunság, Protestants do outnumber Catholics, but only narrowly). This ethnic consciousness was linked to the legal privileges attached to the Cumans' territory.[109]: 265 Their 19th-century biographer, Gyárfás István, in 1870 was of the opinion that they originally spoke Hungarian, together with the Iazyges population. Despite this mistake, he has the best overview on the subject[citation needed] concerning details of material used. Cuman influence is also present in the modern Hungarian language in the form of loanwords, particularly in the areas of horse-breeding, eating, hunting and fighting.[109]: 265
In 1918, after World War I, the Cuman National Council was formed in Hungary, which was an attempt to separate the Kunság region (Greater Cumania and Little Cumania) from the Hungarian state, with the aim of forming a new independent Cuman state in Europe. The Cuman National Council declared the independence of Kunság, and elected its president Count Gedeon Ráday on 18 December.[170] However, the council's efforts remained unsuccessful. In 1939, Cuman descendants organized celebrations for the 700th anniversary of their arrival in Hungary, where they emphasized their separate ethnic existence and identity with ceremonial speeches.[171] In 1995, The Cuman Memorial Site was inaugurated as a tribute to the Cuman ancestors and the redemption of the former Nagykun District. In 2009, and subsequently 2012, a World Meeting of the Cumans was held in Karcag.[106] During the first meeting, which lasted two weeks, academic conferences, historical exhibitions, publications, presentations of traditional and cultural festivals and lectures in relation to the Cumans were held. In the 2012 meeting, the minister for rural development, Sándor Fazekas, mentioned how Cuman traditions are still kept alive, such as costumes, folk songs, and food.[172]
Toponyms of the Cuman language origin can be found in some Romanian counties of Galați (debatable), Teleorman and Vaslui, including the names of those three counties. When some of the Cumans moved to Hungary, they brought with them their Komondor dogs. The Komondor breed has been declared one of Hungary's national treasures, to be preserved and protected from modification. The name Komondor derives from Koman-dor, meaning "Cuman dog".[173]

In the countries where the Cumans were assimilated, family surnames derived from the words for "Cuman" (such as coman or kun, "kuman") are not uncommon. Traces of the Cumans are the Bulgarian surnames Kunev or Kumanov (feminine Kuneva, Kumanova) and Asenov, its variants in North Macedonia Kunevski, Kumanovski (feminine Kumanovska); the Kazakh surname Kumanov; the widespread Hungarian surname Kun; the Hungarian surnames of Csertan, Csoreg, Kokscor, Karacs, Kekcse; the Hungarian surname of Kangur—a byname of one of the families of Karcag (the words Kangur and Karcag derive from Qongur and Qarsaq respectively, and occur as modern day clan names of the Kazakhs—the Kipchak tribes Qongur and Qarsaq, as well as names used by the Kirgyz in the Manas epic—mentioned as Kongur-bay, lord of the Mongol Kalmyk people and the warrior Kongrolu); the Hungarian surname of Kapscog (from "Kipchak")—Kapsog Tojasos Kovacs, a byname of Kovacs family, as well as the name of Eszenyi Kopscog of Hungary; and the Greek surname Asan.[10]: 40 [21]: 54 [106] The names "Coman" in Romania and its derivatives, however, do not appear to have any connection to the medieval Cumans, as it was unrecorded until very recent times and the places with the highest frequency of such names has not produced any archaeological evidence of Cuman settlement.[174]
Over time, Cuman culture exerted an influence on the Ceangăi/Hungarian Csangos and Romanian culture in Moldavia, due to the Hungarians in Moldavia socializing and mingling with the Cumans between the 14th and 15th centuries.[175] Hakan Aydemir, a Turkic linguist, states that the 'ir' of the Ceangăi/Csangos and Székelys dialect, which means 'carve', 'notch', as well as the words 'urk/uruk' (meaning 'lasso', 'noose'), 'dszepu (meaning 'wool') and 'korhany' (meaning 'small mountain', 'hill') are of Cuman–Kipchak origin.[175] Additionally, the Cumans could have also had some connection with Székelys runes. Several Romanian as well as Hungarian academics believe that a significant Cuman population lived in Moldavia in the 15th century; these Cumans later assimilated into the Romanian population.[175] People in Hungary with the surname Palóc are descended from the Cumans (and possibly Kabars and Pechenegs)—Palóc origintates from the Slavic word Polovets/Polovtsy.[176] Although the Palócs were similar to the Hungarians in origins and culture, they were considered distinct groups by the Turks. The first written record of the word "palóc" as the name of a people appears in the Mezőkövesd register in 1784. Some scholars believe there is also no connection between the Cumans and the Dutch surnames Kooman(s), Koman(s), Koeman(s), (De) Cooman(s) and Coman(s), used particularly in the Flemish area and the Dutch county of Zeeland. They believe these surnames are medieval and were used in the meaning of 'merchant'.[177] However, other scholars believe the Coumans surname found in the Low Countries and France has its origins in the Cumans.[citation needed]
The Cumans appear in Rus' culture in the Rus' epic poem The Tale of Igor's Campaign and are the military enemies of the Rus' in Alexander Borodin's opera Prince Igor, which features a set of Polovtsian Dances.[citation needed]
The name Cuman is the name of several villages in Turkey, such as Kumanlar, including the Black Sea region. The indigenous people in the Altai Republic, Kumandins (Kumandy), are descended from the Cumans.[178] By the 17th century, the Kumandins lived along the river Charysh, near its confluence with the river Ob. A subsequent relocation to the Altai was driven by their unwillingness to pay yasak (financial tribute) to the Russian sovereign.[citation needed] N. Aristov linked the Kumandins—and the Chelkans—to the ancient Turks, "who in the 6th–8th century AD created in Central Asia a powerful nomadic state, which received ... the name Turkic Kaganate".[179]
Persons of Cuman/Kipchak origin also became Mamluk leaders: a prominent Cuman Sultan of the Egyptian Mamluk Sultanate, Sultan Baibars (reigned 1260–1277), defeated King Louis IX of France, and resisted the Mongol invasion, defeating the Mongol army at the Battle of Ain Jalut (1260) and the Battle of Elbistan (1277) (by using the feigned-retreat tactic).[11]: 156 [141] Mamluks in the empire retained a particularly strong sense of Cuman identity, to the degree that the biography of Sultan Baibars, as reflected by Ibn Shaddad, focused on his birth and early years in Desht-i-Kipchak ("Steppe of the Kipchaks"/Cumania), as well as enslavement and subsequent travels to Bulgaria and the Near East.
The historian Dimitri Korobeinikov relates how Baibars' story sums up the tragic fate of many Cumans after the Battle of the Kalka River (1223) and the Mongol invasion of Europe (1223–1242). Roman Kovalev states that this story can further be seen as a mechanism for the preservation of a collective memory broadly reflecting a sense of Cuman identity in the Mamluk Sultanate.[180] In the latter part of the 1260s the Mamluks were allied with the Golden Horde against the Ilkhanate.[143] The creation of this specific warrior class, described as the "mamluk phenomenon" by David Ayalon, was of great political importance.[181]
In the Hungarian village of Csengele, on the borders of what is still called Kiskunsag ("Little Cumania"), an archeological excavation in 1975 revealed the ruins of a medieval church with 38 burials. Several burials had all the characteristics of a Cumanian group: richly jeweled, non-Hungarian, and definitely Cumanian-type costumes; the 12-spiked mace as a weapon; bone girdles; and associated pig bones.[182] In view of the cultural objects and the historical data, the archeologists concluded that the burials were indeed Cumanian from the mid-13th century; hence some of the early settlers in Hungary were from that ethnic group. In 1999 the grave of a high-status Cumanian from the same period was discovered about 50 meters from the church of Csengele; this was the first anthropologically authenticated grave of a Cumanian chieftain in Hungary,[96] and the contents are consistent with the ethnic identity of the excavated remains from the church burials. A separated area of the chieftain grave contained a complete skeleton of a horse.[17]
Genetics
[edit]This section possibly contains original research. (May 2020) |
The ethnic origins of the Cumans are uncertain.[14]: 279 [72]: 30 [183] According to some contemporary sources, the Cumans were reported to have had blond hair, fair skin and blue eyes (which set them apart from other groups and later puzzled historians),[15]: 36 [26]: 43 however, craniometric and genetic data, as well as contemporary art, support a picture of a people who were very heterogeneous in appearance.[151]
A genetic study analyzing putatively Cuman specimens in Hungary determined that they had a high frequency of western Eurasian mitochondrial DNA (mtDNA) lineages.[17] In a 2005 study by Erika Bogacsi-Szabo et al. of the mtDNA of the Cuman nomad population that migrated into the Carpathian basin during the 13th century, six haplogroups were revealed.
One of these haplogroups belongs to the M lineage (haplogroup D) and is characteristic of Eastern Asia, but this is the second most frequent haplogroup in southern Siberia too. All the other haplogroups (H, V, U, U3, and JT) are West Eurasian, belonging to the N macrohaplogroup. Out of the eleven remains, four samples belonged to haplogroup H, two to haplogroup U, two to haplogroup V, and one each to the JT, U3, and D haplogroups. In comparison to the Cumans, modern Hungarian samples represent 15 haplogroups. All but one is a West Eurasian haplogroup [the remaining one is East Asian (haplogroup F)], but all belong to the N lineage. Four haplogroups (H, V, U*, JT), present in the ancient samples, can also be found in the modern Hungarians, but only for haplogroups H and V were identical haplotypes found. Haplogroups U3 and D occur exclusively in the ancient group, and 11 haplogroups (HV, U4, U5, K, J, J1a, T, T1, T2, W, and F) occur only in the modern Hungarian population. Haplogroup frequency in the modern Hungarian population is similar to other European populations, although haplogroup F is almost absent in continental Europe; therefore the presence of this haplogroup in the modern Hungarian population can reflect some past contribution.[184] "The results suggested that the Cumanians, as seen in the excavation at Csengele, were far from genetic homogeneity. Nevertheless, the grave artifacts are typical of the Cumanian steppe culture; and five of the six skeletons that were complete enough for anthropometric analysis appeared Asian rather than European (Horváth 1978, 2001), including two from the mitochondrial haplogroup H, which is typically European. It is interesting that the only skeleton for which anthropological examination indicated a partly European ancestry was that of the chieftain, whose haplotype is most frequently found in the Balkans."[184]
The study concluded that the mitochondrial motifs of Cumans from Csengele show the genetic admixtures with other populations rather than the ultimate genetic origins of the founders of Cuman culture. The study further mentioned, "This may be the result of the habits of the Cumanian nomads. Horsemen of the steppes formed a political unit that was independent from their maternal descent or their language and became members of a tribal confederation. According to legends, Cumanians frequently carried off women from raided territories. So the maternal lineages of a large part of the group would reflect the maternal lineage of those populations that had geographic connection with Cumanians during their migrations. Nevertheless, the Asian mitochondrial haplotype in sample Cu26 may still reflect the Asian origins of the Cumanians of Csengele. However, by the time the Cumanians left the Trans-Carpathian steppes and settled in Hungary, they had acquired several more westerly genetic elements, probably from the Slavic, Ugric, and Turkic-speaking peoples who inhabited the regions north of the Black and Caspian Seas." The results from the Cuman samples were plotted on a graph with other Eurasian populations, showing the genetic distances between them. The Eurasian populations were divided into two distinct clusters. One cluster contained all the Eastern and Central Asian populations and can be divided into two subclusters; one subcluster includes mainly Eastern Asian populations (Buryat, Korean and Kirghiz Lowland populations), and the other subcluster harbors mainly Central Asian populations (Mongolian, Kazakh, Kirghiz Highland and Uyghur populations). The second cluster contained the European populations. Inside the second cluster, based on HVS I motifs, a clear structure was not detectable, but almost all European populations, including the modern Hungarians, assembled in one section with small distances between each other. Cumans were outside this section; they were found to be above the abscissa of the graph—this is the population from the second cluster, which is closest to the East-Central Asian cluster. The modern Cumans of Csengele, Hungary are genetically nearest to the Finnish, Komi and Turkish populations.[185] The modern day Cuman descendants in Hungary are differentiated genetically from the Hungarians and other European populations.[186]
In relation to the Kumandins, Pankratov regarded the Kumandins as being related anthropologically to the Urals, and suggested that they were less East Asian than the Altaians proper.[187] A majority of mitochondrial DNA lines belonged to the North East Asian haplogroups C or D with also a large minority of west Eurasian lineages such as U.
In popular culture
[edit]Cumans appear as one of the civilizations that players can play as in the 2019 strategy game Age of Empires II: Definitive Edition. In addition, players can play a campaign which tells the story of their flight westwards as they retreat from the Mongols.
Cumans appear as antagonists in the 2018 role-playing game Kingdom Come: Deliverance and also in the 2025 sequel Kingdom Come: Deliverance II.
Gallery
[edit]-
Cuman statue "Baba" in Nieborów, Poland
-
"Baba" 11th century, Luhansk
-
"Baba" 11th century, Luhansk
-
"Baba" 11th century, Luhansk
-
"Baba" 11th century, Luhansk
-
"Baba" 11th century, Luhansk
-
Cuman statue
-
Cuman statue
-
Cuman sculpture
-
Cuman statue in Stadnitsja Kiev c. 12th century
-
Cuman battle mask
-
Cuman statue at the Donetsk local history museum
-
Equestrian statue of a Cuman warrior, Kunhegyes, Hungary
-
Cuman, 12th century, Hermitage Museum
-
Cuman statues near the museum on Akademik Yavornitskyi Prospekt, Dnipro
-
Cuman statue
-
"Baba" at the Open Air Museum, Prelesne
-
Chormukhinsk Madonna, Luhansk
-
Cuman Stone statue "baba"
-
Cuman Stone statue "baba"
-
Ladislaus IV of Hungary "the Cuman"
-
Kunkereszt ("Cuman cross") in Belez, periphery of Magyarcsanád, Hungary
-
Cuman stone statues "babas"
-
Cuman statues from Ukraine in Neues Museum, Berlin
-
Cuman chain mail
-
Cuman statue
-
Cuman prairie art, as exhibited in Dnipro
-
Cuman burial mound in Hungary
-
Cuman stone statues in Donetsk damaged in fighting (22 September 2014)
-
Pursuit of Cuman horsemen (right) by the Hungarian King Ladislaus I (left), church of Kraskovo, Slovakia, 14th century
See also
[edit]- Elizabeth the Cuman
- House of Basarab
- Hunyadi family
- History of Kazakhstan
- Kazakhs
- Mamluk
- Mamluk Sultanate
- Bahri Mamluks
- Syrgiannes Palaiologos
- Manavs
- Notable people of Cuman descent
- The Cuman Tsaritsa of Bulgaria
- Roman Catholic Diocese of Cumania
- Andrey Bogolyubsky
- Yuri Dolgorukiy
- Terter clan
- Turkic languages
- Mongol invasion of Rus
- Tatar invasions
- List of Tatar and Mongol raids against Rus'
- History of Romania
- History of Transylvania
- Origin of the Romanians
- Crimean Karaites, an ethnic group with possible Cuman origins
- Madjars
- Bács-Kiskun County
- Romania in the Early Middle Ages
- Judge of the Cumans
- Foundation of Wallachia
- Battle of Adrianople (1205)
- Constantine Euphorbenos Katakalon
- Maria of Bulgaria, Latin Empress
- Cossacks
- Asen dynasty – dynasty of the Second Bulgarian Empire. Historians claim a Bulgarian, Romanian or Cuman origin
- Terter dynasty
- Oină, sport
- Attila József, poet
- Anna of Hungary (1260–1281)
- Basarab I of Wallachia
- Darman and Kudelin – Bulgarians of Cuman origin
- Delhi Sultanate – Qutbuddin Aibak, founder of the Delhi sultanate, was a Cuman; redeemed from slavery by Afghan shakh Mahmud Ghuri, he became his governor in Delhi and proclaimed independence after the death of his patron.
- Elizabeth of Hungary, Queen of Serbia -one of the older children of King Stephen V of Hungary and his wife Elizabeth the Cuman
- Elizabeth of Sicily, Queen of Hungary
- Ladislaus IV of Hungary – he was also known as King Ladislas the Cuman, son of Elizabeth the Cuman
- Roman the Great – he waged two successful campaigns against the Cumans
- Shishman of Vidin (Shishman dynasty of the Second Bulgarian Empire is most probably of Cuman origin)
- Yaropolk II of Kiev
References
[edit]Footnotes
[edit]- ^ In various languages:
- ^ Identified with either Kipchaks[57] or Yellow Uyghurs[58]
- ^ In another account, Köten had already realised the barons' intention, so he had killed himself and his wives. The barons then cut off their heads and threw them onto the streets outside the house in an act of brutality that had dire consequences.
Citations
[edit]- ^ Williams, Brian G. (2001). The Crimean Tatars: The Diaspora Experience and the Forging of a Nation. Brill. pp. 42–43. ISBN 90-04-12122-6.
- ^ a b "Kumanowie". encyklopedia.pwn.pl (in Polish). Wydawnictwo Naukowe PWN. Retrieved 8 August 2025.
- ^ a b Kovács, Szilvia (2020). "Kumans". In Fleet, Kate; Krämer, Gudrun; Matringe, Denis; Nawas, John; Rowson, Everett (eds.). Encyclopaedia of Islam (3rd ed.). Brill Online. ISSN 1873-9830.
- ^ GÖKBEL, Ahmet. "Cuman/Kipchak Turks in the Pre-Ottoman Balkans". Journal of Universal History Studies.
- ^ Robert Lee Wolff: "The 'Second Bulgarian Empire'. Its Origin and History to 1204". Speculum, Volume 24, Issue 2 (April 1949), 179. "Thereafter, the influx of Pechenegs and Cumans turned Bulgaria into a battleground between Byzantium and these Turkish tribes ..."
- ^ a b c d e Bartusis, Mark C. (1997). The Late Byzantine Army: Arms and Society, 1204–1453. University of Pennsylvania Press. pp. 26–27. ISBN 978-0-8122-1620-2.
- ^ a b c d e f g h i j k l m n Spinei, Victor (2009). The Romanians and the Turkic Nomads North of the Danube Delta from the Tenth to the Mid-Thirteenth Century. Leiden: Brill. ISBN 978-90-04-17536-5. Archived from the original on 2016-12-07. Retrieved 2015-10-19.
- ^ "Polovtsy". Encyclopedia.com. 31 May 2023.
- ^ "Cumans". Encyclopediaofukraine.com. Archived from the original on 5 August 2011. Retrieved 13 April 2011.
- ^ a b c d e f g h i j k l m n o p q r s t u v w Vásáry, István (2005). Cumans and Tatars: Oriental Military in the Pre-Ottoman Balkans, 1185–1365. Cambridge University Press. ISBN 978-0-5218-3756-9.
- ^ a b c Bartlett, W. B. (2012). The Mongols: From Genghis Khan to Tamerlane. Amberley Publishing Limited. ISBN 978-1-4456-0791-7.
- ^ Prawdin, Michael (1940). The Mongol Empire: Its Rise and Legacy. Transaction Publishers. pp. 212–15. ISBN 978-1-4128-2897-0. Archived from the original on 8 January 2016. Retrieved 14 June 2015.
{{cite book}}: ISBN / Date incompatibility (help) - ^ a b c d e Nicolle, David; Shpakovsky, Victor (2001). Kalka River 1223: Genghiz Khan's Mongols Invade Russia. Osprey Publishing. ISBN 978-1-84176-233-3.
- ^ a b c d e f g h i j k l m n o p q r Sinor, Denis, ed. (1990). The Cambridge History of Early Inner Asia, Volume 1. Cambridge University Press. ISBN 978-0-5212-4304-9.
- ^ a b c d e f g Grumeza, Ion (4 August 2010). The Roots of Balkanization: Eastern Europe C.E. 500–1500. University Press of America. ISBN 978-0-7618-5135-6. Archived from the original on 8 January 2016. Retrieved 19 October 2015.
- ^ Golev, Konstantin (2018). "The Bulgarophilia of the Cumans in the Times of the First Asenids of Bulgaria". Golden Horde Review. 6 (3): 455. doi:10.22378/2313-6197.2018-6-3.452-471.
- ^ a b c d "Mitochondrial-DNA-of-ancient-Cumanians". Goliath.ecnext.com. Archived from the original on 2010-01-24. Retrieved 1 March 2014.
- ^ Pliny the Elder, The Natural History of Pliny Volume 2 Archived 2016-01-08 at the Wayback Machine, p. 21.
- ^ One or more of the preceding sentences incorporates text from a publication now in the public domain: Chisholm, Hugh, ed. (1911). "Darial". Encyclopædia Britannica. Vol. 7 (11th ed.). Cambridge University Press. p. 832.
- ^ Ostrowski, Donald (2018). Portraits of Medieval Eastern Europe, 900-1400. Christian Raffensperger. Abingdon, Oxon. p. 62. ISBN 978-1-315-20417-8. OCLC 994543451.
{{cite book}}: CS1 maint: location missing publisher (link) - ^ a b c d e Boĭkova, Elena Vladimirovna; Rybakov, R. B. (2006). Kinship in the Altaic World. Otto Harrassowitz Verlag. ISBN 978-3-4470-5416-4.
- ^ Khazanov, Anatoly M.; Wink, André, eds. (2001). Nomads in the Sedentary World. Psychology Press. p. 44. ISBN 978-0-7007-1370-7.
- ^ Imre Baski, "On the ethnic names of the Cumans of Hungary", Kinship in the Altaic World: Proceedings of the 48th Permanent International Altaistic Conference, Moscow 10–15 July 2005 (eds Elena V. Boikova, Rosislav B. Rybakov) Wiesbaden, Harrassowitz Verlag, pp. 48, 52.
- ^ John Mandeville, The Travels of Sir John Mandeville, ch 6., 27
- ^ a b c d e f g h i j k l Dragosani-Brantingham, Justin (19 October 2011) [1999]. "An Illustrated Introduction to the Kipchak Turks" (PDF). kipchak.com. Archived (PDF) from the original on 2013-09-30. Retrieved 1 March 2014.
- ^ a b c d e Nicolle, David; McBride, Angus (1988). Hungary and the Fall of Eastern Europe 1000–1568. Osprey Publishing. ISBN 978-0-8504-5833-6. Archived from the original on 8 January 2016. Retrieved 14 June 2015.
The Cumans' characteristic blonde hair and blue eyes gave them their name in Russian and German, both of which meant 'yellow'
- ^ Dobrodomov I. G., 1978, 123
- ^ Ignjatić, Zdravko (2005). ESSE English-Serbian Serbian-English Dictionary and Grammar. Belgrade, Serbia: Institute for Foreign Languages. p. 1033. ISBN 978-86-7147-122-0.
- ^ Rick Derksen, Etymological Dictionary of the Slavic Inherited Lexicon (Brill: Leiden-Boston, 2008), 412.
- ^ Pletnyova, S. A. Kipchaks (1990). p. 35
- ^ Kroonen, Guus (2013). Etymological dictionary of Proto-Germanic. Leiden Indo-European Etymological Dictionary Series. Vol. II. Brill. pp. 126–127.
- ^ Julian Baldick, Animal and Shaman: Ancient Religions of Central Asia Archived 2020-02-05 at the Wayback Machine, p.55.
- ^ Golden, Peter B. (1992). An Introduction to the History of the Turkic People. Otto Harrassowitz, Wiesbaden. p. 271
- ^ Golden, Peter, B. The Turkic world of Mahmud al-Kashgari Archived 2019-12-23 at the Wayback Machine, p. 522
- ^ Clauson. ED. p. 411; cited in Golden, Peter B. (1995–1997) Cumanica IV: The Cumano-Qıpčaq Clans and Tribes. Archivum Eurasiae Medii Aevi 9. p. 111
- ^ Clauson. ED. p. 693; cited in Golden, Peter B. (1995–1997) Cumanica IV: The Cumano-Qıpčaq Clans and Tribes. Archivum Eurasiae Medii Aevi 9. p. 114
- ^ Clauson. ED. p. 695-696; cited in Golden, Peter B. (1995–1997) Cumanica IV: The Cumano-Qıpčaq Clans and Tribes. Archivum Eurasiae Medii Aevi 9. p. 115
- ^ Golden, Peter B. (1990). "The peoples of the south Russian steppes". In Sinor, Denis (ed.). The Cambridge History of Early Inner Asia. Cambridge University Press. p. 280 of pp. 256–284
- ^ Golden, Peter Benjamin. Nomads and their Neighbours in the Russian Steppe: Turks, Khazars and Qipchaqs. p. 307.
- ^ Radloff, V.V. (1893–1911). Opyt slovarja tjurkskix narečij; cited in Golden, Peter B. (1995–1997) Cumanica IV: The Cumano-Qıpčaq Clans and Tribes. Archivum Eurasiae Medii Aevi 9. p. 116
- ^ Golden, Peter B. "The Polovci Dikii" in Harvard Ukrainian Studies Vol. 3/4, Part 1. pp. 296–309
- ^ Golden, Peter B. (1995–1997). "Cumanica IV: The Cumano-Qıpčaq Clans and Tribes". Archivum Eurasiae Medii Aevi 9 (1995-1997). Archivum Eurasiae Medii Aevi 9: 118.
- ^ Lessing p. 879; cited in Golden, Peter B. (1995–1997) Cumanica IV: The Cumano-Qıpčaq Clans and Tribes. Archivum Eurasiae Medii Aevi 9. p. 118
- ^ Clauson. ED. p. 536; cited in Golden, Peter B. (1995–1997) Cumanica IV: The Cumano-Qıpčaq Clans and Tribes. Archivum Eurasiae Medii Aevi 9. p. 119
- ^ Akhmetova, Zhanculu et al. "Kipchak Ethnoyms in the 'Tale of Bygone Years'" in International Journal of Psychosocial Rehabilitation, Vol. 24, Issue 06, 2020. p. 1195
- ^ Altheim, Franz. (1959) Geschichte der Hunnen (Berlin), I. Berlin. pp. 278-279; cited in Golden, Peter B. (2003) Nomads and Their Neighbours in the Russian Steppe: Turks, Khazars and Qipchaqs. Routledge. p. 42
- ^ Clauson, Gerard (1972). An Etymological Dictionary of Pre-13th Century Turkish. Oxford University Press. p. 239
- ^ Golden, Peter B. (1992). An Introduction to the History of the Turkic People. Otto Harrassowitz, Wiesbaden. p. 278–279
- ^ Radloff, W (1893–1911). Versuch eines Wörterbuches der Türk-Dialekte (II ed.). p. 506.
- ^ Letopis'po Ipatskomu spisku. Izd. Arheogr. Komm. 1871. p. 563.
- ^ Onomasticon Turcicum.
- ^ "On the Ethnic Names of the Cumans of Hungary". In: Kinship in the Altaic World. Proceedings of the 48th PIAC, Moscow 10–15 July 2005. Ed. by E. V. Boikova and R. B. Rybakov. Harrasowitz Verlagh, Wiesbaden 2006, pp. 43–54.
- ^ Golden, Peter B. (1988). "Cumanica IV: The Tribes of the Cumans-Qıpčaqs" in Archivum Eurasiae Medii Aevi 9 (1995–1997). p. 122 of pp. 99–122
- ^ Golden, Peter B. (1992). An Introduction to the History of the Turkic People. Wiesbaden: Otto Harrassowitz. p. 275.
- ^ Cheng, Fanyi (2012). "The Research on the Identification between the Tiele (鐵勒) and the Oğuric tribes". Archivum Eurasiae Medii Aevi. 19. Wiesbaden: Harrassowitz Verlag: 104–108.
- ^ a b c d Wolff, Robert Lee (1976). Studies in the Latin Empire of Constantinople. London: Variorum. ISBN 978-0-9020-8999-0.
- ^ Pletnyova, S. A. Kipchaks, p. 34 (in Russian)
- ^ a b Czeglédy, K. (1949): "A kunok eredetéről" MNy, XLV, pp. 47-48. 50 of pp. 43-50. cited in Golden, P. B. (1992) An Introduction to the History of the Turkic Peoples. Wiesbaden: Otto Harrassowitz. p. 276, fn. 252
- ^ Minorsky, V. (1942), Sharaf al-Zaman Tahir Marvazī on China, the Turks and India. Arabic text (circa A.D. 1120) with an English translation and commentary. London. 1, pp. 242–243.
- ^ Golden, Peter B. (1992). An Introduction to the History of the Turkic People. Otto Harrassowitz, Wiesbaden. p. 273-274
- ^ Golden, Peter B. (2006). "Cumanica V: The Basmils and Qipchaqs" in Archivum Eurasiae Medii Aevi 15. p.
- ^ Golden, Peter (1987). "Cumanica II: The Ölberli (Ölperli): The Fortunes and Misfortunes of an Inner Asian Nomadic Clan". Archivum Eurasiae Medii Aevi. VI: 22. Retrieved 2 May 2022.
- ^ Yaqut, Kitab mu'jam al-budan, p. 31.
- ^ a b c d e f g h i j k l m n o Kincses-Nagy, Éva (2013). A Disappeared People and a Disappeared Language: The Cumans and the Cuman language of Hungary. Szeged University.
- ^ Spinei, Victor (2006). The Great Migrations in the East and South East of Europe from the Ninth to the Thirteenth Century: Cumans and Mongols. Hakkert. p. 323. ISBN 978-9-0256-1214-6.
- ^ Golden, Peter B. (1992). An Introduction to the History of the Turkic People. Otto Harrassowitz, Wiesbaden. p. 276 "The attempts, on philological grounds, to link the Quman-Qun-Sârî and Qıpčaqs, while possible, seem somewhat forced. Corroborating historical data are needed. If the Türkmen attacked by the Sârî are the Oğuz, the case for the identification of the Sârî with the Qıpčaqs is strengthened on geographical grounds. If the Türkmen in question are Qarluqs, however, then we are not compelled to view the Sârî as Qıpčaqs."
- ^ Golden Peter B."The Shaping of the Cuman-Qïpchaqs" in Il Codice Cumano e il Suo Mondo, ed. Felicitas Schmieder and Peter Schreiner, Rome (2005), pp.247–277; reprinted with different pagination in: P. B. Golden, Studies on the Peoples and Cultures of the Eurasian Steppes (Bucharest-Braila, 2011), pp. 303–332. "Thus, Marwazî, as we have seen, mentions a 'group of Shârî' led by a chief called 'Bâsm.l.' These may have been Yellow Uyghurs (Sarï Uyghur/Shera Yoghur) who resisted Islam and have remained non-Muslims (Buddhists) to the present day. The Basmïl had been part of the Toquz Oghuz/Uyghur confederation."
- ^ Akhmetova, Zhanculu et al. "Kipchak Ethnonyms in the 'Tale of Bygone Years'" in International Journal of Psychosocial Rehabilitation, Vol. 24, Issue 06, 2020. p. 1193 quote: "But the Kumans represent only one small western part of the Desht-i-Kipchak tribal union"
- ^ Golden, P.B. (1992) An Introduction to the History of the Turkic peoples, 276-279
- ^ a b Golden, Peter B. (1992). An Introduction to the History of the Turkic Peoples. Wiesbaden: Otto Harrassowitz. p. 277. ISBN 978-3-4470-3274-2.
- ^ Drobny, Jaroslav. Cumans and Kipchaks: Between Ethnonym and Toponym. p. 208.
- ^ a b c d Paksoy, H. B., ed. (1992). Central Asian Monuments. ISIS Press. ISBN 978-975-428-033-3. Archived from the original on 2016-01-08. Retrieved 2015-10-19.
- ^ Columbia Encyclopedia
- ^ Martin, Janet (1993). Medieval Russia, 980–1584. Cambridge University Press. pp. 48–49. ISBN 978-0-5213-6832-2.
- ^ a b c d e "Cumans". Encyclopediaofukraine.com. Archived from the original on 2013-12-27. Retrieved 2014-03-01.
- ^ Kristó & Makk 1996, p. 120.
- ^ Bánlaky, József. "László második hadjárata a kúnok ellen 1091-ben" [The Second Campaign of Ladislaus Against the Cumans in 1091]. A magyar nemzet hadtörténelme [The Military History of the Hungarian Nation] (in Hungarian). Budapest.
- ^ "Boniak". Archived from the original on 2 August 2015. Retrieved 29 April 2015.
- ^ Makk, Ferenc (1989). The Árpáds and the Comneni: Political Relations between Hungary and Byzantium in the 12th Century. Translated by Novák, György. Budapest: Akadémiai Kiadó. p. 13. ISBN 978-963-05-5268-4. Archived from the original on 2016-01-08. Retrieved 2015-10-19.
- ^ The Hungarian Illuminated Chronicle (ch. 145.104), p. 132.
- ^ Golden, Peter B. (2003). Nomads and Their Neighbours in the Russian Steppe: Turks, Khazars and Qipchaqs. Ashgate/Variorum. p. 138. ISBN 978-0-8607-8885-0.
- ^ The meaning of "Vlach" in this case, as mentioned in the Robert de Clari Chronicle, was the subject of fierce dispute in the late 19th and 20th centuries (see also Kaloyan of Bulgaria).
- ^ In his History of the Byzantine Empire (ISBN 978-0-299-80925-6, 1935), Russian historian A. A. Vasiliev concluded in this matter, "The liberating movement of the second half of the 12th century in the Balkans was originated and vigorously prosecuted by the Wallachians, ancestors of the Romanians of today; it was joined by the Bulgarians, and to some extent by the Cumans from beyond the Danube."
- ^ a b c d e MacDermott, Mercia (1998). Bulgarian Folk Customs. Jessica Kingsley Publishers. p. 27. ISBN 978-1-8530-2485-6.
- ^ Krüger, Peter (1993). Ethnicity and nationalism: case studies in their intrinsic tension and political dynamics. Hitzeroth. p. 32. ISBN 978-3-89398-128-1. Archived from the original on 8 January 2016. Retrieved 14 June 2015.
- ^ Ivanov, Ivelin (2025-07-16). "Bulgarians, Cumans, Teutons, and Vlachs in the First Decades of the Thirteenth Century". Studia Ceranea. Journal of the Waldemar Ceran Research Centre for the History and Culture of the Mediterranean Area and South-East Europe. 12: 491–505. doi:10.18778/2084-140X.12.05. hdl:11089/45851.
- ^ a b c Turnbull, Stephen (2003). Genghis Khan & the Mongol Conquests 1190–1400. Osprey Publishing. ISBN 978-1-8417-6523-5.
- ^ Curta, Florin (2006). Southeastern Europe in the Middle Ages, 500–1250. Cambridge University Press. p. 409. ISBN 978-0-521-81539-0.
- ^ Hildinger, Erik (2001). Warriors of the Steppe: Military History of Central Asia, 500 BC to 1700 AD. Da Capo Press. p. 134. ISBN 978-0-7867-3114-5. Archived from the original on 2016-01-08. Retrieved 2015-10-19.
- ^ Rapp 1997, p. 620.
- ^ Scott, Richard Bodley (2008). Eternal Empire: The Ottomans at War. Osprey Publishing. p. 30. ISBN 978-1-84603-401-5. Archived from the original on 2016-01-08. Retrieved 2015-10-19.
- ^ Waldman, Carl; Mason, Catherine (2006). Encyclopedia of European Peoples. Infobase Publishing. p. 189. ISBN 978-1-4381-2918-1. Archived from the original on 2015-11-28. Retrieved 2015-10-19.
- ^ The murder of Köten is described in the novel Batu by Vasily Yan, in the chapter "The End of Khan Kotyan".
- ^ Roger Finch, Christianity among the Cumans Archived 2015-09-24 at the Wayback Machine, p. 5.
- ^ Sugar, Peter F.; Hanák, Péter; Frank, Tibor, eds. (1994). A History of Hungary. Indiana University Press. p. 26. ISBN 978-0-253-20867-5. Archived from the original on 2015-10-01. Retrieved 2015-10-19.
- ^ a b c Horvath 2001
- ^ a b c d e Linehan, Peter; Nelson, Janet L., eds. (2013). The Medieval World. Routledge. ISBN 978-1-1365-0005-3.
- ^ (Hungarian) Kristó, Gyula; Makk, Ferenc (1996). Az Árpád-ház uralkodói [Rulers of the House of Árpád]. I. P. C. Könyvek. ISBN 963-7930-97-3], p. 268.
- ^ Klaniczay, Gábor (2002). Holy Rulers and Blessed Princes: Dynastic Cults in Medieval Central Europe. Cambridge University Press. p. 439. ISBN 978-0-5214-2018-1.
- ^ Škvarna, Dušan; Bartl, Július; et al. (2002). Daniel, David P.; Devine, Albert (eds.). Slovak History: Chronology & Lexicon. Translated by Daniel, David P. Bratislava: Bolchazy-Carducci Publishers. p. 33. ISBN 978-0-86516-444-4. Archived from the original on 2016-01-08. Retrieved 2015-10-19.
- ^ a b c Horváth, András Pálóczi (1989). Pechenegs, Cumans, Iasians: Steppe Peoples in Medieval Hungary. Corvina. ISBN 978-9-6313-2740-3.
- ^ a b Linehan, Peter; Nelson, Janet Laughland, eds. (2003). The Medieval World. Routledge Worlds Series. Vol. 10. Routledge. pp. 82–83. ISBN 978-0-415-30234-0.
- ^ "Nyelv és Tudomány- Rénhírek – Kunok legyünk vagy magyarok?". Nyelv és Tudomány. 2012-10-12. Archived from the original on 5 July 2015. Retrieved 29 April 2015.
- ^ On the middle shield Kingdom of Hungary, on the back shield "king" of Croatia, Dalmatia, Slavonia, Lodomeria, Galicia, Bosnia, Serbia, Cumania and Bulgaria
- ^ Szakaly 2000.
- ^ a b c "Karcag: Year of the Cumans 2009" (PDF). karcag.hu. 2009. Archived (PDF) from the original on 15 February 2015. Retrieved 14 June 2015.
- ^ Meszaros 2000.
- ^ Lango 2000a.
- ^ a b c d e f Berend, Nora (2001). At the Gate of Christendom: Jews, Muslims and 'Pagans' in Medieval Hungary, c.1000–c.1300. Cambridge University Press. ISBN 978-0-5216-5185-1.
- ^ Akdes Nimet Kurat, IV-XVII1. Yüzyıllarda Karadeniz Kuzeyindeki Türk Kavimleri ve Devletleri, Ankara 1972, Sayfa 83-84.
- ^ "TARİH VE ARKEOLOJİ: Kuman Duası " Babamız Kun" ve Codex Cumanicus". August 17, 2014.
- ^ Андреев, Йордан; Лазаров, Иван; Павлов, Пламен (1999). Кой кой е в средновековна България [Who is Who in Medieval Bulgaria] (in Bulgarian). Петър Берон. ISBN 978-954-402-047-7.
- ^ Fine, John V. A. (1994). The Late Medieval Balkans: A Critical Survey from the Late Twelfth Century to the Ottoman Conquest. University of Michigan Press. ISBN 978-0-472-08260-5. Archived from the original on 2016-01-08. Retrieved 2015-10-19.
- ^ Yalvar, Cihan (February 2023). "Doğu Avrupa'nın Efendileri Kuman-Kıpçaklar". Derin Tarih Journal.
- ^ a b c d e Heath, Ian (1995). Byzantine Armies AD 1118–1461. Osprey Publishing. ISBN 978-1-8553-2347-6.
- ^ a b Yalvar, Cihan (2024). "BİR BİYOGRAFİ DENEMESİ DEŞT-İ KIPÇAK'TAN BİZANS SARAYINA SYRGİANNES PALEOLOGOS PHİLANTHROPENOS KOMNENOS (1290-1334)". İnalcık Ve Oğuzoğlu Anısına Osmanlı Devleti'nin Kuruluşundan Cumhuriyet Türkiyesi'ne Yalakova'dan Yalova'ya 2024 Sempozyumu Bildiri Kitabı Editör: Doç. Dr. Hacer Karabağ.
- ^ Arbel, Benjamin (2013). Intercultural Contacts in the Medieval Mediterranean: Studies in Honour of David Jacoby. Routledge. p. 143. ISBN 978-1-1357-8188-0.
- ^ GOLUBOVSKİY, P.V., Peçenegi, Torki i Polovtsı Rus i Step Do Naşestviya Tatar, Veçe, Moskva, 2011.
- ^ ÖZTÜRK, Meriç T., The Provıncıal Arıstocracy In Byzantine Asia Minor (1081-1261), Boğaziçi Üniversitesi, Yayınlanmamış Yüksek Lisans Tezi, İstanbul, 2013.
- ^ a b WOLF, Robert Lee, "The Latın Empire Of Constantinople 1204-1261", A History Of The Crusaders, Volume II Later Crusades (1189-1311), General ed. Kenneth M. Setton, ed. By. Robert Lee Wolf and Harry W. Hazard, The Unıversıty Of Wısconsın Press, Madıson, Milwaukee and London, 1969, s. 187-233.
- ^ a b c Ayönü, Yusuf (August 2012). "Bati Anadolu'dakı Türk Yayilișina Karși Bızans İmparatorluğu'nun Kuman-Alan Topluluklarini Balkanlardan Anadolu'ya Nakletmesi" [The Transfer of Cumans and Alans from Balkans to Anatolia by Byzantine Empire against the Turkish Expansion in the Western Anatolia]. Belleten (in Turkish). 76 (276). Turkish Historical Society: 403–418. doi:10.37879/belleten.2012.403. S2CID 245309166. DOI: English version
- ^ a b Dimitri Korobeinikov (2015). "The Cumans in Paphlagonia". Karadeniz İncelemeleri Dergisi (18): 29–44.
- ^ Caroline Gurevich (May 2017). The Image of the Cumans in Medieval Chronicles: Old Russian and Georgian Sources in the Twelfth and Thirteenth Centuries (PDF) (MA thesis). Budapest: Central European University. Archived from the original (PDF) on 2020-08-23.
- ^ Rustam M. Shukurov. "Latent Turkification of Byzantium (ca. 1071–1461)". Dumbarton Oaks.
- ^ Grubu, Haber Ajansı Yayın. "Anadolu'ya yerleştirilen Kumanlar (Manavlar)". www.belediyehaberleri.com.tr.
- ^ Yilmaz, Adil (2018). "Bızans'in Anadolu'ya Yerleştırdığı Son Türkler" [The Last Turks Settled in Anatolia by Byzantium]. Eski̇çağ Araştirmalari Dergi̇si̇ [Journal of Ancient Researches] (in Turkish) (3): 29–32.
- ^ "YALAKOVA'DAN YALOVA'YA Prof. Dr. Halil İnalcık Anısına Yalova Tarihi Araştırmaları" (PDF).
- ^ "Acar, Kenan (2010). Kuzeybatı Anadolu Manav Türkmen Ağızları Üzerine Birkaç Not" (PDF).
- ^ "Muharrem ÖÇALAN SAKARYA- İZMİT YÖRESİ YERLEŞİK TÜRKMENLERİ MANAV AĞIZLARINDA ÖTÜMSÜZ PATLAYICI ÜNSÜZ DEĞİŞMELERİ" (PDF).
- ^ a b Yalvar, Cihan (February 19, 2021). "ANADOLU'DA SON TÜRK İSKÂNI: İZNİK İMPARATORLUĞU'NDA KUMAN-KIPÇAKLAR VE YALOVA KAZIMİYE (YORTAN) İLE ELMALIK (SARUHANLI) KÖYLERİNDEKİ VARLIKLARI". Türk Dünyası Araştırmaları. 127 (250): 11–36 – via dergipark.org.tr.
- ^ Pintescu, Florin (April 2020). "Vlachs and Scandinavians in the Early Middle Ages". ResearchGate. p. 48. Retrieved 9 August 2023.
- ^ a b c "Polovtsy". TheFreeDictionary.com. Archived from the original on 3 May 2015. Retrieved 29 April 2015.
- ^ As mentioned in Robert de Clari's chronicle.
- ^ Ovidiu Pecican Troia Venetia Roma
- ^ a b "Cumans". Encyclopediaofukraine.com. Archived from the original on 2013-12-27. Retrieved 2014-03-01.
- ^ a b c d e Baldick, Julian (2012). Animal and Shaman: Ancient Religions of Central Asia. I.B. Tauris. p. 53. ISBN 978-1-78076-232-6. Archived from the original on 2016-01-08. Retrieved 2015-10-19.
- ^ Rockhill, W. W., The journey of William of Rubruck to the eastern parts of the world, 1253–55, as narrated by himself, with two accounts of the earlier journey of John of Pian de Carpine. London: Hakluyt Society. [1] Archived 2011-08-05 at the Wayback Machine
- ^ Golden, Peter B., "Cumanica IV: The Qipchaq Tribes", Archivum Eurasiae Medii Aevi, v. IX (1997), p. 107
- ^ Chambers, Anatoly M. (1979). The Devil's Horsemen: The Mongol Invasion of Europe. Atheneum. ISBN 978-0-6891-0942-3.
- ^ Nicholle, David (1990). Attila and the Nomad Hordes. Osprey Publishing. ISBN 978-0-8504-5996-8.
- ^ a b Slack, Corliss K. (2013). Historical Dictionary of the Crusades. Scarecrow Press. p. 195. ISBN 978-0-8108-7831-0.
- ^ Szilvia Kovács Bortz, a Cuman Chief in the 13th Century Archived 2019-12-29 at the Wayback Machine Acta Orientalia Academiae Scientiarum Hungaricae Vol. 58, No. 3, Proceedings of the First International Conference on the Mediaeval History of the Eurasian Steppe: Szeged, Hungary May 11—16, 2004: Part III (2005), pp. 255-266
- ^ a b c d Paksoy, H. B., ed. (1992). Codex Cumanicus – Central Asian Monuments. CARRIE E Books. ISBN 978-975-428-033-3. Archived from the original on 20 March 2017. Retrieved 29 April 2015.
- ^ Yule and Cordier 1916
- ^ "Manta – Big finds from small businesses". Goliath.ecnext.com. Archived from the original on 2010-01-24. Retrieved 2014-03-01.
- ^ Brook, Kevin Alan (2006). The Jews of Khazaria. Rowman & Littlefield Publishers. p. 181. ISBN 978-1-4422-0302-0.
- ^ Bonyak at the Great Soviet Encyclopedia.
- ^ Yilmaz, Adil (2018). "Bızans'in Anadolu'ya Yerleştırdığı Son Türkler" [The Last Turks Settled in Anatolia by Byzantium]. Eski̇çağ Araştirmalari Dergi̇si̇ [Journal of Ancient Researches] (in Turkish) (3): 29–32.
- ^ Oshanin, L.V. 1964. Anthropological Composition of the Population of Central Asia, and the Ethnogenesis of its Peoples (trans. V.M. Maurin, ed. H. Field). Cambridge (MA): Peabody Museum of Archaeology.
- ^ Bogacsi-Szabo, Erika; Kalmar, Tibor; Csanyi, Bernadett; Tomory, Gyongyver; Czibula, Agnes; et al. (October 2005). "Mitochondrial DNA of Ancient Cumanians: Culturally Asian Steppe Nomadic Immigrants with Substantially More Western Eurasian Mitochondrial DNA Lineages". Human Biology. 77 (5). Detroit: Wayne State University Press: 639–662. doi:10.1353/hub.2006.0007. ISSN 0018-7143. LCCN 31029123. OCLC 1752384. PMID 16596944. S2CID 13801005.
- ^ a b c Lee, J. Y., & Kuang, S. (2017). A comparative analysis of Chinese historical sources and Y-DNA studies with regard to the early and medieval turkic peoples. Inner Asia, 19(2), 197-239.
- ^ Ibn Fadlān. "Ibn Fadlān and the Land of Darkness". Translated by Paul Lunde; Caroline Stone. Penguin Books.
- ^ Runciman, Steven (December 3, 1987). A History of the Crusades. CUP Archive. ISBN 978-0-521-34772-3 – via Google Books.
- ^ Entangled Histories of the Balkans - Volume Three: Shared Pasts, Disputed Legacies Balkan Studies Library, Roumen Daskalov, Alexander Vezenkov, Publisher BRILL, 2015, ISBN 9004290362, pp. 289-316.
- ^ Yalvar, Cihan (19 February 2021). "CİHAN YALVAR, ANADOLU'DA SON TÜRK İSKÂNI: İZNİK İMPARATORLUĞU'NDA KUMAN-KIPÇAKLAR VE YALOVA KAZIMİYE (YORTAN) İLE ELMALIK (SARUHANLI) KÖYLERİNDEKİ VARLIKLARI". Türk Dünyası Araştırmaları. 127 (250): 11–36.
- ^ Yalvar, Cihan (February 19, 2021). "ANADOLU'DA SON TÜRK İSKÂNI: İZNİK İMPARATORLUĞU'NDA KUMAN-KIPÇAKLAR VE YALOVA KAZIMİYE (YORTAN) İLE ELMALIK (SARUHANLI) KÖYLERİNDEKİ VARLIKLARI". Türk Dünyası Araştırmaları. 127 (250): 11–36 – via dergipark.org.tr.
- ^ Erdem, İlhan. "ORHANGAZİ KARSAK KÖYÜ VE KUMAN KIPÇAKLAR (1)". Edebiyat Defteri. Archived from the original on 3 March 2024.
- ^ Dikbasan, Sabriye. "KIRIM BİR RUS TOPRAĞI MIYDI".
Tatars were mercenaries in the Mongol armies that arrived in Eastern Europe in the 1240s. After the Ottomans took the Crimean Khanate there, other regions were subject to the Golden Horde Mongol Khanate. As subjects of the Mongol state, they were called Tatars. Tatar is a wrong term, we should call them Kipchak Turks. The dictionary of Kipchaks has been published, they speak a Kipchak language.
- ^ "İlber ORTAYLI" (in Turkish). Retrieved 2023-02-04.
Today, those who carry Tatar name partially dislike it. Scholars and intelligentsia in the Kazan Tatarstan Republic don't like this name. It is also true that Tatarstan is not Tatar. This name needs to be changed, Crimean Tatars also say this. This is a wrong represenatation.
- ^ István Vásáry (2005) Cumans and Tatars, Cambridge University Press.
- ^ Stearns(1979:39–40).
- ^ "CUMAN". Christusrex.org. Archived from the original on 16 October 2012. Retrieved 24 October 2012.
- ^ Stearns (1978). "Sources for the Krimgotische". p. 37. Archived from the original on 24 July 2011. Retrieved 12 February 2011.
- ^ Vozgrin, Valery "Historical fate of the Crimean Tatars" Archived 11 July 2006 at the Wayback Machine
- ^ Sevortyan E. V. Crimean Tatar language. // Languages of the peoples of the USSR.— t. 2 (Turkic languages).— N., 1966.— Pp. 234–259.
- ^ "Baskakov – on the classification of Turkic languages". www. philology. ru. Retrieved 16 February 2017.
- ^ Essays on the history and culture of the Crimean Tatars. / Under. edited by E. Chubarova.Simferopol, Crimecity, 2005.
- ^ Brian Glyn Williams, Brian Glyn (2015). The Crimean Tatars: From Soviet Genocide to Putin's Conquest. Oxford University Press. p. xi–xii. ISBN 978-0-19-049470-4.
- ^ "Sea of azov – Learn everything there is to know about Sea of azov at Reference.com". Reference.com. Archived from the original on 30 December 2010. Retrieved 29 April 2015.
- ^ "Független Kiskunságot!". Halasmédia. Archived from the original on 3 May 2015. Retrieved 29 April 2015.
- ^ A. Gergely András: Kun etnoregionális kisvárosi sajátosságok? MTA POLITIKAI TUDOMÁNYOK INTÉZETE, ETNOREGIONÁLIS KUTATÓKÖZPONT, MTA PTI Etnoregionális Kutatóközpont Munkafüzetek 4. (Hungarian Academy of Sciences)[mek.oszk.hu/10600/10674/10674.doc]
- ^ Hírhatár Online Lapcsoport. "Kiskun, nagykun: kunok világtalálkozója Karcagon – Kecskeméti Hírhatár" [Kiskun, nagykun: world meeting of kunos in Karcagon - Kecskemét Hírhatár] (in Hungarian). Archived from the original on 23 July 2015. Retrieved 29 April 2015.
- ^ "32/2004. (IV. 19.) OGY határozat". Hungarian Parliament. 2004. Archived from the original on 2005-02-16. Retrieved 2009-03-15.
- ^ Spinei, Victor. The Cuman Bishopric – Genesis and Evolution. in The Other Europe: Avars, Bulgars, Khazars and Cumans. Edited by Florin Curta and Roman Kovalev. Brill Publishing. 2008. p. 64
- ^ a b c Tánczos, Vilmos (2012). Language Shift among the Moldavian Csángós. Editura ISPMN. ISBN 978-606-8377-10-0. Retrieved 29 April 2015.
- ^ Andrew Bell-Fialkoff, The Role of Migration in the History of the Eurasian Steppe: Sedentary Civilization vs. 'Barbarian' and Nomad Archived 2016-01-08 at the Wayback Machine, Palgrave Macmillan, 2000, p. 247
- ^ Debrabandere, Frans. "Woordenboek van de familienamen in Zeeland" [Dictionary of the surnames in Zeeland] (PDF) (in Dutch). Archived (PDF) from the original on 2016-03-04. Retrieved 2016-02-16.
- ^ Pritsak O., "Stammesnamen und Titulaturen der altaischen Volker. Ural-Altaische JahrMcher", Bd. 24, 1952, Sect. 1–2, pp. 49–104
- ^ Aristov N. A., Notes on ethnic composition of Türkic tribes and nations//Olden Times Alive, 1896, v. 3–4, p. 341
- ^ Curta, Florin; Kovalev, Roman, eds. (2008). "The" Other Europe in the Middle Ages: Avars, Bulgars, Khazars and Cumans. Brill. p. 9. ISBN 978-9-0041-6389-8.
- ^ Ayalon, David (1979). The Mamlūk military society. Variorum Reprints. ISBN 978-0-86078-049-6.
- ^ Horvath 1978; Kovacs 1971; Sandor 1959.
- ^ Glatz, Ferenc (1990). Institute of History of the Hungarian Academy of Sciences (ed.). Modern Age--modern Historian: In Memoriam, György Ránki (1930-1988). Institute of History of the Hungarian Academy of Sciences. p. 23. ISBN 978-96-38-31176-4.
- ^ a b Bogacsi-Szabo, Erika; Kalmar, Tibor; Csanyi, Bernadett; Tomory, Gyongyver; Czibula, Agnes; et al. (October 2005). "Mitochondrial DNA of Ancient Cumanians: Culturally Asian Steppe Nomadic Immigrants with Substantially More Western Eurasian Mitochondrial DNA Lineages". Human Biology. 77 (5). Detroit: Wayne State University Press: 639–662. doi:10.1353/hub.2006.0007. ISSN 0018-7143. LCCN 31029123. OCLC 1752384. PMID 16596944. S2CID 13801005.
- ^ Bogácsi-Szabó, Erika (2006). Population genetic and diagnostic mitochondrial DNA and autosomal marker analyses of ancient bones excavated in Hungary and modern samples (PDF) (Thesis). Szeged, Hungary: University of Szeged. Archived (PDF) from the original on 2014-01-11. Retrieved 2014-03-01.
- ^ Bennett, Casey; Kaestle, Frederika A. (2006). "A Reanalysis of Eurasian Population History: Ancient DNA Evidence of Population Affinities". Human Biology. 78 (4): 413–440. arXiv:1112.2013. doi:10.1353/hub.2006.0052. PMID 17278619. S2CID 13463642.
- ^ Pankratov, Vasili; Litvinov, Sergei; Kushniarevich, Alena (25 July 2016). "East Eurasian ancestry in the middle of Europe: genetic footprints of Steppe nomads in the genomes of Belarusian Lipka Tatars". Scientific Reports. 6 (30197) 30197. Bibcode:2016NatSR...630197P. doi:10.1038/srep30197. PMC 4958967. PMID 27453128. S2CID 2132782.
Sources
[edit]- Kristó, Gyula; Makk, Ferenc (1996). Az Árpád-ház uralkodói [Rulers of the House of Árpád] (in Hungarian). I.P.C. Könyvek. ISBN 963-7930-97-3.
- Rapp, Stephen H. (1997). Imagining History at the Crossroads: Persia, Byzantium, and the Architects of the Written Georgian Past (Ph.D. dissertation). University of Michigan. OCLC 41881042.
- Sinor, Denis (1990). The Cambridge History of Early Inner Asia.
Further reading
[edit]- "History of the Cumans to the Mongol invasion". Szilvia Kovács. Chronica 13 (2017): 99-104.
- (in Russian) Golubovsky Peter V. (1884) Pechenegs, Torks and Cumans before the invasion of the Tatars. History of the South Russian steppes in the 9th-13th Centuries (Печенеги, Торки и Половцы до нашествия татар. История южно-русских степей IX–XIII вв.) at Runivers.ru in DjVu format.
- (in Russian) Golubovsky Peter V. (1889) Cumans in Hungary. Historical essay (Половцы в Венгрии. Исторический очерк) at Runivers.ru in DjVu format.
- István Vásáry (2005) "Cumans and Tatars", Cambridge University Press.
- Gyárfás István: A Jászkunok Története
- Györffy György: A Codex Cumanicus mai kérdései
- Györffy György: A magyarság keleti elemei
- Hunfalvy: Etnographia
- Perfecky (translator): Galician-Volhynian Chronicle
- Stephenson, Paul. Byzantium's Balkan Frontier: A Political Study of the Northern Balkans, 900–1204, Cambridge University Press, 2000
External links
[edit]Cumans
View on GrokipediaNomenclature and Etymology
Designations in Primary Sources
In Rus' chronicles, including the Primary Chronicle (Povest' vremennykh let), the Cumans are consistently referred to as Polovtsy or Polovtsiane, a Slavic term derived from polova ("chaff" or "straw"), interpreted as denoting their pale or yellowish hair color or possibly the light hue of their felt tents.[2] This designation appears in entries from the 11th century onward, such as the 1055 record of their first major raids into Rus' territories.[3] Western European and Latin sources, including annals and papal correspondence from the 12th century, employ Cumani or Comani, derived by most scholars from the Turkic root qu, qun, or quman, meaning "pale," "sallow," "straw-colored," or "yellowish-grey," with the suffix -man often functioning as an augmentative or intensive (cf. Turkmen). This ethnonym reflects their self-perception as "pale" or "yellowish" in complexion and is paralleled by cross-linguistic evidence where other cultures' designations also connoted paleness or yellowness: Slavic Polovtsy from Old East Slavic polovъ ("pale/yellow"), Germanic Folban or Falven from High German falbe ("pale/fallow"), and Armenian Xartešk'n ("blond" or "fair").[4][5] Byzantine Greek texts similarly use Koumanoi or variants, as seen in chronicles documenting their alliances and conflicts around 1091–1185.[2] Eastern Islamic sources, such as Persian and Arabic histories from the 11th–12th centuries, identify them primarily as Qipchaq or Kipchak, encompassing a broader confederation of which the Cumans formed the western segment; this term appears in works like those of al-Idrisi and Rashid al-Din, denoting steppe nomads from the Irtysh River to the Dnieper.[6] Some German accounts from the 11th–12th centuries, including those by Adam of Bremen, render variants like Folban or Vallani/Valwe, possibly corruptions of Polovtsy or local adaptations tied to early encounters in the Baltic or Hungarian frontiers.[7] Among settled Cumans in 13th-century Hungary, the self-designation Cuni emerges in legal and ecclesiastical records, indicating retention of core ethnonyms post-migration.[8]Relation to Kipchak Identity and Tribal Confederations
The Cumans' nomenclature aligns closely with Kipchak designations in eastern sources, reflecting their integration into a westward-migrating tribal horizon during the 10th and 11th centuries. Arabic and Persian geographers, such as those in Hudud al-'Alam (ca. 982 CE), identify the Kipchaks as a nomadic group originating as an offshoot of the Kimak confederation in the Irtysh River region, with early expansions linking them to the Ural steppes by the late 10th century.[9] These accounts portray Kipchak territories—later termed Desht-i Kipchak—as encompassing areas from Siberia to the Volga, into which Cuman groups appear to have fused through alliance and displacement. Chinese annals provide indirect corroboration via references to proto-Kipchak entities under variants like Knyushe in Tang dynasty records (7th-9th centuries), tracing eastern roots before the 11th-century migrations that brought these populations into contact with Pechenegs and Oghuz.[10] Scholarly debate centers on whether Cumans represented a discrete tribe or a Kipchak subgroup, with linguistic data prioritizing shared Kipchak Turkic substrate over notions of isolated ethnic origins. The Cuman language, preserved in the Codex Cumanicus (late 13th century), demonstrates phonological and morphological traits—such as vowel harmony patterns and ablaut alternations—hallmarks of the West Kipchak dialect continuum, aligning it phylogenetically with languages like Karachay-Balkar rather than eastern Oghuz branches.[11] This evidence, derived from comparative reconstruction, indicates that Cuman nomenclature likely denoted western Kipchak factions post-migration, as steppe polities absorbed and rebranded subgroups without implying genetic discontinuity; romanticized views of "pure" tribes overlook the causal dynamics of nomadic adaptation, where intermarriage and conquest homogenized identities.[12][6] Primary texts underscore the confederative structure of Kipchak-Cuman polities, emphasizing alliances over fixed tribal monoliths. The Secret History of the Mongols (ca. 1240) enumerates Kipchak adversaries as comprising subgroups like the Qangli, integrated into a loose union that Mongols fragmented through targeted campaigns, revealing internal hierarchies led by khans rather than unified ethnicity.[13] Persian sources similarly depict the Kipchak confederation as a multi-component entity blending Turkic cores with Mongolic and Iranian fringes, sustained by pastoral mobility and tribute networks across subregions from the Aral Sea to the Black Sea.[6] Such fluidity in tribal listings—evident in 11th-century Arabic itineraries equating western "Cumans" with eastern "Kipchaks"—highlights how nomenclature served political utility in denoting allied hordes, adapting to conquests and ecological pressures rather than denoting immutable descent.[6]Origins and Early History
Hypotheses on Pre-Cuman Roots Including Qun
Hypotheses linking the Cumans to the Qun, a nomadic group recorded in Tang dynasty Chinese annals (618–907 CE) as inhabiting regions near the northern borders of China, posit these as potential proto-Cumans based on phonetic correspondences and shared nomadic lifestyles. Chinese sources describe the Qun as part of eastern steppe confederations engaging in raids and alliances during the 7th–8th centuries, preceding the Kipchak-Cuman expansion westward. This view interprets Qun migrations amid pressures from Uyghur and Karluk expansions as early phases of the same population movements that formed the Cuman-Kipchak entity, though direct genealogical links remain conjectural without confirmatory inscriptions or artifacts.[14] The Cumans' emergence in the Pontic-Caspian steppe around 1050–1060 CE stemmed from Central Asian migrations, driven by displacements following Oghuz Turk incursions into Kimak territories along the Irtysh River in the 10th century. These dynamics displaced proto-Kipchak bands westward, filling vacuums left by Pecheneg retreats toward Byzantium and the Balkans. Verifiable textual evidence from Persian geographers like al-Biruni (d. 1048 CE) notes Kipchak presence east of the Volga by the early 11th century, aligning with archaeological evidence of transitional nomadic sites in the southern Urals exhibiting Turkic-style metallurgy and horse gear.[15] Non-Turkic origin hypotheses, such as Iranian or Mongolic primacy, are unsubstantiated by linguistic data; the attested Cuman language belongs to the Northwestern (Kipchak) Turkic subgroup, with vocabulary and grammar continuous from attested Orkhon Turkic inscriptions (8th century CE). Onomastic analysis of Cuman names in Rus' and Hungarian chronicles yields Turkic roots (e.g., qun denoting "pale" or "yellowish," matching descriptive ethnonyms), precluding significant non-Turkic substrates. Genetic studies of medieval steppe remains further indicate East Eurasian paternal lineages (e.g., Q1a and R1a-Z93 subclades) consistent with Turkic nomadic gene pools from the Altai region, rather than local Pontic indigenes. Diffusionist claims of cultural borrowing without ethnic replacement ignore causal realities of nomadic conquests, where linguistic dominance follows military hegemony, as seen in prior Oghuz overlays.[16]Formation of the Cuman-Kipchak Confederation
The Kipchak tribes, originating from the Irtysh River region in southwestern Siberia, initiated westward migrations in the early 11th century, expanding into territories held by Oghuz groups during the preceding 9th and 10th centuries and achieving independence from the Kimak Khanate.[17] [18] These movements culminated in the mid-11th century with the collapse of the Kimak state, prompting Kipchaks to advance across the Ural Mountains and into the Pontic-Caspian steppe, where they encountered and clashed with Pecheneg tribes, displacing them westward.[17] By 1055, Kipchak and Cuman elements had merged into a political confederation in the Black Sea steppes, establishing dominance as neighbors to Kievan Rus' principalities and extending their influence from Kazakhstan to the Danube.[19] This loose alliance of tribal units, led by independent khans rather than a centralized authority, controlled the steppe from the Volga River to the Black Sea, including the North Caucasus, with further expansion to the Dniester and Danube by the 1120s.[17] [19] The confederation's decentralized structure, sustained by pastoral nomadism and reliance on horse-mounted warfare, prioritized military flexibility and raiding economies over fixed state institutions, enabling effective exploitation of the steppe's vast grazing lands and superiority over less mobile settled polities.[17] Interactions with preceding nomads like the Pechenegs and Oghuz involved both conquest and selective alliances, such as temporary Byzantine pacts against common foes, which facilitated the Kipchaks' consolidation of power without requiring unified governance.[17]Political Organization and Steppe Conquests
The Cumans maintained a decentralized political organization characterized by a confederation of semi-autonomous tribes, each led by a khan whose authority derived from military prowess and clan loyalty rather than hereditary succession. Nobles known as begs formed an advisory elite, facilitating decisions through informal councils during assemblies (qurultai-like gatherings), which allowed for rapid reconfiguration of alliances amid the steppe's volatile geopolitics. This fluid hierarchy contrasted sharply with the rigid bureaucracies of neighboring sedentary states, enabling the Cumans to prioritize mobility and tactical opportunism over administrative permanence.[20][14] By the mid-11th century, Cuman tribes had consolidated control over the Pontic-Caspian steppe through systematic displacement of preceding nomads, notably the Pechenegs, whom they outmaneuvered in open-field engagements leveraging composite bows and horse archery. Historical records indicate that Pecheneg power waned from the early 11th century onward, with Cuman incursions forcing westward migrations and culminating in the Cumans' dominance west of the Volga by 1055. This expansion demonstrated the confederation's adaptive realism, as tribal autonomy permitted decentralized scouting and strikes without the logistical burdens of unified command structures.[21][22] Cuman forces extended their influence eastward and southward, raiding Volga Bulgaria repeatedly from the late 11th century to extract tribute and disrupt trade routes, though without establishing lasting territorial conquests due to the Bulgars' fortified urban defenses. Similarly, in the North Caucasus, Cumans conducted predatory campaigns against the Alans during the 1080s and 1090s, often in coordination with Rus' princes, exploiting vulnerabilities in the rugged terrain while avoiding prolonged sieges. These operations underscored tactical superiority in steppe warfare, where light cavalry enabled hit-and-run tactics far more effective than the heavy infantry of settled foes.[23][24] The confederation's eschewal of urbanism—relying instead on portable felt tents, vast herds, and seasonal migrations—bolstered resilience against counterattacks, as there were no fixed capitals to capture, rendering the Cumans elusive to empires burdened by static infrastructure. This nomadic paradigm, rooted in causal dependencies of pastoral economics and equine logistics, sustained their hegemony across Dasht-i-Kipchak until external pressures mounted.[25][20]Expansion and Conflicts in Eastern Europe
Raids and Battles Against Kievan Rus'
The Cumans, known as Polovtsians in Rus' sources, initiated raids into Kievan Rus' territory as early as 1055, establishing initial peaceful relations that deteriorated by 1061 with renewed incursions that disrupted southern principalities.[26] These nomadic assaults exploited the mobility of Cuman horse archers, allowing rapid strikes on settlements and retreats that outpaced Rus' heavy infantry responses, demonstrating the efficacy of asymmetric steppe warfare.[27] A pivotal engagement occurred in 1068 at the Battle of the Alta River, where a Cuman force decisively defeated the combined armies of Grand Prince Iziaslav I, Sviatoslav II, and Vsevolod I, comprising thousands of Rus' warriors; the princes fled, enabling Cuman plunder near Kyiv and triggering the Kiev uprising due to perceived princely incompetence.[28] This victory underscored Cuman tactical superiority in open terrain, where their composite bows and feigned retreats inflicted heavy casualties on pursuing Rus' forces.[2] Throughout the late 11th century, Cuman khans frequently allied with rival Rus' princes, providing auxiliary cavalry in internecine conflicts while betraying others through sudden raids, as documented in the Primary Chronicle; such opportunistic partnerships amplified nomadic leverage over fragmented Rus' polities.[2] Prince Vladimir Monomakh countered these threats with coalition campaigns, notably defeating Cuman forces in 1103 and at the Salnitsa River in 1111, where Rus' armies numbering over 50,000 inflicted significant losses, forcing temporary retreats but not eliminating the raid threat.[28] In the 12th century, Prince Igor Svyatoslavich of Novgorod-Seversky launched an unauthorized expedition in May 1185 against Cuman encampments along the Donets River, engaging in a three-day battle that ended in Rus' defeat, Igor's capture, and the death of many warriors, as chronicled in the Hypatian Codex and immortalized in The Tale of Igor's Campaign.[27] Subsequent coordinated Rus' offensives under Svyatoslav Vsevolodovich in 1183, 1185, and 1187 repelled Cuman incursions, capturing khans and securing southern borders temporarily through superior numbers and fortified river defenses.[2] These engagements highlight how Cuman raid success relied on surprise and dispersion, yielding territorial gains and tribute, though pitched coalitions often reversed gains via attrition.[27]Incursions into the Balkans and Hungary
In the early 12th century, following the Byzantine Empire's decisive victory over the Pechenegs at the Battle of Levounion in 1091, the Cumans emerged as the primary nomadic threat to imperial territories in Thrace and the lower Danube region. By the 1120s, Cuman warbands crossed the Danube in significant numbers, launching raids that penetrated deep into Thrace, exploiting the empire's stretched defenses amid internal recovery efforts. These incursions, characterized by rapid hit-and-run tactics leveraging superior horse archery, devastated rural areas and smaller settlements, highlighting the limitations of Byzantine static fortifications against mobile steppe forces. During the 1180s, Cumans forged opportunistic alliances with Vlach pastoralists in Wallachia and the Asenid brothers—Peter and Ivan Asen—who initiated rebellions against Byzantine overlordship in 1185. This partnership enabled coordinated raids into Thrace, where Cuman cavalry supported Vlach-Bulgarian forces in sacking key outposts and disrupting supply lines, contributing to the erosion of Byzantine control south of the Danube. By 1187, these joint expeditions had compelled Emperor Isaac II Angelos to negotiate truces, though violations persisted, with Cumans plundering as far as Adrianople's outskirts; their nomadic agility allowed evasion of heavy infantry, underscoring feudal armies' vulnerability to dispersed, high-mobility assaults that prioritized looting over pitched battles.[29][30] Parallel to Balkan forays, Cuman groups probed Hungary's eastern frontiers from the late 11th century, with a notable invasion in 1068 ravaging Transylvanian territories and defeating Hungarian forces under King Solomon near the Tisza River, compelling temporary retreats and exposing gaps in Árpád dynasty border defenses. Renewed clashes in the 12th century saw Cumans serving intermittently as Rus' auxiliaries against Hungarian expeditions, further straining the kingdom's feudal levies ill-suited to counter steppe incursions. By the 1220s, under King Andrew II, Hungarian campaigns pushed into Cuman-held lands east of the Carpathians, culminating in 1227 when tribes between the Olt and Siret rivers submitted to annual tribute payments, marking a shift from unchecked raids to coerced vassalage amid Hungary's southward expansions. These encounters repeatedly demonstrated sedentary kingdoms' challenges in securing vast frontiers, as Cuman forces sacked undefended villages and evaded pursuit, destabilizing local economies reliant on fixed agrarian structures.[31][1]Internal Dynamics and Defensive Alliances
The Cumans maintained a decentralized political structure characterized by a loose confederation of tribes and clans, each governed by independent khans whose rivalries fostered internal factionalism and opportunistic power struggles. Absent a centralized empire or overarching authority, these khans operated autonomously, often aligning with or opposing one another based on immediate gains, which fragmented collective action against external pressures.[32] This tribal autonomy, rooted in nomadic kinship networks, enabled rapid mobilization for raids but hindered unified defense, as evidenced by the distinct regional groups referenced in Rus' chronicles, such as those active along the Don River versus the Dnieper steppe.[33] Facing existential threats from rival nomads and consolidating sedentary powers, Cumans resorted to pragmatic, short-term defensive alliances with neighbors to preserve their steppe dominance. In the western steppe, individual khan-led contingents allied with Kievan Rus' princes against internal Rus' rivals or residual nomadic foes, exemplified by pacts between Chernigov-based Olgovichi princes and Cuman leaders in the 1140s–1160s to counter the influence of Vladimir-Suzdal forces, thereby stabilizing frontiers amid inter-princely wars.[32] These coalitions were causal responses to the Cumans' vulnerability post-Rus' victories, such as the 1103 Battle of Dolobsk and 1111 Battle of Salnitsa, which compelled a pivot from unilateral offensives to mutual defense arrangements for mutual deterrence.[32] Further west, Cumans forged tactical partnerships with the Byzantine Empire against the Pechenegs, who posed a direct threat to shared borders. Cuman horsemen reinforced Byzantine armies in the 1091 Battle of Levounion, where their archery superiority contributed to the decisive rout of approximately 80,000 Pechenegs on April 29, exploiting the invaders' wagon-fort vulnerabilities and securing the Danube frontier.[34] Such alliances underscored the Cumans' adaptive realism: by leveraging Byzantine resources against depleting Pecheneg remnants, they neutralized a competitor while gaining plunder and temporary imperial favor, though these pacts dissolved once immediate threats subsided. By the early 1200s, escalating eastern incursions and Rus' consolidation accelerated this defensive orientation, prioritizing survival coalitions over expansion amid khan-level infighting.[5]Mongol Conquest and Subsequent Dispersal
The 1230s-1240s Invasions and Subjugation
Batu Khan, grandson of Genghis Khan, led the Mongol western expedition starting in 1236, initially targeting the Volga Bulgaria, which fell after a series of sieges and battles by early 1237.[35] Following this victory, Mongol tumens advanced into the Kipchak-Cuman steppe territories of Desht-i-Kipchak, where the nomadic confederation had dominated since the early 12th century.[36] Cuman forces, disorganized across tribal lines and numbering in the tens of thousands of mounted archers, attempted localized resistance against the invaders, but lacked the unified command structure of the Mongols.[37] Mongol tactics, emphasizing mobility, feigned retreats, and massed composite bow volleys, exploited the Cumans' similar but less coordinated steppe warfare style, leading to repeated defeats in skirmishes across the Pontic-Caspian region from 1237 to 1239.[37] Batu's army, reinforced to approximately 120,000-150,000 warriors drawn from multiple uluses, overwhelmed Cuman khans through encirclement and pursuit, forcing many clans into submission as vassals obligated to provide tribute and auxiliary troops.[38] Empirical accounts from Persian chronicler Juvayni highlight the Cumans' flight and dispersal rather than sustained battles, underscoring numerical and logistical inferiority against the Mongol host's sustained campaign logistics.[36] Khan Köten, leading a significant faction, evaded subjugation by migrating westward with tens of thousands of followers toward Hungary in 1239, prompting Mongol vanguard probes into border regions.[39] This partial escape did not halt the broader confederation's collapse; by 1240, surviving Cuman groups either integrated into the Golden Horde as subjects or scattered, with resistance crumbling under relentless Mongol pressure.[35] The subsequent 1241 incursion into Hungary, culminating in the Battle of Mohi on April 11, where Cuman auxiliaries fought alongside King Béla IV's forces but suffered rout against Batu's flanking maneuvers, exemplified the futility of fragmented defenses against the invaders' superior horde.[39]Mass Migrations and Settlements in Hungary
In the wake of Mongol conquests in the Pontic steppes during the late 1230s, Khan Köten led a large group of Cumans seeking refuge into the Kingdom of Hungary in 1239, with the migration intensifying amid the 1241 Mongol invasion.[39] King Béla IV, anticipating further steppe threats, permitted their entry and settlement primarily in the Great Hungarian Plain between the Danube and Tisza rivers, granting lands sufficient to support their nomadic pastoralism while integrating them into the realm's defense structure.[40] Estimates based on land allocations and contemporary accounts place the influx at around 40,000 Cuman families, equivalent to 70,000–80,000 individuals, though the precise figure remains debated due to varying interpretations of medieval terminology for family units.[1] In return, Köten pledged collective baptism and auxiliary military service, with royal charters formalizing territorial grants and privileges such as tax exemptions conditional on these obligations.[41] Cultural clashes quickly emerged between the semi-nomadic Cumans and Hungary's agrarian populace, exacerbated by suspicions of divided loyalties during the Mongol onslaught. In March 1241, amid rising unrest in Pest, Köten and his entourage were assassinated by Hungarian nobles, reportedly over fears of espionage or failure to fully abandon pagan rites, prompting a Cuman backlash of pillaging and southward flight toward the Balkans. Béla IV, having fled the Mongol advance, pursued and reasserted control over surviving groups post-withdrawal in 1242, resettling them under stricter oversight to prevent further disorder.[42] To mitigate persistent revolts and ensure loyalty, Béla mandated accelerated Christianization, including mass baptisms and missionary oversight, though enforcement proved uneven as steppe traditions lingered. The Cumans' assimilation, though fraught, yielded strategic benefits, as their expertise in mounted archery bolstered the royal army's light cavalry wing, critical for post-invasion recovery and border defense. Charters from Béla's reign affirmed their role in campaigns, with Cuman contingents providing mobile forces that complemented heavy knightly units, while their herds contributed to economic revitalization in depopulated plains regions. These policies, balancing inducements like autonomy in internal affairs with demands for cultural conformity, gradually curbed nomadic unrest, though full integration spanned generations amid ongoing noble grievances over land encroachments.[43]Involvement in Serbia, Bulgaria, and Byzantine Mercenary Service
In the 13th century, Cuman groups formed alliances with Serbian rulers of the Nemanjić dynasty, serving as auxiliary forces amid regional conflicts with Byzantium and Hungary; these nomadic warriors provided mobile cavalry support, integrating partially into the Serbian military elite despite tensions arising from their steppe customs and pagan practices.[44] Such alliances were pragmatic, leveraging Cuman horsemanship for border defense, though primary chronicles note occasional unreliability due to tribal loyalties. Cuman settlements emerged in Bulgarian territories during the Second Bulgarian Empire (1185–1396), where displaced groups from the Pontic steppe sought refuge and were absorbed as settlers and warriors; archaeological evidence from sites like Rahovets Fortress in central northern Bulgaria includes a headless horse skeleton unearthed in 2024, indicative of nomadic burial rites, alongside a 2017 skeleton analyzed as Cuman-origin based on cranial features and grave goods.[45] [46] These findings, dated to the late 12th–mid-13th centuries, reveal semi-permanent dwellings adapted from yurt-like structures, reflecting gradual sedentarization while maintaining pastoral economy.[47] Cuman auxiliaries bolstered Bulgarian armies against Byzantine incursions, contributing to victories like those in the 1190s uprisings, but their integration faced resistance from Orthodox clergy over shamanistic rituals.[48] Byzantine emperors increasingly recruited Cuman mercenaries in the 13th century to replenish depleted tagmata, valuing their expertise in hit-and-run archery tactics; at the Battle of Pelagonia in 1259, Cuman light cavalry, alongside Turkish horsemen, outmaneuvered Latin heavy knights, securing a decisive victory for Emperor Michael VIII Palaiologos.[49] Historian George Pachymeres documented their service in imperial campaigns through the early 14th century, noting deployments as flankers in mixed armies, though disciplinary issues—stemming from nomadic indiscipline and conversion pressures—led to revolts and purges by the 1320s.[44] Their role declined with the empire's shrinking resources and rising Ottoman threats, as native levies and Western adventurers supplanted steppe hires.[50]Integration into the Golden Horde
Following the Mongol subjugation of the Cuman-Kipchak confederation in the 1240s, surviving Kipchak (Cuman) elites and warriors were integrated into the Ulus of Jochi's military hierarchy, receiving appanage territories known as uluses that permitted limited tribal autonomy under Jochid overlords.[51] These ulus assignments, often in the Volga and Crimean regions, allowed Kipchak beks to maintain nomadic retinues and levy forces, blending steppe confederative traditions with Mongol decimal organization while subordinating them to khanal authority.[52] By the 1260s, Kipchaks formed a core component of Nogai Khan's western ulus forces, comprising much of his 30,000–50,000-strong cavalry that projected power into Crimean mint operations and Volga trade routes, as well as influencing internal Horde successions through alliances against rival Jochids like Töle Buqa in 1287.[53] Nogai's de facto control over these areas until his defeat by Toqta in 1299 relied on Kipchak loyalty, evident in joint campaigns that stabilized Volga politics amid Ilkhanate border skirmishes.[54] Kipchak Turkic emerged as the administrative lingua franca of the Golden Horde by the late 13th century, used in military dispatches and court correspondence alongside initial Mongolian scripts, reflecting the numerical dominance of Turkic-speakers in the ulus bureaucracy.[12] This linguistic shift paralleled broader Turkicization, verifiable in coinage evolution: early dirhams struck at Bolgar circa 1240–1250 bore Arabic caliphal tamgas, but by Özbeg Khan's reign (1313–1341), issues from Crimea and Sarai incorporated Turkic khanal titles like "sultan" alongside personal names such as Özbeg, signaling Kipchak elites' fiscal integration and erosion of pure Mongol terminologies.[55]Society, Culture, and Economy
Military Tactics, Warfare, and Horse Archery Superiority
The Cumans, as Kipchak Turkic nomads, centered their warfare on light cavalry horse archers, leveraging the inherent advantages of steppe mobility to outpace and outmaneuver infantry-dependent armies of sedentary foes. Core to their operations were composite recurve bows, crafted from layered wood, animal horn, and sinew, which delivered high-velocity arrows—up to 300 meters in range—while compact enough for firing from horseback without dismounting.[56] This setup enabled sustained hit-and-run harassment, where warriors could loose volleys in rapid succession, often employing the Parthian shot technique: twisting backward to fire during gallops, maximizing disruption during advances or withdrawals. Their ponies, bred for endurance rather than speed, supported multi-day operations with minimal resupply, allowing tactical feigned retreats to draw pursuers into kill zones where encirclement by flanking tumens (units of 10,000) could annihilate disorganized infantry.[57] From first-principles, this system's efficiency stemmed from causal asymmetries in open terrain: horses amplified human agility, permitting archers to maintain distance from melee-range threats while projectiles inflicted attrition without risking close-quarters losses. Light cavalry formations—lacking heavy infantry or phalanxes—prioritized dispersion and reformation, evading countercharges and exploiting gaps in enemy lines through superior reconnaissance and signaling via flags or horns. Armor emphasized mobility over protection; warriors favored leather or minimal lamellar scales, though archaeological evidence indicates selective use of chainmail hauberks and iron helmets for elite riders, as evidenced by 13th-century fragments from a Cuman horseman's grave at Viminacium in Serbia, including a spangenhelm-style helmet and mail links alongside a sword.[58] Similarly, a 13th–14th-century helmet and chainmail from the Ludoška mound near Zrenjanin reveal adoption of Byzantine-influenced gear without sacrificing agility.[59] These methods yielded rapid conquests across unfortified plains, where nomadic forces could cover 100 kilometers daily to raid supply lines or force battles on favorable terms, depleting foes through famine and desertion before engagement.[60] However, vulnerabilities emerged against entrenched defenses; lacking specialized engineers or massed infantry for breaching walls, Cumans often bypassed fortified cities, content with extorting tribute rather than sieges, which exposed their dispersed formations to concentrated artillery or boiling oil from above.[61] This limitation underscored the tactical realism of steppe warfare: dominance in fluid, field-based conflicts but reliance on psychological intimidation or alliances for urban subjugation.[56]Religious Beliefs and Shamanistic Practices
The Cumans, as part of the broader Qipchaq confederation, practiced Tengrism, a shamanistic and animistic religion that elevated Tengri as the supreme sky god and creator.[62] This system emphasized harmony with natural forces, including veneration of sacred sites such as holy mountains and rivers, where shamans conducted rituals to invoke spirits and ensure communal prosperity.[62] Ancestor worship and protective deities like Umay-ana, associated with fertility and childbirth, further characterized these beliefs, drawing from longstanding steppe traditions.[62] Shamanistic practices involved blood rituals and ecstatic mediation, with shamans glorifying martial deeds through sacrificial customs that reinforced tribal cohesion and warrior ethos..pdf?dl=1) Kurgan burials, typical of Cuman funerary rites, often included horse sacrifices—evidenced in steppe archaeology as selective slaughter of steeds to accompany the deceased—symbolizing the horse's spiritual role in shamanic journeys to the afterlife and affirming the nomadic bond between rider and mount.[63] Post-Mongol dispersal led to partial conversions, with approximately 40,000 Qipchaq warriors and families adopting Christianity in Georgia by 1118 under Nestorian influence, and elites later embracing Islam through Golden Horde alliances.[62] Despite these shifts, animistic residues endured, as pagan terminology like "tamu" for hell persisted in Islamicized contexts, indicating superficial overlays rather than wholesale abandonment of indigenous shamanism.[62] Such syncretism, while enabling political integration, arguably attenuated the pure martial discipline rooted in unadulterated Tengrist fatalism and ritual purity.[62]Nomadic Economy, Animal Husbandry, and Material Culture
The Cumans sustained their nomadic economy primarily through pastoralism, herding large flocks of sheep, horses, cattle, goats, and camels across the Pontic-Caspian steppe prior to their 13th-century migrations.[64] Horses held central economic value, often traded as a premium commodity equivalent to multiple cattle in contemporary Kievan Rus' legal norms, such as one unbroken stallion matching two head of cattle.[64] This system was supplemented by raiding for loot and limited opportunistic cultivation, with trade networks extending to Rus' principalities, Byzantium, and Levantine markets for slaves—capturing up to 5,000 in single campaigns—and animal products like fox, beaver, and squirrel skins.[64] Slaves integrated into herds management, performing labor unsuited to nomadic mobility, while tribute and alliances with sedentary states provided grain to offset pastoral shortfalls.[64] Animal husbandry demanded intensive oversight tailored to species: sheep required year-round daytime herding to prevent straying, while horses necessitated nocturnal guarding for five months after foaling to deter theft, alongside seasonal milking for both.[64] Large herds relied on extended family networks or dependent herdsmen, enabling elite households to amass wealth through surplus production, dowries, and gifts.[64] Archaeozoological analyses from medieval Hungarian Cuman sites, such as Csengele and Kiskunhalas, reveal faunal assemblages dominated by cattle (up to 60%), followed by sheep/goat (20%), pigs (15%), and horses (5%), indicating continuity in pastoral focus amid integration, with hunting and fishing as ancillary pursuits.[64] By the 15th century, specialization emerged to meet feudal market demands, though core practices persisted in the Carpathian Basin post-arrival.[64][65] Upon settling in Hungary after the 1239 arrival under Khan Kötény and Béla IV's 1241 invitation, Cumans adapted toward semi-sedentary patterns, establishing permanent winter camps and commissioning small-scale farming of millet and wheat by dependents or slaves within restricted mobility zones of 40-50 km² per family.[64] This shift supplemented herds with crop yields, aligning with 1279 Cuman laws regulating slave releases and land use, yet animal husbandry remained dominant, resisting full sedentarization.[64] Material culture emphasized portability and status, with elite kurgan burials among Kipchak-Cuman groups featuring horse sacrifices, bone tools like skates and gaming pieces, and ornaments reflecting pastoral wealth hierarchies.[64] [66] Daily artifacts included felt-lined tents displayed with silver dishes on carts, caftans, belts, and high caps, often buried with steppe saddles to signify equestrian economic prowess.[64] In Hungarian contexts, these persisted into the 14th century, blending with local elements under Christianization pressures from rulers like Louis the Great.[64]Linguistic and Literary Artifacts Like the Codex Cumanicus
The Codex Cumanicus, a manuscript compiled primarily in the early 14th century, serves as a key linguistic artifact documenting the Kipchak Turkic language spoken by the Cumans. It consists of two main sections: a trilingual dictionary featuring Kipchak terms alongside Latin and Persian equivalents, dated to July 11, 1303, and a later "Missionaries' Book" with religious texts, grammar notes, and German glosses assembled around 1330–1340.[67][68] The dictionary, oriented toward practical vocabulary for commerce and daily life, includes over 1,300 Kipchak words, emphasizing terms related to nomadic pastoralism such as horse breeds (at for horse, yay for mare), equestrian gear, and kinship structures (ata for father, ana for mother, qarındaş for sibling), which highlight the centrality of equine husbandry and familial clans in Cuman society.[69][70] Compiled by Franciscan missionaries and Italian merchants active among Cuman communities in the Black Sea region and Volga steppes, the codex facilitated communication for evangelical efforts and Genoese-Venetian trade networks, where Cumans acted as intermediaries in fur, slave, and livestock exchanges.[68][71] The missionary section incorporates translated sermons, psalms, and riddles adapted into Kipchak, demonstrating efforts to convey Christian doctrine while incorporating local idioms, though the Persian influence suggests mediation via Mongol Ilkhanate cultural exchanges.[67] This compilation indicates limited but functional literacy in Kipchak among elite or converted Cumans in contact with literate Europeans and Persians, rather than widespread native script use, as the text employs Latin script transliterations.[72] While providing invaluable phonological and lexical data—such as verb conjugations reflecting agglutinative Turkic grammar—the codex's utilitarian focus limits its representation of Cuman oral traditions, excluding epic poetry or folklore beyond a few aphoristic riddles.[73] Its content, shaped by external compilers' priorities, prioritizes transactional and proselytizing needs over indigenous literary forms, thus offering a filtered glimpse into Kipchak rather than a comprehensive cultural archive.[71]Physical Anthropology and Genetics
Contemporary Accounts of Appearance and Physique
Rus' chronicles, such as the Primary Chronicle, referred to the Cumans as Polovtsy, a term derived from the Slavic word polový meaning "blond" or "pale," reflecting observations of their light hair and complexion among steppe nomads otherwise associated with eastern origins.[74] This portrayal emphasized their distinctive appearance as tall and fair-haired warriors, contrasting with darker-featured neighbors and underscoring their visibility in conflicts from the 11th century onward.[75] Byzantine sources similarly noted their imposing stature and savage demeanor in battle, as recorded by historians like Niketas Choniates during 12th-century incursions, portraying them as physically formidable horsemen capable of swift, enduring campaigns.[76] Early European accounts, including that of Adam of Bremen in the 11th century, corroborated the fair-skinned and light-haired traits, attributing these features to Kipchak groups encountered in northern contexts.[74] Chinese chronicles from the Tang and Song eras further described Kipchaks as having fair hair and blue eyes, traits uncommon among central Asian peoples, suggesting a heterogeneous physique shaped by steppe migrations.[75] These textual depictions align with skeletal evidence from kurgan burials, where remains exhibit robust bone structures, enlarged muscle attachments on limbs, and pelvic adaptations consistent with lifelong horsemanship and archery demands, indicating physiques optimized for mobility and combat endurance on the open plains.[77] Facial reconstructions from Kipchak kurgans, such as a 2025 anthropological effort on a 10th-13th century burial in Znam'yanka, Luhansk, reveal mixed Europoid and East Eurasian features, including prominent brows and robust jaws, supporting contemporary notes on varied yet predominantly light complexions among warriors.[78] Such evidence highlights adaptations for harsh steppe conditions, with taller statures—averaging over 170 cm for males based on long bone measurements—and dense cortical bone indicative of physical resilience forged through nomadic rigors rather than settled labor.Ancient DNA Evidence and Paternal East Eurasian Lineages
Ancient DNA analyses of Cuman remains from Hungary, particularly from the Csengele site dated to the 13th century, revealed mitochondrial DNA (mtDNA) profiles dominated by Western Eurasian haplogroups such as H, U, J, and T, comprising over 90% of the sampled lineages, which contrasts with their culturally Asian steppe nomadic origins and suggests substantial maternal admixture with local European populations prior to or during settlement.[79] This 2006 study, the first ancient DNA characterization of eastern pastoral nomads migrating into Europe, indicated that while mtDNA showed limited East Asian affinity (e.g., minor D and M lineages), the genetic trace emphasized gene flow from indigenous groups rather than direct maternal continuity from core steppe territories.[79] In contrast, Y-chromosome (Y-DNA) studies highlight persistent paternal East Eurasian lineages among Cuman elites and their descendants, underscoring male-mediated Turkic input. A 2024 archaeogenetic analysis of the medieval Hungarian Aba noble family, associated with steppe migrant origins including possible Cuman ties, identified shared East Eurasian Y-haplogroups (e.g., branches under N1a1) among four male burials from prominent graves, linking them to broader Árpád-era dynasties and refuting notions of complete genetic dilution through assimilation.[80] Similarly, a 2022 examination of paternal genetics in the Hungarian-speaking Rétköz population, a region with historical Cuman settlement influences, detected Y-haplotypes shared with ancient Xiongnu, Avars, and Caucasian nomadic groups, including East Eurasian markers like those in haplogroup Q and C2 sublineages prevalent in Kipchak confederations.[81][82] These findings counter claims of rapid over-assimilation by demonstrating the endurance of Cuman-specific paternal haplogroups such as Q-M242 and C2-M217 in relic populations and elite contexts, with frequencies persisting into modern Hungarian subgroups despite maternal European dominance.[81] Recent 2025 relic analyses further corroborate this, identifying East Eurasian Y-signals in steppe-derived Hungarian lineages that align with Kipchak nomadic profiles, emphasizing elite male continuity over broader population replacement.[83] Such patterns reflect patrilineal transmission of Turkic genetic elements, consistent with historical accounts of Cuman warrior clans maintaining endogamous structures amid settlement.[80]Notable Leaders and Dynasties
Prominent Khans and Their Strategic Victories
Boniak, a prominent Cuman khan active in the late 11th century, orchestrated devastating raids on Kievan Rus' during the 1090s, capitalizing on princely infighting to plunder key sites. In 1096, his forces assaulted Kiev itself, sacking the Pechersk Monastery and seizing captives while Grand Prince Sviatopolk II was absent, demonstrating tactical exploitation of enemy disunity as recorded in the Russian Primary Chronicle. This incursion inflicted severe losses on Rus' territories, temporarily asserting Cuman dominance in the steppe frontier.[22] Boniak further showcased strategic acumen through opportunistic alliances, notably aiding Byzantine Emperor Alexios I Komnenos against the Pechenegs at the Battle of Levounion on April 29, 1091, where combined forces annihilated the Pecheneg host of approximately 80,000, securing Byzantine frontiers and enhancing Cuman leverage in regional diplomacy. In 1099, Boniak's warriors repelled Hungarian King Coloman's invasion near the Transylvanian borders, forcing a retreat and affirming Cuman military prowess against sedentary powers. However, such successes were undermined by internal Cuman factionalism, with khans like Boniak facing later defeats, such as Vladimir Monomakh's victories in 1103 and 1111, highlighting the confederation's vulnerability to unified opposition.[22] Tugorkan, another key leader in the early 12th century, conducted raids into Rus' lands around 1093, leading roughly 8,000 horsemen in incursions that pressured southern principalities before clashing at the Battle of the Stuhna River on May 26, 1093. Though Rus' forces under Sviatopolk II and Vladimir Monomakh prevailed, with Tugorkan drowning in the river during retreat, his prior depredations exemplified Cuman hit-and-run tactics that disrupted agriculture and trade. Tugorkan's diplomatic maneuvering included marrying his daughter to Sviatopolk II in 1094, a short-lived pact aimed at stabilizing borders but reflective of recurring Cuman betrayals amid shifting steppe alliances.[22][32] Köten (Kotyan), khan in the early 13th century, pursued survival strategies amid Mongol expansion, forging alliances with Rus' princes against the invaders, including appeals before the disastrous Battle of the Kalka River in 1223. Facing relentless Mongol pressure, Köten orchestrated the mass migration of up to 40,000 Cumans westward to Hungary in 1239, securing asylum from King Béla IV in exchange for feudal oaths and military aid, thereby integrating Cuman cavalry into Hungarian defenses prior to the 1241 Mongol onslaught. This maneuver temporarily preserved Cuman autonomy and bolstered allied forces at the Battle of Mohi, though ensuing unrest—fueled by suspicions of Cuman-Mongol collusion—led to Köten's assassination by Hungarian nobles in 1241, underscoring the fragility of nomadic-sedentary pacts marred by mutual distrust and factional intrigue.[19][32]
_eng.png/250px-Cumania_(1200)_eng.png)
_eng.png)